Water Leaching Kinetics of Boron from the Alkali-Activated Ludwigite Ore
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Water Leaching Parameters on Boron Leaching
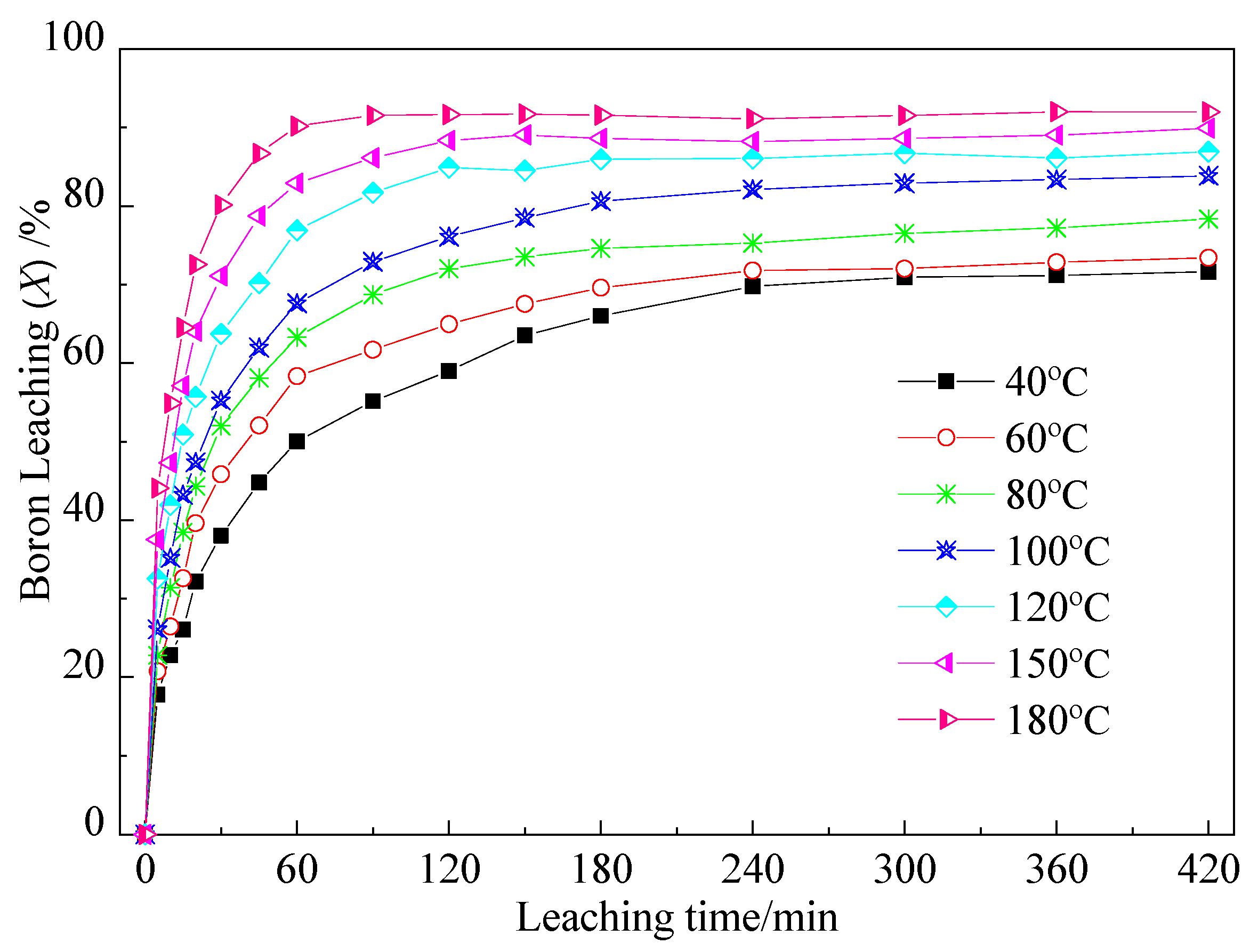
2.1.1. Effect of Leaching Temperature on Boron Leaching
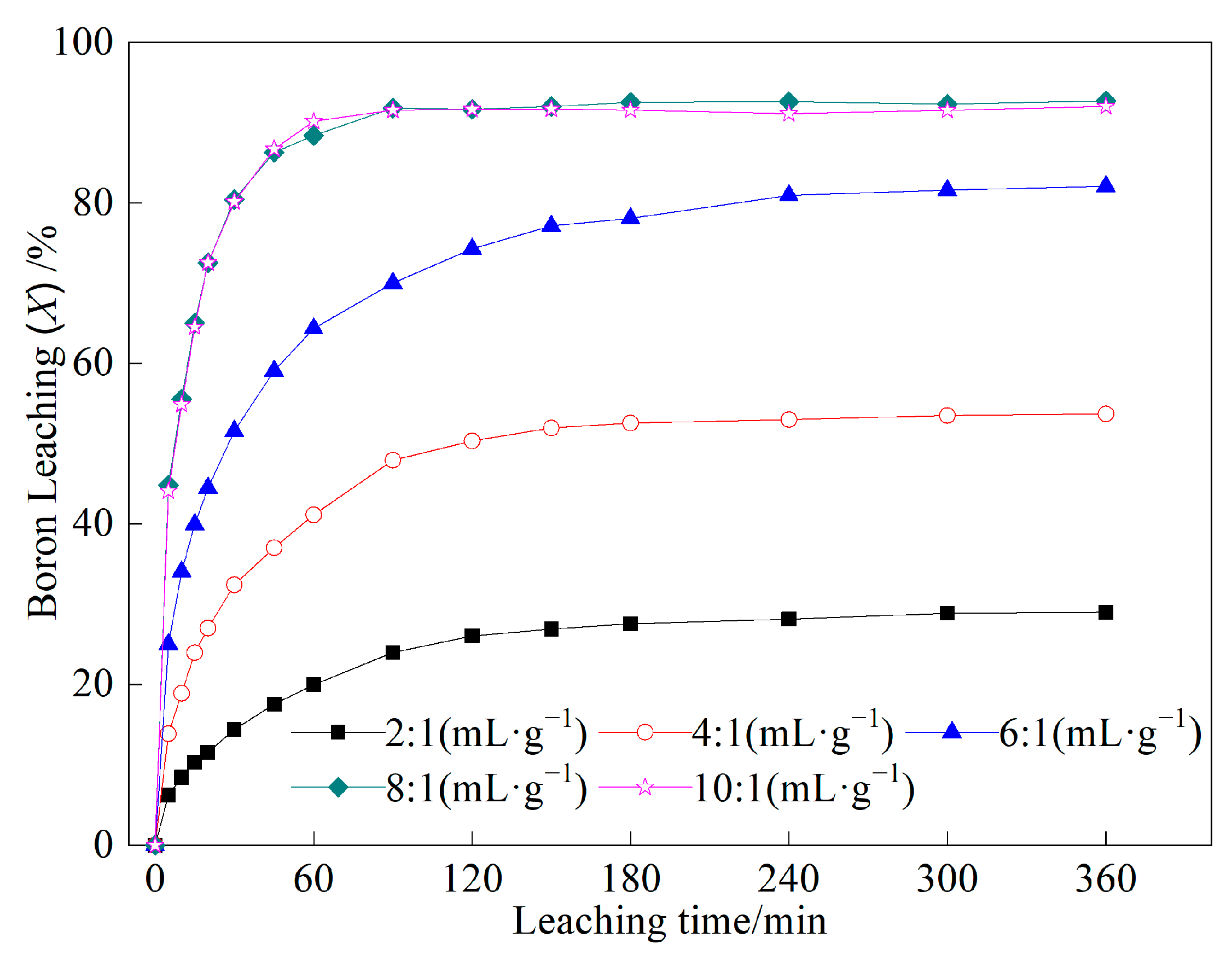
2.1.2. Effect of Liquid-to-Solid Ratio on Boron Leaching
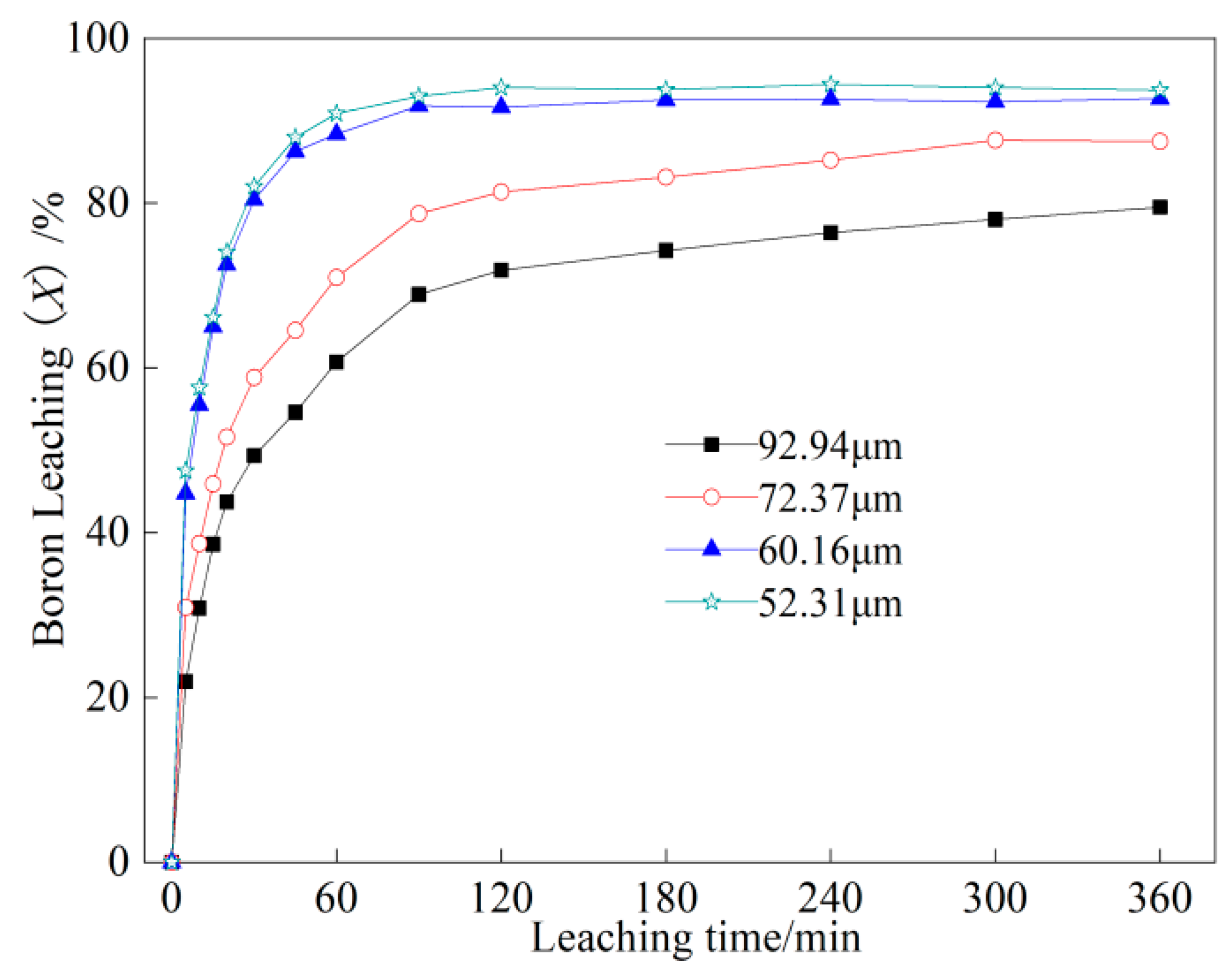
