Inhibitory Effects of the Polyphenols from the Root of Rhizophora apiculata Blume on Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Human Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation of R. apiculata Extract and Pure Compounds
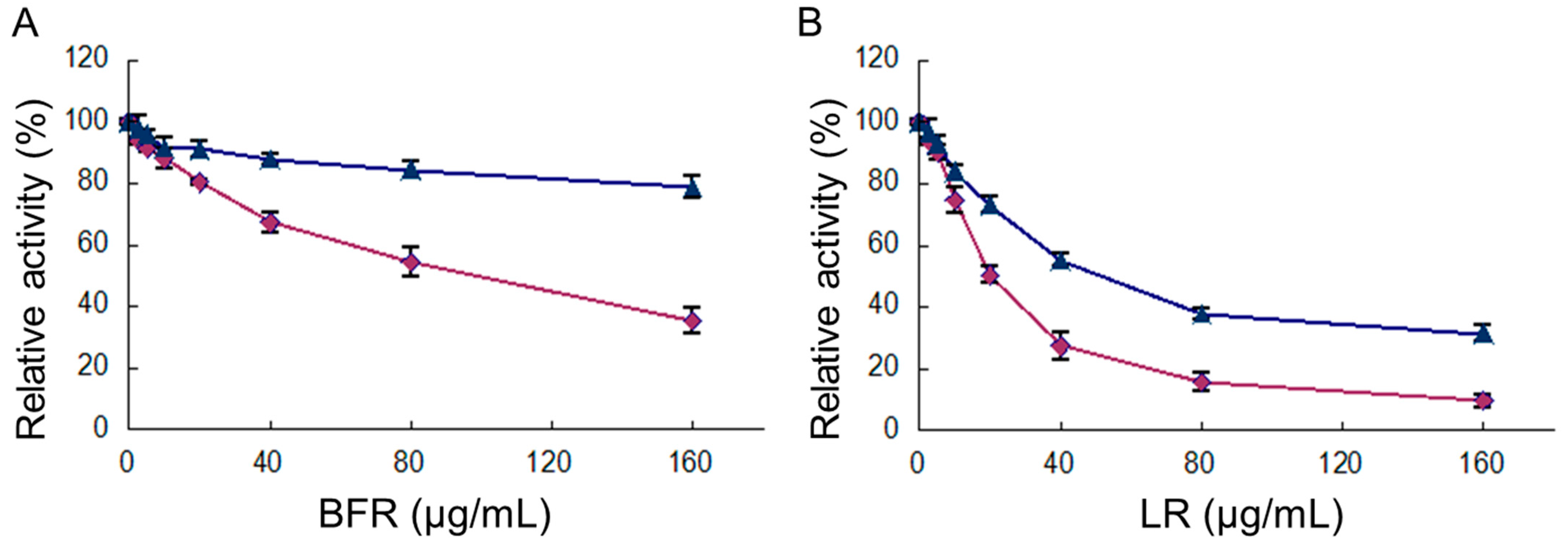
2.2. The Inhibition of FAS Activity by Different Fractions of R. apiculata Extract
2.3. Inhibition of Overall Reaction and KR Reaction of FAS by BFR and LR
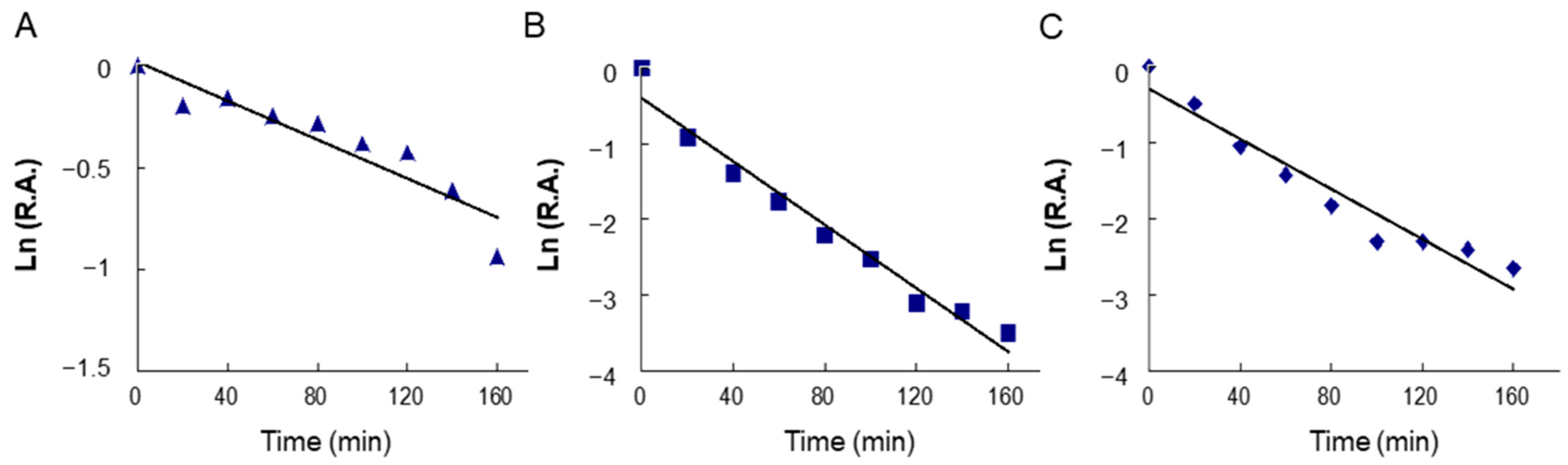
2.4. Time-Dependent Inhibition of Overall and KR Reactions of FAS by BFR and LR
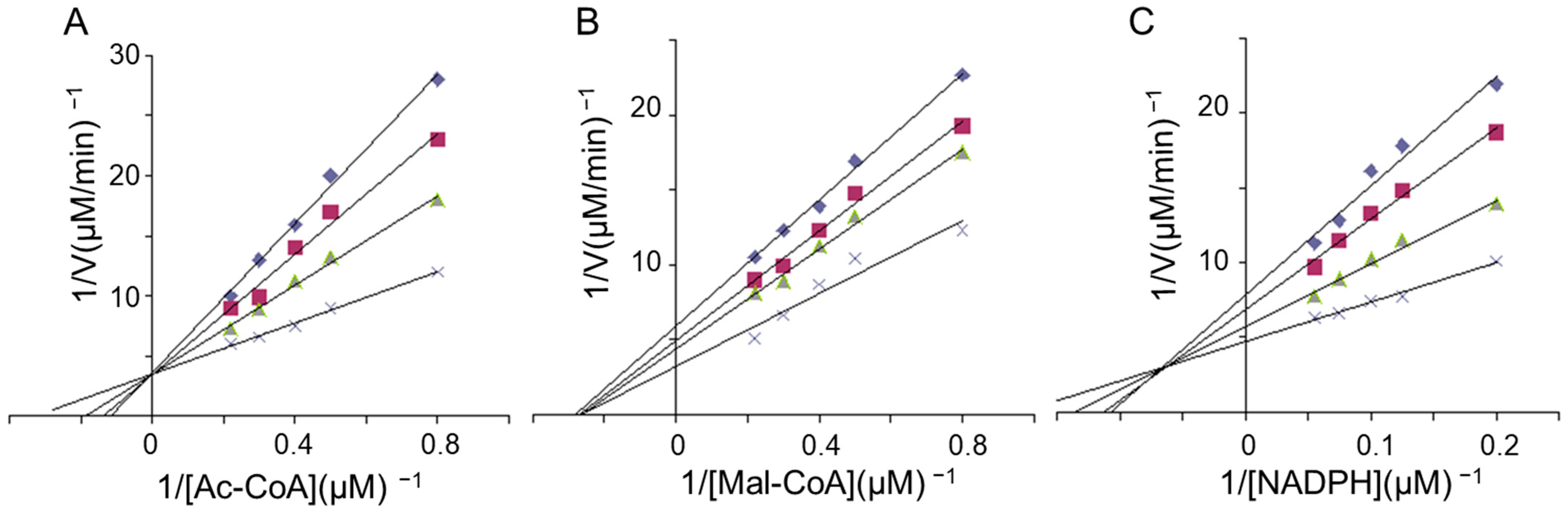
2.5. Kinetics Studies of FAS Inhibition by LR
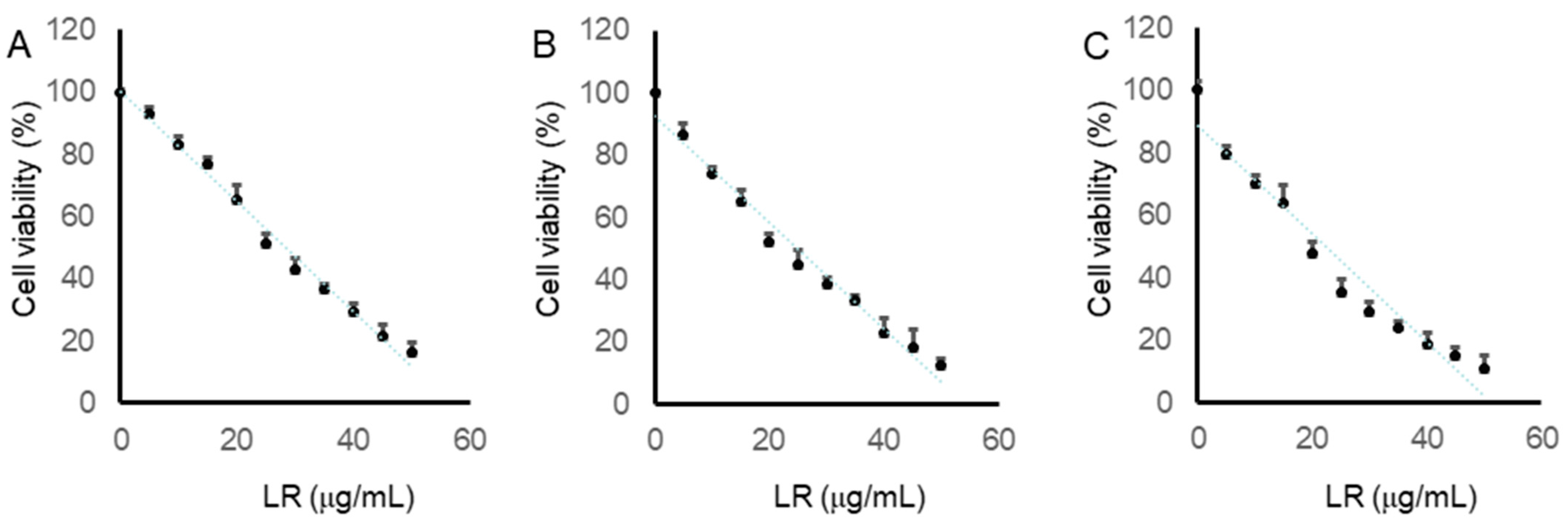
2.6. LR Reduced the Cell Viabilities of CaCo2, LoVo, and SW620 Cells
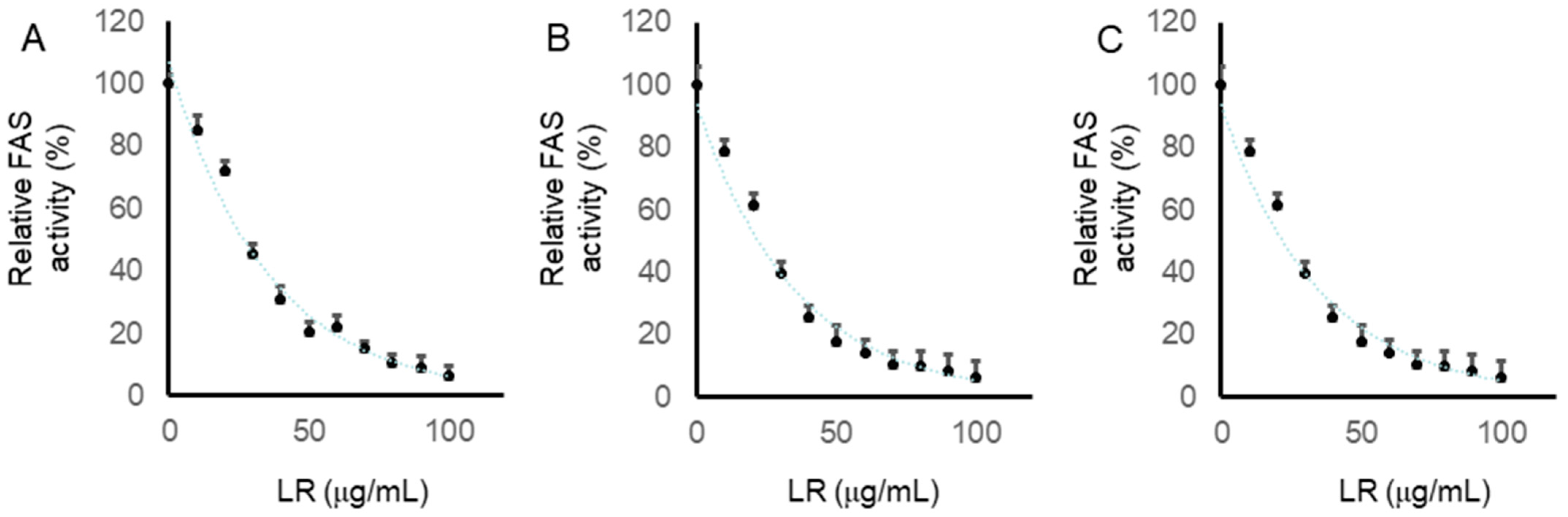
2.7. LR Inhibited the Intracellular FAS Activity in CaCo2, LoVo, and SW620 Cells
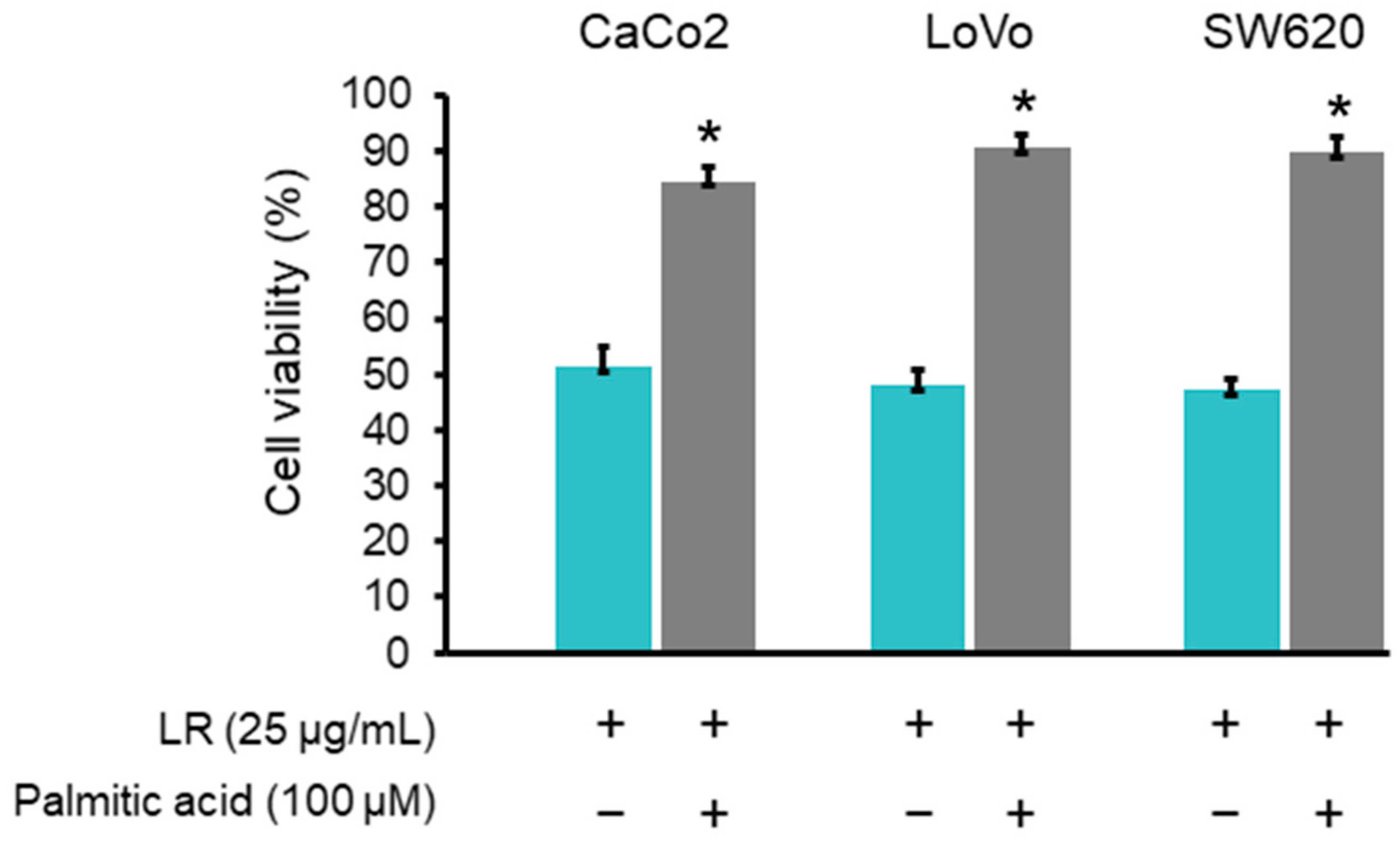
2.8. Palmitic Acid Rescued the Reduction of Colon Cancer Cell Viability Induced by LR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Plant Source
4.3. Preparation of FAS and Its Substrates
4.4. Assay of FAS Activity
4.5. Assay of Fast-Binding Inhibition Activity
4.6. Assay of Time-Dependent Inhibition Activity
4.7. Enzyme Kinetics Study
4.8. Cell Lines and Culture
4.9. Cell Proliferation Inhibitory Activity Assay
4.10. Intracellular FAS Activity Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | afzelechin-3-rhamnopyranoside |
| BFR | n-butanol fraction of R. apiculata extract |
| DTT | 1,4-dithiothreitol |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGCG | epigallocatechin gallate |
| EtOAc | ethyl acetate |
| FAS | fatty acid synthase |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| IC50 | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| KR | β-ketoacyl reductase |
