Abstract
2,8-Dithia-5-aza-2,6-pyridinophane (L1) has been used as a receptor unit in the construction of the conjugated redox chemosensor 5-ferrocenylmethyl-2,8-dithia-5-aza-2,6-pyridinophane (L3). In order to further explore the coordination chemistry of L1, and comparatively, that of its structural analogue 2,11-dithia-5,8-diaza-2,6-pyridinophane (L2), featuring two secondary nitrogen atoms in the macrocyclic unit, the crystal structures of the new synthesised complexes [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN, [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN and [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3 were determined by X-ray diffraction analysis. The electrochemical response of L3 towards the metal ions Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) in CH2Cl2/CH3CN 0.25:1 (v/v) mixture. Upon addition to L3 of increasing amounts of the aforementioned metal cations, the wave corresponding to the Fc+/Fc redox couple of the un-complexed L3 was gradually replaced by a new reversible wave at more positive potentials and corresponding to the Fc+/Fc redox couple of the complexed ligand. The maximum anodic shift of the ferrocene oxidation wave is observed in the presence of Pb2+ (230 mV), to which corresponds a reaction coupling efficiency (RCE) value as large as 7.9 × 103. The response selectivity of L3 is discussed in reference to the optical selectivity observed for conjugated chemosensors featuring L1 as receptor unit and different fluorogenic fragments as signalling units.
1. Introduction
The development of sensitive and selective analytical tools for the rapid detection and monitoring of toxic heavy metal ions (such as Hg2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+) in environmental, industrial, and biological samples is a very active area of research [1,2,3,4,5]. These cations can be seriously deleterious to human health, and their use in many industrial processes results in a highly concerning level of contamination in soil, water and food, thus representing a huge pollution problem [6,7,8,9,10,11,12].
The development of selective and sensitive molecular sensors or chemosensors de- signed according to the principles of supramolecular chemistry [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] and the related sensor technology (sensor arrays, electro/optical noses and tongues) [23,24,25,26,27] represent well-established possible solutions to this difficult analytical problem due to their simplicity, versatility, low response time and cost.
From a structural point of view, according to the supramolecular “receptor-spacer-active unit” paradigm, conjugated chemosensors featuring a signalling site (active unit) linked through an appropriate spacer to a binding site (receptor unit) are the most studied and exploited. The recognition event, namely the host–guest interaction of the target species with the receptor unit, is converted into detectable changes in the chemical/physical properties of the active unit. Such changes can be exploited for analytical purposes provided that the chemosensor shows a signalling selectivity for the target species.
Over the last decade, by applying this general supramolecular synthetic approach, a great number of optical/electrochemical-conjugated chemosensors based on polyoxa- polyaza-, and aza/oxa-macrocycles as the guest binding sites have been reported. This choice can guarantee good water solubility, synthetic accessibility and binding selectivity towards hard and borderline hard/soft metal ions following an easily achievable ring size complementarity with the guest dimensions [28,29,30,31]. On the other hand, the potential of S- or mixed N/S-, and N/S/O-macrocyclic binding sites has in comparison been barely explored, reflecting a generally increased difficulty encountered both in the synthetic preparation of these systems [32,33,34,35,36,37,38], and in achieving a high binding selectivity towards target analytes within the category of soft metal ions with marked thiophilicity [28,29,30,31]. Fortunately, signalling selectivity can still be achieved with chemosensors featuring sulphur-containing donor atoms, and is dependent on the choice of the signalling unit and the medium for the host–guest interaction.
Following our general interest in the coordination chemistry of macrocyclic ligands aimed at application purposes, we have developed numerous optical chemosensors featuring the 12-membered pyridine-based macrocycle 2,8-dithia-5-aza-2,6-pyridinophane (L1) as a receptor unit, and various covalently linked fluorogenic fragments as a signalling unit (La–Li in Figure 1) [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. A different optical selectivity (indicated in parentheses in Figure 1) was observed for L1-based developed chemosensors, depending on the nature of the signalling unit and the experimental conditions used for the host–guest interaction. The observed optical selectivity does not generally correspond to the thermodynamic stabilities of the 1:1 complexes formed by L1 with the same metal ions, but this did not preclude the use of the chemosensors in the analytical determination of the target metal ions in real matrices of environmental and biological provenance. In fact, despite L1 not exhibiting a marked binding selectivity for any of the metal ions among Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+, its functionalisation with different fluorogenic fragments has allowed the construction of optically selective fluorescent chemosensors as outlined in Figure 1 [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. In some cases, a binding selectivity was achieved by supporting the resulting chemosensors in PVC membranes or nanoparticles where other parameters (e.g., the lipophilicity of the chemosensors and their metal complexes, their mobility within the membrane, and other factors determining the transport processes) can improve the binding selectivity and the sensitivity of the chemosensor observed in solution (for a detailed analysis and discussion of the optical properties in the presence of metal cations and applications of the chemosensors La–Li, refer to the relevant references [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]).
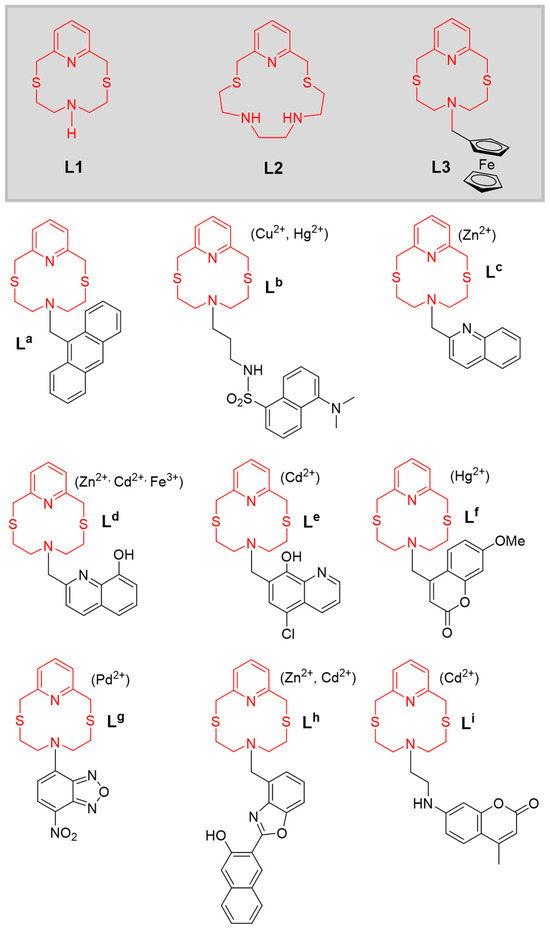
Figure 1.
Molecular schemes of the macrocyclic ligands L1, L2 and L3, and fluorescent chemosensors for metal ions La–Li built using L1 as the receptor unit (optical selectivity in parentheses) [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47].
The synthetic “receptor-spacer-active unit” modular scheme outlined above does not necessarily apply to the construction of chemosensors involving an optical transduction mechanism for the host–guest interaction, so linking a redox-active centre to a receptor unit may allow a selective electrochemical detection of binding via a redox potential change of the reporter group (voltammetric sensing). In this context, ferrocene has been widely studied in the field of chemosensing, especially in combination with macrocyclic receptor units, due to its well-defined electrochemical profile, chemical stability and ease of functionalisation on either one or both of its cyclopentadienyl (Cp) rings [48,49,50,51,52].
In this paper, we provide new insight into the coordination chemistry of L1 towards the dipositive metal ions Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+. We also compare the behaviour of L1 with that of its structural analogue 2,11-dithia-5,8-diaza-2,6-pyridinophane (L2, Figure 1), featuring two secondary nitrogen atoms in the macrocyclic cavity. The synthesis of the N-ferrocenylmethyl derivative L3 (Figure 1) was also achieved, and its electrochemical response to the above-mentioned metal ions was also investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV), underlining the synergic cooperation between the receptor and signalling units within conjugated chemosensors in achieving signalling selectivity.
2. Results
2.1. Coordination Chemistry of L1 and L2
We have previously observed that the 1:1 complex cations [M(L1)]2+, (M = Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+) are formed in aqueous solutions with formation constants (log K, determined potentiometrically) increasing in the order Zn2+ (7.13) < Pb2+ (8.45) < Cd2+ (9.12) < Cu2+ (10.05) < Hg2+ (10.68) [39]. A similar trend [Cd2+ (5.6) < Zn2+ (9.56) < Pb2+ (11.01) < Cu2+ (14.70) < Hg2+ (14.95)] was observed in CH3CN/H2O (1:1 v/v) solution for L2 (Figure 1), the structural analogue of L1 featuring a larger ring size due to the presence of two secondary amine groups in its structure [41]. As expected, the binding constants measured for L2 are generally higher than those measured for L1 due to the presence of five donor atoms and the larger cavity in the former. Interestingly, despite Pb2+ being third in the order of binding affinity, the L2-based chemosensor featuring two (5-chloro-8-hydroxy-7-quinolinyl)methyl pendant arms shows higher optical selectivity towards Pb2+ [41] than towards Cu2+ and Hg2+; a similar behaviour is in general observed for the L1-based chemosensors shown in Figure 1, most of which display a high optical selectivity for Zn2+ and/or Cd2+, i.e., the metal ions featuring the lowest binding constant with L1.
