Abstract
Fungi are important resource for the discovery of novel bioactive natural products. This study investigated the metabolites produced by Mariana-Trench-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. SY2601 in EY liquid and rice solid media, resulting in the isolation and structure determination of 28 metabolites, including five new compounds, asperindopiperazines A–C (1–3), 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21), and 12S-aspertetranone D (26). Structures of the new compounds were elucidated based on extensive NMR spectral analyses, HRESIMS data, optical rotation, ECD, and 13C NMR calculations. The new compound 12S-aspertetranone D (26) exhibited antibacterial activity against both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli with MIC values of 3.75 and 5 μg/mL, respectively.
1. Introduction
Marine fungi are important resources for the discovery of novel bioactive natural products and drug lead compounds [1,2,3,4,5]. Among them, Aspergillus fungi have been proved to be one of the most abundant novel bioactive compound producers [3,4,5]. It was reported that a total of 512 new marine-derived natural products were isolated from Aspergillus fungal origins from 1992 to 2014, of which 36% exhibited diverse bioactivities [3]. Recent updates indicated that 361 new secondary metabolites were identified from the Aspergillus fungi from 1915 to 2020. Since then, more and more novel bioactive natural products have been continuously isolated from marine-derived Aspergillus species, including p-terphenyl derivatives of asperterphenyls A-N from A. sp. SCSIO41315 [6], cyclopentapeptides of pseudoviridinutans A-F from A. pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 [7], and indoloquinazoline alkaloids of clavutoines A-U from A. clavutus LZD32-24 [8].
The Mariana Trench is well known for being the deepest site in the Earth’s oceans, and a number of investigations showed that the Mariana Trench is rich in microorganisms [9,10,11,12]. Previously reported metabolites from the Mariana Trench microorganisms included phenazines [13,14], aniline-tetramic acids [15], phenylbutenote and nocapyrone [16], and n-acetylglutaminyl glutamine amide and desferrioxamine B [17]. Obviously, the diversity of chemical structures and bioactivities of the metabolites produced by the Mariana Trench microorganisms is unclear.
Recently, we have conducted chemical investigations on the metabolites of several Mariana-Trench-associated microorganisms, leading to the isolation and structure elucidation of number of novel compounds, such as streptothiazolidine A, streptodiketopiperazines A and B, and (S)-1-(3-ethylphenyl)-1,2-ethanediol [18]. Streptothiazolidine A and streptodiketopiperazines A and B had antifungal activity against Candida albicans [18]. In current study, we further investigated the metabolites produced by a Mariana-Trench-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SY2601 cultured in EY liquid and rice solid media, resulting in the isolation and identification of twenty-eight metabolites (1–28, Figure 1), including five new compounds, asperindopiperazine A–C (1–3), 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21), and 12S-aspertetranone D (26). Herein, we report the culture of strain SY2601 and the isolation, structure elucidation, and bioactive evaluation of these isolated compounds.
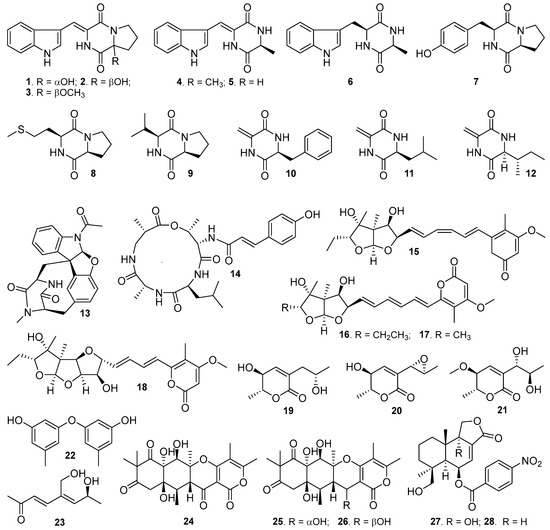
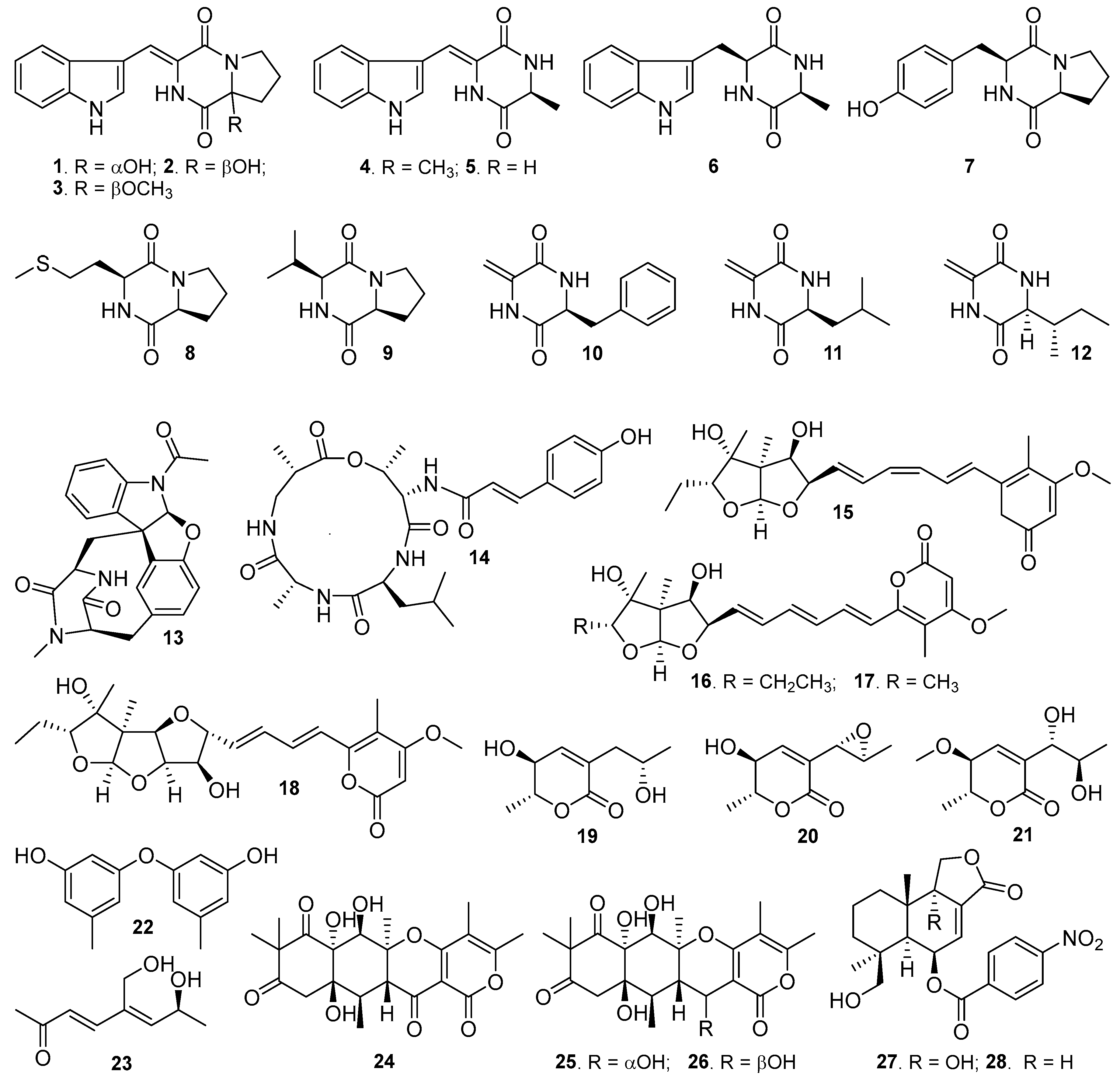
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–28 isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus sp. SY2601.
