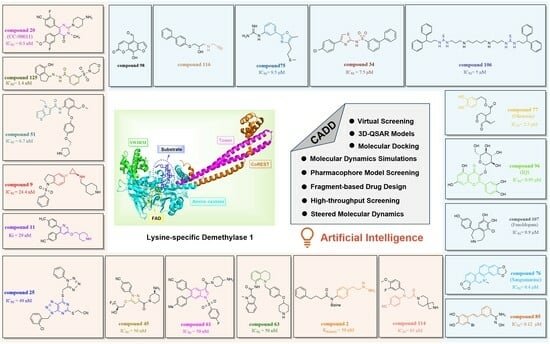
Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review Utilizing Computer-Aided Drug Design Technologies
Abstract
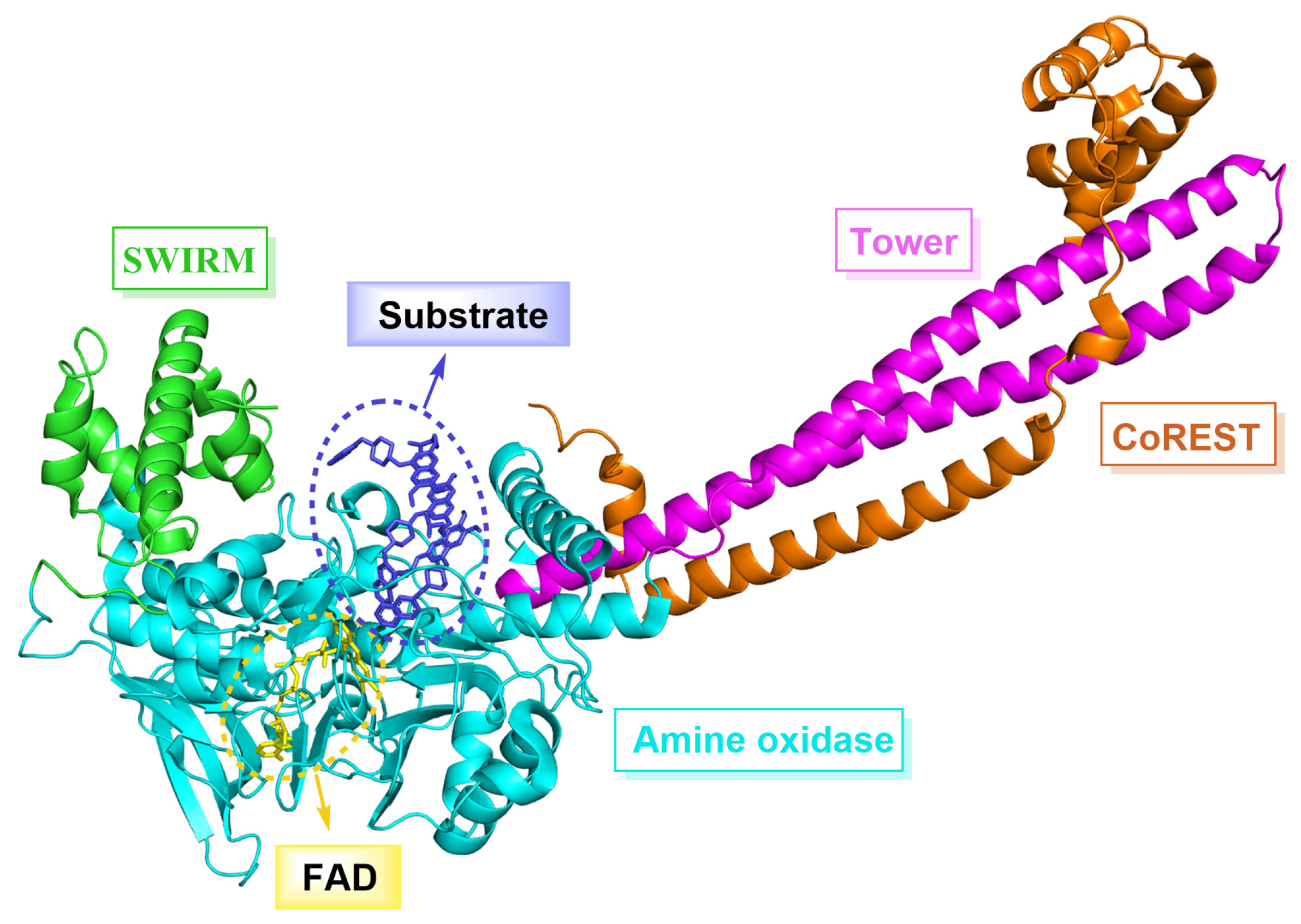
1. Introduction
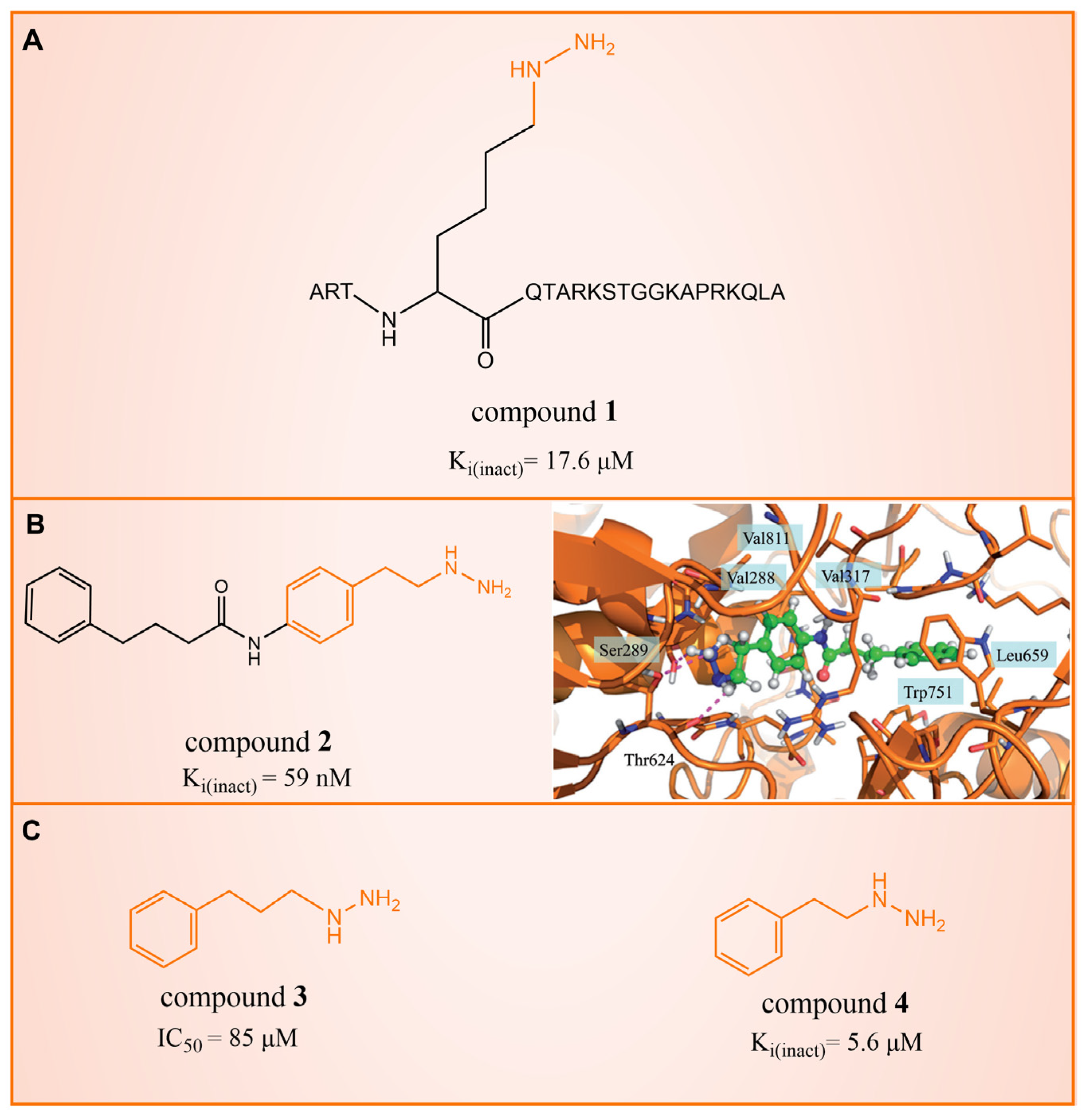
2. Phenelzine Derivatives
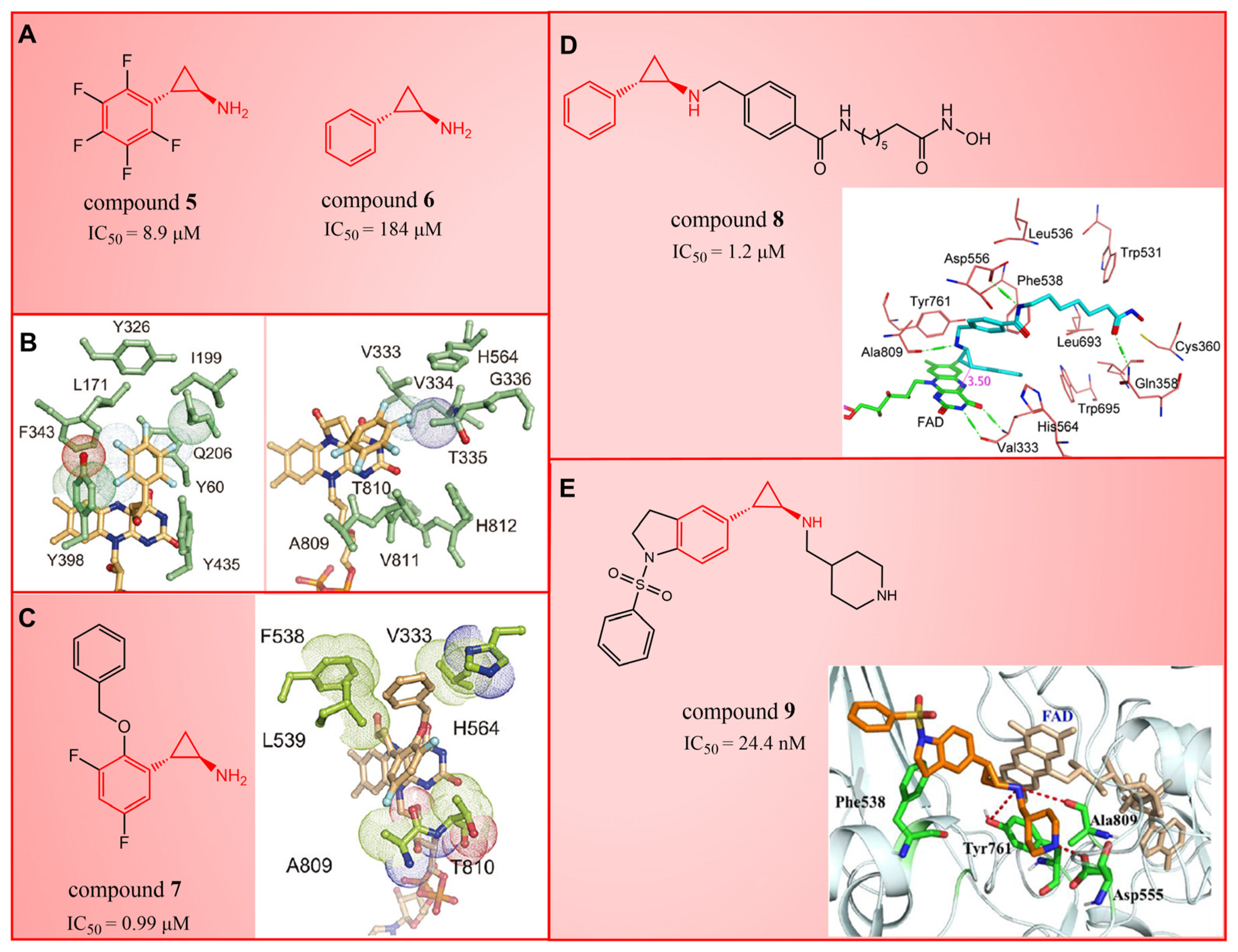
3. Tranylcypromine (TCP/2-PCPA) Derivatives
4. Nitrogen-Containing Heterocyclic Derivatives
4.1. Pyridine Derivatives
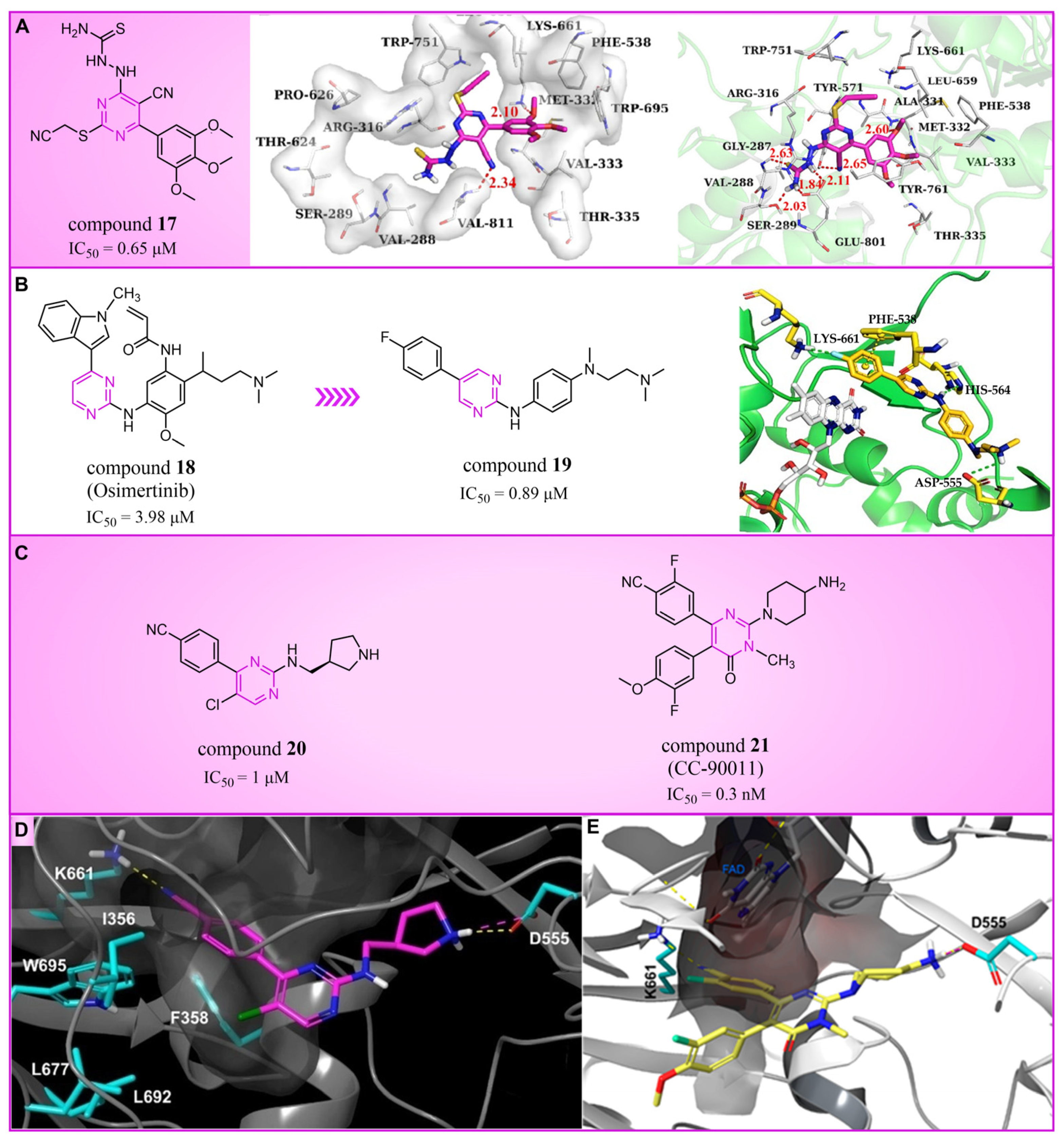
4.2. Pyrimidine Derivatives
4.3. Azole Derivatives
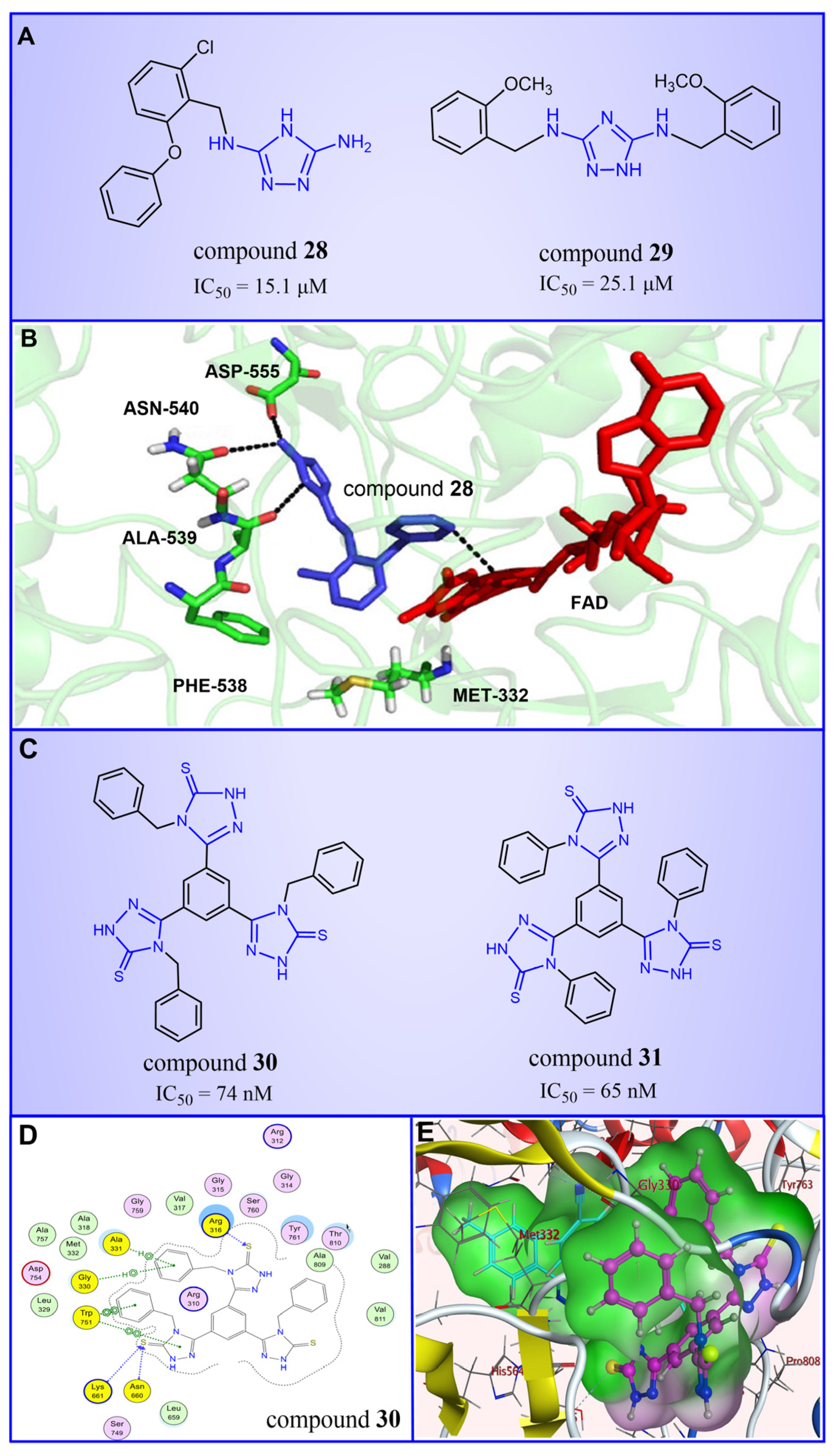
4.3.1. Triazole Derivatives
4.3.2. Thiazole Derivatives
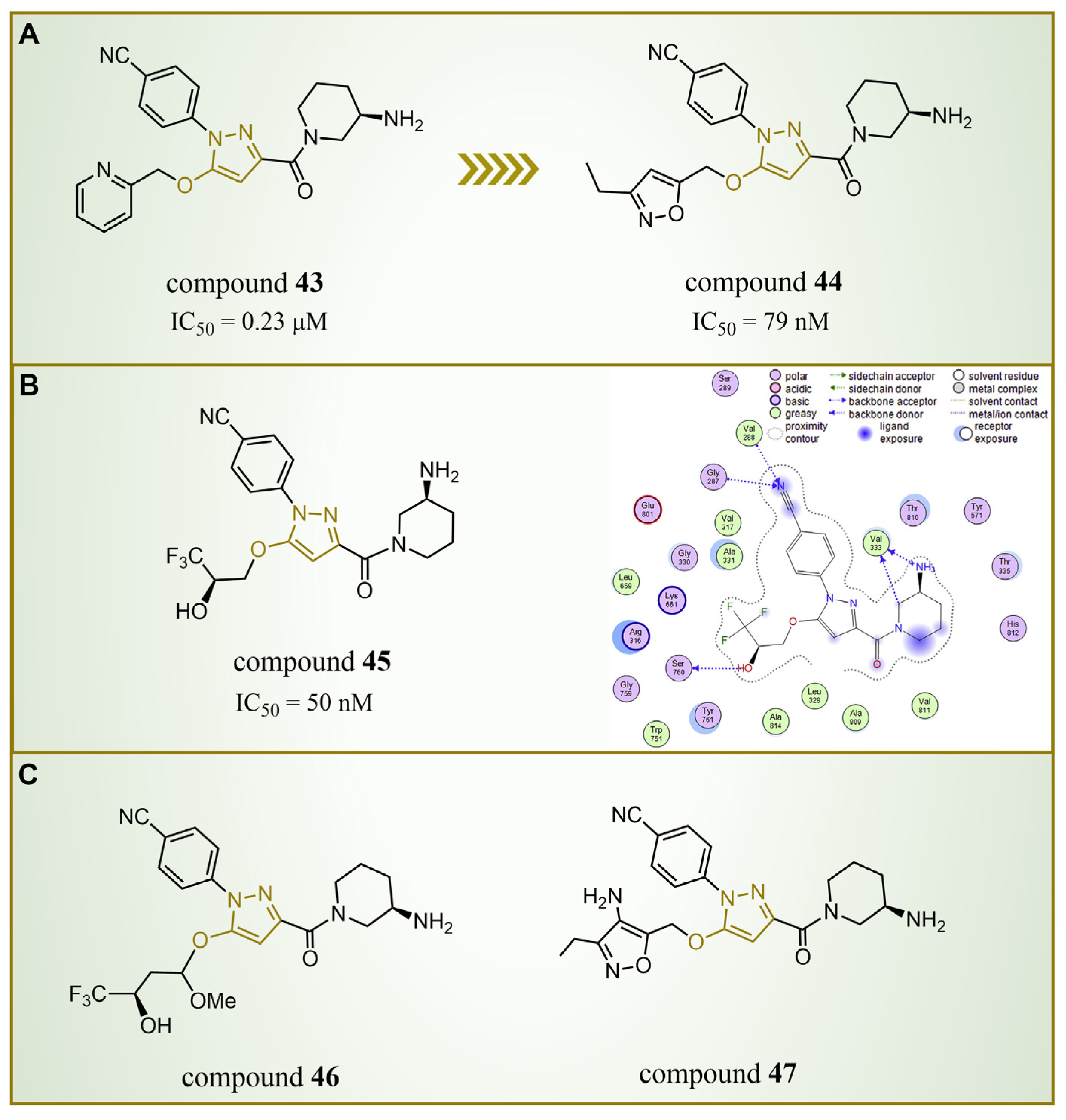
4.3.3. Pyrazole Derivatives
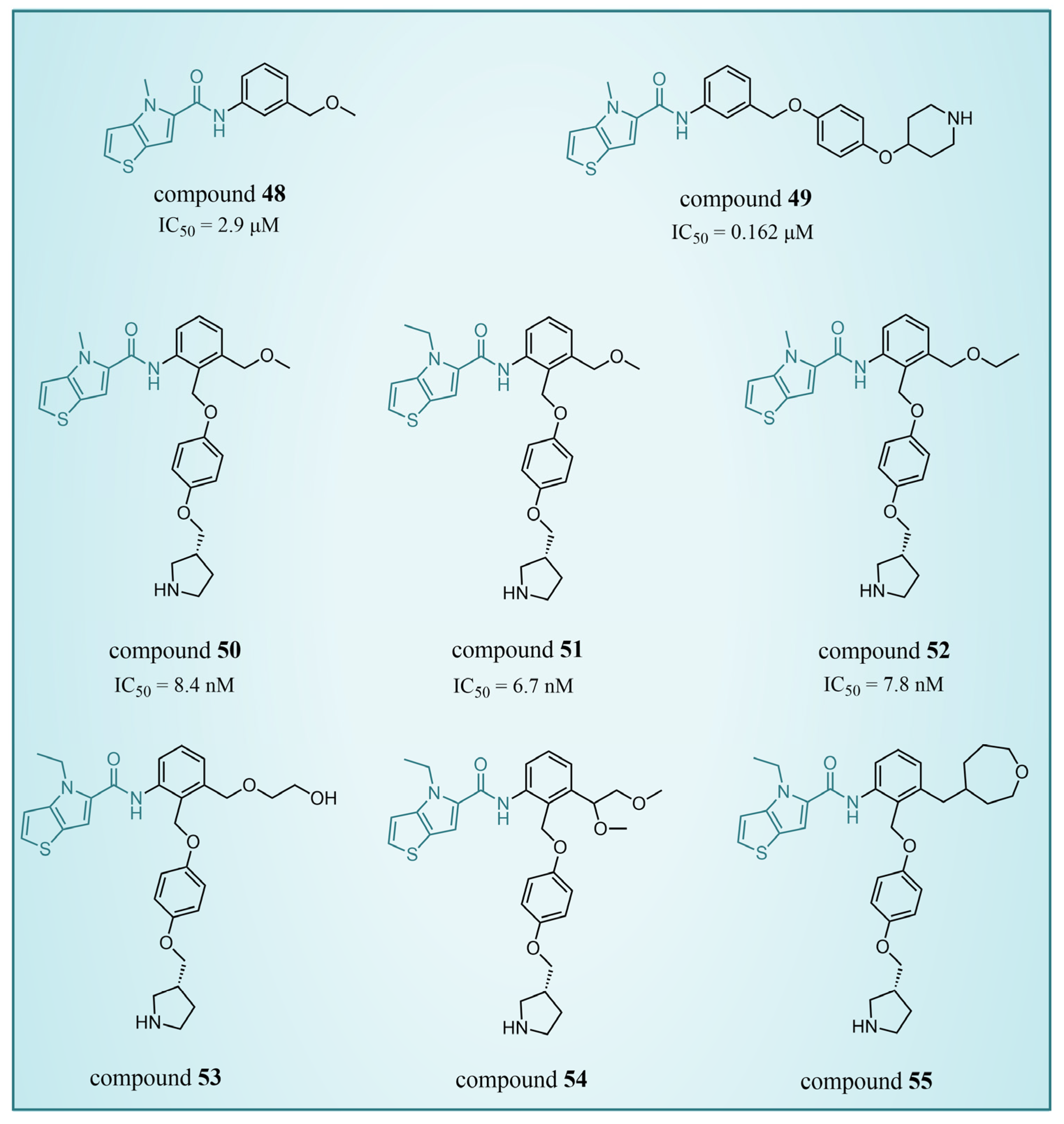
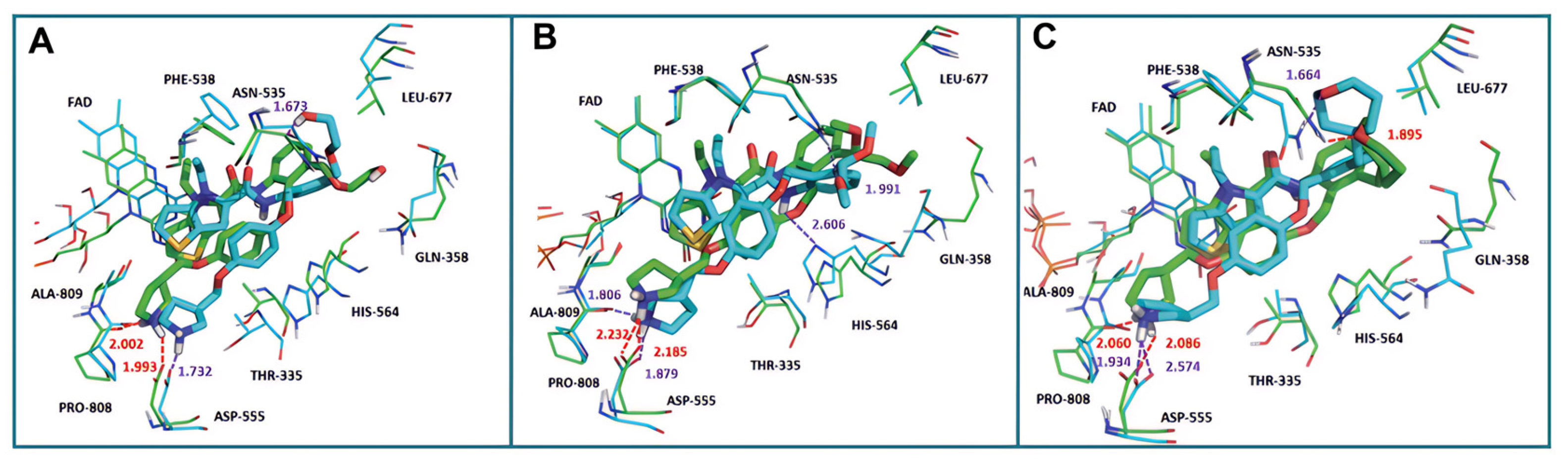
4.4. Thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole Derivatives
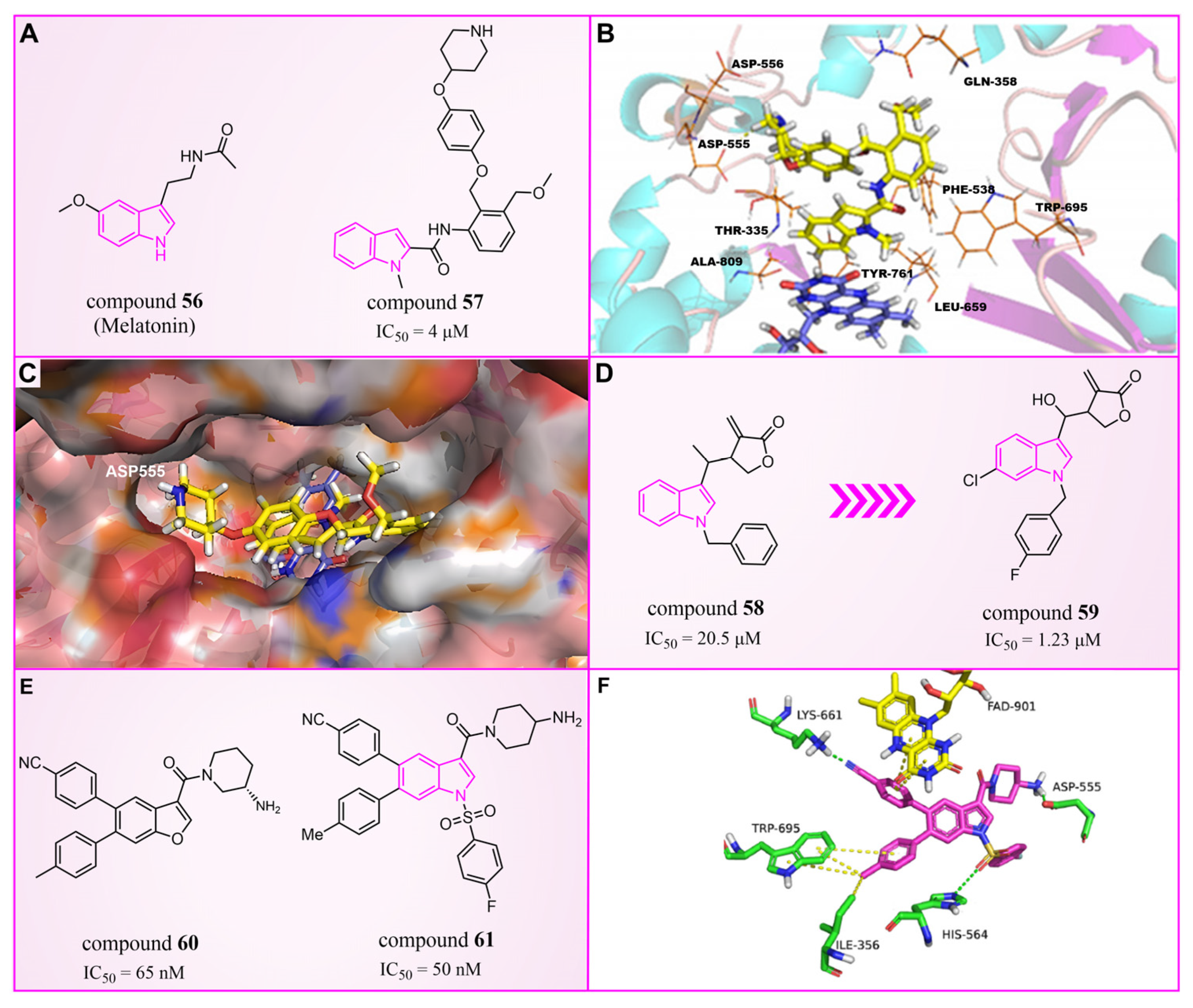
4.5. Indole Derivatives
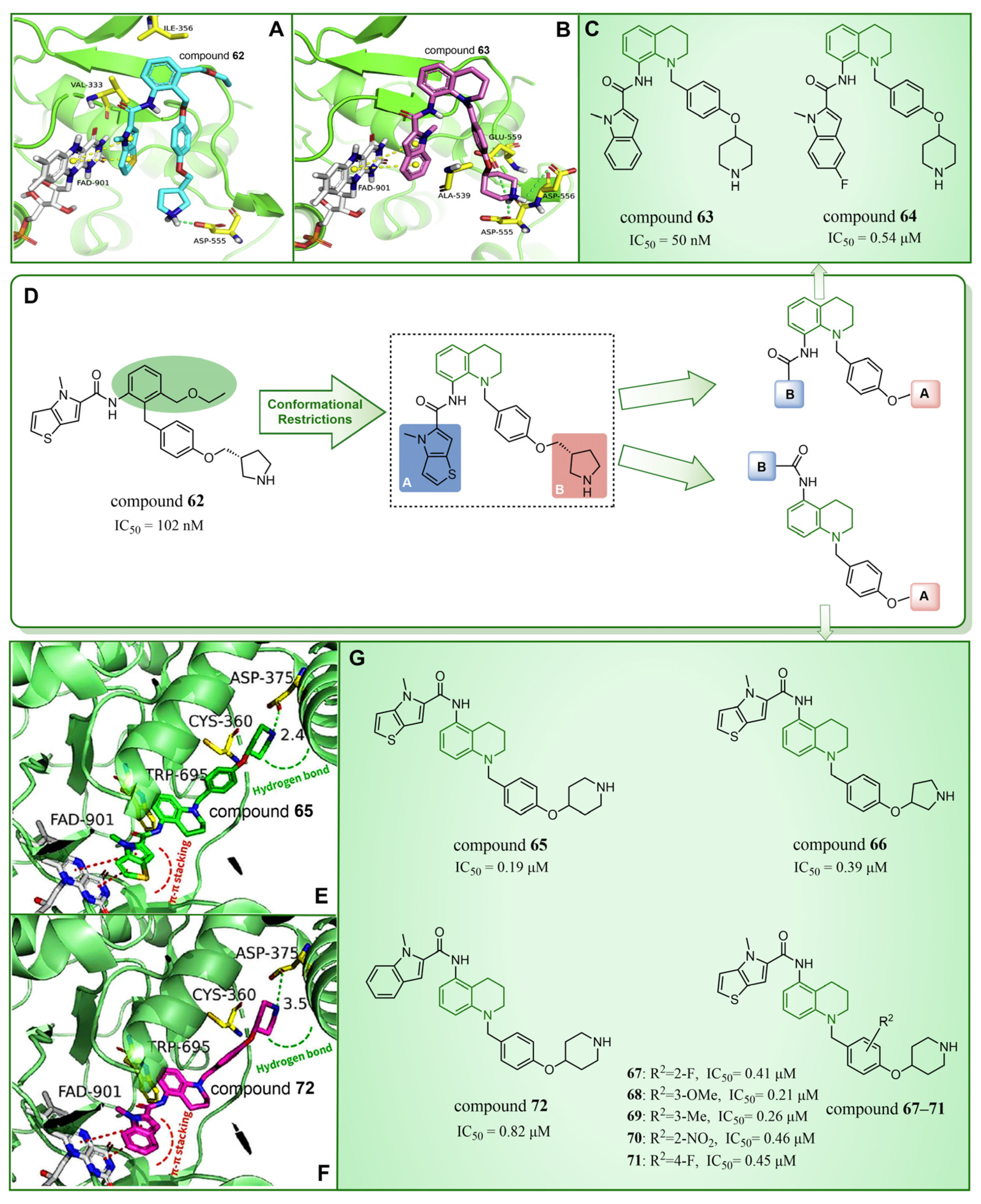
4.6. Quinoline Derivatives
4.7. Phenyloxazole Derivatives
5. Natural Products
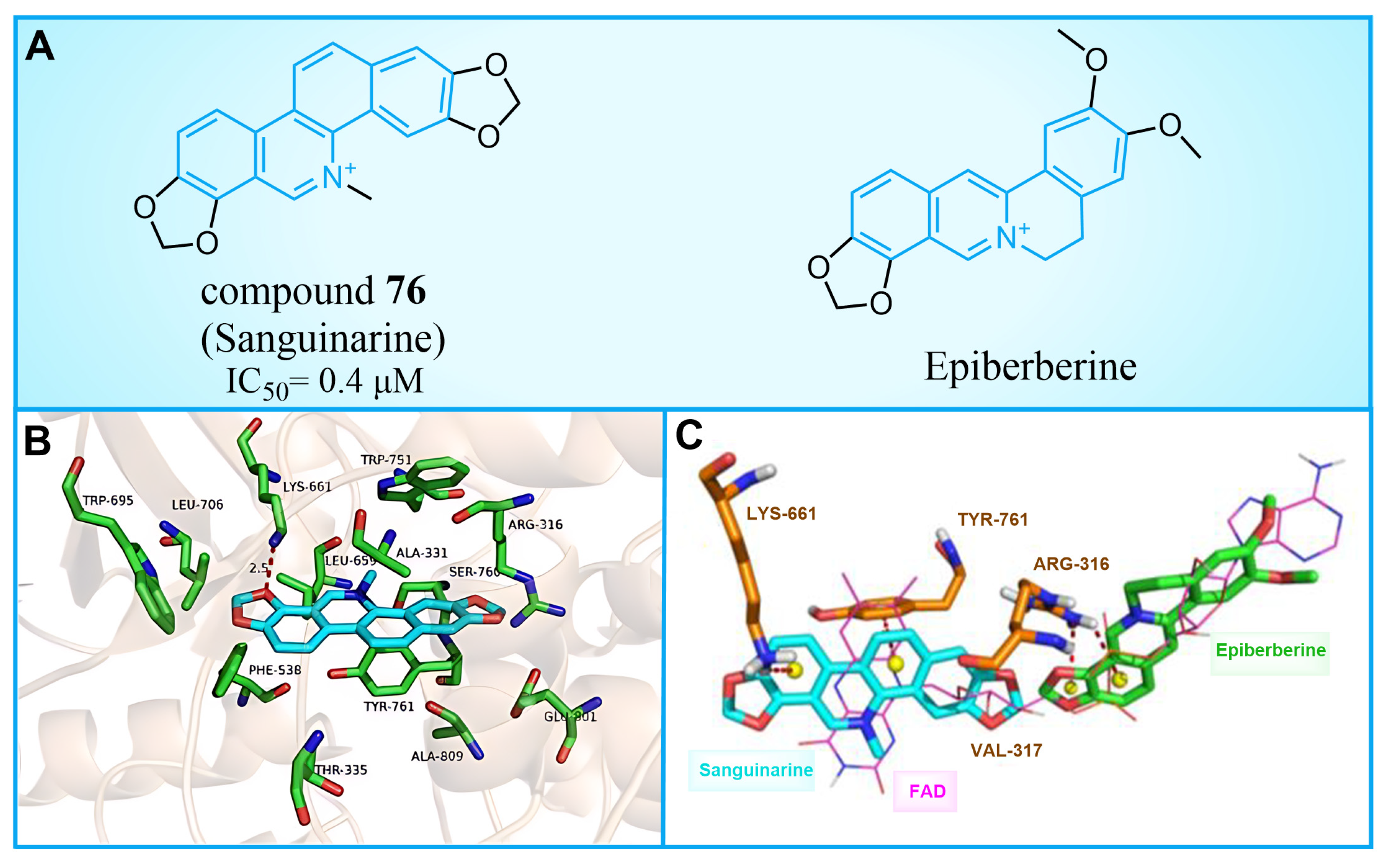
5.1. Sanguinarine
5.2. Phenolic Compounds
5.3. Resveratrol Derivatives
5.4. Flavonoids
5.5. Other Natural Products
6. Others
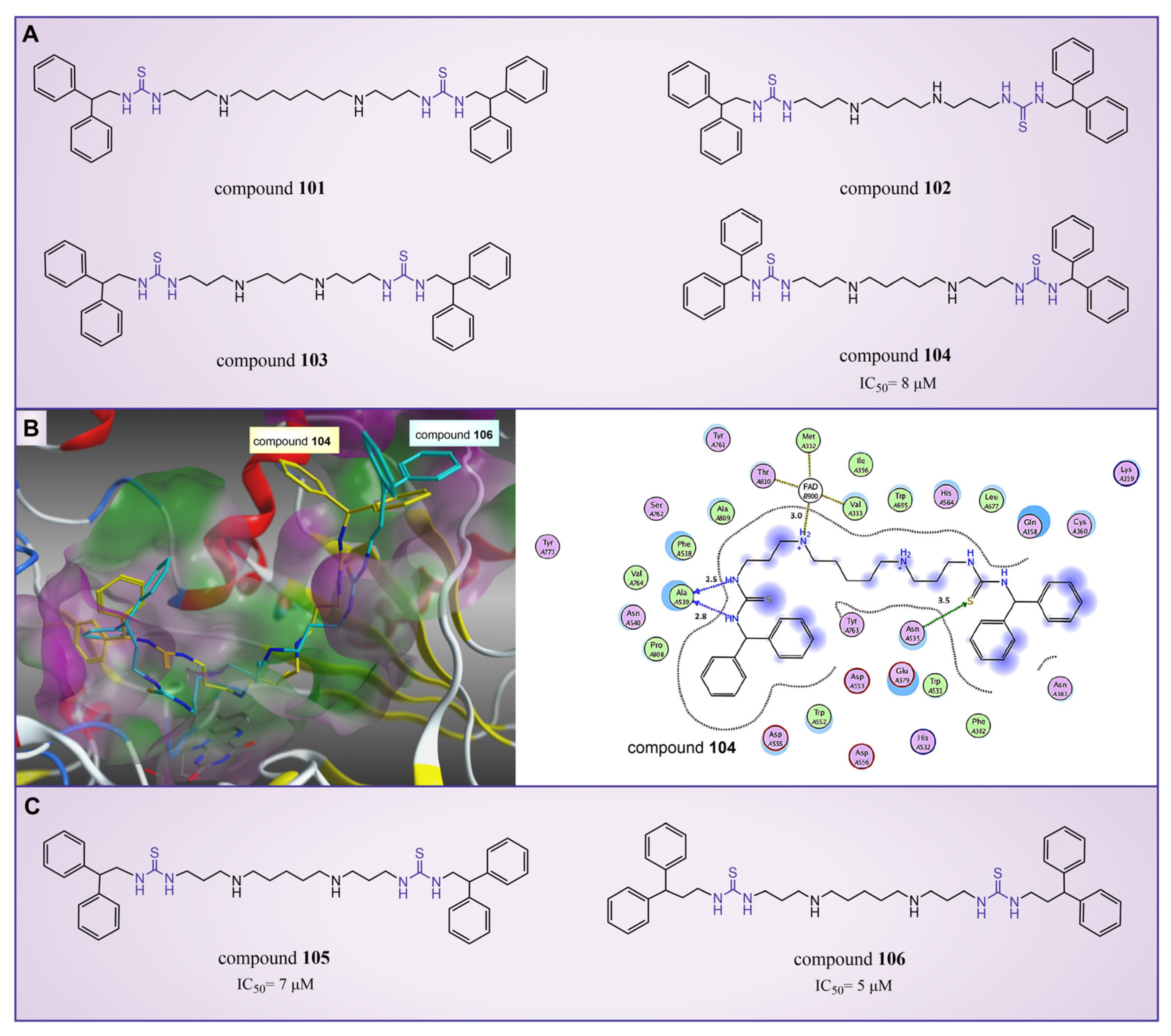
6.1. Thiourea Compounds
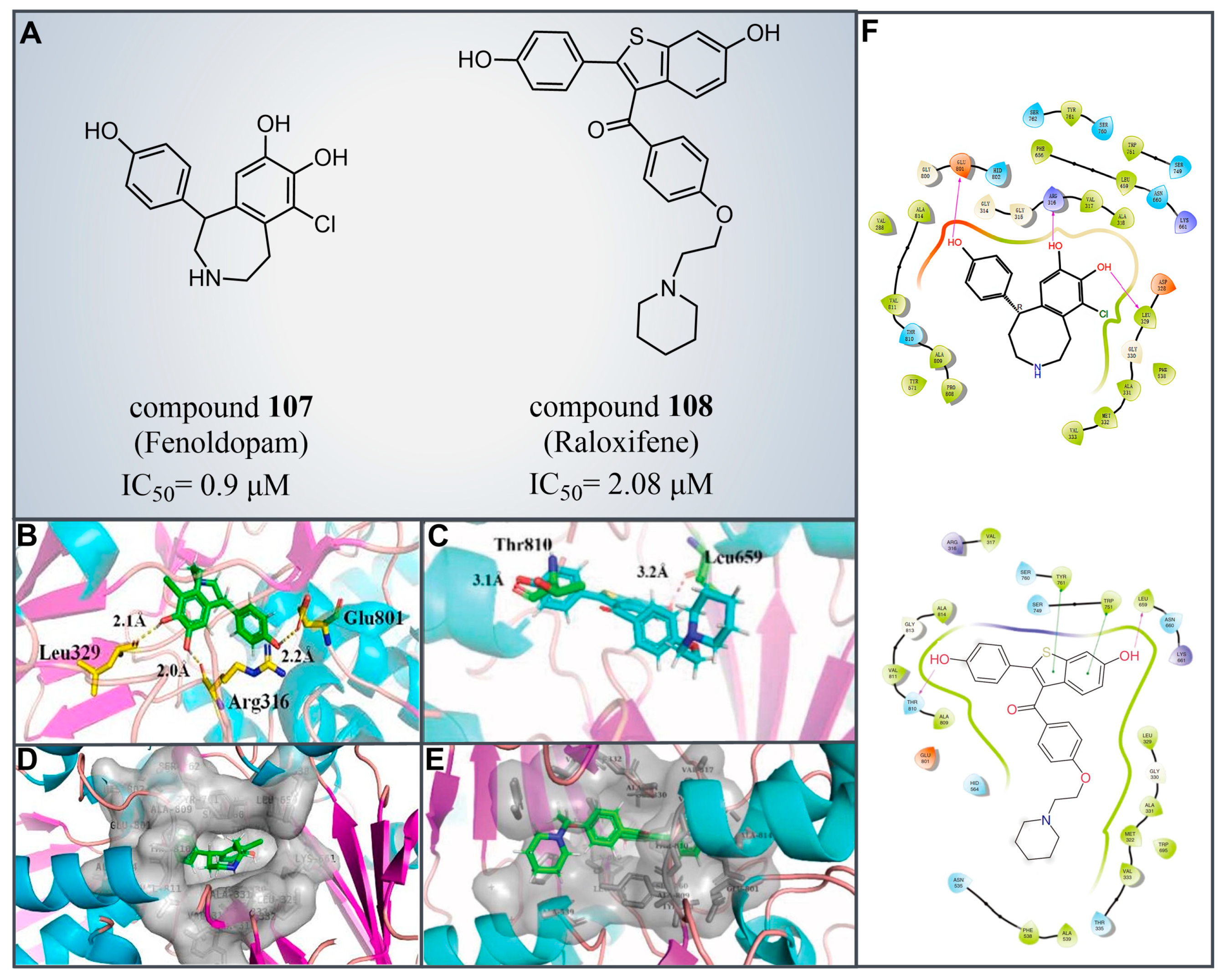
6.2. Fenoldopam and Raloxifene
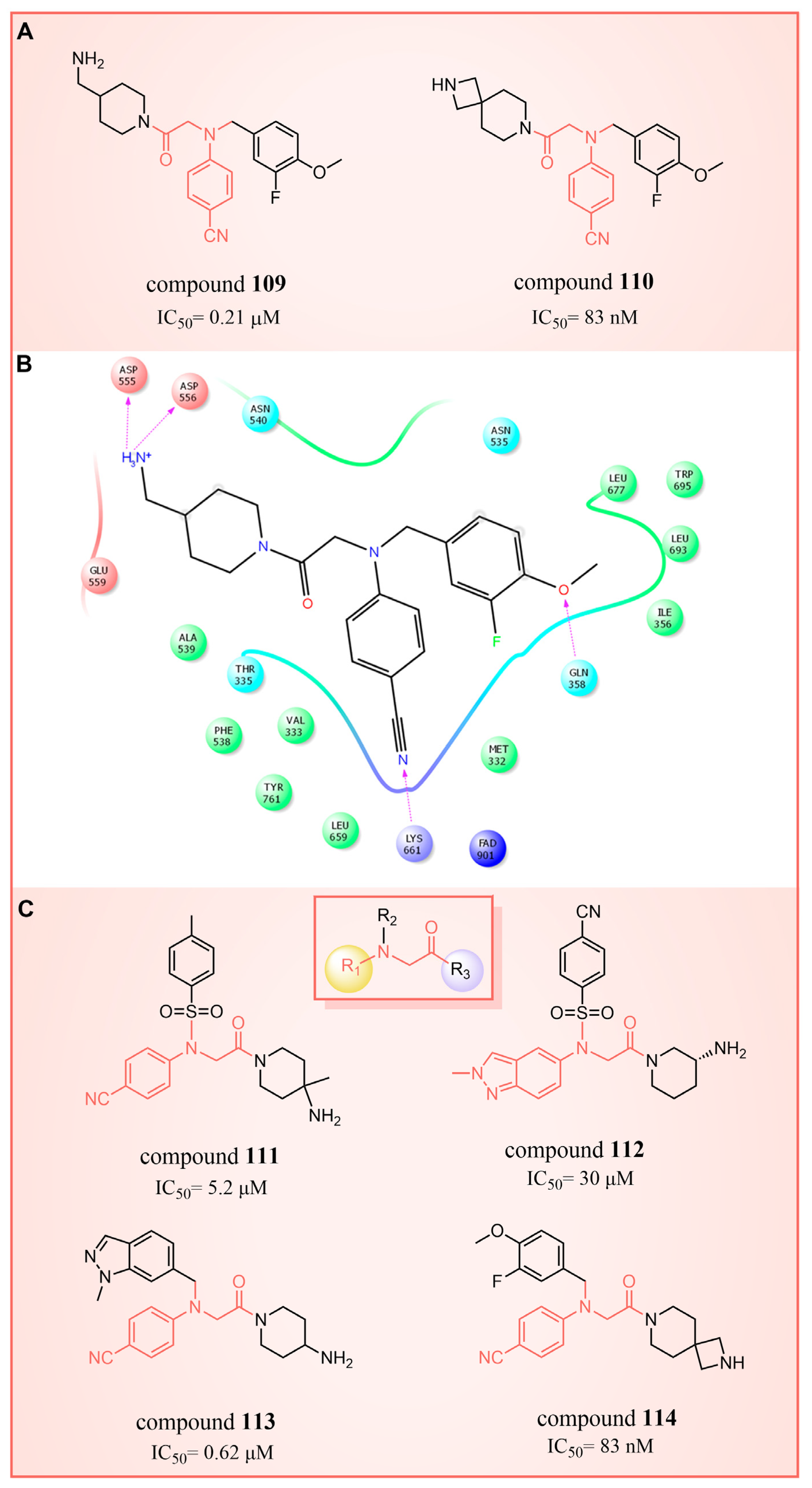
6.3. (4-Cyanophenyl)glycine Derivatives
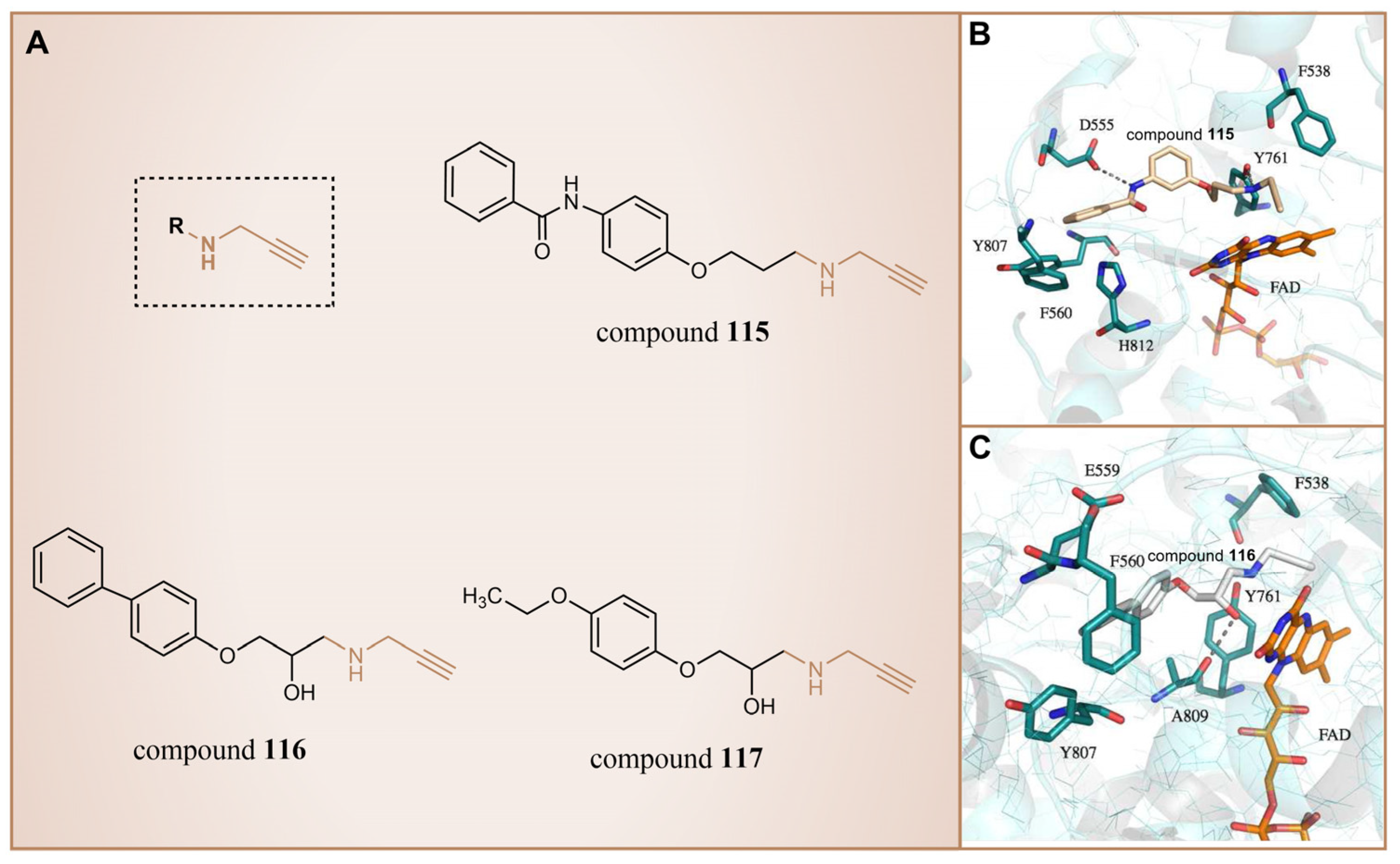
6.4. Propargylamine Derivatives
6.5. Benzoylhydrazine Derivatives
6.6. LSD1 Inhibitors Discovered through Artificial Intelligence Techniques
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 2000, 403, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, P.A. Chemical probes for histone-modifying enzymes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losi, L.; Lauriola, A.; Tazzioli, E.; Gozzi, G.; Scurani, L.; D’Arca, D.; Benhattar, J. Involvement of epigenetic modification of TERT promoter in response to all-trans retinoic acid in ovarian cancer cell lines. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Lan, F.; Matson, C.; Mulligan, P.; Whetstine, J.R.; Cole, P.A.; Casero, R.A.; Shi, Y. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 2004, 119, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.-W.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Duan, Y.-C.; Wang, M.-M.; Yu, B.; Ren, J.-L.; Ma, J.-L.; Zhang, E.; Liu, H.-M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin–1,2,3-triazole–dithiocarbamate hybrids as potent LSD1 inhibitors. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooden, D.M.; Schmidt, D.M.; Pollock, J.A.; Kabadi, A.M.; McCafferty, D.G. Facile synthesis of substituted trans-2-arylcyclopropylamine inhibitors of the human histone demethylase LSD1 and monoamine oxidases A and B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3047–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forneris, F.; Battaglioli, E.; Mattevi, A.; Binda, C. New roles of flavoproteins in molecular cell biology: Histone demethylase LSD1 and chromatin. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Schmitt, A.A.; Luteran, A.E.; Toone, E.J.; McCafferty, D.G. Thermodynamic characterization of the binding interaction between the histone demethylase LSD1/KDM1 and CoREST. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egolf, S.; Aubert, Y.; Doepner, M.; Anderson, A.; Maldonado-Lopez, A.; Pacella, G.; Lee, J.; Ko, E.K.; Zou, J.; Lan, Y.; et al. LSD1 inhibition promotes epithelial differentiation through derepression of fate-determining transcription factors. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 1981–1992.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, A.; Sesé, B.; Boue, S.; Castaño, J.; Paramonov, I.; Barrero, M.J.; Belmonte, J.C.I. LSD1 regulates the balance between self-renewal and differentiation in human embryonic stem cells. Nature 2011, 13, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokken, A.A.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J. Breaking the LSD1/KDM1A addiction: Therapeutic targeting of the epigenetic modifier in AML. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, R.J.; Zhang, Y. Regulation of histone methylation by demethylimination and demethylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozub, M.M.; Carr, R.M.; Lomberk, G.L.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. LSD1, a double-edged sword, confers dynamic chromatin regulation but commonly promotes aberrant cell growth. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forneris, F.; Binda, C.; Battaglioli, E.; Mattevi, A. LSD1: Oxidative chemistry for multifaceted functions in chromatin regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Sengupta, R.; Espejo, A.B.; Lee, M.G.; Dorsey, J.A.; Richter, M.; Opravil, S.; Shiekhattar, R.; Bedford, M.T.; Jenuwein, T. p53 is regulated by the lysine demethylase LSD1. Nature 2007, 449, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hevi, S.; Kurash, J.K.; Lei, H.; Gay, F.; Bajko, J.; Su, H.; Sun, W.; Chang, H.; Xu, G. The lysine demethylase LSD1 (KDM1) is required for maintenance of global DNA methylation. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Dasgupta, M.; Sears, N.; Miyagi, M.; Wang, B.; Chance, M.R.; Chen, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y. Reversible methylation of promoter-bound STAT3 by histone-modifying enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21499–21504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontaki, H.; Talianidis, I. Lysine methylation regulates E2F1-induced cell death. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-S.; Suzuki, T.; Dohmae, N.; Hayami, S.; Unoki, M.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Toyokawa, G.; Takawa, M.; Chen, T.; Kurash, J.K. Demethylation of RB Regulator MYPT1 by Histone Demethylase LSD1 Promotes Cell Cycle Progression in Cancer CellsDemethylation of MYPT1 in Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketscher, A.; Jilg, C.; Willmann, D.; Hummel, B.; Imhof, A.; Rüsseler, V.; Hölz, S.; Metzger, E.; Müller, J.; Schüle, R. LSD1 controls metastasis of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells through PXN and LPAR6. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Janzer, A.; Becker, A.; Zimmer, A.; Schüle, R.; Buettner, R.; Kirfel, J. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) is highly expressed in ER-negative breast cancers and a biomarker predicting aggressive biology. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Shan, J.; Shen, J.; Qian, C. LSD1 Stimulates Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts to Drive Notch3-Dependent Self-Renewal of Liver Cancer Stem–like CellsLSD1 Regulates Liver CSC Self-Renewal via Notch3 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-M.; Lang, W.-Y.; Yao, L.-J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.-L.J.W. shRNA-interfering LSD1 inhibits proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells via VEGF-C/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiques-Diaz, A.; Spencer, G.J.; Lynch, J.T.; Ciceri, F.; Williams, E.L.; Amaral, F.M.; Wiseman, D.H.; Harris, W.J.; Li, Y.; Sahoo, S. Enhancer activation by pharmacologic displacement of LSD1 from GFI1 induces differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3641–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerenyi, M.A.; Shao, Z.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Guo, G.; Luc, S.; O’Brien, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Peng, C.; Nguyen, M.; Orkin, S.H. Histone demethylase Lsd1 represses hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell signatures during blood cell maturation. eLife 2013, 2, e00633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojoga, L.H.; Williams, J.S.; Yao, T.M.; Kumar, A.; Raffetto, J.D.; do Nascimento, G.R.; Reslan, O.M.; Adler, G.K.; Williams, G.H.; Shi, Y.; et al. Histone demethylase LSD1 deficiency during high-salt diet is associated with enhanced vascular contraction, altered NO-cGMP relaxation pathway, and hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1862–H1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mould, D.P.; McGonagle, A.E.; Wiseman, D.H.; Williams, E.L.; Jordan, A.M. Reversible inhibitors of LSD1 as therapeutic agents in acute myeloid leukemia: Clinical significance and progress to date. Med. Res. Rev. 2015, 35, 586–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egolf, S.; Capell, B.C. LSD1: A viable therapeutic target in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Zhou, S.-F.; Gao, S.-H.; Yu, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.-F.; Tang, M.-K.; Sun, J.-N.; Ma, D.-L.; Han, Y.-F.; Fong, W.-F.; et al. New perspectives on how to discover drugs from herbal medicines: CAM’s outstanding contribution to modern therapeutics. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 627375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.M.; Mytelka, D.S.; Dunwiddie, C.T.; Persinger, C.C.; Munos, B.H.; Lindborg, S.R.; Schacht, A.L. How to improve R&D productivity: The pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, M.; Gagnon, J.P. Key factors in the rising cost of new drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Cao, Y.; Fan, W.; Chen, L.; Mo, Y. Computer-aided drug design: Lead discovery and optimization. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2012, 15, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.H.; Ahmad, K.; Rabbani, G.; Danishuddin, M.; Choi, I. Computer aided drug design and its application to the development of potential drugs for neurodegenerative disorders. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2018, 16, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaraj, B.; Al-Subaie, A.M.; Ahmad, F.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Alsamman, K. Effect of novel leukemia mutations (K75E & E222K) on interferon regulatory factor 1 and its interaction with DNA: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations and docking studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 5235–5247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, S. Discovery of boceprevir, a direct-acting NS3/4A protease inhibitor for treatment of chronic hepatitis C infections. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Wynder, C.; Schmidt, D.M.; McCafferty, D.G.; Shiekhattar, R. Histone H3 lysine 4 demethylation is a target of nonselective antidepressive medications. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culhane, J.C.; Wang, D.; Yen, P.M.; Cole, P.A. Comparative analysis of small molecules and histone substrate analogues as LSD1 lysine demethylase inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3164–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Diwu, Z.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N.; Haugland, R.P. A stable nonfluorescent derivative of resorufin for the fluorometric determination of trace hydrogen peroxide: Applications in detecting the activity of phagocyte NADPH oxidase and other oxidases. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusevich, P.; Kalin, J.H.; Ming, S.A.; Basso, M.; Givens, J.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Taylor, M.S.; Cieniewicz, A.M.; Hsiao, P.Y.; et al. A selective phenelzine analogue inhibitor of histone demethylase LSD1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Insight into the binding mode of a novel LSD1 inhibitor by molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2015, 35, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Lim-Wilby, M. Molecular docking. Mol. Model. Proteins 2008, 443, 365–382. [Google Scholar]
