Design and Characterization of Epoxy Resin Systems Based on Mixtures of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with Docusate and Dicyanamide Anions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Properties of Ionic Liquids
2.2. Mixtures of Ionic Liquids
2.3. Epoxy Resin Polymerization with Ionic Liquids and Their Mixtures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Ionic Liquids
3.2.1. 1,3-Didodecylimidazolium Chloride [dDDIM Cl]
3.2.2. 1,3-Didodecylimidazolium Docusate [dDDIM DOSS]
3.2.3. 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Docusate [EMIM DOSS]
3.2.4. 1,3-Didodecylimidazolium Dicyanamide [dDDIM DCA]
3.3. Mixture Preparation
3.4. Ion Chromatography (IC)
3.5. Water Content Analysis
3.6. Differential Scaning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.7. NMR Analysis
3.8. Curing Proces
3.9. Hardness Measurements
3.10. Viscosity Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shamshina, J.L.; Zavgorodnya, O.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 3rd ed.; Worsfold, P., Poole, C., Townshend, A., Miró, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 218–225. ISBN 978-0-08-101984-9. [Google Scholar]
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Tojo, J.; Rodríguez, A. Toxicity and Biodegradability of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobras, G.; Kasperczyk, K.; Jurczyk, S.; Orlińska, B. N-Hydroxyphthalimide Supported on Silica Coated with Ionic Liquids Containing CoCl2 (SCILLs) as New Catalytic System for Solvent-Free Ethylbenzene Oxidation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiago, G.A.O.; Matias, I.A.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. Application of Ionic Liquids in Electrochemistry—Recent Advances. Molecules 2020, 25, 5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebresilassie Eshetu, G.; Armand, M.; Scrosati, B.; Passerini, S. Energy Storage Materials