A Comparative Study on Absorption of Gaseous Formaldehyde by Electrospun Biomass Carbon Nanofiber Membranes Modified by Plasma Activation and Chemical Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
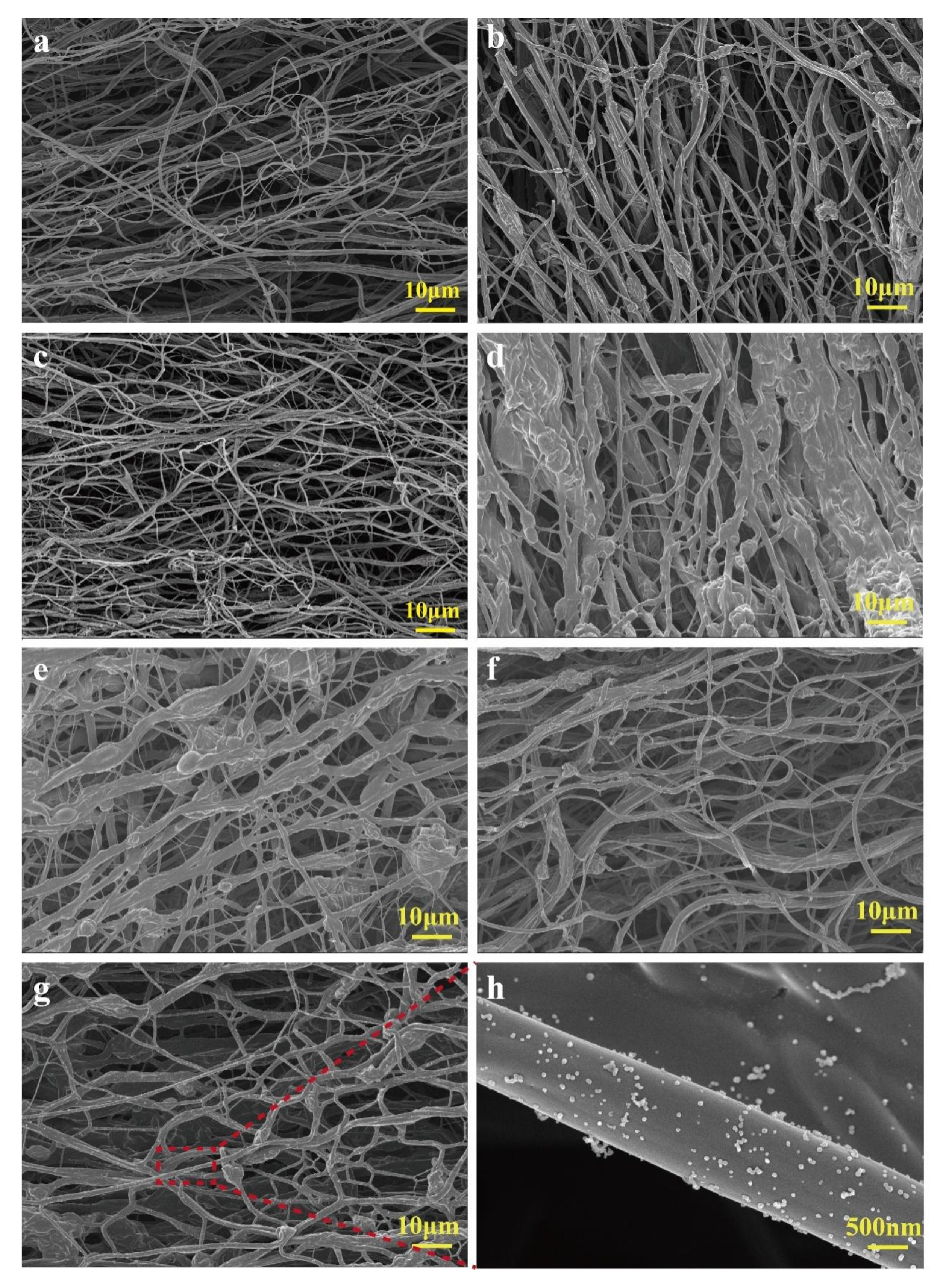
2.1. Analysis of Morphology of BCNMs Before and After Chemical Treatment
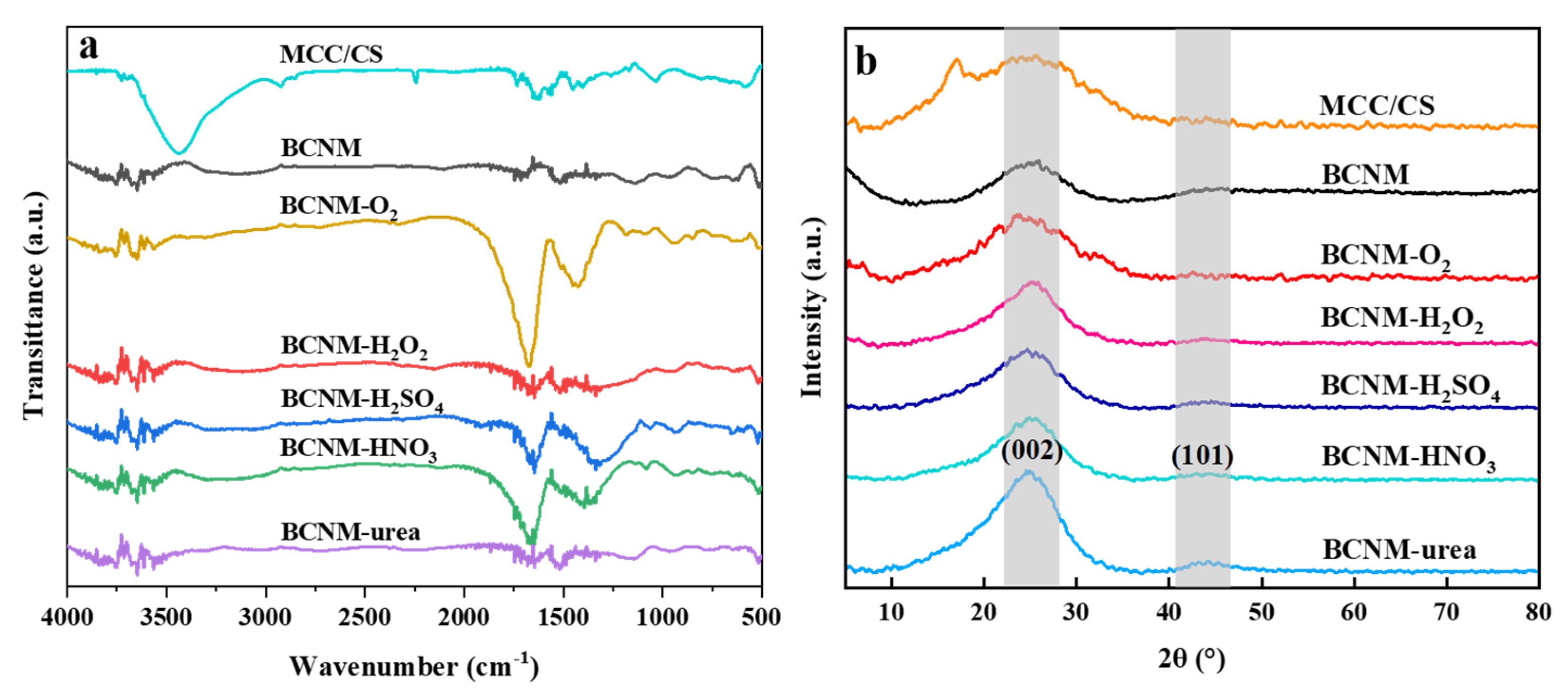
2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Adsorption Properties of Formaldehyde
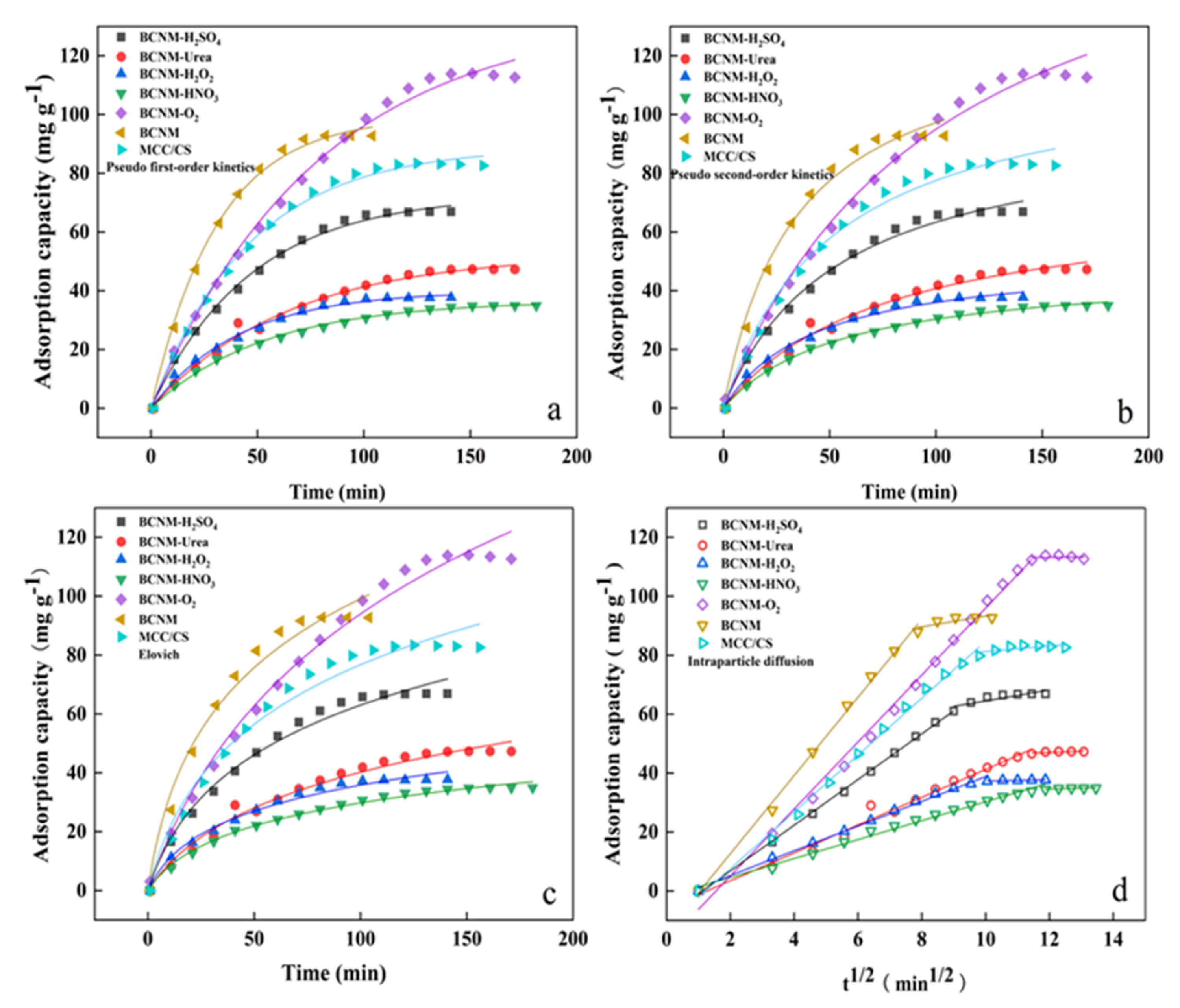
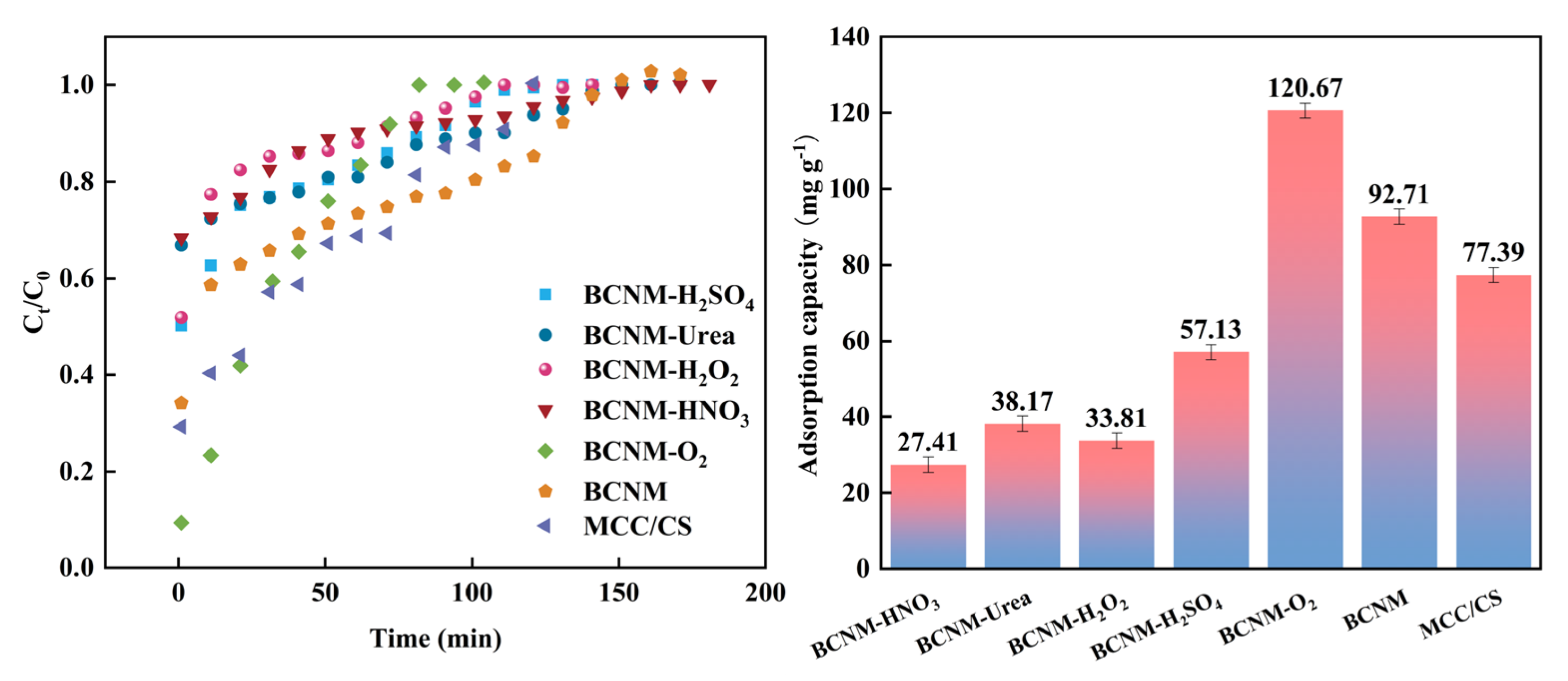
2.4.1. Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.2. Formaldehyde Adsorption Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation and Modification of Biomass Carbon Nanofiber Membranes
3.3. Characterization and Measurement
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vikrant, K.; Lim, D.H.; Younis, S.A.; Kim, K.H. An efficient strategy for the enhancement of adsorptivity of microporous carbons against gaseous formaldehyde: Surface modification with aminosilane adducts. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Lee, J.T. Exposure to formaldehyde and its potential human health hazards. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2011, 29, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.M. Revision and prospect of “Standards for indoor air quality (GB/T 18883-2022)” in China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2023, 57, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Na, C.J.; Yoo, M.J.; Tsang, D.C.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.H. High-performance materials for effective sorptive removal of formaldehyde in air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Su, Y.H.; Zhao, S.Y. An efficient plant–microbe phytoremediation method to remove formaldehyde from air. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 18, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, R. Identifying an indoor air exposure limit for formaldehyde considering both irritation and cancer hazards. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 672–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Creamer, A.E.; Cao, C.; Li, Y. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, H.; Jin, Y.; Luo, H.