Study on Design, Synthesis and Herbicidal Activity of Novel 6-Indazolyl-2-picolinic Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
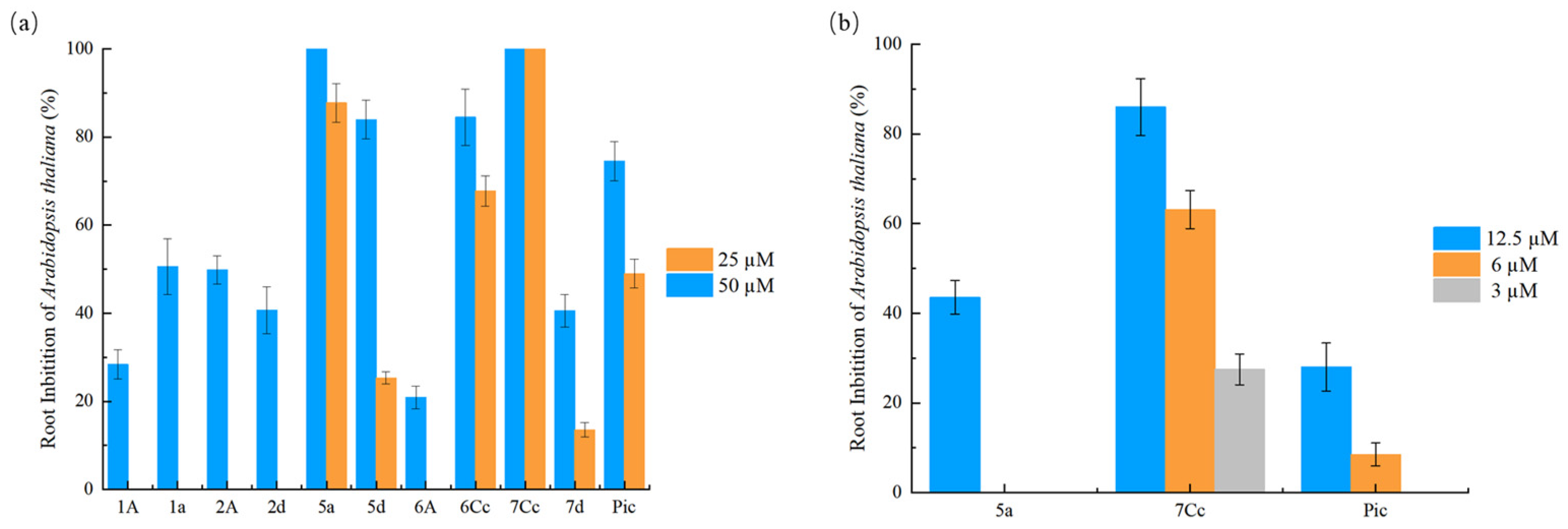
2.2. Phenotypic Study of Arabidopsis thaliana and SAR Analysis
2.3. Evaluation of Herbicidal Activity
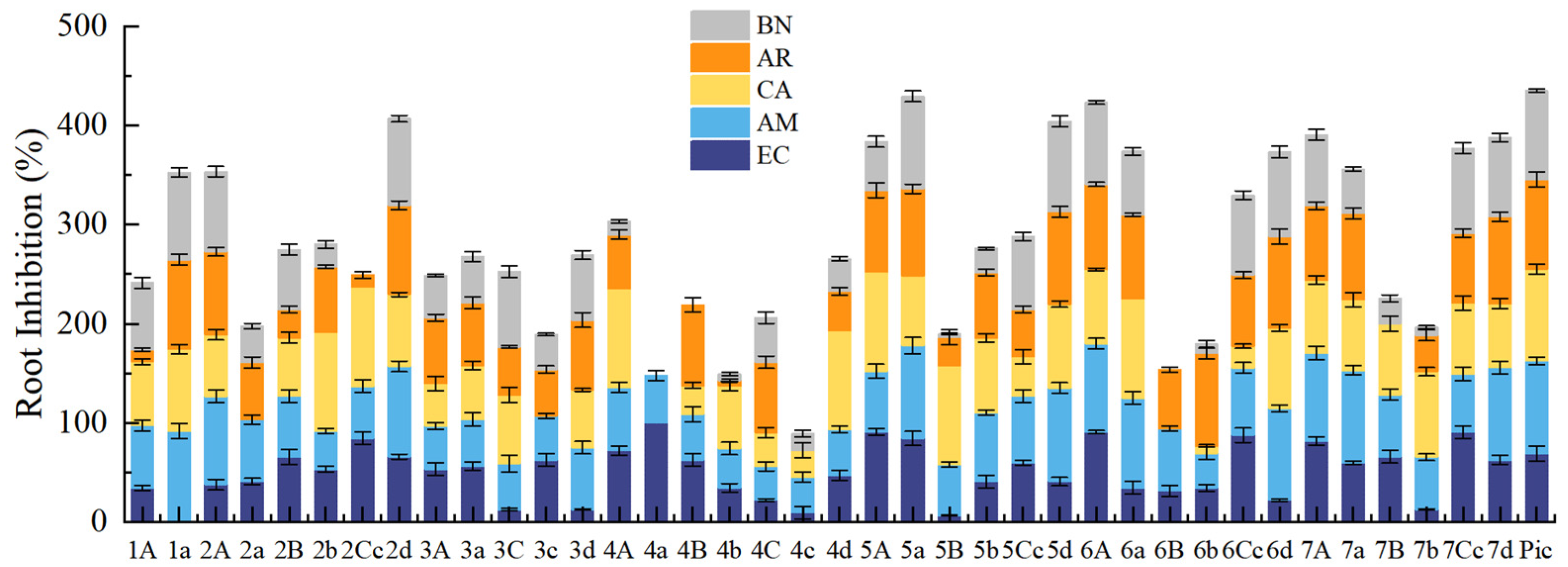
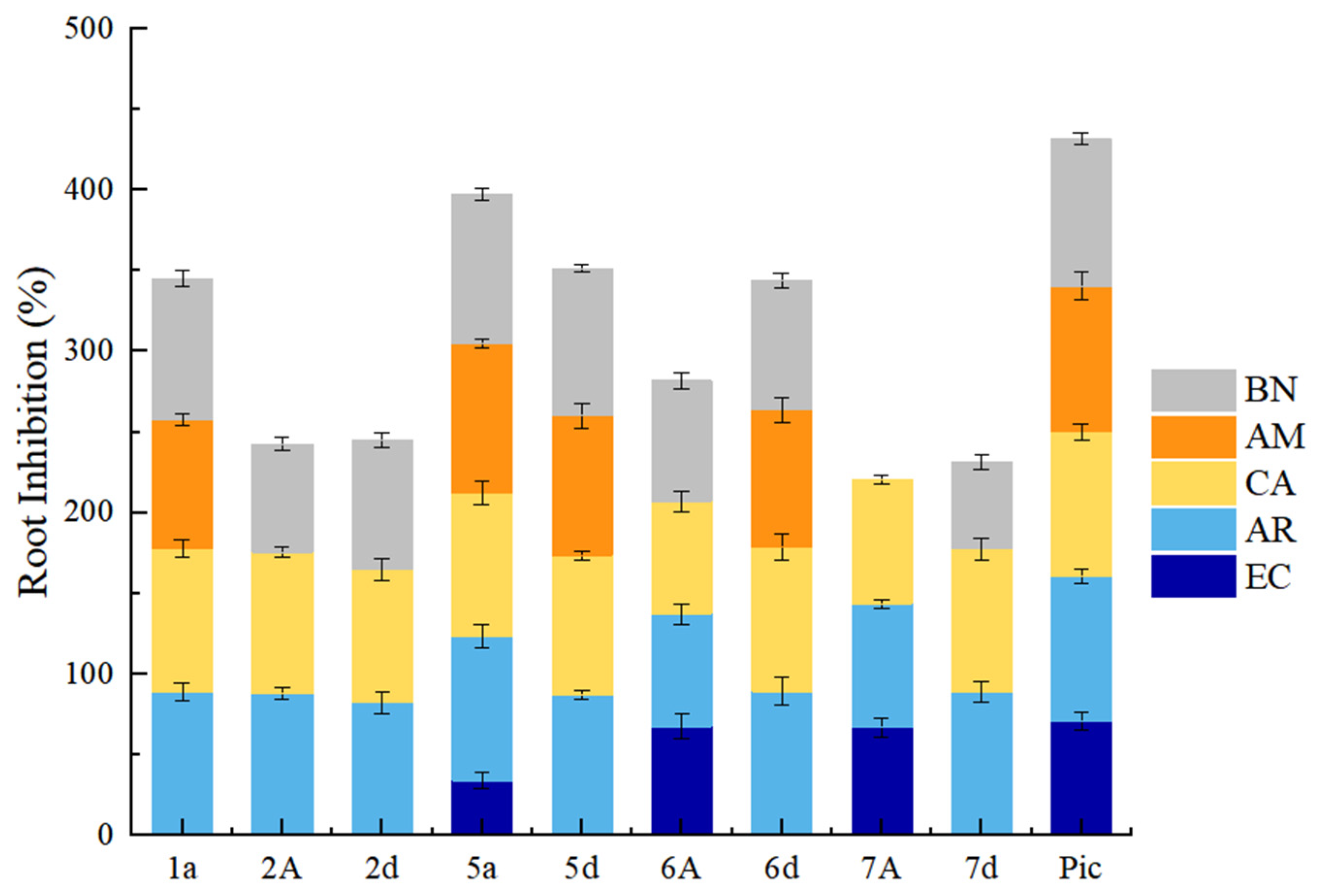
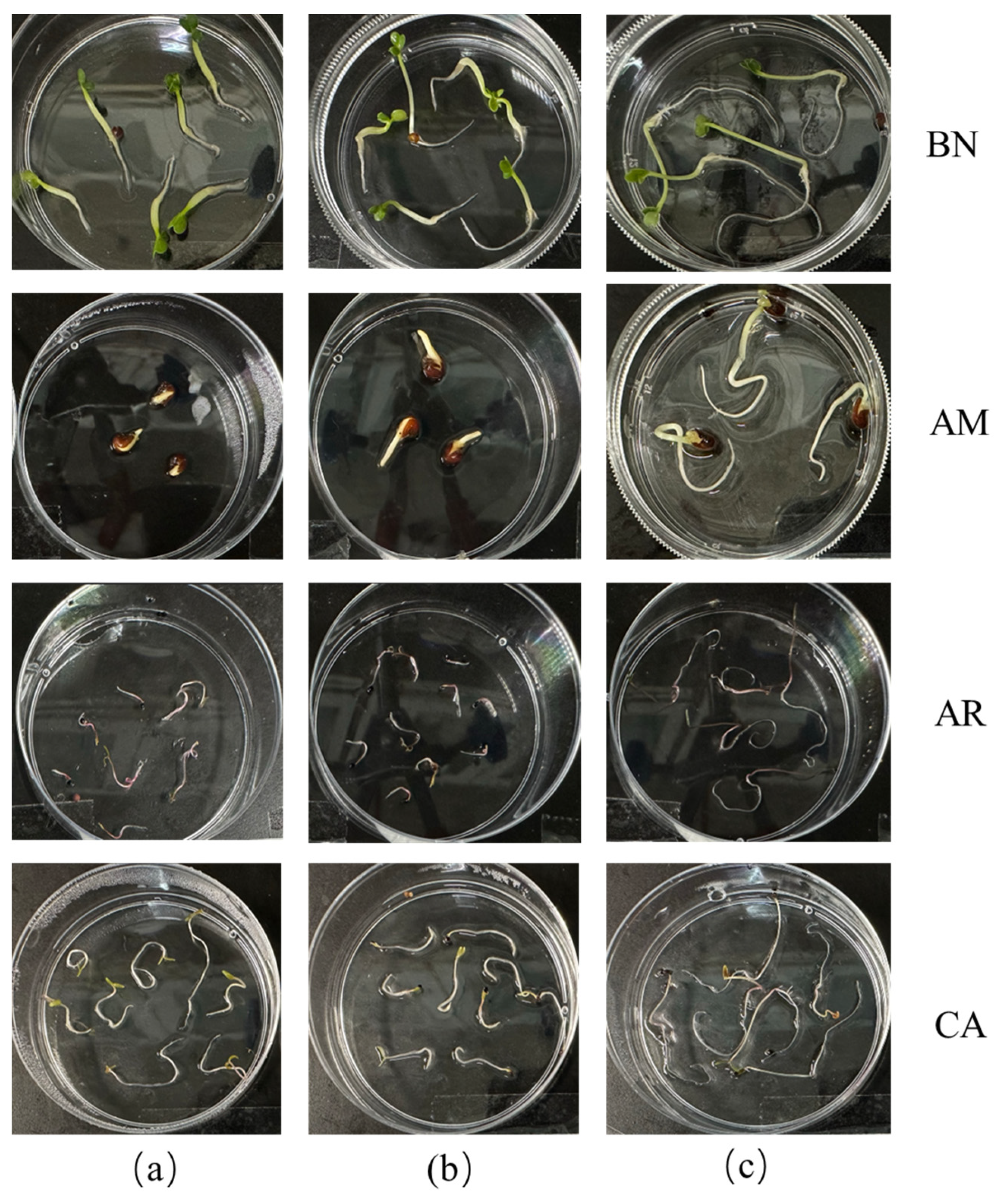
2.3.1. Root Growth Inhibition of Weeds in Petri Dishes
2.3.2. Herbicidal Activity
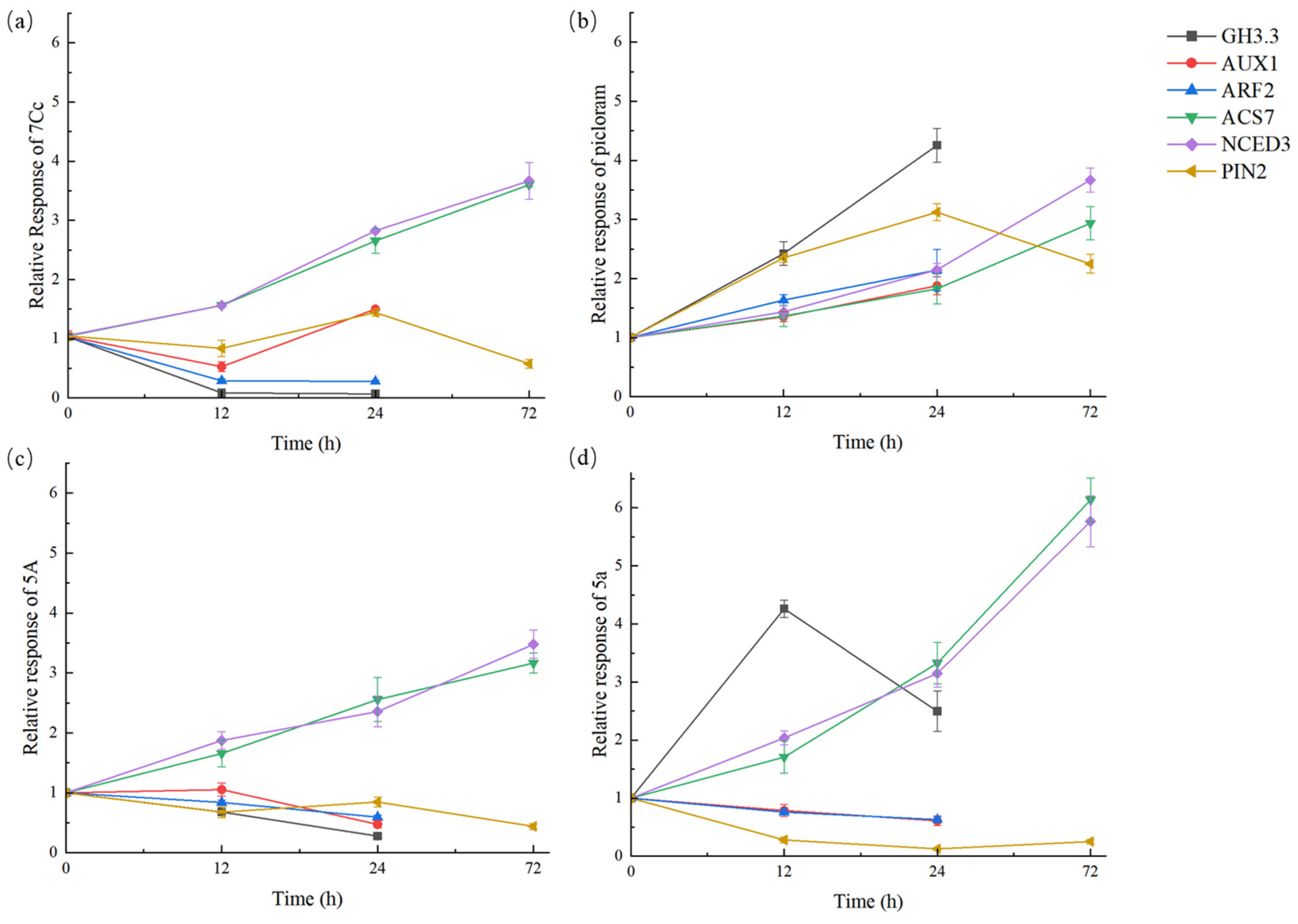
2.4. The Response of Auxin Relative Genes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals, Experimental Instruments and Plant Materials
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. General Synthetic Procedure of Intermediates II
3.2.2. General Synthetic Procedure of Intermediate III
3.2.3. General Synthetic Procedure of Product
3.3. Determination of the Biological Activities
3.3.1. Phenotypic Study for the Inhibition of A. thaliana Root Growth
3.3.2. Evaluation of the Herbicidal Activity
3.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L. Analysis of Global Pesticide Market Overview, Market Capacity, Product Structure and Market Competition Pattern in 2017. Available online: http://www.chyxx.com/industry/201707/539506.html (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Oliveira, M.C.; Osipitanc, O.A.; Begcyd, K.; Werle, R. Cover crops, hormones and herbicides: Priming an integrated weed management strategy. Plant Sci. 2020, 301, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagavathiannan, M.V.; Graham, S.; Ma, Z.; Barney, J.N.; Coutts, S.R.; Caicedo, A.L.; De Clerck-Floate, R.; West, N.M.; Blank, L.; Metcalf, A.L.; et al. Considering weed management as a social dilemma bridges individual and collective interests. