Traceability of Microplastic Fragments from Waste Plastic Express Packages Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Feasibility Analysis of the Experiment
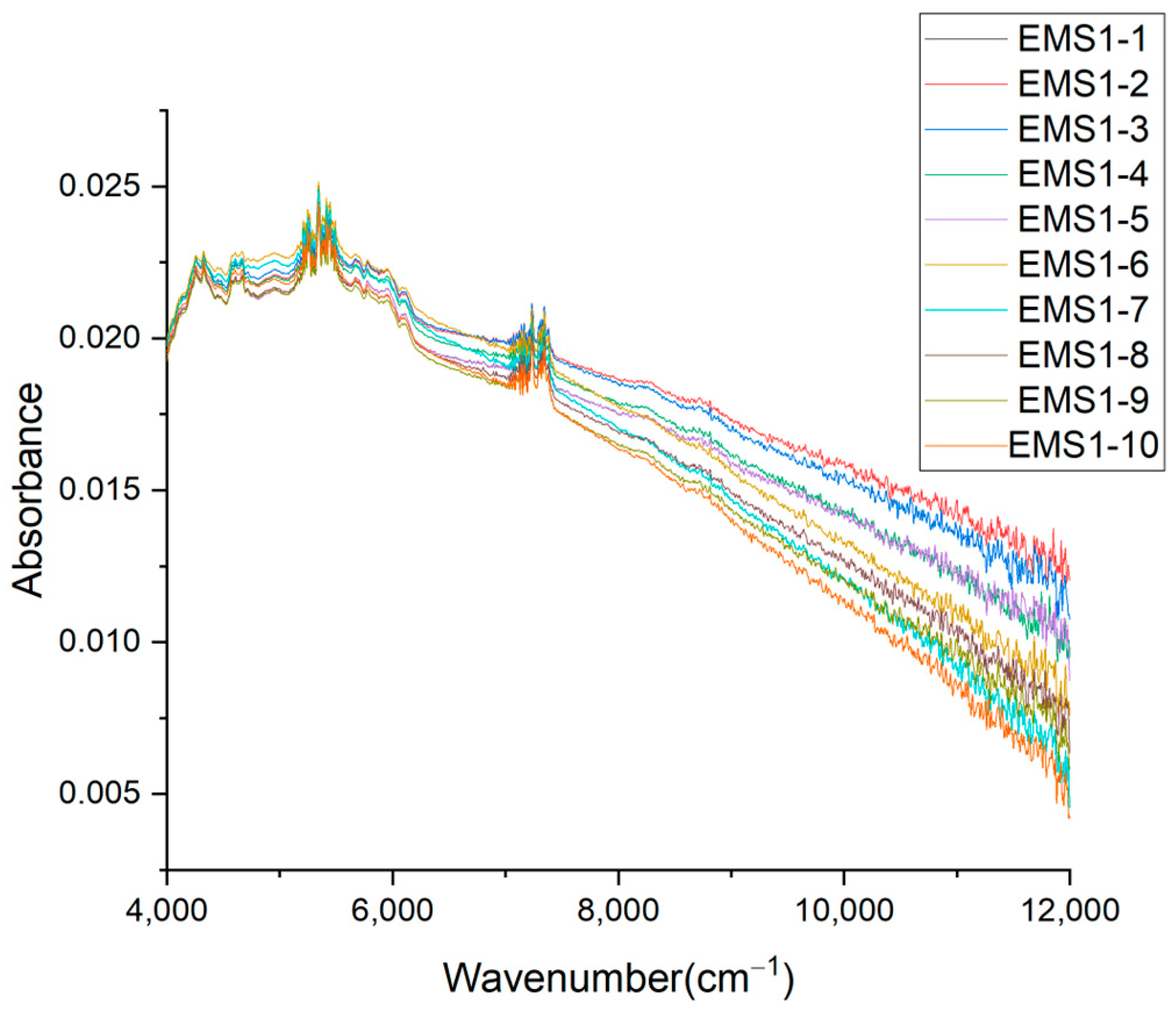
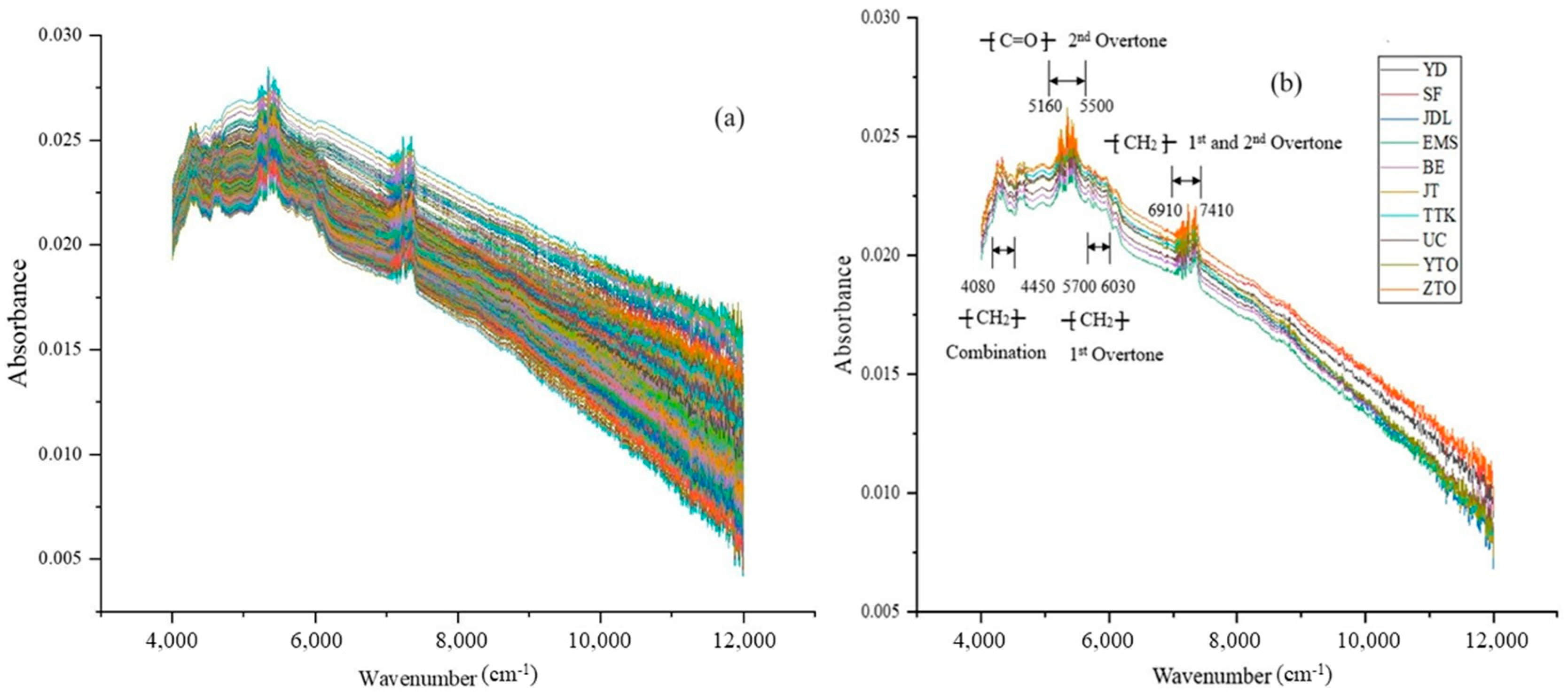
2.2. NIR Spectroscopy Data Analysis of MPs from WPEPs
2.3. Outlier Elimination
2.4. Sample Set Division
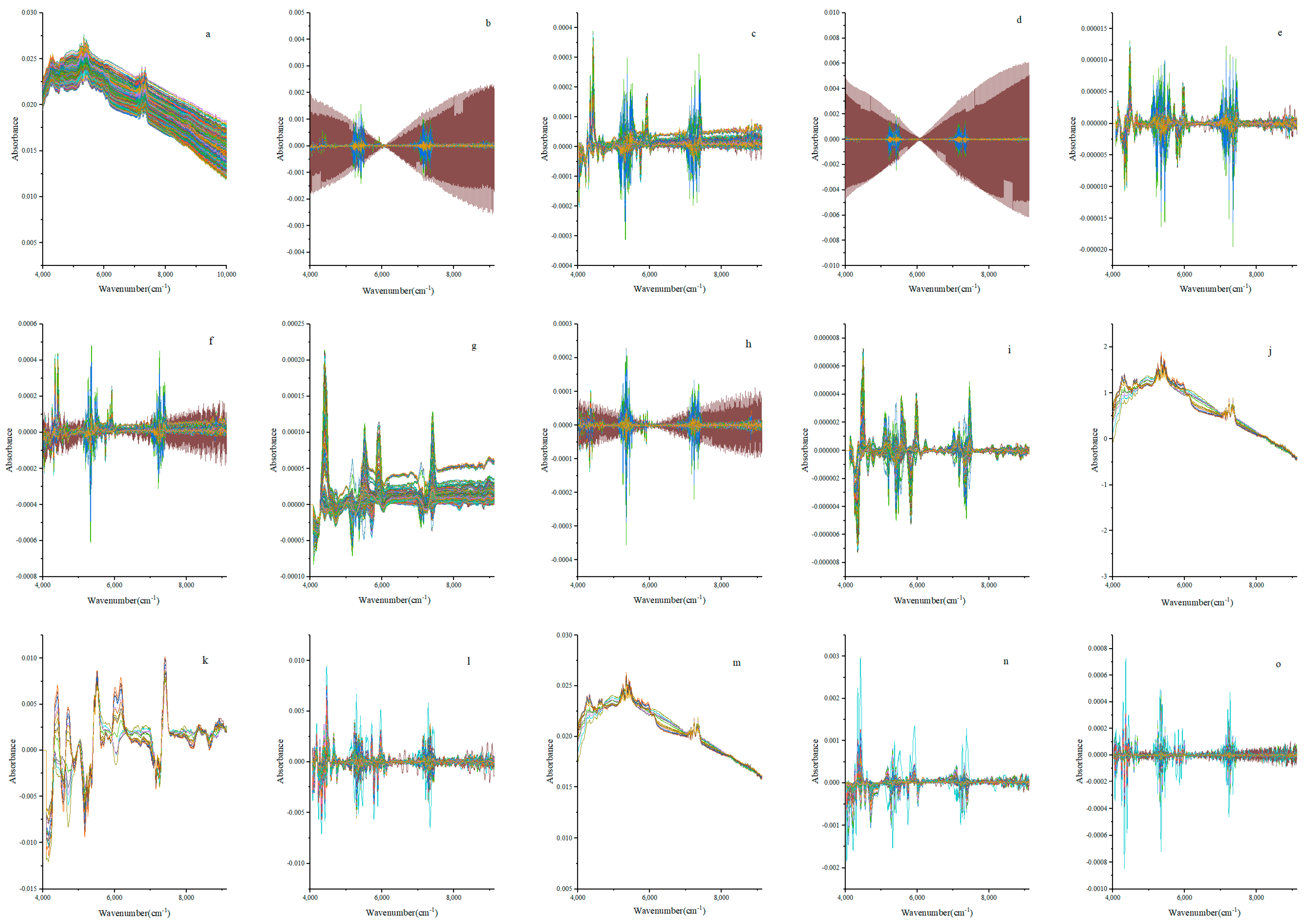
2.5. NIR Spectrogram Pretreatment
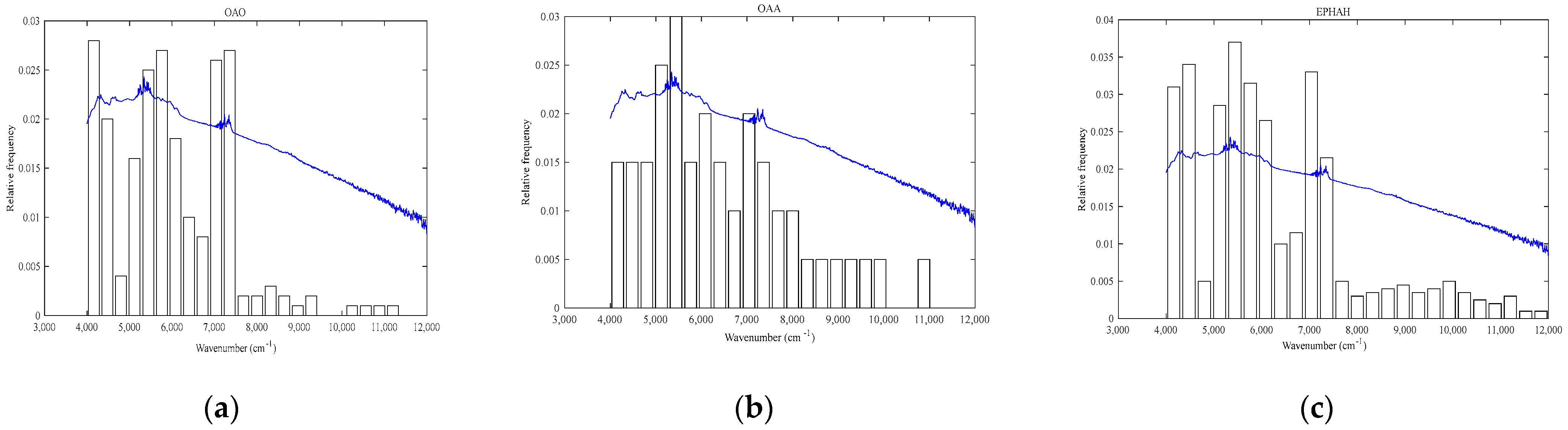
2.6. Characteristic Spectral Interval Selection
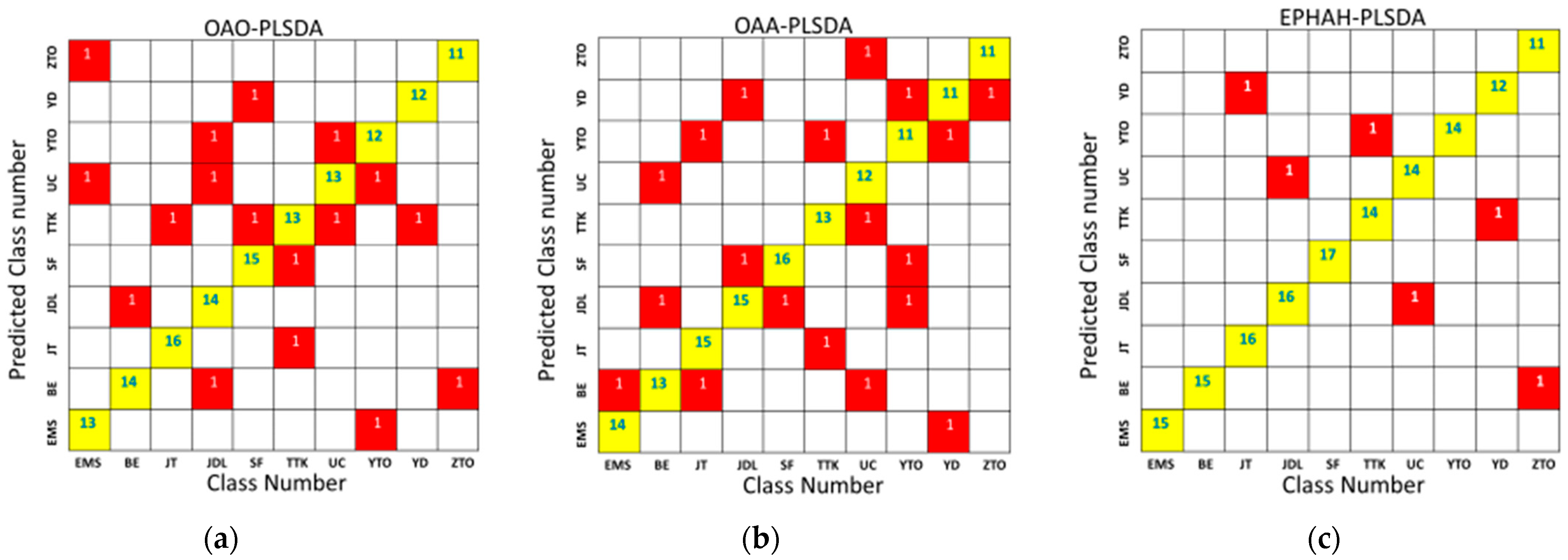
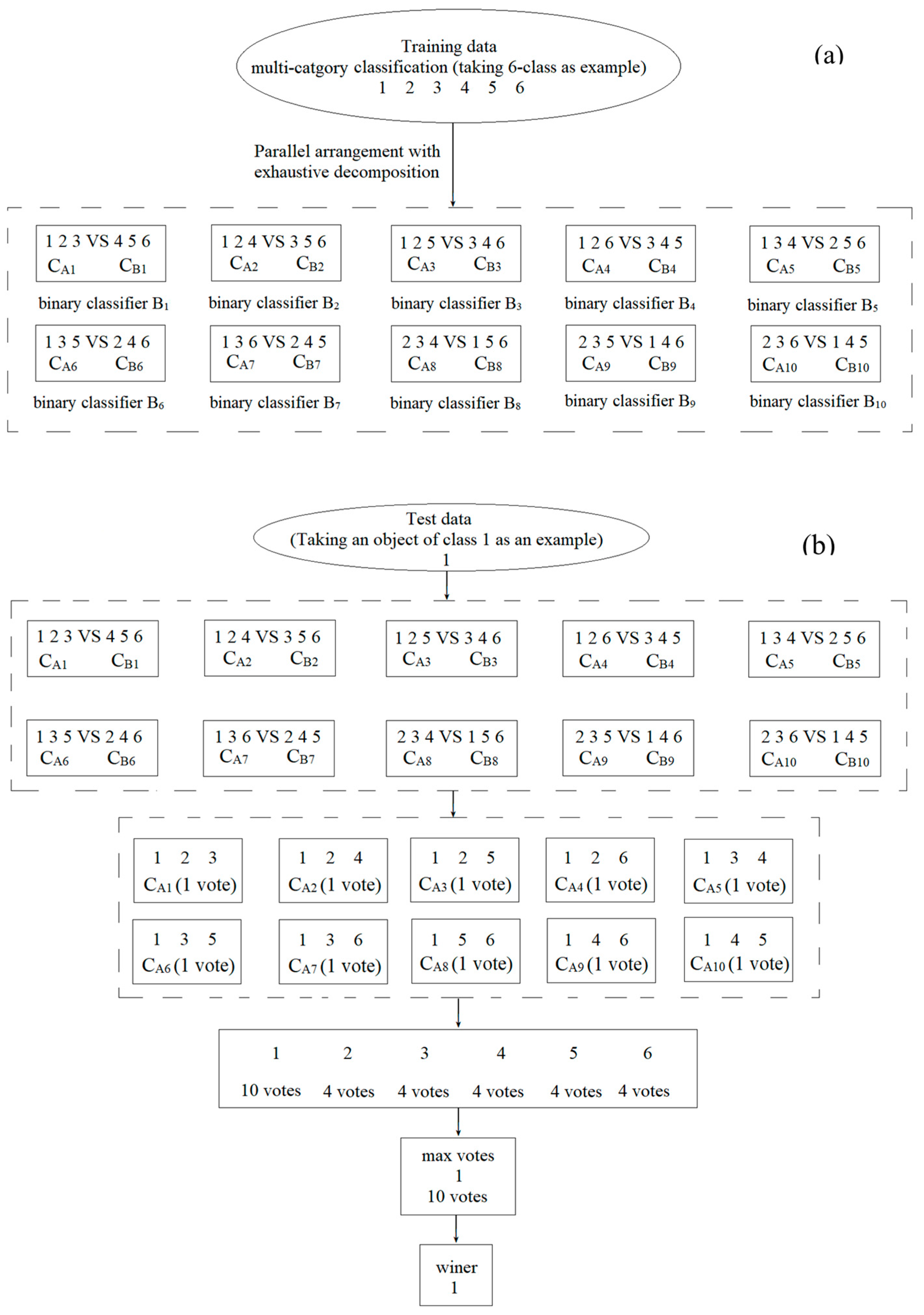
2.7. Large-Class-Number Classification Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Materials
3.2. Instrument and Sample Spectral Acquisition
3.3. Outlier Elimination
3.4. Sample Set Division Method
3.5. Spectral Pretreatment
3.6. Characteristic Wavelength Selection
3.7. Chemometric Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Anderson, S.J.; Harvey, G.R.; Miklas, H.P.; Peck, B.B. Polystyrene spherules in coastal waters. Science 1972, 178, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L., Jr. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Microplastic in three urban estuaries, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.D.; Wertz, H.; Leads, R.R.; Weinstein, J.E. Microplastic in two South Carolina Estuaries: Occurrence, distribution, and composition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, T.; Blarer, P.; Storck, F.R.; Pittroff, M.; Wernicke, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Repeated detection of polystyrene microbeads in the lower Rhine River. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.; McGrattan, S.; Sullivan, P.J.; Walter, M.T. The effect of dams on river transport of microplastic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Quik, J.T.K.; Sun, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Fate of nano-and microplastic in freshwater systems: A modeling study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.; Peters, R.J. Potential health impact of environmentally released micro-and nanoplastics in the human food production chain: Experiences from nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post Office of the People’s Republic of China. 2019 Postal Industry Development Statistical Bulletin [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.spb.gov.cn/gjyzj/c100015/c100016/202005/3b737880d332463bb63e027d70fd4476.shtml (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Post Office of the People’s Republic of China. December 2021 China Express Development Index Report [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.spb.gov.cn/gjyzj/c100278/202201/f39ae0633d1b4443bcd5b3f6b7ddfe33.shtml (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derraik, J.G. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J.; Boldgiv, B. