The Degradation of Aqueous Oxytetracycline by an O3/CaO2 System in the Presence of
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
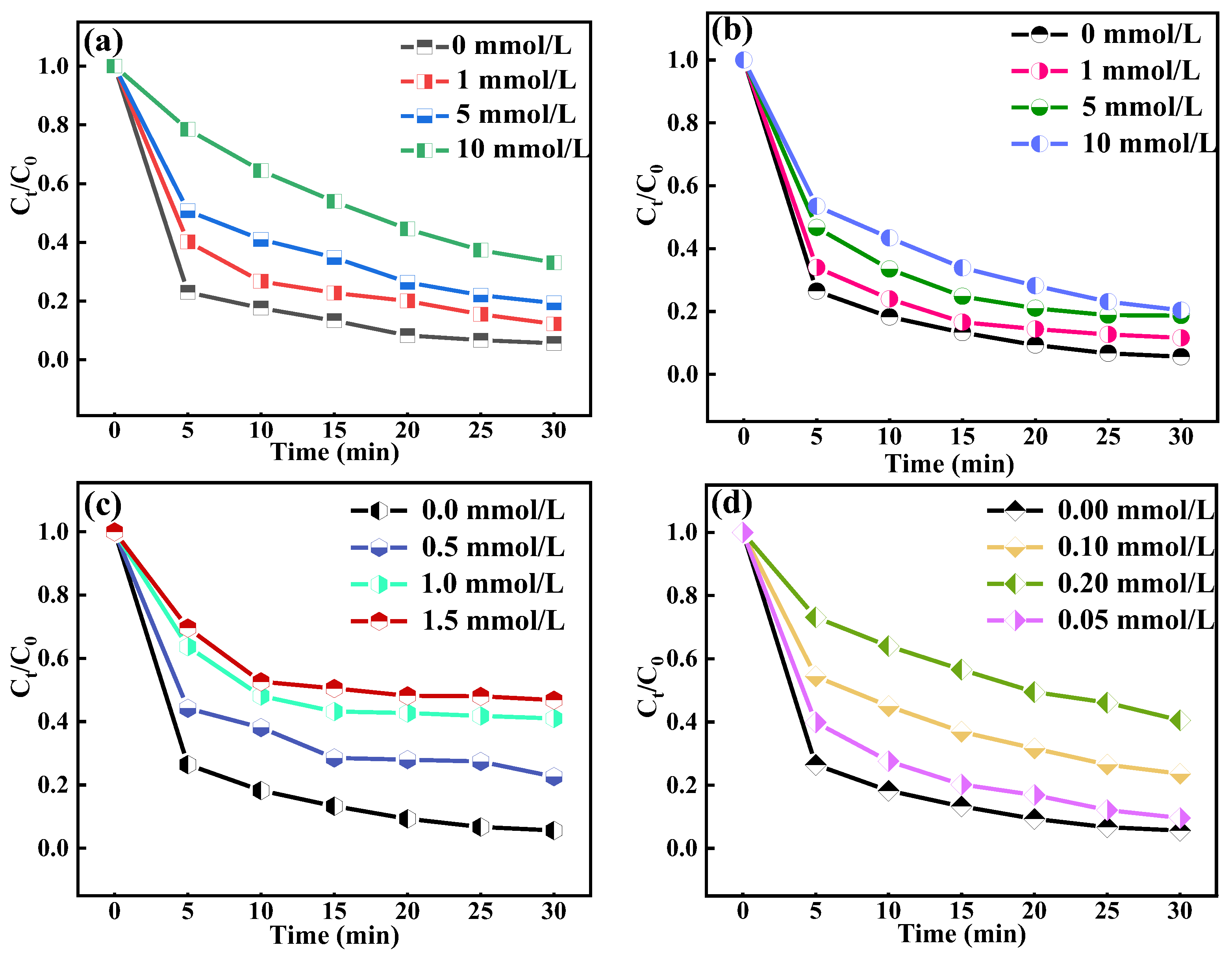
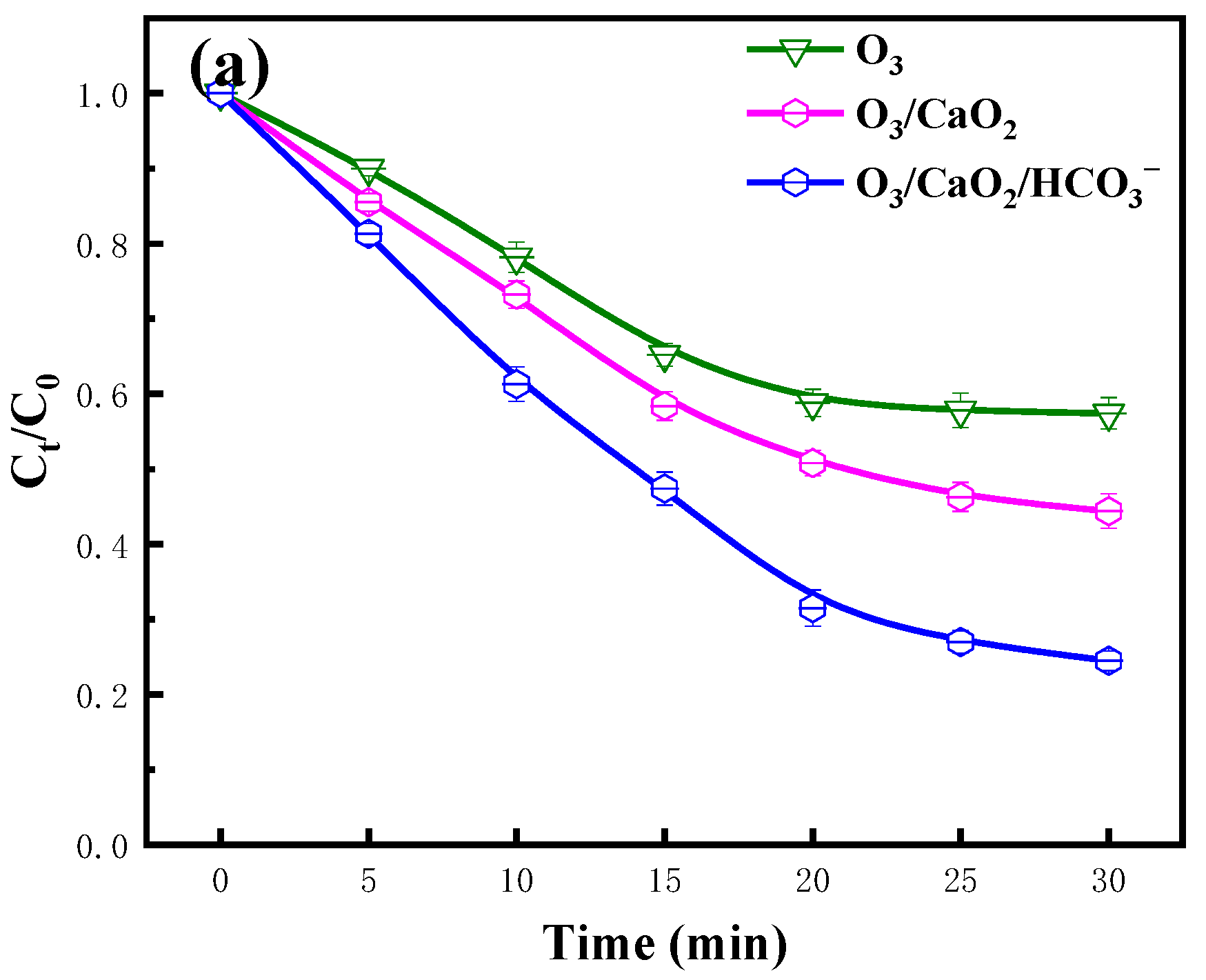
2.1. Effect of CaO2
2.2. Effect of Dosage
2.3. Effect of O3 Dosage
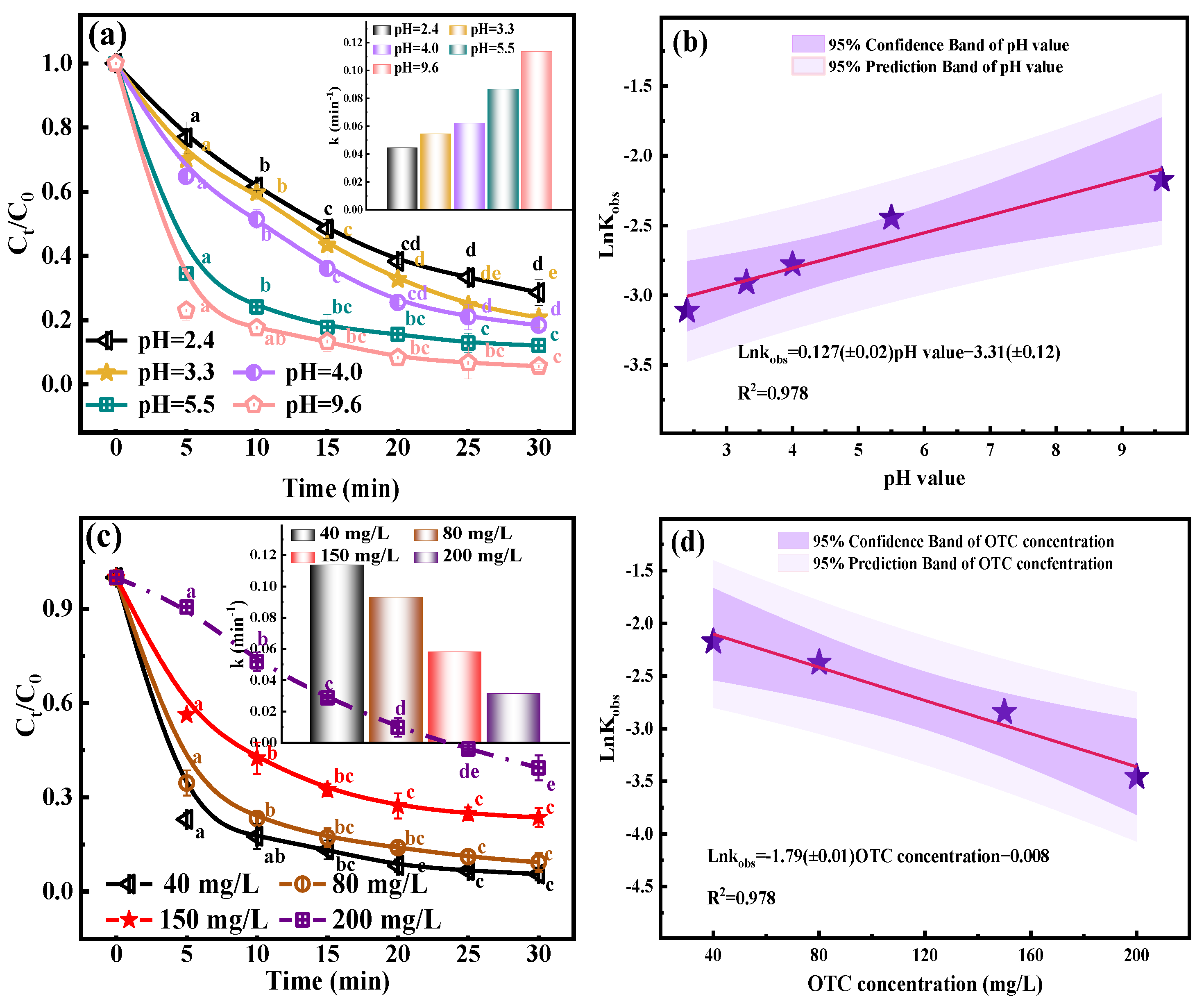
2.4. Effect pH Value
2.5. Effect OTC Concentration
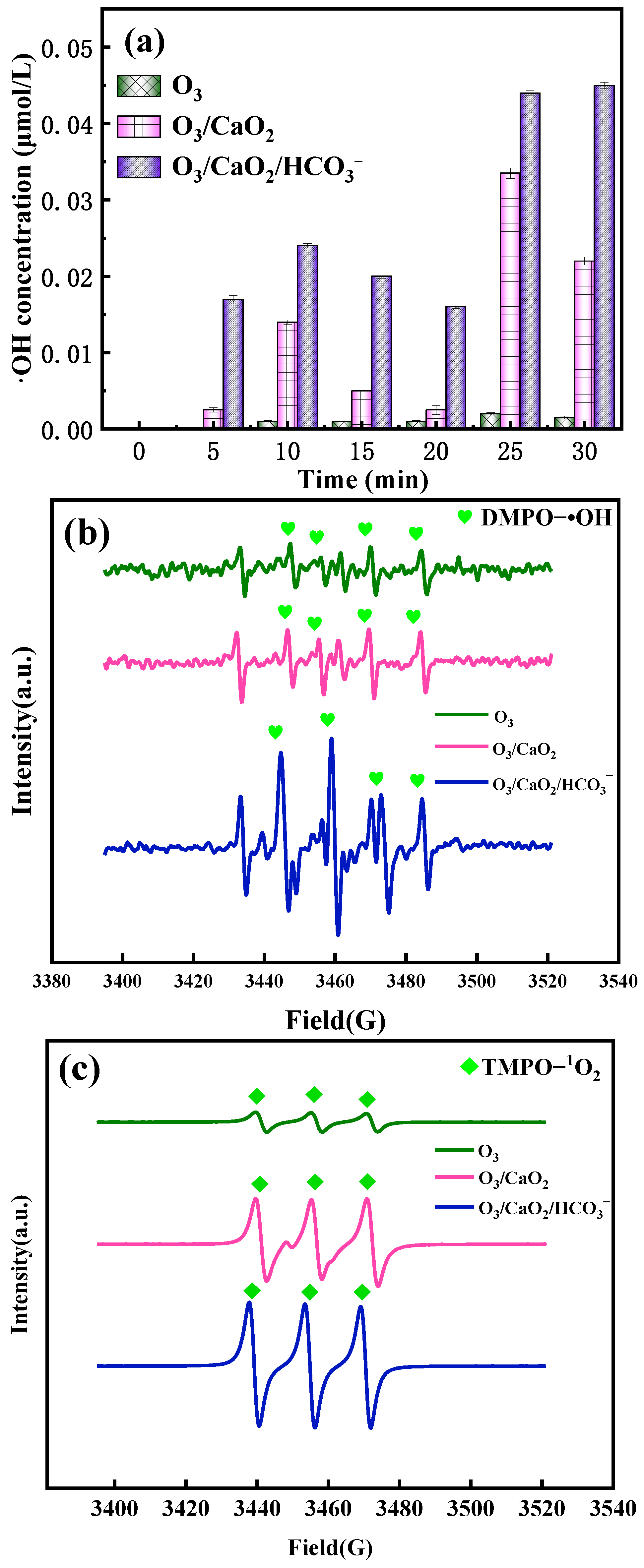
2.6. Active Substance Analysis
2.6.1. Role of ·OH, 1O2, , and
2.6.2. Formation of Active Species
2.7. OTC Degradation Process
2.7.1. UV-Vis Spectra
2.7.2. 3D EEMFS
2.7.3. Variation of TOC and COD
2.7.4. Variation of pH and Conductivity
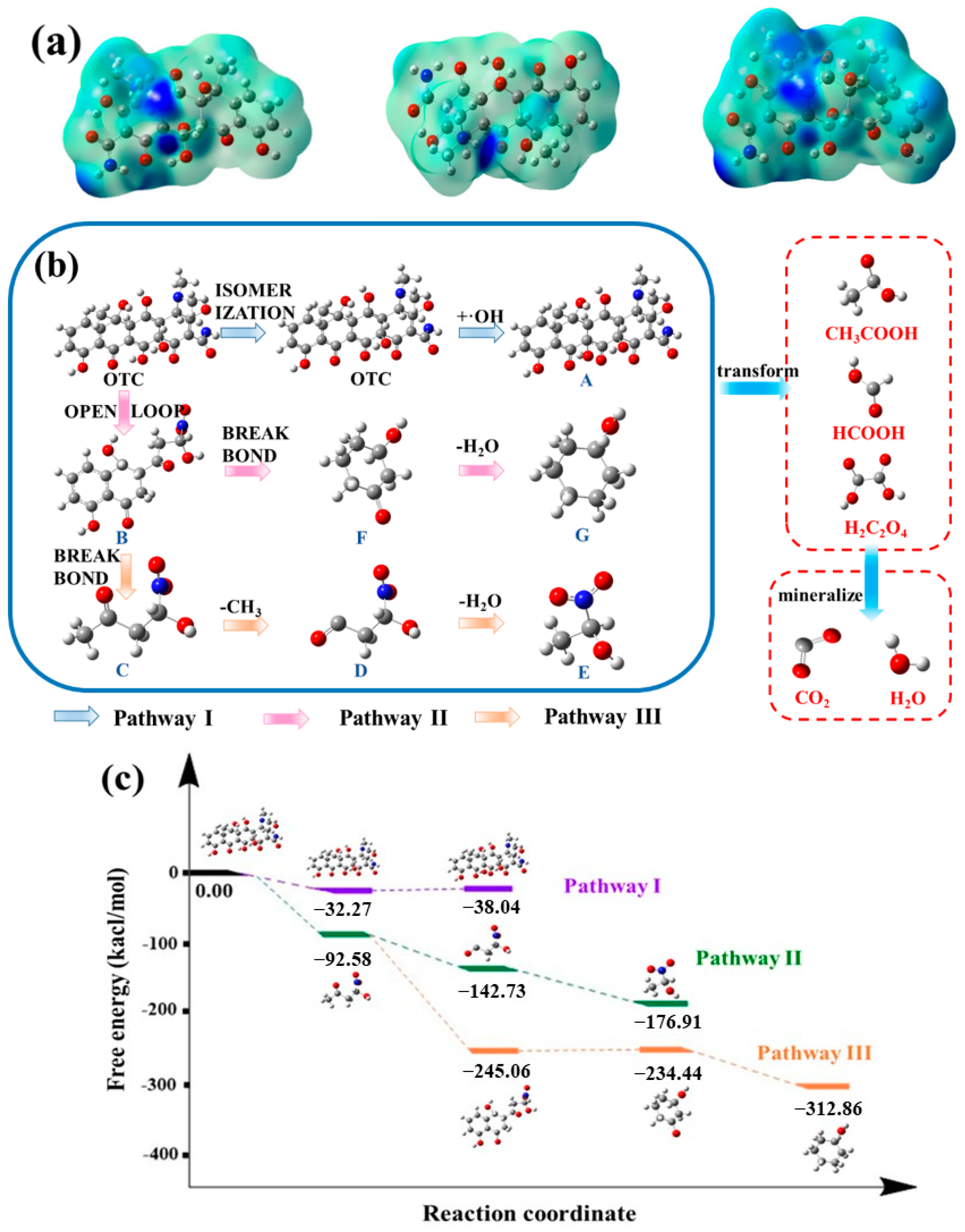
2.8. DFT Analysis and Degradation Pathway
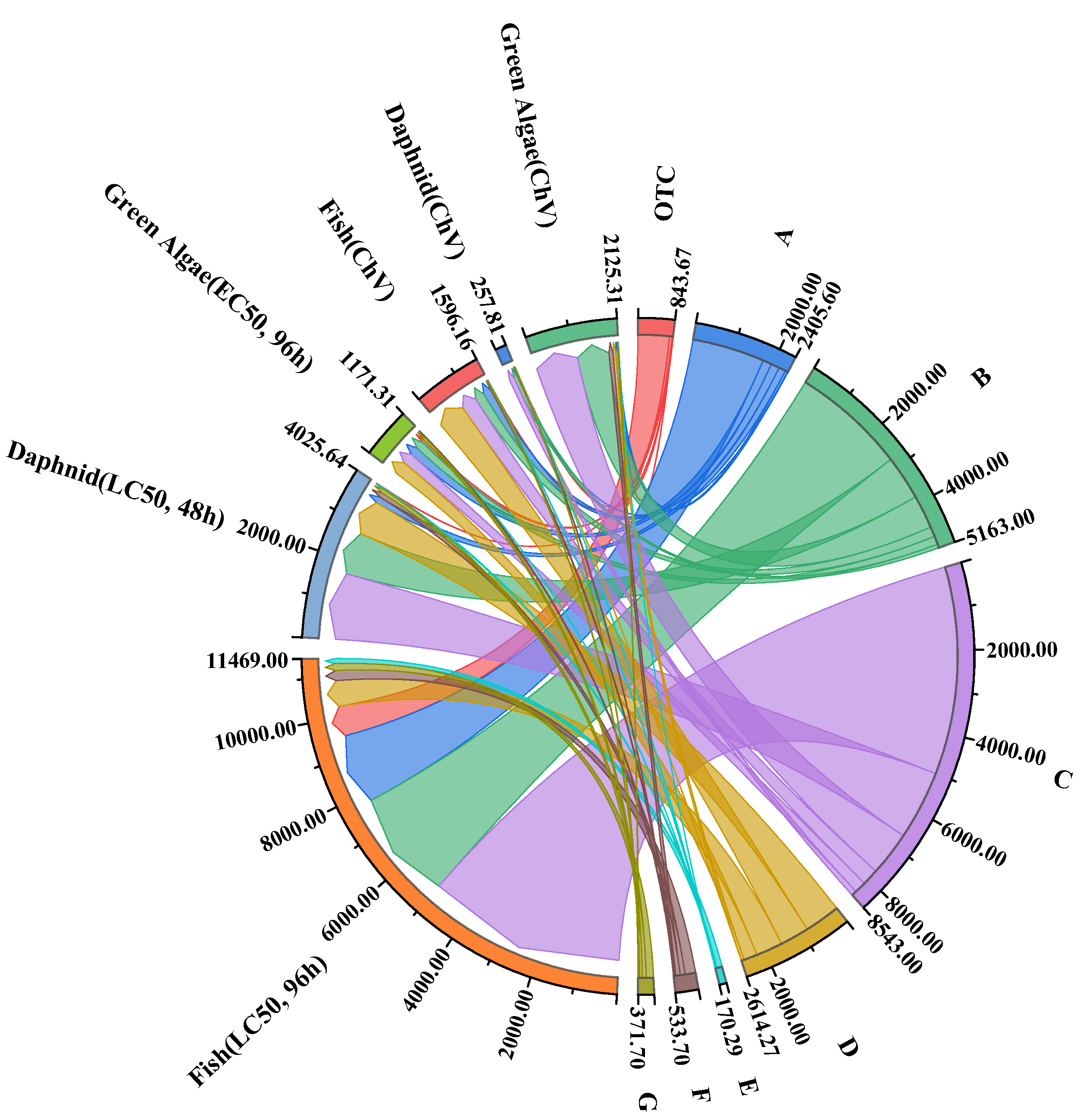
2.9. Toxicity Evaluation
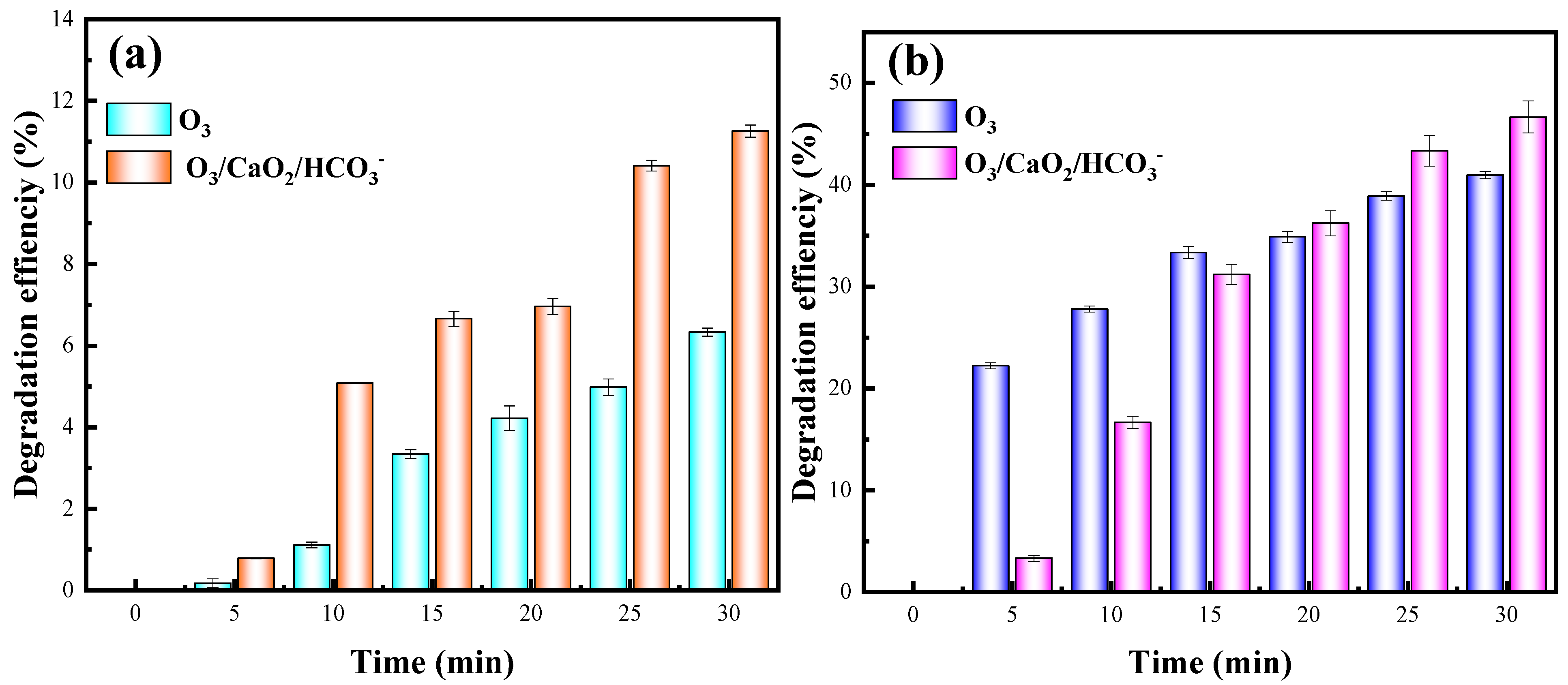
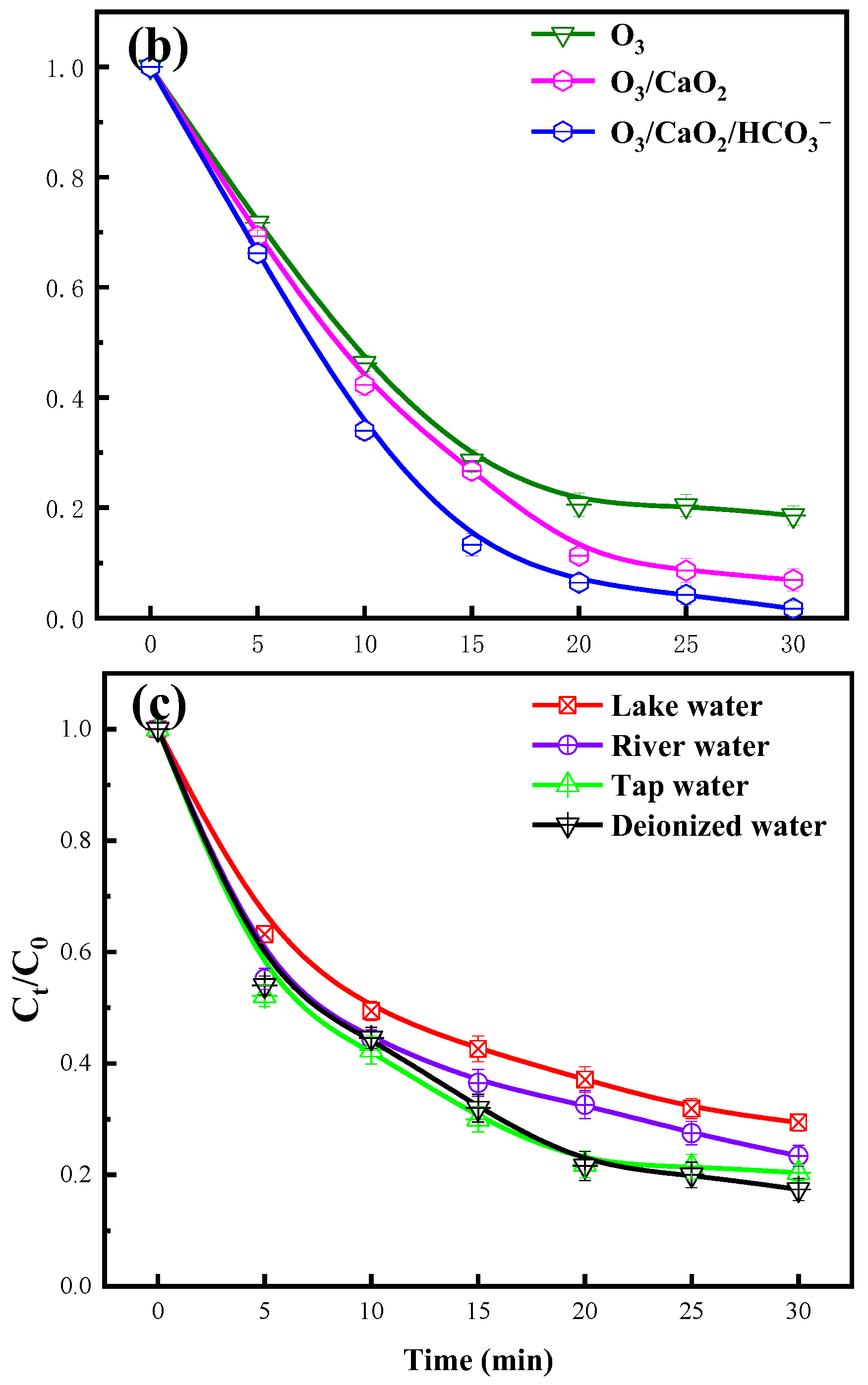
2.10. Feasible for Treatment of Other Antibiotics and Actual Wastewater
2.11. Energy Efficiency Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Experimental Process
3.3. Analysis
3.4. DFT Analysis and Toxicity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, N.; Teng, C.; Frei, C. Brief Overview of approaches and challenges in new antibiotic development: A focus on drug repurposing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 17, 684515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, K.; Kumar, M.; Balan, B.; Dhaulaniya, A.; Shree, P.; Sharma, N.; Singh, D. Perspectives on the antibiotic contamination, resistance, metabolomics, and systemic remediation. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Han, J.; Xu, L.; Qiao, W.; Li, J.; et al. A comprehensive insight into plasma-catalytic removal of antibiotic oxytetracycline based on graphene-TiO2-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Fan, S.; Zhao, Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. The impacts of oxytetracycline on humification during manure composting can be alleviated by adjusting initial moisture contents as illustrated by NMR. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, W.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Du, L.; Xing, W. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Long, J.; Feng, C.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, D.; Liu, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, Z. Fe3+ enhanced degradation of oxytetracycline in water by pseudomonas. Water Res. 2019, 160, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Lehmler, H.; Cai, X.; Chen, J. Antibiotic pollution in marine food webs in laizhou bay, north china: Trophodynamics and human exposure implication. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, G.; Soledad, G.; Ismael, R.; Francisco, L.; Roberto, R.; Karina, B.; Eduardo, M.; Francisca, F. Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: Implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; He, X.; Duan, X.; Fu, Y.; Dionysiou, D. Photochemical degradation of oxytetracycline: Influence of pH and role of carbonate radical. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, P.; Hassani, A.; Wacławek, S.; Lin, K.A.; Sayyar, Z.; Ghanari, F. Recent advances in design and engineering of MXene-based catalysts for photocatalysis and persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes: A state-of-the-art review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Ghosh, P.; Vaidya, A.; Mudliar, S. Hybrid ozonation process for industrial wastewater treatment: Principles and applications: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Aurelio, H. Reducing the formation of trihalomethanes (THMs) by ozone combined with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2/O3). Desalination 2006, 194, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Abramova, A.; Nikonov, R.; Cravotto, G. Sonozonation (sonication/ozonation) for