Abstract
LR004 is a novel chimeric (human/mouse) monoclonal antibody developed for the treatment of advanced colorectal carcinoma with detectable epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression. We aimed to investigate the preclinical pharmacokinetics (PK) and in vivo biodistribution of LR004. The PK profiles of LR004 were initially established in rhesus monkeys. Subsequently, 125I radionuclide-labeled LR004 was developed and the biodistribution, autoradiography, and NanoSPECT/CT of 125I-LR004 in xenograft mice bearing A431 tumors were examined. The PK data revealed a prolonged half-life and nonlinear PK characteristics of LR004 within the dose range of 6–54 mg/kg. The radiochemical purity of 125I-LR004 was approximately 98.54%, and iodination of LR004 did not affect its specific binding activity to the EGFR antigen. In a classical biodistribution study, 125I-LR004 exhibited higher uptake in highly perfused organs than in poorly perfused organs. Prolonged retention properties of 125I-LR004 in tumors were observed at 4 and 10 days. Autoradiography and NanoSPECT/CT confirmed the sustained retention of 125I-LR004 at the tumor site in xenograft mice. These findings demonstrated the adequate tumor targeting capabilities of 125I-LR004 in EGFR-positive tumors, which may improve dosing strategies and future drug development.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most lethal and common cancers worldwide. Approximately 25% of patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage with metastasis, whereas an additional 20% of the cases may subsequently develop metachronous metastasis [1,2]. The 5-year survival rate of patients with metastatic CRC is 65%; thus, the development of new therapeutic approaches for metastatic CRC is necessary [3,4].
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is commonly upregulated in various cancers, such as non-small–cell lung cancer, metastatic colorectal cancer, head and neck cancer, and breast cancer. EGFR plays a crucial role in the proliferation, survival, and transformation of cancer cells and has emerged as an important molecule for enhanced tumor targeting. Because of its overexpression in 25–82% of colorectal carcinomas, EGFR has been identified as an invaluable therapeutic target for colorectal carcinoma metastases [5,6]. Many EGFR-targeted agents have been developed to date, including small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as gefitinib, erlotinib, and lapatinib, as well as monoclonal antibodies such as cetuximab and panitumumab. Compared with traditional cytotoxic drugs, monoclonal antibodies exhibit better selectivity and fewer adverse side effects. Cetuximab (Erbitux®), a recombinant human/mouse chimeric anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, approved by the FDA in 2004, was the first monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR for patients with EGFR-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer after failure of both irinotecan- and oxaliplatin-based regimens or for those who are intolerant of irinotecan-containing regimens [7,8]. However, recent studies have shown that KRAS mutations are detected in 36–46% of colorectal cancer cases, rendering cetuximab ineffective for the treatment of such patients [9,10,11]. Despite the expiration of the patent in Europe in 2014 and projected annual sales of approximately USD 1.681 million in 2022, Erbitux® has not yet faced any approved biosimilar challenges in the United States or in Europe [12]. The exorbitant costs associated with multiple treatment courses underscore the pressing need for novel anti-EGFR agents.
