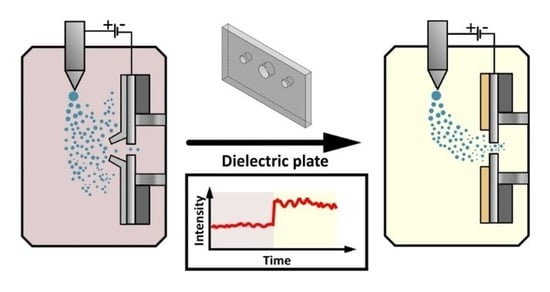
Moderate Signal Enhancement in Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry by Focusing Electrospray Plume with a Dielectric Layer around the Mass Spectrometer’s Orifice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
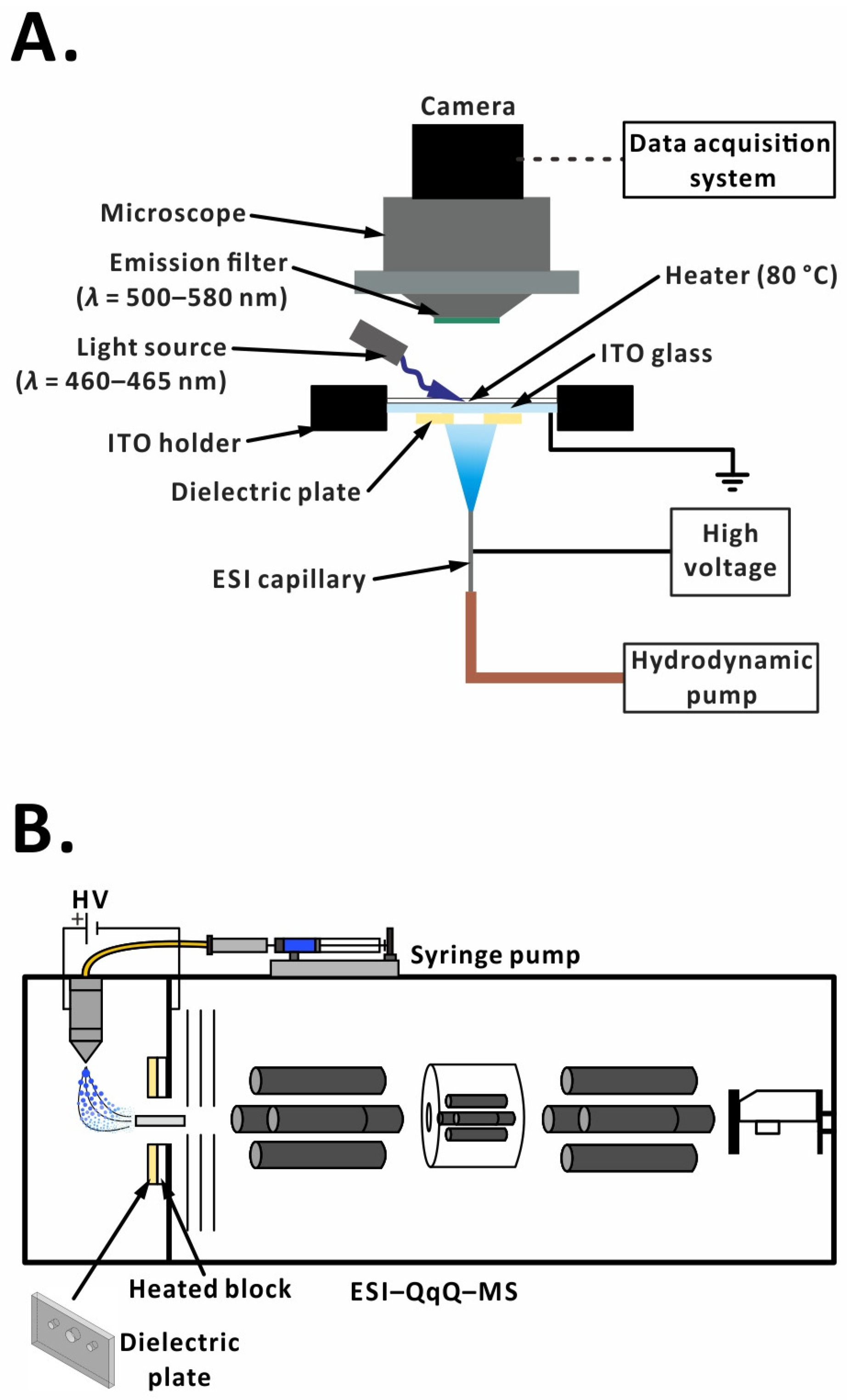
2.2. Offline Setup
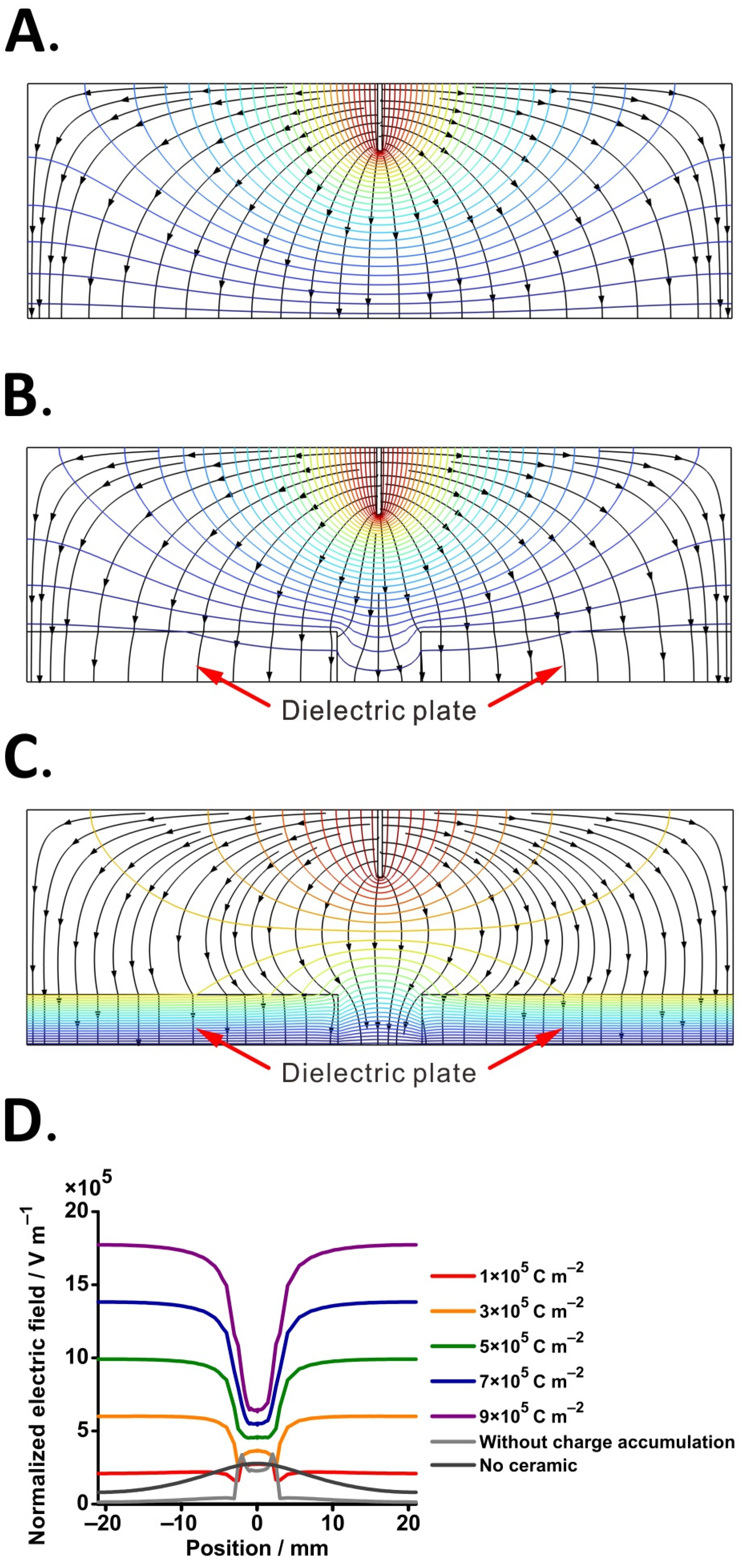
2.3. Computational Simulation of Electric Field
2.4. Measurement of Surface Charge Density
2.5. Offline Experiment Data Analysis
- The raw image sequence was imported into ImageJ software (version 1.53k; National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA; see the Supporting Information for the code to execute points 1–4).