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, B.I.P.; Moran, V.C.; Bigler, F. The status of biological control and recommendations for improving uptake for the future. BioControl 2017, 63, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds. Available online: http://weedscience.org (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Busi, R.; Goggin, D.E.; Heap, I.M.; Horak, M.J.; Jugulam, M.; Masters, R.A.; Napier, R.M.; Riar, D.S.; Satchivi, N.M.; Torra, J.; et al. Weed resistance to synthetic auxin herbicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerd, L.L.V.; Mclean, M.D.; Stephenson, G.R.; Hall, J.C. Resistance to quinclorac and ALS-inhibitor herbicides in Galium spurium is conferred by two distinct genes. Weed Res. 2004, 44, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. Global perspective of herbicide-resistant weeds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, T.A.; Neal, R.; Merlo, A.O.; Honma, M.; Hicks, G.R.; Wolff, K.; Matsumura, W.; Davies, J.P. Mutations in an auxin receptor homolog AFB5 and in SGT1b confer resistance to synthetic picolinate auxins and not to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid or indole-3-acetic acid in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.J.; Maguire, N.; Powles, S.B. Combined effects of wheat competition and 2,4-D amine on phenoxy herbicide resistant Raphanus raphanistrum populations. Weed Res. 2008, 49, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
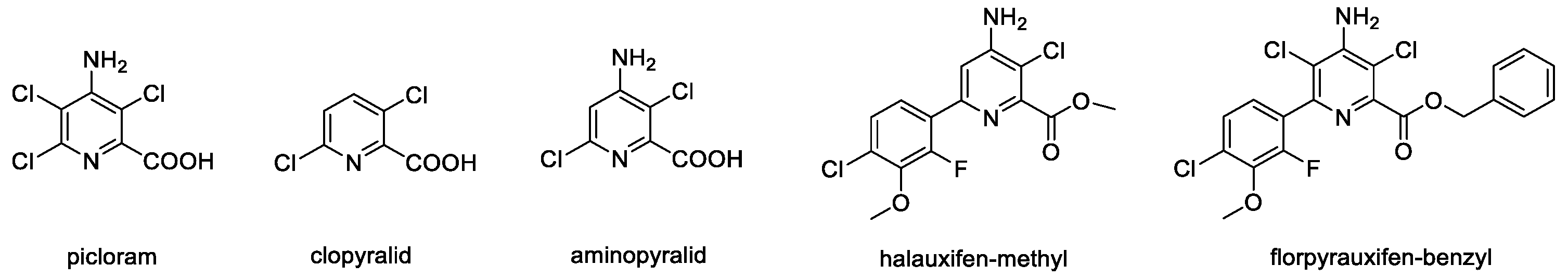
- Schmitzer, P.R.; Balko, T.W.; Daeuble, J.F.; Epp, J.B.; Satchivi, N.M.; Siddall, T.L.; Weimer, M.R.; Yerkes, C.N. Discovery and SAR of Halauxifen Methyl: A Novel Auxin Herbicide. In Discovery and Synthesis of Crop Protection Products; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, J.B.; Alexander, A.L.; Balko, T.W.; Buysse, A.M.; Brewster, W.K.; Bryan, K.; Daeuble, J.F.; Fields, S.C.; Gast, R.E.; Green, R.A.; et al. The discovery of Arylex active and Rinskor active: Two novel auxin herbicides. Bioorganic. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.; Schmitzer, P.; Masters, R.A.; Lo, W.C.; Gast, R.E.; Claus, J.S.; Finkelstein, B.L. New Auxin Mimics and Herbicides. In Modern Crop Protection Compounds; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2019; Chapter 5; pp. 303–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitzer, P.; Epp, J.; Gast, R.; Lo, W.; Nelson, J. Herbicidal Carboxylic Acids as Synthetic Auxins. In Bioactive Carboxylic Compound Classes; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; Chapter 20; pp. 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.G.; Brünjes, M.; Döller, U.; Dietrich, H. Substituted Picolinic Acid and Pyrimidine-4-carboxylic Acids, Method for the Production Thereof, and Use Thereof as Herbicides and Plant Growth Regulators. WO 2013/014165 Al, 10 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eckelbarger, J.D.; Epp, J.B.; Fischer, L.G.; Lowe, C.T.; Petkus, J.; Roth, J.; Satchivi, N.M.; Schmitzer, P.R.; Siddall, T.L. 4-Amino-6-(heterocyclic)picolinates and 6-Amino-2-(heterocyclic)pyrimidine-4-carboxylates and Their Use as Herbicides. WO 2014151008 A1, 28 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.K.; Kim, E.A.; Lee, I.Y.; Koo, D.W.; Ryu, J.W.; Yon, G.H. Pyridine-Based Compound Including Isoxazoline ring, and Use Thereof as Herbicide. WO 2018004223 A1, 4 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
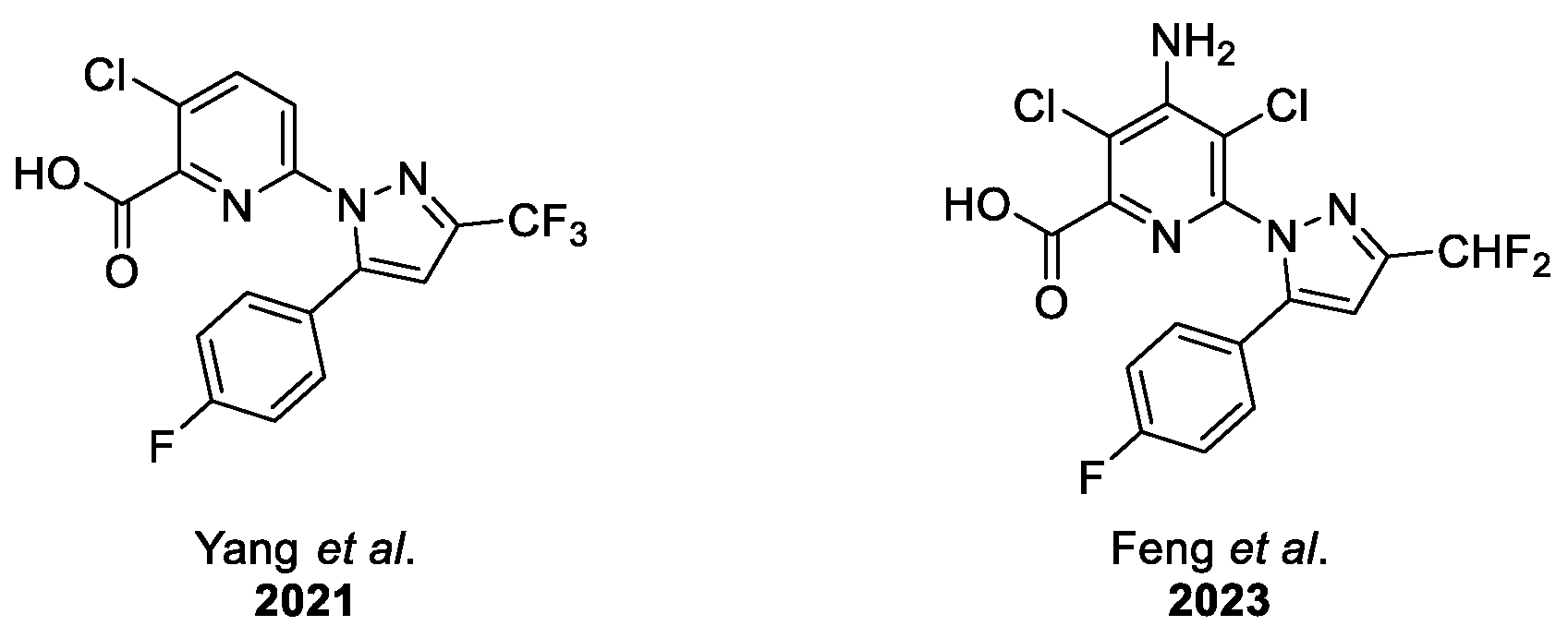
- Yang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yin, J.; Liu, R.; Tian, H.; Duan, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Tan, W.; Liu, S. Design, synthesis and mode of action of novel 3-chloro-6-pyrazolyl picolinate derivatives as herbicide candidates. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.Y.; Li, H.T.; Wei, W.; Shi, R.C.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.M.; Liu, S.Z. Design, Synthesis, Herbicidal Activity, and Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Novel 6-(5-Aryl-Substituted-1-Pyrazolyl)-2-Picolinic Acid as Potential Herbicides. Molecules 2023, 28, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerecetto, H.; Gerpea, A.; González, M.; Aránb, V.J.; Ocáriz, C.O.d. Pharmacological Properties of Indazole Derivatives: Recent Developments. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikwad, D.D.; Chapolikar, A.D.; Devkate, C.G.; Warad, K.D.; Tayade, A.P.; Pawar, R.P.; Domb, A.J. Synthesis of indazole motifs and their medicinal importance: An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 707–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.R.; Baker, D.R.; Mielich, S.D.; Michaely, W.J.; Fitzjohn, S.; Knudsen, C.G.; Mathews, C.; Gerdes, J.M. Preparation of Arylindazoles and Their Use as Herbicides. WO9318008, 29 December 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, I.T.; Kim, H.R.; Jeon, D.J.; Hong, K.S.; Song, J.H.; Chung, C.K.; Cho, K.Y. New 2-phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2H-indazole derivatives as paddy field herbicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, D.; Amaruka, H.; Christopher, K.; Melissa, L.; Fangzheng, L. Improved Synthesis of 4-Amino-6-(heterocyclic)picolinates. WO 2021/188639 Al, 23 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.; Grossmann, K. Auxin-Induced Ethylene Triggers Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis and Growth Inhibition. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Napier, R.; Dong, L.; Li, J. Mode of Action of a Novel Synthetic Auxin Herbicide Halauxifen-Methyl. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Li, P.; Yang, X.F.