Synthesized from Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13342–13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Song, Z.; Zhu, D.; Li, L.; Gan, L.; Liu, M. Ionic Liquids for Supercapacitive Energy Storage: A Mini-Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 8443–8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic Liquids as Lubricant Additives: A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Cheng, H.-L.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Cui, H.-R. Ionic Liquids in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Du, F.; Pang, A. Dual-Functionalized Imidazolium Ionic Liquids as Curing Agents for Epoxy Resins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 3024–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, F.C.; Cavalli, G.; Henningsen, M.; Howlin, B.J.; Hamerton, I. Investigating the Mechanism through Which Ionic Liquids Initiate the Polymerisation of Epoxy Resins. Polymer 2018, 139, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, L.F.C.; Soares, B.G. Polyaniline/Carbon Nanotube Hybrids Modified with Ionic Liquids as Anticorrosive Additive in Epoxy Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 143, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mąka, H.; Spychaj, T.; Zenker, M. High Performance Epoxy Composites Cured with Ionic Liquids. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, F.C.; Cavalli, G.; Henningsen, M.; Howlin, B.J.; Hamerton, I. Examining the Kinetics of the Thermal Polymerisation Behaviour of Epoxy Resins Initiated with a Series of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Based Ionic Liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 663, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, D.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Docusate Ionic Liquids: Effect of Cation on Water Solubility and Solvent Extraction Behavior. ChemPlusChem 2017, 82, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibel, R.; Knoll, P.; Le-Vinh, B.; Kali, G.