the degradation of organic contaminants-A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 68, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecha, A.C.; Chollom, M.N. Photocatalytic ozonation of wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1491–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu, M.; Mika, S. Removal of natural organic matter from drinking water by advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 351–365. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Rajic, L.; Chen, L.; Lyu, S.; Alshawabkeh, A. Electrolytic control of hydrogen peroxide release from calcium peroxide in aqueous solution. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 93, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelalak, R.; Hassani, A.; Heidari, Z.; Zhou, M. State-of-the-art recent applications of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) material in Fenton-based oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Huang, Q.S.; Wei, W.; Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.J. Improving the treatment of waste activated sludge using calcium peroxide. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Q. Ferric ion-ascorbic acid complex catalyzed calcium peroxide for organic wastewater treatment: Optimized by response surface method. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Performance of calcium peroxide for removal of endocrine-disrupting compounds in waste activated sludge and promotion of sludge solubilization. Water Res. 2015, 71, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xue, G.; Miruka, A.C.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Motivation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species by a novel non-thermal plasma coupled with calcium peroxide system for synergistic removal of sulfamethoxazole in waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ji, H. Synergistic catalytic oxidation of cinnamaldehydes by poly (vinyl alcohol) functionalized β-cyclodextrin polymer in CaO2/ system. Supramol. Chem. 2018, 30, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gong, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Mu, Y. Carbonate-activated hydrogen peroxide oxidation process for azo dye decolorization: Process, kinetics, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garoma, T.; Umamaheshwar, S.; Mumper, A. Removal of sulfadiazine, sulfamethizole, sulfamethoxazole, and sulfathiazole from aqueous solution by ozonation. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Zeng, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, J.; Fu, R.; Lyu, S. Comparison of naphthalene removal performance using H2O2, sodium percarbonate and calcium peroxide oxidants activated by ferrous ions and degradation mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Yan, X.; Guo, H.; Mao, D.; Yi, C. Dielectric barrier discharge plasma coupled with WO3 for bisphenol A degradation. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, P.; Zhang, G. Enhanced degradation of PFOA in water by dielectric barrier discharge plasma in a coaxial cylindrical structure with the assistance of peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. Monitoring graphene oxide’s efficiency for removing Re(VII) and Cr(VI) with fluorescent silica hydrogels. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 11426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; He, Z.; Ying, H.; Chen, J. Mineralization of CI Reactive Yellow 145 in Aqueous Solution by UItraviolet-Enhanced Ozonation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X. Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by nanoscale calcium peroxide: Implication for groundwater remediation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunten, U. Ozonation of drinking water: Part II Disinfection and by-product formation in presence of bromide, iodide or chlorine. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Abdul, G.L.; Salman, A. Water purification by electrical discharges, Plasma sources. Sci. Technol. 2001, 10, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Merényi, G.; Lind, J.; Naumov, S.; Sonntag, C. Reaction of ozone with hydrogen peroxide (peroxone process): A revision of current mechanistic concepts based on thermokinetic and quantum-chemical considerations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3505–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, G.; Sun, Q.; Jia, H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L. Endogenously activated persulfate by non-thermal plasma for Cu(II)-EDTA decomplexation: Synergistic effect and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Ren, N.; Ho, S. Advanced oxidation processes for water disinfection: Features, mechanisms and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Degradation of p-nitrophenol by DBD plasma/Fe2+/persulfate oxidation process. Sep. Purifi. Technol. 2019, 218, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gu, X.; Lu, S.; Miao, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Sui, Q. Benzene depletion by Fe2+-catalyzed sodium percarbonate in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gu, X.; Lu, S.; Xu, M.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Sui, Q. Enhanced degradation of benzene in aqueous solution by sodium percarbonate activated with chelated-Fe(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Lu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yin, G. Degradation of chlorophenols by supported Co-Mg-Al layered double hydrotalcite with bicarbonate activated hydrogen peroxide. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 10028–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, J. Zn-Fe-CNTs catalytic in situ generation of H2O2 for Fenton-like degradation of sulfamethoxazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, A.; Jia, J.; Tian, J.; Xing, Z. Hierarchical defect-rich flower-like BiOBr/Ag nanoparticles/ultrathin g-C3N4 with transfer channels plasmonic Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for accelerated visible-light-driven photothermal-photocatalytic oxytetracycline degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yao, B.; Zhang, W.; He, Y.; Yu, Y.; Niu, J. Fabrication of PVDF-based piezocatalytic active membrane with enhanced oxytetracycline degradation efficiency through embedding few-layer E-MoS2 nanosheets. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 129000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Ren, F.; Sun, P.; Zhou, L. Core-shell Zn/Co MOFs derived Co3O4/CNTs as an efficient magnetic heteroge-neous catalyst for persulfate activation and oxytetracycline degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; Kulis, J.; Thomson, B.; Chapman, T.; Mawhinney, D. Occurrence of antibiotics in hospital, residential, and dairy effluent, municipal wastewater, and the rio grande in new Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Mo, Y.; Lu, H. Determination of oxytetracycline, tetracycline and chloramphenicol antibiotics in animal feeds using subcritical water extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 619, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, J.; Obholzer, T.; Winkler, K.; Jabornig, S.; Rupprich, M. Combining ultrafiltration and non-thermal plasma for low energy degradation of pharmaceuticals from conventionally treated wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7377–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Liu, P.; Gu, Y.; Fan, H.; Song, X. Degradation of tetrabromobisphenol a by ozonation: Performance, products, mechanism and toxicity. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Revisiting the role of reactive oxygen species for pollutant abatement during T catalytic ozonation: The probe approach versus the scavenger approach. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 280, 119418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ma, F.; Elm, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, H. Atmospheric oxidation mechanism and kinetics of indole initiated by ·OH and ·Cl: A computational study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11543–11555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, C.; Guo, J.; Guo, H.; Yin, Y.; Xu, X.; Fei, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wen, X. Highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by CO3O4/Bi2WO6 p-nheterojunction composites for the degradation of ciprofloxacin under visible light irradiation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 588, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J. Degradation and mineralization of ofloxacin by ozonation and peroxone (O3/H2O2) process. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Yuan, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, R. Study on the efficiency and mechanism of direct red 80 dye by conventional ozonation and peroxone (O3/H2O2) treatment. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3175–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radko, M.; Rutkowska, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Mikrut, P.; Swięs, A.; Díaz, U.; Palomares, A.; Macyk, W.; Chmielarz, L. Catalytic oxidation of organic sulfides by H2O2 in the presence of titanosilicate zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 302, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Bae, H.; Jung, J. Tetracycline degradation by ozonation in the aqueous phase: Proposed degradation intermediates and pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Mcconchie, R.; Li, W.; Zhou, R.; Thompson, E.W.; Ostrikov, K.; Cullen, P.J. Degradation of cefixime antibiotic in water by atmospheric plasma bubbles: Performance, degradation pathways and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mao, D.; Wang, H.; Guo, H. An insightful analysis of dimethyl phthalate degradation by the collaborative process of DBD plasma and Graphene-WO3 nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, D.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Li, J. Multi-catalysis induced by pulsed discharge plasma coupled with graphene-Fe3O4 nanocomposites for efficient removal of ofloxacin in water: Mechanism, degradation pathway and potential toxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Shang, K.; Lu, N.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Enhanced catalytic performance of graphene-TiO2 nanocomposites for synergetic degradation of fluoroquinolone antibiotic in pulsed discharge plasma system. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 248, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jia, H.; Guo, X.; Xia, T.; Qu, G.; Sun, Q.; Yin, X. Evaluation of the potential of dimethyl phthalate degradation in aqueous using sodium percarbonate activated by discharge plasma. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Degradation of chloramphenicol by pulsed discharge plasma with heterogeneous Fenton process using Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Xiang, L.; Pan, S.; Zhu, D.; Li, S.; Guo, H.
The Degradation of Aqueous Oxytetracycline by an O3/CaO2 System in the Presence of
Li Z, Xiang L, Pan S, Zhu D, Li S, Guo H.
The Degradation of Aqueous Oxytetracycline by an O3/CaO2 System in the Presence of
Li, Zedian, Liangrui Xiang, Shijia Pan, Dahai Zhu, Shen Li, and He Guo.
2024. "The Degradation of Aqueous Oxytetracycline by an O3/CaO2 System in the Presence of
Li, Z., Xiang, L., Pan, S., Zhu, D., Li, S., & Guo, H.
(2024). The Degradation of Aqueous Oxytetracycline by an O3/CaO2 System in the Presence of