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, X.K.; Hua, X.W.; Sun, B.; Ji, L.S.; Xu, X.H. Design and Synthesis of Novel 4-Hydroxyl-3-(2-phenoxyacetyl)-pyran-2-one Derivatives for Use as Herbicides and Evaluation of Their Mode of Action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10489–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Song, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Y. An auxin-responsive endogenous peptide regulates root development in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasiri, S.; Swarup, R.; Mockaitis, K.; Dharmasiri, N.; Singh, S.K.; Kowalchyk, M.; Marchant, A.; Mills, S.; Sandberg, G.; Bennett, M.J.; et al. AXR4 Is Required for Localization of the Auxin Influx Facilitator AUX1. Science 2006, 312, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfulian, M.H.; Jalili, E.; Roberto, D.K.; Moss, B.L.; Khoo, K.; Nemhauser, J.L.; Crosby, W.L. Oligomerization of SCFTIR1 Is Essential for Aux/IAA Degradation and Auxin Signaling in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.B.; Riechers, D.E. Recent developments in auxin biology and new opportunities for auxinic herbicide research. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2007, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, S.; Qian, C.; He, C. Synthesis of 1H-indazole: A combination of experimental and theoretical studies. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2012, 38, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Fujioka, S.; Peng, J.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Chen, R. The E3 ubiquitin ligase SCFTIR1/AFB and membrane sterols play key roles in auxin regulation of endocytosis, recycling, and plasma membrane accumulation of the auxin efflux transporter PIN2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Calderon-Villalobos, L.I.; Sharon, M.; Zheng, C.; Robinson, C.V.; Estelle, M.; Zheng, N. Mechanism