2.1.3. Effect of Feed Particle Size on Boron Leaching
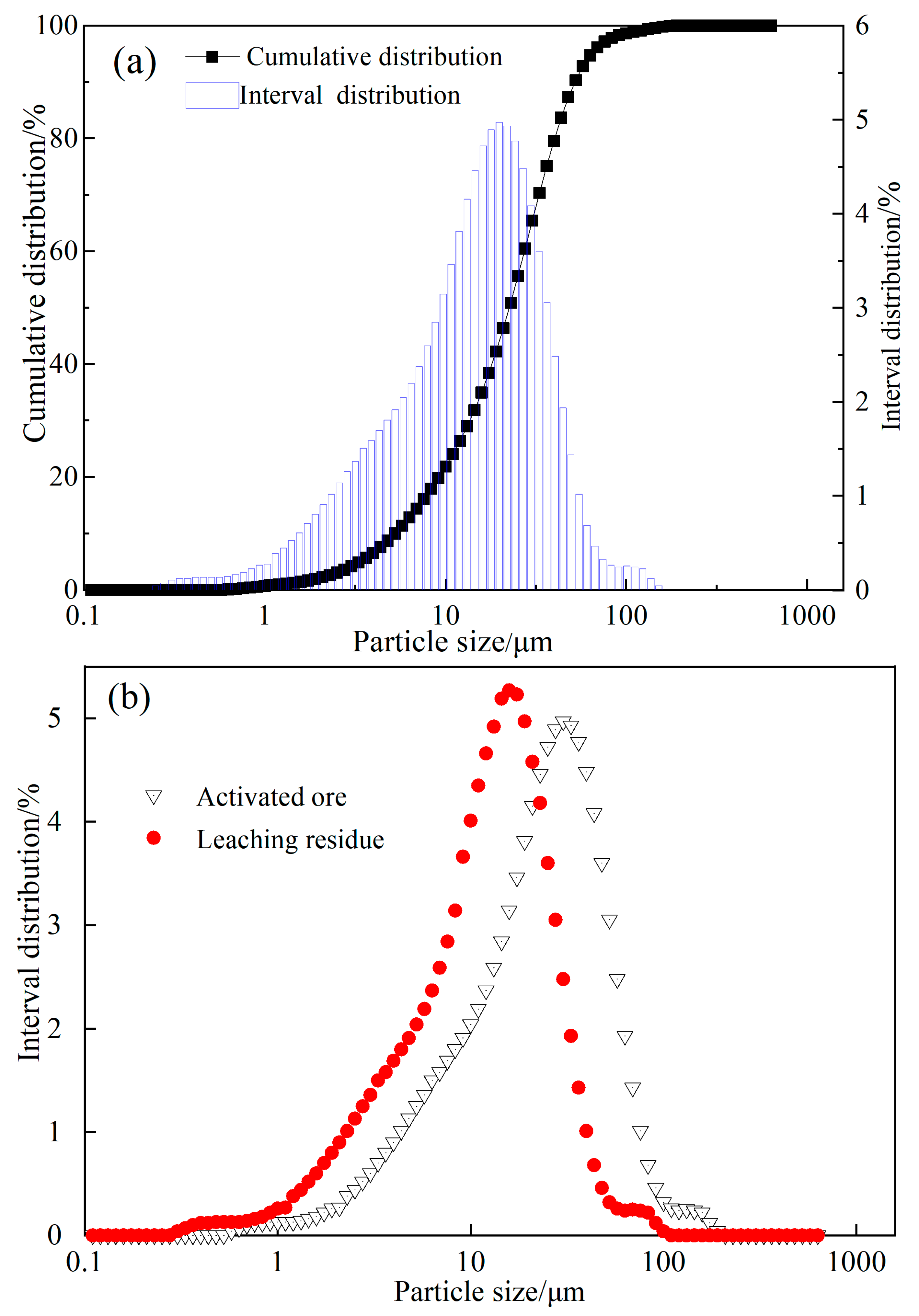
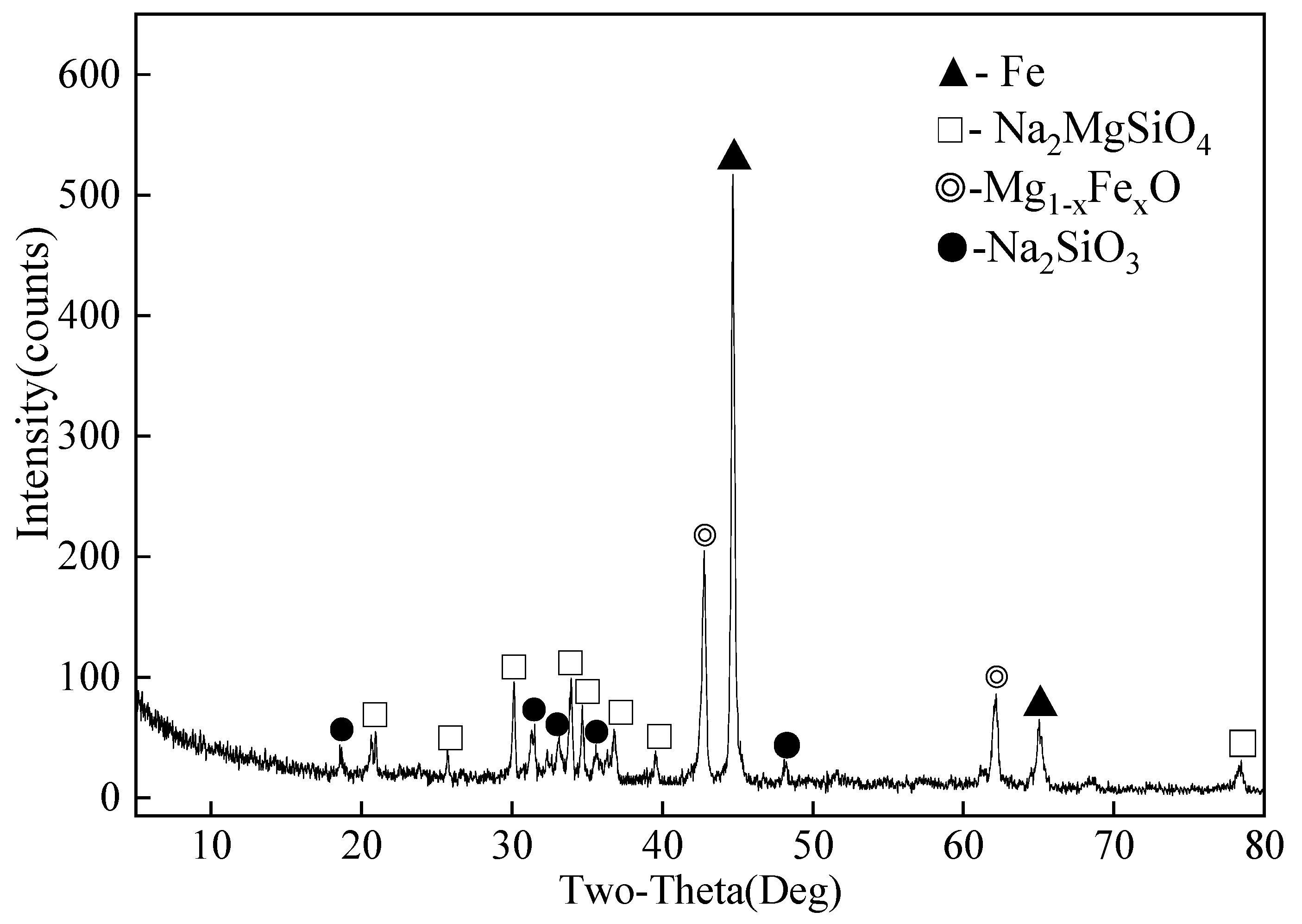
2.2. Characterization of Leach Residues
2.3. Kinetics of Boron Water Leaching
2.3.1. Kinetic Model Selection
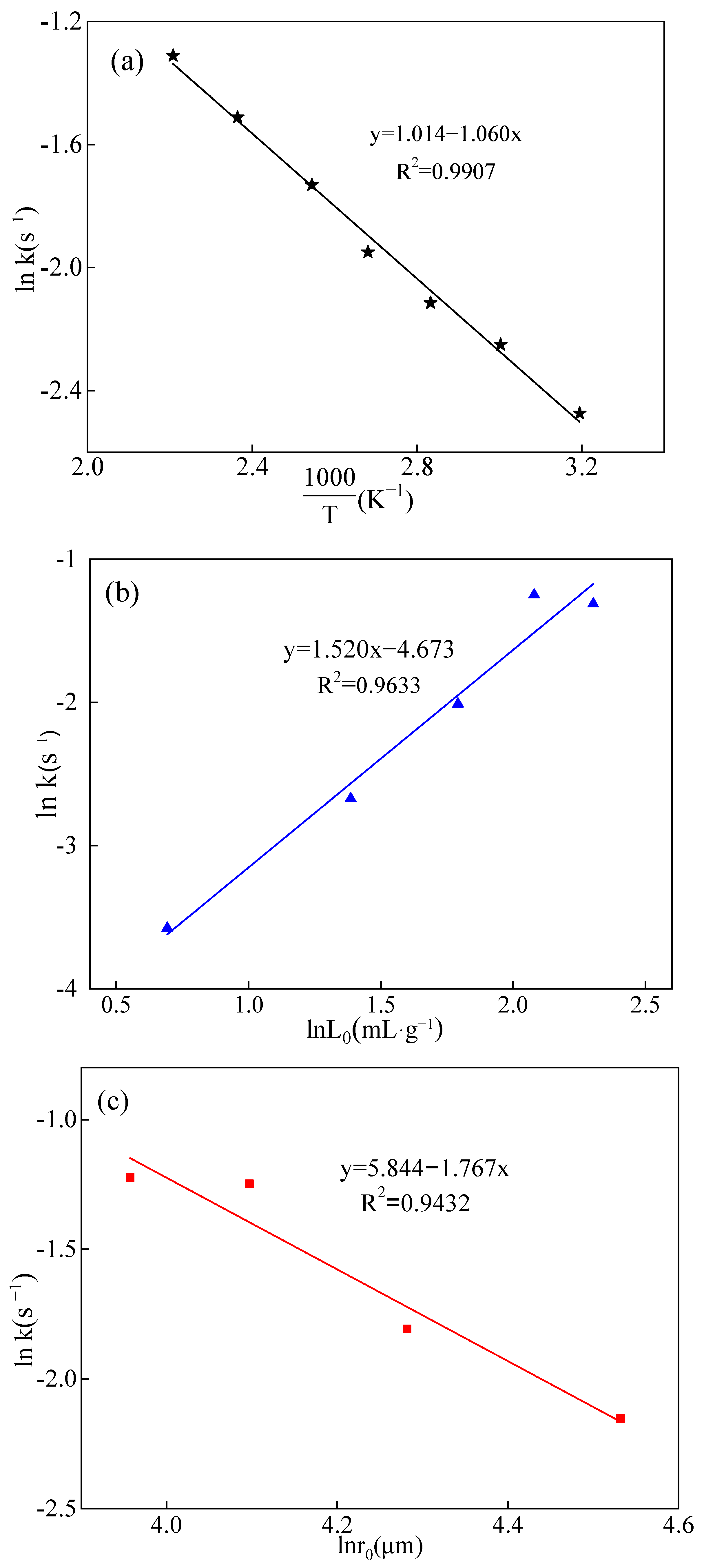
2.3.2. Discussion and Analysis of Kinetics
2.3.3. Derivation of the Kinetic Equation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Alkali-Activated Ludwigite Ore Process
3.2.2. Water Leaching Process of Boron
3.2.3. Analysis of Ore Particle Morphology
3.2.4. Particle Size Analysis of Ore
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The extraction of boron from the ludwigite ore demonstrated remarkable efficiency under specific conditions. Specifically, the ludwigite ore underwent the reduction process at 1050 °C for 60 min in the presence of 20% sodium carbonate. Subsequently, the impressive boron extraction rate of 93.71% was achieved through water leaching at 180 °C for 6 h, with a liquid-to-solid ratio of 8:1 and an average feed particle size of 52.31 μm. These specific parameters illustrated a successful method for optimizing boron extraction from the ludwigite ore.
- (2)
- Optimizing boron leaching efficiency requires careful control of key parameters including temperature, leaching time, liquid-to-solid ratio, and ore particle size. Higher temperatures accelerate reactions and dissolution; prolonged times allow complete mineral dissolution; higher liquid-to-solid ratios increase solution–particle contact; and smaller particle sizes increase surface area and solution interaction. Precisely optimizing these parameters is essential for effective and sustainable boron extraction.