2. Results and Discussion
The isolated strain SY2601 (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials) was assigned as Aspergillus sp. SY2601 based on its ITS rDNA sequence (Figure S2), which was an over 99.8% match to those of eleven Aspergillus species (Table S1). The extracts prepared from the large-scale cultures of strain SY2601 in EY liquid and rice solid media were separated by column chromatography, followed by HPLC purification, to afford compounds 1–28.
Based on their NMR spectroscopic analyses, optical rotation values, co-HPLC analysis with authentic samples, and comparison to reported data, 23 known compounds were identified: 2-deisoprenyl-neoechinulin A (4) [19], dipodazine (5) [20], cyclo-L-tryptophan-L-alanine (6) [21], cyclo-L-proline-L-tyrosine (maculosin, 7) [22], cyclo-L-proline-L-methionine (8) [22], cyclo-L-proline-L-valine (9) [22], (6S)-3-methylene-6-benzyl-2,5-piperazinedione (10) [23], (6S)-3-methylene-6-(2-methylpropyl)-2,5-piperazinedione (11) [24], (6S,8S)-3-methylene-6-(1-methylpropyl)-2,5-piperazinedione (12) [25], azonazine (13) [26], aspergillipeptide A (14) [27], isoasteltoxin (15) [28], asteltoxin (16) [28], asteltoxins C (17) and B (18) [29], dihydroaspyrone (19) [30], aspyrone (20) [31], diorcinol (22) [32], aspinonediol (23) [30], aspertetranones A (24) and D (25) [33], insolicolide A (27) [34], and 9-deoxyinsolicolide (28) [34]. The 13C and 1H NMR data of these known compounds are listed in Tables S2–S11 in Supplementary Materials.
The HRESIMS spectrum of compound 1 showed ion peaks at m/z 298.1192 [M + H]+ (calcd. C16H16N3O3, 298.1192), 320.1011 [M + Na]+ (calcd. C16H15N3NaO3, 320.1011), and 617.2123 [2M + Na]+ (calcd. C32H30N6NaO6, 617.2125), corresponding to molecular formulate C16H15N3O3. Extensive NMR spectroscopic analyses showed that compound 1 is composed of an indole (A), 3-methylene-6-hydroxy-2,5-piperazinedione (B), and 2-hydroxypyrrolidine (C) (Figure 2) substructure. The presence of the indole group (A) was indicated by its characteristic NMR signals at δC 126.8 (CH, C-2), 108.1 (C, C-3), 118.1 (CH, C-4), 119.9 (CH, C-5), 122.0 (CH, C-6), 111.8 (CH, C-7), 135.7 (C, C-8), and 127.0 (C, C-9); and δH 11.67 (1H, s, H-1), 7.94 (1H, s, H-2), 7.66 (1H, d, 8.0 Hz, H-4), 7.10 (1H, t, 8.0 Hz, H-5), 7.16 (1H, t, 8.0 Hz, H-6), and 7.43 (1H, d, 8.0 Hz, H-7) (Table 1). Similarly, the 3-methylene-6-hydroxy-2,5-piperazinedione unit (B) was deduced from its NMR signals at δC 108.0 (CH, C-10), 123.7 (C, C-11), 166.1 (C, C-13), 86.5 (C, C-14), and 159.9 (C, C-19); and δH 7.02 (1H, s, H-10), 9.57 (1H, br s, H-12), and 6.75 (1H, br s, OH-14). The 2-hydroxypyrrolidine moiety (C) resonated at δC 86.5 (C, C-14), 35.7 (CH2, C-15), 19.4 (CH2, C-16), and 44.7 (CH2, C-17); and δH 2.12 (2H, m, H-15), 2.03 (1H, m, H-16a), 1.88 (1H, m, H-16b), 3.62 (1H, m, H-17a), 3.50 (1H, m, H-17b), and 6.75 (1H, br s, OH-14). As depicted in Figure 2, HMBC correlations of H-2 with C-10; H-10 with C-2, C-9, and C-19; H-15 with C-13 and C-14; and H-17 with C-14 established the linkage of the three groups. The absolute configuration at C-14, the only chiral carbon, was determined through optical rotation (OR) calculations [35,36]. The results showed a positive OR value (+85.6) for 14R (Table S12) and a negative OR value (–85.6) for 14S (Table S14). Accordingly, a 14R configuration was assigned for 1 because of its positive OR value (+78.7). Thus, the structure of 1 was elucidated as a new indolyl diketopiperazine, named asperindopiperazine A. Its 13C and 1H NMR data (Table 1) were assigned based on HMQC and HMBC correlations.
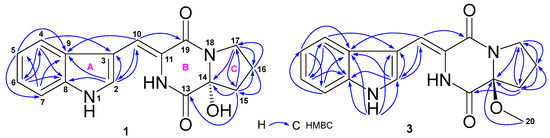
Figure 2.
Key HMBC correlations of asperindopiperazines A (1) and C (3).

Table 1.
13C and 1H NMR data of asperindopiperazines A–C (1–3) (in DMSO-d6).
Compound 2 had the same molecular formulate as that of 1 based on its HRESIMS ion peaks at m/z 298.1191 [M + H]+, 320.1011 [M + Na]+, and 617.2122 [2M + Na]+, as well as 13C NMR data. Both 2 and 1 had very close UV absorptions. Detailed analysis of the 13C and 1H NMR spectra of 2 indicated that the chemical shifts of 2 bore a resemblance to those of 1. However, compound 2 showed a negative OR value (–80.0). Thus, compound 2 should be an isomer of 1 with a 14S configuration. The structure of 2 was thus determined to be a new indolyl diketopiperazine, named asperindopiperazine B. Its 13C and 1H NMR data are reported in Table 1.