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, B.; Cheng, X.; Yang, H. Low-temperature oxidative removal of formaldehyde using oxygen-vacancy enhanced silver-based catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 152766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Nallathambi, G. Indoor formaldehyde removal by catalytic oxidation, adsorption and nanofibrous membranes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2551–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; An, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; He, M.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Lai, S.; Han, S.; Jiao, Y. The impact of water co-adsorption on the removal of formaldehyde from the indoor air by oxygen-rich activated carbons: A theoretical and experimental study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 635, 157729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, R.; Wang, C.; Zhou, K.; Su, C.; Li, H. Synthesis of nitrogen-rich nanoporous carbon materials with C3N-type from ZIF-8 for methanol adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Cho, D.W.; Ahmad, W.; Jo, J.; Jurng, J.; Kurade, M.; Jeon, B.; Choi, J. Efficient removal of formaldehyde using metal-biochar derived from acid mine drainage sludge and spent coffee waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Deng, Q.; Wang, L.; Xiang, P.; Lin, J.; Murugadoss, V.; Song, G. Modifying coconut shell activated carbon for improved purification of benzene from volatile organic waste gas. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Zhao, C.; Zuo, M.; Tang, J.; Ye, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C. Review on the preparation of high value-added carbon materials from biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 168, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Feng, J.; Song, Y.; Xu, L.; Cui, X.; Yu, B. Preparation of the carbonized Zif−8@PAN nanofiber membrane for cadmium ion adsorption. Polymers 2022, 14, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Dai, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, H. Low-temperature plasma treatment-assisted layer-by-layer self-assembly for the modification of nanofibrous mats. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Xiong, J.; Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, T.; Harper, D.; Tang, Z.; Xie, L.; Xu, K. Gaseous formaldehyde adsorption by eco-friendly, porous bamboo carbon microfibers obtained by steam explosion, carbonization, and plasma activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.S.; Bae, J.Y. Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde. Micromachines 2023, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, T.T.; Vikrant, K.; Szulejko, J.E.; Kim, K.H. Uncharacteristic Adsorption Breakthrough Behavior of a Core–Shell Copper Hydroxysulfate Metal–Organic Framework Against Gaseous Formaldehyde. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2312022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.Y.; Shimohara, T.; Nakabayashi, K.; Miyawaki, J.; Park, J.I.; Yoon, S.H. Urea/nitric acid co-impregnated pitch-based activated carbon fiber for the effective removal of formaldehyde. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qing, P.; Guo, G.; Shi, B.; Hu, Q. Effect of potassium-permanganate modification on the microstructure and adsorption property of activated carbon. Mater. Technol. 2019, 53, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unglaube, N.; Florent, M.; Otto, T.; Stötzer, M.; Grothe, J.; Kaskel, S.; Bandosz, T.J. Doping of porous carbons with sulfur and nitrogen markedly enhances their surface activity for formaldehyde removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 653, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, F.G.; Barczak, M.; Montagnaro, F.; Bandosz, T.J. A new generation of surface active carbon textiles as reactive adsorbents of indoor formaldehyde. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8066–8076. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Meng, M.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Q. Adsorptivity and kinetics for low concentration of gaseous formaldehyde on bamboo-based activated carbon loaded with ammonium acetate particles. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; He, Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Chai, X.; Wang, S.; Peng, W.; Du, G.; Xu, K. Effects of various cold plasma atmospheres and external influencing factors on the adsorption of formaldehyde gas by bamboo-based carbon microfibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 215, 118607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Luo, R.; Jia, Z.; Ge, S.; Lam, S.; Xie, L.; Chai, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, K. Electrospun microcrystalline cellulose/chitosan porous composite nanofibrous membranes modified by non-thermal plasma for gaseous formaldehyde adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Chai, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, W.; Wang, S.; Du, G.; Xu, K. Electrospun biomass carbon-based porous nanofibers modified by green-dry cold plasma for gaseous formaldehyde adsorption. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cui, S.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; He, H.; Luo, L. Synthesis of Ag-Au/reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 nanocomposites: Application as a non-enzymatic amperometric H2O2 sensor. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2020, 16, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Feng, X.; Zuo, X.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhu, B.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Facile fabrication of highly porous MgO-modified biochar derived from agricultural residue for efficient Cd (II) removal from wastewater. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 154, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, K.; Wu, J.; Hu, Q.; Harper, D.P.; Du, G.; Wang, S.; Xu, K. Comparative effects of electrospinning ways for fabricating green, sustainable, flexible, porous, nanofibrous cellulose/chitosan carbon mats as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidifard, S.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Hosseini, S.; Rezaei, S.; Karamipour, A.; Irani, M. Incorporation of UiO-66-NH2 MOF into the PAN/chitosan nanofibers for adsorption and membrane filtration of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Cr (VI) ions from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, M.; Jin, S.; Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Yao, Z. Surface