| LA | lyoniresinol-3α-O-β-arabinopyranoside |
| LR | lyoniresinol-3α-O-β-rhamnopyranoside |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
References
- Sivasubramanian, B.P.; Dave, M.; Panchal, V.; Saifa-Bonsu, J.; Konka, S.; Noei, F.; Nagaraj, S.; Terpari, U.; Savani, P.; Vekaria, P.H.; et al. Comprehensive review of red meat consumption and the risk of cancer. Cureus 2023, 15, e45324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, M.; Ilic, I. Cancer of colon, rectum and anus: The rising burden of disease worldwide from 1990 to 2019. J. Public Health 2023, fdad197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörgren, F.; Agger, E.; Lydrup, M.L.; Buchwald, P. Tumour deposits in colon cancer predict recurrence and reduced survival in a nationwide population-based study. BJS Open 2023, 7, zrad122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.H.; Thulasingam, S.; Nagarajan, S. Terpenoids as anti-colon cancer agents—A comprehensive review on its mechanistic perspectives. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 795, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, J.X.; Qiao, J.Y.; Chen, Q.W.; Sun, Y.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Colon-targeted bacterial hydrogel for tumor vascular normalization and improved chemotherapy. J. Control Release 2023, 356, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.G.; Tang, M.Y.; Pan, X.; Liu, Z.H. Metastatic colon cancer treated using traditional Chinese medicine combined with chemotherapy: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 4670–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, N.H.; Makpol, S.; Mohd Yusof, Y.A. A review on dietary