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, J.C.; Frias, J.; Micaelo, A.C.; Sobral, P. Resin pellets from beaches of the Portuguese coast and adsorbed persistent organic pollutants. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Hylland, K.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiero, L.; Castoldi, E.; Tuffi, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Identification and characterization of plastics from small appliances and kinetic analysis of their thermally activated pyrolysis. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2014, 109, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirk, M.; Burkhard, P.; Jochen, A.; Gunschera, J.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Salthammer, T. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy for the fast detection and sorting of wood-plastic composites and waste wood treated with wood preservatives. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 313–331. [Google Scholar]
- Saman, S.R.; Nikbin, I.M.; Allahyari, H.; Habibi, S.T. Sustainable approach for recycling waste tire rubber and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to produce green concrete with resistance against sulfuric acid attack. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 126, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Liang, Y.; Kim, M.; Byun, J.; Choi, H. Microplastics with adsorbed contaminants: Mechanisms and treatment. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astray, G.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Barreiro, E.; Mejuto, J.C.; Cid-Samamed, A. Machine Learning to Predict the Adsorption Capacity of Microplastics. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Luan, Y.; Dai, W. Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants on microplastics. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cid-Samamed, A.; Diniz, M.S. Recent Advances in the Aggregation Behavior of Nanoplastics in Aquatic Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.A.; Corcoran, P.L. Effects of mechanical and chemical processes on the degradation of plastic beach debris on the island of Kauai, Hawaii. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, A.; Boldrin, A.; Guerriero, P.; Moschino, V.; Rella, R.; Sturaro, A.; Da Ros, L. Microplastic particles in sediments of Lagoon of Venice, Italy: First observations on occurrence, spatial patterns and identification. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Dekiff, J.H.; Willmeyer, J.; Nuelle, M.T.; Ebert, M.; Remy, D. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaut, A.; Cassone, A.L.; Frere, L.; Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Rinnert, E.; Riviere, G.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P.; Huvet, A.; et al. Microplastics in seafood: Benchmark protocol for their extraction and characterization. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Scholz-Bottcher, B.M. Simultaneous Trace Identification and Quantification of Common Types of Microplastics in Environmental Samples by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5052–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Barthel, A.K.; Braun, U.; Bannick, C.G.; Brand, K.; Jekel, M.; Senz, R. Analysis of polyethylene microplastics in environmental samples, using a thermal decomposition method. Water Res. 2015, 85, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Bartholomeus, H.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Geissen, V. Predicting soil microplastic concentration using vis-NIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrows, A.P.W.; Christiansen, K.S.; Bode, E.T.; Hoellein, T.J. A watershed-scale, citizen science approach to quantifying microplastic concentration in a mixed land-use river. Water Res. 2018, 147, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Loder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Eppe, G.; Parmentier, E.; Das, K. Detection of Anthropogenic Particles in Fish Stomachs: An Isolation Method Adapted to Identification by Raman Spectroscopy. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagg, A.S.; Sapp, M.; Harrison, J.P.; Ojeda, J.J. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in Wastewater Using Focal Plane Array-Based Reflectance Micro-FT-IR Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6032–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Loder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, Z.; He, Y. Transfer learning strategy for plastic pollution detection in soil: Calibration transfer from high-throughput HSI system to NIR sensor. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.D.; Vianna, S.G.T.; Cunha, P.H.P.; Folli, G.S.; de Paulo, E.H.; Moro, M.K.; Romao, W.; de Oliveira, E.C.; Filgueiras, P.R. Characterization of crude oils with a portable NIR spectrometer. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, J.R.; Puig, R.; Cantero, R. Portable Instruments Based on NIR Sensors and Multivariate Statistical Methods for a Semiautomatic Quality Control of Textiles. Machines 2023, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, R.F.; Ramaker, H.J.; Sap, S.; Van Asten, A.C. A calibration friendly approach to identify drugs of abuse mixtures with a portable near-infrared analyzer. Drug Test Anal. 2022, 14, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, P.; Boswell, R. Rule Induction with CN2: Some Recent Improvements; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; Volume 19, pp. 