LR004 is a novel antibody molecule that shares several key characteristics with cetuximab, including its mouse-human chimeric composition structure, its targeting of a domain of EGFR, its relatively long half-life, and its activity in colorectal cancer. Unlike cetuximab, which has murine glycan structures, LR004 has only a human glycan structure. This characteristic diminishes the antibody’s heterogeneity and enhances its suitability for future clinical applications in humans. LR004 has demonstrated antitumor activity in various tumor models, including epidermoid carcinoma (A431), colon cancer (GEO), and breast cancer (MDA-MB-468) [13]; however, comprehensive preclinical pharmacokinetic (PK) and biodistribution profiles for LR004 have not been established. These profiles are necessary for dosage formulations and clinical studies as a novel antibody agent.
Here, we conducted a preclinical investigation of the PK properties and in vivo biodistribution profile of LR004. Initially, we determined the affinity and kinetics of the LR004 antibody toward the EGFR antigen using a BIAcore X100 capture assay. Next, we examined the PK of LR004 at various doses by intravenous infusion in rhesus monkeys. Furthermore, we labeled LR004 with the 125I isotope and used three methods to examine the biodistribution of 125I-LR004 within tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice models, with a particular emphasis on its distribution within tumor tissues. Among these methods, the radionuclide-based biodistribution study represents a conventional and straightforward approach that provides detailed data on the accumulation of radiolabeled antibodies in excised tissues, which offers more accurate prognostic and predictive information. The combination of antibody labeling and bio-imaging techniques plays an important role in establishing the in vivo distribution characteristics of novel antibody molecules. This approach has been increasingly adopted because of its ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of tumor biology as well as its specific binding affinity toward the intended targets [14,15,16]. Therefore, we applied autoradiography and single photon emission computer tomography (SPECT) imaging technology to obtain direct visual verification of the distribution properties of 125I-LR004.
2. Results
2.1. Antibody Affinity and Kinetics Assay
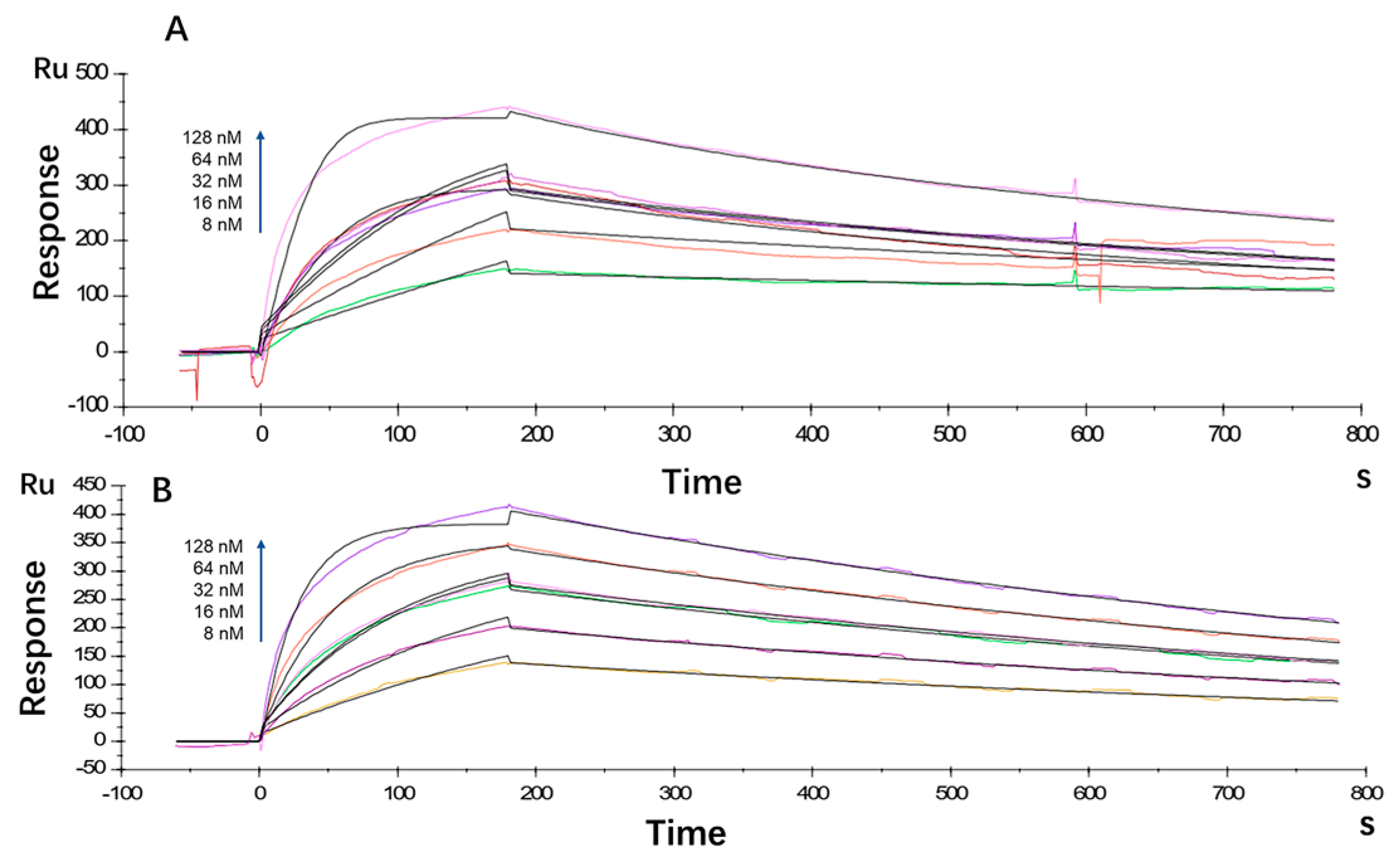
The antibody affinity and kinetics assay using the BIAcore X100 System showed that the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) for LR004 was 2.80 × 10−9 M, with a ka value of 5.26 × 105 1/Ms and a kd value of 1.47 × 10−3 1/s (Figure 1A). Cetuximab exhibited a KD of 3.88 × 10−9 M, ka of 2.86 × 105 1/Ms, and kd of 1.11 × 10−3 1/s (Figure 1B). Thus, the affinity between LR004 and EGFR showed moderate strength comparable with that of the commercially available cetuximab.
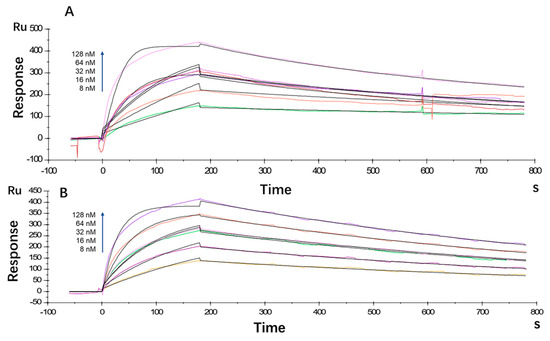
Figure 1.
Kinetic analysis/affinity test fitting curves from BIAcore analysis. (A) Kinetic analysis/affinity test fitting curve of LR004; (B) Kinetic analysis/affinity test fitting curve of cetuximab.
2.2. PK Profiles of LR004 in Rhesus Monkeys
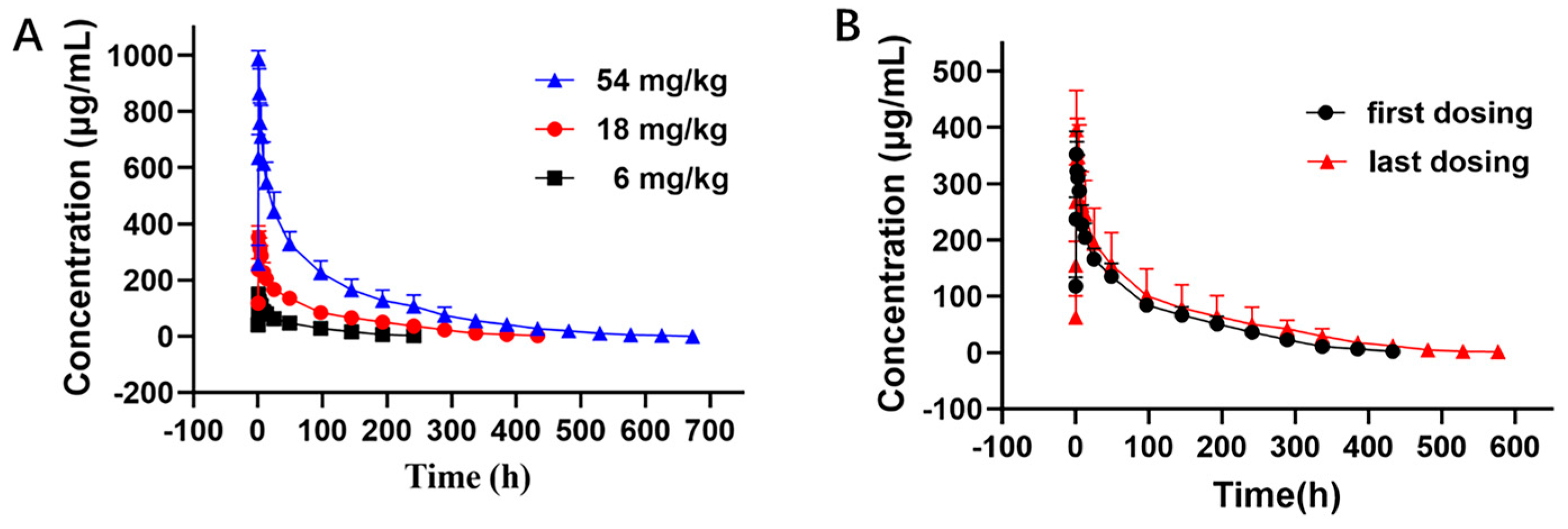
The PK curves of LR004 following a single intravenous infusion are shown in Figure 2A. The PK parameters in Table 1 indicate that the elimination half-lives (t1/2) at doses of 6, 18, and 54 mg/kg were 51.60 ± 8.36, 104.62 ± 13.42, and 130.72 ± 39.57 h, respectively, and the t1/2 gradually extended with increasing doses. The respective AUClast were 6900.24 ± 1243.11, 25,398.82 ± 4774.38, and 72,301.13 ± 16,411.89 mg·h/L. The AUC rate was 1:3.68:10.48, which was consistent with the dose rate of 1:3:9. The MRTlast and Vd also significantly increased with increasing doses. These parameters suggest that LR004 exhibits nonlinear PK characteristics within a dose range of 6–54 mg/kg in rhesus monkeys. As shown in Figure 2B, after four consecutive intravenous infusions of LR004 at a dose of 18 mg/kg, there were no statistically significant differences between the first and last dosing profiles, indicating negligible plasma accumulation of LR004 following continuous administration. The PK parameters had no statistical differences among different sexes (p > 0.05).
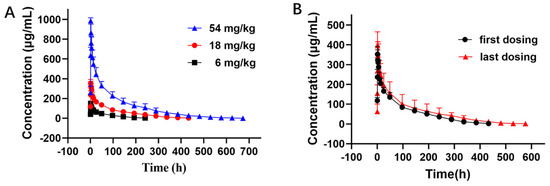
Figure 2.