modification of activated carbon fiber by low-temperature oxygen plasma: Textural property, surface chemistry, and the effect of water vapor adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, S.; El-Deen, G.S. Characterization of activated carbon prepared by phosphoric acid activation of olive stones. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1155–S1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Doping of nitrogen into biomass-derived porous carbon with large surface area using N2 non-thermal plasma technique for high-performance supercapacitor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 2432–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedin, K.C.; Martins, A.C.; Cazetta, A.L.; Pezoti, O.; Almeida, V.C. KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon: Adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene Blue removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y. Study the effect of drying on the oxidation thermogravimetric and functional group composition characteristics of immersed lignite. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, F.G.; Li, W.; Cimino, S.; Bandosz, T.J. Role of sulfur and nitrogen surface groups in adsorption of formaldehyde on nanoporous carbons. Carbon 2018, 138, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Wang, Z.; Qin, M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Ji, D.; Yu, D. Synthesis and characterization of UiO-66-NH2 incorporated PVA/cellulose nanofibers composite aerogel for enhanced oil–water separation and formaldehyde adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 325, 124673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, A.; Evaristo, M.; Kalin, M.; Cavaleiro, A. Effect of silicon and oxygen co-doping on structure and properties of non-hydrogenated amorphous carbon. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 496, 131616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, E.M. Plasma treatment for improved bonding: A review. J. Adhes. 