- Raval, K.; Ganatra, T. Basics, types and applications of molecular docking: A review. IP Int. J. Compr. Adv. Pharmacol. 2022, 7, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular dynamics simulation for all. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Purohit, R. Computational investigation on effect of mutations in PCNA resulting in structural perturbations and inhibition of mismatch repair pathway. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 38, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaraj, B.; Purohit, R. Mutational analysis on membrane associated transporter protein (MATP) and their structural consequences in oculocutaeous albinism type 4 (OCA4)—A molecular dynamics approach. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 2608–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salo-Ahen, O.M.; Alanko, I.; Bhadane, R.; Bonvin, A.M.; Honorato, R.V.; Hossain, S.; Juffer, A.H.; Kabedev, A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Larsen, A.S. Molecular dynamics simulations in drug discovery and pharmaceutical development. Processes 2020, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V.; Sethumadhavan, R. Drug resistance mechanism of PncA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimasu, S.; Sengoku, T.; Fukuzawa, S.; Umehara, T.; Yokoyama, S. Crystal structure of histone demethylase LSD1 and tranylcypromine at 2.25 A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Li, M.; Hubalek, F.; Restelli, N.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Insights into the mode of inhibition of human mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B from high-resolution crystal structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9750–9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimasu, S.; Umezawa, N.; Sato, S.; Higuchi, T.; Umehara, T.; Yokoyama, S. Structurally designed trans-2-phenylcyclopropylamine derivatives potently inhibit histone demethylase LSD1/KDM1. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6494–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.C.; Ma, Y.C.; Qin, W.P.; Ding, L.N.; Zheng, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhai, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.Y.; Guan, Y.Y. Design and synthesis of tranylcypromine derivatives as novel LSD1/HDACs dual inhibitors for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Su, M.; Zhu, W.; Kan, W.; Ge, T.; Xu, G.; Wang, S.; Sheng, L.; Gao, F.; Ye, Y.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Indolin-5-yl-cyclopropanamine Derivatives as Selective Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 4335–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanak, D. Drugging the cancer epigenome. In Proceedings of the 104th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Washington, DC, USA, 6–10 April 2013; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hitchin, J.R.; Blagg, J.; Burke, R.; Burns, S.; Cockerill, M.J.; Fairweather, E.E.; Hutton, C.; Jordan, A.M.; McAndrew, C.; Mirza, A.J.M. Development and evaluation of selective, reversible LSD1 inhibitors derived from fragments. MedChemComm 2013, 4, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, C.; Yao, Y.; Wei, L.; Feng, Z.; Deng, L.; Song, Y. 3-(Piperidin-4-ylmethoxy) pyridine containing compounds are potent inhibitors of lysine specific demethylase 1. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, X.-D.; Ma, C.-Y.; Gao, Q.-B.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.-M.J. Probing the binding mechanism of substituted pyridine derivatives as effective and selective lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitors using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 37, 3482–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A.; Christou, N. 5-Fluorouracil resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer: From classical pathways to promising processes. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3142–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versporten, A.; Bruyndonckx, R.; Adriaenssens, N.; Hens, N.; Monnet, D.L.; Molenberghs, G.; Goossens, H.; Weist, K.; Coenen, S.J. Consumption of tetracyclines, sulphonamides and trimethoprim, and other antibacterials in the community, European Union/European Economic Area, 1997–2017. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, ii45–ii59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conneely, S.E.; Cooper, S.L.; Rau, R.E. Use of allopurinol to mitigate 6-mercaptopurine associated gastrointestinal toxicity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, B.; Yurttaş, L.; Sağlik, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancikli, Z.A. Novel 1-(2-pyrimidin-2-yl) piperazine derivatives as selective monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivara, S.; Piersanti, G.; Bartoccini, F.; Diamantini, G.; Pala, D.; Riccioni, T.; Stasi, M.A.; Cabri, W.; Borsini, F.; Mor, M.; et al. Synthesis of (E)-8-(3-chlorostyryl) caffeine analogues leading to 9-deazaxanthine derivatives as dual A2A antagonists/MAO-B inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotti, A.; Catto, M.; Leonetti, F.; Campagna, F.; Soto-Otero, R.; Méndez-Álvarez, E.; Thull, U.; Testa, B.; Altomare, C. Synthesis and monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity of new pyridazine-, pyrimidine-and 1,2,4-triazine-containing tricyclic derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5364–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.