The coordination chemistry in the solid state of both L1 and L2 towards Cu2+ and d10 metal ions such as Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ has barely been studied [53]: for L1, only the 1:1 complexes [Cu(L1)(NO3)2] and [Zn(L1)(NO3)2] were reported as nitrate salts [39], while no X-ray crystal structures of L2-based metal complexes are known. The coordination spheres around the metal centres in both [Cu(L1)(NO3)2] and [Zn(L1)(NO3)2] complexes are pseudo-octahedral, with four positions occupied by the donor atoms of the macrocyclic ligand in a folded conformation, and the remaining two mutually cis-positions accommodating two unidentate nitrate anions. In order to have an insight into the solid state binding properties of L1 towards larger d10 metal ions, we reacted the ligand with Pb(ClO4)2·3H2O (1:1 molar ratio) in CH3CN. The colourless crystals obtained by diffusion of Et2O vapour into the reaction mixture, and corresponding to the formulation [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN were analysed by X-ray diffraction on a single crystal [see Table S1 in the Supporting Information (SI) for the crystallographic parameters].
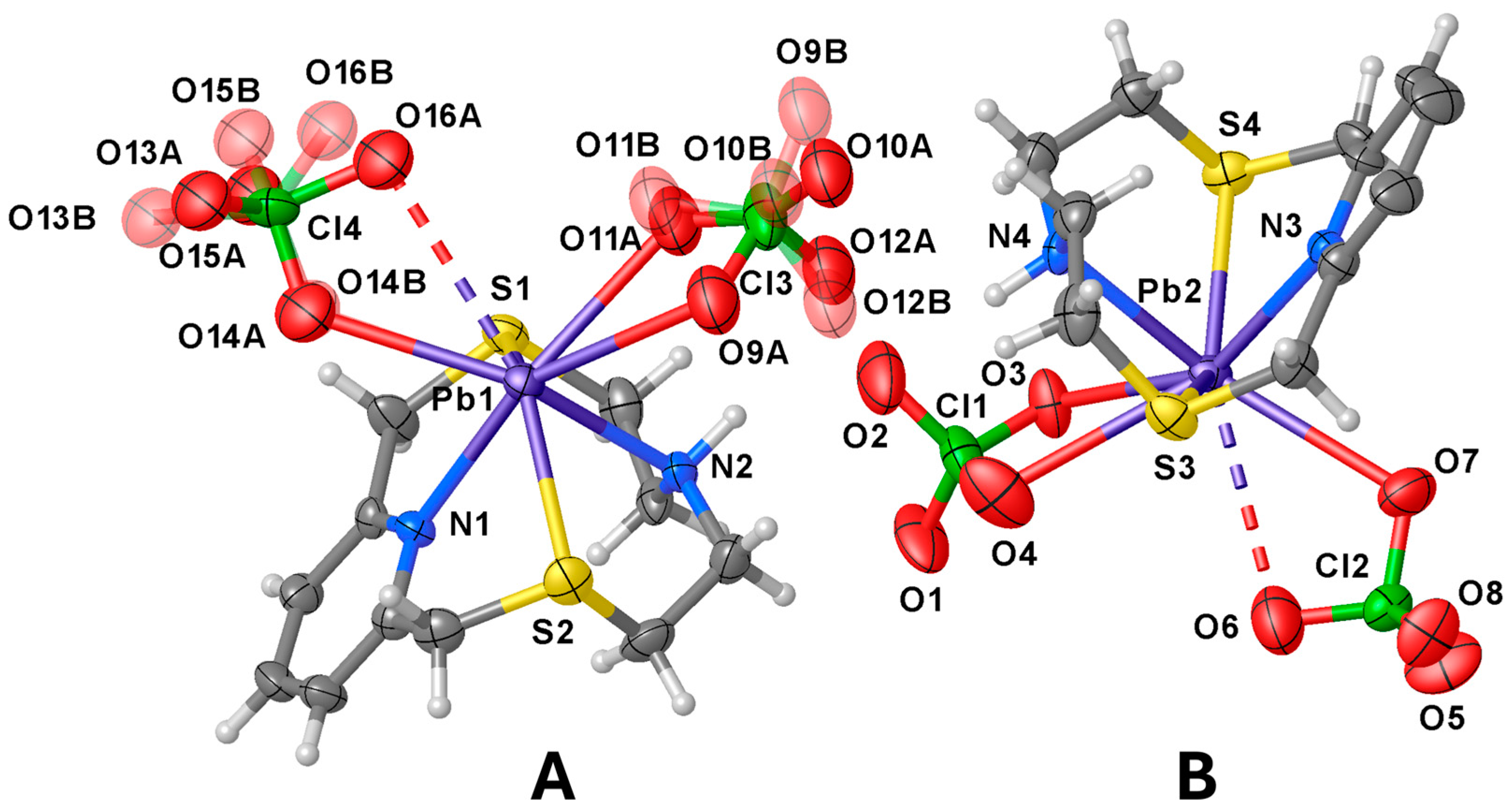
The asymmetric unit features two independent [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2] complex units (A and B in Figure 2) and one CH3CN molecule. In both complex units the metal ion is coordinated to L1 through all four donor atoms of the macrocyclic ligand [Pb–N and Pb–S distances in the range 2.529(6)–2.566(7) Å and 2.846(2)–2.878(2) Å, respectively], and to two perchlorate anions, one acting in a unidentate (κ1O) [Pb1–O14A = 2.89(2), Pb2–O7 = 2.999(7) Å] and the other in a chelating bidentate (κ2O,O′) fashion to afford an overall hepta-coordination [Pb1–O9A = 2.954(15), Pb1–O11A = 2.78(3) Å; Pb2–O3 = 2.822(7), Pb2–O4 = 3.059(11) Å, Figure 2]. It is worth noting that although O16A and O6 point towards the metal centres they sit at significantly long distances from Pb1 and Pb2, respectively [Pb1–O16A = 3.294(18), Pb2–O6 = 3.339(11) Å] (see discussion below).
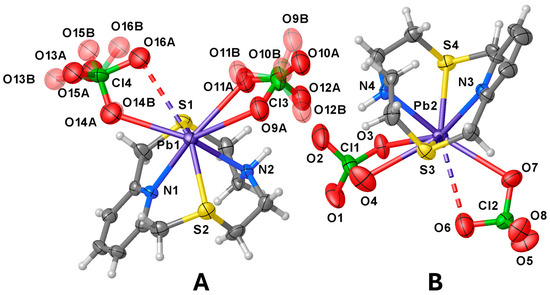
Figure 2.
View of the two independent [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2] complex units (A,B) present in the asymmetric unit of compound [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN with the numbering scheme adopted. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 30% probability level. The co-crystallised CH3CN molecule is omitted for clarity. In the case of unit A, the disorder components of the coordinated ClO4− anions are shown. The Pb–O contacts longer than 3.2 Å are drawn as dashed lines (see Tables S2 and S3 in the SI for a list of selected bond distances and angles).
The macrocycle in each independent [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2] unit assumes the folded conformation already observed in both [Cu(L1)(NO3)2] and [Zn(L1)(NO3)2] [28]. Interestingly, as compared to the Cu2+ and Zn2+ complexes, in [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2] the N–Pb–N and S–Pb–S angles {83.5(2) [unit A], 82.5(2) [unit B], and 130.12(8) [unit A], 129.97(8)o [unit B], respectively} are significantly smaller than those observed in the Cu2+ and Zn2+ complexes of L1 [N–M–N = 90.47(1) and 90.48(12)o for M = Cu and Zn, respectively; S–M–S = 165.78(7) and 163.50(4)o for M = Cu and Zn, respectively] [28], indicating a displacement of the Pb2+ ion out of the ring cavity towards the O-donor manifold of the perchlorate anions. This structural aspect of the coordination chemistry of L1, presumably determined by the larger ionic radius of Pb2+ with respect to that of Cu2+ and Zn2+ and/or by the presence of a stereochemically active 6s2 lone pair for lead(II), is also observed upon comparing the same bond angles in the compounds [Cu(Lc)](ClO4)2·½CH3CN, [Zn(Lc)(H2O)](ClO4)2, [Hg(Lc)(CH3CN)](ClO4)2, and [Pb(Lc)(ClO4)2] (Figure 1). In these four complexes, the ligand coordinates the metal centres via all five donor atoms including the N-donor from the quinoline moiety, the coordination sphere being completed by a water molecule and an acetonitrile molecule in the case of the zinc(II) and mercury(II) complexes, respectively, and two perchlorate anions in the case of the lead(II) one [40]. The Pb–O(ClO4−) bond distances with the perchlorate anions fall in the range 2.70–3.10 Å, which comprises 65% of the Pb–O(ClO4−) distances retrieved from the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD); 72% of all reported Pb–O(ClO4−) distances fall in the range 2.70–3.20 Å (CSD version 5.45 accessed on 20 August 2024, see Figure S1 in the SI and refs. [54,55,56,57,58] for some examples of discrete binuclear lead(II) complexes featuring perchlorate anions bridging the two metal ions). However, except for Pb1–O14A and Pb1–O11A in asymmetric unit A, and Pb2–O3 in unit B, the other Pb–O distances (see Figure 2) should be rather considered as contacts due to their length exceeding the sum of the Shannon ionic radii of lead(II) (1.23, 1.29 and 1.35 Å for hepta-, octa-, and nona-coordinated metal ion, respectively) [59] and the van der Waals radius of oxygen (1.50 Å) [60].