- (3)
- The study utilized the Avrami Equation to characterize the water leaching kinetics of boron and established the kinetics equation by fitting the experimental data; the equation could be expressed as: .
- (4)
- This study applied the Arrhenius Equation to ascertain the activation energy (Ea) of 8.812 kJ·mol−1 for the water leaching of boron. The finding suggested that the boron leaching process occurred within the diffusion control range, affirming the nature of the leaching process as the solvation reaction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helvaci, C. Borate Deposits: An Overview and Future Forecast with Regard to Mineral Deposits. J. Boron 2017, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Elevli, B.; Yaman, İ.; Laratte, B. Estimation of the Turkish Boron Exportation to Europe. Mining 2022, 2, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiya, S.; Pandey, M.; Bhattacharya, S. Nanoparticles Containing Boron and Its Compounds—Synthesis and Applications: A Review. J. Micromanufacturing 2020, 3, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berionni, G. Future Prospects in Boron Chemistry: New Boron Compounds and Lewis Acids for Catalysis and Materials Science. Chem. Synth. 2021, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. International Trade Evolution and Competition Prediction of Boron Ore: Based on Complex Network and Link Prediction. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpekçi, D.; Kabay, N.; Bunani, S.; Altıok, E.; Arda, M.; Yoshizuka, K.; Nishihama, S. Application of Heterogeneous Ion Exchange Membranes for Simultaneous Separation and Recovery of Lithium and Boron from Aqueous Solution with Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis (EDBM). Desalination 2020, 479, 114313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2022; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- China Mineral Resources; Ministry of Natural Resources: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Najid, N.; Kouzbour, S.; Ruiz-García, A.; Fellaou, S.; Gourich, B.; Stiriba, Y. Comparison Analysis of Different Technologies for the Removal of Boron from Seawater: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-C.; Kim, N.-I.; Jiang, T.; Kim, J.-C.; Kang, C.I. Boron Recovery from Salt Lake Brine, Seawater, and Wastewater—A Review. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 218, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Chao, Q.; Jiang, M. Efficient Acid Leaching of High-Magnesium Boron Tailings and the Low Cost Recovery of Siliceous Residues with Good Adsorption Capacity. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 209, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J. Production and Application of Boron Compounds; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.J. Processing of ferroludwigite; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Du, Y.; Guo, Z. Competitive Crystallization of B, Si, and Mg and Two-Stage Separation of Olivine and Suanite from Boron-Bearing Slag in Supergravity Field. Miner. Eng. 2020, 155, 106471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Qu, J.K.; Wei, G.Y.; Qi, T. Influence of Na2CO3 as Additiveon Direct Reduction of Boron-bearing Magnetite Concentrate. J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 23, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Xue, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Sayyed, M.I.; Agar, O. Using Iron Concentrate in Liaoning Province, China, to Prepare Material for X-ray Shielding. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Gao, H.; Chen, W.; Xue, X. The Changes of Surface Properties and Enhancement of B2O3 Leaching Ratio of Boron Concentrate via Wet Ball Milling. Powder Technol. 2018, 326, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Hu, D. Comprehensive Utilization Research Progress and Development Prospect of Ludwigite Ore. Liaoning Chem. Ind. 1995, 45, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q. Research on New Process of Comprehensive Utilization of Lwdwigite Ore. China Resour. Compr. Util. 2002, 49, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, F.; Yu, T.; Zhong, J.; Wang, H. Study on Process of Ludwigite ore with CO2-Soda Method. Ind. Miner. Process. 