Preparation of a Novel Oat β-Glucan–Chromium(III) Complex and Its Hypoglycemic Effect and Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of OBG-Cr(III)
2.2. Structural Characterization of OBG-Cr(III)
2.2.1. Molecular Weight Analysis of OBG and OBG-Cr(III)
2.2.2. Chromium Content Analysis of OBG-Cr(III)
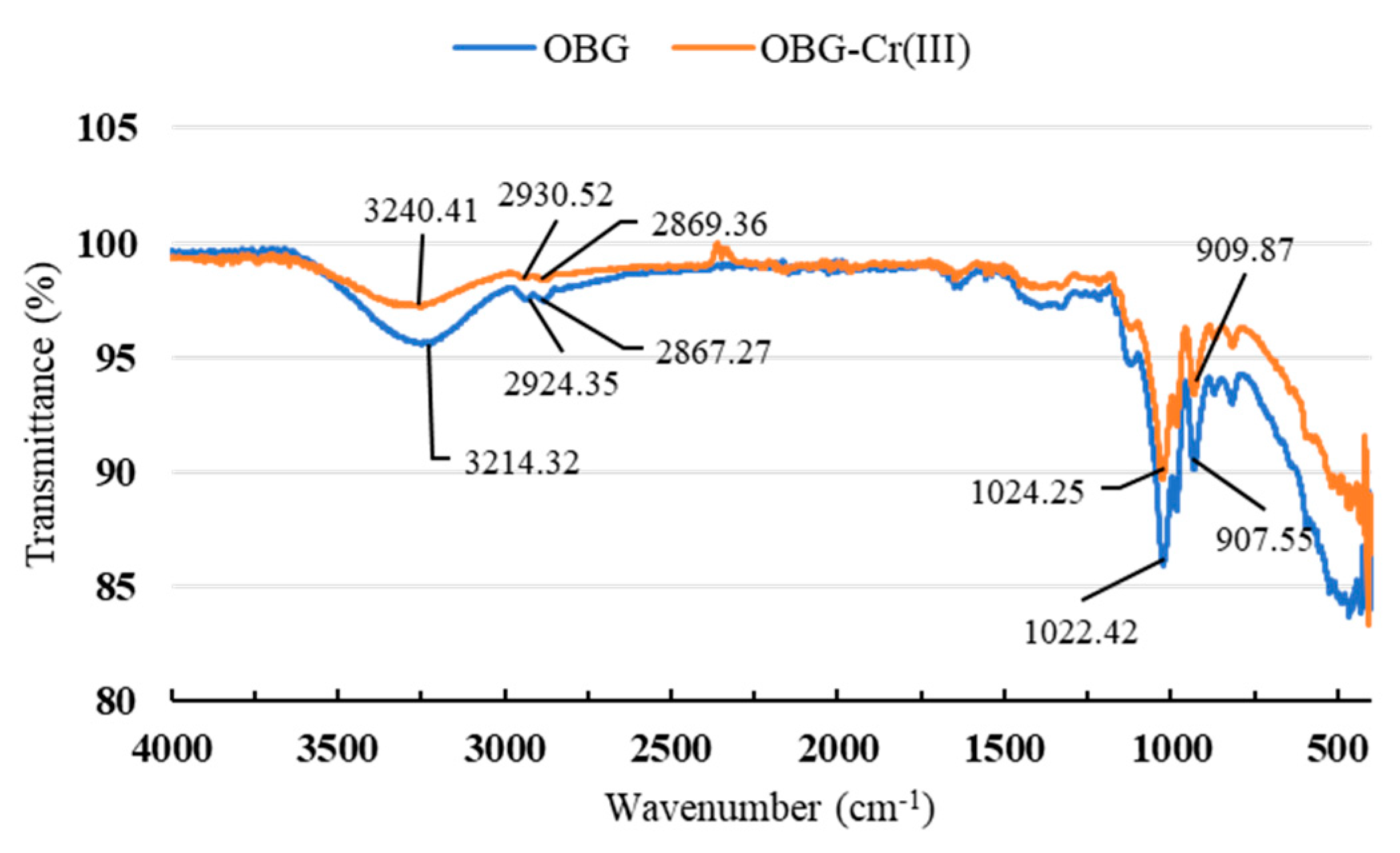
2.2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrum Analysis
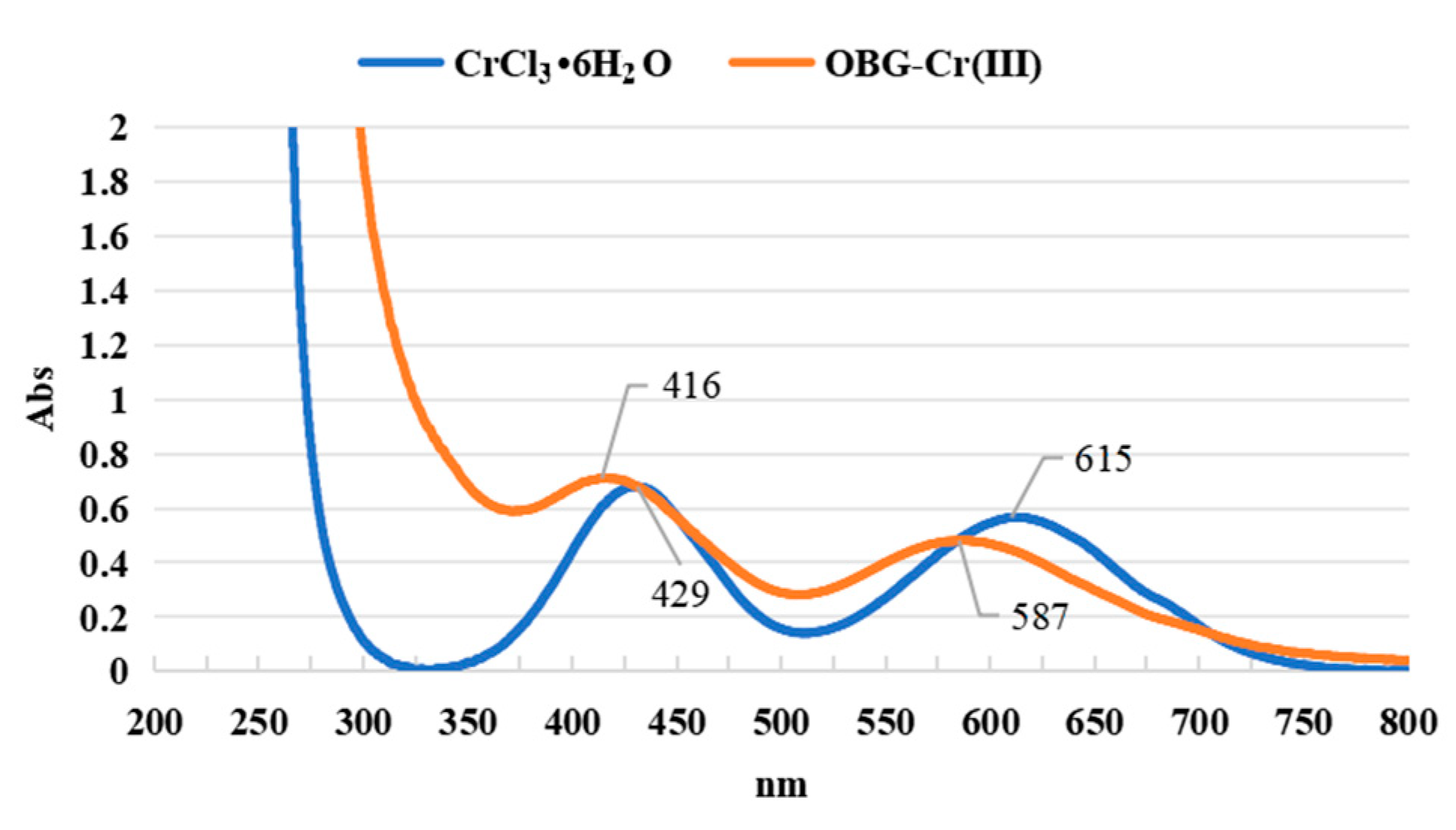
2.2.4. Ultraviolet and Visible (UV-VIS) Spectrum Analysis
2.2.5. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectrogram Analysis
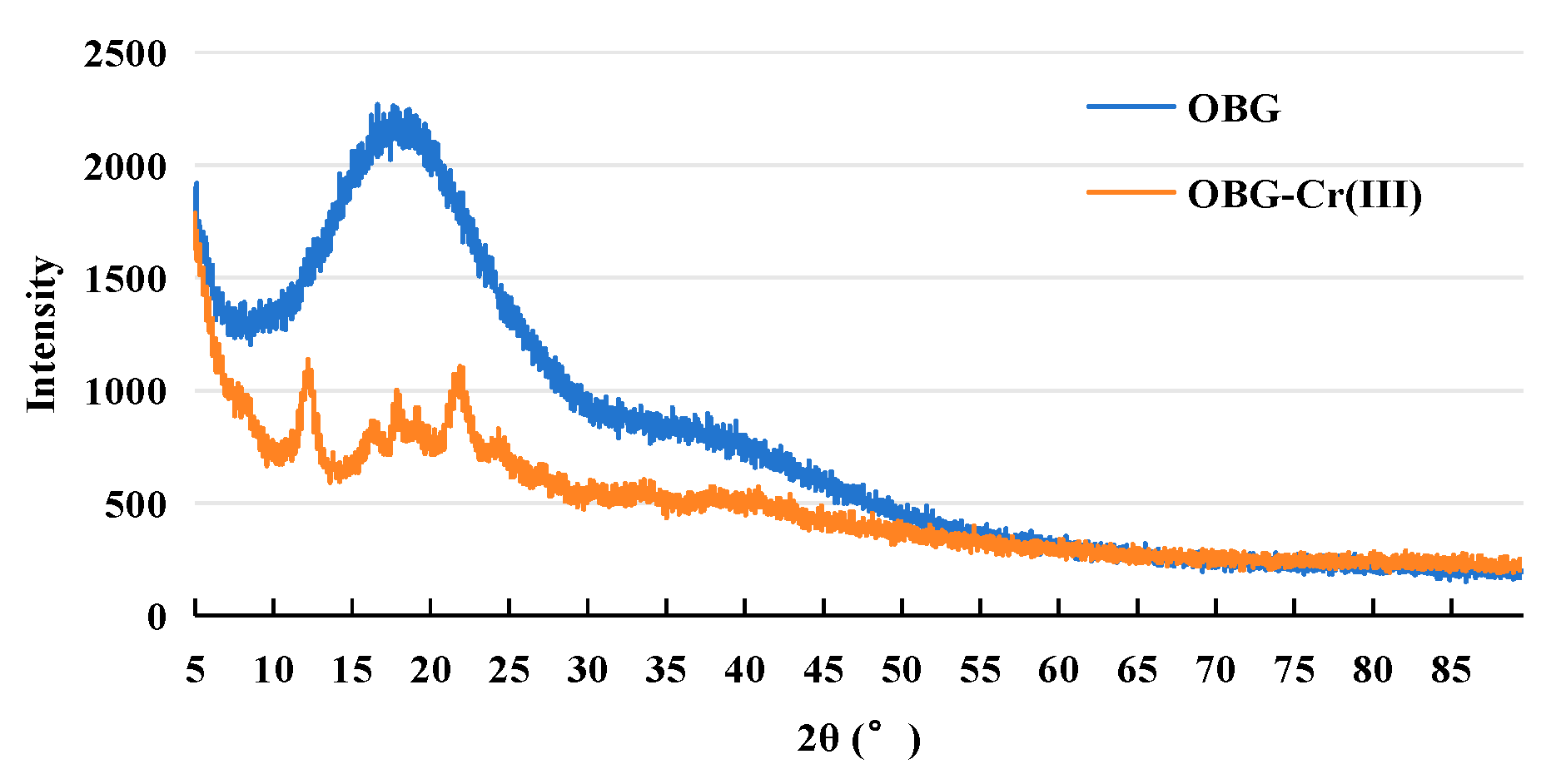
2.2.6. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
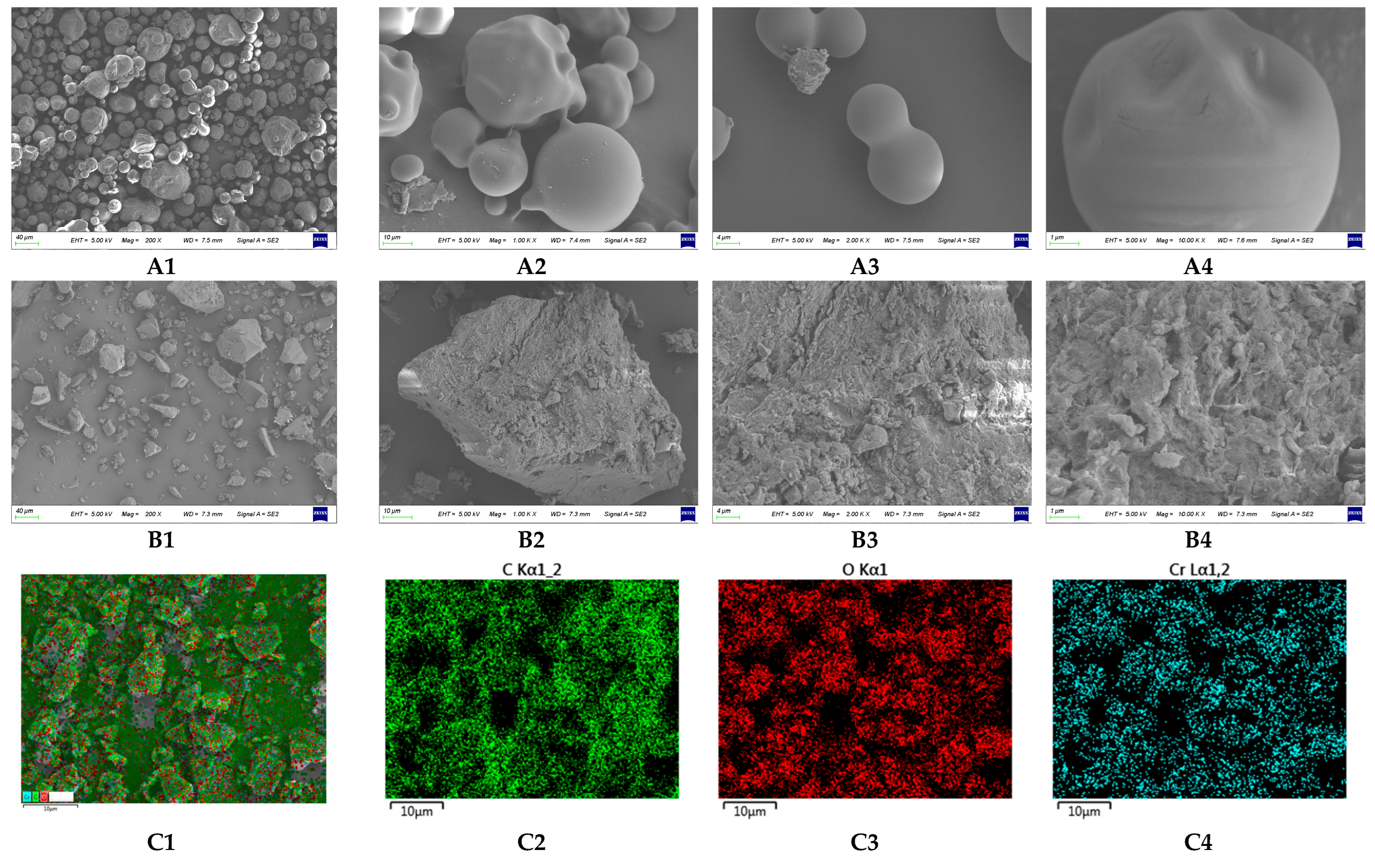
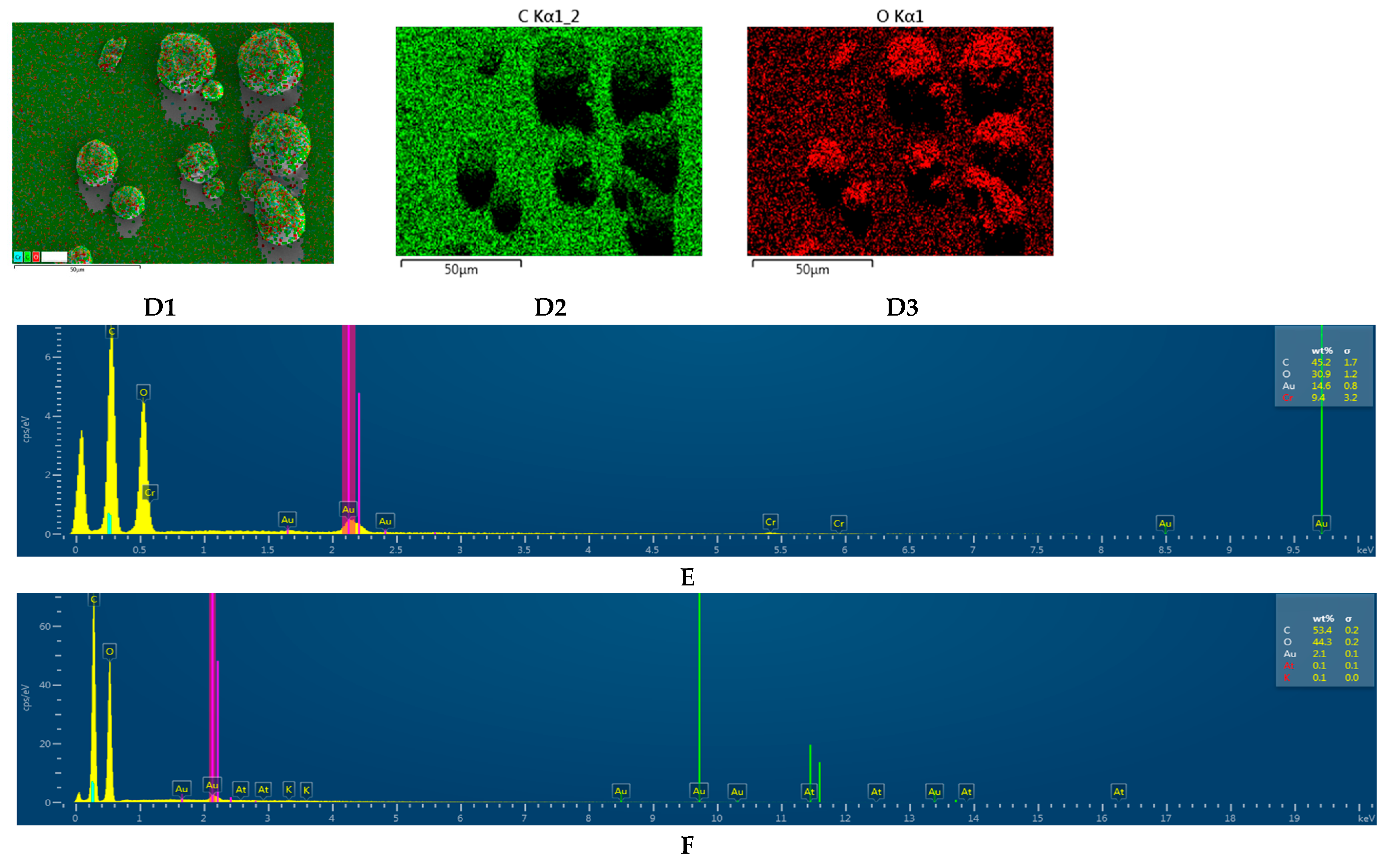
2.2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)–Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis
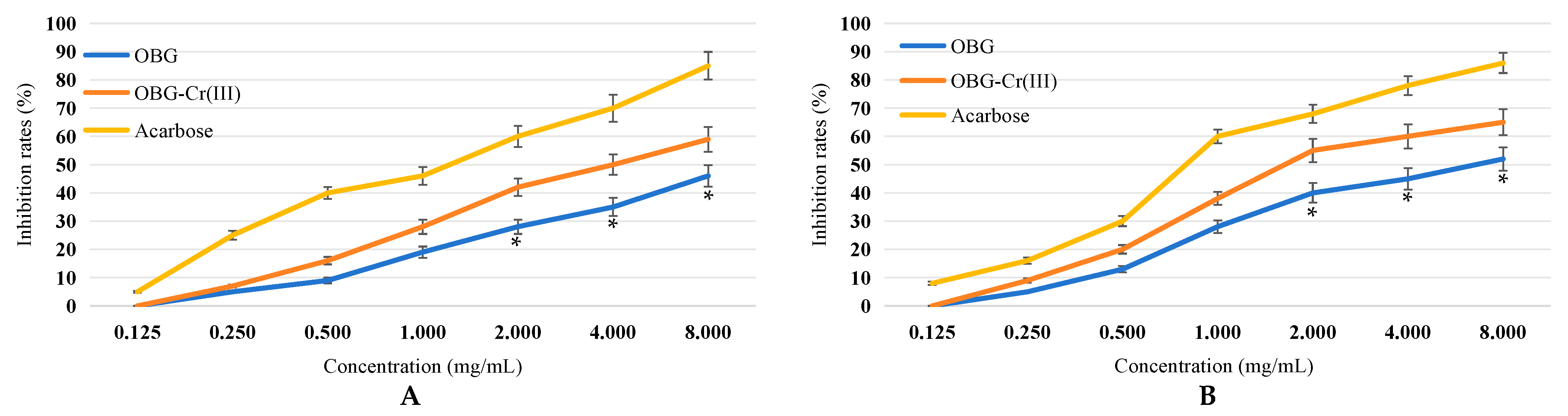
2.3. Determination of Inhibitory Activity against α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase
2.4. Hypoglycemic Activity in IR-HepG2 Cells
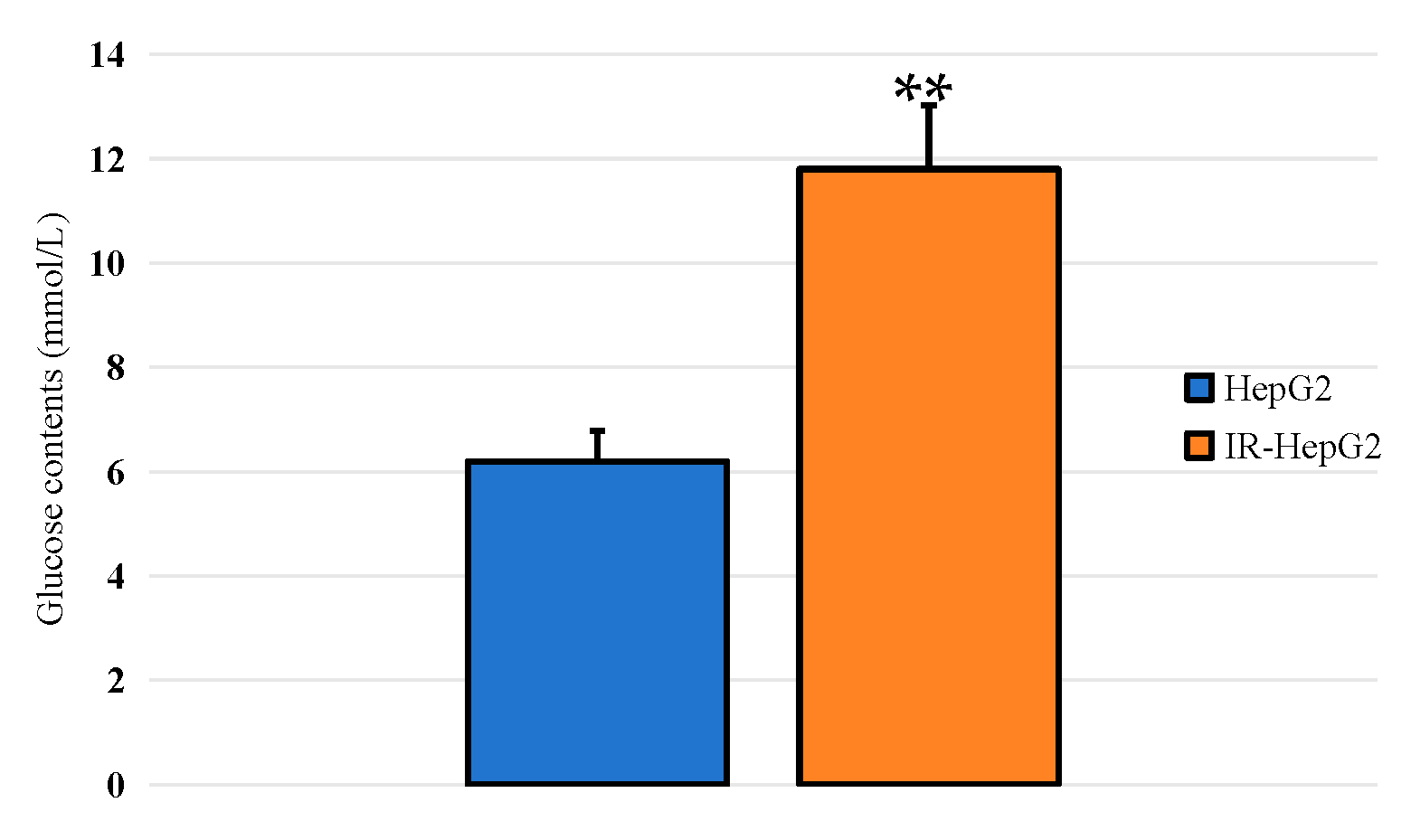
2.4.1. IR-HepG2 Cells Model Detection
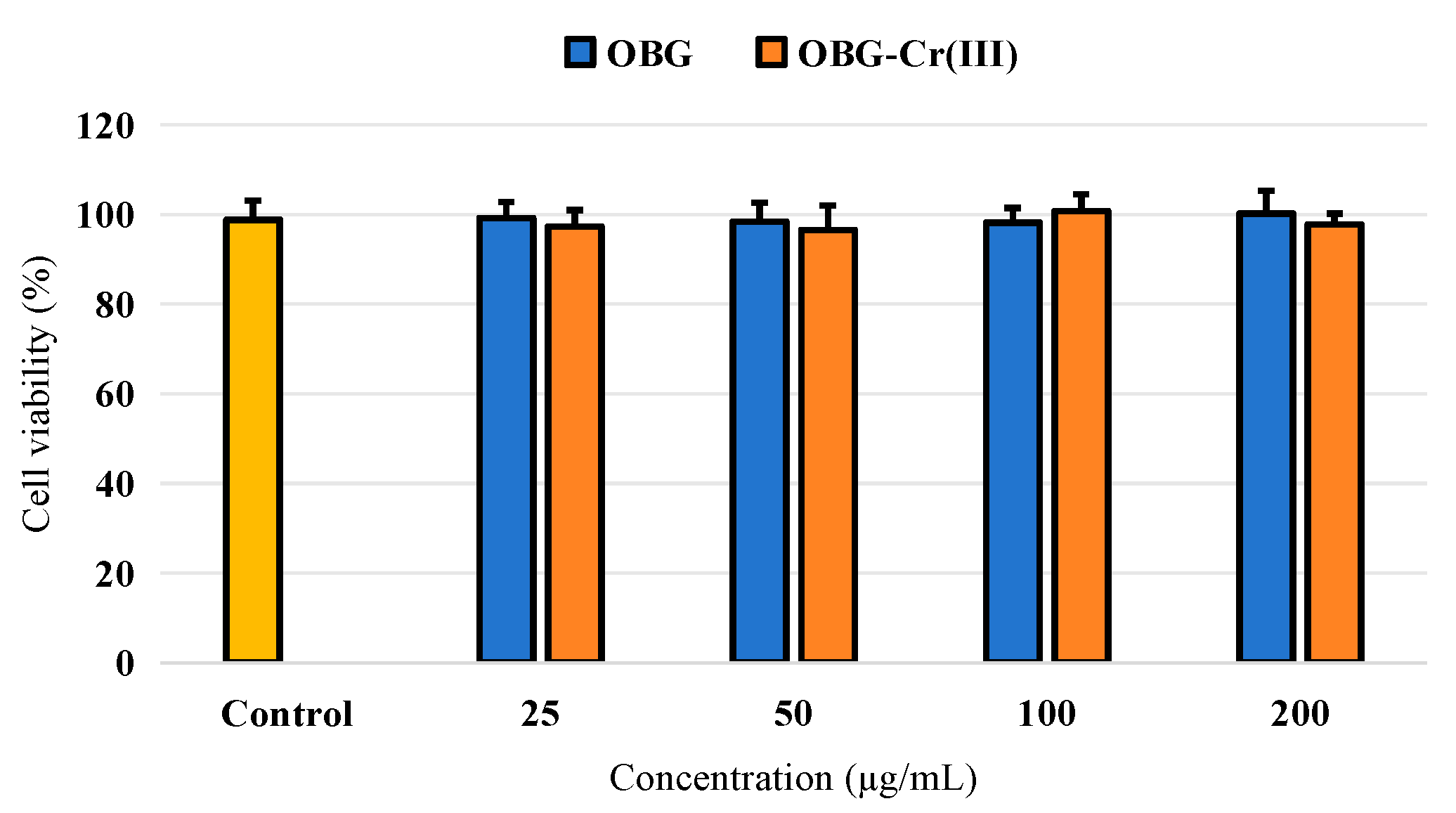
2.4.2. Effects on Cell Viability
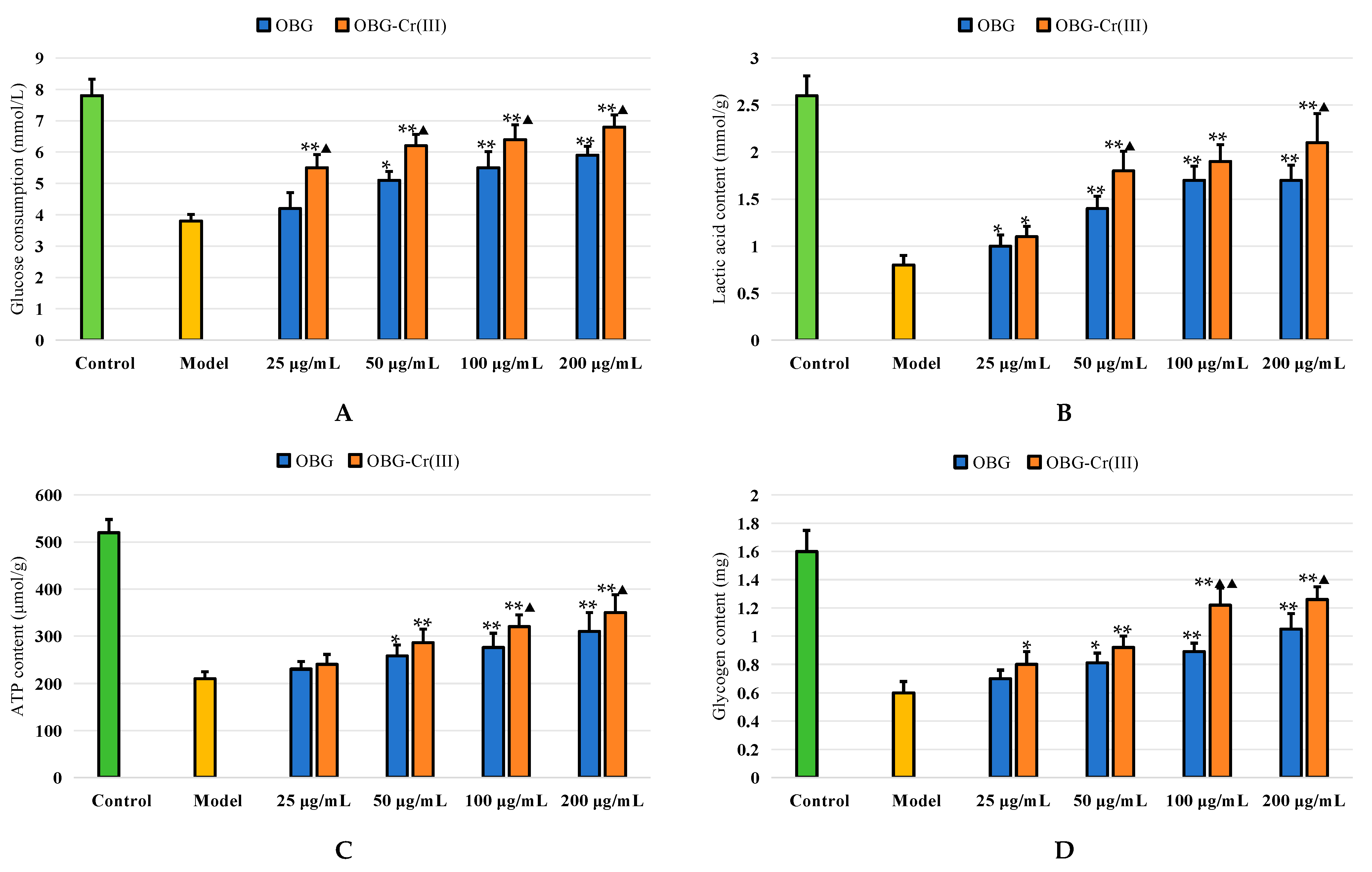
2.4.3. Effects on Glycometabolism in IR-HepG2 Cells
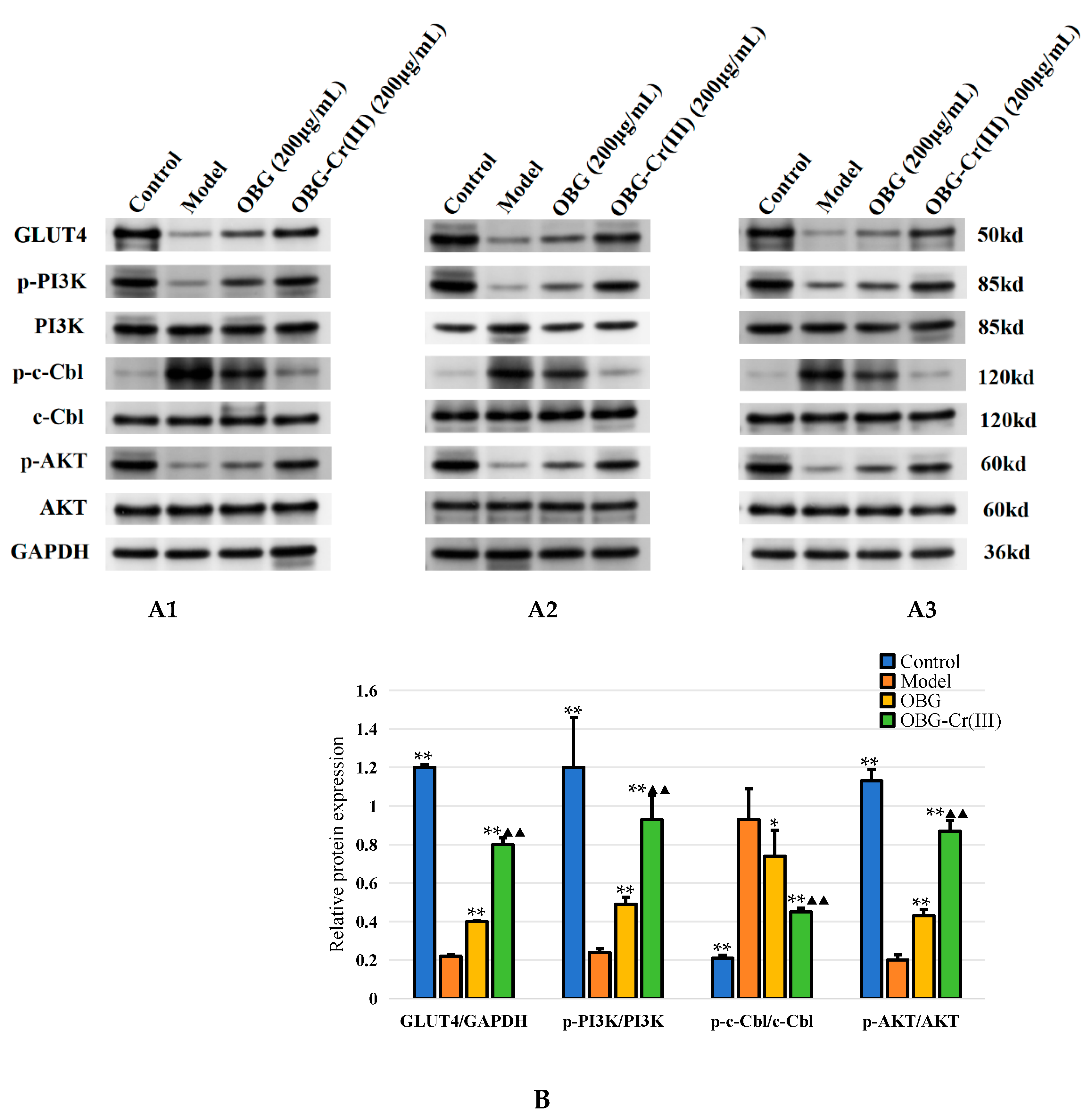
2.4.4. OBG and OBG-Cr(III) Regulated the Expression of c-Cbl/PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 in IR-HepG2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of the Oat β-Glucan–Chromium(III) Complex [OBG-Cr(III)]
4.3. Characterization of OBG-Cr(III)
4.3.1. Molecular Weight Determination of OBG and OBG-Cr(III)
4.3.2. Chromium Content Determination of OBG-Cr(III)
4.3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy Determination
4.3.4. UV-VIS Spectroscopy Determination
4.3.5. CD Determination
4.3.6. XRD Determination
4.3.7. SEM-EDS Determination
4.4. Inhibitory Activity against α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase [27]
4.4.1. Inhibitory Activity against α-Amylase
4.4.2. Inhibitory Activity against α-Glucosidase
4.5. Study on Improving Insulin Resistance of HepG2 Cells
4.5.1. HepG2 Cell Culture
4.5.2. HepG2 Cell Viability Assay
4.5.3. Hypoglycemic Activity in IR-HepG2 Cells