Compound 3 gave HRESIMS ion peaks at m/z 312.1348 [M + H]+ (calcd. C17H18N3O3, 312.1348), 334.1171 [M + Na]+ (calcd. C17H17N3NaO3, 334.1168), and 645.2427 [2M + Na]+ (calcd. C34H34N6NaO6, 645.2438), 14 mass units higher than those of 2 and 1. Compound 3 also shared very similar UV absorptions as 2 and 1, suggesting that 3 was an analogue of 2 and 1. Detailed comparison of the 13C and 1H NMR data (Table 1) of 3 with those of 2 and 1 concluded that the chemical shifts of carbons and protons of the three compounds were almost superimposable, excepted for additional signals (δC 51.1; δH 3.16, 3H, s) for a methoxy group in 3. HMBC correlation (Figure 2) of H-20 (δH 3.16) with C-14 (δC 91.3) established the position of this methoxy group at C-14. The downfield chemical shift (Δ 4.8 ppm) of C-14 in 3, when compared to those in 2 and 1, also supported the position of this methoxy group. The 14S configuration in 3 was assigned based on its negative OR value (–29.6). Therefore, the structure of 3 was elucidated as an analogue of compounds 2 and 1, a new indolyl diketopiperazine, named asperindopiperazine C. The 13C and 1H NMR data of 3 are reported in Table 1.
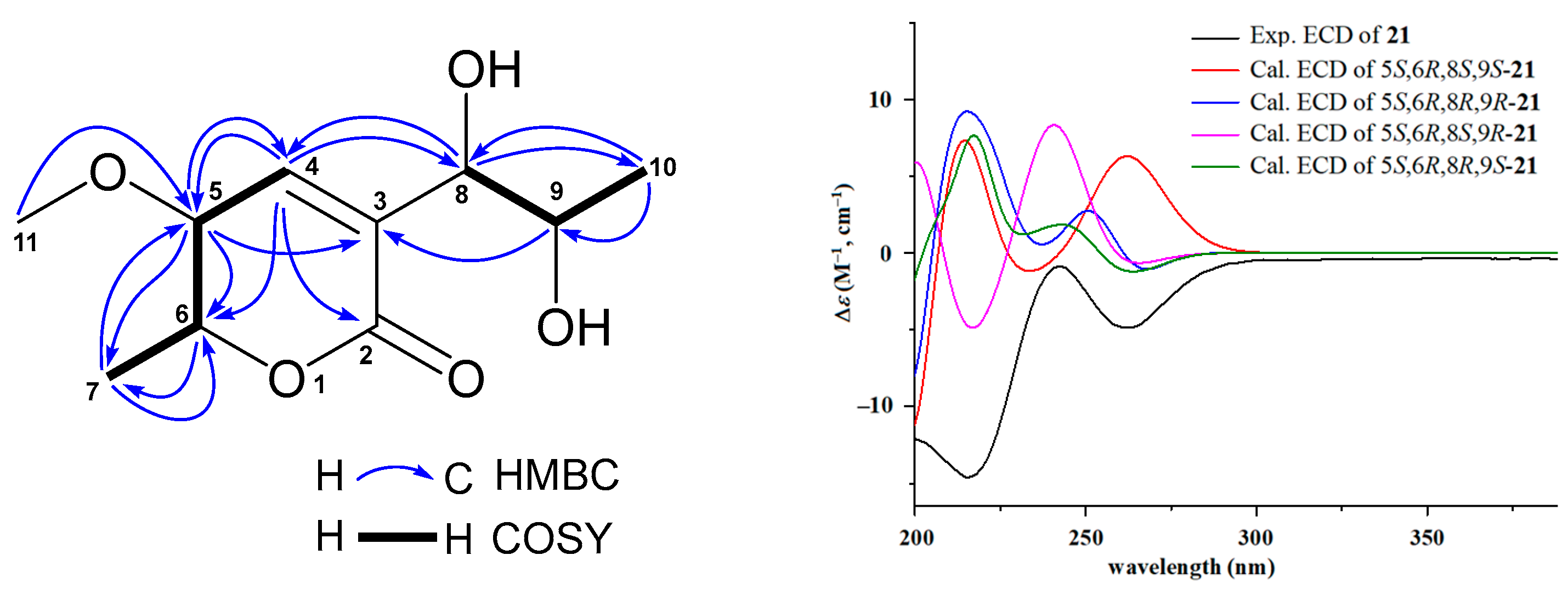
Compound 21 showed HRESIMS ion peaks at m/z 217.1072 [M + H]+ (calcd for C10H17O5, 217.1076) and 239.0897 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H16NaO5, 239.0895), suggesting a molecular formula C10H16O5. Compound 21 shared similar UV absorptions with those of the known compounds 19 and 20, implying they are aspyrone analogues. Interpretation of its 13C, 1H, HMQC, and HMBC NMR spectra indicated that 21 had one carbonyl (δC 163.2), two olefinic carbons (δC 146.2 and 128.2), four oxymethines (δC 82.1, 77.9, 68.0, and 66.7), one methoxy (δC 57.0), and two methyls (δC 18.5 and 17.6). Further comparison of its NMR data with those of 19 (Table S8) showed that both 21 and 19 exhibited very similar patterns of NMR chemical shifts, exception for that the methylene (δC 39.7; δH 2.44, 2.40) at C-8 in 19 was replaced by an oxymethine (δC 77.9; δH 4.15) in 21 and additional NMR signals (δC 57.0; δH 3.20) for a methoxy group were observed in the NMR spectra of 21. HMBC correlation (Figure 3) of H-11 (δH 3.20) with C-5 (δC 82.1) determined this methoxy group at C-5 position. The absolute configurations of 21 were assigned based on the results from ECD and 13C NMR calculations [37,38]. Because all previously reported aspyrone analogues [30,31,39,40,41] including compounds 19 and 20 shared the same 5S,6R-configuration, only four model molecules of 5S,6R,8S,9S-21, 5S,6R,8R,9R-21, 5S,6R,8S,9R-21, and 5S,6R,8R,9S-21 were applied for ECD calculations. The results (Figure 3) indicated that the experimental ECD spectrum was in agreement with the calculated ECD curve of the model molecule 5S,6R,8S,9R-21, suggesting a 5S,6R,8S,9R-configuration for 21, which was further supported by the results from 13C NMR calculations. As shown in Table S24, the experimental 13C NMR data of 21 were close to those of the model molecule of 5S,6R,8S,9R-21 with a DP4+ probability score of 98.87%. Therefore, the structure of 21 was identified as 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone, a new member of the aspyrone family with a 5S,6R,8S,9R-configuration, which was the same as that of a reported compound of 8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone [40,41]. The 13C and 1H NMR data (Table 2) of 21 were unambiguously assigned based on the HMQC, COSY, and HMBC correlations (Figure 3).
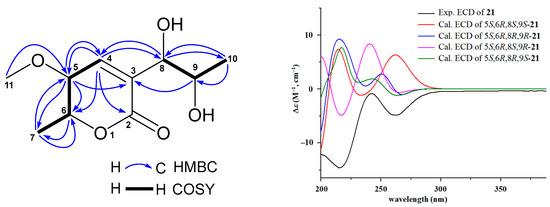
Figure 3.