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Sulfosuccinate-Based Surfactants as Counterions for Hydrophobic Ion Pairing. Acta Biomater. 2022, 144, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzo, C.P.; Wust, K.; Tier, A.Z.; Beck, T.S.; Rodrigues, L.V.; Vaucher, R.A.; Bolzan, L.P.; Terra, S.; Soares, F.; Martins, M.A.P. Novel Ibuprofenate- and Docusate-Based Ionic Liquids: Emergence of Antimicrobial Activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100476–100486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, D.; Szpecht, A.; Pomázi, Á.; Kovács, Z.; Szolnoki, B.; Pinke, B.; Toldy, A.; Smiglak, M. Multifunctional Modifying Systems Based on Ionic Liquids for Epoxy Resin Systems and Composites. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, D.; Szpecht, A.; Nadobna, P.; Palacz, M.; Smiglak, M. Behavior, Synthesis, and Effectiveness of an Activity of Anilinium-Based Ionic Liquids (AnILs) as a Hardeners and Modifiers for Epoxy-Coatings of Flax Biocomposites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 189, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, D.; Szpecht, A.; Smiglak, M. Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid Mixtures for Curing and Modifying Flax-Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 408, 125340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpecht, A.; Zajac, A.; Zielinski, D.; Maciejewski, H.; Smiglak, M. Versatile Method for the Simultaneous Synthesis of Two Ionic Liquids, Otherwise Difficult to Obtain, with High Atom Economy. ChemistryOpen 2019, 8, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, A.; Szpecht, A.; Zielinski, D.; Rola, K.; Hoppe, J.; Komorowska, K.; Smiglak, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Potentially Polymerizable Amine-Derived Ionic Liquids Bearing 4-Vinylbenzyl Group. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 283, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, D.; Szpecht, A.; Hinc, P.; Maciejewski, H.; Smiglak, M. Mono N-Alkylated DABCO-Based Ionic Liquids and Their Application as Latent Curing Agents for Epoxy Resins. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5481–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
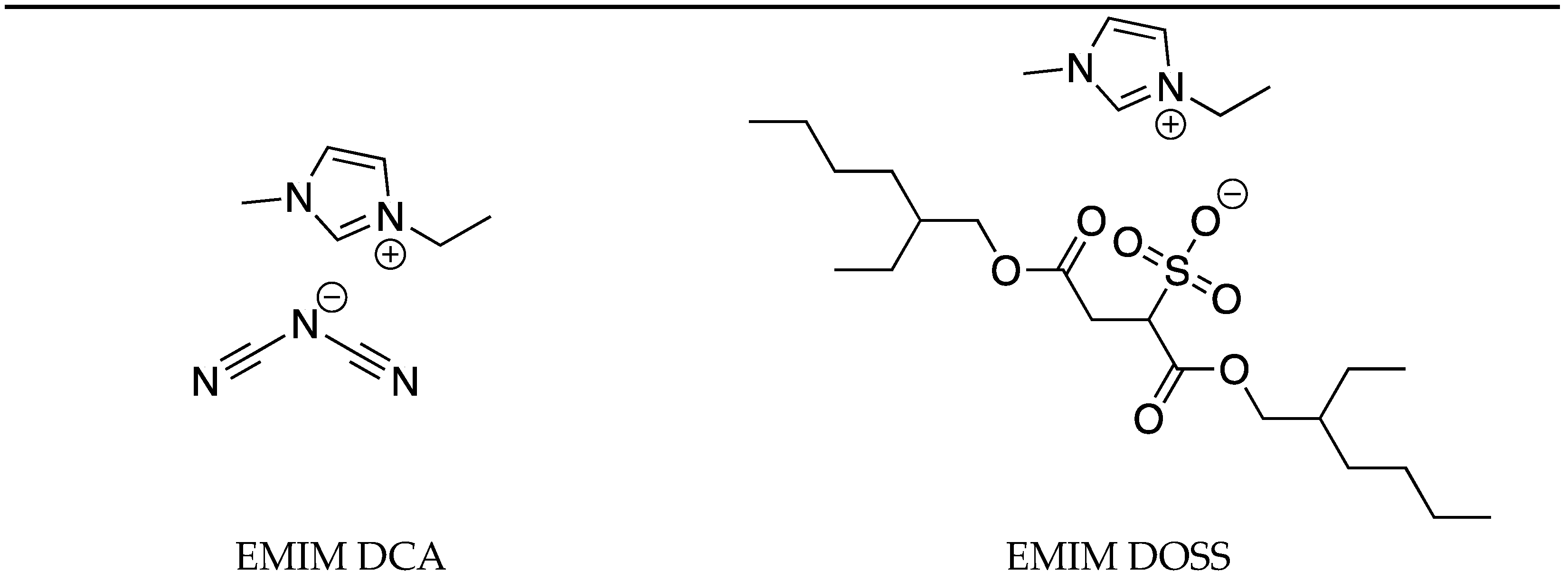
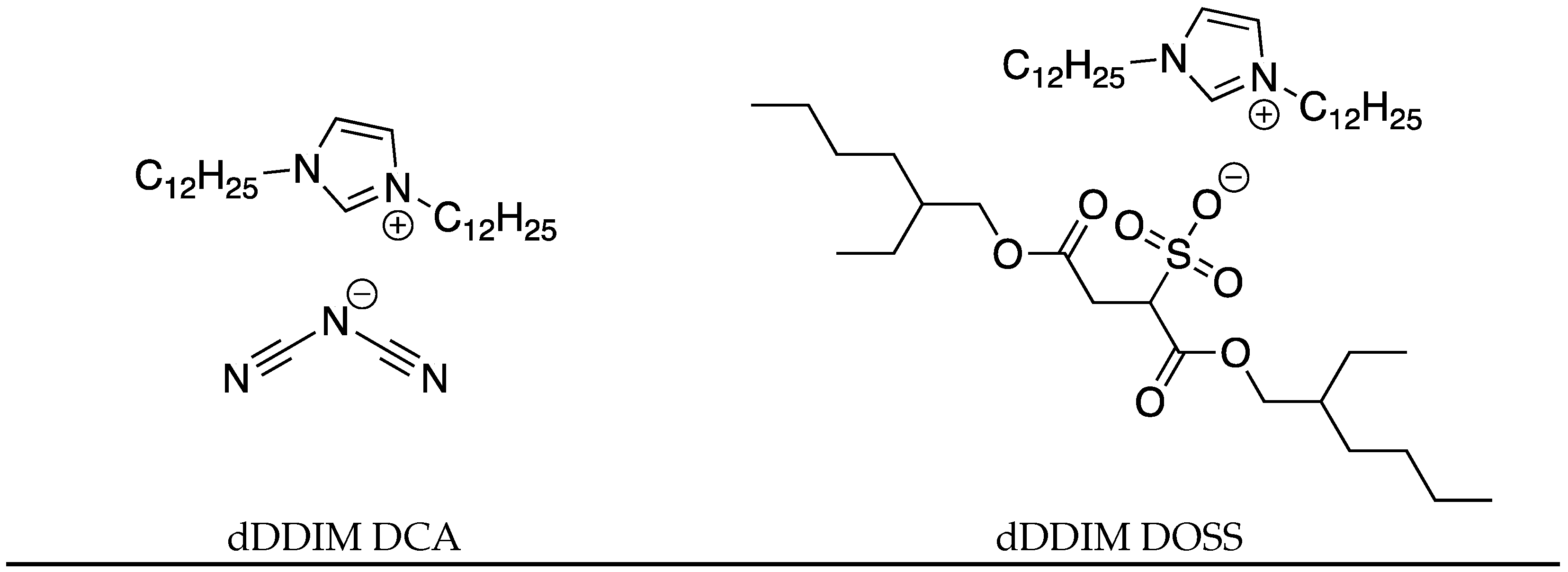
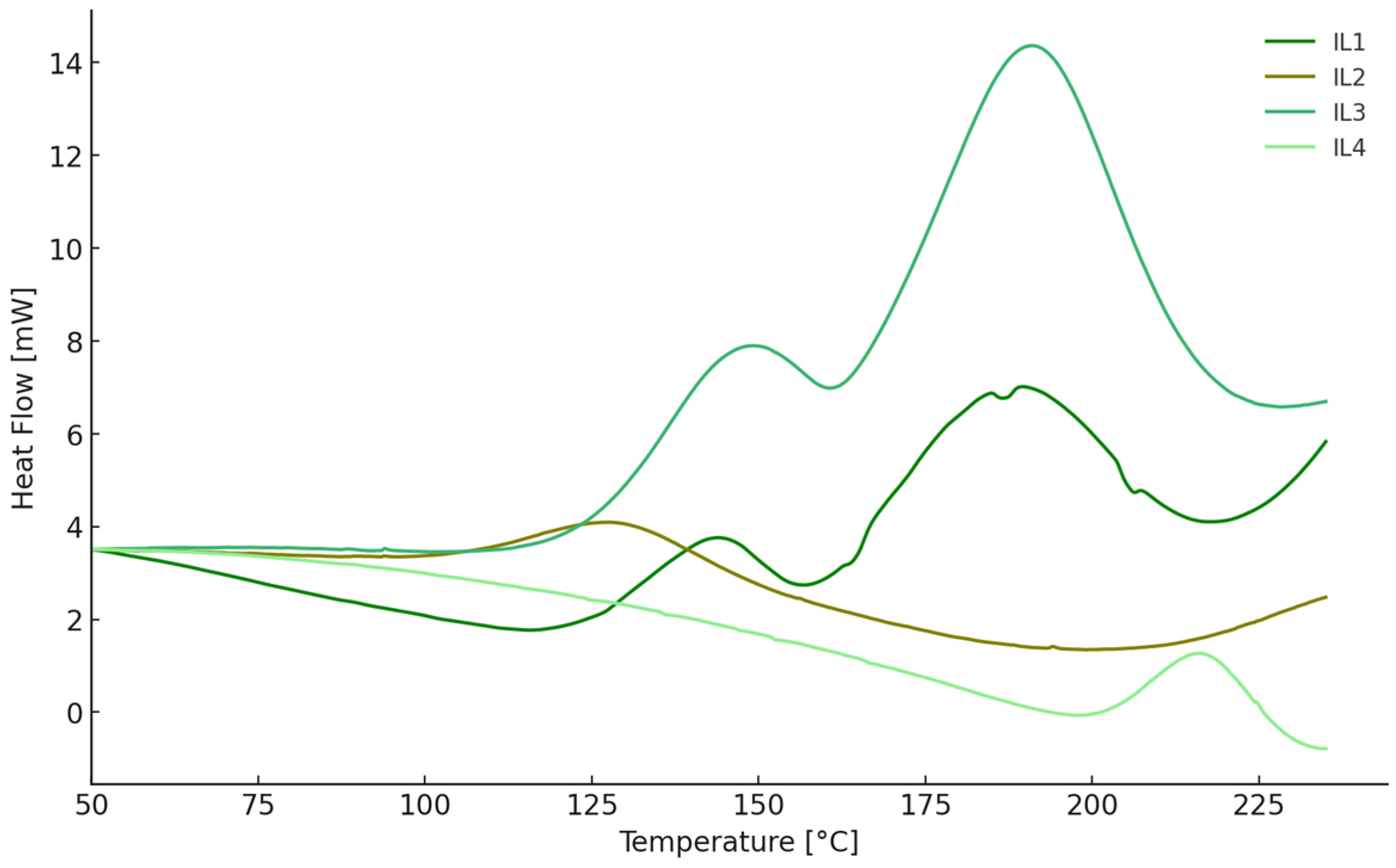
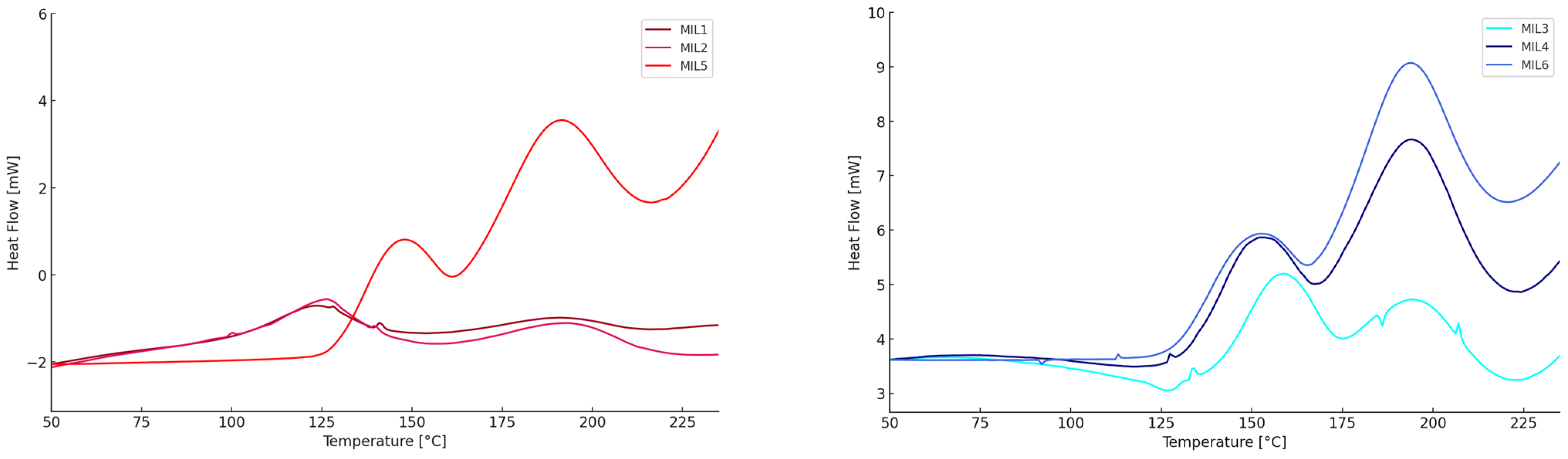
| IL | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMIM DOSS | −56.3 | −13.0 | −25.8 | |
| dDDIM DCA | 7.0 | 9.0 | 41.2 | 2.3 |
| dDDIM DOSS | −43.9 | −26.0 | −1.4 | −30.3 |
| Mixture | Viscosity (Pa⋅s) | IL1 | IL2 | IL3 | IL4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL1 | 0.46 | 1 | 1 | ||
| MIL2 | 0.21 | 2 | 1 | ||
| MIL3 | 0.13 | 1 | 1 | ||
| MIL4 | 0.07 | 3 | 1 | ||
| MIL5 | 0.10 | 5 | 1 | ||
| MIL6 | 0.05 | 5 | 1 |
| Mixture | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL1 | −39.7 | −24.0 25.0 | −16.5 −6.8 −6.6 −39.6 | |
| MIL2 | −18.9 | −10.7 −4.3 | 33.2 | 7.9 −22.3 |
| MIL3 | −67.7 | |||
| MIL4 | ||||
| MIL5 | 2.2 | 38.9 | 19.2 −6.5 | |
| MIL6 | −79.2 * |
| Ionic Liquid | Tonset (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Tendset (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMIM DCA 6 phr * | 129/169 | 146/192 | 160/214 | 98 |
| EMIM DCA 12 phr * | 131/167 | 146/191 | 166/214 | 184 |
| EMIM DOSS 6 phr | 202 | 214 | 225 | 8 |
| EMIM DOSS 12 phr | 203 | 216 | 228 | 12 |
| dDDIM DCA 6 phr * | 136/164 | 147/183 | 155/203 | 21 |
| dDDIM DCA 12 phr * | 126/165 | 143/189 | 164/208 | 55 |
| dDDIM DOSS 6 phr | 96 | 117 | 133 | 11 |
| dDDIM DOSS 12 phr | 107 | 129 | 148 | 18 |
| Mixture | Tonset (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Tendset (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL1 6 phr | 129/150 | 130/150 | 131/151 | 4 |