-R.; Pang, L.-P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.-W.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; et al. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of novel LSD1 inhibitors based on pyrimidine-thiourea hybrids as potent, orally active antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Sun, X.-D.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.-Y.; Li, W.; Liu, H.-M. 3D-QSAR (CoMFA, CoMSIA), molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations study of 6-aryl-5-cyano-pyrimidine derivatives to explore the structure requirements of LSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3521–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-R.; Suo, F.-Z.; Hu, B.; Guo, Y.-J.; Fu, D.-J.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-M. Identification of osimertinib (AZD9291) as a lysine specific demethylase 1 inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, M. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-aminopyrimidine-based LSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 121, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanouni, T.; Severin, C.; Cho, R.W.; Yuen, N.Y.-Y.; Xu, J.; Shi, L.; Lai, C.; Del Rosario, J.R.; Stansfield, R.K.; Lawton, L.N.; et al. Discovery of CC-90011: A potent and selective reversible inhibitor of lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1). J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 14522–14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.J.W.C. Progress in anti-tumor agents: Triazoles. Arch. Pharm. 2008, 23, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; ChengHe, Z. Recent advances in the researches of triazole compounds as medicinal drugs. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2011, 41, 1429–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.H.; Wang, Y. Recent researches in triazole compounds as medicinal drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 239–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.-C.; Ma, Y.-C.; Zhang, E.; Shi, X.-J.; Wang, M.-M.; Ye, X.-W.; Liu, H.-M. Design and synthesis of novel 1,2,3-triazole-dithiocarbamate hybrids as potential anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-C.; Duan, Y.-C.; Ma, J.-L.; Xu, R.-M.; Zi, X.; Lv, W.-L.; Wang, M.-M.; Ye, X.-W.; Zhu, S.; Mobley, D.; et al. Triazole–dithiocarbamate based selective lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inactivators inhibit gastric cancer cell growth, invasion, and migration. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8543–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.-M. Probing the binding mode and unbinding mechanism of LSD1 inhibitors by combined computational methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 29833–29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-D.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Ma, C.-Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Q.-B.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Li, W.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H.-M.; et al. Identifying the novel inhibitors of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) combining pharmacophore-based and structure-based virtual screening. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 37, 4200–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-H.; Liu, X.-Q.; Geng, P.-F.; Suo, F.-Z.; Ma, J.-L.; Yu, B.; Zhao, T.-Q.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Huang, C.-X.; Zheng, Y.-C.; et al. Discovery of [1,2,3]Triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives as novel LSD1 inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ding, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Suo, F.; Shen, D.; Zhao, T.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Development of the triazole-fused pyrimidine derivatives as highly potent and reversible inhibitors of histone lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A). Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Ma, J.-L.; Liu, G.-Z.; Zhang, X.-H.; Qin, T.-T.; Ren, W.-H.; Zhao, T.-Q.; Chen, X.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Q. [1,2,3]Triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives incorporating (thio) urea moiety as a novel scaffold for LSD1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, H.; You, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H. Exploration of 5-cyano-6-phenylpyrimidin derivatives containing an 1, 2, 3-triazole moiety as potent FAD-based LSD1 inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, C.J.; Holshouser, S.L.; Marrow, E.A.; Woster, P.M. 3,5-Diamino-1,2,4-triazoles as a novel scaffold for potent, reversible LSD1 (KDM1A) inhibitors. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsehli, M.; Aljuhani, A.; Ihmaid, S.K.; El-Messery, S.M.; Othman, D.I.; El-Sayed, A.-A.A.; Ahmed, H.E.; Rezki, N.; Aouad, M.R. Design and Synthesis of Benzene Homologues Tethered with 1,2,4-Triazole and 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Motifs Revealing Dual MCF-7/HepG2 Cytotoxic Activity with Prominent Selectivity via Histone Demethylase LSD1 Inhibitory Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltarollo, V.G.; Honório, K.M.; Emery, F.S.; Ganesan, A.; Trossini, G.H. Hologram quantitative structure–activity relationship and comparative molecular interaction field analysis of aminothiazole and thiazolesulfonamide as reversible LSD1 inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnabulsi, S.; Al-Hurani, E.A.; El-Elimat, T. Amino-carboxamide benzothiazoles as potential LSD1 hit inhibitors. Part I: Computational fragment-based drug design. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2019, 93, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.-J.; Liu, Y.; Xue, L.-P.; Xiong, X.-P.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-M. Reversible lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inhibitors: A promising wrench to impair LSD1. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2466–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mould, D.P.; Bremberg, U.; Jordan, A.M.; Geitmann, M.; Maiques-Diaz, A.; McGonagle, A.E.; Small, H.F.; Somervaille, T.C.; Ogilvie, D. Development of 5-hydroxypyrazole derivatives as reversible inhibitors of lysine specific demethylase 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3190–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraj, K.; Asadollahi-Baboli, M. In silico evaluation of 5-hydroxypyrazoles as LSD1 inhibitors based on molecular docking derived descriptors. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1179, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, L.; Mercurio, C.; Amigoni, F.; Cappa, A.; Faga, G.; Fattori, R.; Legnaghi, E.; Ciossani, G.; Mattevi, A.; Meroni, G. Thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole-5-carboxamides as new reversible inhibitors of histone lysine demethylase KDM1A/LSD1. Part 1: High-throughput screening and preliminary exploration. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1673–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, P.; Sartori, L.; Amigoni, F.; Cappa, A.; Faga, G.; Fattori, R.; Legnaghi, E.; Ciossani, G.; Mattevi, A.; Meroni, G. Thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole-5-carboxamides as new reversible inhibitors of histone lysine demethylase KDM1A/LSD1. Part 2: Structure-based drug design and structure–activity relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1693–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z. 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation study of thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole-5-carboxamide derivatives as LSD1 inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 6927–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D. Molecular docking, 3D-QSAR, and molecular dynamics simulations of thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole derivatives against anticancer targets of KDM1A/LSD1. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sa Alves, F.R.; Barreiro, E.J.; Manssour Fraga, C.A. From nature to drug discovery: The indole scaffold as a ‘privileged structure’. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, A.-R. Synthesis of some new indole derivatives containing pyrazoles with potential antitumor activity. Arkivoc 2010, 11, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, G.W. Heterocyclic Scaffolds II: Reactions and Applications of Indoles; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-K.; Tsao, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Lin, G.-J.; Ma, K.-H.; Shieh, Y.-S.; Sytwu, H.-K.; Chen, Y.-W. Melatonin exerts anti-oral cancer effect via suppressing LSD1 in patient-derived tumor xenograft models. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Bi, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lan, F.; Zha, X. Design, synthesis and biological activity of 4-(4-benzyloxy) phenoxypiperidines as selective and reversible LSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 78, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-M.; Suo, F.-Z.; Li, X.-B.; You, Y.-H.; Lv, C.-T.; Zheng, C.-X.; Zhang, G.-C.; Liu, Y.-J.; Kang, W.-T.; Zheng, Y.-C. Discovery and synthesis of novel indole derivatives-containing 3-methylenedihydrofuran-2 (3H)-one as irreversible LSD1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 175, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Yin, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, D.; et al. Identification of novel indole derivatives as highly potent and efficacious LSD1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 239, 114523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, M. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of tetrahydroquinoline-based reversible LSD1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 194, 112243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Gu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, M. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 5-aminotetrahydroquinoline-based LSD1 inhibitors acting on Asp375. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, 2100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulla, B.; Kirla, K.T.; Rathore, V.; Deora, G.S.; Kavela, S.; Maddika, S.; Chatti, K.; Reiser, O.; Iqbal, J.; Pal, M. Synthesis and evaluation of 3-amino/guanidine substituted phenyl oxazoles as a novel class of LSD1 inhibitors with anti-proliferative properties. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 3103–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.T.; Li, Z.H.; Li, L.X.; Du, K.; Yang, J.G.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wu, X.X.; Ma, J.L. Sanguinarine, identified as a natural alkaloid LSD1 inhibitor, suppresses lung cancer cell growth and migration. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 781–788. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.R.; Suo, F.Z.; Guo, Y.J.; Cheng, H.F.; Niu, S.H.; Shen, D.D.; Zhao, L.J.; Liu, Z.Z.; Maa, M.; Yu, B.; et al. Natural protoberberine alkaloids, identified as potent selective LSD1 inhibitors, induce AML cell differentiation. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 97, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Design and identification of two novel resveratrol derivatives as potential LSD1 inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 1415–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Fan, T.; Li, W.; Xing, W.; Huang, H. The anti-inflammatory effects of sanguinarine and its modulation of inflammatory mediators from peritoneal macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 689, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigacci, S.; Stefani, M. Nutraceutical properties of olive oil polyphenols. An itinerary from cultured cells through animal models to humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboredo-Rodríguez, P.; Varela-López, A.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Gasparrini, M.; Afrin, S.; Cianciosi, D.; Zhang, J.; Manna, P.P.; Bompadre, S.; Quiles, J.L.; et al. Phenolic compounds isolated from olive oil as nutraceutical tools for the prevention and management of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, M.; Maggisano, V.; Lepore, S.M.; Russo, D.; Bulotta, S. Secoiridoids of olive and derivatives as potential coadjuvant drugs in cancer: A critical analysis of experimental studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Lepore, S.M.; Morittu, V.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Colica, C.; Procopio, A.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Costa, N.; Mignogna, C.J.F.i.E. Effects of oleacein on high-fat diet-dependent steatosis, weight gain, and insulin resistance in mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedret, A.; Fernández-Castillejo, S.; Valls, R.M.; Catalán, Ú.; Rubió, L.; Romeu, M.; Macià, A.; Lopez de las Hazas, M.C.; Farràs, M.; Giralt, M.; et al. Cardiovascular benefits of phenol-enriched virgin olive oils: New insights from the virgin olive oil and HDL functionality (VOHF) study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeloni, C.; Malaguti, M.; Barbalace, M.C.; Hrelia, S. Bioactivity of olive oil phenols in neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyàs, E.; Gumuzio, J.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Carreras, D.; Verdura, S.; Llorach-Parés, L.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Selga, E.; Pérez, G.J.; Scornik, F.S.; et al. Extra virgin olive oil contains a phenolic inhibitor of the histone demethylase LSD1/KDM1A. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsillou, E.; Liang, J.; Hung, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. Chromatin modification by olive phenolics: In silico molecular docking studies utilising the phenolic groups categorised in the OliveNet™ database against lysine specific demethylase enzymes. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2020, 97, 107575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, A.; Zhao, X.; Yang, F. Natural Polyphenols Inhibit Lysine-Specific Demethylase-1 in vitro. J. Biochem. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 1, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.-C.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Zhai, X.-Y.; Ding, L.-N.; Qin, W.-P.; Shen, D.-D.; Liu, X.-Q.; Sun, X.-D.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-M. Discovery of resveratrol derivatives as novel LSD1 inhibitors: Design, synthesis and their biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Qin, W.; Suo, F.; Zhai, X.; Guan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H. Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of stilbene derivatives as novel LSD1 inhibitors for AML therapy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 6000–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, R.D.; Patterson, D.E.; Bunce, J.D. Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5959–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, R.D., III; Bunce, J.D.; Patterson, D.E.; Frank, I.E. Crossvalidation, bootstrapping, and partial least squares compared with multiple regression in conventional QSAR studies. Quant. Struct. Relatsh. 1988, 7, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebe, G. Comparative molecular similarity indices analysis: CoMSIA. In 3D QSAR in Drug Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.-Q.; Lei, M.; Lu, A.-J.; Zhao, X.; Yin, X.-J.; Gao, Q.-Z. 3D-QSAR studies of boron-containing dipeptides as proteasome inhibitors with CoMFA and CoMSIA methods. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, M.; Gao, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Investigating the binding mode of reversible LSD1 inhibitors derived from stilbene derivatives by 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. Molecules 2019, 24, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z. Protective effects of baicalin and quercetin on an iron-overloaded mouse: Comparison of liver, kidney and heart tissues. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Gu, Y.; Peng, T.; Yang, D.; Chang, R.C.; So, K.F.; Liu, K.; Shen, J. Baicalin can scavenge peroxynitrite and ameliorate endogenous peroxynitrite-mediated neurotoxicity in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Shen, D.D.; Ren, M.