Key HMBC and COSY correlations of 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21), the experimental ECD spectrum of 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21), and the calculated ECD curves of the four model molecules at the b3lyp/6-311+g (d, p) level in MeOH.

Table 2.
13C and 1H NMR data of 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21) and 12S-aspertetranone D (26) (in DMSO-d6).
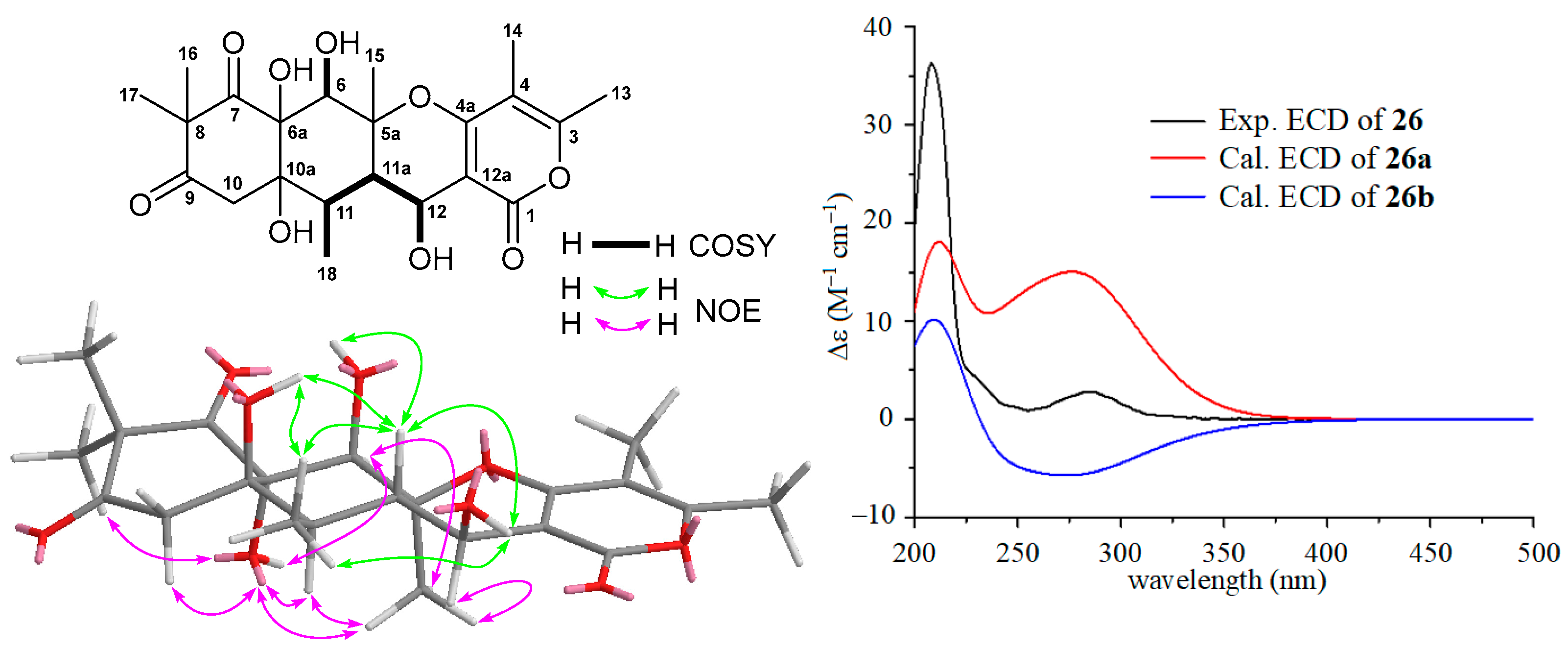
The HRESIMS spectrum of compound 26 gave ion peaks at m/z 437.1821 [M + H]+ (calcd for C22H29O9, 437.1812) and 459.1631 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C22H28NaO9, 459.1631), corresponding to molecular formula C22H28O9, which is the same as that of aspertetranone D (25). Careful analyses of the 1H, 13C, COSY, and NOESY spectra of 26 and comparing its NMR data (Table 2) with those (Table S10) of 25 concluded that the only difference between 26 and 25 was the configuration at the C-12 position. The larger coupling constant of 9.0 Hz (3J11a-12) in 26 and the small coupling constant of 3.9 Hz (3J11a-12) in 25 suggested a trans-configuration between H-11a and H-12 in 26 compared to its counterpart with a cis-configuration in 25. The relative configurations of 26 were further supported by NOE information. As depicted in Figure 4, NOE correlations of H-6 (δH 4.23) with OH-6a (δH 6.69) and H3-15 (δH 1.26), H-11 (δH 1.87) with OH-6a and H3-15, and H3-15 with OH-6a and H-12 (δH 4.36) suggested an α-orientation for these protons, while the β-orientations for OH-6, OH-10a, H-11a, OH-12, and H3-18 were indicated by NOE correlations of OH-6 (δH 6.62) with H-11a (δH 2.12), OH-10a (δH 4.86) with H-11a and H3-18 (δH 1.10), H-11a with OH-12 (δH 4.76) and H3-18, and OH-12 with H3-18. A combination of ECD and 13C NMR calculations was used to determine the absolute configuration of 26. Two model molecules of 5aS,6R,6aR,10aR,11R,11aS,12S (26a) and 5aR,6S,6aS,10aS,11S,11aR,12R (26b) were applied for ECD and 13C NMR calculations, respectively. As shown in Figure 4, the experiment ECD spectrum of 26 was close to the calculated curve of the model molecule 26a, indicating 26 had a 5aS,6R,6aR,10aR,11R,11aS,12S-configuration, which was further supported by the results of the 13C NMR calculations with a DP4+ probability score of 77.86% (Table S29). Therefore, the structure of 26 with a β-OH group at C-12, an analogue of 25, was elucidated as a new putative meroterpenoid [33], named 12S-aspertetranone D. Its 13C and 1H NMR are reported in Table 2.
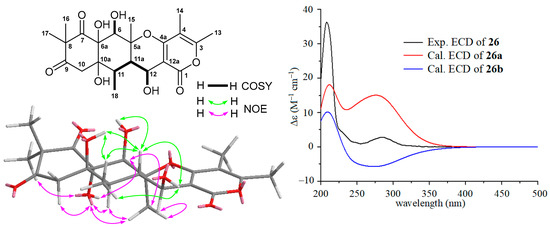
Figure 4.
COSY and key NOE correlations of 12S-aspertetranone D (26), the experimental ECD spectrum of 12S-aspertetranone D (26), and the calculated ECD curves of the two model molecules of 26a and 26b at the b3lyp/6-311+g (d, p) level in MeOH.