Two asymmetric A units are bridged by a μ2- κ1O, κ1O′ perchlorate ion through O13A and O14 atoms [Pb1–O13Ai = 2.83(3), Pb1–O14A 2.89(2) Å, i = 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z] to form dimers lying across an inversion centre (Figure 3a), and each metal centre reaching an overall octa-coordination. In these dimers the two pyridyl rings assume an anti-periplanar arrangement with respect the Pb1−Pb1i axis (Figure 3a). Similarly, two B units related by a two-fold rotation axis are arranged in pseudo-dimers with the pyridyl rings in a periplanar disposition with respect the Pb2–Pb2ii axis (ii = 2 − x, +y, 3/2 − z) (Figure 3b). However, considering the quite long Pb2−O5ii distance [3.296(8) Å, only 4% of all reported Pb–O(ClO4−) distances in the CSD occupy the range 3.20–3.40 Å (see SI, Figure S1 and Table S3] [61,62,63,64,65,66], and despite the fact that O5 points towards the Pb2ii, the two symmetry-related B units cannot be considered as bridged by perchlorate anions as for the case of the dimeric aggregates formed by unit A. This structural feature might be indicative of the presence of a stereochemically active 6s2 lone pair positioned in the coordination hemisphere left free by the macrocyclic ligand for the lead(II) atom in unit B. Interestingly, among the 26 structures (out of a total of 106) reported in the CSD of lead(II) complexes featuring bridging perchlorate anions [Pb2(μ2−κ1O,κ1O′−ClO4)], very few are characterised by short Pb–O(ClO4−) bridging bond lengths similar to those observed in the dimers formed by the asymmetric units A in [Pb2(L1)2(ClO4)4]·½CH3CN (Figure 3a) [67,68,69].
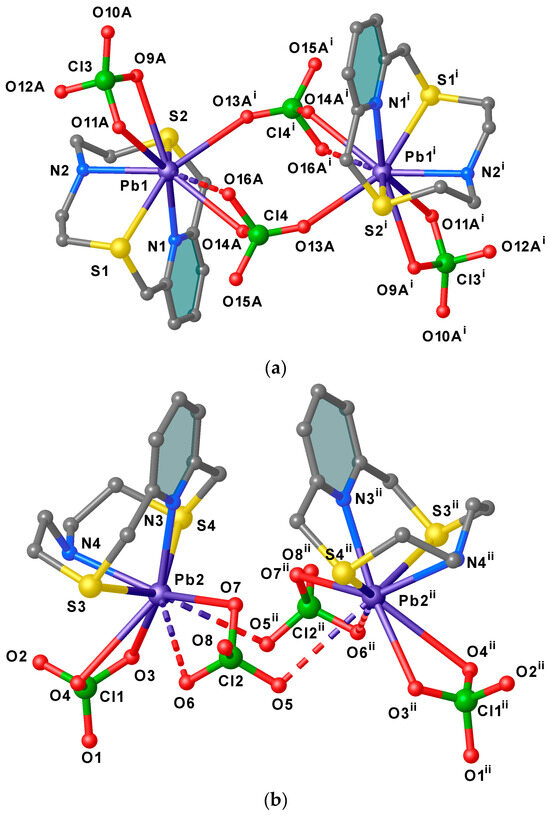
Figure 3.
View of the dimeric arrangements of units A (a) and B (b) in [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN with the adopted numbering scheme. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. The Pb–O contacts longer than 3.2 Å are drawn as dashed lines. Symmetry codes: i = 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; ii = 2 − x, +y, 3/2 − z.
With the aim of obtaining more information on the chelating ability of L2 in the solid state, we treated this ligand with Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ or Pb2+ as a nitrate or a perchlorate salt in 1:1 molar ratio in CH3CN or EtOH. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were successfully grown for compounds [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN and [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3, while crystallisation with the other two metal ions led to uncharacterizable rubbery/oily compounds. Figure 4 shows the coordination sphere around the metal centres in the two metal complex cations [Cd(L2)(NO3)]+ and [Cu(L2)]2+, and Table S4 in the SI summarises selected bond distances and angles.
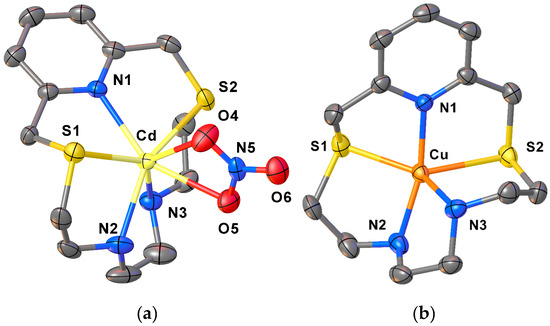
Figure 4.
View of the complex cations [Cd(L2)(NO3)]+ (a), and [Cu(L2)]2+ (b) in [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3 and [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN, respectively, with the numbering scheme adopted. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms, counter anions and co-crystallised solvent molecules have been omitted for clarity (see Table S4 in the SI for a list of selected bond distances and angles).
In [Cd(L2)NO3]+, an overall N3S2O2 hepta-coordination is achieved at the metal centre via the five donor atoms of the macrocyclic framework [Cd–N1 2.416(4), Cd–N2 2.397(4), Cd–N3 2.338(4), Cd–S1 2.7264(13), Cd–S2 2.7695(13) Å] and two O-donors from one asymmetrical bidentate NO3− anion [Cd–O4 2.380(4) and Cd–O5 2.516(4) Å] (Figure 4a, Table S4 in the SI).
An interesting structural feature of the compound [Cd(L2)NO3]NO3 is the hydrogen-bonding network (Figure 5) involving adjacent complex cation units and both nitrate anions. In particular, each coordinated NO3− anion forms a CH···O hydrogen bond with the macrocyclic ligand of a neighbouring [Cd(L2)NO3]+ cation complex, while each un-coordinated nitrate anion bridges two adjacent complex cations via NH···O and CH···O hydrogen bonds to form extended chains running along the a-axis.
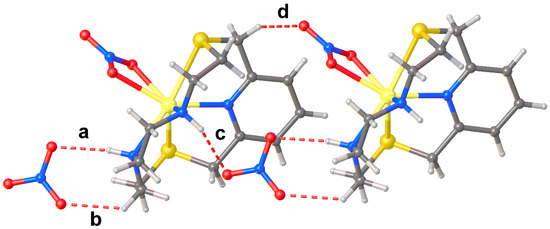
Figure 5.
Partial view (ball and stick representation) of the extended chains of H-bonded [Cd(L2)NO3]+ cations and NO3− anions in [Cd(L2)NO3]NO3. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. (a) N2–H2···O3 [N2–H2 (0.93 Å), N2···O3 (3.159(8) Å), H2···O3 (2.25 Å), N2–H2···O3 (167°)]; (b) C9–H9A···O1 [C9–H9A (0.99 Å), C9···O1 (3.031(8) Å), H9A···O1 (2.39 Å), C9–H9A···O1 (122°)]; (c) N3–H3···O2i [N3–H3 (0.93 Å), N3···O2i (2.928(6) Å), H3···O2i (2.09 Å), N3–H3···O2i (149°)]; (d) C14–H14B···O6i [C14–H14B (0.99 Å), C14 ···O6i (3.251(7) Å), H14B···O6i (2.37 Å), C14–H14B···O6i (147°)]. Symmetry code: i = +x, +y, 1 + z.
In [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2, the stereoelectronic requirements of the metal centre are satisfied by the five donor atoms of the macrocyclic ligand, which imposes a N3S2 coordination sphere in a distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry with the two S-donors in equatorial positions [Cu–N1 1.983(3), Cu–N2 2.109(3), Cu–N3 2.006(3), and Cu–S1 2.4697(11) and Cu–S2 2.3117(11) Å] (Figure 4). As expected, the Cu–N and Cu–S bond distances in [Cu(L2)]2+ are shorter than those observed in [Cd(L2)NO3]+ (due to the different ionic radii of the two metal ions) and similar to those observed in [Cu(L1)(NO3)2] [39].
Interestingly, the bond angles and the folded conformation assumed by L2 in [Cd(L2)NO3]+ and [Cu(L2)]2+ are quite similar (Figure 6, Table S4 in the ESI), thereby indicating the absence of particular constraints upon coordination due to the different dimensions of the two metal ions, as well as the ability of L2 to fully encapsulate both metal ions.
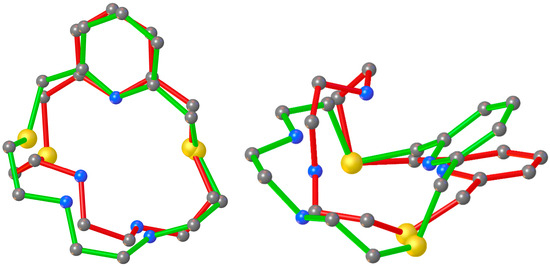
Figure 6.
Superimposition of the structures of macrocyclic ligand L2 in [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN (red) and [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3 (green).
2.2. Synthesis of L3 and Its Electrochemical Behaviour in the Presence of Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+
The reaction of L1 with (ferrocenylmethyl)trimethylammonium iodide in CH3CN in the presence of K2CO3 (anhydrous) afforded L3 in 82% yield as an orange solid after standard work-up (see Section 3.5). Unfortunately, the insolubility of L3 in aqueous solutions prevented a potentiometric study of its coordination properties towards the metal cations of interest, namely Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, or Pb2+. However, it was possible to investigate by cyclic voltammetry the electrochemical response of L3 to these metal cation species in the CH2Cl2/CH3CN 0.25:1 (v/v) solvent mixture (the most suitable for solubility reasons) at 25 °C. We were therefore able to unveil the effect on the response selectivity of this new chemosensor based on L1 upon changing the transduction mechanism of the host-guest interaction (from optical to electrochemical) as compared to La–Li (see above).