4.5.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.; Ding, M.; Su, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Feng, B.; Chu, Y. Research Progress of miR-200b in Diabetic Complications. Med. Recapitul. 2022, 28, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Xu, W. Research Progress on Clinical Classification of Diabetic Mellitus and Anti-diabetic Drugs. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, B.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, W. Research advances in the relationship among diabetes, its complications, and m6A methylation. J. Clin. Pathol. Res. 2023, 43, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S. Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetic complications. J. China Prescr. Drug 2021, 19, 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J. Physiochemical Properties, Safety and Hypoglycemic Activity of Cr(pic)3 Derivatives; Shanxi University: Taiyuan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; He, Z. Advance of Study on Relationship between Chromium or Its Complexes and Diabetes Mellitus. Food Sci. 2008, 29, 774–779. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, B.; Xu, M. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of chromium for adjuvant treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cent. South Pharm. 2022, 20, 926–934. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Huang, R.; Ying, Y. Chromium and Insulin Sensitivity. Chin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 25, 608–614. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L. Effect of Chromium and Iron on Glucose Metabolism and Its Mechanism; Ningxia Medical University: Yinchuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, X. Biological function of trivalent chromium and its effects on animal organism metabolism. Feed Ind. 2015, 36, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress on Hypoglycemic Effect of Natural Active Polysaccharides. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.M.; Kong, X.J. Research Progress on Molecular Structure and Biological Functions of Oat β-Glucan. China Condiment 2021, 46, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Fan, M.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y. Isolation and Perification of Oat β-Glucan and its Molecular Weight Extent. J. Inn. Mong. Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2008, 29, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Baldassano, S.; Accardi, G.; Vasto, S. Beta-glucans and cancer: The influence of inflammation and gut peptide. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. The anti-diabetic activity of oat β-D-glucan in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiichiro, A.; Yasunori, I.; Noriko, K.; Kozo, K.; Asuka, T.; Daigo, A.; Toji, Y.; Takashi, Y. Effects of high β-glucan barley on visceral fat obesity in Japanese individuals: A randomized, double-blind study. Nutrition 2017, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Final rule for food labelling: Health claims; Oats and coronary heart disease. Fed. Regul. 1997, 62, 3584–3681. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lin, Q.; Luo, F. Research progress on physiological functions of oat β-glucan. Cereals Oils 2016, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ren, J.L.; Yang, J.; Liao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Sumiya, ·A.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Oat β-Glucan on Renal Function and Intestinal Flora in Diabetic Rats. Food Nutr. China 2020, 26, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, Y. Effect of oat β-glucan on Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Food Sci. 2016, 37, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zou, S. Oat β-glucan complex ameliorates the symptoms of type II diabetic rats and its mechanism. Light Ind. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 107–108+110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ye, H.; Cui, J.; Chi, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, P. Hypolipidemic efect of chromium-modifed enzymatic product of sulfated rhamnose polysaccharide from Enteromorpha prolifera in type 2 diabetic mice. Mar. Life. Sci. Tech. 2022, 4, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, M.; Hong, R.; Chen, H. Preparation of a Momordica charantia L. polysaccharide-chromium(III) complex and its anti-hyperglycemic activity in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Shen, Z.; Cui, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chi, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, P. Hypoglycemic activity and mechanism of the sulfated rhamnose polysaccharides chromium(III) complex in type 2 diabetic mice. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102942–102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.C.