Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligands
Abstract
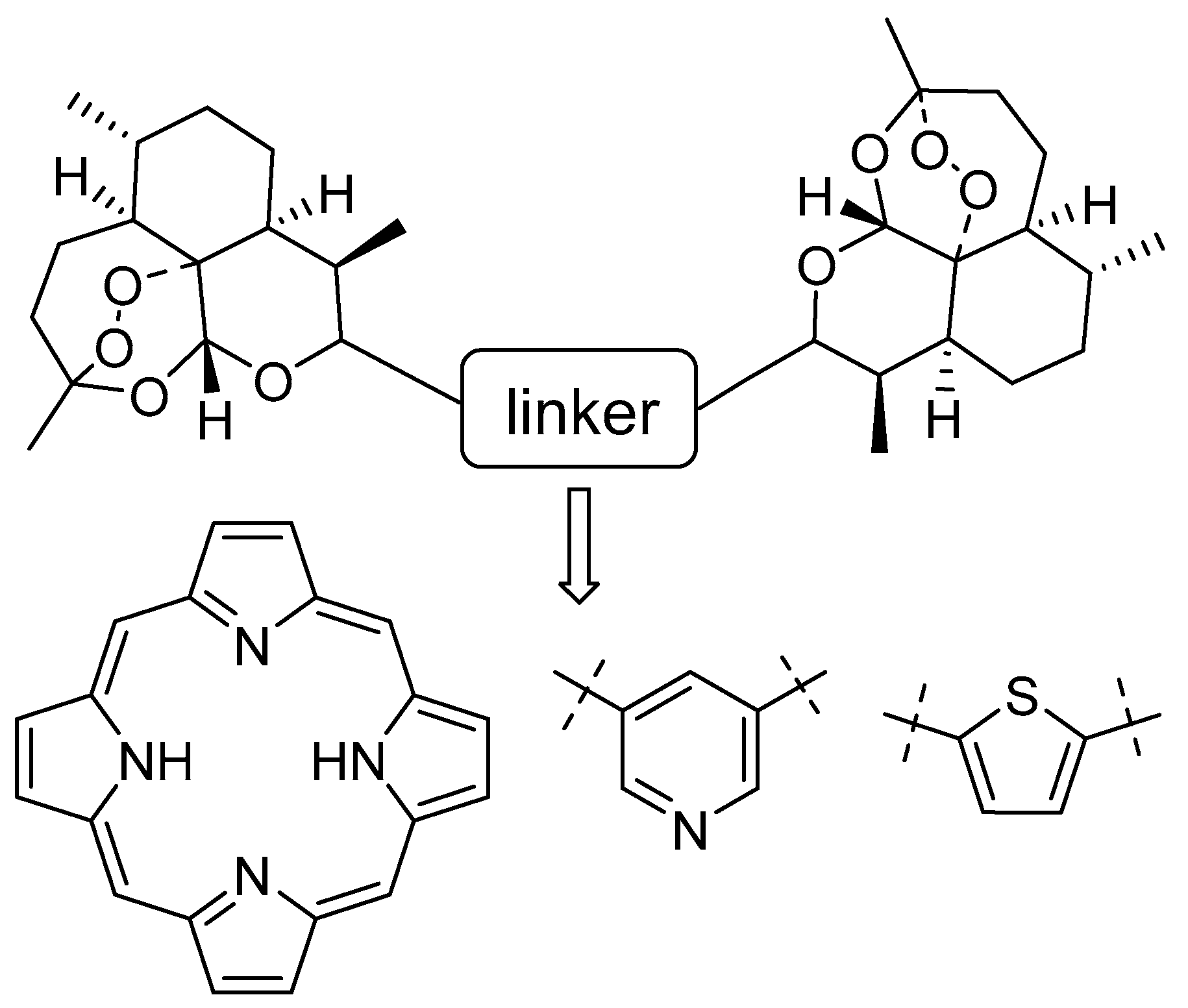
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
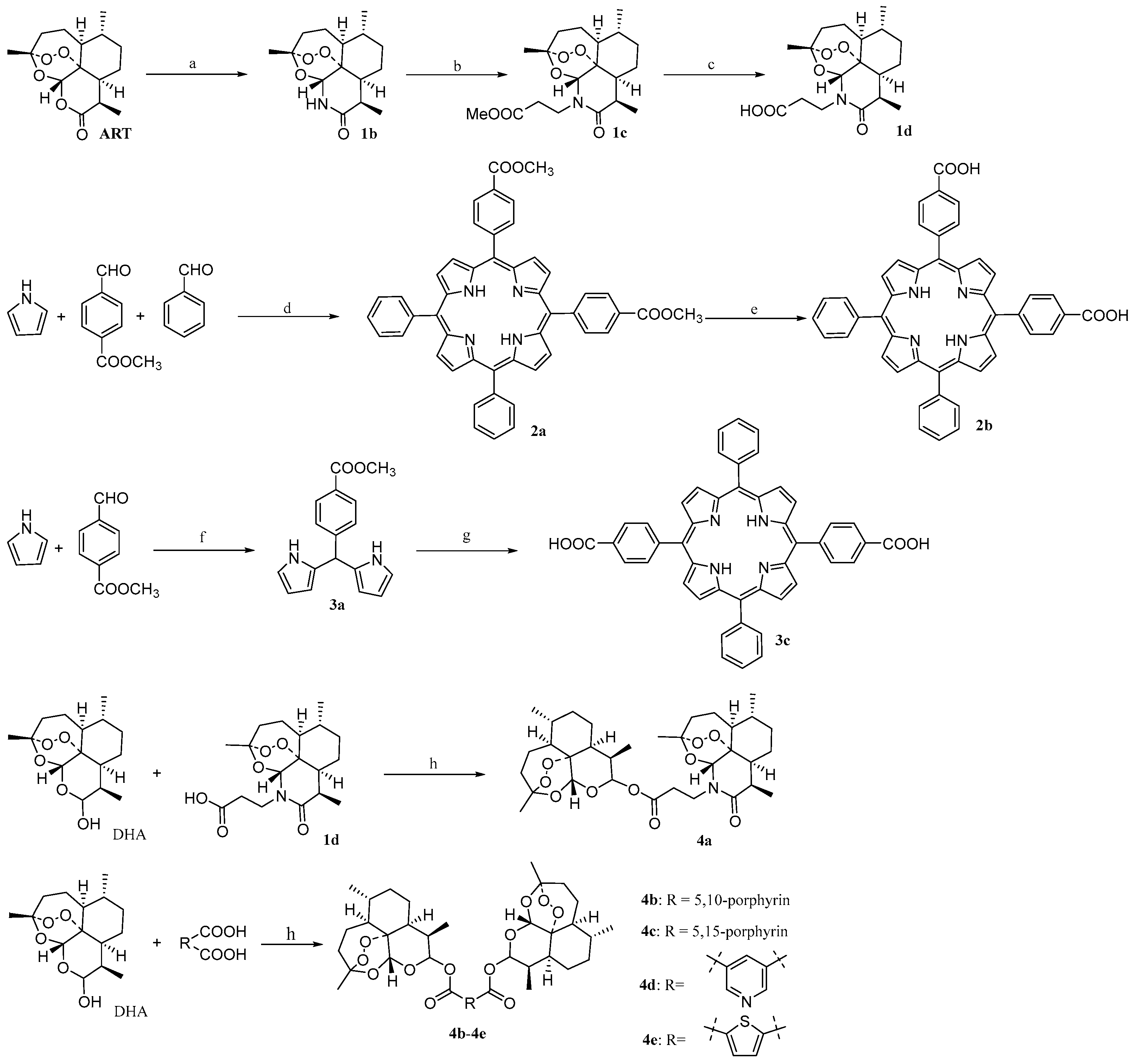
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. Screening of Anti-Cancer Activity
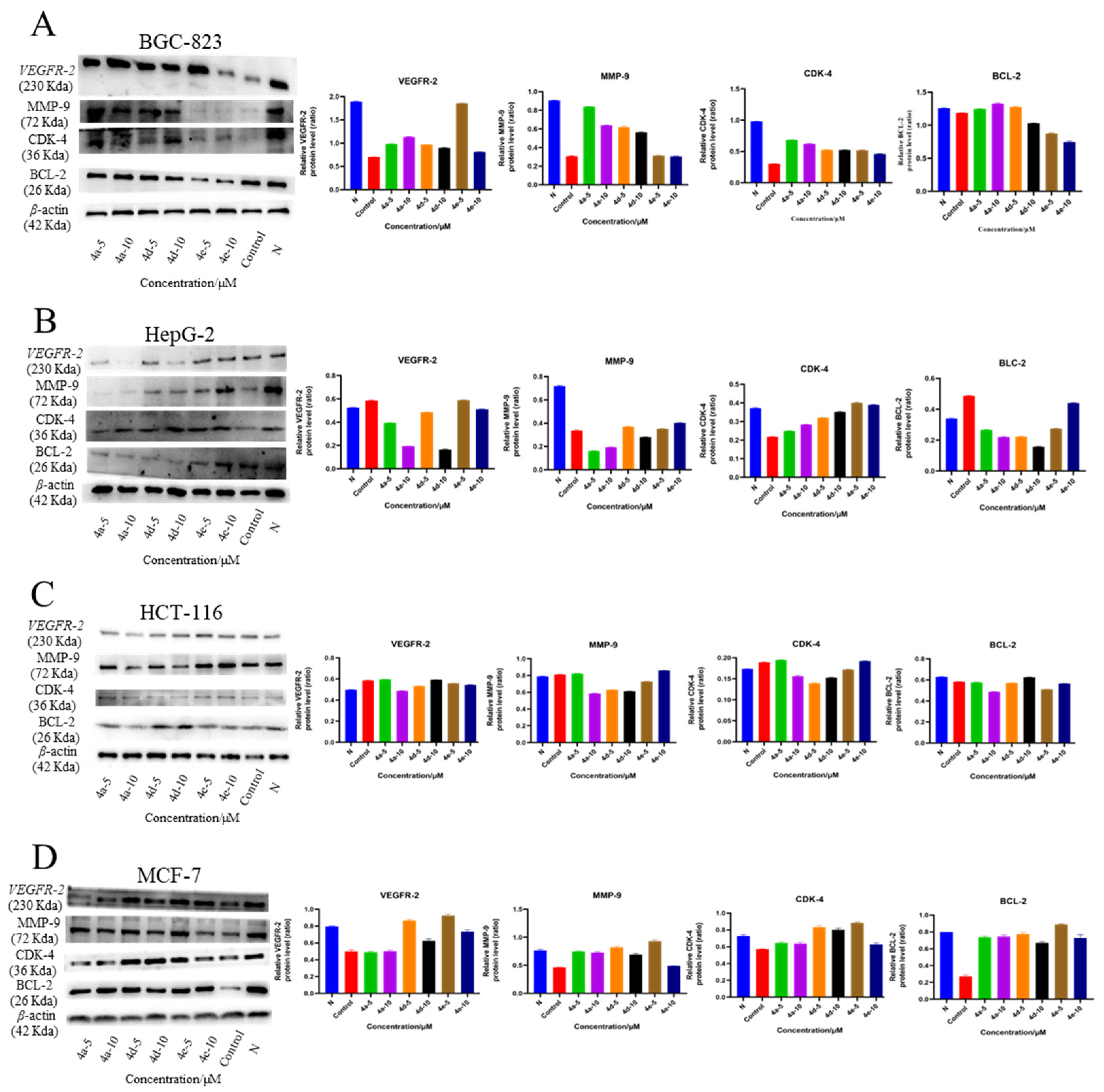
2.2.2. Western Blot Analysis
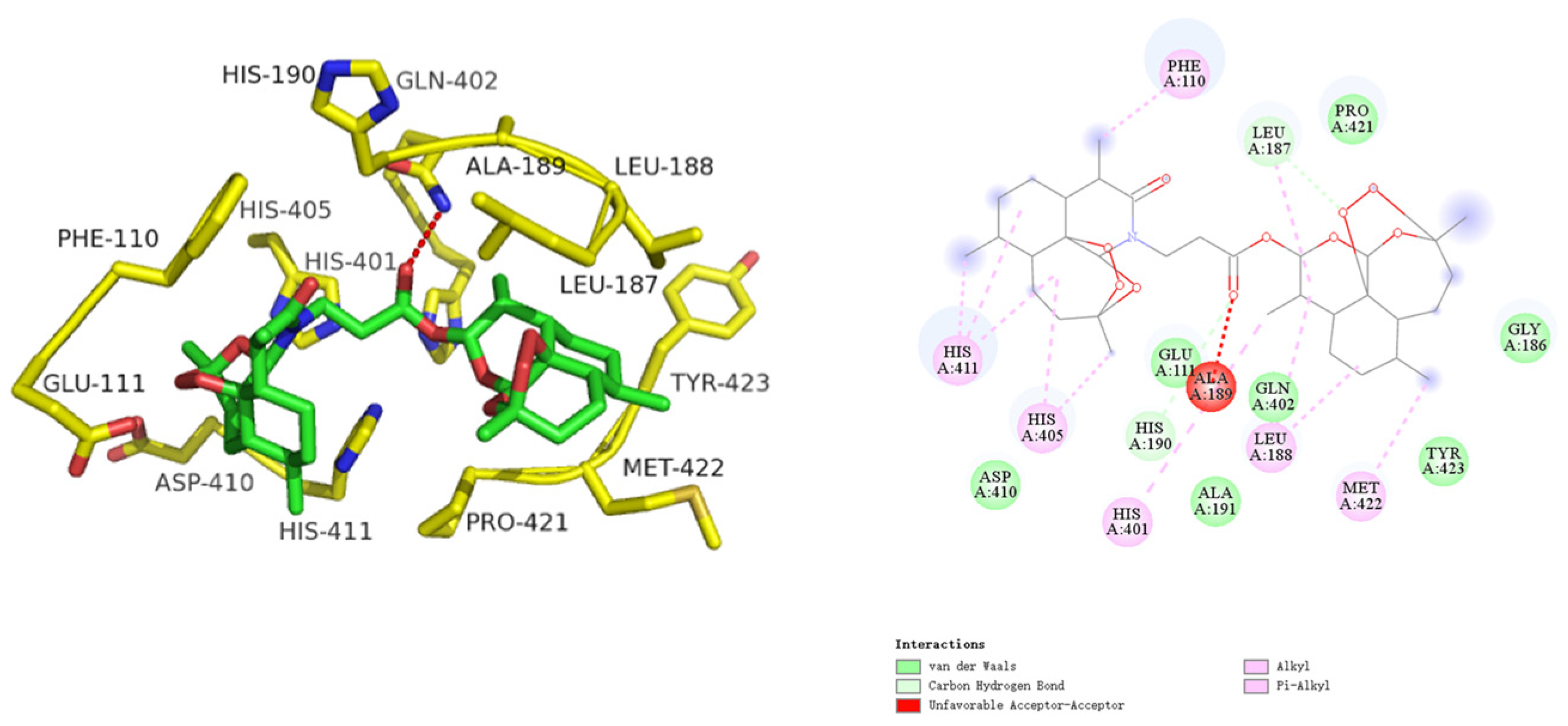
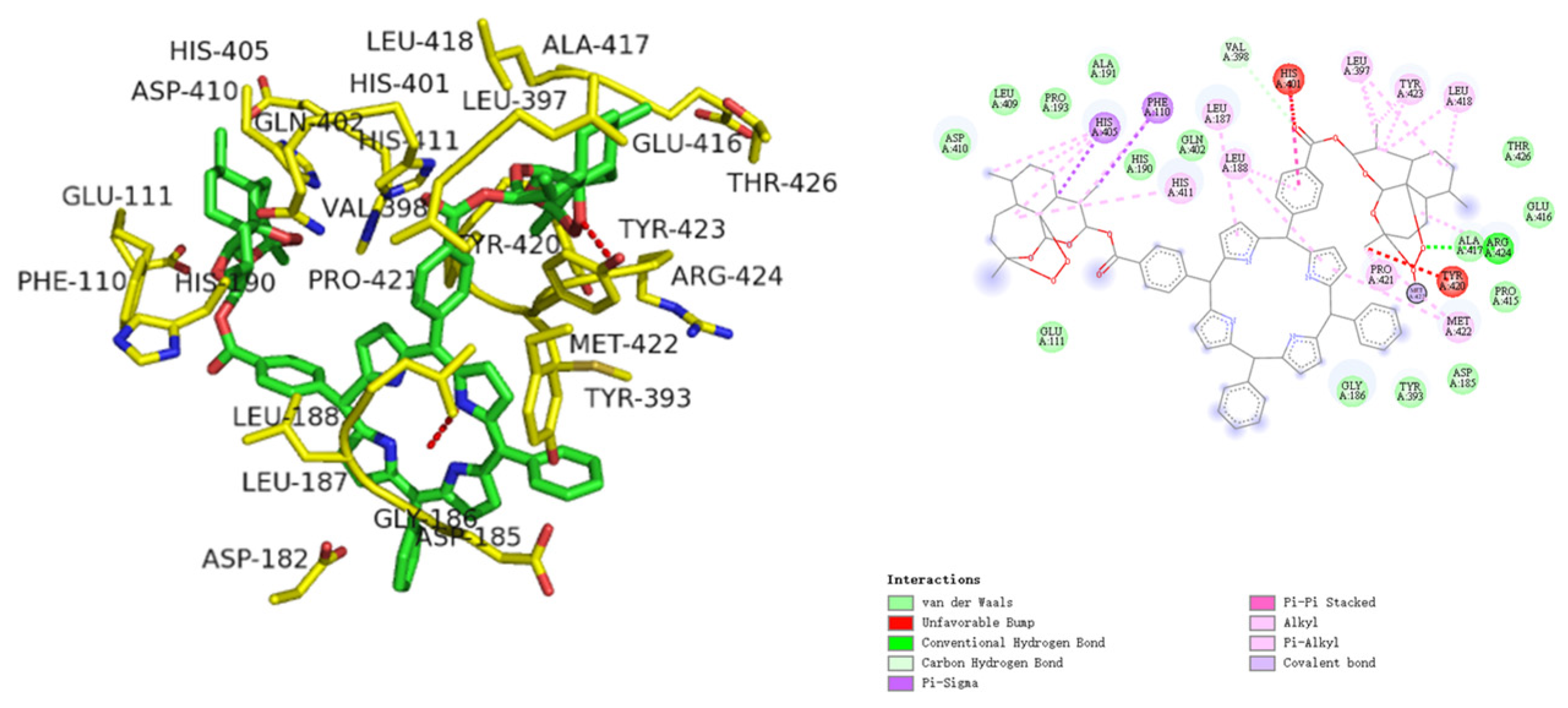
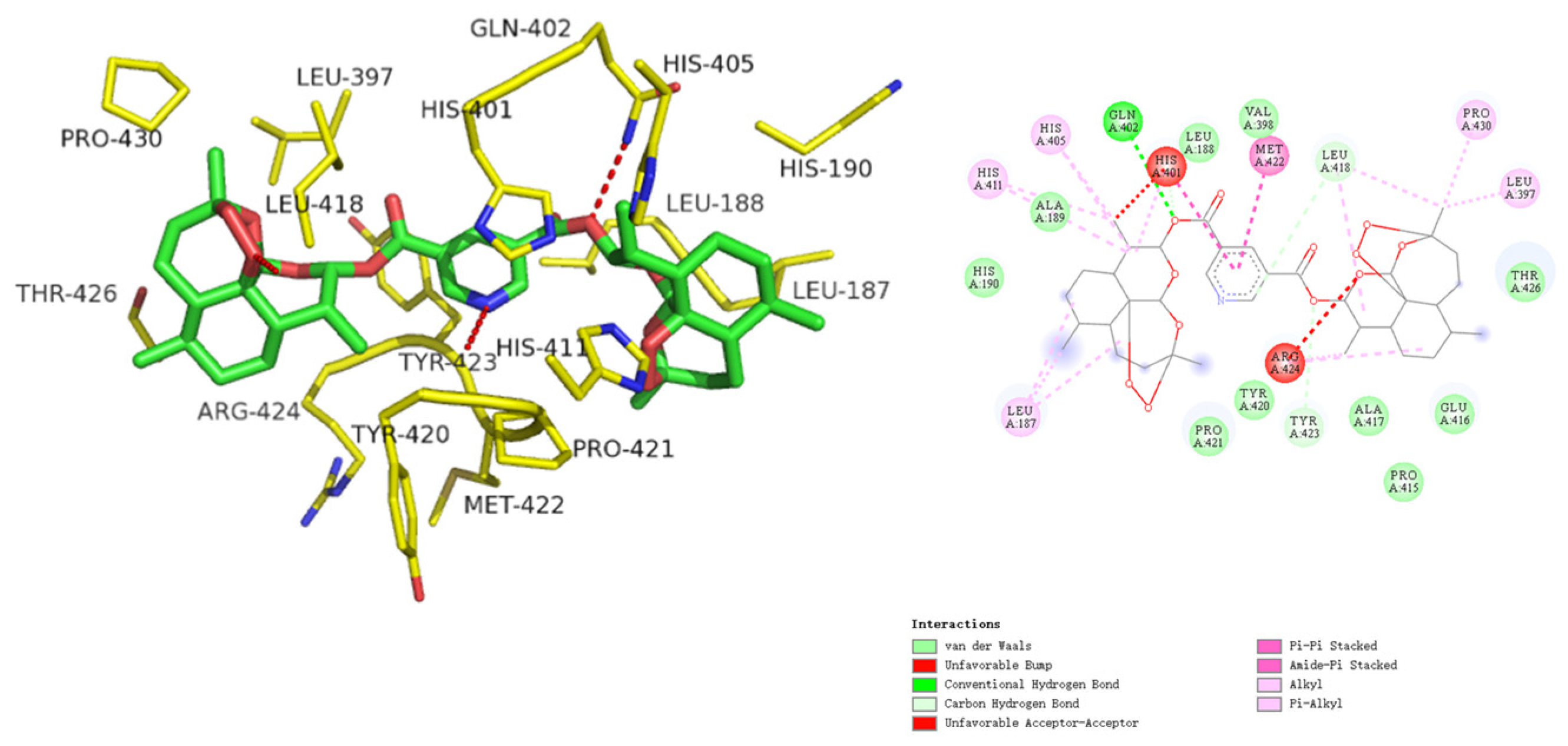
2.2.3. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligand (4a)
3.1.2. Synthesis of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligand (4b)
3.1.3. Synthesis of artemisinin bivalent ligand (4c)
3.1.4. Synthesis of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligand (4d)
3.1.5. Synthesis of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligand (4e)
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Cell Culture Conditions
3.2.2. Cytotoxicity In Vitro
3.2.3. Western Blot Analysis
3.2.4. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njuguna, N.M.; Ongarora, D.S.B.; Chibale, K. Artemisinin derivatives: A patent review (2006–present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 1179–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyad, A.; Tilaoui, M.; Jaafari, A.; Oukerrou, M.A.; Mouse, H.A. More insights into the pharmacological effects of artemisinin. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zou, X.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bian, H.; Shen, Z. Novel Bis-Artemisinin-Phloroglucinol hybrid molecules with dual anticancer and immunomodulatory Activities: Synthesis and evaluation. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 139, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SLEZAKOVA, S.; RUDA-KUCEROVA, J. Anticancer Activity of Artemisinin and its Derivatives. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 5995–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, B.H.; Kayani, W.K.; Khayam, A.U.; Dilshad, E.; Ismail, H.; Mirza, B. Artemisinin and its derivatives: A promising cancer therapy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6321–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.N.; Bu, S.X.; Sun, J.Y.; Guo, Y.; Lai, D.M. Artemisinin derivatives inhibit epithelial ovarian cancer cells via autophagy-mediated cell cycle arrest. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestone, G.L.; Sundar, S.N. Anticancer activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazquez, A.G.; Fernandez-Dolon, M.; Sanchez-Vicente, L.; Maestre, A.D.; Gomez-San Miguel, A.B.; Alvarez, M.; Serrano, M.A.; Jansen, H.; Efferth, T.; Marin, J.J.G.; et al. Novel artemisinin derivatives with potential usefulness against liver/colon cancer and viral hepatitis. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4432–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazfar, A.A.; Zare, P.; Ranjbaran, M.; Tayefi-Nasrabadi, H.; Fakhri, O.; Farshi, Y.; Shadi, S.; Khoshkerdar, A. A survey on anticancer effects of artemisinin, iron, miconazole, and butyric acid on 5637 (Bladder cancer) and 4T1 (Breast cancer) cell lines. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2014, 10, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, A.M.; Gul, W.; Slade, D.; Ross, S.A.; Feng, S.; Hollingshead, M.G.; Alley, M.C.; Kaur, G.; ElSohly, M.A. Synthesis and evaluation of dihydroartemisinin and dihydroartemisitene acetal dimers showing anticancer and antiprotozoal activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, J.; Mercer, A.E.; Park, B.K.; Cosstick, R.; O’Neill, P.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of extraordinarily potent C-10 carba artemisinin dimers against P. falciparum malaria parasites and HL-60 cancer cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. Ca-A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-S.; Luo, L.-P.; Xu, G.; Xu, X.-J.; Xu, C.; Ou, E.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-Q.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Steviol Derivatives with Improved Cytotoxic Activity and Selectivity. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; de Blanco, E.J.C.; Fuchs, J.R.; Soejarto, D.D.; Burdette, J.E.; Swanson, S.M.; Kinghorn, A.D. Potential Anticancer Agents Characterized from Selected Tropical Plants. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 657–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauquelin, G.; Charlton, S.J. Exploring avidity: Understanding the potential gains in functional affinity and target residence time of bivalent and heterobivalent ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzinski, J.; Maschauer, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Couvineau, P.; Vogt, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Roggenhofer, A.; Prante, O.; Bouvier, M.; Weikert, D. Bivalent ligands promote endosomal trafficking of the dopamine D3 receptor-neurotensin receptor 1 heterodimer. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, S.; Li, L.; Zhong, J.; Yan, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Feng, P.; Hu, K. 18F- or 177Lu-labeled bivalent ligand of fibroblast activation protein with high tumor uptake and retention. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Onge, C.M.S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y. Design of bivalent ligands targeting putative GPCR dimers. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, D.; Goswami, A.; Pratim Saikia, P.; Barua, N.C.; Rao, P.G. Artemisinin and its derivatives: A novel class of anti-malarial and anti-cancer agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, T.; Çapcı Karagöz, A.; Reiter, C.; Tsogoeva, S.B. Artemisinin-Derived Dimers: Potent Antimalarial and Anticancer Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7360–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, T.; Hahn, F.; Belmudes, L.; Leidenberger, M.; Friedrich, O.; Kappes, B.; Couté, Y.; Marschall, M.; Tsogoeva, S.B. Synthesis of Artemisinin-Derived Dimers, Trimers and Dendrimers: Investigation of Their Antimalarial and Antiviral Activities Including Putative Mechanisms of Action. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 8103–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capci, A.; Herrmann, L.; Kumar, H.M.S.; Fröhlich, T.; Tsogoeva, S.B. Artemisinin-derived dimers from a chemical perspective. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2927–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Efferth, T. Repurposing of artemisinin-type drugs for the treatment of acute leukemia. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 68, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Bhupathiraju, N.V.S.D.K.; Arianna, G.; Tiwari, K.; Drain, C.M. Glycosylated Porphyrins, Phthalocyanines, and Other Porphyrinoids for Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10261–10306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Singh, P.K.; Verma, H.; Singh, H.; Silakari, O. Success stories of natural product-based hybrid molecules for multi-factorial diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 62–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. Porphyrin-based compounds and their applications in materials and medicine. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 188, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.M.; Wang, S.W.; Li, Q.; Pan, W.; Deng, P.X.; Zhou, H.; Pan, Z.Q. Synthesis and Characterization of Curcumin Bridged Porphyrins as Photosensitizers. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2012, 33, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.M.; Wang, S.W.; Deng, P.X.; Zhou, H.; Hu, X.L.; Pan, Z.Q. Synthesis and Characterization of Honokiol Bridged Porphyrins as Photosensitizers. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 32, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, G.; Trandafirescu, C.; Prodea, A.; Milan, A.; Cristea, A.; Ghiulai, R.; Racoviceanu, R.; Mioc, A.; Mioc, M.; Ivan, V.; et al. Semisynthetic derivatives of pentacyclic triterpenes bearing heterocyclic moieties with therapeutic potential. Molecules 2022, 27, 6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.W.; Woon, C.Y.N.; Liu, C.G.; Cheng, J.T.; You, M.L.; Sethi, G.; Wong, A.L.A.; Ho, P.C.L.; Zhang, D.P.; Ong, P.; et al. Repurposing Artemisinin and its Derivatives as Anticancer Drugs: A Chance or Challenge? Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 828856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.W.; Chen, D.; Chen, L.; He, B.; Li, Y. A comprehensive overview of Artemisinin and its derivatives as anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kaldis, P. Cdks, cyclins and CKIs: Roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development 2013, 140, 3079–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, C.F.A.; Wong-Brown, M.W.; Bowden, N.A. BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigan, A.S.; Bellutti, F.; Kollmann, K.; Tebb, G.; Sexl, V. CDK6—A review of the past and a glimpse into the future: From cell-cycle control to transcriptional regulation. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.K.; Wong, H.-N.; Lee, K.-W.; Lung, C.-M.; Shek, L.Y.; Williams, I.D.; Croft, S.L.; Vivas, L.; Rattray, L.; Stewart, L.; et al. Preparation of N-Sulfonyl- and N-Carbonyl-11-Azaartemisinins with Greatly Enhanced Thermal Stabilities: In vitro Antimalarial Activities. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen Le, T.; De Borggraeve, W.M.; Grellier, P.; Pham, V.C.; Dehaen, W.; Nguyen, V.H. Synthesis of 11-aza-artemisinin derivatives using the Ugi reaction and an evaluation of their antimalarial activity. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 4892–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Wang, Y.-S.; Yu, Q.; Li, J. Synthetic Methodology for the Fabrication of Porous Porphyrin Materials with Metal–Organic–Polymer Aerogels. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 5287–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 39 Miao, J.; Zhu, L. Hydrogen Bonding Induced Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Linear Doubly Discotic Triad Supermolecules. Chem. Asian J. 2010, 5, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H. Experimental Therapy of Hepatoma with Artemisinin and Its Derivatives: In vitro and In vivo Activity, Chemosensitization, and Mechanisms of Action. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5519–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willoughby, J.A., Sr.; Sundar, S.N.; Cheung, M.; Tin, A.S.; Modiano, J.; Firestone, G.L. Artemisinin Blocks Prostate Cancer Growth and Cell Cycle Progression by Disrupting Sp1 Interactions with the Cyclin-dependent Kinase-4 (CDK4) Promoter and Inhibiting CDK4 Gene Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-N.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Peng, S.-Q.; Zhu, J.-S.; Zhang, J.; Qu, G.-Q. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating cyclin D1-CDK4-Rb signaling. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Shi, X.; Li, S.; Tang, P.M.-K.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, C. Antimalarial Dihydroartemisinin triggers autophagy within HeLa cells of human cervical cancer through Bcl-2 phosphorylation at Ser70. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Hao, M. Effect of artemisinin on proliferation and apoptosis-related protein expression in vivo and in vitro. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Tan, W.; Zhang, A. Development of high potent and selective Bcl-2 inhibitors bearing the structural elements of natural product artemisinin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 159, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S. In silico Drug Repurposing of FDA-Approved Artemisinins as Potent Chemotherapeutics Targeting Bcl-2, CDK-6 & VEGFR-2: Density Functional Exploration and Molecular Docking Study. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 11, 9604–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Song, Z.; Xi, Z. The anticancer potency of artemisinin and its derivatives. Sci. Prog. Res. 2021, 1, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, G.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, B.