Effects of Different Concentrations of AmB on the Unsaturated Phospholipid–Cholesterol Membrane Using the Langmuir Monolayer and Liposome Models
Abstract
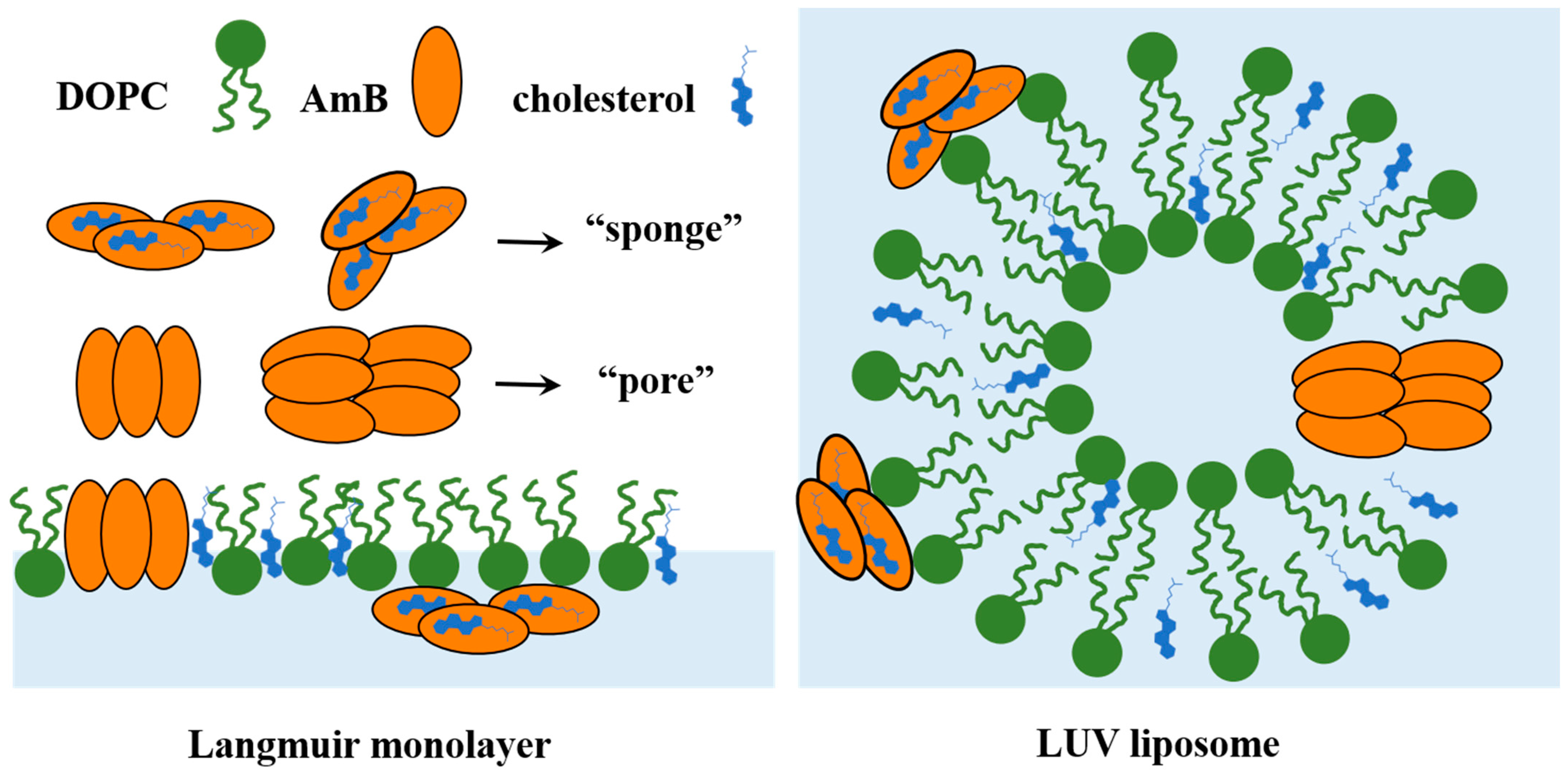
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
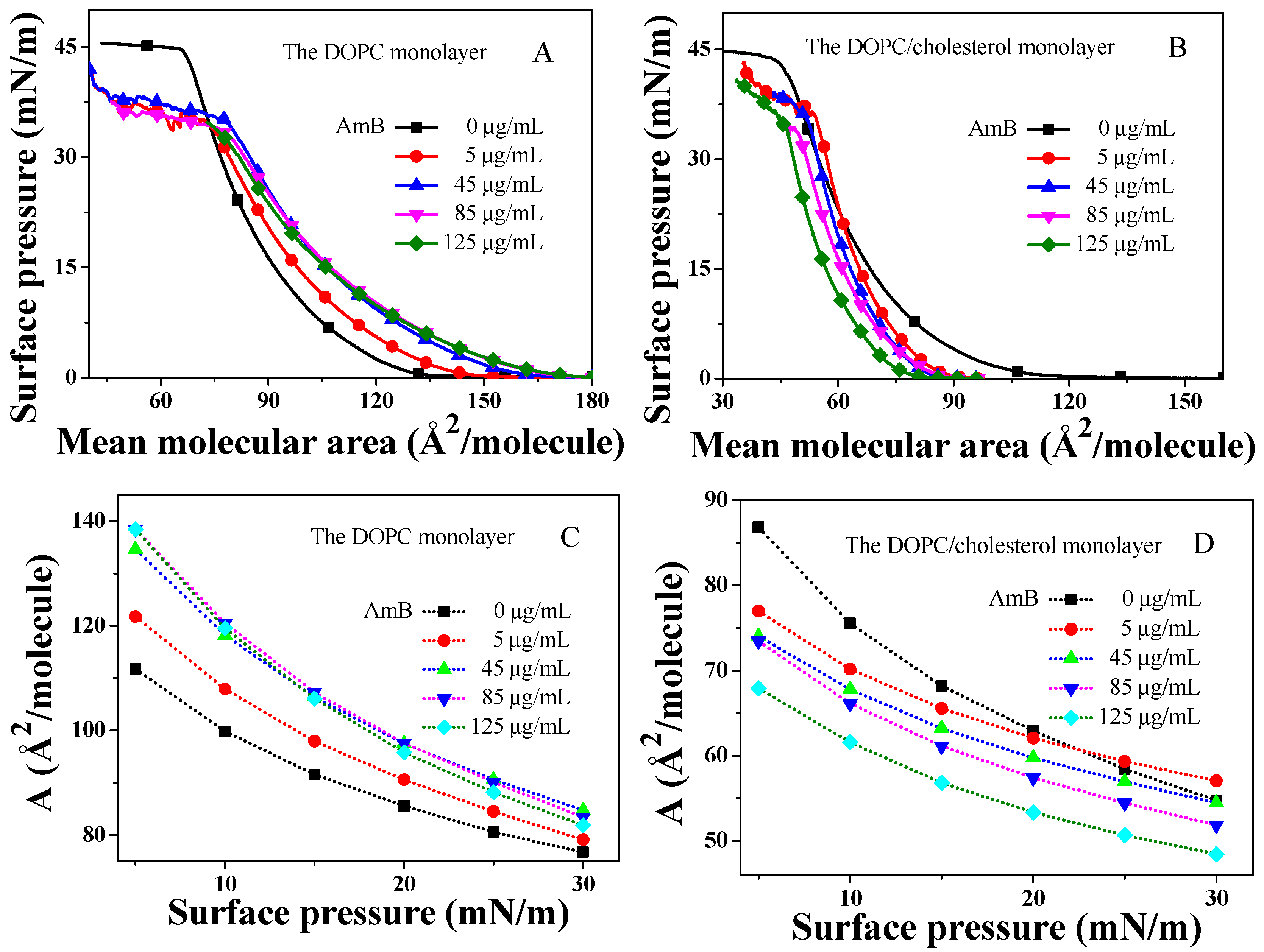
2.1. The Isotherm
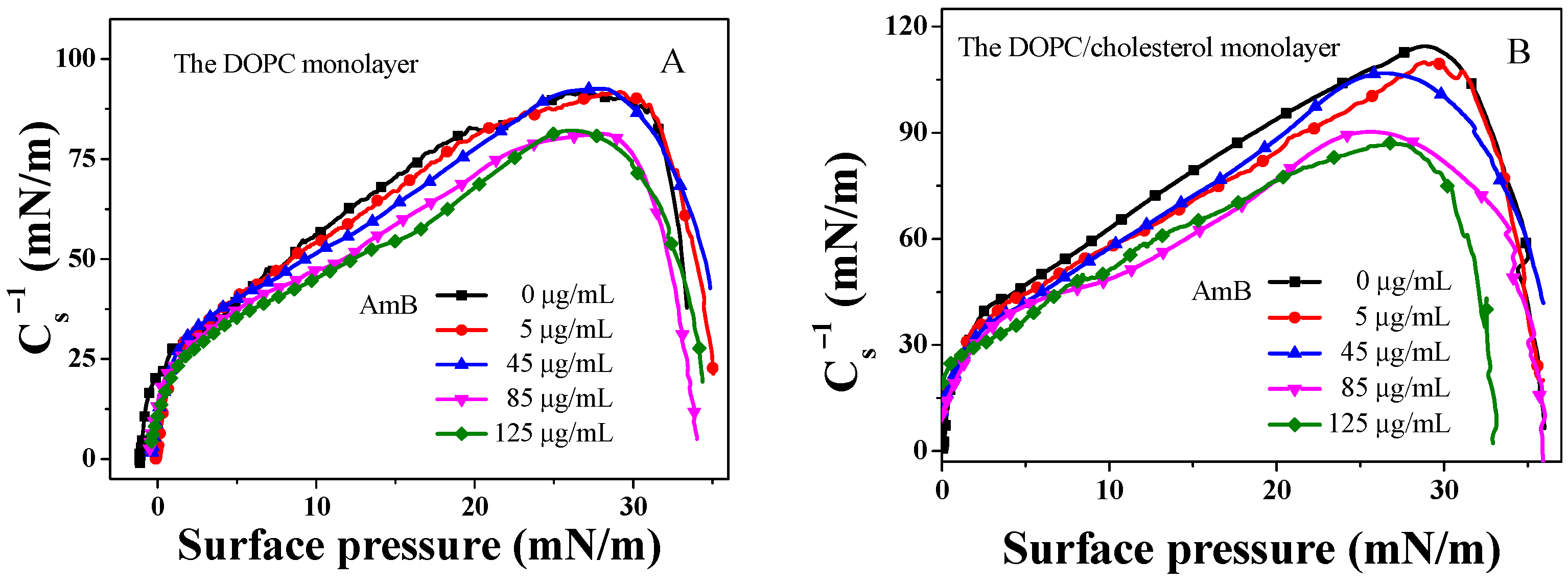
2.2. Modulus of Elasticity
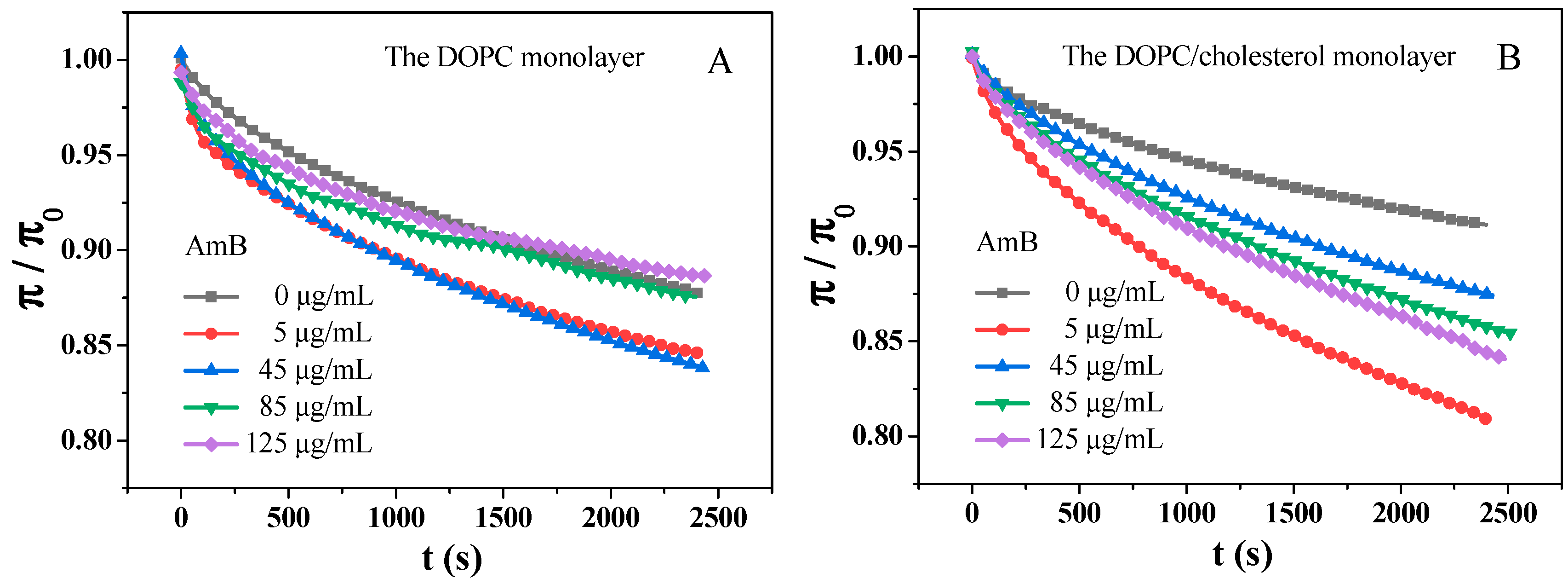
2.3. Adsorption of AmB Molecules on the DOPC Monolayer and the DOPC/Chol Monolayer
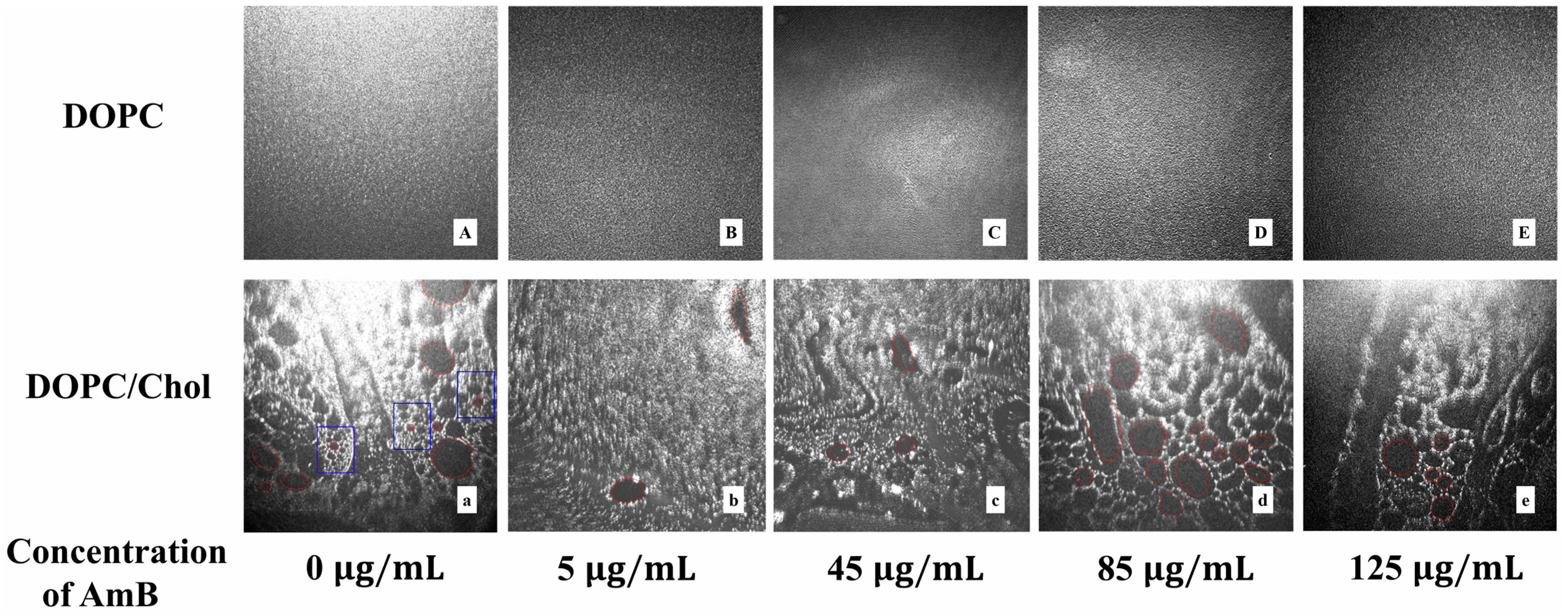
2.4. Real Time Morphology of Lipid Monolayer
2.5. Fluorescence Lifetime of NBD Probes in DOPC Liposomes and DOPC/Cholesterol Liposomes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Langmuir Monolayer Experiment
3.3. The Real Time Morphology of Monolayer by BAM
3.4. Preparation of Large Unilamellar Vesicle (LUV) Liposomes
3.5. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagiya, H.; Nishimura, Y.; Otsuka, F. Safety and usefulness of nebulized liposomal amphotericin B: Systematic scoping review. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 82, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Kumar, V.; Tiwari, R.K.; Ravidas, V.; Pandey, K.; Kumar, A. Amphotericin B: A drug of choice for Visceral Leishmaniasis. Acta Trop. 2022, 235, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.; Kinh, N.V.; Cuc, N.T.; Tung, N.L.; Lam, N.T.; Thuy, P.T.; Cuong, D.D.; Phuc, P.T.; Vinh, V.H.; Hanh, D.T.; et al. Atrial of itraconazole or amphotericin B for HIV-associated talaromycosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, A.H.; Piscitelli, S.C.; Walsh, T.J. Clinical pharmacology of systemic antifungal agents: A comprehensive review of agents in clinical use. current investigational compounds, and putative targets for antifungal drug development. Adv. Pharmacol. 1998, 44, 343–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baran, M.; Borowski, E.; Mazerski, J. Molecular modeling of amphotericin B–ergosterol primary complex in water ii. Biophys. Chem. 2009, 141, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, H.; Liu, H. Effect of Amphotericin B on the thermodynamic stability, aggregation state, hemolysis and antifungal activity of Amphotericin B-nonionic surfactant micellar system. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liao, B.; Ye, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Liao, M.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Ren, B. Artemisinin elevates ergosterol levels of Candida albicans to synergise with amphotericin B against oral candidiasis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, D.M.; Pociecha, D.; Górecka, E.; Gagoś, M. The influence of amphotericin B on the molecular organization and structural properties of DPPC lipid membranes modified by sterols. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1082, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.M.; Clay, M.C.; Cioffi, A.G. Amphotericin forms an extramembranous and fungicidal sterol sponge. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertut-Doi, A.; Hannaert, P.; Bolard, J. The polyene antibiotic amphotericin B inhibits the Na+/K+ pump of human erythrocyte. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 157, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, L.O.; Kalaeva, E.A.; Artyukhov, V.G.; Putintseva, O.V.; Nakvasina, M.A.; Litvinov, N.V.; Gizetdinova, L.R. The Effect of Polyene Antibiotic Amphotericin B on Erythrocyte Cytoarchitectonics and Osmotic Resistance. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 175, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olumuyiwa-Akeredolu, O.O.; Soma, P.; Buys, A.V.; Debusho, L.K.; Pretorius, E. Characterizing pathology in erythrocytes using morphological and biophysical membrane properties: Relation to impaired hemorheology and cardiovascular function in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 2381–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.; Lee, J.; Svirkin, Y.; Yoon, S.; Landrau, N.; Kaisar, M.A.; Qin, B.; Park, J.H.; Alam, K.; Kozak, D.; et al. Physicochemical surrogates for in vitro toxicity assessment of liposomal amphotericin B. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 628, 122273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, W.T.; Cotlove, E. Increased permeability of human erythrocyte induced by amphotericin B. J. Infect. Dis. 1971, 123, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardina, T.; Fawcett, A.J.; Patel, S.J. Amphotericin-Associated Infusion-Related Reactions: A Narrative Review of Pre-Medications. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Nava, R.; Galván-Hernández, A.; Fernández-Zertuche, M.; Ortega-Blake, I. Study of Self-Association of Amphotericin B and its Synthetic Derivatives using UV-Vis Spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 86a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Dong, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shangguan, W.; Zhao, W.; Feng, J. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel N-aminoacyl derivative of amphotericin B methyl ester as an antifungal agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 211, 113104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luka, K.; Bojan, B.; Špela, Z.J.; Marija, S.D.; Gregor, G. The pore-forming action of polyenes: From model membranes to living organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 418–430. [Google Scholar]
- Yilma, S.; Cannon-Sykora, J.; Samoylov, A.; Lo, T.; Liu, N.; Brinker, C.J.; Neely, W.C.; Vodyanoy, V. Large-conductance cholesterol–amphotericin B channels in reconstituted lipid bilayers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, A.; Soutar, C.P.; Greenwood, A.I. Fungicidal amphotericin B sponges are assemblies of staggered asymmetric homodimers encasing large void volumes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.C.M.; Morato, L.F.C.; Pazin, W.M.; Oliveira Jr, O.N.; Constantino, C.J.L. In situ interaction between the hormone 17α-ethynylestradiol and the liquid-ordered phase composed of the lipid rafts sphingomyelin and cholesterol. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 143, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.R.; Regen, S.L. The structural role of cholesterol in cell membtanes:from condensed bilayers to lipid rafts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 47, 3512–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeagle, P.L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 822, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.M. A new specific cholesterol assay gives reduced cholesterol/phospholipid molar ratios in cell membranes. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A.; Gazgalis, D.; Logothetis, D.E. PI (4,5) P2 and Cholesterol: Synthesis, Regulation, and Functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1422, 3–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.A.; Romero, A. Effects of troglitazone on intracellular cholesterol distribution and cholesterol-dependent cell functions in MA-10 leydig tumor cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagoś, M.; Arczewska, M. Spectroscopic studies of molecular organization of antibiotic amphotericin B in monolayers and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine lipid multibilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñones, J.; Dynarowicz-Łątka, P.; Conde, O.; Miñones, J.; Iribarnegaray, E.; Casas, M. Interactions of amphotericin B with saturated and unsaturated phosphatidylcholines at the air/water interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 29, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, S.; Murata, M. Membrane permeabilizing activity of amphotericin B is affected by chain length of phosphatidylcholine added as minor constituent. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1617, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynarowicz-Łątka, P.; Seoane, R.; Miñones, J.; Velo, M.; Miñones, J. Study of penetration of amphotericin B into cholesterol or ergosterol containing dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine Langmuir monolayers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 27, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Influence of amphotericin B on the thermodynamic properties and surface morphology of saturated phospholipid monolayer with different polar head at the air-water interface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 617, 126298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgeny, G.C.; Svetlana, S.E.; Ludmila, V.S.; Olga, S.O. Direct visualization of solid ordered domains induced by polyene antibiotics in giant unilamellar vesicles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 183, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroumova, O.S.; Efimova, S.S.; Schagina, L.V. Probing amphotericin B single channel activity by membrane dipole modifiers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.; Vaz, W.L. Model systems, lipid rafts, and cell membranes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2004, 33, 269–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Q.; Feng, S.; Wang, Z. Regulation of calcium ions on the interaction between amphotericin B and