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikar, R. Essemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag. 2006, 6, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Govindaraju, V. Half-Against-Half Multi-Class Support Vector Machines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forina, M.; Oliveri, P.; Lanteri, S.; Casale, M. Class-modeling techniques, classic and new, for old and new problems. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2008, 93, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Sun, C.J.; Luo, L.B.; He, Y. Determination of tea polyphenols content by infrared spectroscopy coupled with iPLS and random frog techniques. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2015, 112, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yan, S.M.; Cai, C.B.; Yu, X.P. One-class partial least squares (OCPLS) classifier. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2013, 126, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.S.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.P.; Ye, Z.H.; Cui, H.F. Robust and Automated Internal Quality Grading of a Chinese Green Tea (Longjing) by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 7, 139347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yan, S.M.; Ye, Z.H.; Fu, X.S.; Yu, X.P. Combining Electronic Tongue Array and Chemometrics for Discriminating the Specific Geographical Origins of Green Tea. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 5, 350801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, L.; Tang, L.J.; Yang, J.T.; Wu, B.Q.; Chen, N.; Jiang, J.H.; Yu, R.Q. Simultaneous detection of multiple inherited metabolic diseases using GC-MS urinary metabolomics by chemometrics multi-class classification strategies. Talanta 2018, 186, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkano, M.; Galar, M.; Sanz, J.; Bustince, H. Fuzzy Rule-Based Classification Systems for multi-class problems using binary decomposition strategies: On the influence of n-dimensional overlap functions in the Fuzzy Reasoning Method. Inform. Sci. 2016, 332, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesmero, M.P.; Alonso-Weber, J.M.; Sanchis, A. CCE: An ensemble architecture based on coupled ANN for solving multiclass problems. Inform. Fusion 2020, 58, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galar, M.; Fernandez, A.; Barrenechea, E.; Bustince, H.; Herrera, F. Dynamic classifier selection for One-vs-One strategy: Avoiding non-competent classifiers. Pattern Recogn. 2013, 46, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonville, J.M.; Richards, S.E.; Barton, R.H.; Boulange, C.L.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Dumas, M.E. The evolution of partial least squares models and related chemometric approaches in metabonomics and metabolic phenotyping. J. Chemom. 