1989, 30, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliwa, A.A.; Mubark, A.E.; Abdelfattah, N.A.; Gawad, E.A. Maximizing the exploitation of phosphogypsum wastes using soaking technique with citric acid, recovering rare-earth and residual phosphate contents. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 3896–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Miao, H.; Rui, Z.; Ji, H. Enhanced formaldehyde removal from air using fully biodegradable chitosan grafted beta-cyclodextrin adsorbent with weak chemical interaction. Polymers 2019, 11, 11020276. [Google Scholar]
- Gerente, C.; Lee, V.K.; Cloirec, P.L.; McKay, G. Application of chitosan for the removal of metals from wastewaters by adsorption—Mechanisms and models review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 41–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouei, F.; Nekouei, S.; Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.K. Kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies for acid blue 129 removal from liquids using copper oxide nanoparticle-modified activated carbon as a novel adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 201, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamkeaw, A.; Phisalaphong, M.; Jongsomjit, B.; Lin, K.A.; Yip, A.C. Synthesis of mesoporous MFI zeolite via bacterial cellulose-derived carbon templating for fast adsorption of formaldehyde. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Sengupta, S.; Das, P.; Bhowal, A.; Bhattacharjee, C. Experimental and numerical modeling on dye adsorption using pyrolyzed mesoporous biochar in Batch and fixed-bed column reactor: Isotherm, Thermodynamics, Mass transfer, Kinetic analysis. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Ding, C.; Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L. Efficient Separation of Uranium (VI) by CaCO3-Doped Chitosan with PO43− Modification: Adsorption Behaviors and Mechanism Study. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 4885–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Yuan, S.H.; Xie, W.J.; Zhang, W.; Tong, M.; Wang, K. Adsorption of nitrogen-heterocyclic compounds on bamboo charcoal kinetics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 390, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Cao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Du, X.; Dou, H.; Yan, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B. Performance optimization and kinetic analysis of HNO3 coupled with microwave rapidly modified coconut shell activated carbon for VOCs adsorption. Front. Energy. Res. 2023, 10, 1047254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paajanen, J.; Lönnrot, S.; Heikkilä, M.; Meinander, K.; Kemell, M.; Hatanpää, T.; Ainassaari, K.; Ritala, M.; Koivula, R. Novel electroblowing synthesis of submicron zirconium dioxide fibers: Effect of fiber structure on antimony (v) adsorption. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4373–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
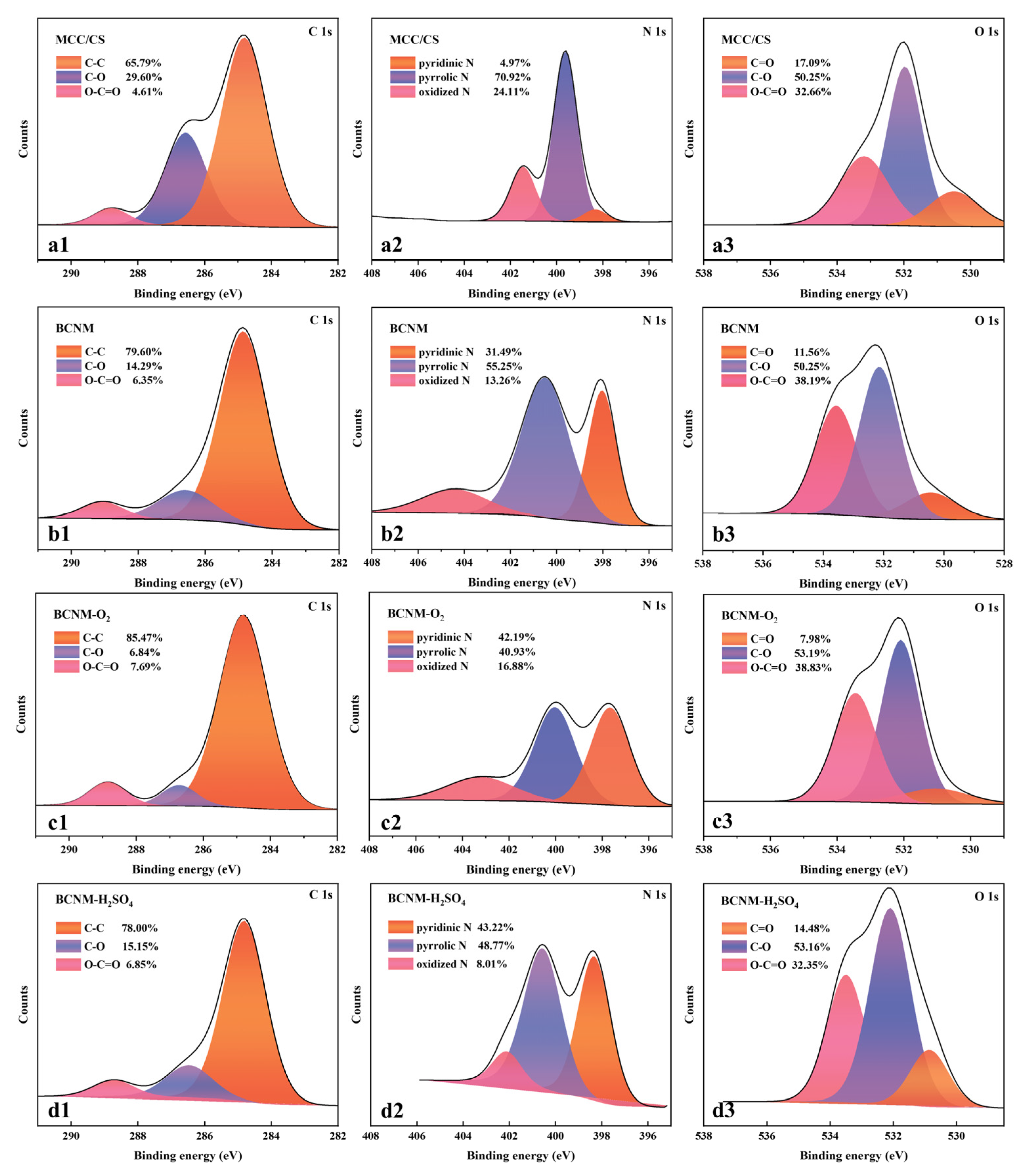
| Atomic States and Contents | MCC/CS | BCNM | BCNM-O2 | BCNM-H2SO4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N 1s content (%) | 8.31 | 7.16 | 2.06 | 6.23 |
| Pyridinic N (%) | 0.41 | 2.20 | 0.87 | 2.69 |
| Binding energy (eV) | 398.31 | 398.01 | 397.65 | 398.39 |
| Pyrrolic N (%) | 5.89 | 3.85 | 0.84 | 3.04 |
| Binding energy (eV) | 399.61 | 400.49 | 400.02 | 400.53 |
| Oxidized N (%) | 2.00 | 0.92 | 0.35 | 0.50 |
| Binding energy (eV) | 401.44 | 404.41 | 403.22 | 402.99 |
| O 1s content (%) | 13.92 | 10.27 | 16.03 | 13.93 |
| C=O (%) | 2.38 | 1.15 | 1.28 | 2.02 |
| Binding energy (eV) | 530.48 | 530.42 | 531.02 | 530.69 |
| C–O (%) | 6.99 | 5.04 | 8.83 | 7.40 |
| Binding energy (eV) | 531.96 | 532.13 | 532.08 | 532.09 |
| O–C=O (%) | 4.55 | 3.82 | 6.22 | 4.51 |
| Binding energy (eV) | 533.18 | 533.56 | 533.44 | 533.75 |
| Groups | C/% | N/% | H/% | O/% | (O+N)/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCC/CS | 44.63 | 4.04 | 6.39 | 44.94 | 1.0974 |
| BCNM | 57.97 | 9.30 | 1.535 | 31.14 | 0.6976 |
| BCNM-O2 | 51.34 | 14.22 | 0.886 | 33.467 | 0.9389 |
| BCNM-H2O2 | 59.57 | 11.05 | 0.642 | 28.623 | 0.6660 |
| BCNM-H2SO4 | 54.88 | 11.39 | 0.768 | 31.213 | 0.7763 |
| BCNM-HNO3 | 58.28 | 11.99 | 0.516 | 29.104 | 0.7051 |
| BCNM-Urea | 57.86 | 14.37 | 0.764 | 26.912 | 0.7135 |
| Sample | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg g−1) | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | R2 | α (mg g−1 min−1) | β (g mg−1) | R2 | |