of auxin perception by the TIR1 ubiquitin ligase. Nature 2007, 446, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon Villalobos, L.I.; Lee, S.; De Oliveira, C.; Ivetac, A.; Brandt, W.; Armitage, L.; Sheard, L.B.; Tan, X.; Parry, G.; Mao, H.; et al. A combinatorial TIR1/AFB-Aux/IAA co-receptor system for differential sensing of auxin. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

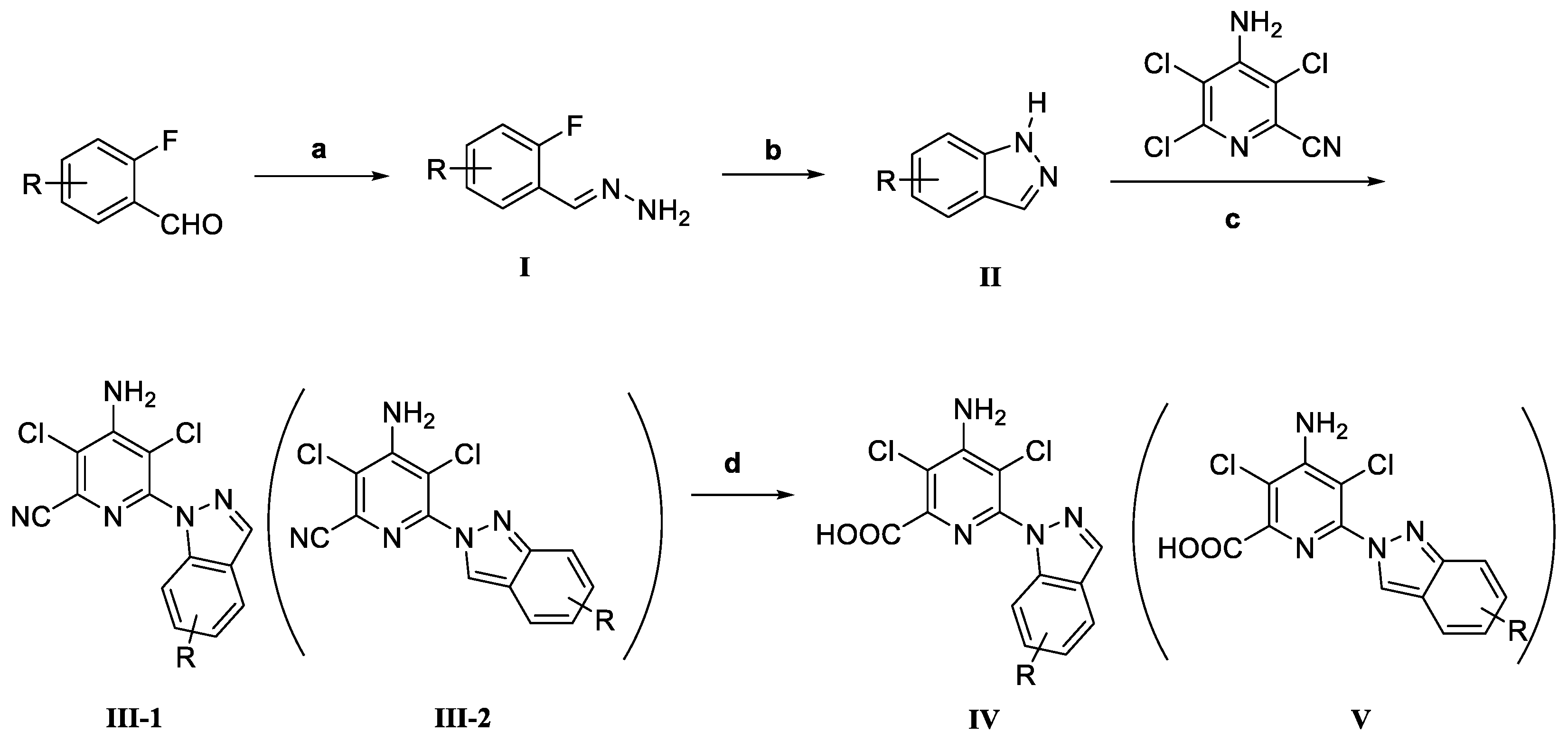

| No. | Compd. | R | No. | Compd. | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | IV | H | 3c | V | 6-NH2 |
| 2A | IV | 4-CH3 | 3d | V | 7-NH2 |
| 2B | IV | 5-CH3 | 4a | V | 4-OCH3 |
| 3A | IV | 4-NH2 | 4b | V | 5-OCH3 |
| 3C | IV | 6-NH2 | 4c | V | 6-OCH3 |
| 4A | IV | 4-OCH3 | 4d | V | 7-OCH3 |
| 4B | IV | 5-OCH3 | 5a | V | 4-F |
| 4C | IV | 6-OCH3 | 5b | V | 5-F |
| 5A | IV | 4-F | 5d | V | 7-F |
| 5B | IV | 5-F | 6a | V | 4-Cl |
| 6A | IV | 4-Cl | 6b | V | 5-Cl |
| 6B | IV | 5-Cl | 6d | V | 7-Cl |
| 7A | IV | 4-Br | 7a | V | 4-Br |
| 7B | IV | 5-Br | 7b | V | 5-Br |
| 1a | V | H | 7d | V | 7-Br |
| 2a | V | 4-CH3 | 2Cc | IV+V | 6-CH3 |
| 2b | V | 5-CH3 | 5Cc | IV+V | 6-F |
| 2d | V | 7-CH3 | 6Cc | IV+V | 6-Cl |
| 3a | V | 4-NH2 | 7Cc | IV+V | 6-Br |
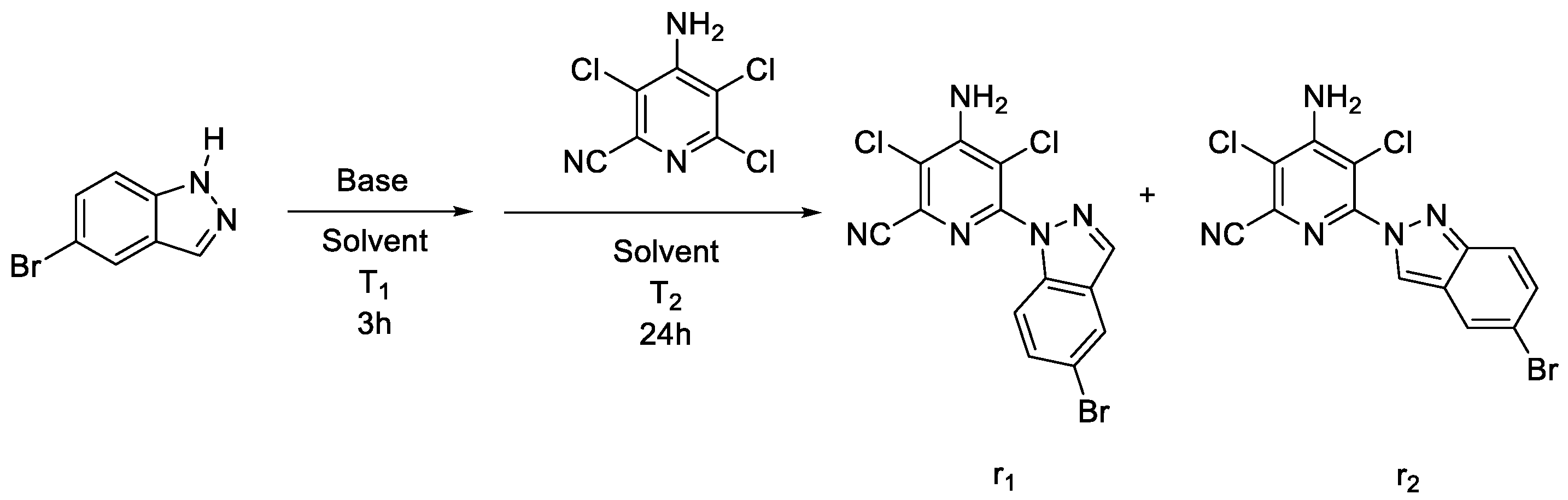
| Solvent | Base | Temperature (T1) a | Temperature (T2) b | Reaction Progress Conversion/Ratio of r1:r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra dry dioxane | NaH | 50 °C | 100 °C | Complete/r1:r2 = 1:1 |
| Extra dry dioxane | NaH | 25 °C | 100 °C | Incomplete (5%) c/r1:r2 = 1:1 |
| Extra dry dioxane | K2CO3 | 50 °C | 100 °C | No reaction |
| Extra dry dioxane | KOH | 50 °C | 100 °C | No reaction |
| Extra dry dioxane | NaOH | 50 °C | 100 °C | No reaction |
| Extra dry dioxane | CsCO3 | 50 °C | 100 °C | Incomplete (10%) c/r1:r2 = 2.5:1 |