The antimicrobial activity of compounds 1–28 against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans were evaluated by the micro-broth dilution method [42]. The results (Table 3) showed that new putative meroterpenoid 12S-aspertetranone D (26) exhibited antibacterial activity against both MRSA and E. coli with MIC values of 3.75 and 5 μg/mL, respectively. Known compound aspyrone (20) also had antibacterial activity, with MIC values of 40 μg/mL for MRSA and 21 μg/mL for E. coli; while cyclo-L-proline-L-valine (9), (6S)-3-methylene-6-(2-methylpropyl)-2,5-piperazinedione (11), aspergillipeptide A (14), and diorcinol (22) showed weak antifungal activity (MIC: 48–49 μg/mL) against C. albicans. In addition, diorcinol (22, 25 μg/mL) and insolicolide A (27, 4 μg/mL) displayed antibacterial activity against E. coli.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial activity of tested compounds (MIC: μg/mL).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
The materials for extraction, isolation, and bioactivity evaluation of compounds, and the instruments used for compound purification, optical rotation, UV, ECD, IR, NMR, and HRESIMS measurement were the same as our previous publication [18]. Culture media used in this study were prepared by the authors, including B solid medium (soluble starch 20.0 g, KNO3 1.0 g, MgSO4⋅7H2O 0.5 g, NaCl 0.5 g, K2HPO4 0.5 g, FeSO4 0.01 g, agar 30.0 g, water 1 L), BY solid medium (B solid medium 1 L, sea salt 35.0 g), CA solid medium (glycerol 6 mL, arginine 1.0 g, K2HPO4 1.0 g, MgSO4·7H2O 1.0 g, agar 30.0 g, water 1 L), CAY solid medium (CA solid medium 1 L, sea salt 35.0 g), D solid medium (potato dextrose broth 28.0 g, agar 30.0 g, water 1 L), DY solid medium (D solid medium 1 L, sea salt 35.0 g), E solid medium (yeast 1.0 g, tryptone 5.0 g, FeCl3⋅6H2O 0.17 g, KH2PO4 0.12 g, agar 30.0 g, water 1 L), EY solid medium (E solid medium 1 L, sea salt 35.0 g), SC solid medium (peptone 5.0 g, lactose 4.0 g, Na2HPO4 5.5 g, NaH2PO4 4.5 g, NaHSeO3 4.0 g, L-cystine 0.01 g, agar 30.0 g, water 1 L), and SCY solid medium (SC solid medium 1 L, sea salt 35.0 g).
3.2. Isolation and Identification of Strain SY2601
The strain SY2601 was isolated from sediment obtained from the Mariana Trench at a depth of 5842 m, as per the described procedure in our previous publication [18] by using ten different solid media (B, BY, CA, CAY, D, DY, E, EY, SC, SCY). The signal-purified colony of SY2601 was obtained on the E medium coated with a 10–3 g/mL sample suspension.
The strain SY2610 was identified by comparing its ITS rDNA sequence (accession number: OR646740) with the data of the GenBank. The ITS rDNA sequence analysis was performed by Legenomics (Hangzhou, China). The strain Aspergillus sp. SY2601 can be obtained from the Laboratory of Institute of Marine Biology and Pharmacology, Ocean College, Zhoushan Campus, Zhejiang University, China.
3.3. Mass Culture of Strain SY2601 in EY Liquid and Rice Solid Media
For strain SY1601 cultured in EY medium, a pure colony of the strain SY2601 picked from the E slant medium was transferred into a 250 mL EY liquid medium in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask and incubated at 28 °C for 3 days with shaking (180 rpm) to obtain a seed broth. The 5 mL seed broth was further transferred into 250 mL of an EY liquid culture medium in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and then statically incubated at 28 °C for 30 days. A total of 300 bottle cultures (75 L) were prepared for this study.
For strain SY2610 cultured in rice solid medium, the above prepared seed broth (5 mL) was transferred into a rice medium (40 g rice, 60 mL of 25 g/L sea salt solution) in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask and then incubated at 28 °C for 24 days. A total of 200 bottles of rice medium cultures were prepared for this study.
3.4. Extraction and Isolation of Compounds 1–28
Compounds 1–17 were isolated from the cultures of strain SY 2601 in EY liquid medium. The 75 L cultures of strain SY 2601 were filtered to give filtrate and mycelia. The filtrate was extracted with EtOAc three times to give EtOAc extract (2.95 g), and the mycelia were extracted with MeOH three times to give MeOH extract (20.01 g). The combination (22.96 g) of the two extracts dissolved in MeOH was mixed with silica gel (25 g). After removal of the solvent, the dried mixture was separated using a column of silica gel (350 g), successively eluting with a mixture of petroleum ether and EtOAc (10:1, 5:1,1:1, each 2 L) and a mixture of EtOAc and MeOH (10:1, 5:1, 1:1, 0:1, each 2 L) to furnish 28 fractions (Frs. 1–28, each 500 mL). Based on the results of HPLC analyses, the 28 fractions were combined into six fractions of Fr.A (Frs.1–5), Fr.B (Frs.6–9), Fr.C (Frs.10–13), Fr.D (Frs.14–17), Fr.E (Frs.18–20), and Fr.F (Frs.21–28).
Fr.D (0.7 g) was fractionated on a column of ODS (70 g), successively eluting with 30, 50, 70, and 100% MeOH (each 270 mL) to give eight subfractions (SFrs.D1–D8, each 135 mL). Compounds 10 (0.6 mg, tR 37.9 min), 11 (2.2 mg, tR 34.5 min), and 12 (0.5 mg, tR 30.6 min) were obtained from SFr. D5 by HPLC separation using a Zorbax SB-C18 column (250 × 9.4 mm, 5 µm; mobile phase: ACN/H2O, 16/84; flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; UV detection: 210 nm).