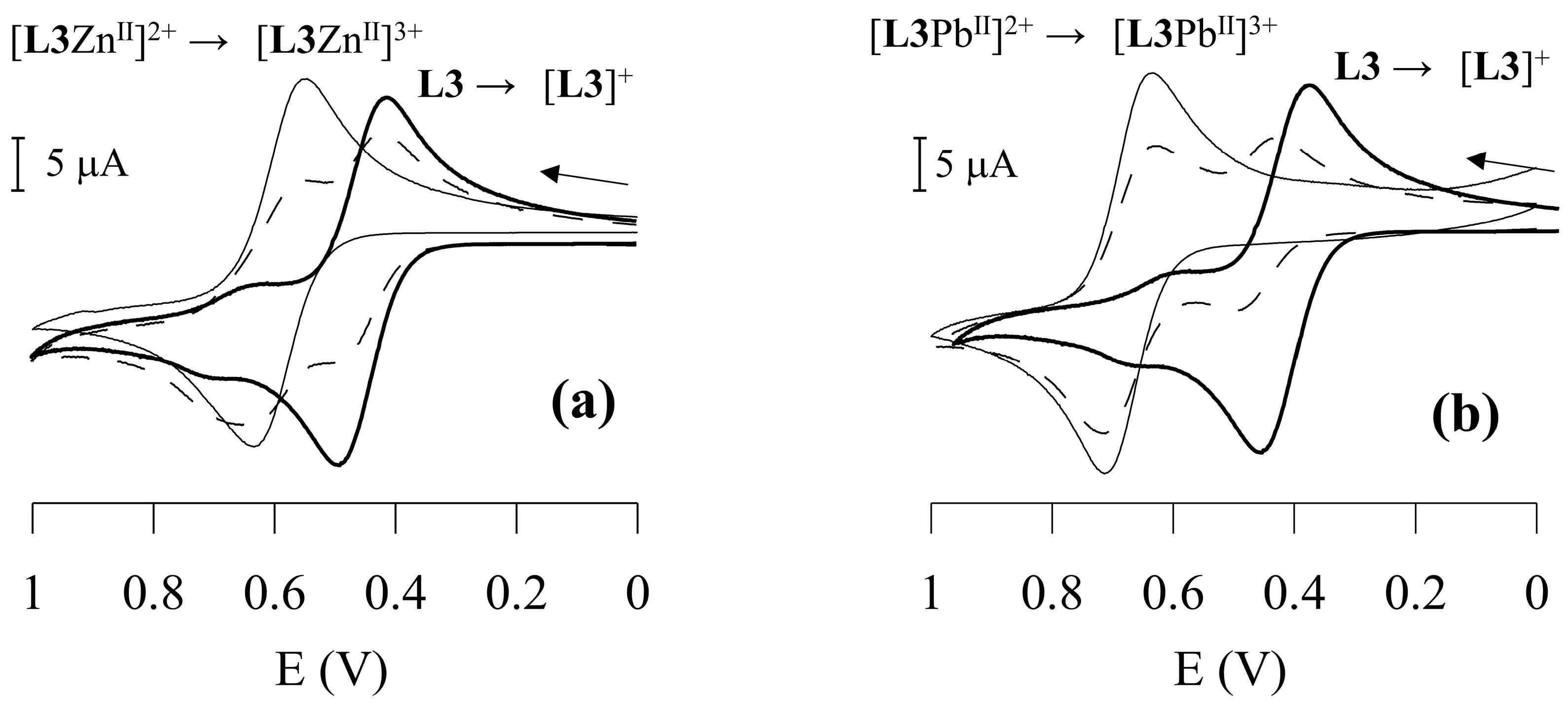
The cyclic voltammogram (scanned in the anodic direction with a scan rate of 100 mV/s) of the free ligand L3 reveals a one-electron reversible (ia ≈ ic) redox process at E½ = 450 mV vs. Ag/AgCl [calculated from the average of the oxidation (Epox) and reduction (Epred) peak potentials], corresponding to the Fc+/Fc redox couple. While one-wave electrochemical behaviour is observed upon addition of HClO4 to the L3 solution (due to the protonation of the macrocyclic moiety with an anodic shift of the Fc+/Fc redox couple of 190 mV), a two-wave behaviour is observed upon addition of increasing amounts of Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ or Hg2+. The oxidation wave corresponding to the Fc+/Fc redox couple in free L3 is gradually replaced by a new reversible wave at more positive potentials upon addition of increasing amounts of the metal ions, corresponding to the Fc+/Fc redox couple of the [LMII]2+ species. Its anodically shifted position with respect to the wave corresponding to un-complexed L3 reflects a less favourable oxidation process for the Fc moiety in [LMII]2+ due to the presence of a positively charged metal cation centre bound to the receptor moiety, in close proximity. The currents for the new reversible redox couple [LMII]3+/[LMII]2+ (M = Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ or Hg2+) increase linearly until one equiv. of the metal cation species is added. At this point, the reversible oxidation wave corresponding to un-complexed L3 disappears (Figure 7).
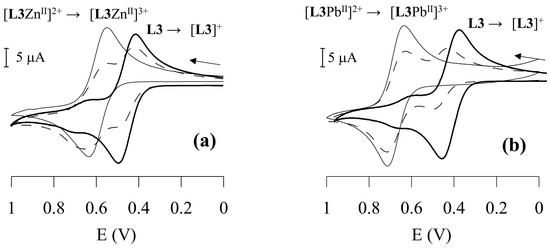
Figure 7.
Cyclic voltammetry (scanned in the anodic direction) in CH2Cl2/CH3CN 0.25:1 (v/v) solvent mixture at 25 °C of: L3 + Zn2+ (a), and L3 + Pb2+ (b). The full bold line refers to free L3, the dashed line to L3 + 0.5 equivs. of the metal ions, and the full thin line to L3 + 1 equiv. of the metal ions. Scan rate 100 mV/s.
Two-wave electrochemical behaviour in the cyclic voltammogram has been already observed for redox chemosensors featuring ferrocenyl signalling unit(s) upon addition of a metal ion, and can be accounted for by a high stability constant of the complex between the metal ion guest and the unoxidised redox responsive ionophore, and a large difference between the half-wave potentials for the two redox couples [L3]+/L3 and [L3MII]3+/[L3MII]2+, with the magnitude of the anodic shift being related to the guest’s polarising power or its charge density [14,48,49,50,51,52,70]. In particular, by coupling in a square thermodynamic scheme the equilibria for the electrode oxidation of the neutral ionophore and its metal complexes with the equilibra for the metal guest complexations of the ionophore in its neutral and oxidised forms, the following equation can be derived [14,48]:
where Kred and Kox are the metal binding constants for the neutral and oxidised forms, respectively, of the redox chemosensor. The ratio Kred/Kox was defined by Beer [57] as reaction coupling efficiency (RCE). Its reciprocal is often referred to as the binding enhancement factor (BEF), and together with the anodic shift in the oxidation potential produced by presence of a metal cation (E1/2complex − E1/2free ionophore), represents a quantitative measure of the perturbation of the redox centre induced by the guest complexation to the receptor unit (the perturbation is mainly electrostatic via through-space interaction); it allows evaluation of the efficiency of the signalling pathway that couples the guest binding event by the receptor unit, and the oxidation process of the ferrocenyl signalling unit, and gives a measure of the response selectivity of the redox chemosensor [60].
ΔE = E½complex − E½free ionophore = (RT/nF)ln (Kred/Kox)
The largest redox shift ΔE½ (E½complex − E½free L3) of 230 mV is observed in the presence of Pb2+ (Table 1) with a value of 7.9 × 103 for RCE, which means that in CH3CN solution, L3 binds Pb2+ ca. 7–8 × 103 times more strongly than its oxidised form [L3]+. Significantly lower RCE and redox shift values are observed for all other metal ions (Table 1).

Table 1.
Electrochemical data of L3 upon addition of H+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ as determined by cyclic voltammetry a.