| BCNM-H2SO4 | 73.8122 | 0.022 | 0.9955 | 100.9800 | 0.00021 | 0.9909 | 2.5454 | 0.0378 | 0.9840 |
| BCNM-Urea | 53.7144 | 0.0164 | 0.9904 | 75.5500 | 0.00022 | 0.9871 | 1.2293 | 0.0473 | 0.9817 |
| BCNM-H2O2 | 40.5122 | 0.0252 | 0.9936 | 53.4455 | 0.00045 | 0.9906 | 1.8001 | 0.0754 | 0.9838 |
| BCNM-HNO3 | 36.8838 | 0.0193 | 0.9962 | 48.1804 | 0.00032 | 0.9968 | 1.2111 | 0.0794 | 0.9921 |
| BCNM-O2 | 134.1152 | 0.0126 | 0.9943 | 193.3992 | 0.00004 | 0.9913 | 2.1183 | 0.0154 | 0.9878 |
| BCNM | 99.2777 | 0.0320 | 0.9952 | 130.5984 | 0.00022 | 0.9866 | 4.9319 | 0.0267 | 0.9745 |
| MCC/CS | 88.9330 | 0.0215 | 0.9956 | 117.5722 | 0.00016 | 0.9867 | 2.8947 | 0.0293 | 0.9743 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Xiong, J.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Chai, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Du, G.; Xu, K. A Comparative Study on Absorption of Gaseous Formaldehyde by Electrospun Biomass Carbon Nanofiber Membranes Modified by Plasma Activation and Chemical Treatment. Molecules 2025, 30, 2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102184
He Q, Xiong J, Wang H, Xie L, Chai X, Zhang L, Wang S, Du G, Xu K. A Comparative Study on Absorption of Gaseous Formaldehyde by Electrospun Biomass Carbon Nanofiber Membranes Modified by Plasma Activation and Chemical Treatment. Molecules. 2025; 30(10):2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102184
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qian, Jinhui Xiong, Huanbo Wang, Linkun Xie, Xijuan Chai, Lianpeng Zhang, Siqun Wang, Guanben Du, and Kaimeng Xu. 2025. "A Comparative Study on Absorption of Gaseous Formaldehyde by Electrospun Biomass Carbon Nanofiber Membranes Modified by Plasma Activation and Chemical Treatment" Molecules 30, no. 10: 2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102184
APA StyleHe, Q., Xiong, J., Wang, H., Xie, L., Chai, X., Zhang, L., Wang, S., Du, G., & Xu, K. (2025). A Comparative Study on Absorption of Gaseous Formaldehyde by Electrospun Biomass Carbon Nanofiber Membranes Modified by Plasma Activation and Chemical Treatment. Molecules, 30(10), 2184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102184