Fr.E (5.5 g) was also fractionated on a column of ODS (150 g), successively eluting with 30, 50, 70, 85, and 100% MeOH (each 600 mL) to give 20 subfractions (Frs.1–20, each 150 mL). According to the results of HPLC analyses, different subfractions were combined into three fractions of SFr.Ea (Frs.2–3), SFr.Eb (Frs.4–6), and SFr.Ec (Frs.7–10). SFr.Ea was separated by prepared HPLC using a Fuji-C18 CT-30 column (280 × 30 mm, 10 µm; mobile phase: MeOH/H2O, 25/75, 0−49 min, 100/0, 49.01−59 min, 25/75, 59.01−69 min; flow rate: 6 mL/min; UV detection: 210 nm) to give compound 7 (10.1 mg, tR 24.6 min), SFr.Ea2 (31.8 mg, tR 31.2 min), SFr.Ea3 (20.8 mg, tR 41.5 min), and SFr.Ea6 (6.5 mg, tR 47.1 min). Further purification of SFr.Ea2, SFr.Ea3, and SFr.Ea6 was performed using the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min, UV detection: 210 nm) to furnish compounds 9 (11.5 mg, tR 24.5 min, ACN/H2O, 15/85), 8 (8.8 mg, tR 39.8 min, ACN/H2O, 10/90), and 6 (0.9 mg, tR 50.0 min, ACN/H2O, 13/87), respectively. SFr.Ec was repeatedly separated on a column of ODS (100 g), successively eluting with 40, 50, 60, 70, and 100% MeOH (each 300 mL) to obtain 20 subfractions (Frs.1–20, each 75 mL) which were combined into four fractions of SFr.Ec1 (Frs.4–7), SFr.Ec2 (Fr.8), SFr.Ec3 (Frs. 9–10), and SFr.Ec4 (Fr. 11–15) based on the results of HPLC analyses. SFr.Ec1 was further separated on the Fuji-C18 CT-30 column (flow rate: 6 mL/min; mobile phase: MeOH/H2O, 48/52; UV detection: 210 nm) to obtain compounds 2 (2.8 mg, tR 32.4 min) and 4 (10.7 mg, tR 24.6 min). Using the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; UV detection: 210 nm), compounds 5 (3.0 mg, tR 41.8 min, ACN/H2O, 20/80) and 3 (2 mg, tR 66.2 min, MeOH/H2O, 48/52) were purified from SFr.Ec2 and SFr.Ec3, respectively. Separation of SFr.Ec4 was performed using the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; mobile phase: ACN/H2O, 34/66, UV detection: 210 nm) to give compounds 13 (8.1 mg, tR 22.4 min), 17 (8.1 mg, tR 40.0 min), 16 (0.4 mg, tR 62.5 min), SFr.Ec4a (10.8 mg, tR 27.2 min), and SFr.Ec4b (4.0 mg, tR 72.4 min). Further purification of SFr.Ec4a and SFr.Ec4b used the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; UV detection: 210 nm) to furnish compounds 14 (6.3 mg, tR 88.1 min, ACN/H2O, 26/74) and 15 (1.3 mg, tR 50.8 min, ACN/H2O, 30/70), respectively.
Similarly, Fr.F (13.1 g) was separated by a column of ODS (280 g), eluting with 30, 50, 70, and 100% MeOH (each 1080 mL) in turn to give 16 subfractions (SFr.F1–16, each 270 mL). SFr.F7 was further separated using the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; mobile phase: ACN/H2O, 24/76; UV detection: 210 nm) to afford compound 1 (1.1 mg, tR 33.1 min).
Compounds 13, 14, and 16–28 were isolated from the cultures of strain SY 2601 in rice medium. Each of the rice cultures in the 200 bottles was extracted by EtOAc three times (each 200 mL). The combined EtOAc extract solution was dried under reduced pressure to give a crude extract (100.75 g).
Initially, this crude extract was fractionated on a column of silica gel (1900 g) eluting with a mixture of petroleum ether and EtOAc (10:1, 5:1, 2:1, 1:1, each 11 L), and then a mixture of EtOAc and MeOH (0:1, 5:1, 1:1, 0:1, each 11 L) to give eight fractions (Frs.1–8, each 11 L), which were combined into five fractions of Fr.A (Frs.1–2), Fr. B (Frs.3–4), Fr. C (Fr.5), Fr. D (Fr. 6–7), and Fr.E (Fr. 8) based on the results of HPLC analyses.
Then, Fr. B (8.6 g) was further fractionated on a column of ODS (300 g), successively eluting with 25, 45, 65, and 100% MeOH (each 1.6 L) to give 16 subfractions (Frs.1–16, each 400 mL), which were further combined into three subfractions of SFr.Ba (Frs.1–2), SFr.Bb (Fr.3), and SFr.Bc (Fr.12). By using the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; UV detection: 210 nm), compounds 20 (6.2 mg, tR 25.3 min, ACN/H2O, 20/80), 21 (3.6 mg, tR 29.3 min, MeOH/H2O, 24/76), and 22 (8.2 mg, tR 49.4 min, MeOH/H2O, 60/40) were purified from SFr.Bb, SFr.Ba, and SFr.Bc, respectively.
Next, Fr. C (6.12 g) was also fractionated on the column of ODS (300 g), successively eluting with 30, 50, 70, 95, and 100% MeOH (each 1.4 L) to give 35 subfractions (Frs. 1–35, each 200 mL), which were combined into five subfractions of SFr.Ca (Fr. 3), SFr.Cb (Frs.12–15), SFr.Cc (Fr.16), SFr.Cd (Fr.17), and SFr.Ce (Fr.18) based on the results of HPLC analyses. Using the SB-C18 column (flow rate: 1.0 mL/min, UV detection: 210 nm), compounds 19 (4.5 mg, tR 39.0 min, MeOH/H2O, 20/80) and 28 (2.3 mg, tR 53.5 min, ACN/H2O, 35/65–60/40, 0–50 min, 100/0, 50.01–60 min) were purified from SFr.Ca and SFr.Ce, respectively; 25 (2.2 mg, tR 38.4 min), 24 (9.6 mg, tR 44.2 min), and 26 (6.7 mg, tR 49.5 min, ACN/H2O, 25/75) from SFr.Cb; 16 (3.6 mg, tR 46.2 min) and 27 (3.8 mg, tR 64.3 min, ACN/H2O, 37/63) from SFr.Cc; and 17 (3.4 mg, tR 33.7 min) and 18 (1.6 mg, tR 31.4 min, ACN/H2O, 36/64) from SFr.Cd.
Finally, Fr.D (10.95 g) was fractionated on the column of ODS (300 g), successively eluting with 30, 50, 70, 90, and 100% MeOH (each 1.2 L) to give 20 subfractions (Frs.1–20, each 300 mL), which were combined into two subfractions of SFr.Da (Frs.1–3) and SFr.Db (Frs.9–11) based on the results of HPLC analyses. By HPLC purification on the SB-C18 column (flow rate:1.0 mL/min; UV detection: 210 nm), compound 23 (1.2 mg, tR 43.9 min, MeOH/H2O, 20/80) was obtained from SFr.Da, and compounds 13 (2.1 mg, tR 41.9 min) and 14 (1.6 mg, tR 54.9 min, ACN/H2O, 28/72) were obtained from SFr.Db.
Asperindopiperazine A (1): White amorphous powder; molecular formula C16H15N3O3; [α]20D +78.7° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 210 (4.78), 346 (4.43) nm; IR (ATR) νmax 3387, 3051, 1690, 1651, 1622, 1489, 1457, 1395, 1232, 1185, 1133, 1083, 744 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 298.1192 [M + H]+ (calcd. C16H16N3O3, 298.1192), 320.1011 [M + Na]+ (calcd. C16H15N3NaO3, 320.1011), 617.2123 [2M + Na]+ (calcd. C32H30N6NaO6, 617.2125).