Serum concentration–time curve of LR004 in rhesus monkeys. (A) Serum concentration profiles of LR004 following a single intravenous infusion to rhesus monkeys at doses of 6, 18, and 54 mg/kg (mean ± SD, n = 6); (B) Serum concentration profiles of LR004 at a dose of 18 mg/kg for first/last dosing (mean ± SD, n = 6).

Table 1.
Mean pharmacokinetic parameters of LR004 following intravenous infusion administration to rhesus monkeys at doses of 6, 18, and 54 mg/kg.
2.3. Radiochemical Purity Identification
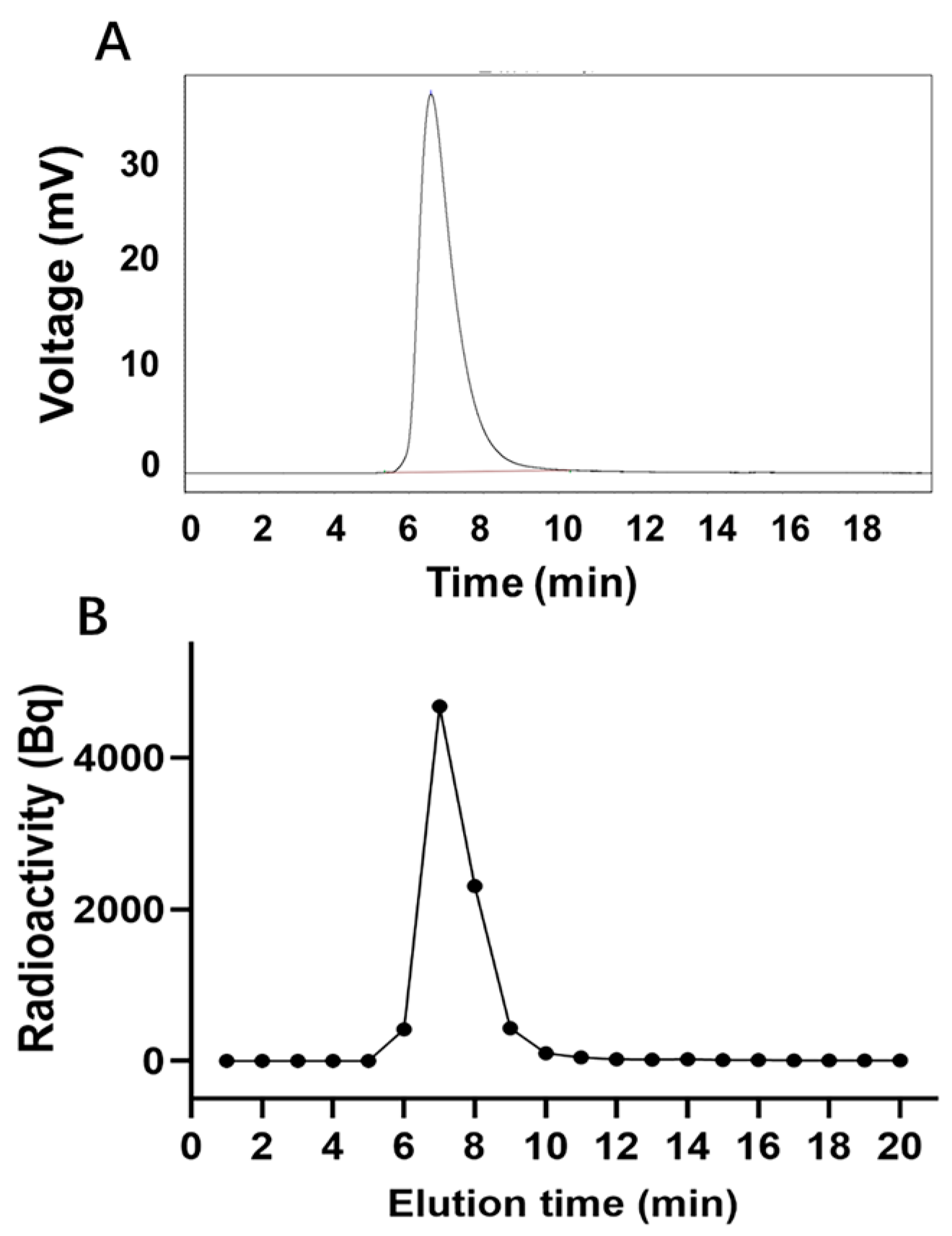
The peak time of unlabeled LR004 was 6.59 min (Figure 3A), whereas the peak time of 125I-LR004 was 6.5 min (Figure 3B), consistent with that of unlabeled LR004. This suggests that the SHPLC elution behavior of LR004 was unchanged before and after 125I-labeling. The radiochemical purity of 125I-LR004 indicated that it was successfully synthesized as evidenced by the radioactive peak area ratio. The average of the three measurements was 98.54%.
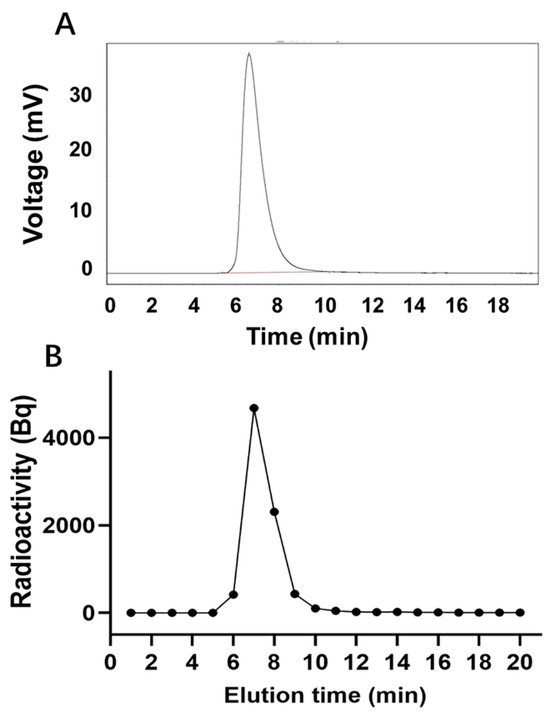
Figure 3.
Radiochemical purity determination. (A) SHPLC profiles of unlabeled LR004; (B) Radiochemical purity profiles of 125I-LR004.