In light of these results, we investigated the coordination of L3 to Pb2+ by DFT calculations. The geometry of the 1:1 complex [Pb(L3)]2+ was optimised at the DFT level (mPW1PW functional [71]; Def2SVP basis set [72]) along with the explicitly solvated species [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)n]2+ (n = 1–4). In all species, the Pb2+ ion is displaced from the ring cavity and coordinated by the S and N atoms of the macrocyclic unit, which adopts a folded conformation recalling that described above for [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN. The CH3CN units complete the coordination of the metal ion (Figure S2 for [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)3]2+), with the ferrocenylmethyl pendant pointing outwards without a direct interaction with the Pb2+ ion. A natural bonding analysis [73] shows that the Wiberg bond indexes [74] of the Pb–S bonds are larger than those of the Pb–N ones, with the aliphatic N-atom binding the metal ion more strongly than the N-atom from the pyridine ring (Table S5). Accordingly, a second order perturbation theory analysis of the Fock matrix in the NBO basis [73] shows that in [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)4]2+ the lone pairs of electrons (LPs) on the S-atom of the macrocyclic moiety contribute to the bond with a charge-transfer energy as large as about 67 kcal·mol−1, while the LPs on the pyridine and the macrocycle N-atoms with about 34 and 26 kcal·mol−1, respectively. The energy corresponding to the LP(CH3CN) → BD*(Pb2+) is calculated in the range 30–35 kcal·mol−1. The effect of the progressive increase in coordinated CH3CN molecules is to weaken the interaction of the macrocycle donor atoms with the Pb2+ ion, simultaneously decreasing the net natural charge QPb on the metal ion (QPb = 1.231, 1.213, 1.188, and 1.158 |e| for n = 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively, in [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)n]2+; Table S5). A thermochemical analysis of the resulting complexes demonstrates that the reaction free energy ΔGr values of the partial reactions is negative for n = 1–4:
[Pb(L3)]2+ + CH3CN = [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)]2+ ΔGr = –16.3 kcal·mol−1
[Pb(L3)(CH3CN)]2+ + CH3CN = [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)2]2+ ΔGr = –7.7 kcal·mol−1
[Pb(L3)(CH3CN)2]2+ + CH3CN = [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)3]2+ ΔGr = –9.47 kcal·mol−1
[Pb(L3)(CH3CN)3]2+ + CH3CN = [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)4]2+ ΔGr = –4.31 kcal·mol−1
Accordingly, the global ΔGr for the reactions [Pb(L3)]2+ + n CH3CN = [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)n]2+. (n = 1–4) is calculated to be exoergonic by –16.23, –23.97, –33.44, and –37.74 kcal·mol−1 for n = 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. These results support that the Pb2+ ion can be successfully coordinated by the ligand L3 in solution, even in the absence of an anion directly participating to coordination as in the structure of [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN, and that the solvent molecules CH3CN actively contribute to the solvation of the Pb2+ ion (with average Wiberg bond indexes of 0.162 for n = 1; 0.158 for n = 2; 0.147 for n = 3; 0.141 for n = 4; Table S5).
The electrochemical behaviour of L3 in the presence of the metal cations considered indicates that the macrocyclic ligand L1 bound to the ferrocenyl group can act as receptor unit in a redox-switchable chemosensor, with the highest shift for E½ observed in the presence of Pb2+. This result is not consistent with the electrochemical response predictable from the low charge density of Pb2+ as compared to the other metal cations considered. Previous studies on crown ethers and polyaza macrocycles linked to ferrocenyl group(s) via a methylene linker suggest a linear correlation between the observed ΔE½ values and the charge density of the complexed cations (in particular for the elements belonging to the first two groups of the periodic table). The electrostatic coupling (repulsion) between the complexed metal cation and the positive charge on the oxidised form of the ferrocenyl unit (either via through-bond or through-space) forms the basis of the mechanism responsible for the electrochemical recognition in these systems [14,48,51,52,75,76].
However, a comparison of the results obtained with L3 with those reported for similar Fc-based redox chemosensors in similar solvent media could give valuable and more general indications. In fact, on considering 12-membered tetracoordinating macrocyclic ligands like L1 linked to a ferrocenyl group through a methylene spacer, and containing donor atoms other than oxygen in the macrocyclic moieties, an interesting trend is observed. For example, the ligand Fc–CH2–([12]aneN4) shows a linear increase in E½ from 0.596V (Cd2+) to 0.659 (Co2+) vs. the charge density of the considered metal cations [Cd2+ < Zn2+ < Ni2+ < Co2+ < Cu2+; measurements were made in CH2Cl2/CH3CN 1:4 (v/v) solutions]. However, the data point for Ni2+ does not lie on the straight correlation line of the plot showing an E½ lower than expected (0.593 V) from the basis of the large charge density of the metal ion [52].
Even more interesting is the comparison with Fc-based redox chemosensors featuring sulphur among the donor atoms in the macrocyclic receptor unit. In Figure 8, the scatter plot of ΔE½ and RCE values vs. the ionic potential q/r (q = +2, r = radius of the metal cation in an octahedral environment [77]), which is equivalent to the charge density, is reported for L3 and the structurally analogues Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS2O) and Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS3). These ligands, which feature-mixed N/S/O- and N/S-donor sets, respectively, in the macrocyclic moiety, result from the replacement of the pyridine moiety in L3 with an oxygen or a sulphur atom [70], respectively, and are characterised by reduced conformational constraints. Both scatter plots clearly demonstrate the absence of a linear correlation between ΔE½/RCE and the ionic potential (q/r) of the metal cations with L3 being unexpectedly highly selective for Pb2+. Note that Pb2+ displays the lowest charge density among the considered metal cations, and Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS2O) and Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS3) show the highest shift for E½ (and consequently the highest RCE value) in the presence of Zn2+ (ΔE½ = 220) and Cu2+ (ΔE½ = 230 mV), respectively, as would be expected on the basis of their higher charge density. However, for all three ligands a significant shift of E½ is observed in the presence of Pb2+ in the order L3 (230 mV) > Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS2O) (210 mV) > Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS3) (200 mV). In general, as the charge density or ionic potential increases, a greater via through-space electrostatic repulsion between the oxidised form of the chemosensor [L]+ and the metal cation coordinated to the receptor unit is expected, resulting in a lower Kox value. A high Kred/low Kox situation for high charge density metal ions would imply a high selectivity in the electrochemical response of redox chemosensors featuring ferrocene as the active unit, such as L3.
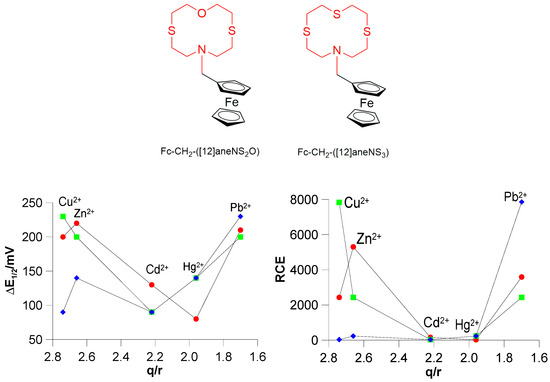
Figure 8.
Scatter plot of ΔE½ = (E½complex − E½free ligand) vs. q/r (bottom left) and RCE vs. q/r (bottom right) for L3 (Table 1) (♦), Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS3) (■), and Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS2O) (●) [70] in the presence of Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ (q = +2; r = atomic radius of the metal cation). For Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS3) (■), and Fc–CH2–([12]aneNS2O) (●) measurements were made in CH3CN [70].
Considering the above, the fact that the three ligands featuring 12-membered mixed donor macrocyclic receptors, in particular L3, exhibit a significant electrochemical response for Pb2+ in terms of measured ΔE½ and RCE values (Figure 8) [despite Kred with this metal cation being lower than those with Cu2+, although slightly higher than those with Zn2+, see above], suggests that Kox with Pb2+ is much lower than expected based only on the electrostatic repulsion with the ligands in the oxidised form. Clearly, under the commonly considered and accepted hypothesis of a sensing mechanism mainly based on an electrostatic via through-space interaction, a fine modulation of this interaction by other factors come into play and become dominant especially in the case of transition and post-transition metal cations (indeed, a linear dependence of ΔE½ and RCE on parameters such as the charge density or the ionic potential appears not to hold for these metal ions), thus dramatically affecting the selectivity of Fc-based redox chemosensors predictable on basis of only the metal cation charge density. Although it is difficult to identify all factors playing a role in the sensing mechanism of Fc-based redox chemosensors, as well as to quantify their effects, in the case of transition metal cations the coordination environment imposed by their electronic requirements, as well as the hard–soft nature of the donor atoms in the macrocyclic receptor unit of the chemosensor, its conformational properties, and finally the nature of the solvent can also be considered to play a very important and crucial role in determining a favourable balance between the thermodynamic selectivities of the host–guest interactions (Kred and Kox) for a net electrochemical response selectivity. Demonstrating the high number of factors beyond the charge density of the metal cation guest, and their complex interconnection in determining the unpredictable response selectivity of Fc-based redox chemosensors, the case of the analogous ionophore 1-ferrocenylmethyl 1-aza-4,7,10-trioxacyclododecane (Fc–CH2–([12]aneNO3), which has an NO3 donor set in the 12-membered macrocyclic receptor unit, is quite emblematic. It exhibits a selective electrochemical response in terms of the largest redox shift ΔE½ measured in CH3CN solution to the heavy and soft metal ions Hg2+ and Pb2+ [78].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Apparatus
All chemicals used, including solvents and metal salts, were analytical reagent-grade; they were purchased from commercial sources where available (Sigma or Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and used without any further purification. L1 [39], L2 [41], and (ferrocenylmethyl)trimethylammonium iodide [79] were prepared according to procedures reported in the literature. Microanalytical data were obtained using a Fisons EA CHNS-O (Fisons, Loughborough, UK) instrument operating at 1000 °C. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on a Varian VXR300 or a Varian VXR600 spectrometer (as specified below) (Varian, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) and the chemical shifts were referred to the signals of the solvent. The FTIR spectra were recorded on a Thermo-Nicolet 5700 spectrometer (Thermo Electron Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) on KBr pellets, by using a KBr beam splitter out and KBr windows (4000–400 cm−1, resolution 4 cm−1). Cyclic voltammetry experiments were recorded on a computer-controlled EG&G (Princeton Applied Research, AMETEK Scientific Instruments, Oak Ridge, TN, USA) potentiostat-galvanostat Model 273 EG&G, using model 270 electrochemical analysis software. The mass spectra were recorded in the m/z 100–1000 range on a triple quadrupole QqQ Varian 310-MS mass spectrometer (Varian, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) by using the atmospheric pressure ESI technique. Sample solutions (CH3CN) were infused into the ESI source with a programmable syringe pump (1.50 mL/h constant flow rate). The mMass 5.5.0 software package [80] was used for analysing the isotopic patterns of the peaks recorded in the mass spectra.