| MIL1 12 phr | 100/164 | 123/190 | 144/211 | 30 |
| MIL2 6 phr | 105/171 | 129/185 | 145/205 | 12 |
| MIL2 12 phr | 106/165 | 127/194 | 144/216 | 36 |
| MIL3 6 phr * | 142 | 160 | 172 | 12 |
| MIL3 12 phr | 141/187 | 158/196 | 173/209 | 33 |
| MIL4 6 phr | 141/169 | 153/189 | 163/209 | 31 |
| MIL4 12 phr | 136/173 | 152/194 | 165/213 | 81 |
| MIL5 6 phr | 140/165 | 149/186 | 159/208 | 32 |
| MIL5 12 phr | 131/167 | 146/190 | 160/212 | 96 |
| MIL6 6 phr | 136/169 | 150/191 | 162/212 | 60 |
| MIL6 12 phr | 132/170 | 149/193 | 165/214 | 142 |
| Curing Temperature (°C) | MIL2 | MIL4 | MIL5 | MIL6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shore Type | A | D | A | D | A | D | A | D |
| 120 | 50 | 30 | 99 | 84 | 70 | 36 | 99 | 62 |
| 135 | 58 | 37 | 99 | 84 | 76 | 43 | 99 | 70 |
| 150 | 65 | 40 | 99 | 85 | 86 | 48 | 99 | 85 |
| Property | Manuscript | Publication 1 [18] | Publication 2 [20] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic Liquids Studied | Imidazolium-based ILs with docusate and dicyanamide anions | ILs with phosphorus atom in the structure (cation and/or anion), IL with silicon atom in the structure and EMIM DCA | DCA-based ILs with long carbon alkyl chains in the cation structure |
| Amount of Ionic Liquids Used | 6–12 wt% | 12 wt% | 4 wt% |
| Onset Polymerization Temperature | Two polymerization peaks 100−170 °C | 110–133 °C | Two polymerization peaks 160 °C–185 °C |
| Peak Polymerization Temperature | Two polymerization peaks 123–196 °C | 121–169 °C | Two polymerization peaks 170–200 °C |
| Enthalpy (ΔH) | Moderate (lower than traditional curing agents but higher than single IL systems) | High with values ranging from 446 to 508 J/g | significantly lower than single IL systems |
| Polymerization Behavior | Slower, controlled polymerization with moderate exothermic release | Lower exothermic release, gradual polymerization | Most controlled polymerization process with lowest exothermic reaction |
