Preparation of Composites Derived from Modified Loess/Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance for Methyl Orange
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Modified Loess
2.2. Material Characterisation
2.2.1. Appearance and Morphology
2.2.2. Zeta Potential Analysis
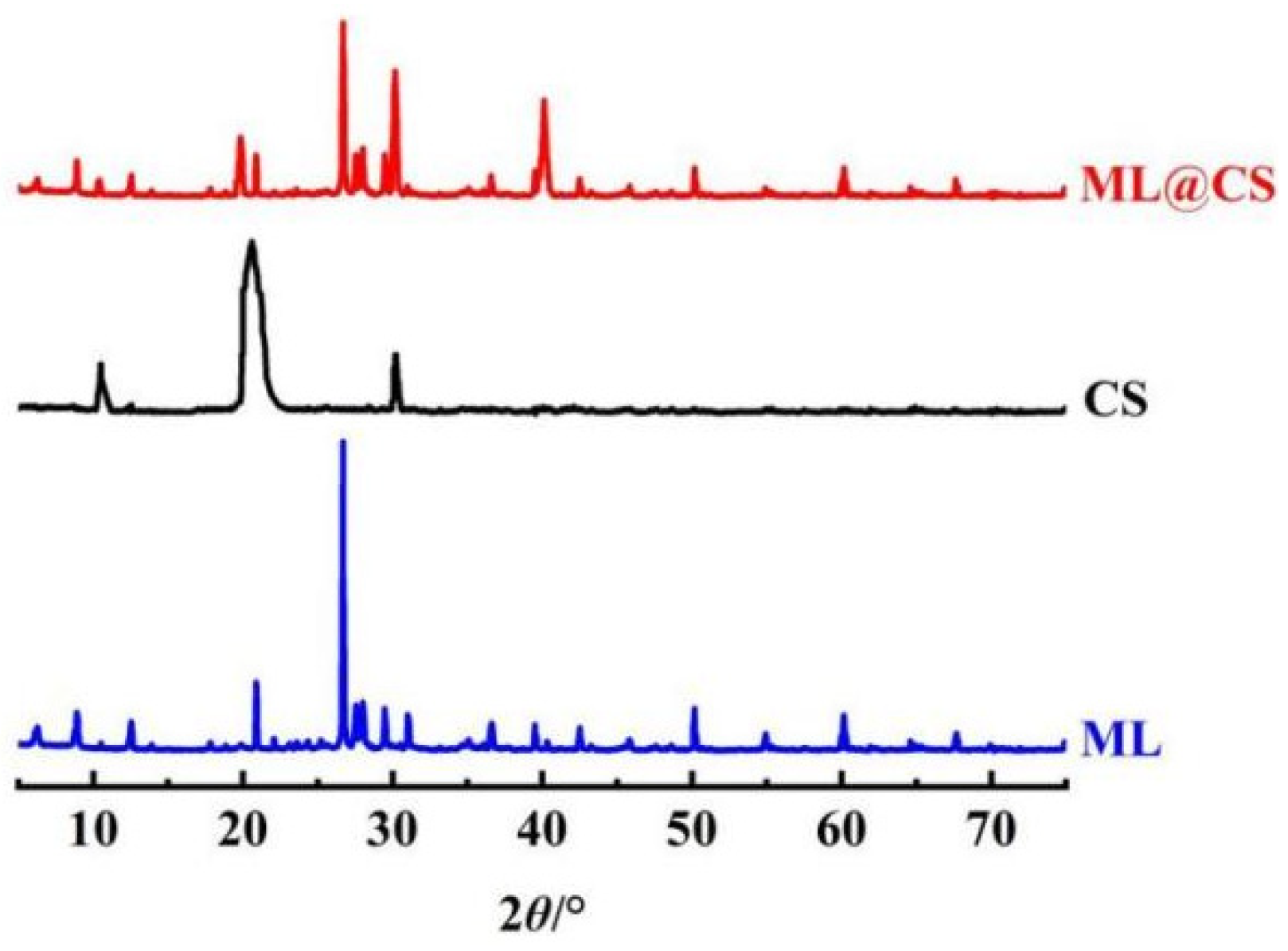
2.2.3. XRD Analysis
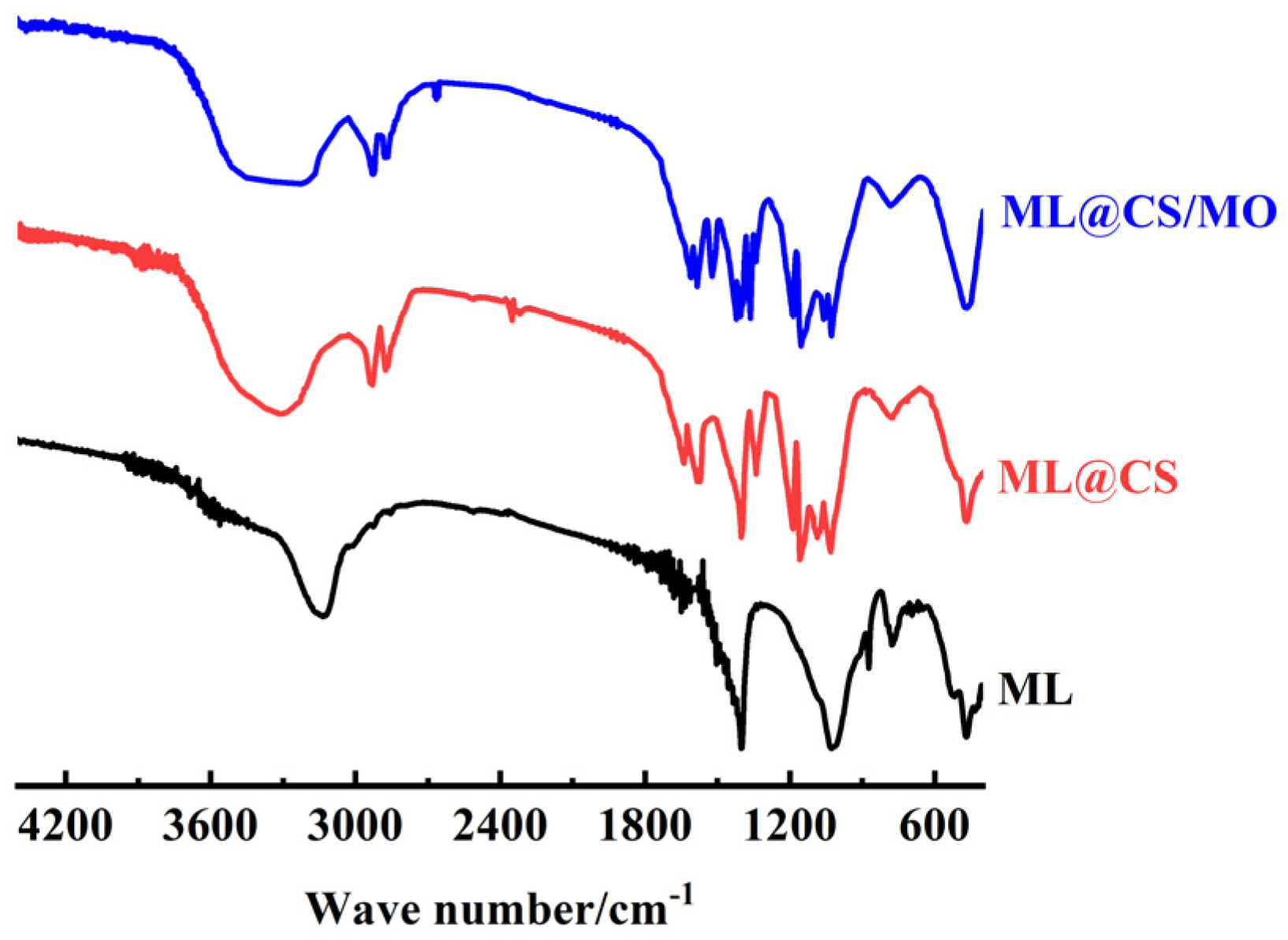
2.2.4. FT-IR Analysis
2.2.5. TGA
2.3. Influence of Adsorption Conditions on the Adsorption Effect
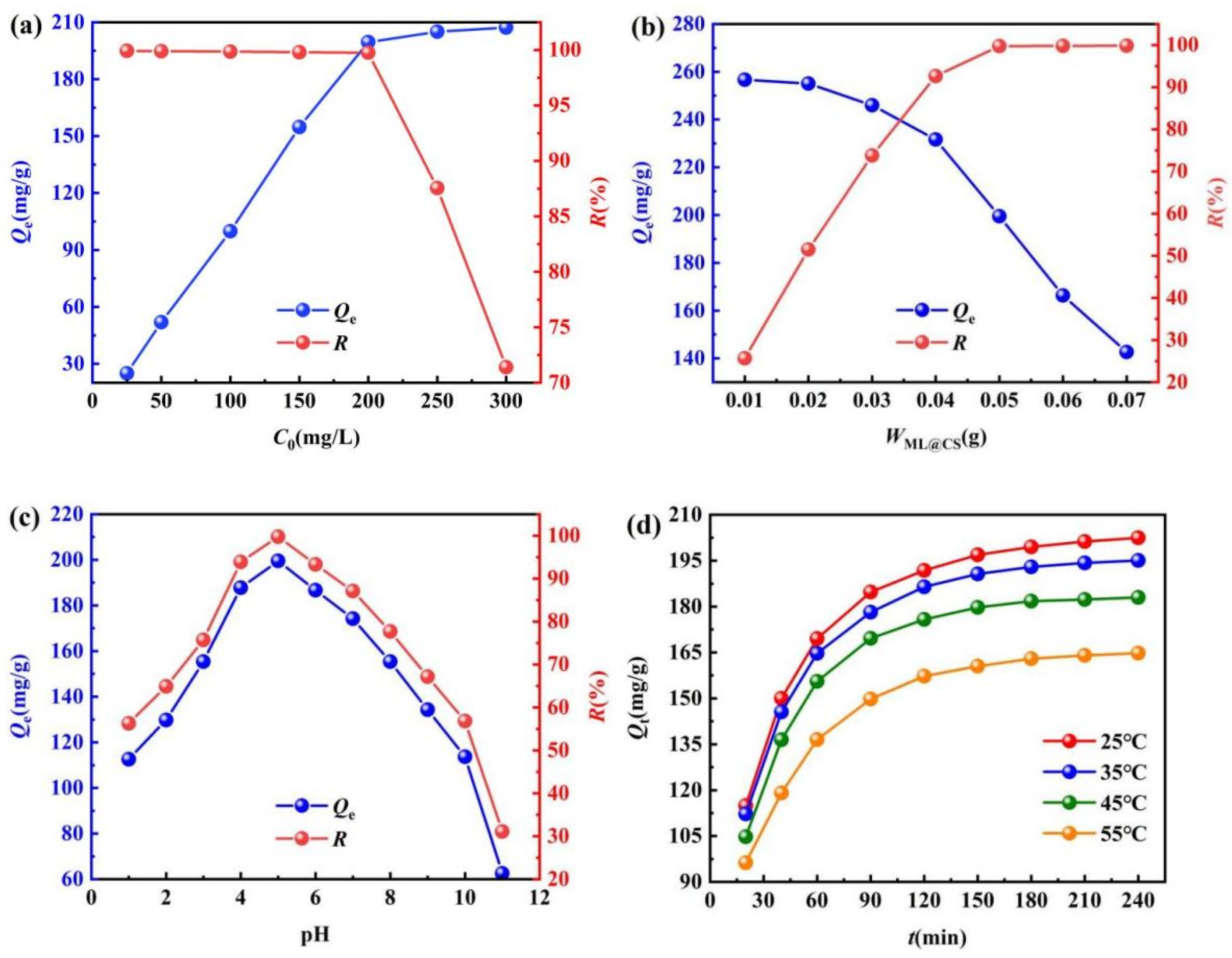
2.3.1. Effect of Initial Concentration
2.3.2. Effect of the Addition Amount of ML@CS
2.3.3. Effect of Solution pH
2.3.4. Effect of Adsorption Temperature and Time
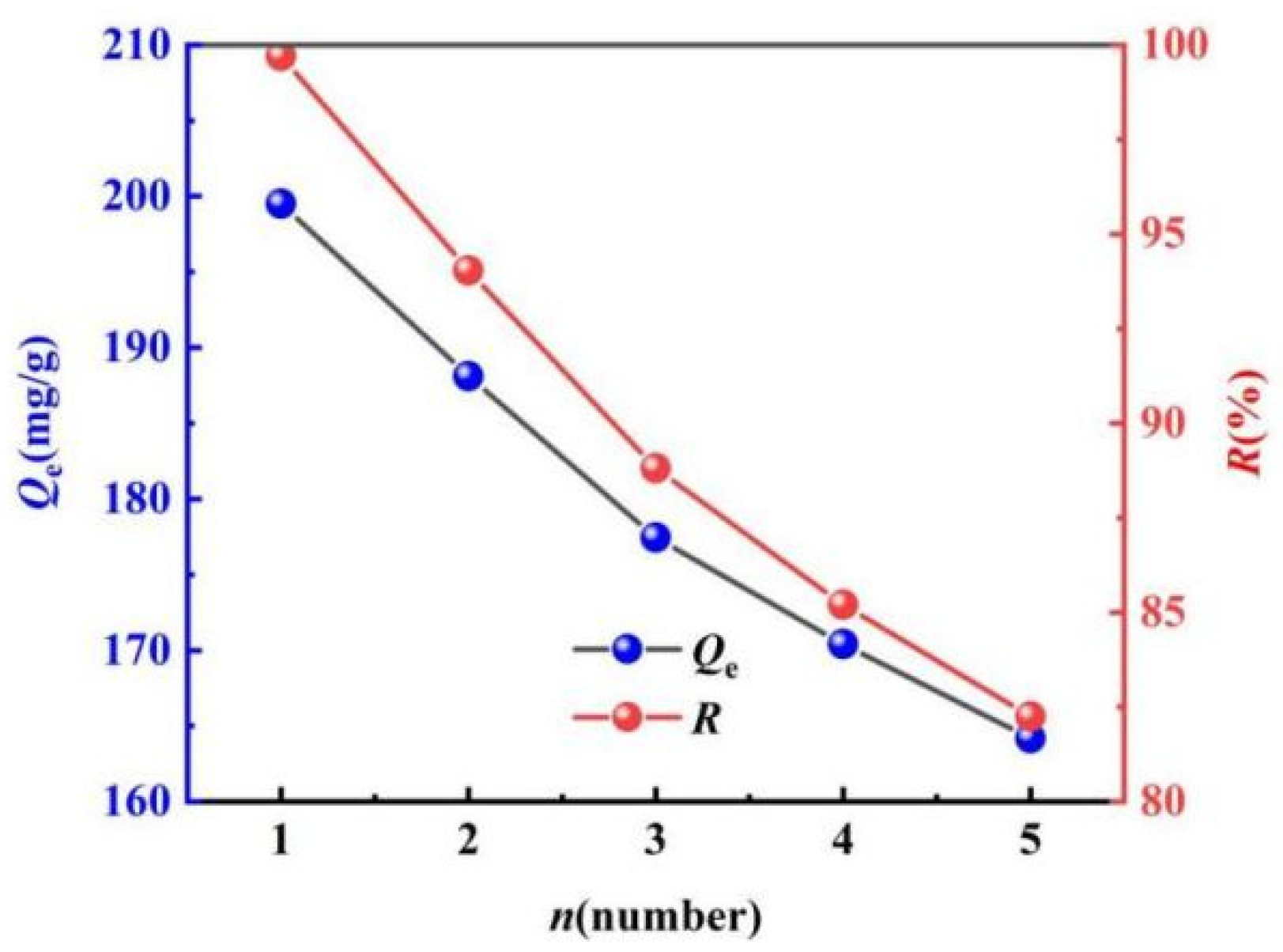
2.3.5. Evaluation of the Regeneration Performance
2.4. Analysis of the Desorption Mechanism
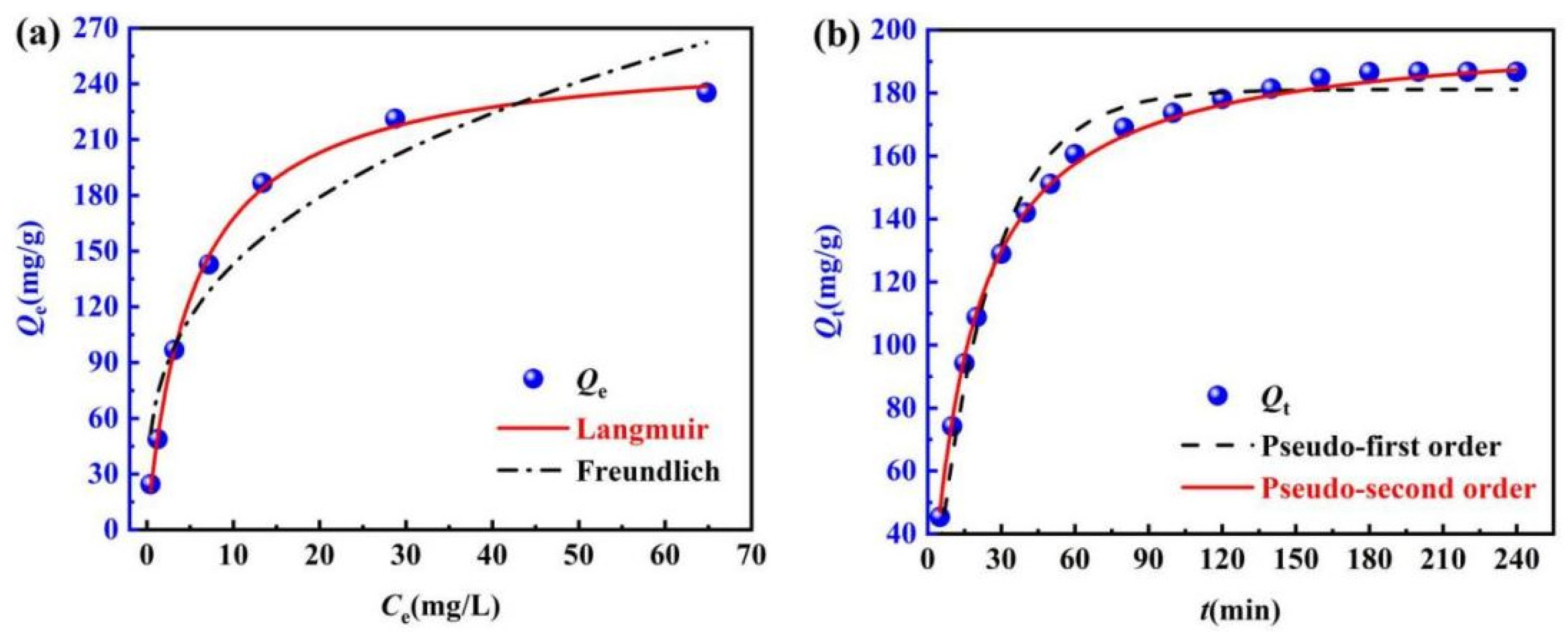
2.4.1. Adsorption Isothermal Analysis
2.4.2. Analysis of the Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.3. Analysis of Adsorption Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Loess Modification
3.3. Preparation of ML@CS
3.4. Characterisation of the Prepared Composite
3.5. Plot of the Standard Curve of MO
3.6. Adsorption Tests
3.6.1. Investigation of the Adsorption Conditions
3.6.2. Establishment of the Adsorption Kinetic Model
3.6.3. Establishment of the Isothermal Adsorption Model
3.6.4. Evaluation of Regeneration Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Lahtinen, M. Preparation and characterization of a novel chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite nanoparticles composite adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of methyl orange adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.A.A.; Rashad, M.; AL-Aoh, H.A. Methyl orange adsorption comparison on nanoparticles: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Dyes Pigments 2019, 160, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Chen, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qi, X. Selective removal of erythromycin by magnetic imprinted polymers synthesized from chitosan-stabilized Pickering emulsion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P. A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour grom textile wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A. Polysaccharides/silica hybrid materials: New perspectives for sustainable raw materials. J. Carbohyd. Chem. 2016, 35, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, Y.A.; Zhu, Q.J.; Ye, C. Chitosan in molecularlyimprinted polymers: Current and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18328–18347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Tang, X.; Xi, J.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, G.; Adesina, A.A. Macroporous ion-imprinted chitosan foams for the selective biosorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4155–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Shang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, S.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, L. Ultra-efficient adsorption of copper ions in chitosan-montmorillo nite composite aerogel at wastewater treatment. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7201–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Teong, L.C.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.F.; Ran, F.; Yang, Q.; Feng, E.; Lei, Z.Q. Eco-friendly superabsorbent composite based on sodium alginate and organo-loess with high swelling properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53819–53828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Dijkstra, T.; Wasowski, J.; Meng, X.M. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Zhao, M.; Ma, Z. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution using red loess as an adsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Guan, W.; Zeng, Y. Adsorption characteristics of iron on different layered loess soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.M.; Li, H.R.; Wang, Y. Loess clay based copolymer for removing Pb (II) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227/228, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Song, H.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y. Preparation and properties of loess-based hydrophobic materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 305, 127962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Hou, X.; Mu, Y.H.; Ma, W.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Y.C. Engineering properties of loess stabilized by a type of eco-material, calcium lignosulfonate. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bao, C.L.; Jia, Q.; Xiao, P.F.; Liu, X.T.; Zhang, Q.P. Preparation and characterization of chitosan graphene oxide composites for the adsorption of Au(III) and Pd(II). Talanta 2012, 93, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Zhang, D.H. Preparation of modified zeolite/chitosan composites and study on the adsorption performance of Pb2+. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 64, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Lee, S.M. Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2013, 201–202, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, A.; Mucha, M. Thermogravimetric and FTIR studies of chitosan blends. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 396, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.C.; Ma, N.; Chiang, T.C.; Tsai, L.C.; Shi, J.J.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, T.; Su, S.K.; Chuang, F.S. Adsorptive removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution with crosslinking chitosan microspheres. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, D.S.; Narayanam, P.K.; Singh, G.; Botcha, V.D.; Talwar, S.S.; Srinivasa, R.S.; Major, S.S. Spectroscopic studies of large sheets of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide monolayers prepared by Langmuir-Blodgett technique. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 5991–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, L. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cd (II) on loess soil from China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of loess soil towards chromium ion. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Sun, W.; Guo, N.; Ding, S.; Su, S. Comparison of Co2+ adsorption by chitosan and its triethylene-tetramine derivative: Performance and mechanism. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 151, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yu, S.J.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.D.; Lu, S.S.; Ai, Y.J.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Enhanced removal of methyl orange on calcined glycerol-modified nanocrystallined Mg/Al layered double hydroxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, J.; Pan, K.; Hou, H.; Hu, J.; Yang, J. Cross-linked chitosan/β-cyclodextrin composite for selective removal of methyl orange: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 182, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, P.; Cai, J.; Xiao, S.; Yang, H.; Li, A. Efficient adsorption of both methyl orange and chromium from their aqueous mixtures using a quaternary ammonium salt modified chitosan magnetic composite adsorbent. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, S.D.; Yang, L.; Dong, J.J.; Mo, X.L.; Zeng, M.T. Thermal degradation kinetics of chitosan-cobalt complex as studied by thermogravimetric analysis. Carbohyd. Polym. 