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z. Artemisinin Inhibits Tumor Lymphangiogenesis by Suppression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C. Pharmacology 2008, 82, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-B.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Xue, Y.-X.; Yao, Y.-L.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.-H. Artemether Combined with shRNA Interference of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Significantly Inhibited the Malignant Biological Behavior of Human Glioma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magenta, D.; Sangiovanni, E.; Basilico, N.; Haynes, R.K.; Parapini, S.; Colombo, E.; Bosisio, E.; Taramelli, D.; Dell’Agli, M. Inhibition of metalloproteinase-9 secretion and gene expression by artemisinin derivatives. Acta Trop. 2014, 140, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compd. | IC50 (μmol/L) a,b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGC-823 | HepG-2 | HCT-116 | MCF-7 | |
| ART | 34.82 ± 1.50 | 41.02 ± 1.64 | 31.47 ± 0.97 | 32.74 ± 0.45 |
| DHA | 29.64 ± 0.60 | 32.73 ± 0.99 | 41.69 ± 1.03 | 34.32 ± 0.65 |
| 4a | 12.48 ± 0.60 | 11.75 ± 0.71 | 13.60 ± 0.74 | 18.24 ± 0.20 |
| 4b | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 4c | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 |
| 4d | 16.31 ± 0.21 | 12.68 ± 0.87 | 21.68 ± 0.59 | 33.67 ± 0.47 |
| 4e | 8.30 ± 0.14 | 40.31 ± 1.38 | 16.83 ± 0.30 | 24.27 ± 0.35 |
| Compd. | Targets | Receptor Residues Involved in Hydrogen Bonding | Binding Energies (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | BCL-2 | ARG143, TYR105 | −5.64 |
| CDK-4 | - | −6.37 | |
| VEGFR-2 | ASN923 | −5.78 | |
| MMP-9 | HIS405, LEU187 | −6.50 | |
| 4b | BCL-2 | ASN140, ALA97 | −8.40 |
| CDK-4 | - | −7.67 | |
| VEGFR-2 | - | −5.43 | |
| MMP-9 | ARG424, VAL398 | −9.64 | |
| 4c | BCL-2 | ARG136, GLU133, GLY142 | −7.31 |
| CDK-4 | LYS123, THR89, HIS84 | −6.46 | |
| VEGFR-2 | - | −3.94 | |
| MMP-9 | THR426, GLN402 | −10.71 | |
| 4d | BCL-2 | - | −6.54 |