2.4. In Vitro Inhibition of Tumor Cells
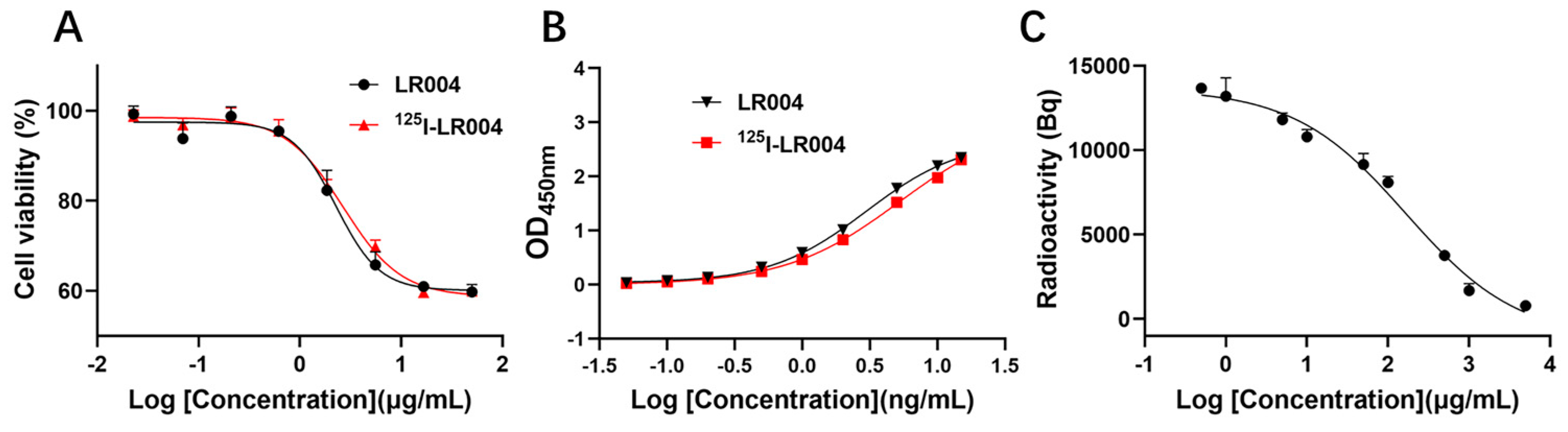
As shown in Figure 4A, the curves of the inhibition of proliferation by unlabeled LR004 and 125I-radiolabeled LR004 were similar, and the EC50 values were 2.278 and 2.671 µg/mL, respectively. Thus, iodination of LR004 did not affect its inhibitory effect on tumor cells.
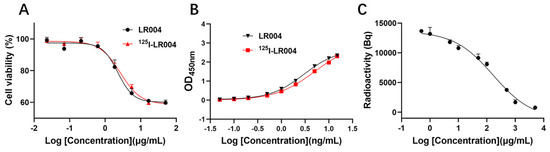
Figure 4.
Inhibition and binding activities of LR004 before and after radiolabeling. (A) Curves showing the inhibition of proliferation by unlabeled LR004 and 125I-LR004 in MDA-MB-468 cells, as detected by CCK-8. The concentration of LR004 and 125I-LR004 were 0.023, 0.07, 0.21, 0.62, 1.85, 5.56, 16.67, and 50 μg/mL (left to right on the X-axis); (B) Comparison of antigen binding activities between unlabeled LR004 and 125I-LR004, as determined via ELISA. The concentration of LR004 and 125I-LR004 were 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, and 15 ng/mL (left to right on the X-axis); (C) Competitive binding of 125I-LR004 and unlabeled LR004 to MDA-MB-468 cells, as quantified via γ counter. The concentrations of unlabeled LR004 were 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, 5000 μg/mL (left to right on the X-axis).
2.5. In Vitro Binding Activities to the EGFR Antigen
The antigen binding curves of a series of 125I-LR004 concentrations were identical to those of non-labeled LR004, as determined via ELISA (Figure 4B). The binding activities of the two groups to the EGFR antigen were in good agreement.
2.6. Specific Binding Affinity toward MDA-MB-468 Cells
As shown in Figure 4C, the concentration of 125I-labeled LR004 was fixed at 50 µg/mL. When the concentration of unlabeled LR004 was varied (0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, and 5000 μg/mL), cell-bound radioactivity analysis demonstrated that unlabeled LR004 exhibited a dose-dependent competition with 125I-LR004 for binding to the EGFR antigen. With an increase in the concentration of unlabeled LR004, the detected radioactivity decreased. The results indicated that 125I-LR004 and LR004 bound to the same site on MDA-MB-468 cells, suggesting that the high affinity of LR004 toward EGFR antigen was not affected by 125I-labeling.
2.7. Biodistribution in Xenograft Mice
The concentrations of LR004 in tissues and body fluids were determined by 125I isotope labeling combined with TCA protein precipitation. Quantitative data in tissues harvested from tumor-bearing mice were obtained, and the concentration of 125I-LR004 in tissues is shown in Figure 5A. 125I-LR004 exhibited higher uptake in highly perfused organs (e.g., heart, liver, lung, kidney) compared with poorly perfused organs (e.g., brain, muscle). The concentration of 125I-LR004 in normal tissues exhibited a gradual decline from 4 h to 10 d, whereas the concentration in tumors remained stable. Figure 5B shows the concentration of 125I-LR004 in tissues compared with that in serum. From 4 d to 10 d, 125I-LR004 in tumors relative to serum was significantly higher compared with that in the highly perfused organs, indicating a pronounced tumor target tendency of 125I-LR004. The prominent radioactivity accumulation in the liver, particularly at 4 h postadministration, was the result of hepatic clearance of the antibody-based tracer.
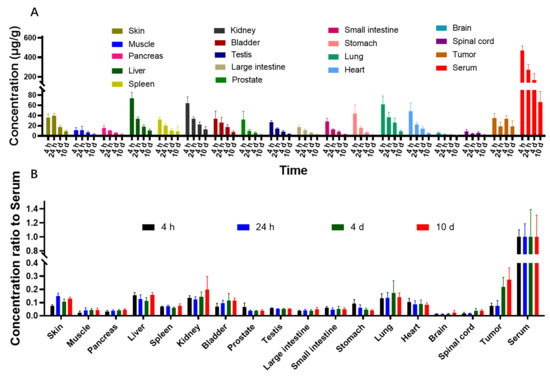
Figure 5.
Biodistribution of 125I-LR004 in xenograft mice. (A) 125I-LR004 in tissues at 4 h, 24 h, 4 d, and 10 d following the administration of 60 mg/kg to tumor-bearing mice (n = 6); (B) 125I-LR004 level in tissues relative to that in serum at 4 h, 24 h, 4 d, 10 d at a dose of 60 mg/kg in tumor-bearing mice (n = 6).