2010, 82, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneerung, T.; Liew, J.; Dai, Y.; Kawi, S.; Chong, C.; Wang, C.H. Activated carbon derived from carbon residue from biomass gasification and its application for dye adsorption: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbia, M.; Hariri, S.A.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. Adsorptive removal of anionic dyes by modified nanoporous silica SBA-3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3228–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Quan, C.; Guo, M.; Ye, X.; Wu, Z. Competitive adsorption of methyl orange and ethyl orange by AB-8 resin. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2017, 6, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Jun, J.W.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with a metal-organic framework material, iron terephthalate (MOF-235). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Dou, C.; Han, R. Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solutions using cationic surfactant modified wheat straw in batch mode: Kinetic and equilibrium study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2578–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by an adsorbent based on metal-organic framework and polyoxometalate. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Tan, T.; Wu, W. Adsorption behavior of Th (IV) onto illite: Effect of contact time, pH value, ionic strength, humic acid and temperature. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2016, 127–128, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyinka, G.C.; Moodley, B. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) between aqueous solution and modeled individual soil particle grain sizes. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 76, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitei, M.D.; Prasad, M.N.V. Adsorption of Cu(II), Mn(II) and Zn (II) by Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) schleiden: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Malviya, A.; Kaur, D.; Mittal, J.; Kurup, L. Studies on the adsorption kinetics and isotherms for the removal and recovery of methyl orange from wastewaters using waste materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattabi, E.H.E.; Rachdi, Y.; Bassam, R.; Mourid, E.H.; Naimi, Y.; Alouani, M.E.; Belaaouad, S. Enhanced elimination of methyl orange and recycling of an eco-friendly adsorbent activated carbon. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2021, 15, S149–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, F.; Lu, Z.; Jin, L.; Yang, M.X.; Luan, J.S.; Tang, Y.H.; Fan, H.B.; Yuan, Z.W.; Chen, J.H. Enhanced adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution by alkali-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5749–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Zhou, Z. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of azo dyes by powdered activated carbon. J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 50, 2938–2947. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, F.; Hossein, A.; Mohamad, E.; Ghadir, N.; Bettina, R. Experimental study on the adsorptive behavior of Congo red in cationic surfactant-modified tea waste. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Annadurai, G.; Ling, L.Y.; Lee, J.-F. Adsorption of reactive dye from an aqueous solution by chitosan: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, H.; Bai, Z.S.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.J.; Tang, Z.Y.; Luque, R.; Xuan, J. Microfluidic synthesis of high performance monodispersed chitosan microparticles for methyl orange adsorption. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 78352–78360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | Specific Surface Area/(m2/g) | Mean Pore Volume/(cm3/g) | Mean Aperture/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| ML | 10.63 | 0.228 | 2.43 |