2010, 24, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Verboven, S. A fast method for robust principal components with applications to chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2002, 60, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, R.K.; Araujo, M.C.; Jose, G.E.; Pontes, M.J.; Silva, E.C.; Saldanha, T.C. A method for calibration and validation subset partitioning. Talanta 2005, 67, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Feng, D.J.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, M.; Sui, Q.; Jia, L. Fast determination of oxide content in cement raw meal using NIR spectroscopy with the SPXY algorithm. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3936–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snee, R.D. Validation of regression models: Methods and examples. Technometrics 1977, 19, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, F. Freshness measurement of eggs using near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2011, 12, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgaard, L.; Saudland, A.; Wagner, J.; Nielsen, J.P.; Munck, L.; Engelsen, S.B. Interval Partial Least-Squares Regression (iPLS): A Comparative Chemometric Study with an Example from Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardi, R.; Nørgaard, L. Sequential application of backward interval PLS and genetic algorithms for the selection of relevant spectral regions. J. Chemom. 2004, 18, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesel, K.M.F.; da Costa, F.S.L.; Pimenta, A.S.; de Lima, K.M.G. Near-infrared spectroscopy and wavelength selection for estimating basic density in Mimosa tenuiflora Willd. Poiret wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, U.; Guha, P.; Mishra, S. Characterization of Chickpea Flour by Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leno, I.J.; Sankar, S.S.; Ponnambalam, S.G. An elitist strategy genetic algorithm using simulated annealing algorithm as local search for facility layout design. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 84, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Selection of the efficient wavelength regions in FT-NIR spectroscopy for determination of SSC of ‘Fuji’ apple based on BiPLS and FiPLS models. Vib. Spectrosc. 2007, 44, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati-Rad, M.; Hasani, M. Principle component analysis (PCA) and second-order global hard-modelling for the complete resolution of transition metal ions complex formation with 1,10-phenantroline. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal Projection to Latent Structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
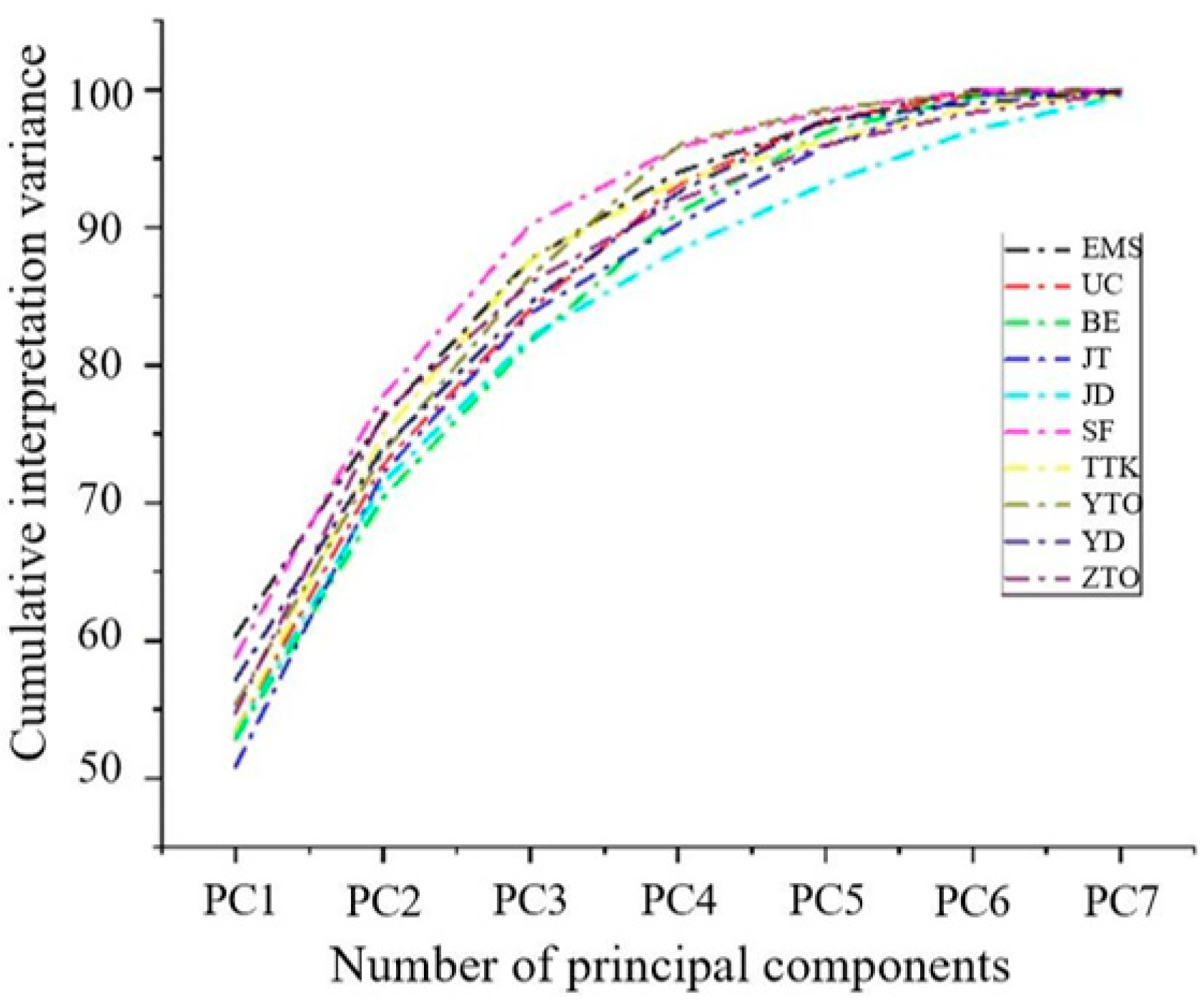
| Sample Name | Cumulative Interpretation Variance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | |
| EMS | 60.3371 | 76.1853 | 87.6718 | 94.0001 | 97.6533 | 99.9848 | 99.9978 |
| UC | 53.3567 | 72.8124 | 84.0012 | 93.1071 | 97.8365 | 99.5811 | 99.6728 |
| BE | 52.8379 | 70.3580 | 81.6930 | 91.0320 | 96.9940 | 99.5114 | 99.9037 |