| CDK-4 | - | −7.49 | |
| VEGFR-2 | ASP1046, GLU885, GLY922 | −7.16 | |
| MMP-9 | GLN402, LEU418, TYR423 | −8.70 | |
| 4e | BCL-2 | ARG143, GLY142 | −6.49 |
| CDK-4 | - | −6.94 | |
| VEGFR-2 | ASP1046 | −6.83 | |
| MMP-9 | GLN402 | −7.51 |
| Compd. | CDK-4 (1GIJ) | BCL-2 (4MAN) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG (kcal/mol) | Ki (μmol/L) | ΔG(kcal/mol) | Ki (μmol/L) | |
| ART | −4.25 | 801.56 | −3.64 | 2230.03 |
| DHA | −4.65 | 430.07 | −3.44 | 3118.96 |
| 4a | −6.37 | 22.88 | −5.64 | 77.86 |
| 4b | −7.67 | 2.59 | −8.40 | 0.76 |
| 4c | −6.46 | 19.68 | −7.31 | 4.73 |
| 4d | −7.49 | 3.50 | −6.54 | 17.21 |
| 4e | −6.94 | 8.80 | −6.49 | 18.71 |
| Compd. | VEGFR-2 (4ASE) | MMP-9 (2OVZ) | ||
| ΔG (kcal/mol) | Ki (μmol/L) | ΔG (kcal/mol) | Ki(μmol/L) | |
| ART | −4.13 | 980.29 | −4.23 | 828.90 |
| DHA | −4.27 | 775.12 | −4.45 | 573.11 |
| 4a | −5.78 | 61.57 | −6.50 | 18.40 |
| 4b | −5.43 | 110.74 | −9.64 | 0.095 |
| 4c | −3.94 | 1348.24 | −10.71 | 0.016 |
| 4d | −7.16 | 6.08 | −8.70 | 0.459 |
| 4e | −6.83 | 10.58 | −7.51 | 3.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, H.; Li, B.; Zhou, X.; Fu, R.; Wang, W.; Sheng, W. Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligands. Molecules 2024, 29, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020409
Zhong H, Jiang Q, Wu C, Yu H, Li B, Zhou X, Fu R, Wang W, Sheng W. Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligands. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020409
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Hui, Qi Jiang, Cong Wu, Huanghe Yu, Bin Li, Xudong Zhou, Ronggeng Fu, Wei Wang, and Wenbing Sheng. 2024. "Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligands" Molecules 29, no. 2: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020409
APA StyleZhong, H., Jiang, Q., Wu, C., Yu, H., Li, B., Zhou, X., Fu, R., Wang, W., & Sheng, W. (2024). Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Artemisinin Bivalent Ligands. Molecules, 29(2), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020409