| Extra dry dioxane | CsCO3 | 25 °C | 100 °C | Incomplete (15%) c/r1:r2 = 3.4:1 |
| Extra dry dioxane | CsCO3 | 25 °C | 50 °C | Incomplete (20%) c/r1:r2 = 1.3:1 |
| Acetonitrile | CsCO3 | −13 °C | 80 °C | Incomplete (25%) c/r1:r2 = 3.9:1 |
| 1,2-Dimethoxyethane | CsCO3 | −10 °C | 85 °C | Incomplete (15%) c/r1:r2 = 4.9:1 |
| 1,2-Diethoxyethane | CsCO3 | −10 °C | 110 °C | Incomplete (5%) c/r1:r2 = 2.25:1 |
| Compound | Dosage (g ha−1) | BN (%) | AM (%) | CA (%) | AR (%) | EC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 1000 | 100 | 30 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | / | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 15 | 100 | 0 | |
| 2b | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | 45 | 70 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 45 | 100 | 0 | |
| 2d | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 80 | 40 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 60 | / | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 3d | 1000 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | / | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 30 | 80 | 0 | |
| 4A | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | 0 | 70 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 10 | 100 | 0 | |
| 4d | 1000 | 100 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | 70 | 65 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | 10 | 30 | 95 | 0 | |
| 5A | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 75 | 100 | 0 | |
| 5a | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 65 | 10 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 15 | / | 40 | 75 | 0 | |
| 6A | 1000 | 100 | 85 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | 10 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 45 | 85 | 0 | |