2011, 40, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.L.; Cui, C.M.; Zhang, X.P. Pyrometallurgical Separation of Boron from lron in Ludwigite Ore. ISIJ Int. 1998, 38, 1077–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Wang, J.S.; Ding, Y.G.; Ma, S.; Xue, Q.G. New Separation Method of Boron and Iron from Ludwigite Based on Carbon Bearing Pellet Reduction and Melting Technology. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-W.; Han, Y.-X.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.-J. Recovery of Boron from High-Boron Iron Concentrate Using Reduction Roasting and Magnetic Separation. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2017, 24, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wu, J.; Xue, X.; Duan, P.; Chu, M. Carbothermal Formation and Microstrutural Evolution of α′-Sialon–AlN–BN Powders from Boron-Rich Blast Furnace Slag. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.S.; Zhao, J.Q.; Fu, X.J.; Liu, Z.G. New Efficient Process Utilizing Ludwigite on Gas-based Shaft Furnace Direct Reduction and Electric Furnace Smelting Separation. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2016, 37, 805–809. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Xue, Q.; She, X.; Wang, J. Carbothermal Reduction of Boron-bearing Iron Concentrate and Melting Separation of the Reduced Pellet. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.R.; Liu, S.R.; Fan, Z.G. On the Relation between Cooling Rate and Activity of Boron-Rich Slag. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2007, 28, 1604–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Lan, X.; Guo, Z. Direct Preparation of Magnesium Borate (Mg2B2O5) Ceramic from Boron-Bearing Slag: Super-Gravity Separation and Microwave Dielectric Properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Lan, X.; Guo, Z. A Novel Method for Efficient Recovery of Boron from Boron-Bearing Iron Concentrate: Mineral Phase Transformation and Low-Temperature Separation via Super-Gravity. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liang, B.; Rao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. An Innovative Process for Extracting Boron and Simultaneous Recovering Metallic Iron from Ludwigite Ore. Miner. Eng. 2014, 56, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rao, M.; Jiang, T.; Liang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Luo, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. A Method to Simultaneous Recovery of Boron and Iron in Ludwigite Ore. Patent CN102899434A, 7 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Li, G.; Rao, M.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. Water Leaching of Boron from Soda-Ash-Activated Ludwigite Ore. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B. Fundamentals and Novel Process for Synchro-Separation and Extraction of Boron and Iron from Ludwigite Ore; Central South University: Changsha, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Mi, H.; Liang, B. Recovery of Powdered Metallic Iron from Ludwigite Ore via Reductive Roasting with Sodium Salts—Magnetic Separation. In 7th International Symposium on High—Temperature Metallurgical Processing; TMS: Nashville, TN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, G.; You, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Duan, J.; Zhang, T.; Peng, Z.; Rao, M.; Jiang, T. Extraction of Boron from Ludwigite Ore: Mechanism of Soda-Ash Roasting of Lizardite and Szaibelyite. Minerals 2019, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.-X.; Wang, J.; Rao, M.-J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Peng, Z.; Li, G. An Integrated and Efficient Process for Borax Preparation and Magnetite Recovery from Soda-Ash Roasted Ludwigite Ore under CO–CO2–N2 Atmosphere. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, J.L.; Edwards, M. Boron in the Environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 35, 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, T.C.; Peixoto, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.S.; Leao, V.A. Kinetics of Chalcopyrite Leaching in Either Ferric Sulphate or Cupric Sulphate Media in the Presence of NaCl. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 148, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhou, F.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chi, R. Kinetics of Column Leaching of Rare Earth and Aluminum from Weathered Crust Elution-Deposited Rare Earth Ore with Ammonium Salt Solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkıran, N.; Künkül, A. Dissolution Kinetics of Ulexite in Perchloric Acid Solutions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 83, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, H.; Tekin, T.; Ozer, A.K.; Bayramoglu, M. Effect of Ultrasound on the Dissolution of Colemanite in H2SO4. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 67, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, S.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, N.; Hong, S. Research on NaCaHSiO4 Decomposition in Sodium Hydroxide Solution. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahruman, C.; Yusufoglu, I. Leaching Kinetics of Synthetic CaWO4 in HCl Solutions Containing H3PO4 as Chelating Agent. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 81, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, Z.W.; Xue, F.Y.; Hong, X.Y. Characterization of the Kinetic Phase Transition of Phospholipids Using Avrami and Tobin Models. Chin. J. Chem. 2001, 19, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Kinetics of Vanadium Leaching from a Spent Industrial V2O5/TiO2 Catalyst by Sulfuric Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokić, M.D.; Marković, B.; Živković, D. Kinetics of Chalcopyrite Leaching by Sodium Nitrate in Sulphuric Acid. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Chen, K.K. Selective Leaching Se from Selenium Residue by Na2SO3 Solutions and Leaching Kinetics. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2012, 22, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Peleg, M.; Normand, M.D.; Corradini, M.G. The Arrhenius Equation Revisited. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 830–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


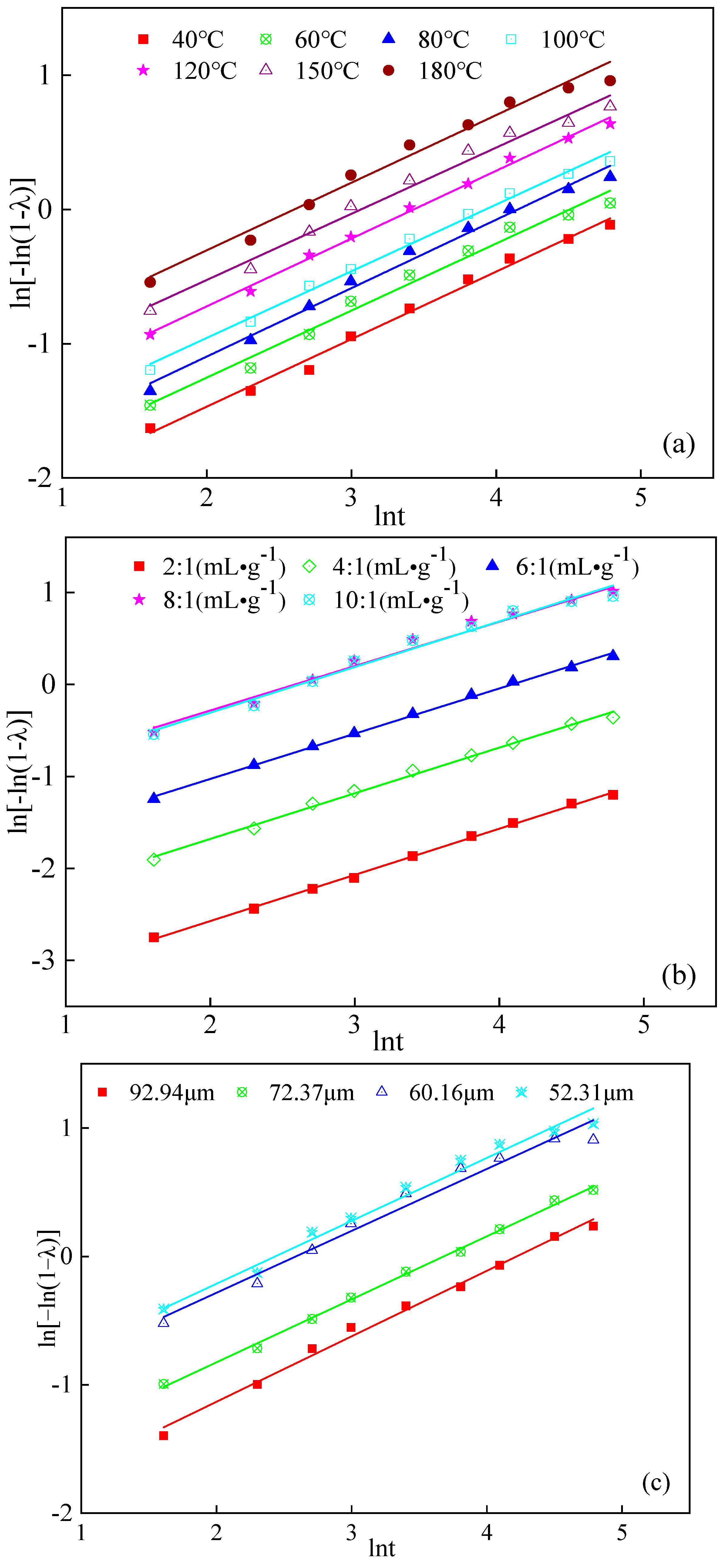
| Leaching Conditions | Correlation Coefficient/R2 | n | lnk | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 40 | 0.9923 | 0.5027 | −2.4738 |
| 60 | 0.9849 | 0.4993 | −2.2507 | |
| 80 | 0.9902 | 0.5096 | −2.1147 | |
| 100 | 0.9938 | 0.4966 | −1.9498 | |
| 120 | 0.9964 | 0.5049 | −1.7313 | |
| 150 | 0.9854 | 0.4929 | −1.5112 | |
| 180 | 0.9789 | 0.5034 | −1.3110 | |
| Liquid-to-solid ratio (mL·g−1) | 2:1 | 0.9983 | 0.5019 | −3.5755 |
| 4:1 | 0.9946 | 0.4962 | −2.6715 | |
| 6:1 | 0.9978 | 0.4917 | −2.0104 | |
| 8:1 | 0.9701 | 0.4825 | −1.2481 | |
| 10:1 | 0.9789 | 0.5034 | −1.3110 | |
| Particle size (μm) | 92.94 | 0.9916 | 0.5103 | −2.1528 |
| 72.37 | 0.9972 | 0.4911 | −1.8071 | |
| 60.16 | 0.9701 | 0.4825 | −1.2481 | |
| 52.31 | 0.9792 | 0.4959 | −1.2240 | |
| TFe * | FeO | B2O3 | Na2O | SiO2 | MgO | Al2O3 | CaO | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58.23 | 5.25 | 5.12 | 7.22 | 6.18 | 14.05 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.014 | 1.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, B.; Hu, H.; Xiao, B.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, W.; Huang, Z. Water Leaching Kinetics of Boron from the Alkali-Activated Ludwigite Ore. Molecules 2024, 29, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040826
Liang B, Hu H, Xiao B, Lu Z, Yuan W, Huang Z. Water Leaching Kinetics of Boron from the Alkali-Activated Ludwigite Ore. Molecules. 2024; 29(4):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040826
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Binjun, Haixiang Hu, Bin Xiao, Zhigang Lu, Weiquan Yuan, and Zheyu Huang. 2024. "Water Leaching Kinetics of Boron from the Alkali-Activated Ludwigite Ore" Molecules 29, no. 4: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040826
APA StyleLiang, B., Hu, H., Xiao, B., Lu, Z., Yuan, W., & Huang, Z. (2024). Water Leaching Kinetics of Boron from the Alkali-Activated Ludwigite Ore. Molecules, 29(4), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29040826







