Abstract
Tumors have a huge impact on human life and are now the main cause of disease-related deaths. The main means of treatment are surgery and radiotherapy, but they are more damaging to the organism and have a poor postoperative prognosis. Therefore, we urgently need safe and effective drugs to treat tumors. In recent years, Chinese herbal medicines have been widely used in tumor therapy as complementary and alternative therapies. Medicinal and edible herbs are popular and have become a hot topic of research, which not only have excellent pharmacological effects and activities, but also have almost no side effects. Therefore, as a typical medicine and food homology, some components of Paeoniae Radix Alba (PRA, called Baishao in China) have been shown to have good efficacy and safety against cancer. Numerous studies have also shown that Paeoniae Radix Alba and its active ingredients treat cancer through various pathways and are also one of the important components of many antitumor herbal compound formulas. In this paper, we reviewed the literature on the intervention of Paeoniae Radix Alba in tumors and its mechanism of action in recent years and found that there is a large amount of literature on its effect on total glucosides of paeony (TGP) and paeoniflorin (PF), as well as an in-depth discussion of the mechanism of action of Paeoniae Radix Alba and its main constituents, with a view to promote the clinical development and application of Paeoniae Radix Alba in the field of antitumor management.
1. Introduction
Cancer continues to grow globally and has become the second leading cause of death worldwide [1,2]. At present, the main treatment modalities are surgical resection, radiotherapy and chemotherapy [3], but these treatments are more damaging to the organism, and the treatment process is characterized by high toxicity and side effects, a poor postoperative prognosis and a high recurrence rate [4,5]. The quality of patients’ survival is still not effectively ensured, and their metastasis and recurrence cannot be prevented [6,7]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find non-toxic natural drugs to treat tumors [8].
With the prosperous development of Chinese medicine, Chinese herbal medicines have been widely used in tumor treatment as complementary and alternative therapies [9]. They have the advantages of good therapeutic effects and low toxicity and side effects, which can ensure the quality of survival and prolong the survival rate of cancer patients [10,11]. In recent years, more and more people have started to pay attention to Chinese herbs with health benefits and therapeutic effects [12]. Most of the Chinese herbs can be used for both healing and dietary purposes, so they are called medicinal herbs. The concept of medicine and food homology has been around for a long time, dating back to the “Huangdi Neijing” [13], where it is mentioned that food can be used as medicine to enhance one’s immunity and thus prevent or treat diseases [14,15]. With the change in time, the theory of the medicine and food homology has been enriched and developed, and its core content has continued to this day. Paeoniae Radix Alba is one of these herbs, and as a natural medicine, it has been used for nearly a thousand years.
Paeoniae Radix Alba (PRA) is the dried root of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. in the buttercup family [16]. PRA has a wide range of uses and has been widely used clinically for the treatment of visceral pain [17,18], cancerous pain [19], chronic gastritis [20,21], chronic hepatitis B [22], rheumatoid arthritis, etc. [23]. It also has a high frequency of use in the prevention and treatment of tumors [24]. With the in-depth development of chemical technology, there have been many reports on the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of PRA and its active ingredients, confirming that it has a wide range of pharmacological effects, including analgesic [25], anti-inflammatory [26], antidepressant [27,28], hepatoprotective [29], immune modulation [30] and significant antitumor activity, and it plays a therapeutic role in gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer and other malignant tumors [31,32]. This paper mainly introduces the main active ingredients of PRA and summarizes the mechanism of action of PRA and its active ingredients in the treatment of various malignant tumors.
2. Effects of the Main Active Ingredients of PRA
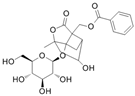
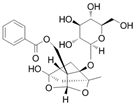
The chemical composition of PRA is diverse, mainly including monoterpenes and their glycosides, triterpenoids, flavonoids, tannins and polysaccharides [33,34]. Among them, the ones with significant efficacy and wide application in the treatment of various tumors are total glucosides of paeony (TGP) and paeoniflorin (PF). TGP is considered to be the main bioactive component of PRA, while PF is the main component of TGP [35]. The chemical structure formula is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Active ingredients and structural formula of Paeoniae Radix Alba.
2.1. Total Glucosides of Paeony (TGP)
Total glucosides of paeony (TGP) is a group of glycosides in the Chinese herb PRA [36], including paeoniflorin, paeonin [37], albiflorin [38,39], hydroxy-paeoniflorin [40], benzoyl-paeoniflorin [41], etc. [42,43]. Modern pharmacological studies have found that TGP not only has immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects, but also has a variety of effects such as inhibition of cell proliferation [44,45], which has good prospects for application and development.
2.2. Paeoniflorin (PF)
Paeoniflorin (PF), the main active ingredient of PRA, is a naturally occurring pharmacologically active ingredient that is highly valued for its low toxicity, high efficiency and safety, as well as for its association with a variety of antitumor, inflammatory, depressive and oxidative stress pharmacological effects [46,47]. In recent years, scholars at home and abroad have conducted in-depth studies on the antitumor effects of PF and found that PF has a good inhibitory effect for hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric carcinoma, intestinal carcinoma, lung carcinoma, leukemia [48] as well as skin carcinoma [49], and its mechanism of action is related to apoptosis induced by different signaling pathways, preventing the proliferation of cancer cells and inhibiting metastasis [50,51].