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Y.J.; Li, L.; Guo, W.L.; Lin, X.B.; Huang, Z.R.; Rao, P.F.; Ai, L.Z.; Ni, L. Organic chromium derived from the chelation of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide and chromium(III) alleviates metabolic syndromes and intestinal microbiota dysbiosis induced by high-fat and high-fructose diet. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Z. Structural Characterization and Hypoglycemic Activity of a Novel Pumpkin Peel Polysaccharide-Chromium(III) Complex. Foods 2022, 11, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Li, C.; Na, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Characterization of sweet corncob polysaccharide -chromium (III) complex and its digestion properties and hypoglycemic effect. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 187, 115291–115302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappy, L.; Gugolz, E.; Wursch, P. Effects of Breakfast Cereals Containing Various Amounts of β-Glucan Fibers on Plasma Glucose and Insulin Responses in NIDDM Subjects. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.J.; Braaten, J.T.; Scott, F.W.; Riedel, K.D.; Wolynetz, M.S.; Collins, M.W. Effect of dose and modification of viscous properties of oat gum on plasma glucose and insulin following an oral glucose load. Brit. J. Nutr. 1994, 72, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pick, M.E.; Hawrysh, Z.J.; Gee, M.I.; Toth, E.; Garg, M.L.; Hardin, R.T. Oat bran concentrate bread products improve long-term control of diabetes: A pilot study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1996, 96, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, L.; Song, D. Progress in polysaccharide-trace element complex. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, W.J.; Ye, J.Z. Chemical constituents and structural characterization of polysaccharides from four typical bamboo species leaves. Molecules 2015, 20, 4162–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, M.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.X. Purification, composition analysis and antioxidant activity of a polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma atrum. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Study on Physicochemical Properties, Structural Characteristics of Oat β-Glucan and Its Application in Bread; Liaoning University: Shenyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Rafat, M.E.; Faizah, S.A.; Faizah, S.A.; Hessah, A.A.; Seraj, A.; Gehad, E.; Mohamed, I. Synthesis, structural elucidation, DFT calculation, biological studies and DNA interaction of some aryl hydrazone Cr3+, Fe3+, and Cu2+ chelates. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2022, 97, 107643–107658. [Google Scholar]
- Faizah, S.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Rafat, M.E.; Hessah, A.A.; Arwa, A.; Asmaa, M.; Mohamed, E.K.; Nashwa, M.E. Structural inspection for novel Pd(II), VO(II), Zn(II) and Cr(III)-azomethine metal chelates: DNA interaction, biological screening and theoretical treatments. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1246, 131139–131153. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Laila, H.A.; Antar, A.A.; Adel, A.M.; Mohamed, R.S.; Mohamed, A.B.; Omar, A.A.; Ayman, N. Synthesis and characterization of new Cr(III), Fe(II) and Cu(II) complexes incorporating multi-substituted aryl imidazole ligand: Structural, DFT, DNA binding, and biological implications. Spectrochim. Acta A 2020, 228, 117700. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Studies on Chemical Structure, Solution Behavior, and Hypoglucemic Effect Mechanism of β-Glucan from Oat; Huazhong Agricultural University: Wuhan, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, W.S.; Ahmed, M.A. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalysis enhancement of Eu2O3-ZnO mixed oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2018, 116, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Mohamed, W.S. α-Bi2O3 nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and UV-photocatalytic activity. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 035039–035349. [Google Scholar]
- Alahmadi, M.; Alsaedi, W.H.; Mohamed, W.S.; Hassan, H.M.A.; Ezzeldien, M.; Ahmed, M.A. Development of Bi2O3/MoSe2 mixed nanostructures for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J. Taibah. Univ. Sci. 2023, 17, 216133–216144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Kamal, M.A. Wogonin alleviates hyperglycemia through increased glucose entry into cellls via AKT/GLUT4 pathway. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2602–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.F. Study on the assisting blood sugar reduction function of oat β-glucan. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2019, 10, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, F. Research on Hypoglycemic Effect of Oat Products and Its Mechanism; Zhengzhou University of Light Industry: Zhengzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Xie, J.; Shao, Z.H.; Gan, J.H.; Li, X.H.; Xue, B.; Sun, T. Research Progress of Hypoglycemic Effect of Oat β-glucan. J. Triticeae Crops 2020, 40, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Wu, H.; Kong, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Dong, X.; Li, Z. Oat β-glucan ameliorates diabetes in high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced mice by regulating metabolites. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 113, 109251–109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.L.; Shi, F.F.; Li, L.; Xu, J.X.; Chen, M.; Wu, L.; Hong, J.L.; Qian, M.; Bai, W.D.; Liu, B.; et al. Preparation of a novel Grifola frondosa polysaccharide-chromium(III) complex and its hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities in high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, J.X.; Cao, Y.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Guo, W.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Bai, W.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ni, L.; Liu, B.; et al. Preparation of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide chromium(III) complex and its hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities in high-fat and high-fructose diet-induced pre-diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Pan, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, H. Anti-diabetic effects of Inonotus obliquus polysaccharides-chromium(III) complex in type 2 diabetic mice and its sub-acute toxicity evaluation in normal mice. Food Chem. Toxicol 2017, 108, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, G.; Tsygankov, A.Y. The Cbl family proteins: Ring leaders in regulation of cell signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 209, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, C.B.; Langdon, W.Y. Cbl: Many adaptations to regulate protein tyrosine kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 2, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Sun, L.; Pessetto, Z.Y.; Zang, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhong, L.; Su, Q.; Zan, W.