2.8. Autoradiography Study in Xenograft Mice
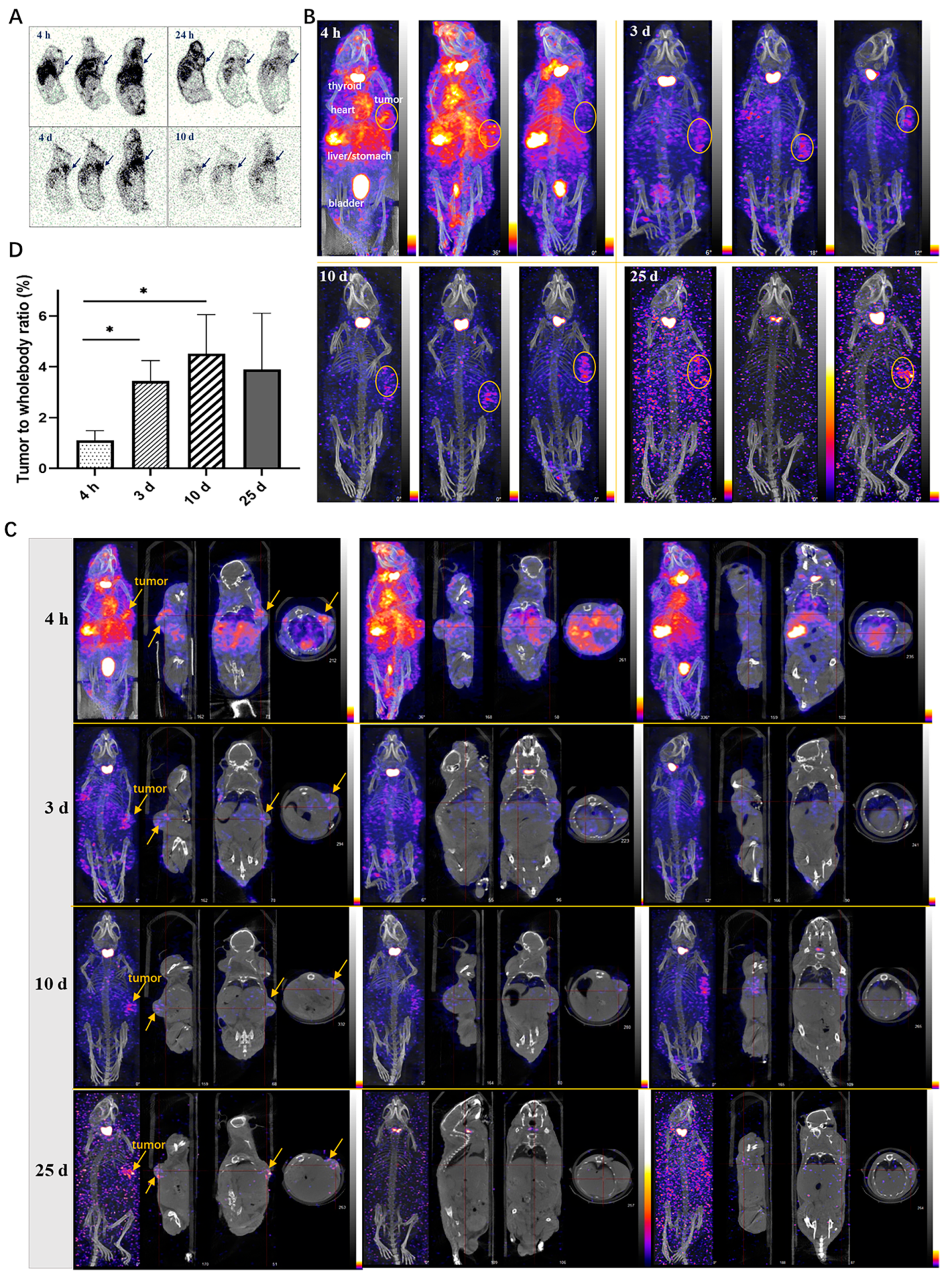
The autoradiography results of frozen tissues in tumor-bearing mice revealed the widespread distribution of 125I-LR004 across various tissues (Figure 6A). The radiation exposure in blood flow-rich tissue was significantly higher than that in other tissues. Over time, the concentration of 125I-LR004 in the serum gradually decreased, and radiation exposure levels in tissues also diminished; however, the radioactivity in tumor tissues increased. Marked aggregation of radiation in tumor tissues (black arrow) was observed at 24 h, 4 d, and 10 d postadministration, highlighting the targeted distribution of 125I-LR004 in tumors.
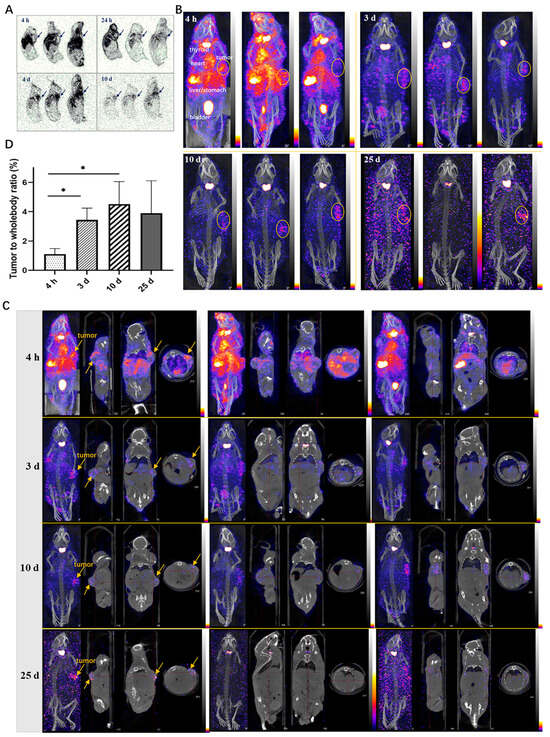
Figure 6.
Tumor-targeting of 125I-LR004 in xenograft mice through Autoradiography and NanoSPECT/CT imaging. (A) Autoradiography of 125I-LR004 at a dose of 60 mg/kg for 4 h, 24 h, 4 d, and 10 d in tumor-bearing mice. The black arrows indicate the location of the tumors; (B) NanoSPECT/CT of 125I-LR004 in tumor-bearing mice at 4 h, 3 d, 10 d, and 25 d postadministration (n = 3). The tumor regions are marked with yellow ellipses; (C) In vivo tumor targeting of 125I-LR004 assessed via NanoSPECT/CT. The tumor regions are marked with yellow arrows; (D) The tumor-to-whole body ratios of radioactivity at 4 h, 3 d, 10 d, and 25 d postadministration of 125I-LR004 (* p < 0.05).
2.9. NanoSPECT/CT in Xenograft Mice
NanoSPECT/CT results of 125I-LR004 are presented in Figure 6B. A significant radioactive exposure of 125I-LR004 was observed in the highly vascularized tissues (stomach, bladder, heart, and liver) as early as 4 h postadministration, and a high distribution of 125I-LR004 was also observed in the tumors. Radiation exposure levels in the whole body decreased with time, particularly in the highly radioactive organs (e.g., liver, lung, and kidney) during the initial time points. As shown in Figure 6C, tumor tissues with significantly higher drug concentrations showed a marked accumulation of radioactivity compared with the other tissues on Day 3. This high radioactivity level persisted until Day 10, consistent with the findings from our biodistribution study. Although the residual radioactivity in the whole body was considerably low at day 25, hotpots in the tumors were still evident and exhibited a clear contrast with surrounding tissues and background. From 4 h to 10 d postadministration, the prolonged retention of 125I-LR004 in tumors combined with its rapid clearance from other tissues resulted in favorable tumor-to-whole body ratios (Figure 6D). The residual radioactivity in the whole body was considerably low at 25 days postadministration, whereas the hot spots within tumors in most mice were still visible with an excellent target–background contrast. These results indicated that 125I-LR004 exhibits good tumor targeting capability with a prolonged half-life.