2.3. Others
In addition to TGP and PF, PRA contains various active ingredients such as albiflorin, oxypaeoniflorin, 6′-O-galloylpaeoniflorin and paeoniflorigenone [52]. However, TGP and PF are more well-studied for tumor therapeutic purposes, and therefore, the focus of this paper is on TGP and PF.
3. Antitumor Therapy Mechanisms
Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis, inhibition of cell metastasis, anti-inflammation and immunomodulation are the main pathways and phenotypes of the antitumor effects of PRA [53,54], as shown in Table 2.
3.1. Inhibits Tumor Cell Proliferation
The most basic characteristics of a cancer cell include its ability to proliferate persistently and over a long period of time [55]. The coordinated action between out-of-control cell metabolism, growth and proliferation is essential for tumorigenesis [56]. Cancer cells interfere with normal signals in the body that autonomously control cell growth [57,58]. These signaling pathways are able to regulate the entire process through the cell cycle and cell growth, also known as cell size increase. PF derived from PRA was found to be a potential novel therapeutic agent for gastric cancer. PF acted on gastric cancer MGC803 cells and could inhibit cell viability and induced apoptosis by up-regulating miR-124 and inhibiting PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling [59]. PF also inhibited the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells in the Notch-1 signaling pathway by interfering with breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells [60]. In addition, TGP extracted from PRA inhibited the proliferation, invasion and migration ability of laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cells in a concentration-dependent manner, a process that may be related to the inhibition of the activation of the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway [61]. Thus, PF and TGP can inhibit cancer cell proliferation through signaling pathway regulation.
3.2. Induces Apoptosis in Tumor Cells
Apoptosis is a fundamental biological phenomenon of the cell and is a tightly controlled polygenic process [62]. If there is a problem with this process, apoptosis does not occur in cells that are supposed to die, and damaged cells can survive and develop into cancer cells [63,64]. In the case of cancer cells, an interruption of the apoptotic process means the development and spread of cancer [65,66]. Therefore, balancing the process of cellular metabolism in the body can combat the onset and development of cancer [67]. It was found that PF intervention in gastric cancer SGC7901 cells significantly inhibited NF-kappaB activity and enhanced 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by preventing I kappaB alpha phosphorylation and reducing the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB [68]. Further, apoptosis was significantly induced in human cervical cancer cell line HeLa cells after PF treatment, which could result in the down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 and the up-regulation of the pro-apoptotic genes Bax and caspase-3 [69]. In addition, PF enhances the expression of caspase-9 and -3 proteins as well as Bax proteins in prolactinoma MMQ cells, whereas it inhibits the expression of Bcl-2 proteins and induces apoptosis mediated by the mitochondrial pathway [70]. The apoptosis-inducing effect is seen in a variety of cancers.
3.3. Inhibits Tumor Metastasis
Malignant tumor cells have the ability to invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to distant tissues [71], and in some cases, they can penetrate the body’s barriers and destroy surrounding tissues after invading the environment [72,73]. Once the cancer metastasizes, it is difficult to control and will spread step-by-step in the body. Secondly, early tumors are difficult to detect, and by the time obvious symptoms appear, the tumor is likely to be in the middle or late stage of malignant transformation, so the process of controlling metastasis is particularly urgent [74]. It was found that PF acted on gastric cancer AGS cells and inhibited the migration and invasion-promoting ability of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts (GCAFs) by targeting microRNA-149 and IL-6 [75]. PF also decreased the expression of MMP-9 and ERK in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 and Bel-7402 cells and increased the expression of E-cadherin in both cell lines [76]. PF also significantly decreased the expression of Vimentin in colorectal cancer cells while increasing the expression of E-cadherin, which in turn reversed the EMT process [77,78]. It can be seen that PF can inhibit metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinases and EMT-related proteins [79,80]. In addition, TGP could inhibit the metastasis of pancreatic cancer ASPC-1 cells, and the expression levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins in the cells of the TGP group were significantly reduced compared with those of the blank control group [81]. Therefore, both PF and TGP are involved in regulating the anticancer microenvironment [82], which inhibits the growth of cancer cells while suppressing their metastasis.
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory
Inflammation has been shown to be closely associated with the stage of development of action and malignant progression of most types of tumors, as well as with the efficacy of anticancer therapies [83,84]. Specifically, long-term chronic inflammation is associated with immunosuppression and would provide a favorable microenvironment for tumorigenesis, progression and metastasis [85,86]. Therefore, anti-inflammation and immunomodulation have unique advantages in regulating the tumor microenvironment, and immunotherapy is becoming more and more important in the treatment of tumors [87,88]. PRA, as a kind of traditional Chinese medicine, overcomes the characteristics of western medicines, which have high side effects and lower immunity, and has a natural advantage in anti-inflammation and immunomodulation therapy [89,90,91]. In a mouse model, PF improved survival and reduced the number and size of colon tumors. Medicinal plants and their extracts with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties may be an effective strategy for the treatment and prevention of chronic inflammation in colitis-associated colorectal cancer by mechanisms that may be related to the inhibition of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway and IL-17 levels [92,93]. Controlling inflammation will open new possibilities for long-term, multilevel tumor control [94].

Table 2.
The therapeutic mechanism of Paeoniae Radix Alba and its active ingredients in antitumor therapy.
Table 2.