cholesterol-rich phospholipid monolayer in LE phase and LC phase. Biophys. Chem. 2023, 297, 107012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiński, D.M.; Czernel, G.; Murphy, B.; Runge, B.; Magnussen, O.M.; Gagoś, M. Effect of cholesterol and ergosterol on the antibiotic amphotericin B interactions with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine monolayers: X-ray reflectivity study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, I.; Barwicz, J.; Auger, M.; Tancrède, P. The chain conformational order of ergosterol- or cholesterol-containing DPPC bilayers as modulated by Amphotericin B: A FTIR study. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2008, 151, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolle, E.; Kučerka, N.; Hoopes, M.I.; Choi, Y.; Katsaras, J.; Karttunen, M.; Leonenko, Z. Effect of melatonin and cholesterol on the structure of DOPC and DPPC membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, M.S.; Tomasz, R.; Marta, P.G.; Ilpo, V.; Mikko, K.; Ramon, R. Interplay of unsaturated phospholipids and cholesterol in membranes: Effect of the doublebond position. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 3295–3305. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus, D.M.; Cibely, S.M.; Priscila, A. Bisphenol A exposure induces multiple effects in DOPC membrane models. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119253. [Google Scholar]
- Ripa, P.; Debajyoti, B.; Syed, A.H. Interaction of amoxicillin with DOPC layer. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2718–2722. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Laman, J.D.; Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Maintaining sidedness and fluidity in cell membrane coatings supported on nano-particulate and planar surfaces. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 32, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Träger, J.; Meister, A.; Hause, G.; Harauz, G.; Hinderberger, D. Shaping membrane interfaces in lipid vesicles mimicking the cytoplasmic leaflet of myelin through variation of cholesterol and myelin basic protein contents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2023, 1865, 184179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, F.; Magalhaes-Mota, G.; Geraldo, V.P.N.; Ribeiro, P.A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Raposo, M. The impact of blue light in monolayers representing tumorigenic and nontumorigenic cell membranes containing epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, F.; Geraldo, V.P.N.; Rodrigues, B.; Granada-Flor, A.D.; Almeida, R.F.M.; Oliveira, O.N.; Victor, B.L.; Machuqueiro, M.; Raposo, M. Evaluation of EGCG loading capacity in DMPC membranes. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6771–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochelavicius, K.; Pereira, A.R.; Fiamingo, A.; Nobre, T.M.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Oliveira, O.N. Chitosan effects on monolayers of zwitterionic, anionic and a natural lipid extract from E. coli at physiological pH. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 209, 112146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurak, M.; Szafran, K.; Cea, P.; Martín, S. Analysis of molecular interactions between components in phospholipid-immunosuppressant-antioxidant mixed Langmuir films. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5601–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachowski, A. Phospholipids in animal eukaryotic membranes: Transverse asymmetry and movement. Biochem. J. 1993, 294, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurr, M.I.; Harwood, J.L.; Frayn, K.N. Lipid Biochemistry, 5th ed.; WileyBlackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sackmann, E. Chapter 1-Biological Membranes Architecture and Function. In Handbook of Biological Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hirakawa, R.; Ochiai, H. Correlation between sphingomyelin and the membrane stability of mammalian erythrocyte. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 265, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.E.; Conserva, G.A.A.; Lago, J.H.G.; Caseli, L. Monolayer nanoarchitectonics at the air-water interface for molecular understanding of the interaction of isolinderanolide E with cholesterol. Thin Solid Films 2022, 754, 139305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.K.; Fang, L.; Lancaster, G.I.; Murphy, A.J. Hematopoiesis is regulated by cholesterol efflux pathways and lipid rafts: Connections with cardiovasculardiseases: Thematic Review Series: Biology of Lipid Rafts. JLR (J. Lipid Res.) 2020, 61, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecka, J.; Trouillas, P.; Gašparović, A.C.; Gazzano, E.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Riganti, C. Phospholipids and cholesterol: Inducers of cancer multidrug resistance and therapeutic targets. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 49, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, S.D.; Villanueva, M.E.; Selzer, S.M.; Ferreyra, N.F.; Vico, R.V. A systematic study of the impact of aromatic/aliphatic amines and protein corona as coatings of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles on the interaction with DPPC Langmuir monolayers. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 51, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, S.; Zhu, H. Influence of amphotericin B on the DPPC/DOPC/sterols mixed monolayer in the presence of calcium ions. Biophys. Chem. 2021, 279, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miñones, J.; Conde, O.; Dynarowicz-Łątka, P.; Casas, M. Penetration of amphotericin B into DOPC monolayers containing sterols of cellular membranes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 270, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Liggieri, L.; Santini, E.; Ferrari, M.; Ravera, F. DPPC-DOPC Langmuir monolayers modified by hydrophilic silica nanoparticles: Phase behavior, structure and rheology. Colloids Surf. A 2012, 413, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, C.J.; Bryant, S.J.; Elbourne, A.; Hunt, T.; Kent, B.; Kreuzer, M.; Strobl, M.; Steitz, R.; Bryant, G. Phase separation in a ternary DPPC/DOPC/POPC system with reducing hydration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 638, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Takagi, S.; Asano-Mori, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yuasa, M.; Kageyama, K.; Kaji, D.; Nishida, A.; Ishiwata, K.