3. Discussion
This is the first study to investigate the in vivo PK properties and biodistribution profile of a novel anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody (LR004). Our findings demonstrated that LR004 can specifically bind to the EGFR antigen with appropriate antigen binding activity. This characteristic limits any side effects associated with higher affinity while mitigating the poor therapeutic effects resulting from lower affinity. Detailed studies on the PK of therapeutic antibodies are essential for their continued development. We revealed that LR004 exhibits a prolonged elimination half-life and nonlinear PK characteristics within a dose range of 6–54 mg/kg in rhesus monkeys. According to literature reports [17], cynomolgus monkeys administered a single intravenous dose of 5 mg/kg cetuximab exhibited an accelerated elimination of the drug from plasma at 3–10 days post-administration, with plasma cetuximab concentration falling below the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) within 10–14 days. In our PK experiment, rhesus monkeys received a low intravenous dose of LR004 at 6 mg/kg, and similarly, blood concentration started to decline significantly after 3 days and became undetectable after 240 h (10 days). This observation closely resembles the behavior observed with cetuximab. In addition, based on the PK parameters determined through non-compartmental pharmacokinetics analysis, cetuximab exhibited a CL of 0.87 mL/h/kg and a t1/2 of 36 h. Similarly, LR004 demonstrated comparable values with a CL of 0.86 ± 0.18 mL/h/kg and a t1/2 of 51.60 ± 8.36 h. Furthermore, LR004 displayed nonlinear pharmacokinetic characteristics in monkeys that were consistent with those previously reported for cetuximab [17,18]. Nonlinear PK phenomenon may be associated with target-mediated drug disposition, which is more frequently observed in monoclonal antibody drugs, especially for those targeting membrane receptors [19]. There was no statistically significant plasma accumulation of LR004 after four consecutive intravenous infusions at a dose of 18 mg/kg, indicating that LR004 may have a better safety profile.
Radionuclide tracing technology is an important means of preclinical and clinical pharmaceutical research. The elimination half-life (t1/2) of LR004 at a medium dose in rhesus monkeys was >100 h. 125I exhibits a high labeling efficiency and prolonged physical half-life (60 days), which corresponds to the long biological half-life of LR004 in the blood. The classical biodistribution study of 125I-LR004 revealed higher concentrations and rapid elimination in highly perfused organs, such as the heart, liver, lung, and kidney, which probably reflects hepatic metabolism and renal excretion. In tumor tissue, the levels of 125I-LR004 remained relatively constant, with a peak concentration occurring as early as 4 h and sustained concentrations up to 10 days, indicating the targeted distribution tendency in EGFR-positive tumors. The enhanced visualization of the biodistribution tumor targeting properties of 125I-LR004 was further confirmed through autoradiography and NanoSPECT/CT imaging findings.
125I-LR004 exhibited reduced radioactivity in poorly perfused organs (e.g., brain, spinal cord, muscle), which may contribute to mitigating potential side effects in these tissues. The accumulation of radioactivity in the thyroid can be attributed to the in vivo deiodination and specific uptake of iodine by the thyroid glands. To accurately reflect real physiological conditions, we did not preblock the thyroid gland with iodine in our experiment. In this study, we employed the conventional iodogen method to label 125I onto LR004. In future investigations, we could potentially explore alternative radiolabeling methods such as Bolton–Hunter reagent [20] or N-succinimidyl-para-iodobenzoate (SPIB) [21]. As previously reported, EGFR inhibition may cause lesions in the upper torso, face, neck, and scalp of >50% of the patients [22,23]. Consistent with these reports, our biodistribution results showed relatively high radioactivity in the skin. These factors should be taken into consideration for future studies.
LR004 has only human glycan structure, which can reduce the heterogeneity of the antibody and renders it more suitable for future clinical application in humans. In preclinical studies of antibodies, the evaluation of PK and biodistribution in suitable animal models is a central consideration. We performed PK studies of LR004 in monkeys because it is generally considered the most relevant species for predicting the human PK of monoclonal antibodies. This approach can provide more compelling predictive data for appropriate dosage and timing for future clinical application. For biodistribution studies, we utilized the human tumor cell-xenografted mouse models and employed the noninvasive SPECT/CT imaging techniques, which may also be closer to the clinical investigations. Although the data obtained from animal models differ from that collected in human subjects, this data can still provide valuable insights for subsequent human experiments involving LR004. Overall, LR004 shows promising preclinical PK and biodistribution characteristics, supporting its potential as an effective antibody for treating colorectal cancer.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents, Cells, and Animal Models
All the reagents used were of analytical grade. LR004 was generated by Synermore Biologics Co., Ltd., Suzhou, China (protein content: 5 mg/mL, storage: −20 °C). 125I was purchased from PerkinElmer Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. with a radiation radionuclide purity of 99.90%. Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) was purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd, Beijing, China. The BCA Protein assay kit (Lot. 162495,) was purchased from ThermoFisher Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. The TMB Kit (Lot. 101095992) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. The human breast cancer MDA-MB-468 cells and human epidermal carcinoma A431 cells were obtained from JOINN Laboratory (Beijing). Human epidermal carcinoma A431 cells were subcutaneously implanted into BALB/c nude mice (40 males, body weight: 20–30 g) at JOINN Laboratories. Rhesus monkeys with a body weight of 4.5 ± 1.0 kg were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Academy of Military Medical Sciences and raised in the Experimental Animal Center of Academy of Military Medical Sciences (Beijing). All animal experiments were performed under standardized conditions, with an ambient temperature of 22 °C ± 2 °C, relative air humidity 40–70%, a 12-h light/12-h dark cycle, with free access to water and food. All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and approved and reviewed by the Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine (Beijing, China, IACUC-DWZX-2021-735).
4.2. BIAcore Analysis of Antibody Affinity and Kinetics
BIAcore analysis was performed as previously described with minor modifications [24]. The affinity of LR004 and cetuximab toward the EGFR antigen was assessed separately under identical experimental conditions. LR004 or cetuximab was diluted to 5.0 μg/mL with HEPES buffered saline supplemented with EDTA and Surfactant P20 (HBS-EP), whereas recombinant human EGFR was diluted to 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 nM with HBS-EP buffer. A consistent concentration of 32 nM was established as the repeat concentration. A regeneration solution consisting of 10 mM glycine–HCl at pH 2.5 was used. The run program in the WorkFlow wizard mode was employed, and multiple cycles were selected. The resulting data were fitted using BIAcore X100 analysis software(version 1.0, GE Healthcare) by plotting time on the x-axis and signal value on the y-axis to determine the kinetic constants.
4.3. PK of LR004 in Rhesus Monkeys
A total of 24 rhesus monkeys (12 males and 12 females) weighing 4.5 ± 1.0 kg were randomly divided into 4 groups, with 6 animals per group. Three groups were administered with a single intravenous infusion at different dose levels (low dose: 6 mg/kg, medium dose: 18 mg/kg, and high dose: 54 mg/kg), and the fourth group received a series of doses with a medium dose (18 mg/kg) of LR004 for four intravenous infusions. For the single dose groups, blood samples were collected at 0 (predose), 20 min, 40 min, 60 min (at the end of intravenous infusion), 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h, 2 days (d), 4 d, 6 d, 8 d, 10 d, 12 d, 14 d, 16 d, 18 d, 20 d, 22 d, 24 d, 26 d, 28 d, and 30 d postadministration. For the group receiving a series of doses, blood sampling for the first and fourth time postadministration was performed according to the abovementioned method, and sampling for the second and third time was performed at 7 days postadministration. All blood samples were coagulated for 30 min at room temperature, after which the serum was harvested and stored at −20 °C until analysis. Serum samples were analyzed via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and serum concentration–time profiles were used to estimate the PK parameters via noncompartmental analysis (WinNonlin, version 5.2.1; Pharsight Corporation, Mountain View, CA, USA).