The therapeutic mechanism of Paeoniae Radix Alba and its active ingredients in antitumor therapy.
| Cancer | Ingredient | Experimental Model | Mechanism | Target of Action | Phenotype | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric cancer | Paeoniflorin | AGS | IL-6-STAT3-MMP | Inhibition of IL-6 production and secretion by up-regulation of microRNA149 expression in GCAFs and subsequent blocking of IL-6-STAT3-MMP signaling in AGS cells activated by GCAFs | Metastasis | [75] |
| Gastric cancer | Paeoniflorin | MGC803, SGC7901 | Hippo | Inhibits cell growth, enhances apoptosis and reduces cell infiltration | Proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis | [95] |
| Gastric cancer | Paeoniflorin | MGC803 | microRNA-124, PI3K/AKT/STAT3 | Inhibits cell activity and induces apoptosis by up-regulating miR-124 and inhibiting PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling | Proliferation apoptosis | [59] |
| Gastric cancer | Paeoniflorin | SGC7901 | NF-κB | Inhibits NF-κB activity and enhances apoptosis in gastric cancer cells | Apoptosis | [68] |
| Breast cancer | Paeoniflorin | MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 | Notch-1 | PF inhibits the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells by inhibiting the Notch-1 signaling pathway | Proliferation, metastasis | [60] |
| Breast cancer | Paeoniflorin | MCF-7 | miR-15b/FOXO1/CCND1/β-catenin | Inhibition of breast cancer cell growth, pro-apoptosis and promotion of FOXO1 expression through down-regulation of miR-15b, leading to transcriptional inhibition of CCND1 and subsequent blockade of β-catenin protein signaling | Proliferation, apoptosis | [96] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Paeoniflorin | Panc-1 | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | The expression of caspase-3 and Cleave caspase3 increased with the increase in PF concentration, and the opposite was true for Bcl-2 | Proliferation, apoptosis | [97] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Paeoniflorin | Capan-1, MIAPaCa-2 | HTRA3 | Decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptotic Bax protein expression | Proliferation, apoptosis | [98] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Paeoniflorin | BxPC-3 and L3.6pl. A tumor model in BALB/c nude mice | ErbB3/PI3K/AKT | Inhibition of ErbB3/PI3K/Akt phosphorylation | Proliferation, apoptosis | [99] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Total glucosides of paeony | ASPC-1 | - | PCNA, MMP-2, MMP-9 protein and mRNA expression levels were significantly reduced in the administered group | Proliferation, metastasis | [81] |
| Tongue cancer | Total glucosides of paeony | HSC3 | LINC00319/miR-608 | LINC00319 targets to negatively regulate miR-608 expression and LINC00319 overexpression reverses the effect of TGP on proliferation, migration and invasion of HSC3 cells | Proliferation, metastasis | [100] |
| Laryngeal cancer | Total glucosides of paeony | Hep-2 | PI3K/Akt/GSK3β | p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-GSK3β protein expression levels were significantly reduced | Proliferation, metastasis | [61] |
| Liver cancer | Paeoniflorin | BEL-7402 | Hedgehog/Gli | Associated with inhibition of Hedgehog/Gli signaling pathway activation, inhibition of MAPK/ERK pathway activity and inhibition of MMP-9 expression | Metastasis | [101] |
| Liver cancer | Paeoniflorin | HepG2, BEL-7402 | MMP-9/E-CAD/ERK | Growth inhibition and significant reduction in invasion, metastasis and adhesion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines | Metastasis | [76] |
| Liver cancer | Paeoniflorin | HepG2, SMMC-7721 | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | Induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through down-regulation of EP2 expression and concomitant increase in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, leading to up-regulation of caspase-3 activity | Proliferation, apoptosis | [102] |
| Liver cancer | Paeoniflorin | HepG2, SMMC-7721 | 5-HT1D, Wnt/β-catenin | Blocking Wnt/β-conjugated protein pathway expression by down-regulating 5-HT1D | Proliferation, metastasis | [103] |
| Lung cancer | Paeoniflorin | A tumor model in C57BL/6J mice | - | Lung metastatic colonization in Lewis lung cancer-loaded mice in the paeoniflorin group was significantly less than that in the model group | Metastasis | [104] |
| Lung cancer | Paeoniflorin | A549 | Fas/APO-1 | Antiproliferative activity is mediated by cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase block and Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptotic pathways | Proliferation, apoptosis | [105] |
| Ovarian cancer | Paeoniflorin | HO8910 | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | The expression level of intracellular caspase-3 in the paeoniflorin-treated group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the expression levels of Bcl-2 and nuclear factor-κB p56 were significantly lower than those in the control group | Proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis | [106] |
| Cervical carcinoma | Paeoniflorin | HeLa | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | Decreased expression of Bcl-2 and enhanced expression of Bax and caspase-3 | Apoptosis | [69] |
| Colorectal cancer | Paeoniflorin | A tumor model in CAC mice | IL-6/STAT3 | PF increased survival and decreased the number and size of colon tumors in mice | Anti-inflammatory, immunomodulation | [92] |
| Colorectal cancer | Paeoniflorin | A tumor model in CAC mice. HT29 | p53/14-3-3 | Cell cycle arrest mainly in G1 phase, activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 demonstrated the pro-apoptotic effect of PF | Proliferation, apoptosis | [107] |