| JT | 50.8246 | 72.1578 | 83.7645 | 90.2234 | 95.8934 | 99.5841 | 99.9124 |
| JD | 53.1784 | 71.4354 | 81.9812 | 88.3655 | 93.1596 | 97.0560 | 99.5321 |
| SF | 58.7845 | 77.7124 | 90.2134 | 95.8125 | 98.3921 | 99.9571 | 99.9982 |
| TTK | 53.3485 | 74.9454 | 87.7445 | 93.3754 | 96.3187 | 98.7465 | 99.5689 |
| YTO | 55.3312 | 73.6155 | 86.3698 | 96.0328 | 98.6134 | 99.6752 | 99.9378 |
| YD | 57.1178 | 73.9856 | 84.5418 | 92.5794 | 97.7823 | 99.0198 | 99.9078 |
| ZTO | 54.7328 | 76.4512 | 85.9872 | 91.9633 | 95.9877 | 98.3578 | 99.7328 |
| Sample Name | Quantity of Samples | Abnormal Sample Code | PCs | Score Distance (SD) | Orthogonal Distance (OD) | Threshold Value | Type of Outlier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | OD | |||||||
| EMS | 75 | / | 6 | / | / | 14.35 | 14.54 | / |
| BE | 75 | / | 6 | / | / | 14.35 | 14.54 | / |
| JT | 85 | JT-43 | 6 | 4.20 | 15.42 | 14.16 | 14.32 | SD small, OD large |
| JD | 85 | / | 7 | / | 16.06 | 16.25 | / | |
| SF | 85 | / | 6 | / | 14.16 | 14.33 | / | |
| TTK | 75 | TTK-18 | 7 | 17.45 | 16.96 | 16.38 | 16.60 | SD large, OD large |
| UC | 75 | UC-13 | 6 | 15.54 | 6.78 | 14.35 | 14.54 | SD large, OD small |
| YTO | 70 | YTO-25 | 6 | 2.70 | 15.66 | 14.49 | 14.70 | SD small, OD large |
| YD | 65 | / | 6 | / | / | 14.71 | 14.94 | / |
| ZTO | 60 | / | 7 | / | / | 17.07 | 17.35 | / |
| Sample Name | EMS | BE | JT | JDL | SF | TTK | UC | YTO | YD | ZTO | Total Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | 75 | 75 | 84 | 85 | 85 | 74 | 74 | 69 | 65 | 60 | 750 |
| Training sets | 52 | 52 | 59 | 60 | 60 | 51 | 51 | 48 | 45 | 42 | 520 |
| Test sets | 23 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 23 | 23 | 21 | 20 | 18 | 226 |
| Method Name | Joint Interval Number | Average Number of Latent Variables (LVs) | Interactive Validation Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| SG+2D+OAA | 5 | 4.89 | 9.0034% |
| SG+2D+OAO | 5 | 5.04 | 9.2413% |
| SG+2D+EPHAH | 5 | 3.15 | 3.5681% |
| Sample Name | EMS | BE | JT | JDL | SF | TTK | UC | YTO | YD | ZTO | Total Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | 75 | 75 | 84 | 85 | 85 | 74 | 74 | 69 | 65 | 60 | 746 |
| Training sets | 45 | 45 | 50 | 51 | 51 | 44 | 44 | 41 | 39 | 36 | 446 |
| Verification sets | 15 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 150 |
| Test sets | 15 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 150 |
| LCNC Model | LVs | ERMCCV | Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| OAO-PLSDA | 6.35 | 0.155 | 0.801 |
| OAA-PLSDA | 5.37 | 0.103 | 0.792 |
| EPHAH-PLSDA | 3.12 | 0.054 | 0.950 |