4.4. Iodination and Purification of LR004
LR004 was labeled using the iodogen method [25,26]. Briefly, 1 mg of iodogen (Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was dissolved in 0.5 mL of chloroform, and the mixture was added to the bottom of a tube and dried under nitrogen. Then, 1 mL of recombinant anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody (LR004) and 6 mCi of Na125I were added. The mixture was incubated for 6 min at 22 ± 2 °C under shaking conditions to complete the reaction. The mixture was purified on a Sephacryl G-50 column pre-equilibrated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and the intelligent calibration instrument was used to determine the γ radiation of the eluant.
The radiochemical purity of 125I-labeled LR004 was determined by high performance liquid chromatography (SHPLC) (SHIMADZU LC-20 AT) with a TSK-GEL G300SWXL gel filtration column (300 mm × 7.8 mm, 5 mm) and an eluent of 0.05 mol/L phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Each tube of eluent was collected per minute with a fraction collector and γ radioactivity was detected. The radioactive peak area percentage with the same chromatographic profile as the non-labeled LR004 standard was calculated.
4.5. In Vitro Inhibition of Tumor Cells
The inhibitory effect of the radiotracer in tumor cells was assessed through CCK-8 cell viability analysis [27]. MDA-MB-468 cells were cultured in DMEM/F12K (1:1) containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin and streptomycin at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Cells in the logarithmic growth phase were diluted with detection medium to a density of 5 × 104 cells/mL, 100 μL were added to each well, and incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 1 h. LR004 and 125I-LR004 were separately diluted to 50, 16.67, 5.56, 1.85, 0.62, 0.21, 0.07, and 0.023 μg/mL using DMEM/F12 medium without bovine serum. After incubating at 37 °C for 24 h, medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum was added, and the cells were incubated for 96 h. CCK-8 solution was added followed by measurement of optical density (OD) values at a wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader. The binding rate curve and EC50 (amount of antibody for 50% binding) values were determined using GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
4.6. In Vitro Binding Activities with EGFR Antigen
The antigen binding activities of LR004 before and after labeling were assessed by ELISA. Specifically, the wells were coated with 0.04 μg/mL EGFR antigen overnight at 4 °C. Subsequently, the plates were washed and blocked with 2% BSA for 2 h at 37 °C. Radiolabeled and non-labeled LR004 were gradually diluted (15, 10, 5, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.2, 0.1, and 0.05 ng/mL) and added to the wells in duplicate. After incubation for 2 h at 37 °C, the plates were washed and anti-human Fc-HRP was added and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. After washing, 100 μL of TMB substrate working solution was added to each well and the reaction was terminated by adding 2 mol/mL H2SO4. The OD was measured using a microplate reader at 450 nm and 630 nm.
4.7. Specific Binding Affinity of 125I-Labeled LR004 toward MDA-MB-468 Cells
Unlabeled LR004 was initially diluted into nine concentration gradients (0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, and 5000 μg/mL), and 50 µL of the solution was added to each triplicate tube. Subsequently, 125I-labeled LR004 was diluted to a concentration of 50 µg/mL, and 100 µL of the solution was added to each tube. MDA-MB-468 cells at a density of 1 × 105/mL (50 µL) in DMEM/F12 medium (without bovine serum) were added to the solution while stirring gently to prevent cell precipitation. The samples were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h, followed by an additional incubation at 4 °C for 30 min. All samples were washed thrice with PBS. Cell-bound 125I-LR004 was separated via centrifugation and quantified via γ counter.
4.8. Mouse Tumor Xenografts
Mice bearing human epidermal carcinoma A431 tumors were euthanized via cervical dislocation after isoflurane anesthesia. Tumors were removed under aseptic conditions, sliced into small pieces with a volume of 3 mm3, and subsequently inoculated into male nude mice in the right axillary subcutaneous region near the dorsal region. The tumors were allowed to grow for 4 weeks until reaching an approximate volume of 300 mm3. The tumor-bearing mice were then used for in vivo studies.
4.9. Biodistribution Study in Xenograft Mice
Biodistribution study was conducted following the established methodology described in the literature [28,29]. Four groups of A431 xenograft tumor-bearing mice (n = 6) were intravenously injected with 125I-LR004 at a dose of 60 mg/kg and a radiation dosage of 10,641 KBq/kg. The mice were euthanized at 4 h, 24 h, 4 d, and 10 d postadministration. Tissue samples including the skin, muscle, pancreas, liver, spleen, kidney, bladder, prostate, testis, large intestine, small intestine, stomach, lung, heart, brain, spinal cord, tumor, and serum were collected and weighed. Equal amounts of saline and 30% TCA were added to the tissue samples for protein precipitation. After centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 5 min, the supernatant was discarded, and radioactivity in the precipitate per gram of tissue was quantified using a γ counter (Wallac 1470, PerkinElmerTM, Waltham, MA, USA). The biodistribution data are expressed as the concentration of 125I-LR004 in tissues and the ratio of 125I-LR004 in tissues relative to that in the serum.
4.10. Autoradiography in Xenograft Mice
Autoradiography was performed as previously described with minor modifications [30]. Tumor-bearing mice were administered 125I-LR004 via tail vein injection at a dose of 60 mg/kg and a radiation dosage of 10,641 kBq/kg. Mice were euthanized at 4 h, 24 h, 4 d, and 10 d postadministration. Carcasses were embedded in 2.5% carboxymethyl cellulose and frozen at −20 °C. After being completely frozen, mice were positioned on their left side and fixed onto a slice airborne platform. Overall, 40-µm thick sections were collected at three different positions: tumor sections, right-side limbs, and spinal position. The dried sections were exposed to a phosphor imaging plate for 3 h and scanned using a bio-imaging analyzer (Cyclone Plus, PerkinElmerTM) to obtain images.
4.11. NanoSPECT/CT Imaging in Xenograft Mice
Twelve tumor-bearing mice (n = 3) were injected with 125I-LR004 at a dose of 50 mg/kg and a radiation dose of 199,633 kBq/kg. NanoSPECT/CT scans were performed at 4 h, 3 d, 10 d, and 25 d after administration using a NanoSPECT/CT scanner (Bioscan Inc., Poway, CA, USA). The mice were anesthetized with 3% pentobarbital (50 mg/kg body weight) and placed in a prone position on an imaging platform for each scan. Whole body radionuclide images were reconstructed using an iterative ordered subset expectation maximization two-dimensional algorithm and fused with CT images using the integrated CT system [31,32]. For semi-quantitative analysis, the tumor-to-whole body ratios of radioactivity were determined by drawing a region of interest around the tumors.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for graph generation and statistical analysis. Significance was evaluated using a Student’s t-test, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
We conducted a comprehensive preclinical study to assess the PK properties and biodistribution of LR004, a novel antitumor antibody. LR004 exhibits specific binding to the EGFR antigen with appropriate antigen binding activity. The elimination half-life (t1/2) of LR004 at a medium dose in rhesus monkeys exceeded 100 h, and there was no statistically significant plasma accumulation after four consecutive intravenous infusions. 125I-LR004 displayed good tumor targeting capabilities in tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mouse models. Prolonged retention properties of 125I-LR004 in tumors were observed at 4 and 10 days. The overall preclinical PK and biodistribution profiles strongly support the potential clinical development of LR004 as an effective antibody for treating colorectal cancer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and H.G.; methodology, Y.Z., G.Y. and P.H.; data curation, Y.Z. and H.G.; formal analysis, X.Z., R.G. and Z.W.; investigation, G.D. and Z.M.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, E.I.T. and H.G.; project administration, S.L. and Y.S.; funding acquisition, H.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported partially by the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation [No. 7202148].