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, Z.R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.N.; Zhao, L.J.; Zhao, L.J.; Ma, J.L.; et al. Baicalin, a natural LSD1 inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 69, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Hou, J.; Xu, D.; Wang, R.; Lin, Y.; Luo, J.; Kong, L. Bioactivity-guided cut countercurrent chromatography for isolation of lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitors from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1016, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Lei, J.; Wang, Z.; Kong, L.; Han, C. Flavone-based natural product agents as new lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitors exhibiting cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells in vitro. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, N.Q.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Nguyen, C.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Ho, K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Li, M.S. Screening potential inhibitors for cancer target LSD1 from natural products by steered molecular dynamics. Mol. Simul. 2018, 44, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.-C. TCM Database@ Taiwan: The world’s largest traditional Chinese medicine database for drug screening in silico. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Wu, Y.; Steinbergs, N.; Crowley, M.L.; Hanson, A.S.; Casero, R.A.; Woster, P.M. (Bis)urea and (bis)thiourea inhibitors of lysine-specific demethylase 1 as epigenetic modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5197–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotarski, S.L.; Pachaiyappan, B.; Holshouser, S.L.; Kutz, C.J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; Woster, P.M. Structure–activity study for (bis) ureidopropyl-and (bis) thioureidopropyldiamine LSD1 inhibitors with 3-5-3 and 3-6-3 carbon backbone architectures. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yu, B. Annual review of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) inhibitors in 2021. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 228, 114042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cao, H.; Yan, L.; Gu, Y.; Ren, X.; Jiao, X.; Wan, S.; Shao, F. Identification of fenoldopam as a novel LSD1 inhibitor to abrogate the proliferation of renal cell carcinoma using drug repurposing strategy. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, B. Raloxifene, identified as a novel LSD1 inhibitor, suppresses the migration of renal cell carcinoma. Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, D.P.; Alli, C.; Bremberg, U.; Cartic, S.; Jordan, A.M.; Geitmann, M.; Maiques-Diaz, A.; McGonagle, A.E.; Somervaille, T.C.P.; Spencer, G.J.; et al. Development of (4-Cyanophenyl)glycine Derivatives as Reversible Inhibitors of Lysine Specific Demethylase 1. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7984–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Z.; Ma, C.-Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Q.-B.; Sun, X.-D.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.-M. Investigating the binding mechanism of (4-Cyanophenyl)glycine derivatives as reversible LSD1 by 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1175, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 1. The accuracy of binding free energy calculations based on molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.L.; Hauser, A.T.; Carlino, L.; Pippel, M.; Schulz-Fincke, J.; Metzger, E.; Willmann, D.; Yiu, T.; Barton, M.; Schule, R.; et al. Nonpeptidic propargylamines as inhibitors of lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) with cellular activity. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7334–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culhane, J.C.; Cole, P.A. LSD1 and the chemistry of histone demethylation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraaije, M.W.; Mattevi, A. Flavoenzymes: Diverse catalysts with recurrent features. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorna, V.; Theisen, E.R.; Stephens, B.; Warner, S.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Vankayalapati, H.; Sharma, S. High-throughput virtual screening identifies novel N′-(1-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazides as potent, specific, and reversible LSD1 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9496–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.J.; Xiang, P.; Luo, X.M.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel (E)-N′-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-ylidene) benzohydrazides as potent LSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4552–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Lee, B.G.; Chen, T.; He, Z.; Lei, Y.; Tang, B.; Hirst, J.D. Machine-Learning-Enabled Virtual Screening for Inhibitors of Lysine-Specific Histone Demethylase 1. Molecules 2021, 26, 7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, Z.; Shen, C.; Bao, L.; Luo, H.; Wang, Z.; Yao, H.; Kong, D.-X.; Luo, C.; Hou, T. Learning with uncertainty to accelerate the discovery of histone lysine-specific demethylase 1A (KDM1A/LSD1) inhibitors. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, K.-T.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Choi, M.K.; Kim, I.; Nam, K.-Y.; Yoon, J. PHI-101, a potent and novel inhibitor of CHK2 in ovarian and breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| ∆EVdw | ∆Eele | ∆GGB | ∆GSA | ∆G (pred) a | Ki (exp) b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| compound 2 | −43.88 (0.39) c | −22.18 (1.02) | 22.41 (0.70) | −6.37 (0.017) | −50.04 (0.43) | 0.059 |
| compound 3 | −24.45 (0.27) | 34.39 (0.99) | −33.74 (0.86) | −3.56 (0.0084) | −27.35 (0.32) | NA |
| compound 4 | −23.01 (0.33) | −20.39 (1.09) | 12.89 (0.78) | −3.62 (0.0089) | −34.13 (0.48) | 5.6 |