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Casitas B-lineage lymphoma Ring domain inhibitors protect mice against high-fat diet induced obesity and resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0135916–0135928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, J.C.; Waring, S.G.; Cooper, A.; Turner, N.; Laybutt, R.; Cooney, G.J.; James, D.E. Casitas b-Lineage Lymphoma-Deficient Mice are Protected against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, B.; Fan, Y.; Li, X. Research progress in the treatment of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus with traditional chinese medicine based on PI3k/Akt signaling pathway. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2017, 39, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.Z. Triterpenoid saponins from stauntonia chinensis ameliorate insulin resistance via the AMP-Activated protein kinase and IR/IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathways in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10446–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Yu, D.M. GLUT4 and insulin resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 22, 308–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Cui, W.; Eskin, N.A.M.; Goff, H.D. A molecular modeling approach to understand conformation-functionality relationships of galactomannans with different mannose/galactose ratios. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Khan, B.M.; Cheong, K.L.; Liu, Y. Pumpkin polysaccharides: Purification, characterization and hypoglycemic potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 842–849. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.M.; Han, X.D.; Huang, X.; Xie, W.Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yu, Q.H.; Tao, L.; Li, T.P.; Li, S.H. Effects of different sources of β-glucan on pasting, gelation, and digestive properties of pea starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108172–108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Guo, Y.Y.; Duan, S.Y.; Wei, H.; Liu, Y.S.; Wang, L.B.; Huo, X.; Yang, Y. Effects of ultrasound irradiation on the characterization and bioactivities of the polysaccharide from blackcurrant fruits. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wei, Y.; Liang, L.; Huang, L.; Yu, G.; Li, Q. A novel low-molecular-mass pumpkin polysaccharide: Structural characterization, antioxidant activity, and hypoglycemic potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117090–117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Huang, R.; Jiao, D.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, H. Protection by Hosta ventricosa polysaccharides against oxidative damage induced by t-BHP in HepG2 cells via the JNK/Nrf2 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Fang, Z.; Nisar, T.; Zou, L.; Li, D.; Guo, Y. Lycium ruthenicum Murray anthocyanins effectively inhibit α-glucosidase activity and alleviate insulin resistance. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100949–100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Test Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Sample Quality m0 (g) | 0.0412 |
| Volume V0 (mL) | 10 |
| Test Elements | Cr |
| Element Concentration of Test Solution C0 (mg/L) | 8.9541 |
| Dilution Ratio f | 50 |
| Element Concentration of Digestion Solution C1 (mg/L) | 447.7025 |
| Sample Element Content Cx (mg/kg) | 108,665.66 |
| Sample Element Content W | 10.8666% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, C.; Ma, Q.; Sun, J.; et al. Preparation of a Novel Oat β-Glucan–Chromium(III) Complex and Its Hypoglycemic Effect and Mechanism. Molecules 2024, 29, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29091998
Li P, Wang Y, Wang X, Li R, Wang K, Jiang Y, Zhang M, Huang C, Ma Q, Sun J, et al. Preparation of a Novel Oat β-Glucan–Chromium(III) Complex and Its Hypoglycemic Effect and Mechanism. Molecules. 2024; 29(9):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29091998
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengshou, Yunlu Wang, Xiaoting Wang, Rui Li, Kaihui Wang, Yu Jiang, Mingyuan Zhang, Chuhan Huang, Qixiang Ma, Jian Sun, and et al. 2024. "Preparation of a Novel Oat β-Glucan–Chromium(III) Complex and Its Hypoglycemic Effect and Mechanism" Molecules 29, no. 9: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29091998
APA StyleLi, P., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Li, R., Wang, K., Jiang, Y., Zhang, M., Huang, C., Ma, Q., Sun, J., & Quan, J. (2024). Preparation of a Novel Oat β-Glucan–Chromium(III) Complex and Its Hypoglycemic Effect and Mechanism. Molecules, 29(9), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29091998