3.2. Procedure for Cyclic Voltammetry Experiments
Cyclic voltammetry experiments were conducted at 25 °C in anhydrous solvents [CH2Cl2/CH3CN 0.25:1 (v/v)] using a conventional three-electrode cell, consisting of a combined working and counter platinum electrode and a standard Ag/AgCl (in KCl 3.5 mol·dm−3; standard reduction potential 0.2223 V at 25 °C) reference electrode (scan rate of 100 mV/s). The solutions were 2.28 × 10−3 mol·dm−3 in the electroactive species L3 with nBu4NBF4 (0.1 mol·dm−3) as supporting electrolyte. A stream of argon was passed through the solution prior to the scan. Different solutions were prepared for L3 containing an increasing amount of the metal guest cation as hydrated perchlorate or nitrate salt (molar ratio ranging from 0 to 1:1), and the cyclic voltammogram was recorded for each solution. The titration of the ligands with HClO4 was performed by cautiously adding μL amounts of the concentrated acid (1 mol·dm−3) to the solution of the electroactive species.
3.3. X-Ray Crystallography
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data for [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN and [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN were collected at 293 K on a Bruker APEX II CCD diffractometer using ω scans. Data reduction and processing were carried out using SAINT [81] and SADABS [82]. The structures were solved by dual methods using SHELXT [83], and the models were refined through iterative cycles of least-squares refinement on F2 with SHELXL [84].
For compound [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN, two perchlorates [those belonging to unit A (see above)] were disordered and modelled over two sites using geometric restraints for Cl–O distances and constraining the atomic displacement parameters of O atoms to be the same.
One disordered acetonitrile molecule per asymmetric unit could not be modelled, and its electron density was accounted by using the SQUEEZE routine implemented in Platon [85].
For compound [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN, a perchlorate was disordered and modelled over two positions with fractional occupancies 62:38, respectively.
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data for [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3 were collected at 150 K on a Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer. The structure was refined as a two-component inversion twin, solved by direct methods using SHELXS [86], and the model developed with SHELXL [84]. Olex2 [87] was used as the graphical interface for structure solution and refinement and for the preparation of figures.
All non-H atoms were refined anisotropically. H atoms were introduced at calculated positions and thereafter incorporated into a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
3.4. DFT Calculations
Theoretical calculations were carried out on L3, CH3CN, and the model compounds [Pb(L3)]2+ and [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)n]2+ (n = 1–4) at the density functional theory (DFT) level with the commercial suite of programs Gaussian 16 [88], adopting the mPW1PW hybrid functional [71], and the Def2SVP [72] basis set, including pseudopotential parameters for the heavier Pb atom (Tables S5–S11). Harmonic frequency calculations were carried out at the optimised geometries to check the nature of the energy minima by verifying the absence of significative negative frequencies. Free energy variations ΔGr associated with the solvation reactions were calculated as differences of the sum of electronic and thermal free energies calculated for products and reactants. All thermochemical calculations assumed T = 298.15 K as a part of harmonic frequency calculations. Natural charge distributions [73] and Wiberg [74] bond indexes (Table S5) were calculated at the same level of theory. The program GaussView 6.0.16 [89] was used to investigate the optimised structures and natural charge distribution.
3.5. Synthesis of 5-Ferrocenylmethyl-2,8-dithia-5-aza-2,6-pyridinophane (L3)
A solution of (ferrocenylmethyl)trimethylammonium iodide (1.21 g, 3.15 mmol) in anhydrous CH3CN (50 mL) was added dropwise to a refluxing solution of L1 (0.5 g, 2.08 mmol) and K2CO3 (2.32 g, 16.8 mmol) in anhydrous CH3CN (40 mL). The resulting orange solution was stirred overnight at 80 °C under an atmosphere of N2. K2CO3 was then filtered off and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was taken up in CH2Cl2 and washed with water. The organic extracts were dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent removed under reduced pressure to give the desired compound as an orange solid (yield 0.75 g, 1.7 mmol, 82%). Mp.: 135 °C. Anal. found (calc. for C22H26FeN2S2): C, 59.88 (60.27); H, 6.15 (5.98); N, 6.60 (6.39); S, 14.60 (14.63) %. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, Figure S3): δH 2.55 (m, 8H), 3.30 (s, 2H), 3.80 (s, 4H), 4.07 (s, 5H), 4.30 (s, 4H), 7.25 (d, 2H, J = 12 Hz), 7.68 ppm (t, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3, Figure S4): δC 25.5, 36.6, 51.1, 52.7, 67.3, 68.5, 69.6, 70.7, 72.1, 121.6, 138.2, 157.7 ppm. ESI(+) MS (CH3CN solution, Figure S5) m/z: 439.1 ([C22H26FeN2S2]+).
3.6. Synthesis of [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN
To a solution of L1 (0.020 g, 0.083 mmol) in CH3CN (10 mL) was added Pb(ClO4)2·3H2O (0.038 g, 0.083 mmol) dissolved in CH3CN (2 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature under N2 for several hours. Colourless micro crystals (yield 0.05 g, 45%) were obtained by diffusion of Et2O vapour into the CH3CN solution. Mp: 250 °C with decomposition. Elem. Anal. found (calc. for C12H17.5Cl2N2.5O8PbS2): C, 21.70 (21.61); H, 2.48 (2.64); N, 5.22 (5.25); S, 9.50 (9.61) %. FT-IR (KBr): ν = 3508 (w,br), 3251 (m), 2978 (w), 2932 (w), 1595 (m), 1449 (m), 1240 (w), 1090 (s,br), 999 (w), 785 (w), 623 (m) cm−1. 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CD3CN): δH 2.55 (m, 2H), 3.73 (m, 2H), 3.09 (m, 2H), 3.50 (m, 2H), 4.08 (d, 2H, J = 16.9 Hz), 4.61 (d, 2H, J = 16.9 Hz), 7.34 (d, 2H, J = 6.6 Hz), 7.83 ppm (t, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, CD3CN): δC 31.7, 38.0, 52.1, 126.9, 141.5, 161.4 ppm (aromatic carbons). ESI(+) MS (CH3CN solution) m/z: 448.3 ([C11H16N2PbS2]+).
3.7. Synthesis of [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN
To a solution of L2 (0.020 g, 0.070 mmol) in CH3CN (10 mL) was added Cu(ClO4)2·2H2O (0.021 g, 0.070 mmol) dissolved in EtOH (2 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature under N2 for 2 h. Blue crystals (yield 0.025 g, 61%) were obtained by diffusion of Et2O vapour into the reaction mixture. Mp: 163° C with decomposition. Elem. Anal. found (calc. for C15H24Cl2CuN4O8S2): C, 30.55 (30.69); H, 3.88 (4.12) N, 9.32 (9.54); S, 10.54 (10.92) %. FT-IR (KBr): ν = 3436 (m,br), 1644 (m), 1462 (w), 1384 (w), 1087 (s), 810 (w), 627(m) cm−1. ESI(+) MS (CH3CN solution) m/z: 445.8 ([C13H21ClCuN3O4S2]+).
3.8. Synthesis of [Cd(L2)NO3]NO3
To a solution of L2 (0.020 g, 0.070 mmol) in CH3CN (10 mL) was added Cd(NO3)2·4H2O (0.022 g, 0.070 mmol) dissolved in CH3CN (2 mL). The mixture was stirred at 50 °C under nitrogen for 24 h. Colourless crystals (yield 0.023 g, 62%) were obtained by diffusion of Et2O vapour into CH3CN solution. Mp: 230 °C with decomposition. Elem. Anal. found (calc. for C13H21CdN5O6S2): C, 30.39 (30.03); H, 4.25 (4.07) N, 13.40 (13.47); S, 12.45 (12.34) %. FT-IR (KBr): ν = 3448 (w,br), 2917 (w), 1624 (m), 1384 (m), 1120 (s), 620 (w) cm−1. ESI(+) MS (CH3CN solution) m/z: 459.2 ([C13H21CdN4O3S2]+).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we report on the use of L1 as a receptor unit in the construction of a conjugated redox chemosensor for heavy metal ions, L3, featuring a ferrocenyl signalling unit. Cyclic voltammetry experiments proved the compound to be selective for lead(II), showing the highest anodic shift for this metal ion, among the metal ions considered (Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Hg2+), in reversible two-wave behaviour of the Fc+/Fc redox couple, in CH2Cl2/CH3CN 0.25:1 (v/v) solvent mixture at 25 °C. These results confirm the complex interplay of the many factors, beyond the charge density of the metal ion guests, in determining the signalling selectivity for transition metal cations of Fc-based redox chemosensors. To date, the major role of the electrostatic via through-space interactions on the selectivity of Fc-based redox chemosensors is not fully understood and quantifiable/rationalizable.