| Colorectal cancer | Paeoniflorin | HCT116 | FOXM1 | PF inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis and suppressed cell cycle progression in the G0/G1 phase. It also inhibited colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion | Proliferation, metastasis | [108] |
| Colorectal cancer | Paeoniflorin | HCT116, SW480 | EMT | Inhibition of migration and invasive ability of colorectal cancer cells and reversal of epithelial–mesenchymal transition by suppressing HDAC2 expression | Metastasis | [77] |
| Multiple myeloma | Paeoniflorin | SKO-007 | MMP-2/microRNA(miR)-29b | Inhibition of cell proliferation and promotion of apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells by inhibiting MMP-2 expression in multiple myeloma cells through miR-29b up-regulation | Proliferation, apoptosis | [109] |
| Osteosarcoma | Paeoniflorin | HOS, Saos-2 | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | Proliferation, apoptosis | [110] |
| Glioma | Paeoniflorin | U87 | MMP-9/microRNA-16 | Increased miR-16 expression and decreased MMP-9 protein expression | Proliferation, apoptosis | [111] |
| Glioma | Paeoniflorin | U87, U251 | Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway | Proteasome-dependent STAT3 degradation induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human glioma cells | Proliferation, apoptosis | [112] |
| Glioblastoma | Paeoniflorin | T98G, U251 | HGF/c-Met/RhoA/ROCK | Inhibition of HGF/c-Met/RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway | Metastasis | [113] |
| Glioblastoma | Paeoniflorin | U87, U251 and T98G cells. A tumor model in BALB/c nude mice | EMT, TGFβ/MMP-2/9 | Treatment of glioblastoma by inhibition of the TGFβ signaling pathway and inhibition of EMT | Metastasis | [78] |
| Prolactinoma | Paeoniflorin | MMQ, GH3 | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in prolactinoma cells | Proliferation, apoptosis | [70] |
| Bladder carcinoma | Paeoniflorin | RT4. A tumor model in mice | Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway | Pro-apoptotic, blocked the translocation of STAT3 to the nucleus | Proliferation, apoptosis | [114] |
In general, PRA and its active ingredients or derivatives mainly produce antitumor effects on cell proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis and anti-inflammation and immunomodulation through signaling pathways, mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, EMT, MMPs, etc., as shown in Figure 1.
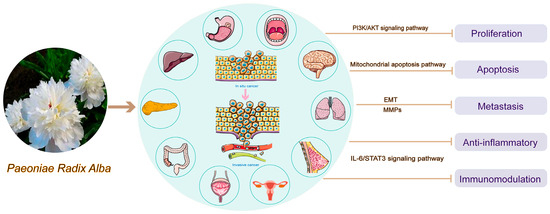
Figure 1.
Antitumor mechanism of Paeoniae Radix Alba.
4. Preventive Effect
PRA is found in many foods and medicines and not only has antitumor activity, but also has auxiliary therapeutic and preventive effects in many diseases [115]. Postoperative patients with low immunity can take soup with PRA to improve their physical condition and enhance their immunity [116,117]. In the late stage of various diseases, it helps patients having a loss of appetite to open the stomach and replenish nutrition in time [118]. Long-term illnesses, bedridden conditions, all kinds of chronic diseases and the patients’ long-term medication will damage the spleen and stomach, and a medicinal diet made of PRA can be very good to protect the patient’s spleen and stomach, without harming the organism, but also to achieve the role of treatment of the disease [119,120]. Therefore, we can consume medicinal meals with PRA for a long time to regulate the body. As shown in Table 3, we add PRA to many nutritious porridges, medicinal diets and other foods, which play a key role in preventing diseases.

Table 3.
Paeoniae Radix Alba diet prescription.
5. Conclusions and Outlook
The current treatment of tumors is still conventional Western medicine, which can quickly kill tumor cells and reduce the tumor load, but it also inevitably brings a series of toxic side effects and adverse reactions [130]. Traditional Chinese medicine and its long-term clinical experience have shown that PRA has a tonic effect and has therapeutic and preventive effects on a variety of diseases [131]. Among them, it has a remarkable pain-relieving effect, which can significantly relieve cancer pain and alleviate patients’ suffering. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that PRA has a wide range of anticancer activity, with obvious inhibitory effect on tumor cells, which can reduce the invasion and migration of cancer cells and inhibit the spread of cancer cells. In addition, PRA can enhance human immunity, making cancer patients more resistant to cancer cells. The concept of medicine and food homology is based on the advantage of boosting one’s immunity, thus achieving the effect of preventing and treating diseases [132,133]. PRA has a long history of medicinal use, and as a dual-purpose herb, it has great development and application value in clinical application, health food and diet [134].
We searched PubMed, Google Scholar, and China national knowledge infrastructure (CNKI) with the keywords “Paeoniae Radix Alba”, “cancer”, “carcinoma”, “tumor” and so on and found that there are no reviews on the treatment of tumors by PRA in the past five years. More attention was paid to PRA and its active ingredients for the treatment of single cancers such as breast cancer and colorectal cancer. We retrieved a review of paeoniflorin for tumor therapy published in 2022 [135], which focused only on paeoniflorin’s tumor-suppressing effects through various mechanisms and modulation of signaling pathways, but it talked little about paeoniflorin derived from the traditional Chinese medicine PRA, which is of little reference value to the advantages of traditional Chinese medicine.