| Class Sample Name | Collection Location | Collection Region | Date | Average Size (Standard Deviation) (mm) | Average Weight (Standard Deviation) (mg) | Microplastics | Plastics | Total Microp Lastics | Total Plastics | Final Number of Samples Selected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMS | China Post, garbage disposal stations. | (1) Shanghai: Pudong, Xuhui, and Hongkou district; (2) Hangzhou: Shangcheng, Gongshu, and Qiantang district; (3) Nanjing: Xuanwu and Baixia district. | 10 May–30 December 2021 | 2.5(0.7) | 1.3(0.5) | 70 | 12 | 130 | 77 | 75 |
| 5.5(1.8) | 2.8(1.0) | 60 | 20 | |||||||
| 10.3(2.1) | 6.2(2.3) | 0 | 45 | |||||||
| BE | BE direct stores and agency points, Cainiao courier station, and garbage disposal stations. | (1) Shanghai: Changning, Putuo, and Hongkou district; (2) Hangzhou: Xihu, Binjiang, and Qiantang district; (3) Nanjing: Qinhuai and Jianye district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 3.5(1.4) | 2.1(0.6) | 80 | 0 | 146 | 93 | 75 |
| 6.8(1.6) | 3.4(1.5) | 66 | 33 | |||||||
| 9.6(2.2) | 5.8(2.7) | 0 | 60 | |||||||
| JT | JT Courier station, garbage collection stations, Cainiao courier station, and courier agencies. | (1) Shanghai: Hongkou, Yangpu, Huangpu, and Jingan district; (2) Hangzhou: Shangcheng, Yuhang, Linping, and Qiantang district; (3) Nanjing: Drum Tower, Xiaguan, and Pukou district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 3.7(0.6) | 2.1(0.6) | 67 | 0 | 149 | 112 | 85 |
| 6.4(1.8) | 3.4(1.7) | 82 | 52 | |||||||
| 11.7(2.2) | 6.1(2.7) | 0 | 60 | |||||||
| JD | JD courier stations, garbage collection stations, Cainiao courier station, and courier agencies. | (1) Shanghai: Xuhui, Yangpu, Chongming, Jingan district; (2) Hangzhou: Qiantang, Shangcheng, Gongshu, and Xihu district; (3) Nanjing: Baixia, Qinhuai, Jianye, and Yuhuatai district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 3.1(1.2) | 1.9(0.8) | 102 | 0 | 158 | 108 | 85 |
| 6.2(1.5) | 3.2(1.9) | 56 | 33 | |||||||
| 10.5(3.1) | 5.9(2.3) | 0 | 75 | |||||||
| SF | SF special express stations, garbage collection stations. | (1) Shanghai: Baoshan, Minhang, and Jiading district; (2) Hangzhou: Xihu, Binjiang, Xiaoshan, and Shangcheng district; (3) Nanjing: Jianye, Gulou, and Xiaguan district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 3.0(1.1) | 1.8(1.3) | 95 | 10 | 155 | 135 | 85 |
| 5.5(1.2) | 3.4(1.3) | 60 | 50 | |||||||
| 11.5(2.5) | 6.9(1.8) | 0 | 75 | |||||||
| TTK | TTK special express stations, garbage collection stations, Cainiao stations, and express agents. | (1) Shanghai: Jinshan, Songjiang, and Fengxian district; (2) Hangzhou: Xihu, Gongshu, and Linping district; (3) Nanjing: Pukou, Liuhe, Qixia, Yuhuatai, and Jiangning district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 2.8(1.3) | 2.3(0.8) | 82 | 0 | 112 | 114 | 75 |
| 6.1(1.5) | 4.8(1.3) | 30 | 44 | |||||||
| 10.7(1.9) | 7.3(2.0) | 0 | 70 | |||||||