Besides this, we have also shown the great versatility of L1 as a receptor unit (despite its low binding selectivity) in the design of conjugated chemosensors involving either an optic or electrochemical transduction mechanism, with a “synergism cooperation” between the receptor and signalling units determining at least a signalling selectivity towards different metal ions. The crystal structures of the compounds [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN, [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN and [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3 have allowed us to gain a deeper knowledge of the coordination properties of L1 in comparison with those of L2.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules30010130/s1, Figure S1: Distribution of the Pb–O(ClO4−) distances retrieved from the Cambridge Crystallographic Database (CSD); Figure S2: Structure of the model complex [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)3]2+ optimised at DFT level; Figure S3: 1H-NMR spectrum of L3 in CDCl3; Figure S4: 13C-NMR spectrum of L3 in CDCl3; Figure S5: ESI(+) MS of L3 in CH3CN; Table S1: Crystallographic data and refinement parameters for [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN, [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN, and [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3; Table S2: Selected bond and distances (Å) and angles (°) for [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN; Table S3: Pb–O distances (Å) and selected O–Pb–O angles (o) in [Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN; Table S4: Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°) for [Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN and [Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3; Table S5: Selected bond lengths (Å) and corresponding Wiberg bond indexes (in parentheses) calculated for the complexes [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)n]2+ (n = 1–4) at the DFT-optimised geometry; Tables S6–S11: Optimised geometry calculated at DFT level for CH3CN, [Pb(L3)]2+, [Pb(L3)(CH3CN)n]2+ (n = 1–4), respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, A.G. and V.L.; methodology, A.G., V.L., A.J.B., F.D. and E.P.; validation, all authors; investigation, A.G., M.C.A., M.A., A.J.B., F.D., E.P., C.C. and G.P.; data curation, A.G., V.L., A.J.B., F.D. and E.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G. and V.L.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, A.G. and V.L.; funding acquisition, M.A., C.C., and V.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge Fondazione di Sardegna (FdS Progetti Biennali di Ateneo, annualità 2022) for financial support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request. Crystallographic data have been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) under deposition no. 2391106 ([Pb(L1)(ClO4)2]·½CH3CN), 2391107 ([Cd(L2)(NO3)]NO3), 2391105 ([Cu(L2)](ClO4)2·CH3CN). These data can be obtained free charge at: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.
Acknowledgments
We thank the EPSRC (UK) for the award of X-ray diffractometers, and the Centre for Research University Services (CeSAR, Università degli Studi di Cagliari) for NMR measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hu, T.; Lai, Q.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Advances in Portable Heavy Metal Ion Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Qian, K. Nanomaterials-based sensors and strategies for heavy metal ion detection. Green. Anal. Chem. 2022, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargavi Gumpu, M.; Sethuraman, S.; Maheswari Krishnan, U.; Bosco Balaguru Rayappan, J. A review on detection of heavy metal ions in water—An electrochemical approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 213, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Nie, C.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Z.-L.; Xiang, P. FRET-based innovative assays for precise detection of the residual heavy metals in food and agriculture-related matrices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 469, 214676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Khalid, M.; Shahnawaz Khan, M.; Shahid, M. Metal organic frameworks and their composites as effective tools for sensing environmental hazards: An up to date tale of mechanism, current trends and future prospects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 474, 214859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet, J.-P. Heavy Metals in the Environment; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 0444890645. [Google Scholar]
- Sigel, A.; Sigel, H.; Sigel, R.K.O. Neurodegenarative Disease and Metal Ions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 1, ISBN 978-0-470-02810-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Fowler, B.A.; Nordberg, M.; Friberg, L. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-12-369413-3. [Google Scholar]
- Charlet, L.; Chapron, Y.; Kirsch, R.; Stone, A.T.; Baveye, P.C. Neurodegenerative diseases and exposure to the environmental metals Mn, Pb, and Hg. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meret, W.; Moulis, J.-M. The bioinorganic chemistry of cadmium in the context of its toxicity. Met Ions Life Sci. 2013, 11, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, W.F.; Lamborg, C.H.; Hammerschmidt, C.R. Marine Biogeochemical Cycling of Mercury. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, R.; Zilli Vieira, C.L.; Rosembaum, M.H.; Bischoff, K.; Mordarski, D.C.; Brown, M.J. The urban lead(Pb) burden in humans, animals and the natural environment. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, A.P.; Gunaratne, H.Q.G.; Gunlaugsson, T.; Huxley, A.J.M.; McCoy, C.P.; Rademacher, J.T.; Rice, T.E. Signaling Recognition Events with Fluorescent Sensors and Switches. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1515–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A.; Chen, G.Z. Mechanism of Electrochemical Recognition of Cations, Anions and Neutral Guest Species by Redox-Active Receptor Molecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 185, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurack, K. Flipping the light switch “ON”—The design of sensor molecules that show cation-induced fluorescence enhancement with heavy and transition metal ions. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2001, 57, 2161–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodi, L. Luminescent chemosensors: From molecules to nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2005, 29, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, A.; Fabbrizzi, L.; Foti, F.; Licchelli, M.; Mangano, C.; Pallavicini, P.; Poggi, A.; Sacchi, D.; Taglietti, A. Light-emitting molecular devices based on transition metals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, C.; Capelo, J.L.; Mejuto, J.C.; Oliveira, E.; Santos, H.M.; Pedras, B.; Nuñez, C. Light and colour as analytical tools: A journey into the periodic table using polyamines to bio-inspired systems as chemosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2948–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, K.P.; Young, A.M.; Palmer, A.E. Fluorescent Sensors for Measuring Metal Ions in Living Systems. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4564–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Lee, K.H. Optical sensor: A promising strategy for environmental and biomedical monitoring of ionic species. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 72150–72287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xu, Z. Fluorescence imaging of metal ions implicated in diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K. Fluorescent chemosensors containing redox-active ferrocene: A review. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 11681–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Meng, G. Fluorophores-modified nanomaterials for trace detection of polychlorobiphenyls and heavy metal ions. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 243, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Palacios, M.A.; Anzenbacher, P., Jr. Fluorescence sensor array for metal ion detection based on various coordination chemistries: General performance and potential application. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7451–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhang, G. Differentiation and determination of metal ions using fluorescent sensor array based on carbon nanodots. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 246, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ren, C.; Teoh, C.L.; Peng, J.; Gadre, S.H.; Rhee, C.-L.; Lee, C.-L.; Chang, Y.-T. An artificial tongue fluorescent sensor array for identification and quantitation of various heavy metal ions. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8763–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askim, J.R.; Mahmoudi, M.; Suslick, K.S. Optical Sensor arrays for chemical sensing: The optoelectronic nose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8649–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindoy, L.F. The Chemistry of Macrocyclic Ligand Complexes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; ISBN 052125261X. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotov, Y.A. Macrocyclic Compounds in Analytical Chemistry; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-471-17262-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gloe, K. Macrocyclic Chemistry, Current Trends and Future Perspectives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 1-4020-3364-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, D.W.; Ulrich, H.J. Macrocyclic Chemistry: New Research Developments (Chemistry Research and Applications); Nova Science Pub. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 1608768961. [Google Scholar]
- Danks, P.J.; Champness, N.R.; Schroder, M. Chemistry of mixed nitrogen- and sulfur-donor tridentate macrocycles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1998, 174, 417–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, R.T.; Bradshaw, J.S.; Savage, P.B.; Fuangswasdi, S.; Lee, S.C.; Krakowiak, K.E.; Izatt, R.M. Bis-8-hydroxyquinoline-Armed Diazatrithia-15-crown-5 and Diazatrithia-16-crown-5 Ligands: Possible Fluorophoric Metal Ion Sensors. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 4752–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Bradshaw, J.S.; Son, H.; Bronson, R.T.; Savage, P.B.; Krakowiak, K.E.; Izatt, R.M.; Prodi, L.; Montalti, M.; Zaccheroni, N. A convenient synthesis and preliminary photophysical study of novel fluoroionophores: Macrocyclic polyamines containing two dansylamidoethyl side arms. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Water, L.G.A.; ten Honte, F.; Driessen, W.L.; Reedijk, J.; Sherrington, D.C. Selective extraction of metal ions by azathiacrown ether-modified polar polymers. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2000, 303, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenny, M.W.; van de Water, L.G.A.; Driessen, W.L.; Reedijk, J.; Blake, A.J.; Wilson, C.; Schröder, M. Conformational and stereochemical flexibility in cadmium(II) complexes of aza-thioether macrocycles. Dalton Trans. 2004, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, A.; Lodeiro, C.; Escriche, L.; Casabó, J.; Covelo, B.; González, P. New Fluorescent PET Systems Based on N2S2 Pyridine-Anthracene-Containing Macrocyclic Ligands. Spectrophotometric, Spectrofluorimetric, and Metal Ion Binding Studies. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 8105–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindoy, L.F.; Meehan, G.V.; Vasilescu, I.M.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.-E.; Lee, S.S. Transition and post-transition metal ion chemistry of dibenzo-substituted mixed-donor macrocycles incorporating five donor atoms. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.J.; Bencini, A.; Caltagirone, C.; De Filippo, G.; Dolci, L.S.; Garau, A.; Isaia, F.; Lippolis, V.; Mariani, P.; Prodi, L.; et al. A new pyridine-based 12-membered macrocycle functionalised with different fluorescent subunits: Coordination chemistry towards CuII, ZnII, CdII, HgII, and PbII. Dalton Trans. 2004, 2771–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragoni, M.C.; Arca, M.; Bencini, A.; Blake, A.J.; Caltagirone, C.; De Filippo, G.; Devillanova, F.A.; Garau, A.; Gelbrich, T.; Hursthouse, M.B.; et al. Tuning the Selectivity/Specificity of Fluorescent Metal Ion Sensors Based on N2S2 Pyridine-Containing Macrocyclic Ligands by Changing the Fluorogenic Subunit: Spectrofluorimetric and Metal Ion Binding Studies. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 4548–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsipur, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Alizadeh, K.; Bencini, A.; Valtancoli, B.; Garau, A.; Lippolis, V. Novel fluorimetric bulk optode membrane based on 5,8-bis(5′-chloro-8′-hydroxy-7′-quinolinyl)methyl)-2,11-dithia-5,8-diaza-2,6-pyridinophane for selective detection of lead(II) ions. Talanta 2010, 80, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Garau, A.; Lippolis, V. An efficient and selective flourescent chemical sensor based on 5-(8-hydroxy-2-quinolinylmethyl)-2,8-dithia-5-aza-2,6-pyridinophane as a new fluoroionophore for determination of iron(III) ions. A novel probe for iron speciation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 761, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Zahedi, M.M.; De Filippo, G.; Lippolis, V. Development of a novel flow injection liquid-liquid microextraction method for on-line separation, preconcentration and fluorimeteric determination of zinc(II) using 5-(8-hydroxy-2-quinolinylmethyl)-2,8-dithia-5-aza-2,6-pyridinophane as a sensitive and selective fluorescent chemosensor. Talanta 2011, 85, 687–693. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzicalupi, C.; Caltagirone, C.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Di Natale, C.; Garau, A.; Lippolis, V.; Lvova, L.; Liu, H.; Lundström, I.; et al. Multimodal use of new coumarin-based fluorescent chemosensors: Towards highly selective optical sensors for Hg2+ probing. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 14639–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedi, E.; Garau, A.; Lvova, L.; Ambrosi, G.; Aragoni, M.C.; Arca, M.; Caltagirone, C.; Coles, S.J.; Formica, M.; Fusi, V.; et al. N2S2 Pyridinophane-Based Fluorescent Chemosensors for Selective Optical Detection of Cd2+ in Soils. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20834–20852. [Google Scholar]
- Lvova, L.; Pudi, R.; Galloni, P.; Lippolis, V.; Di Natale, C.; Lundstrom, I.; Paolesse, R. Multi-transduction sensing films for Electronic Tongue applications. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2015, 207, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca, M.; Caltagirone, C.; De Filippo, G.; Formica, M.; Fusi, V.; Giorgi, L.; Lippolis, V.; Prodi, L.; Rampazzo, E.; Scorciapino, M.A.; et al. A fluorescent ratiometric nanosized system for the determination of PdII in water. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15259–15262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.C.; Goodnow, T.T.; Rojas, M.T.; Atwood, J.L.; Lynn, B.C.; Kaifer, A.E.; Gokel, G.W. Ferrocenyl Iron as a Donor Group for Complexes Silver ion Ferrocenyldimetyl[2.2]cryptand: A redox-Switched Receptor Effective in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10583–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Bhatta, R.B.; Thakur, A. Recent advances in the development of ferrocene based electroactive small molecules for cation recognition: A comprehensive review of the years 2010–2020. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, R.; Beer, P.D.; Davis, J.J. Electrochemical Anions Sensing: Supramolecular Approaches. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1888–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torriero, A.A.J.; Mruthunjaya, A.K.V. Ferrocene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for cations. Inorganics 2023, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Belousoff, M.J.; Spiccia, L.; Bond, A.M.; Torriero, A.A.J. Macrocycles Bearing Ferrocenyl Pendants and their Electrochemical Properties upon Binding to Divalent Transition Metal Cations. ChemPlusChem 2018, 83, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garau, A.; Picci, G.; Arca, M.; Blake, A.J.; Caltagirone, C.; De Filippo, G.; Demartin, F.; Isaia, F.; Lippolis, V.; Pintus, A.; et al. Can Serendepity Still Hold Any Surprises in the Coordination Chemistry of Mixed-Donor macrocyclic Ligands? The Case Study of Pyridine-Containing 12-Membered macrocycles and Platinum Group Metal ions PdII, PtII, and RhIII. Molecules 2021, 26, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tei, L.; Blake, A.J.; Bencini, A.; Valtancoli, B.; Wilson, C.; Schröder, M. Synthesis, solution studies and structural characterisation of complexes of a mixed oxa–aza macrocycle bearing nitrile pendant arms. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2002, 337, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buist, D.; Williams, N.J.; Reibenspies, J.H.; Hancock, R.D. Control of Metal Ion Size-Based Selectivity through Chelate Ring Geometry. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5033–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, A.-G.; Jung, J.H.; Ikeda, M.; Habata, Y.; Lee, S.S. Macrocycles incorporating isomeric arms: Synthesis and crystal structures of ligands and their mono-, di- and polynuclear supramolecular complexes. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 6515–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaira, M.; Guerra, M.; Mani, F.; Stoppioni, P. Unusual binding of exogenous anions in some lead(II) complexes with a functionalized macrocycle. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrowfield, J.M.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Lewis-base Adducts of Lead(II) Complexes. Part 6. X-Ray Structural Characterisation of Adducts of Lead(II) Bis(perchlorate) with Dimethyl Sulfoxide. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1993, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in halides and Chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. The Nature of Chemical Bond, 3rd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt, L.M.; Harrowfield, J.M.; Miyamae, H.; Patrick, J.M.; Skelton, B.W.; Soudi, A.A.; White, A.H. Lewis-Base Adducts of Lead(II) Compounds. XIV. Synthetic and Structural Studies of Some 2:1 Adducts of 2,2′-Bipyridine With Lead(II) Oxoanion Salts. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrowfield, J.M.; Miyamae, H.; Shand, T.M.; Skelton, B.W.; Soudi, A.A.; White, A. Lewis-Base Adducts of Lead(II) Compounds. IX. Synthetic and Structural Studies of Some 1:1 Adducts of ‘cyclam’ and Its Hexamethylated Derivative ’tet-b’ With Lead(II) Oxoanion Salts. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, A.M.; Tidmarsh, I.S.; Ward, M.D. Lead(II) complexes of bis- and tris-bidentate compartmental ligands based on pyridyl-pyrazole and pyridyl-triazole fragments: Coordination networks and a discrete dimeric box. CrystEngComm 2010, 12, 3642–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoda, K.-I.; Sakiyama, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Okawa, H.; Kida, S. Template Synthesis and Structure of a Dinuclear Lead(II) Complex of Novel Macrocycle Derived from 2,6-Diformyl-4-methylphenol and 1,9-Diamino-3,7-diazanonane. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 65, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragoni, M.C.; Arca, M.; Bencini, A.; Biagini, S.; Blake, A.J.; Caltagirone, C.; Demartin, F.; De Filippo, G.; Devillanova, F.A.; Garau, A.; et al. Interaction of Mixed-Donor Macrocycles Containing the 1,10-Phenanthroline Subunit with Selected Transition and Post-Transition Metal Ions: Metal Ion Recognition in Competitive Liquid−Liquid Solvent Extraction of CuII, ZnII, PbII, CdII, AgI, and HgII. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 8391–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrowfield, J.M.; Miyamae, H.; Skelton, B.W.; Soudi, A.A.; White, A. Lewis-Base Adducts of Lead(II) Compounds. X. Synthetic and Structural Studies of Some 1:1 Adducts of ‘tet-b’ With Lead(II) (Pseudo-)Halides. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, I.V.; Kondinski, A.; Monakhov, K.Y.; Koshevoy, I.O.; Grachova, E.V. Synthesis, photophysical properties and cation-binding studies of bipyridine-functionalized gold(I) complexes. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, D.J.; James, M.P.; Hanton, L.R.; Moratti, S.C. Metal-Induced Isomerization of a Molecules Strand Containing Contraddictory Dynamic Coordination Sites. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 2122–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadarkaraisamy, M.; Caple, G.; Gorden, A.R.; Squire, M.A.; Sykes, A.G. Large Amplitude, Proton- and Cation-Activated Latch-Type Mechanical Switches: O-Protonated Amides Stabilized by Intramolecular Low-Barrier Hydrogen Bonds within Macrocycles. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11644–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caltagirone, C.; Bencini, A.; Demartin, F.; Devillanova, F.A.; Garau, A.; Isaia, F.; Lippolis, V.; Mariani, P.; Papke, U.; Tei, L.; et al. Redox chemosensors: Coordination chemistry towards CuII, ZnII, CdII.; HgII, and PbII of 1-aza-4,10-dithia-7-oxacyclododecane ([12]aneNS2O) and its N-ferrocenylmethyl derivative. Dalton Trans. 2003, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Exchange functionals with improved long-range behavior and adiabatic connection methods without adjustable parameters: The mPW and mPW1PW models. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.; Curtiss, L.A.; Weinhold, F. Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, K.B. Application of the Pople-Santry-Segal CNDO method to the cyclopropylcarbinyl and cyclobutyl cation and to bicyclobutane. Tetrahedron 1968, 24, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A.; Chen, G.Z. Electrochemical molecular recognition: Pathways between complexation and signaling. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1999, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A.; Chen, Z. Electrochemical Recognition of Charged and Neutral Guest Species by Redox-active Receptor Molecules. Adv. Phys. Org. Chem. 1999, 31, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D.; Prewitt, C.T. Revised values of effective ionic radii. Acta Crys. 1970, 26, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloris, J.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Soto, J.; Pardo, T. An electrochemical study in acetonitrile of macrocyclic or open-chain ferrocene-containing oxa-aza or polyaza receptors in the presence of protons, metal cation and anions. J. Organom. Chem. 2001, 637–639, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednicer, D.; Hauser, C.R. N,N-Dimethylaminomethylferrocene methiodide. Org. Synth. 1960, 40, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Strohalm, M.; Kavan, D.; Novak, P.; Volný, M.; Havliček, V. mMass 3: Cross-platform Software Environment for Precise Analysis of Mass Spectrometric Data. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4648–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAINT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2000.
- SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2000.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL—Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2018, 74, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.A.; Millam, J.M. GaussView; Version 6.0. 16; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).