- The frameset was subjected to background subtraction. The first frame was subtracted from all the consecutive images.
- A median filter (radius: 2 pixels) was applied to all the images to lower the noise. Then, the images were converted to 8-bit mode.
- The processed images were transformed into binary images using the threshold function (lower threshold level: 7; upper threshold level: 255).
- The “Analyze Particles” function was applied to the processed images for droplet detection (size: 0.0005–Infinity; circularity: 0.70–1.00). The droplet information for each frame was then displayed.
2.6. Online Setup
2.7. Online Experiment Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
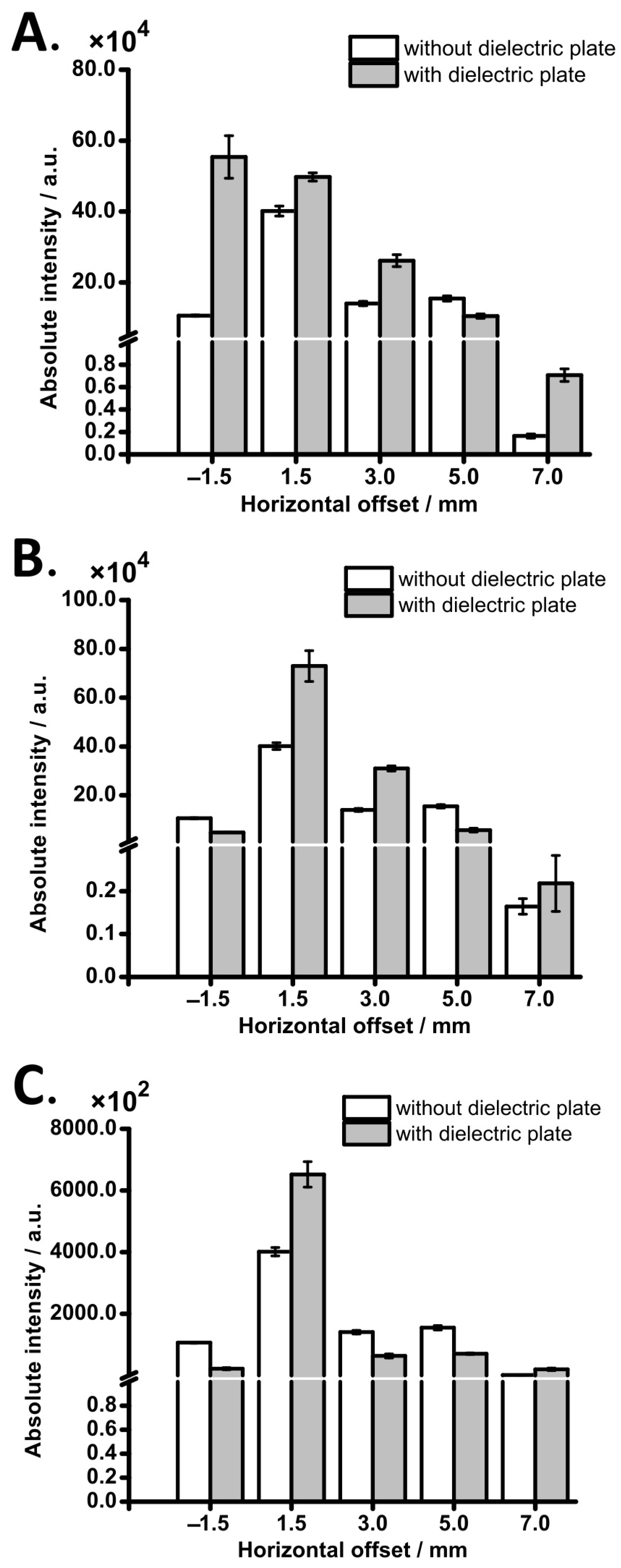
3.1. Proof-of-Concept
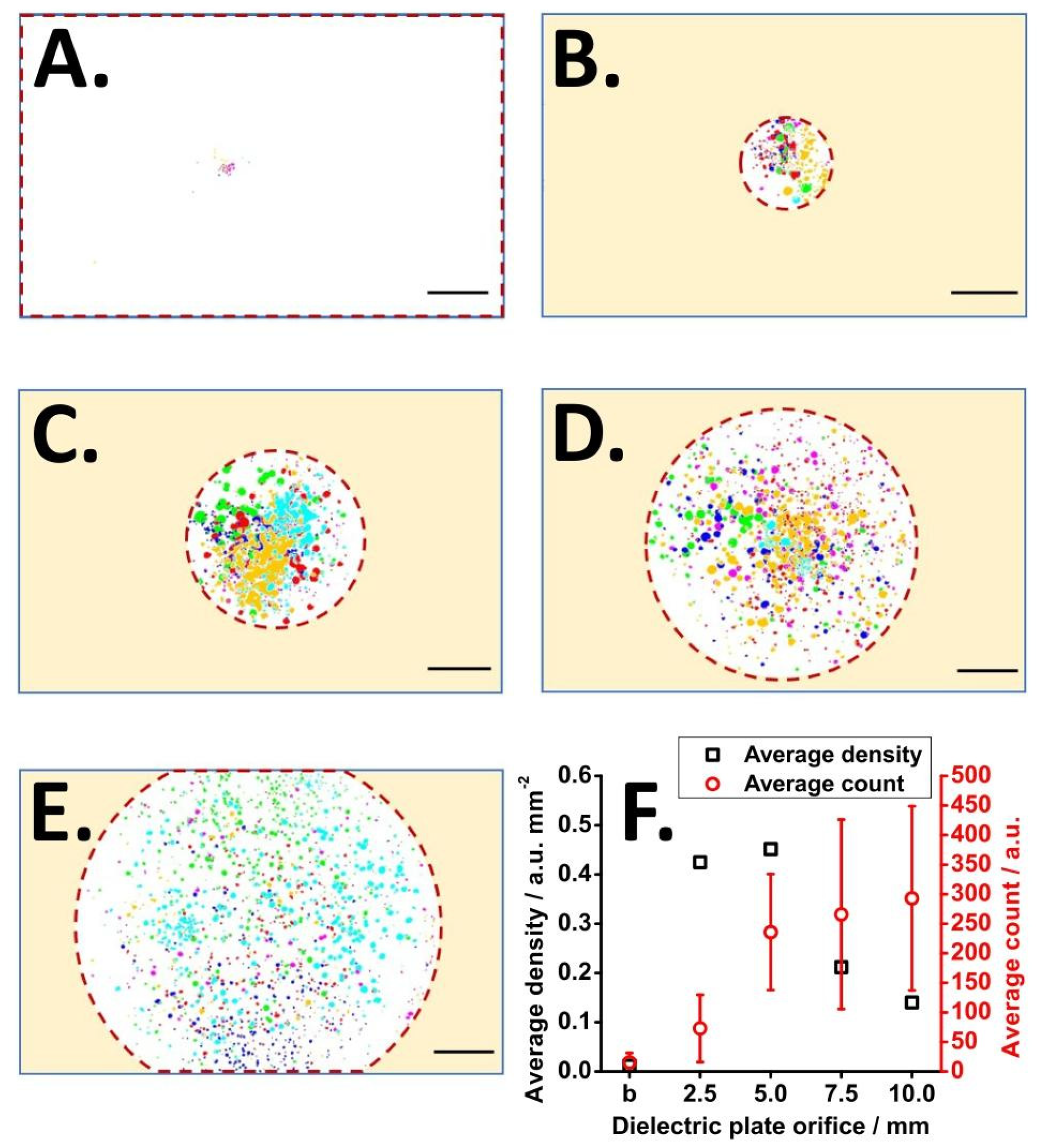
3.2. Offline Experiment
3.3. Online Experiment
3.4. Final Considerations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamashita, M.; Fenn, J.B. Electrospray ion source. Another variation on the free-jet theme. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, M.L.; Gall, L.N.; Krasnov, N.V.; Nikolaev, V.I.; Pavlenko, V.A.; Shkurov, V.A. Extraction of ions from solutions under atmospheric pressure: A method of mass spectrometric analysis of bioorganic compounds. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1984, 277, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verenchikov, A.N.; Krasnov, N.V.; Shkurov, V.A. Electrospray ionization developed by Lidija Gall’s group. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 490, 117067. [Google Scholar]
- Manisali, I.; Chen, D.D.; Schneider, B.B. Electrospray ionization source geometry for mass spectrometry: Past, present, and future. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilm, M. Principles of electrospray ionization. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M111.009407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, G.R.D.; Williams, E.R.; Wilm, M.; Urban, P.L. Mass spectrometry using electrospray ionization. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Kebarle, P.; Verkerk, U.H. Electrospray: From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase, what we know now. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2009, 28, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, S.; Seraglia, R.; Traldi, P. Some thoughts on electrospray ionization mechanisms. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 17, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Mazumdar, S. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: A technique to access the information beyond the molecular weight of the analyte. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 2012, 282574. [Google Scholar]
- Cañas, B.; López-Ferrer, D.; Ramos-Fernández, A.; Camafeita, E.; Calvo, E. Mass spectrometry technologies for proteomics. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2006, 4, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiderio, D.C. Mass Spectrometry: Clinical and Biomedical Applications; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.D. Future directions for electrospray ionization for biological analysis using mass spectrometry. Biotechniques 2006, 41, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, J.S.; Kelly, R.T.; Tang, K.; Smith, R.D. Ionization and transmission efficiency in an electrospray ionization—Mass spectrometry interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oss, M.; Kruve, A.; Herodes, K.; Leito, I. Electrospray ionization efficiency scale of organic compounds. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liigand, P.; Liigand, J.; Kaupmees, K.; Kruve, A. 30 Years of research on ESI/MS response: Trends, contradictions and applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1152, 238117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalcraft, K.R.; Lee, R.; Mills, C.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Virtual quantification of metabolites by capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry: Predicting ionization efficiency without chemical standards. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.M.; Brown, P.R.; Munson, B. Effects of mobile-phase additives, solution pH, ionization constant, and analyte concentration on the sensitivities and electrospray ionization mass spectra of nucleoside antiviral agents. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 5481–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Hamburger, M. Effects of solvent composition on molecular ion response in electrospray mass spectrometry: Investigation of the ionization processes. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1995, 9, 1516–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liigand, J.; Kruve, A.; Leito, I.; Girod, M.; Antoine, R. Effect of mobile phase on electrospray ionization efficiency. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 25, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Karas, M.; Dülcks, T. Effect of different solution flow rates on analyte ion signals in nano-ESI MS, or: When does ESI turn into nano-ESI? J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 14, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Faramawy, A.; Siu, K.W.M.; Thomson, B.A. Efficiency of nano-electrospray ionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, G.R.D.; Witek, H.A.; Urban, P.L. Programmable flow rate scanner for evaluating detector sensitivity regime. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, G.R.D.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Witek, H.A.; Urban, P.L. Sample flow rate scan in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry reveals alterations in protein charge state distribution. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13042–13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.T.; Marginean, I.; Smith, R.D.; Tang, K. On the ionization and ion transmission efficiencies of different ESI-MS interfaces. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.W.; Eschelbach, J.W.; Wilburn, R.T.; Jorgenson, J.W. Investigation of electrospray ionization and electrostatic focusing devices using a three-dimensional electrospray current density profiler. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilm, M.; Mann, M. Analytical properties of the nanoelectrospray ion source. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Prabhu, G.R.D.; Hsu, C.Y.; Urban, P.L. Tuning electrospray ionization with low-frequency sound. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kottke, P.A.; Fedorov, A.G. Electrohydrodynamics of gas-assisted electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.D.; Loo, J.A.; Edmonds, C.G.; Barinaga, C.J.; Udseth, H.R. New developments in biochemical mass spectrometry: Electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 882–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, S.A.; Tang, K.; Anderson, G.A.; Prior, D.C.; Udseth, H.R.; Smith, R.D. A novel ion funnel for focusing ions at elevated pressure using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 11, 1813–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhai, L.; Yue, B.; Lee, E.D.; Lee, M.L. New interface plate for microspray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, A. Mass spectrometry with ion sources operating at atmospheric pressure. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1991, 10, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Udseth, H.R.; Smith, R.D. Improved ion transmission from atmospheric pressure to high vacuum using a multicapillary inlet and electrodynamic ion funnel interface. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 5014–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.B.; Javaheri, H.; Covey, T.R. Ion sampling effects under conditions of total solvent consumption. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, B.; Zhang, B. Recent advancements in nanoelectrospray ionization interface and coupled devices. J. Chromatogr. Open 2022, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.D.; Shen, Y.; Tang, K. Ultrasensitive and quantitative analyses from combined separations−mass spectrometry for the characterization of proteomes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutchinsky, A.N.; Padovan, J.C.; Cohen, H.; Chait, B.T. Maximizing ion transmission from atmospheric pressure into the vacuum of mass spectrometers with a novel electrospray interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susa, A.C.; Xia, Z.; Williams, E.R. Native mass spectrometry from common buffers with salts that mimic the extracellular environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7912–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, A.T.; Jurchen, J.C.; Williams, E.R. Supercharged protein and peptide ions formed by electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, A.T.; Williams, E.R. Mechanism of charging and supercharging molecules in electrospray ionization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnin, C.; Ramrup, P.; Daigle-Young, C.; Vuckovic, D. Improving negative liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry lipidomic analysis of human plasma using acetic acid as a mobile-phase additive. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, M.; Sroka, M.; Reiss, J.; Rinke, G.; Albarghash, A.; Vogelgesang, R.; Rauschenbach, S. A hydrodynamically optimized nano-electrospray ionization source and vacuum interface. Analyst 2014, 139, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.T.; Tolmachev, A.V.; Page, J.S.; Tang, K.; Smith, R.D. The ion funnel: Theory, implementations, and applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 29, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Xiao, D.; Kabir, K.M.; Fletcher, J.; Donald, W.A. Ambient pressure ion funnel: Concepts, simulations, and analytical performance. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15811–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, E.C.; Chung, M.C.; Han, C.C. Characterizing the transmission properties of an ion funnel. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 14, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlottmann, F.; Allers, M.; Kirk, A.T.; Bohnhorst, A.; Zimmermann, S. A simple printed circuit board–based ion funnel for focusing low m/z ratio ions with high kinetic energies at elevated pressure. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, J.; Jurčíček, P.; Wang, G. Microfabrication of a multilayer nano-ESI focusing electrode based on SU-8 material. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 103, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.; Marsh, B.M.; Capek, G.O.; Schrader, R.L.; Tichy, S.; Cooks, R.G. Ion manipulation in open air using 3D-printed electrodes. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Boisdon, C.; Romero-Perez, D.; Sham, T.T.; Bastani, B.; Zhou, Y.; Maher, S. Ambient ion focusing for paper spray ionisation. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 471, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Lin, Y.; Matson, D.W.; Kim, T.; Smith, R.D. Generation of multiple electrosprays using microfabricated emitter arrays for improved mass spectrometric sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.T.; Wright, R.D.; Oleschuk, R.D. Multiple electrosprays generated from a single polycarbonate microstructured fibre. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Gibson, G.T.; Proulx, A.; Croteau, A.; Schneider, B.B.; Covey, T.R.; Oleschuk, R.D. Polymer micronozzle array for multiple electrosprays produced by templated synthesis and etching of microstructured fibers. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Gomez-Sjoberg, R.; Wang, D. Multinozzle emitter array chips for small-volume proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.T.; Page, J.S.; Marginean, I.; Tang, K.; Smith, R.D. Nanoelectrospray emitter arrays providing interemitter electric field uniformity. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5660–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Chen, X.; Smith, A.J.; Espenship, M.F.; Samayoa Oviedo, H.Y.; Wilson, S.M.; Laskin, J. Multiplexing of electrospray ionization sources using orthogonal injection into an electrodynamic ion funnel. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11576–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottke, P.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Jonke, A.P.; Seneviratne, C.A.; Hecht, E.S.; Muddiman, D.C.; Fedorov, A.G. DRILL: An electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry interface for improved sensitivity via inertial droplet sorting and electrohydrodynamic focusing in a swirling flow. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8981–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Yamagata, Y.; Kim, B.J.; Higuchi, T. Direct and dry micro-patterning of nano-particles by electrospray deposition through a micro-stencil mask. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 025021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; You, S.; Pikhitsa, P.V.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S.; Woo, C.G.; Choi, M. Three-dimensional assembly of nanoparticles from charged aerosols. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, B.J.; Pawliczak, E.E.; Hurley, T.R.; Chiarot, P.R. Electrospray printing of polyimide films using passive material focusing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6274–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevich, D.A.; Lei, L.; Han, D.; Kuznetsova, C.; Kooi, S.E.; Lee, H.; Singer, J.P. Self-limiting electrospray deposition for the surface modification of additively manufactured parts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20901–20911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycova, A.; Prikryl, J.; Kotzianova, A.; Datinska, V.; Velebny, V.; Foret, F. Electrospray: More than just an ionization source. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisaznuk, J.M.; Huang, P.; Yong, X.; Chiarot, P.R. Probing colloidal assembly on non-axisymmetric droplet surfaces via electrospray. Langmuir 2023, 39, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, V.N.; Morozova, T.Y. Electrospray deposition as a method for mass fabrication of mono-and multicomponent microarrays of biological and biologically active substances. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, F.C. Faraday’s laws in one equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1961, 38, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Gu, Z.; Wang, S.; Fukuda, T.; Kase, K.; Ju, J.; Tajima, Y. Numerical simulation of nanoparticle pattern fabricated by electrostatic spray deposition. Particuology 2013, 11, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.B.; Douglas, D.J.; Chen, D.D. An atmospheric pressure ion lens to improve electrospray ionization at low solution flow-rates. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 15, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Allmendinger, P.; Zhu, L.; Gröhn, A.J.; Wegner, K.; Frankevich, V.; Zenobi, R. The role of nebulizer gas flow in electrosonic spray ionization (ESSI). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoffmann, E.; Stroobant, V. Analytical Information. In Mass Spectrometry: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 243–268. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, P.L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-S. Time-Resolved Mass Spectrometry: From Concept to Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kiontke, A.; Oliveira-Birkmeier, A.; Opitz, A.; Birkemeyer, C. Electrospray ionization efficiency is dependent on different molecular descriptors with respect to solvent pH and instrumental configuration. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, C.; Thinius, M.; Lehmann, L.; Heintz, C.; Stappert, F.; Wissdorf, W.; Covey, T.R. Observation of charged droplets from electrospray ionization (ESI) plumes in API mass spectrometers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5587–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Sunner, J. Ion transport by viscous gas flow through capillaries. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 5, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garimella, S.; Xu, W.; Huang, G.; Harper, J.D.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Gas-flow assisted ion transfer for mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.A.J.; Joshi, A.; Chen, Y.; McIndoe, J.S. Strategies for avoiding saturation effects in ESI-MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 450, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | MRM Transition | Horizontal Offset = 1.5 mm | Horizontal Offset = 7 mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate A | Plate B | Plate C | Plate A | Plate B | Plate C | ||
| Acetaminophen | 152→110 | 1.24 ± 0.06 | 1.82 ± 0.19 | 1.62 ± 0.08 | 4.35 ± 0.77 | 1.31 ± 0.29 | 12.18 ± 1.48 |
| Alanine | 90→44 | 1.17 ± 0.03 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 1.27 ± 0.06 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 1.86 ± 0.60 | 4.40 ± 0.46 |
| Angiotensin II (singly charged) | 1047→110 | 1.86 ± 0.12 | 1.36 ± 0.13 | 1.47 ± 0.18 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 10.52 ± 0.90 | 30.70 ± 2.98 |
| Angiotensin II (doubly charged) | 524→70 | 1.83 ± 0.16 | 1.39 ± 0.11 | 1.65 ± 0.20 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 3.80 ± 0.40 | 10.19 ± 0.72 |