| UC | UC special express stations, garbage collection stations, Cainiao stations, and express agents. | (1) Shanghai: Xuhui, Hongkou, Yangpu, and Chongming district; (2) Hangzhou: Shangcheng, Gongshu, Xihu, and Binjiang district; (3) Nanjing: Baixia, Qinhuai, Jianye, and Gulou district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 3.3(1.4) | 2.6(0.7) | 93 | 0 | 93 | 102 | 75 |
| 6.3(1.2) | 4.4(1.6) | 0 | 52 | |||||||
| 11.6(2.3) | 8.3(2.4) | 0 | 50 | |||||||
| YTO | YTO special express stations, garbage collection stations, Cainiao stations, and express agents. | (1) Shanghai: Pudong, Huangpu, Jingan, and Songjiang district; (2) Hangzhou: Binjiang, Xihu, Xiaoshan, and Yuhang district; (3) Nanjing: Xuanwu, Gulou, Qixia, and Yuhuatai district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 2.7(1.6) | 3.0(1.7) | 88 | 0 | 123 | 117 | 70 |
| 6.7(2.1) | 5.8(2.1) | 35 | 47 | |||||||
| 11.6(2.3) | 8.3(2.4) | 0 | 70 | |||||||
| YD | YD special express stations, garbage collection stations, Cainiao stations, and express agents. | (1) Shanghai: Songjiang, Jiading, Jinshan, Qingpu, and Fengxian district; (2) Hangzhou: Shangcheng, Gongshu, Xihu, and Binjiang district; (3) Nanjing: Baixia, Qinhuai, Qixia, and Jianye district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 4.0(1.6) | 4.5(1.2) | 105 | 0 | 105 | 102 | 65 |
| 7.6(1.7) | 7.8(2.5) | 0 | 60 | |||||||
| 10.8(1.4) | 9.2(1.7) | 0 | 42 | |||||||
| ZTO | ZTO special express stations, garbage collection stations, Cainiao stations, and express agents. | (1) Shanghai: Qingpu, Fengxian, Chongming, Jingan, and Songjiang district; (2) Hangzhou: Xihu, Qiantang, Binjiang, and Xiaoshan district; (3) Nanjing: Xuanwu, Baixia, Liuhe, Qixia, and Yuhuatai district. | 10 March–30 December 2021 | 2.9(1.3) | 3.5(1.5) | 82 | 0 | 125 | 106 | 60 |
| 6.5(2.1) | 7.8(2.5) | 43 | 51 | |||||||
| 9.3(2.2) | 8.0(1.3) | 0 | 55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, X.; Pan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Ye, Z.; Yu, X. Traceability of Microplastic Fragments from Waste Plastic Express Packages Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. Molecules 2024, 29, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061308
Fu X, Pan X, Chen J, Zhang M, Ye Z, Yu X. Traceability of Microplastic Fragments from Waste Plastic Express Packages Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061308
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Xianshu, Xiangliang Pan, Jun Chen, Mingzhou Zhang, Zihong Ye, and Xiaoping Yu. 2024. "Traceability of Microplastic Fragments from Waste Plastic Express Packages Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics" Molecules 29, no. 6: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061308
APA StyleFu, X., Pan, X., Chen, J., Zhang, M., Ye, Z., & Yu, X. (2024). Traceability of Microplastic Fragments from Waste Plastic Express Packages Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. Molecules, 29(6), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061308