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of liposomal amphotericin B and analysis of the relationship between pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety in patients with hematological diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2024, 30, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, H. The Effect of Chitin Nanoparticles on Surface Behavior of DPPC/DPPG Langmuir Monolayers. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 519, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Liu, H.; Ying, H. Cationic Gemini surfactant at the air/water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Devterova, J.M.; Sokolov, M.E.; BuzKo, V.Y.; Repina, I.N.; Rudnov, P.S.; Panyushkin, V.T. Subphase pH effect on the limiting molecular area of amphiphilic β-diketones in Langmuir monolayers. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J. Mixed monolayers of DOPC and palmitic acid at the liquid–air interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Hou, S.; Miao, Z.; Ma, Q. Interaction of amphotericin B and saturated or unsaturated phospholipid monolayers containing cholesterol or ergosterol at the air-water interface. Biophys. Chem. 2020, 258, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.T.; Rideal, E.K. Interfacial Phenomena, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963; pp. 265–266. [Google Scholar]
- Krajewska, B.; Wydro, P.; Kyziol, A. Chitosan as a subphase disturbant of membrane lipid monolayers. The effect of temperature at varying pH: I. DPPG. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 434, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.C.; Caseli, L. Interaction of nitrofurantoin with lipid langmuir monolayers as cellular membrane models distinguished with tensiometry and infrared spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño, M.R.R.; Caro, A.L.; Patino, J.M.R. Structural, topographical, and rheological characteristics of β-casein–dioleoyl phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) mixed monolayers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 69, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D. Lateral pressure in membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Biomembr. 1996, 1286, 183–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Shen, N.; Luo, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Thomas, R.K. Gemini Surfactant/DNA Complex Monolayers at the Air-Water Interface: Effect of Surfactant Structure on the Assembly, Stability, and Topography of Monolayers. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowska-Mazurkiewicz, M.; Bizoń, T.; Matyszewska, D.; Fontaine, P.; Bilewicz, R. Oxidation of lipid membrane cholesterol by cholesterol oxidase and its effects on raft model membrane structure. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z. Effect of Trastuzumab on the thermodynamic behavior and roughness of fluid membrane using unsaturated phospholipid/cholesterol mixed monolayer model. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 742, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miñones, J.; Pais, S.; Miñones, J.; Conde, O.; Dynarowicz-Łątka, P. Interactions between membrane sterols and phospholipids in model mammalian and fungi cellular membranes—A Langmuir monolayer study. Biophys. Chem. 2009, 140, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, F.G. Time-resolved fluorescence techniques: Methods and applications in biology. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1991, 1, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Raghuraman, H. Reverse micellar organization and dynamics: A wavelength-selective fluorescence approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 13002–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquezin, C.A.; Ito, A.S.; Souza, E.S. Organization and dynamics of NBD-labeled lipids in lipid bilayer analyzed by FRET using the small membrane fluorescent probe AHBA as donor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 182995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albania, J.R. Principles and Applications of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 88–114. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuraman, H.; Shrivastava, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Monitoring the looping up of acyl chain labeled NBD lipids in membranes as a function of membrane phase state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, J.; Wieczór, M.; Chodnicki, P.; Grela, E.; Luchowski, R.; Nierzwicki, Ł.; Bączek, T.; Gruszecki, W.I.; Czubb, J. Self-assembly, stability and conductance of amphotericin B channels: Bridging the gap between structure and function. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3686–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Monolayer | Different Concentration of AmB ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOPC | 0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 5 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | |
| 45 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |
| 85 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.4 | |
| 125 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |
| DOPC/Chol (1:1) | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| 45 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | |
| 85 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |
| 125 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Monolayer | Different Concentrations of AmB ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOPC | 0 | 0.8480.011 | 0.1440.001 | 1603.7525.119 | 0.9970.002 |
| 5 | 0.8200.008 | 0.1500.001 | 1427.7848.214 | 0.9920.006 | |
| 45 | 0.8130.012 | 0.1640.002 | 1396.1585.124 | 0.9930.005 | |
| 85 | 0.8630.011 | 0.1110.001 | 1274.9156.124 | 0.9880.002 | |
| 125 | 0.8780.011 | 0.1050.001 | 1094.7025.112 | 0.9850.001 | |