| Citrulline | 176→159 | 1.33 ± 0.09 | 1.35 ± 0.06 | 1.26 ± 0.04 | 1.08 ± 0.17 | 4.85 ± 0.56 | 10.10 ± 1.97 |
| Cloxacillin | 458→182 | 1.21 ± 0.02 | 1.39 ± 0.09 | 1.50 ± 0.09 | 0.54 ± 0.08 | 103.91 ± 23.75 | 325.69 ± 42.40 |
| Glutathione | 308→179 | 1.47 ± 0.06 | 1.16 ± 0.01 | 1.29 ± 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.05 | 6.99 ± 0.55 | 13.36 ± 0.69 |
| Glycine | 76→30 | 0.81 ± 0.06 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 1.32 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 2.26 ± 0.61 | 4.16 ± 0.33 |
| Glycine-Histidine peptide | 213→156 | 1.52 ± 0.06 | 1.40 ± 0.06 | 1.28 ± 0.05 | 0.61 ± 0.14 | 6.88 ± 0.79 | 24.94 ± 3.70 |
| HPF1 | 400→263 | 1.34 ± 0.05 | 1.42 ± 0.08 | 1.48 ± 0.09 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 10.03 ± 0.56 | 21.62 ± 0.37 |
| HPF2 (singly charged) | 781→364 | 1.12 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 2.19 ± 0.53 | 113.68 ± 21.56 | 294.69 ± 96.95 |
| HPF2 (doubly charged) | 391→110 | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 1.32 ± 0.03 | 0.90 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 7.43 ± 0.47 | 12.30 ± 1.91 |
| HPF3 * (singly charged) | 1163→110 | 0.86 ± 0.03 | 0.96 ± 0.03 | 1.02 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.00 ** | 201.49 ± 196.22 | 622.28 ± 677.48 |
| HPF3 (doubly charged) | 582→110 | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 0.94 ± 0.05 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 4.23 ± 0.47 | 7.50 ± 0.11 |
| HPF3 (triply charged) | 388→110 | 1.11 ± 0.14 | 1.01 ± 0.14 | 1.17 ± 0.12 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 5.64 ± 0.83 | 8.29 ± 0.85 |
| Lysine | 147→84 | 1.65 ± 0.18 | 1.75 ± 0.02 | 1.48 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 2.24 ± 0.40 | 6.11 ± 0.24 |
| Tryptophan | 205→146 | 1.12 ± 0.06 | 1.15 ± 0.08 | 1.09 ± 0.06 | 0.76 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.05 | 15.42 ± 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chua, Z.Q.; Prabhu, G.R.D.; Wang, Y.-W.; Raju, C.M.; Buchowiecki, K.; Ochirov, O.; Elpa, D.P.; Urban, P.L. Moderate Signal Enhancement in Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry by Focusing Electrospray Plume with a Dielectric Layer around the Mass Spectrometer’s Orifice. Molecules 2024, 29, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020316
Chua ZQ, Prabhu GRD, Wang Y-W, Raju CM, Buchowiecki K, Ochirov O, Elpa DP, Urban PL. Moderate Signal Enhancement in Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry by Focusing Electrospray Plume with a Dielectric Layer around the Mass Spectrometer’s Orifice. Molecules. 2024; 29(2):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020316
Chicago/Turabian StyleChua, Zi Qing, Gurpur Rakesh D. Prabhu, Yi-Wun Wang, Chamarthi Maheswar Raju, Krzysztof Buchowiecki, Ochir Ochirov, Decibel P. Elpa, and Pawel L. Urban. 2024. "Moderate Signal Enhancement in Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry by Focusing Electrospray Plume with a Dielectric Layer around the Mass Spectrometer’s Orifice" Molecules 29, no. 2: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020316
APA StyleChua, Z. Q., Prabhu, G. R. D., Wang, Y.-W., Raju, C. M., Buchowiecki, K., Ochirov, O., Elpa, D. P., & Urban, P. L. (2024). Moderate Signal Enhancement in Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry by Focusing Electrospray Plume with a Dielectric Layer around the Mass Spectrometer’s Orifice. Molecules, 29(2), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29020316