| Type | Name | Molecular Structure | Key Residues | Interaction | Activity Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenelzine derivatives | compound 2 |  | Thr624, Ser289, Val288, Val317, Val811, Ala814 | hydrogen bond hydrophobic | Ki = 59 nM |
| TCP derivatives | compound 9 | 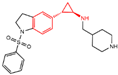 | Asp555, Ala809, Tyr761, Phe538 | hydrogen bond π–π stacking salt bridge | IC50 = 24.4 nM |
| Pyridine derivatives | compound 11 | 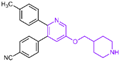 | Asp555, Lys661 | hydrogen bond | Ki = 29 nM |
| Pyrimidine derivatives | compound 20 | 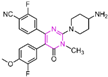 | Asp555, Lys661 | hydrogen bond salt bridge | IC50 = 0.3 nM |
| Triazole derivatives | compound 28 | 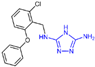 | Ala539, Asn540, Asp555 FAD | hydrogen bond π–π stacking | IC50 = 15.1 μM |
| compound 30 | 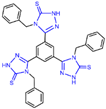 | Arg316, Gly330, Ala331, Asn660, Lys661 Trp751 | hydrogen bond π–π stacking arene–H | IC50 = 74 nM | |
| Thiazole derivatives | compound 40 | 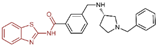 | Asp555, Asp556, FAD | π–π stacking electrostatic interaction | IC50 = 18.4 μM |
| Pyrazole derivatives | compound 45 | 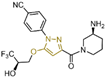 | Gly287, Val288, Val333, Ser760 | hydrogen bond | IC50 = 50 nM |
| Thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole derivatives | compound 54 | 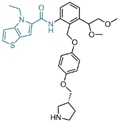 | Asn535, Asp555, His564, Pro808 | hydrogen bond | — |
| Indole derivatives | compound 57 | 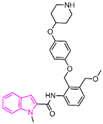 | Asp555, FAD | hydrogen bond π–π stacking | IC50 = 4 μM |
| compound 61 | 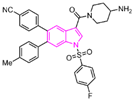 | Met332, Val333, Ile356, Ala539, Trp552, Asp555, His564, Lys661, Trp695 Ala809, FAD | hydrogen bond π–π stacking hydrophobic | IC50 = 50 nM | |
| Quinoline derivatives | compound 63 | 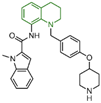 | Asp555, Asp556, Glu559, FAD | hydrogen bond π–π stacking | IC50 = 50 nM |
| compound 65 | 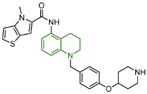 | Cys360, Asp375, Trp695, FAD | hydrogen bond π–π stacking hydrophobic | IC50 = 0.19 μM | |
| Phenyl oxazole derivatives | compound 75 | 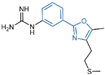 | Arg316, Glu308, Arg310 | hydrogen bond π–cation interaction | IC50 = 9.5 μM |
| Sanguinarine | compound 76 | 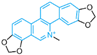 | Lys661, Tyr761, Leu659, Lys661, Thr335, Ala809, Val811 | hydrogen bond hydrophobic | IC50 = 0.4 μM |
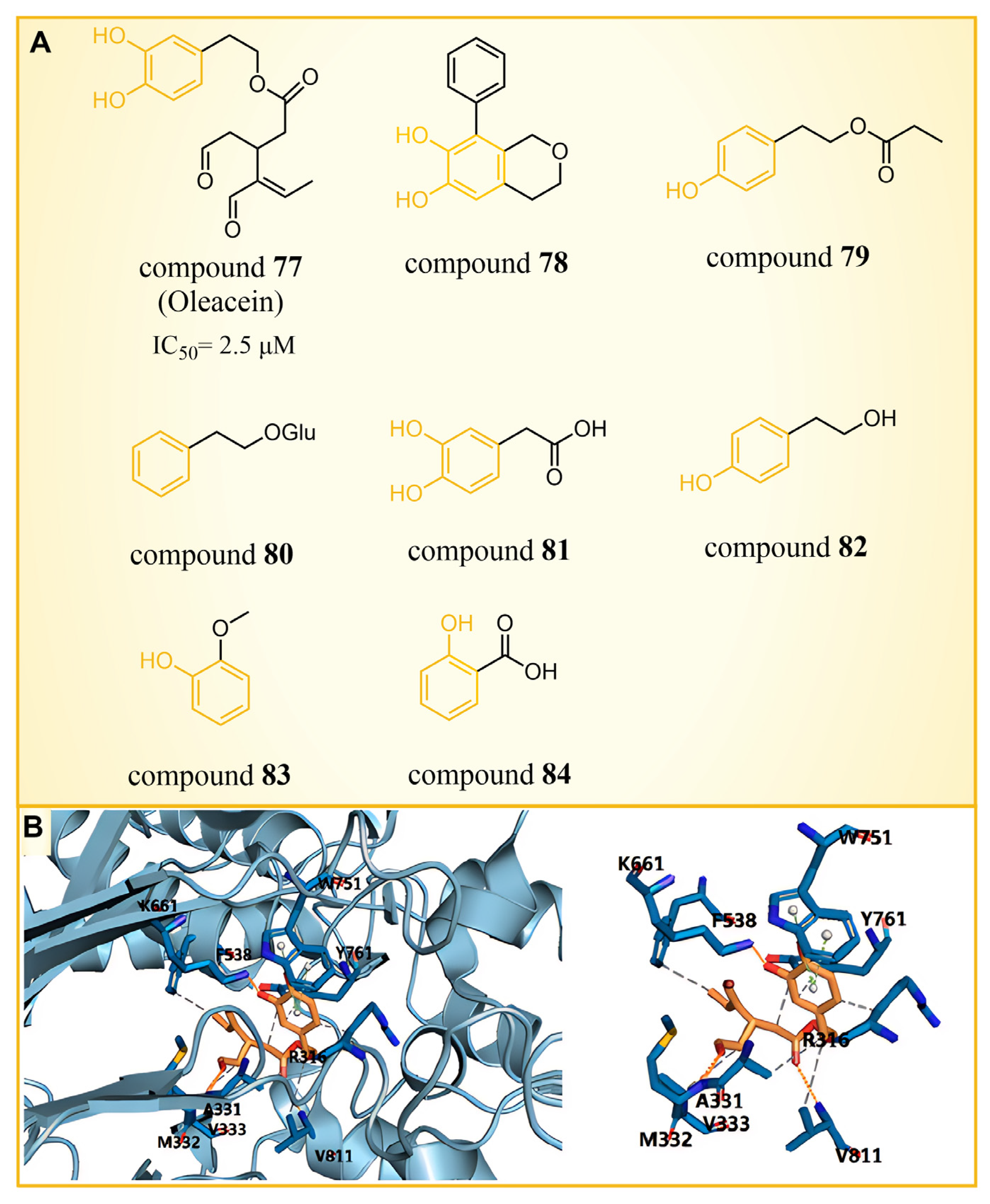
| Phenolic compounds | compound 77 | 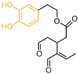 | Lys661, Ala331, Met332, Arg316, Val333, Phe538, Val811 | hydrogen bond hydrophobic | IC50 = 2.5 μM |
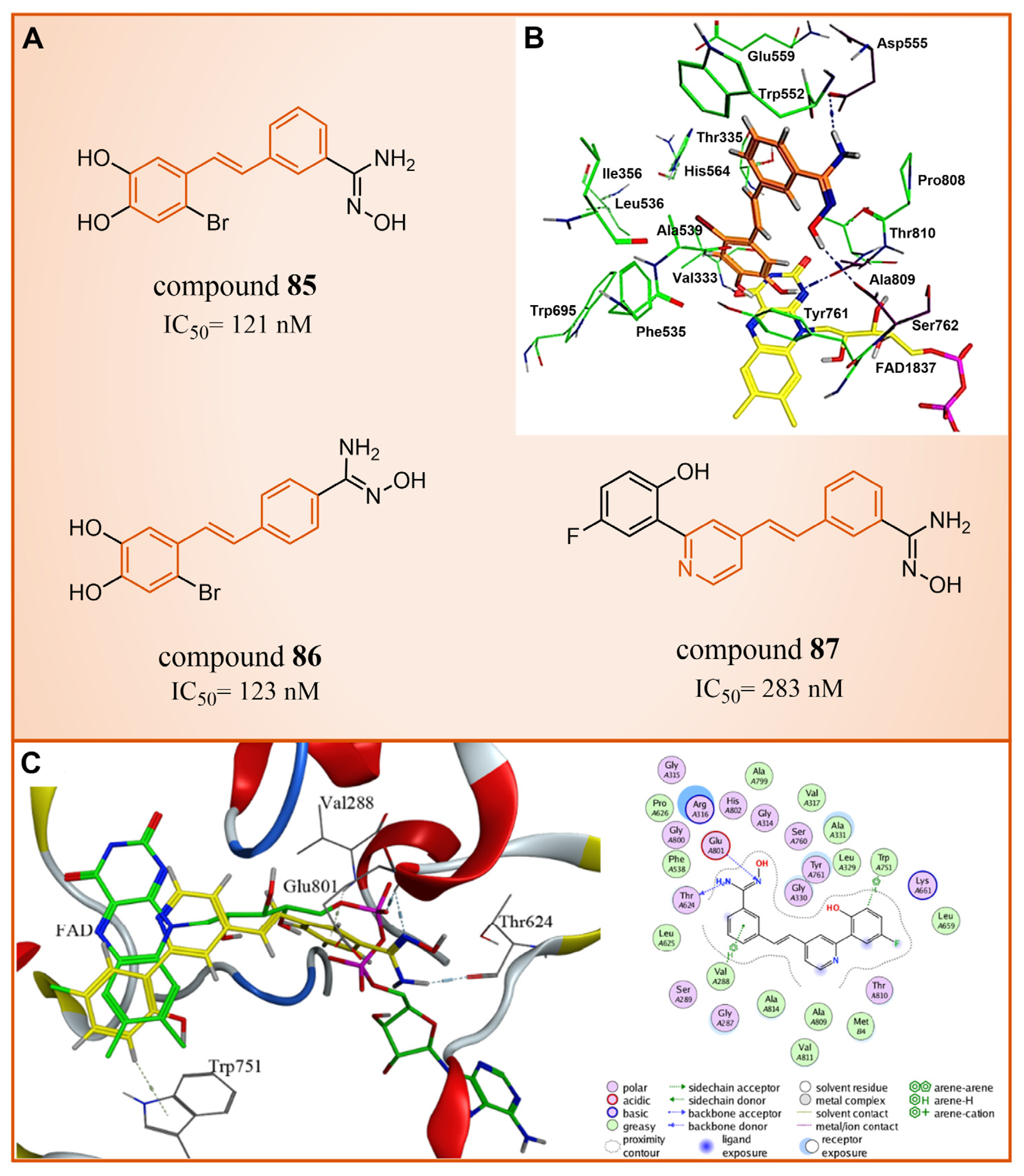
| Resveratrol derivatives | compound 85 | 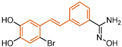 | Asp555, Ser762, Ala809, Trp552, Ala539, Ala809, Thr810, Pro808 | hydrogen bond hydrophobic | IC50 = 121 nM |
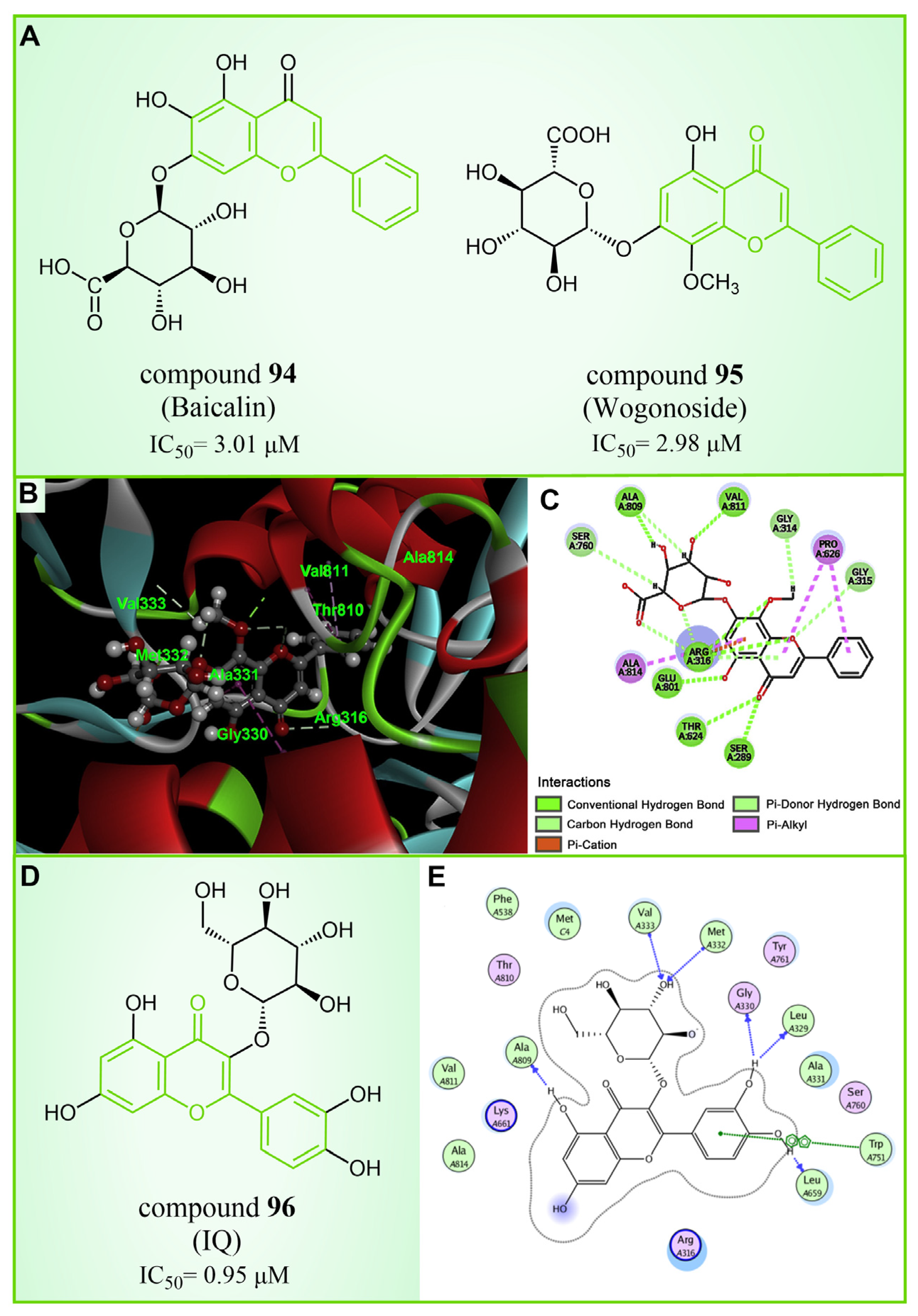
| Flavonoids | compound 96 | 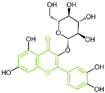 | Trp751, Ala809, Val333, Met332, Gly330, Leu329, Leu659 | hydrogen bond π–π stacking | IC50 = 0.95 μM |
| Thiourea compounds | compound 104 | 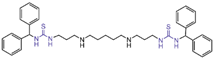 | Asn535, Ala539, Val333, Phe382, Phe538, Ala539, Trp552, Trp695, Tyr761, Val764, Pro808 | hydrogen bond hydrophobic | IC50 = 8 μM |
| Fenoldopam and Raloxifene | compound 107 |  | Arg316, Ala814, Leu329, Glu801, Gly314, Gly315, Arg316, Val317, Ala318, Leu329, Gly330, Glu801 | hydrogen bond hydrophobic | IC50 = 0.9 μM |
| compound 108 | 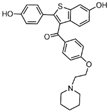 | Leu329, Gly330, Leu659, Ser749, Trp751, Tyr761, Ala809, Thr810, Val811, Gly813, Ala814, Leu659, Thr810, Trp751 Tyr761 | hydrogen bond π–π stacking hydrophobic | IC50 = 2.08 μM | |
| (4-Cyano phenyl) glycine derivatives | compound 114 |  | Asp555, Ile356, Phe538, Leu677, Leu693, Trp695, Asn535, FAD, Val333, Leu659, Lys661, Tyr761 | hydrogen bond π–π stacking hydrophobic | IC50 = 83 nM |
| Propargylamine Derivatives | compound 116 |  | Ala809, Tyr761, Phe560, Tyr807 | hydrogen bond T-shaped and edge-to-face alkyl–aryl interactions | — |
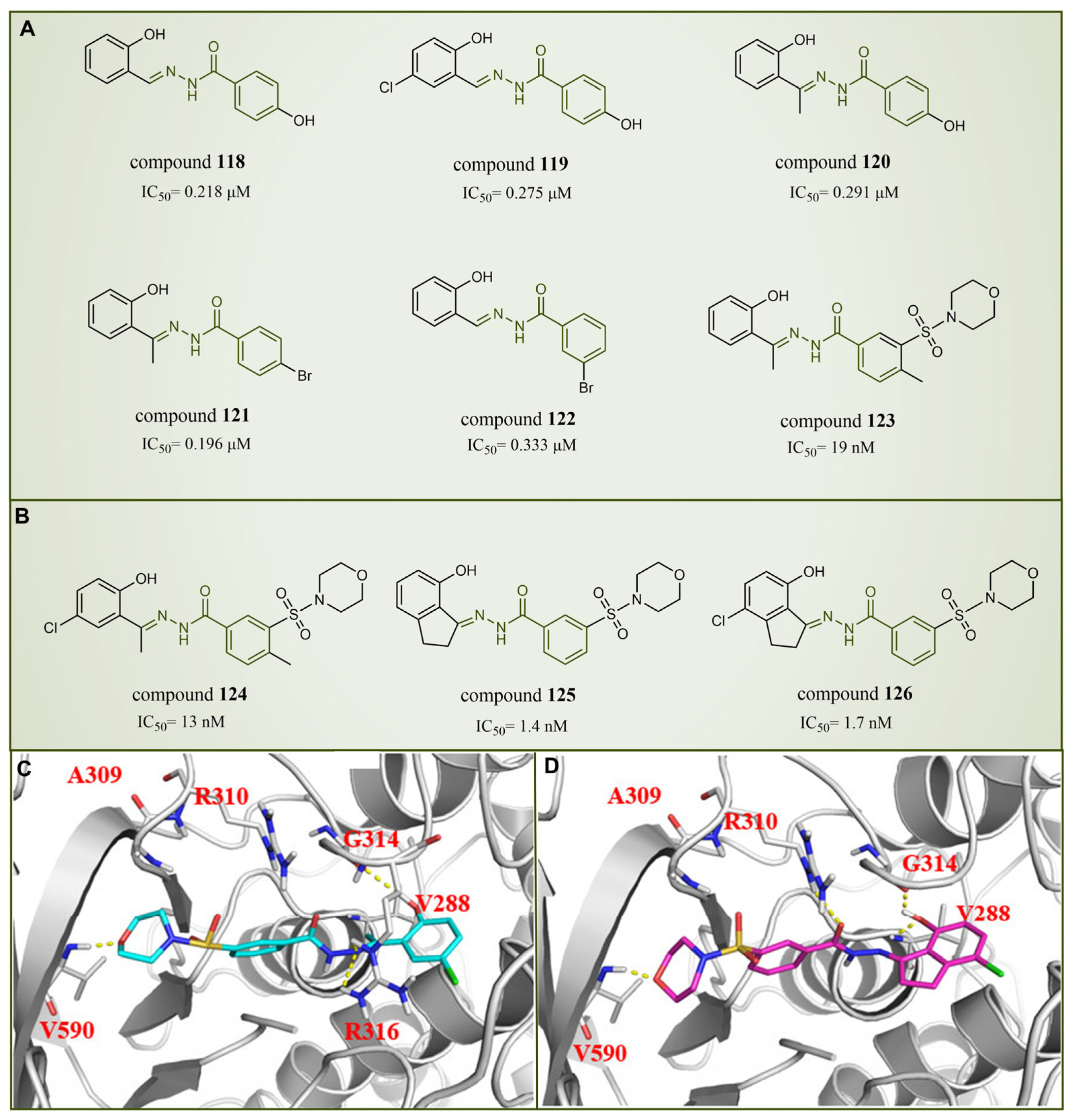
| Benzoyl Hydrazine Derivatives | compound 126 | 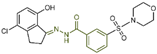 | Gly314, Val590, Arg310 | hydrogen bond | IC50 = 1.7 nM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; Lu, J.; Fan, B.; Lu, W.; Xue, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, T.; Cui, S.; Gao, Q.; Duan, Y.; et al. Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review Utilizing Computer-Aided Drug Design Technologies. Molecules 2024, 29, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020550
Han D, Lu J, Fan B, Lu W, Xue Y, Wang M, Liu T, Cui S, Gao Q, Duan Y, et al. Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review Utilizing Computer-Aided Drug Design Technologies. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020550
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Di, Jiarui Lu, Baoyi Fan, Wenfeng Lu, Yiwei Xue, Meiting Wang, Taigang Liu, Shaoli Cui, Qinghe Gao, Yingchao Duan, and et al. 2024. "Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review Utilizing Computer-Aided Drug Design Technologies" Molecules 29, no. 2: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020550
APA StyleHan, D., Lu, J., Fan, B., Lu, W., Xue, Y., Wang, M., Liu, T., Cui, S., Gao, Q., Duan, Y., & Xu, Y. (2024). Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review Utilizing Computer-Aided Drug Design Technologies. Molecules, 29(2), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020550