intervention in obesity associated colon cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochem, C.; Leitzmann, M. Obesity and colorectal cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2016, 208, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, G.; Poursheikhani, A.; Yassi, M.; Hayatbakhsh, A.; Kerachian, M.; Kerachian, M.A. Obesity, diabetes and the risk of colorectal adenoma and cancer. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Vela, M.E.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. White adipose tissue as endocrine organ and its role in obesity. Arch. Med. Res. 2008, 39, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, W.; Fan, H.; Ma, Q.; Tian, W.; Dai, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, N.; Ma, X. Fatty acid synthase inhibitors from the hulls of Nephelium lappaceum L. Carbohydrate Res. 2011, 346, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Tian, W.; Ma, X. Curcumin induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells via inhibiting fatty acid synthase. Target Oncol. 2014, 9, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, S.J. Fatty acid synthase, a proficient multifunctional enzyme. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 4523–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Liang, Y.; Tian, W.; Ji, M.; Ma, X. Regulating effect of β-ketoacyl synthase domain of fatty acid synthase on fatty acyl chain length in de novo fatty acid synthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, D.J.; Ma, T.; Schneider, A. Fatty acid synthase mediates high glucose-induced EGFR activation in oral dysplastic keratinocytes. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Cao, D.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Y. Fatty acid synthase inhibitor platensimycin intervenes the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a mouse model. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchuluun, B.; Pinkosky, S.L.; Steinberg, G.R. Lipogenesis inhibitors: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, T.M.; Jaworsky, D.E.; Frehywot, G.L.; Townsend, C.A.; Ronnett, G.V.; Lane, M.D.; Kuhajda, F.P. Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors. Science 2000, 288, 2379–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pil, M.W.; Boeger, M.R.T.; Muschner, V.C.; Pie, M.R.; Ostrensky, A.; Boeger, W.A. Postglacial north-south expansion of populations of Rhizophora mangle (Rhizophoraceae) along the Brazilian coast revealed by microsatellite analysis. Amer. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinod Prabhu, V.; Guruvayoorappan, C. Anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activity of the marine mangrove Rhizophora apiculata. J. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 9, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithranga, B.N.; Kandasamy, K.; Subramanian, M.; You-Jin, J. Effect of mangrove tea extract from ceriops decandra (Griff.) Ding Hou. on salivary bacterial flora of DMBA Induced hamster buccal pouch carcinoma. Indian J. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Premanathan, M.; Arakaki, R.; Izumi, H.; Kathiresan, K.; Nakano, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakashima, H. Antiviral properties of a mangrove plant, Rhizophora apiculata Blume, against human immunodeficiency virus. Antiviral Res. 1999, 44, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Xiao, H. Activity-guided isolation of antioxidant compounds from Rhizophora apiculata. Molecules 2012, 17, 10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fhu, C.W.; Ali, A. Fatty acid synthase: An emerging target in cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, J.A.; Lupu, R. Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xi, Q.; Wu, G. Fatty acid synthase regulates invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer via Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, M.; Tutino, V.; Calvani, M.; Lorusso, D.; Guerra, V.; Caruso, M.G. Serum levels of fatty acid synthase in colorectal cancer patients are associated with tumor stage. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2012, 43, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, M.S.; Cha, E.Y.; Sul, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Park, J.B.; Kim, J.Y. Inhibitory effect of emodin on fatty acid synthase, colon cancer proliferation and apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulla, L.S.S.; Begum Ahil, S. Review on target domains and natural compound-based inhibitors of fatty acid synthase for anticancer drug discovery. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarnicola, M.; Pisanti, S.; Tutino, V.; Bocale, D.; Rotelli, M.T.; Gentile, A.; Memeo, V.; Bifulco, M.; Perri, E.; Caruso, M.G. Effects of olive oil polyphenols on fatty acid synthase gene expression and activity in human colorectal cancer cells. Genes Nutr. 2011, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, K.H.; Guo, Q.X.; Tian, W.X. The galloyl moiety of green tea catechins is critical structural feature to inhibit fatty-acid synthase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tian, W.X. Green tea epigallocatechin gallate: A natural inhibitor of fatty-acid synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.; Hung, T.M.; Oh, W.K.; Min, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Bae, K. Fatty acid synthase inhibitory activity of dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans isolated from Schisandra chinensis. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24 (Suppl. S2), S225-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Ma, X.F.; Tian, W.X. Potent inhibition of fatty acid synthase by parasitic loranthus [Taxillus chinensis (dc.) danser] and its constituent avicularin. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.; Xun, H.; He, W.; Lau, H.T.; Ma, X. Apoptotic effect of tannic acid on fatty acid synthase over-expressed human breast cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wu, D.; Tian, W.; Ma, X. Inhibitory effects of tannic acid on fatty acid synthase and 3T3-L1 preadipocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013, 1831, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, W.; Ma, X. Alpha-mangostin inhibits intracellular fatty acid synthase and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tian, W.; Ma, X. Inhibitory effects of grape skin extract and resveratrol on fatty acid synthase. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.S.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, T.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, C.S. Inhibitory effect of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on lipid accumulation of 3T3-L1 cells. Obesity 2007, 15, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Tai, M.H.; Huang, W.Y.; al-Feel, W.; Hsu, M.; Abu-Elheiga, L.; Chirala, S.S.; Wakil, S.J. Human fatty acid synthase: Properties and molecular cloning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8695–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Cheng, Q.; Tian, W.X.; Wu, X.D. A substitutive substrate for measurements of beta-ketoacyl reductases in two fatty acid synthase systems. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2008, 70, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
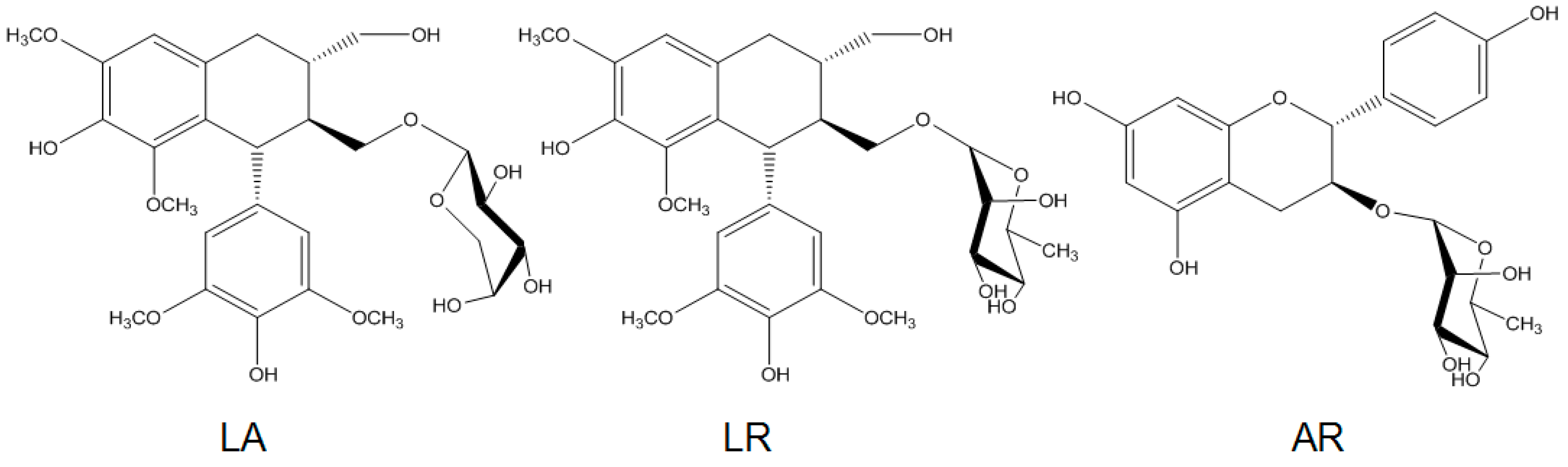
| Fractions/Compounds | FAS Inhibitory Activity IC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| EtOAc | >200 b |
| n-butanol | 93.0 ± 3.3 |
| Water | N/I c |
| LA | >200 |
| LR | 20.1 ± 1.6 |
| AR | >200 |
| EGCG d | 24.8 ± 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Ban, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. Inhibitory Effects of the Polyphenols from the Root of Rhizophora apiculata Blume on Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Human Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2024, 29, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051180
Liang Y, Ban Y, Liu L, Li Y. Inhibitory Effects of the Polyphenols from the Root of Rhizophora apiculata Blume on Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Human Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yan, Yue Ban, Lei Liu, and Yanchun Li. 2024. "Inhibitory Effects of the Polyphenols from the Root of Rhizophora apiculata Blume on Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Human Colon Cancer Cells" Molecules 29, no. 5: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051180
APA StyleLiang, Y., Ban, Y., Liu, L., & Li, Y. (2024). Inhibitory Effects of the Polyphenols from the Root of Rhizophora apiculata Blume on Fatty Acid Synthase Activity and Human Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules, 29(5), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051180