Asperindopiperazine B (2): White amorphous powder; molecular formula C16H15N3O3; [α]20D –80.0° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 210 (4.64), 350 (3.95) nm; IR (ATR) νmax 3312, 2960, 1682, 1666, 1620, 1545, 1423, 1339, 1236, 1176, 1114, 1042, 755 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 298.1191 [M + H]+ (calcd. C16H16N3O3, 298.1192), 320.1011 [M + Na]+ (calcd. C16H15N3NaO3, 320.1011), 617.2122 [2M + Na]+ (calcd. C32H30N6NaO6, 617.2125).
Asperindopiperazine C (3): White amorphous powder; molecular formula C17H17N3O3; [α]20D –29.6° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 213 (4.64), 350 (4.17) nm; IR (ATR) νmax 3274, 2960, 1686, 1653, 1616, 1530, 1431, 1388, 1240, 1184, 1137, 1109, 1056, 748 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 312.1348 [M + H]+ (calcd. C17H18N3O3, 312.1348), 334.1171 [M + Na]+ (calcd. C17H17N3NaO3, 334.1168), 645.2427 [2M + Na]+ (calcd. C34H34N6NaO6, 645.2438).
5-Methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21): colorless oil; molecular formula C10H16O5; [α]20D –80.4° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 225 (3.57) nm; ECD (c 1 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 216 (–14.59), 242 (–0.87), 262 (–4.84) nm; IR (ATR) νmax 3381, 2985, 2937, 1704, 1652, 1460, 1386, 1216, 1203, 1135, 1064 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, see Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 217.1072 [M + H]+ (calcd for C10H17O5, 217.1076), 239.0897 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C10H16NaO5, 239.0895).
12S-Aspertetranone D (26): White crystal; molecular formula C22H28O9; [α]20D +75.2° (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 205 (5.10), 290 (3.98) nm; ECD (c 1 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 208 (+36.28), 286 (+2.79) nm; IR (ATR) νmax 3421, 2989, 2944, 1696, 1674, 1574, 1457, 1432, 1387, 1248, 1128, 1067, 1038, 996 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, see Table 2; HRESIMS m/z 437.1821 [M + H]+ (calcd for C22H29O9, 437.1812), 459.1631 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C22H28NaO9, 459.1631).
3.5. Optical Rotation Calculations
Optical rotation (OR) calculations were conducted as per our previously described method [36].
3.6. ECD Calculations
The previously described method [18] was used for ECD calculations.
3.7. 13C NMR Calculations
13C NMR calculations were carried out referring to our previous publications [18].
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
The micro-broth dilution method as described in the previous study [42] was applied to determine the antimicrobial activities of all tested compounds against the growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans. Gentamicin and amphotericin B were used as positive controls.
4. Conclusions
Chemical investigation on the metabolites produced by the Mariana-Trench-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SY2601 in both EY liquid and rice solid media resulted in the isolation and identification of twenty-eight metabolites, including five new compounds, asperindopiperazines A–C (1–3), 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21), and 12S-aspertetranone D (26). 12S-aspertetranone D (26) had activity in inhibiting the growth of methicillin-resistant S. aureus and E. coli. The twenty-eight isolated compounds belong to different structural types of indolyl diketopiperazines, diketopiperazines, merosesquiterpenoids, putative meroterpenoid, nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids, peptides, aspyrones, and phenols. The data obtained from current study show that the fungus Aspergillus sp. SY2601 is able to produce abundance metabolites, which enriched the diversity of structures and bioactivities of the metabolites produced by the Mariana-Trench-associated microorganisms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29020459/s1. Figure S1: Colonies of fungus Aspergillus sp. SY2601 cultured in E medium; Figure S2: ITS rDNA sequence of Aspergillus sp. SY2601; Figures S3–S63: NMR, HRESIMS, IR, and UV spectra of asperindopiperazines A–C (1–3), 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21), and 12S-aspertetranone D (26); Table S1: Sequences producing significant alignments of Aspergillus sp. strain SY2601; Tables S2–S11: 13C and 1H NMR data of known compounds 4–20, 22–25, 27, and 28; Tables S12–S15: Data of optical rotation calculations for asperindopiperazine A (1); Tables S16–S23: Data of ECD calculations for 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21); Table S24: Data of 13C NMR calculations for 5-methoxy-8,9-dihydroxy-8,9-deoxyaspyrone (21); Tables S25–S28: Data of ECD calculations for 12S-aspertetranone D (26); Table S29: Data of 13C NMR calculations for 12S-aspertetranone D (26).
Author Contributions
X.-Y.L. and Z.Z. conceived and designed the experiments; C.S. performed the chemical and bioactive experiments; Y.H., X.L. and C.S. carried out the OR and ECD calculations and prepared the data; N.W. and Z.Z. analyzed the data, wrote, and revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Basic Public Welfare Research Project of Zhejiang Province (No. LGF21H300005), the Hainan Provincial Joint Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City (No. 2021CXLH0008), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC0310600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81773587), and the HPC Center of Zhejiang University (Zhoushan Campus). We thank Yu-Xia Sun at Ocean College of Zhejiang University for obtaining the IR spectra of all new compounds.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data in this research are presented in the manuscript and Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rateb, M.E.; Ebel, R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 290–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Ansari, M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Mishra, M. Major bioactive metabolites from marine fungi: A Review. Bioinformation 2015, 11, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, H.S.; Zhu, W.M. New natural products from the marine-derived Aspergillus fungi—A review. Acta Microbilogica Sin. 2016, 56, 331–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.W.; Ding, P. New bioactive metabolites from the marine-derived fungi Aspergillus. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1072–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfali, R.; Aboseada, M.A.; Abdel-Wahab, N.M.; Hassan, H.M.; Perveen, S.; Ameen, F.; Alturki, E.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Recent updates on the bioactive compounds of the marine-derived genus Aspergillus. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17116–17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, L.R.; Hu, Y.W.; Wang, X.; Han, W.R.; Xiao, J.; Pang, X.Y.; Yao, X.G.; Liu, S.W.; et al. Structurally various p-terphenyls with neuraminidase inhibitory from a sponge derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO41315. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 132, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.J.; Tian, D.M.; Chen, M.; Xia, Z.X.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Wei, J.H.; Li, X.; Yao, X.S.; Wu, B.; et al. Molecular networking-guided isolation of cyclopentapeptides from the hydrothermal vent sediment derived fungus Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 and their anti-inflammatory effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 1919–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.C.; Fan, A.; Qi, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Lin, W.H. Indoloquinazoline alkaloids suppress angiogenesis and inhibit metastasis of melanoma cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 141, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunoura, T.; Takaki, Y.; Hirai, M.; Shimamura, S.; Makabe, A.; Koide, O.; Kikuchi, T.; Miyazaki, J.; Koba, K.; Yoshida, N.; et al. Hadal biosphere: Insight into the microbial ecosystem in the deepest ocean on Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1230–E1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, J.; Peoples, L.M.; Hardy, K.; Cameron, J.; Bartlett, D.H. Identification of free-living and particle-associated microbial communities present in Hadal regions of the Mariana Trench. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhao, M.; Pedentchouk, N.; Lea-Smith, D.J.; et al. Proliferation of hydrocarbon-degrading microbes at the bottom of the Mariana Trench. Microbiome 2019, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Mara, P.; Vik, D.; Edgcomb, V.P.; Sullivan, M.B.; Wang, Y. Ecogenomics reveals viral communities across the Challenger Deep oceanic trench. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1055. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Milne, B.F.; Wagner, M.; Schumacher, M.; Sandor, P.; Pathom-Aree, W.; Goodfellow, M.; Bull, A.T.; Horikoshi, K.; Ebel, R.; et al. Dermacozines, a new phenazine family from deep-sea dermacocci isolated from a Mariana Trench sediment. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Ebel, R.; Bull, A.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Fiedler, H.P.; Jaspars, M. Dermacozines H-J isolated from a deep-sea strain of Dermacoccus abyssi from Mariana Trench sediments. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; He, X.Q.; Wu, G.W.; Liu, C.C.; Lu, C.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.J.; Zhang, G.J.; Li, D.H. Aniline-tetramic acids from the deep-sea-derived fungus Cladosporium sphaerospermum L3P3 cultured with the HDAC inhibitor SAHA. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Sun, C.X.; Shah, M.; Zhang, G.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, T.J.; Che, Q.; Li, D.H. New metabolites from a Mariana Trench-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. HDN 17-237. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 22, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Lehri, B.; Al-Saleem, M.S.M.; Goodfellow, M.; Kusuma, A.B.; Nouioui, I.; Soleh, H.; Pathom-Aree, W.; Jaspars, M.; et al. Biotechnological and ecological potential of Micromonospora provocatoris sp. nov., a gifted strain isolated from the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.W.; Qin, L.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z. New antifungal metabolites from the Mariana Trench sediment-associated actinomycete Streptomyces sp. SY1965. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, K.; Aoki, T.; Nakazaki, A.; Kamisuki, S.; Takeno, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Kimoto, K.; Watanabe, N.; Kamakura, T.; Arai, T.; et al. Synthesis of neoechinulin A and derivatives. Synthesis 2008, 23, 3810–3818. [Google Scholar]
- Sùrensen, D.; Larsen, T.O.; Carsten Christophersen, C.; Nielsen, P.H.; Anthoni, U. Dipodazine, a diketopiperazine from Penicillium dipodomyis. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 1181–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, E.; Avendano, C.; Menendez, C. Stereochemical issues related to the synthesis and reactivity of pyrazino[20,10 -5,1]pyrrolo[2,3-b]indole-1,4-diones. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1998, 9, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnaz, S.; Saleem, R.S.; Yameen, B.; Pianet, I.; Schnakenburg, G.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; Franzblau, S.G.; et al. Lahorenoic acids A-C, ortho-dialkyl-substituted aromatic acids from the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas aurantiaca PB-St2. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Mori, Y.; Oda, A.; Okuno, Y.; Kiso, Y.; Hayashi, Y. Acid catalyzed monodehydro-2,5-diketopiperazine formation from N-a-ketoacyl amino acid amides. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 3688–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Lou, J.; Chen, L.C.; Li, Y.; Ban, Z.J.; Huang, J. Cyclodipeptides from Bacillus sp. HZ16. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2017, 29, 783–786. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.; Carmeli, S.; Sar, N. Vibrindole A, a metabolite of the marine bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, isolated from the toxic mucus of the boxfish Ostracion cubicus. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.X.; Crews, M.S.; Draskovic, M.; Sohn, J.; Johnson, T.A.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Yao, X.J.; Bjeldanes, L.F.; Crews, P. Azonazine, a novel dipeptide from a Hawaiian marine sediment-derived fungus, Aspergillus insulicola. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4458–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; He, F.; Nong, X.H.; Qi, S.H. New cyclic tetrapeptides and asteltoxins from gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSGAF 0076. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Qin, X.C.; Tian, X.P.; Liao, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, X.W.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, T.Y.; et al. Antiviral merosesquiterpenoids produced by the Antarctic fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Doi, H.; Yuichi, K.; Sawa, R.; Nakajima, K.; Kubota, Y.; Hosokawa, N.; Tateishi, K.; Nomoto, A. Asteltoxins from the entomopathogenic fungus Pochonia bulbillosa 8-H-28. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1730–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kito, K.; Ookura, R.; Yoshida, S.; Namikoshi, M.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Pentaketides relating to aspinonene and dihydroaspyrone from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus ostianus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Nakahara, S.; Fujioka, S. Aspyrone, a nematicidal compound isolated from the fungus, Aspergillus melleus. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1375–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Yang, M.F.; Ma, J.; Xiao, X.J.; Ma, X.Y.; Zheng, D.G.; Han, M.Y.; Xia, M.L.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Mapook, A.; et al. Neogrisphenol A, a potential ovarian cancer inhibitor from a new record fungus Neohelicosporium griseum. Metabolites 2023, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Qi, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, N.W.; Wu, A.A.; Gui, F.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y.R.; Cao, S.G.; Hu, Z.Y.; et al. Aspertetranones A−D, putative meroterpenoids from the marine algal-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. ZL0-1b14. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.H.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.P.; Luo, X.W.; Pang, X.Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, X.J.; Zhou, X.F. Nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids with cytotoxic activities from a marine-derived Aspergillus ochraceus fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdani, S.; Gautun, O.R.; Koch, H.; Åstrand, P.O. Optical rotation calculations for a set of pyrrole compounds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 7351–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.W.; Ge, Z.W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.Z. New metabolites from the marine-derived bacterium Pseudomonas sp. ZZ820R. Fitoterapia 2020, 143, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyk, M.W.; Siebert, M.R.; Tantillo, D.J. Computational prediction of 1H and 13C chemical shifts: A useful tool for natural product, mechanistic, and synthetic organic chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1839–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Q.; Zhou, Y.L.; Du, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Zhu, W.M. Circumdatin-aspyrone conjugates from the coral-associated Aspergillus ochraceus LCJ11-102. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao-Chun Hu, H.C.; Li, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.H.; Yang, D.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Chen, S.L.; Fülöp, F.; Attila Hunyadi, A.; Yen, C.H.; et al. Secondary metabolites and bioactivities of Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis isolated from Anthurium brownii. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20991–20999. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.B.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.M.; He, Z.H.; Yan, Q.X.; Lin, Y.K.; Xie, C.L.; Xia, J.M.; Luo, Z.H.; Luo, L.Z.; et al. Asperochratides A-J, Ten new polyketides from the deep-sea-derived Aspergillus ochraceus. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 105, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Anjum, K.; Song, T.F.; Wang, W.L.; Yu, S.R.; Huang, H.C.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z. A new curvularin glycoside and its cytotoxic and antibacterial analogues from marine actinomycete Pseudonocardia sp. HS7. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).