| Comparison to Single IL Systems | Lower enthalpy and slower curing than single ILs | Reduced enthalpy compared to single IL systems and conventional curing agents | Lowest enthalpy and onset temperatures compared to single ILs |
| Unique Findings | Focus on mixtures with docusate and dicyanamide anions, dual polymerization peaks observed, moderate enthalpy | Multifunctional ILs affecting various properties; lower enthalpy; curing and flexibility improvement | Dual polymerization peaks observed, indicating parallel reactions; extremely low enthalpy; controlled curing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szpecht, A.; Zielinski, D.; Roszyk, S.; Smiglak, M. Design and Characterization of Epoxy Resin Systems Based on Mixtures of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with Docusate and Dicyanamide Anions. Molecules 2024, 29, 4538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194538
Szpecht A, Zielinski D, Roszyk S, Smiglak M. Design and Characterization of Epoxy Resin Systems Based on Mixtures of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with Docusate and Dicyanamide Anions. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194538
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzpecht, Andrea, Dawid Zielinski, Szymon Roszyk, and Marcin Smiglak. 2024. "Design and Characterization of Epoxy Resin Systems Based on Mixtures of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with Docusate and Dicyanamide Anions" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194538
APA StyleSzpecht, A., Zielinski, D., Roszyk, S., & Smiglak, M. (2024). Design and Characterization of Epoxy Resin Systems Based on Mixtures of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with Docusate and Dicyanamide Anions. Molecules, 29(19), 4538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194538