| DOPC/Chol (1:1) | 0 | 0.8880.021 | 0.1050.003 | 1685.9544.125 | 0.9960.007 |
| 5 | 0.7610.019 | 0.2220.002 | 1660.2085.142 | 0.9970.003 | |
| 45 | 0.8350.013 | 0.1590.002 | 1796.34210.241 | 0.9980.001 | |
| 85 | 0.8070.011 | 0.1830.001 | 1933.9259.145 | 0.9960.001 | |
| 125 | 0.7800.011 | 0.2070.003 | 2145.85911.245 | 0.9960.002 |
| Lipid | AmB | NBD-PE | NBD-PC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α1 | τ1/ns | α2 | τ2/ns | <τ>/ns | χ2 | α1 | τ1/ns | α2 | τ2/ns | <τ>/ns | χ2 | ||
| DOPC | 0 | 10.790.03 | 14.160.02 | 3.280.01 | 2.910.02 | 13.500.01 | 0.96 | 1.830.03 | 19.430.02 | 7.560.08 | 2.410.02 | 13.660.01 | 0.96 |
| 5 | 7.740.08 | 13.550.03 | 7.740.03 | 13.550.01 | 13.550.01 | 0.92 | 0.190.01 | 39.960.05 | 5.690.04 | 2.690.01 | 15.050.02 | 0.96 | |
| 45 | 2.110.01 | 18.610.06 | 3.000.03 | 2.790.11 | 15.830.03 | 0.96 | 4.320.06 | 17.900.03 | 4.620.01 | 3.030.01 | 15.620.02 | 0.98 | |
| 85 | 3.570.05 | 20.890.11 | 2.630.02 | 3.470.06 | 18.990.01 | 0.93 | 0.570.01 | 33.690.03 | 1.500.01 | 2.610.01 | 28.430.05 | 0.97 | |
| 125 | 0.730.02 | 27.750.10 | 1.500.01 | 3.110.01 | 23.140.01 | 0.95 | 0.150.01 | 127.270.09 | 5.590.02 | 2.230.02 | 77.880.11 | 0.97 | |
| DOPC-Chol (1:1) | 0 | 44.270.10 | 12.800.08 | 7.730.02 | 1.580.01 | 12.560.01 | 0.95 | 0.260.01 | 26.700.03 | 4.710.02 | 2.800.01 | 11.040.01 | 0.83 |
| 5 | 25.370.09 | 11.210.01 | 25.370.01 | 11.210.08 | 11.210.01 | 0.95 | 28.110.03 | 11.210.05 | 1.120.01 | 2.570.01 | 11.130.01 | 0.95 | |
| 45 | 282.220.11 | 8.200.02 | 3.000.01 | 2.090.01 | 8.180.03 | 0.96 | 882.170.10 | 6.790.03 | 1.080.01 | 1.970.02 | 6.790.02 | 0.87 | |
| 85 | 1621.600.10 | 6.890.02 | 1.180.01 | 3.490.01 | 6.890.03 | 0.90 | 2.730.04 | 3.690.01 | 2.730.01 | 3.690.02 | 3.690.01 | 0.82 | |
| 125 | 0.800.01 | 31.480.08 | 3728.900.13 | 6.680.04 | 6.710.05 | 0.98 | 6.510.03 | 3.490.01 | 6.510.04 | 3.490.03 | 3.490.01 | 0.89 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Li, D. Effects of Different Concentrations of AmB on the Unsaturated Phospholipid–Cholesterol Membrane Using the Langmuir Monolayer and Liposome Models. Molecules 2024, 29, 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235659
Wang J, Wang J, Zheng M, Li D. Effects of Different Concentrations of AmB on the Unsaturated Phospholipid–Cholesterol Membrane Using the Langmuir Monolayer and Liposome Models. Molecules. 2024; 29(23):5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235659
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Juan, Jia Wang, Mingyue Zheng, and Da Li. 2024. "Effects of Different Concentrations of AmB on the Unsaturated Phospholipid–Cholesterol Membrane Using the Langmuir Monolayer and Liposome Models" Molecules 29, no. 23: 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235659
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, J., Zheng, M., & Li, D. (2024). Effects of Different Concentrations of AmB on the Unsaturated Phospholipid–Cholesterol Membrane Using the Langmuir Monolayer and Liposome Models. Molecules, 29(23), 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29235659