| 6a | 1000 | 100 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 20 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | / | / | 45 | 90 | 0 | |
| 6b | 1000 | 100 | 10 | 80 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | / | 60 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 10 | 100 | 0 | |
| 6d | 1000 | 100 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 50 | 25 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | / | / | 65 | 90 | 0 | |
| 7a | 1000 | 100 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | / | 50 | 80 | 0 | |
| 7d | 1000 | 100 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 500 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | / | / | 30 | 85 | 0 | |
| Picloram | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 10 |
| 500 | 100 | 65 | 100 | 100 | 0 | |
| 250 | 100 | 40 | 80 | 85 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Shi, R.-C.; Li, H.-T.; Wei, W.; Yuan, X.; Liu, S.-Z.; Cao, Y.-M. Study on Design, Synthesis and Herbicidal Activity of Novel 6-Indazolyl-2-picolinic Acids. Molecules 2024, 29, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020332
Liu Q, Shi R-C, Li H-T, Wei W, Yuan X, Liu S-Z, Cao Y-M. Study on Design, Synthesis and Herbicidal Activity of Novel 6-Indazolyl-2-picolinic Acids. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020332
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qing, Rong-Chuan Shi, Hui-Ting Li, Wei Wei, Xiao Yuan, Shang-Zhong Liu, and Yi-Ming Cao. 2024. "Study on Design, Synthesis and Herbicidal Activity of Novel 6-Indazolyl-2-picolinic Acids" Molecules 29, no. 2: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020332
APA StyleLiu, Q., Shi, R.-C., Li, H.-T., Wei, W., Yuan, X., Liu, S.-Z., & Cao, Y.-M. (2024). Study on Design, Synthesis and Herbicidal Activity of Novel 6-Indazolyl-2-picolinic Acids. Molecules, 29(2), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020332