| ML@CS | 59.34 | 0.207 | 2.25 |
| T/K | Freundlich | Langmuir | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kF/(mg1−1/n·L1/n/g) | 1/n | R2 | Qmax/(mg/g) | kL/(L/mg) | R2 | |
| 298 | 67.61 | 0.325 | 0.897 | 259.76 | 0.189 | 0.997 |
| C0/ (mg/L) | Qe, exp/ (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kf/min−1 | Qe/(mg/g) | R2 | ks/(g/mg·min) | Qe/(mg/g) | R2 | ||
| 200 | 199.52 | 0.044 | 181.13 | 0.977 | 0.0003 | 200.00 | 0.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.; Song, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L. Preparation of Composites Derived from Modified Loess/Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance for Methyl Orange. Molecules 2024, 29, 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215052
Hu H, Song H, Cheng Z, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Hu H, Zhang L. Preparation of Composites Derived from Modified Loess/Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance for Methyl Orange. Molecules. 2024; 29(21):5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215052
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Haobin, Haiyan Song, Zhenyu Cheng, Yufeng Wang, Qi Zhang, Huaisheng Hu, and Lala Zhang. 2024. "Preparation of Composites Derived from Modified Loess/Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance for Methyl Orange" Molecules 29, no. 21: 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215052
APA StyleHu, H., Song, H., Cheng, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, Q., Hu, H., & Zhang, L. (2024). Preparation of Composites Derived from Modified Loess/Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance for Methyl Orange. Molecules, 29(21), 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215052