In summary, this paper reviewed the application of PRA and its active ingredients, TGP and PF, in tumor therapy, focusing on the antitumor mechanism of action, medicinal food and treatment of disease and other advantages of PRA, which can inhibit the occurrence and malignant progression of tumors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and Y.N.; formal analysis, K.W.; investigation, D.L.; resources, F.M.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y. and L.Y.; supervision, D.X.; funding acquisition, Y.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ningxia Key Research and Development Program, grant number 2023BEG02015; Ningxia Natural Science Foundation, grant number 2022AAC02039; High-level Key Discipline Construction Project of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, grant number 2022-226.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
PRA: Paeoniae Radix Alba; TGP, total glucosides of paeony; PF, paeoniflorin; GCAFs, gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Chen, H.D.; Yu, Y.W.; Li, N.; Chen, W.Q. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Lei, K.F.; Han, F. Tumor microenvironment: Recent advances in various cancer treatments. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3855–3864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schirrmacher, V. From chemotherapy to biological therapy: A review of novel concepts to reduce the side effects of systemic cancer treatment (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Dong, Y.; Kumar, R.; Jeter, C.; Tang, D.G. Slow-cycling (dormant) cancer cells in therapy resistance, cancer relapse and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 78, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeneevassen, L.; Bessède, E.; Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P.; Dubus, P.; Varon, C. Gastric Cancer: Advances in Carcinogenesis Research and New Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, K.; Lu, J.; Bao, X.; Wang, R.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, H. Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Fu, J.L.; Hao, H.F.; Jiao, Y.N.; Li, P.P.; Han, S.Y. Metabolic reprogramming by traditional Chinese medicine and its role in effective cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, P.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y. Traditional Chinese medicine as a cancer treatment: Modern perspectives of ancient but advanced science. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1958–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Shen, W. Research Status and Molecular Mechanism of the Traditional Chinese Medicine and Antitumor Therapy Combined Strategy Based on Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 609705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, Y. Dietary advice in chronic care: Comparing traditional Chinese and western medicine practiced in mainland China. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 292, 114621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, J.; Gu, P.; Fan, X. The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivekanandhan, S.; Bahr, D.; Kothari, A.; Ashary, M.A.; Baksh, M.; Gabriel, E. Immunotherapies in rare cancers. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jo, S.; Cho, M.J.; Cho, Y.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Byun, S. Immunomodulatory functional foods and their molecular mechanisms. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Liu, G.; Wei, Y.; Fu, B.; Li, F.; Wu, D.; Zhang, W. Multi-element Characteristics of Chinese Medical Baishao (Paeoniae Radix Alba) and Their Decoctions. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.C.; Li, J.M.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.L.; Hsieh, C.L. Effect of Paeonia lactiflora, a traditional Chinese herb, on migraines based on clinical application and animal behavior analyses. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, H.F.; Sun, S.Q.; Wu, X.Z. Pharmacokinetic comparisons of two different combinations of Shaoyao-Gancao Decoction in rats: Competing mechanisms between paeoniflorin and glycyrrhetinic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.; Li, C.; Cai, P.; Qi, F. The positive role of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for cancer. Biosci. Trends. 2021, 15, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, X.; Zou, G.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, C. 6’-O-Galloylpaeoniflorin attenuates Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis via modulating Nrf2 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.K.; Jo, S.K.; Jung, U.; Park, H.R.; Lee, H.S. Protective effects of a standardized extract (HemoHIM) using indomethacin- and ethanol/HCl-induced gastric mucosal injury models. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Qiu, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yang, K.; Hu, H.; Liu, F. Promising traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cholestatic liver disease process (cholestasis, hepatitis, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 297, 115550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, S.; Danshiitsoodol, N.; Sugimoto, S.; Noda, M.; Sugiyama, M. Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Substance Generated Newly in Paeoniae Radix Alba Extract Fermented with Plant-Derived Lactobacillus brevis 174A. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.C.; Weng, Q.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.S.; Yang, H.J.; Zhan, Z.L. Textual research on Chinese herbaceous peony in Chinese classical prescriptions. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019, 44, 5496–5502. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Y.; Ling, J.; Ye, F.; Cheng, N.; Wu, F.; Tang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H. Paeoniflorin alleviates CFA-induced inflammatory pain by inhibiting TRPV1 and succinate/SUCNR1-HIF-1α/NLPR3 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Huang, X.L.; Chen, R.R.; Li, T.; Ye, H.J.; Xie, W.; Huang, Z.M.; Cao, G.Z. Paeoniflorin Prevents Intestinal Barrier Disruption and Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Inflammation 2019, 42, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qin, X.M.; Tian, J.S.; Gao, X.X.; Du, G.H.; Zhou, Y.Z. Integrated network pharmacology and metabolomics to dissect the combination mechanisms of Bupleurum chinense DC-Paeonia lactiflora Pall herb pair for treating depression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.T.; Xi, Z.Q.; Wei, X.Q.; Wang, K. A network pharmacology approach to predict potential targets and mechanisms of “Ramulus Cinnamomi (cassiae)—Paeonia lactiflora” herb pair in the treatment of chronic pain with comorbid anxiety and depression. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kan, J.; Zheng, N.; Li, B.; Hong, Y.; Yan, J.; Tao, X.; Wu, G.; Ma, J.; Zhu, W.; et al. A botanical dietary supplement from white peony and licorice attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota and reducing inflammation. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.S.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Yao, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Yao, S.; Qu, H.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. A strategy for practical authentication of medicinal plants in traditional Chinese medicine prescription, paeony root in ShaoYao-GanCao decoction as a case study. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ao, Q.; Luo, C.; Wang, B.; Bai, C.; Ge, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. On the Core Prescriptions and Their Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Hepatitis B, Liver Cirrhosis, and Liver Cancer Treatment. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 5300523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L.; Yan, B. Single Standard Substance for the Simultaneous Determination of Eleven Components in the Extract of Paeoniae Radix Alba (Root of Paeonia lactiflora Pall). J. Anal Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 8860776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Peng, L.; Jin, L.; Fu, H.; Shou, Q. Network Pharmacology Analysis of the Identification of Phytochemicals and Therapeutic Mechanisms of Paeoniae Radix Alba for the Treatment of Asthma. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9659304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Nie, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Fu, C.; He, Y. Total glucosides of paeony: A review of its phytochemistry, role in autoimmune diseases, and mechanisms of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, L. Screening of Biomarkers and Quality Control of Shaoyao Gancao Decoction Using UPLC-MS/MS Combined with Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 2442681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Guo, H. Paeonin extracted from potatoes protects gastric epithelial cells from H2O2-induced oxidative damage in vitro by PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2 signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Yang, Y. Albiflorin attenuates high glucose-induced endothelial apoptosis via suppressing PARP1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, M.; Yan, Y.; Ren, G.; Hou, J.; Qin, G.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Albiflorin alleviates cognitive dysfunction in STZ-induced rats. Aging 2021, 13, 18287–18297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yin, L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Zheng, N.; Li, M.; Zhan, S. Quantitative determination and optimun extraction technique of nine compounds of Paeoniae Radix Alba. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban J. Zhejiang Univ. Med. Sci. 2020, 49, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, P.H.; Kiem, P.V.; Nhiem, N.X.; Tung, N.H.; Quang, T.H.; Minh, C.V.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, E.M.; Kim, Y.H. A new monoterpene glycoside from the roots of Paeonia lactiflora increases the differentiation of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Mo, L.; Ye, C.; Xun, T.; Wang, X.; Lv, B.; Zhan, X.; Liu, B.; Ding, Q.; Peng, J.; et al. Effect of total glucosides of paeony and Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on erythrocyte methotrexate polyglutamates in rats, analysed using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.J.; Qi, X.M.; Wu, Y.G.; Shen, J.J. Effects of total glucosides of paeony on oxidative stress in the kidney from diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Shen, P.; Ba, X.; Lin, W.; Tu, S. Synergistic and Hepatoprotective Effect of Total Glucosides of Paeony on Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, W. The effects of total glucosides of paeony (TGP) and paeoniflorin (Pae) on inflammatory-immune responses in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, S.; Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y. Paeoniflorin: A monoterpene glycoside from plants of Paeoniaceae family with diverse anticancer activities. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Elgaher, W.; Winterhoff, M.; Büssow, K.; Waqas, F.H.; Graner, E.; Pires-Afonso, Y.; Casares Perez, L.; de la Vega, L.; Sahini, N.; et al. Citraconate inhibits ACOD1 (IRG1) catalysis, reduces interferon responses and oxidative stress, and modulates inflammation and cell metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.R.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, B.S.; Chung, T.W.; Kim, K.J.; Joo, J.K.; Ryu, D.; Bae, S.J.; Ha, K.T. Paeoniflorin Enhances Endometrial Receptivity through Leukemia Inhibitory Factor. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, L.; Comito, G.; Parri, M.; Iozzo, M.; Duatti, A.; Virgilio, F.; Lorito, N.; Bacci, M.; Pardella, E.; Sandrini, G.; et al. Lactate Rewires Lipid Metabolism and Sustains a Metabolic-Epigenetic Axis in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1267–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dou, Y.-N.; Zhao, Q.-W.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xia, Y.-F.; Dai, Y.; Wei, Z.-F. Paeoniflorin suppresses TGF-β mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis through a Smad-dependent pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Yu, B. Paeoniflorin Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Cao, H.Y.; Yang, R.H.; Xu, R.X.; Zhu, X.Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.B.; Yan, X.Y.; Fu, P. Genus Paeonia monoterpene glycosides: A systematic review on their pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2024, 127, 155483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghari-Tabari, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Qujeq, D.; Andevari, A.N.; Sabahi, Z.; Moein, S. Signaling, metabolism, and cancer: An important relationship for therapeutic intervention. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 5512–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, T.T.; Wu, C.H.; Hsu, J.D.; Chyau, C.C.; Lee, H.J.; Wang, C.J. Paeonia lactiflora Pall inhibits bladder cancer growth involving phosphorylation of Chk2 in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, D.; Cai, C.; Jia, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, B.; et al. mTORC1 regulates PTHrP to coordinate chondrocyte growth, proliferation and differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Anastasaki, C.; Chen, Z.; Shipman, T.; Papke, J.B.; Yin, K.Y.; Gutmann, D.H.; Le, L.Q. Humanized neurofibroma model from induced pluripotent stem cells delineates tumor pathogenesis and developmental origins. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e139807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 74, 103–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.B.; Xiao, G.C.; Tong, S.L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Q.-S.; Li, S.-B.; Hao, Z.-N. Paeoniflorin inhibits human gastric carcinoma cell proliferation through up-regulation of microRNA-124 and suppression of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7197–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Cui, J.; Xiao, T.; Jiang, D. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells through suppressing Notch-1 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 78, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou Xiahong, Y.X.; Lian Lei, F.Z.; Zhaoxu, Y. Effects of Total Glucosides of Paeony on Proliferation, Invasion, Migration and PI3K/AKT/GSK3β Signaling Pathway of Laryngeal Cancer Hep-2 Cells. Label. Immunoass. Clin. 2022, 29, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Morana, O.; Wood, W.; Gregory, C.D. The Apoptosis Paradox in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, B. Anti-Cancer Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds Inducing ER Stress-Mediated Apoptosis: A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Lai, Y.; Hua, Z.C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Ferrell, J.E., Jr. Apoptosis propagates through the cytoplasm as trigger waves. Science 2018, 361, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, J. Cancer as a Metabolic Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. Paeoniflorin suppress NF-kappaB activation through modulation of I kappaB alpha and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2008, 62, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S. Modulating Bcl-2 family proteins and caspase-3 in induction of apoptosis by paeoniflorin in human cervical cancer cells. Phytother Res. 2011, 25, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ren, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. The prolactin-release inhibitor paeoniflorin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in prolactinoma cells via the mitochondria-dependent pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 5704–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A.R.; Ahadi, A.M.; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S.K. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Baker, D.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-β-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstberger, S.; Jiang, Q.; Ganesh, K. Metastasis. Cell 2023, 186, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, K.; Massagué, J. Targeting metastatic cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Ma, D.G.; Wang, L.; Feng, L.; Fu, J.-W.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.-T.; Jia, Y.-F. Paeoniflorin Inhibits Migration- and Invasion-Promoting Capacities of Gastric Cancer Associated Fibroblasts. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.T.; He, W.; Song, S.S.; Wei, W. Paeoniflorin inhibited the tumor invasion and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2014, 115, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.W.; Li, L.X.; Wu, W.Z.; Pan, T.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Yang, Y.K. Anti-Tumor Effects of Paeoniflorin on Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 6405–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yu, G.; Nie, X.; Jia, W.; Liu, R.-E.; Xu, R. Paeoniflorin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Glioblastoma Cells via Suppression Transforming Growth Factor β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; la Rosa, C.C.-D.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Harvey, S.E.; Zheng, R.; Lyu, J.; Grzeskowiak, C.L.; Powell, E.; Piwnica-Worms, H.; Scott, K.L.; Cheng, C. The RNA-binding protein AKAP8 suppresses tumor metastasis by antagonizing EMT-associated alternative splicing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yang, F.; Yi, Z. Studies on the effects of total white peony glycosides on the proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Chin. Med. Her. 2021, 27, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Yu, D. Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 221, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, C.D.; Norrito, R.L.; Daidone, M.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Pinto, A. Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Huang, T.; Sun, H.; Lin, R.; Zheng, X.; Bian, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Xu, D.; et al. High Targeting Specificity toward Pulmonary Inflammation Using Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Hybrid Nanovehicle for an Efficient Inflammation Intervention. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2300376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, S.; Ghasemi, S.; Rigatelli, A.; Jaillon, S. The complexity of neutrophils in health and disease: Focus on cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 48, 101409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, I.; Manic, G.; Coussens, L.M.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Macrophages and Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.P.; Booker, R.C.; Brosseau, J.P.; Chen, Z.; Mo, J.; Tchegnon, E.; Wang, Y.; Clapp, D.W.; Le, L.Q. Contributions of inflammation and tumor microenvironment to neurofibroma tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2848–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.L.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F.; Dai, Z. Antitumor effects of immunity-enhancing traditional Chinese medicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Zhang, T. Integration of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine in the era of precision medicine. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, X.; Shi, H.; Xia, D. Nutrition and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): A system’s theoretical perspective. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.-X.; Li, Z.; Luo, Y.-P.; Duan, Y.-Q.; Ma, X.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Potential Chemoprevention of Paeoniflorin in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vivo Experiment. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.Q.; Yue, X.Q.; Ling, C. Three advantages of using traditional Chinese medicine to prevent and treat tumor. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 12, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappavigna, S.; Cossu, A.M.; Grimaldi, A.; Bocchetti, M.; Ferraro, G.A.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Filosa, R.; Caraglia, M. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, J. Antitumor Effects of Paeoniflorin on Hippo Signaling Pathway in Gastric Cancer Cells. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 4724938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Luo, G.; Shen, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, L. Paeoniflorin Sensitizes Breast Cancer Cells to Tamoxifen by Downregulating microRNA-15b via the FOXO1/CCND1/β-Catenin Axis. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, C.; Yu, C.; Zhen, P.; Tian, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Jiang, J. Effect of paeoniflorin on proliferation and apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer Panc-1 cell line. J. Guizhou Med. Univ. 2018, 43, 874–878. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gong, L.; Qi, R.; Sun, Q.; Xia, X.; He, H.; Ren, J.; Zhu, O.; Zhuo, D. Paeoniflorin suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth by upregulating HTRA3 expression. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2017, 11, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yang, X.; Ding, X.L.; Guo, L.-M.; Zhu, C.-H.; Ji, W.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.-Z. Paeoniflorin Potentiates the Inhibitory Effects of Erlotinib in Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines by Reducing ErbB3 Phosphorylation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wei, J.; Qin, W.; Chen, M. Mechanism study on the regulation of proliferation, migration and invasion of tongue cancer HSC3 cells by total paeonia lactiflora glycosides. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, 30, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. Hedgehog/Gli Signaling Pathway Mediates Invasive Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and the Effect of Paeoniflorin on It; Anhui Medical University: Anhui, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Sun, W.; Wei, W.; Wang, D.; Jin, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q. Involvement of the prostaglandin E receptor EP2 in paeoniflorin-induced human hepatoma cell apoptosis. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Tan, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Zeng, F. Paeoniflorin Affects Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway through Downregulation of 5-HT1D. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Su, X.; Ling, F.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Li, C. Tumor-suppressive effect of paeoniflorin on Lewis lung cancer in mice with spontaneous lung metastases. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. Clin. 2013, 29, 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, J.Y.; Yang, C.J.; Tsai, Y.M.; Huang, H.W.; Huang, M.S. Antiproliferative activity of paeoniflorin is through cell cycle arrest and the Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptotic pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, X.; Dong, S.; Cheng, C.; Shi, R.; Jia, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, B. Effects of paeoniflorin on the proliferation, apoptosis and migration of human epithelial ovarian cancer HO8910 cells and its mechanisms. Pharm. Res. 2019, 38, 198–200+204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.-X.; Li, Y.-S.; Xie, H.-Y.; Luo, J.-D.; Zhou, Y. Paeoniflorin inhibits growth of human colorectal carcinoma HT 29 cells in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Li, S.; Yan, G.; Li, C.; Kang, Z. Paeoniflorin inhibits cell growth and induces cell cycle arrest through inhibition of FoxM1 in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, W. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells via its effects on microRNA-29b and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.B.; Zhu, J.; Liang, C.Z.; Tao, L.-J.; Liu, B.; Yu, W.; Zou, H.H.; Wang, J.-J.; Tao, H. Paeoniflorin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis through the upregulation of Bcl-2 X-associated protein and downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 in human osteosarcoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5095–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qi, Z.; Wei, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human glioma cells via microRNA-16 upregulation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 downregulation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.-X.; Nie, X.-H.; Jia, O.-Y.; Xing, Y.; Li, D.-Y.; Dong, X.-Y.; Liu, R.-E. Paeoniflorin inhibits human glioma cells via STAT3 degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 5611–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Liu, S.; Zhu, C.; Xu, R.; Liu, R.-E. Paeoniflorin Inhibits Hepatocyte Growth Factor-(HGF-) Induced Migration and Invasion and Actin Rearrangement via Suppression of c-Met-Mediated RhoA/ROCK Signaling in Glioblastoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9053295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ren, Y.; Lou, Z.G.; Wan, X.; Weng, G.B.; Cen, D. Paeoniflorin inhibits the growth of bladder carcinoma via deactivation of STAT3. Acta Pharm. 2018, 68, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, H.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Qu, H.; Zhao, Y. Carbon Dots from Paeoniae Radix Alba Carbonisata: Hepatoprotective Effect. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9049–9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, G.H.; Kim, S.N.; Kim, M.J.; Heo, Y. Protective effect of Paeoniae radix alba root extract on immune alterations in mice with atopic dermatitis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2018, 81, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Kuang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, R.; Luo, Z. Paeoniae radix alba polysaccharides obtained via optimized extraction treat experimental autoimmune hepatitis effectively. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benić, M.S.; Nežić, L.; Vujić-Aleksić, V.; Mititelu-Tartau, L. Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 785790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Effect of Dietary Paeoniae Radix Alba Extract on the Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility and Metabolism, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestine Histomorphology of Raccoon Dog During the Growing Period. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 839450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, M.; Kawashima, D.; Katagiri, K.; Takeuchi, R.; Tohnai, G.; Ohtsuka, K. Protective effect of a molecular chaperone inducer, paeoniflorin, on the HCl- and ethanol-triggered gastric mucosal injury. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X. Watching Red Mansions and Talking about Chinese Medicine; Shandong Pictorial Publishing House: Jinan, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.; Xu, J.H.; Han, J.H.; Liang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Fan, Z.Z. Chinese herbal decoction Shiquan Dabu Tang inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis of metastasis after primary tumor surgical removal in mice. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2012, 10, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Huang, J. Tumor Food Therapy Expert Talk; People’s Military Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; He, X.; Song, X. Chinese Medicine Rehabilitation Terminology; Sunshine Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastric Diseases; Shanghai Science and Technology Literature Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H. Specialized Chinese Medicine Treatment for Stroke; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; You, W.; Jian, H. Home Remedies; China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Wei, J. Aquatic Cuisine; Dalian Publishing House: Dalian, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Cai, X. Dietary Therapy for Gastrointestinal Disorders; People’s Military Medical Publishing House: Beijing, Chin, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Shen, M.; Fang, J.; Wei, D.; Qin, L. Advancement in the chemical analysis of Paeoniae Radix (Shaoyao). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, M.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Peng, F.C.; Lee, H.-J.; Chang, J.-M.; Yang, C.-M.; Chen, C.-H. Gastroprotective potential against indomethacin and safety assessment of the homology of medicine and food formula cuttlebone complex. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Gong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, M. Role of Active Components of Medicinal Food in the Regulation of Angiogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 594050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.X.; Jiang, J.G. Hypolipidemic Components from Medicine Food Homology Species Used in China: Pharmacological and Health Effects. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Si, J.; Wu, L. Metabolites of medicine food homology-derived endophytic fungi and their activities. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1882–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Xia, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Mou, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.N. The multifaceted mechanisms of Paeoniflorin in the treatment of tumors: State-of-the-Art. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).