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and approved and reviewed by the Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine (Beijing, China, IACUC-DWZX-2021-735).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All research data can be found within this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Eric I. Tsao was employed by the company Synermore Biologics Co. Ltd. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest”.
References
- Janani, B.; Vijayakumar, M.; Priya, K.; Kim, J.H.; Prabakaran, D.S.; Shahid, M.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Alsaidan, M.; Othman Bahakim, N.; Hassan Abdelzaher, M. EGFR-Based Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer-Promises and Challenges. Vaccines 2022, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Comprehensive review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yoshida, Y.; Takashima, A.; Kato, Y.; Kawada, M. Current Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spano, J.P.; Fagard, R.; Soria, J.C.; Rixe, O.; Khayat, D.; Milano, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in colorectal cancer: Preclinical data and therapeutic perspectives. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.M.; Grandis, J.R. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of EGFR inhibitors under clinical investigation. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.; Muhsin, M.; Kirkpatrick, P. Cetuximab. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares-Martin, B.; Cebrian Aranda, A.; Del Puerto-Nevado, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Solanes, S.; Gomez-Espana, M.A.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Aranda, E. Improving selection of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer to benefit from cetuximab based on KIR genotypes. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, F.; Hu, T.; He, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, X.; Lan, P. Mutant KRAS triggers functional reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadlow, R.C.; Hezel, A.F.; Abrams, T.A.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Fuchs, C.S.; Kulke, M.H.; Kwak, E.L.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Ryan, D.P.; Szymonifka, J. Panitumumab in patients with KRAS wild-type colorectal cancer after progression on cetuximab. Oncologist 2012, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douez, E.; D’Atri, V.; Guillarme, D.; Antier, D.; Guerriaud, M.; Beck, A.; Watier, H.; Foucault-Fruchard, L. Why is there no biosimilar of Erbitux®? J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 34, 115544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Y.; Wang, R.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, A.L.; Sun, L.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhen, Y.S.; et al. An EGFR-targeting antibody-drug conjugate LR004-VC-MMAE: Potential in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and other malignancies. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.C.; Chiang, P.F.; Kuo, Y.J.; Peng, C.L.; Chen, I.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, C.A.; Chiang, Y.C. Develop companion radiopharmaceutical YKL40 antibodies as potential theranostic agents for epithelial ovarian cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, J.S.; Richey, T.; Stuckey, A.; Donnell, R.; Oosterhof, A.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Smits, N.C.; Kennel, S.J. SPECT imaging of peripheral amyloid in mice by targeting hyper-sulfated heparan sulfate proteoglycans with specific scFv antibodies. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2012, 39, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migotto, M.A.; Mardon, K.; Orian, J.; Weckbecker, G.; Kneuer, R.; Bhalla, R.; Reutens, D.C. Efficient Distribution of a Novel Zirconium-89 Labeled Anti-cd20 Antibody Following Subcutaneous and Intravenous Administration in Control and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis-Variant Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagayasu, M.; Ozeki, K. Combination of cassette-dosing and microsampling for reduced animal usage for antibody pharmacokinetics in cynomolgus monkeys, wild-type mice, and human FcRn transgenic mice. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetuximab (Erbitux) New Drug Application (NDA). PMDA (Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency). 2008. Available online: https://www.pmda.go.jp/drugs/2008/P200800039/index.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Liu, L. Pharmacokinetics of monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, P.; Goswami Sewel, D.; Boylan, M.; Sharma, A.K.; Spallholz, J.E. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Trastuzumab (Tz) and Se-Trastuzumab (Se-Tz) against the Her/2 Breast Cancer Cell Lines JIMT-1 and BT-474. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyeva, A.; Schulga, A.; Rinne, S.S.; Günther, T.; Orlova, A.; Deyev, S.; Tolmachev, V. Indirect Radioiodination of DARPin G3 Using N-succinimidyl-Para-Iodobenzoate Improves the Contrast of HER2 Molecular Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štulhofer Buzina, D.; Martinac, I.; Ledić Drvar, D.; Čeović, R.; Bilić, I.; Marinović, B. The Most Common Cutaneous Side Effects of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors and Their Management. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. ADC 2015, 23, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, R. Anticipating and managing the cutaneous side effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 10 (Suppl. S1), 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zong, H.; Han, L.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, H.; Gilly, J.; Zhang, B.; Lu, H.; Chen, J.; Sun, R.; et al. A novel bispecific antibody targeting CD3 and prolactin receptor (PRLR) against PRLR-expression breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; He, W.; Ma, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, F. In-vitro internalization and in-vivo tumor uptake of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody LA22 in A549 lung cancer cells and animal model. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2009, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Meng, Z.; Gan, H.; Gu, R.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Dou, G. Tissue distribution and metabolism of 125I-rAncrod in Wistar rats. J. Isot. 2015, 28, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Ren, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, C.; Yuan, C.; Li, H.; Tong, X.; et al. Inhibition of CISD2 promotes ferroptosis through ferritinophagy-mediated ferritin turnover and regulation of p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Watabe, T.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Shirakami, Y.; Naka, S.; Ooe, K.; Toyoshima, A.; Nagata, K.; Haberkorn, U.; Kratochwil, C.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein targeted therapy using [177Lu] FAPI-46 compared with [225Ac] FAPI-46 in a pancreatic cancer model. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Z.; He, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yao, G.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, J.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, W.; et al. Development of a Humanized VHH Based Recombinant Antibody Targeting Claudin 18.2 Positive Cancers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 885424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zboralski, D.; Hoehne, A.; Bredenbeck, A.; Schumann, A.; Nguyen, M.; Schneider, E.; Ungewiss, J.; Paschke, M.; Haase, C.; von Hacht, J.L.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of FAP-2286 for fibroblast activation protein targeted radionuclide imaging and therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3651–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Cai, H.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Yuan, C.; Lu, X.; Wan, L. Biological evaluation of 131I- and CF750-labeled Dmab(scFv)-Fc antibodies for xenograft imaging of CD25-positive tumors. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 459676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Pan, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, K.; Ji, H.; Zhu, K.; Song, W.; Song, Y.; Song, X.; et al. Nectin-4-targeted immunoSPECT/CT imaging and photothermal therapy of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).