Pharmacokinetics and Dose Proportionality Study of a Novel Antiparkinsonian Agent, a 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-ylthio-conjugate of Prottremine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
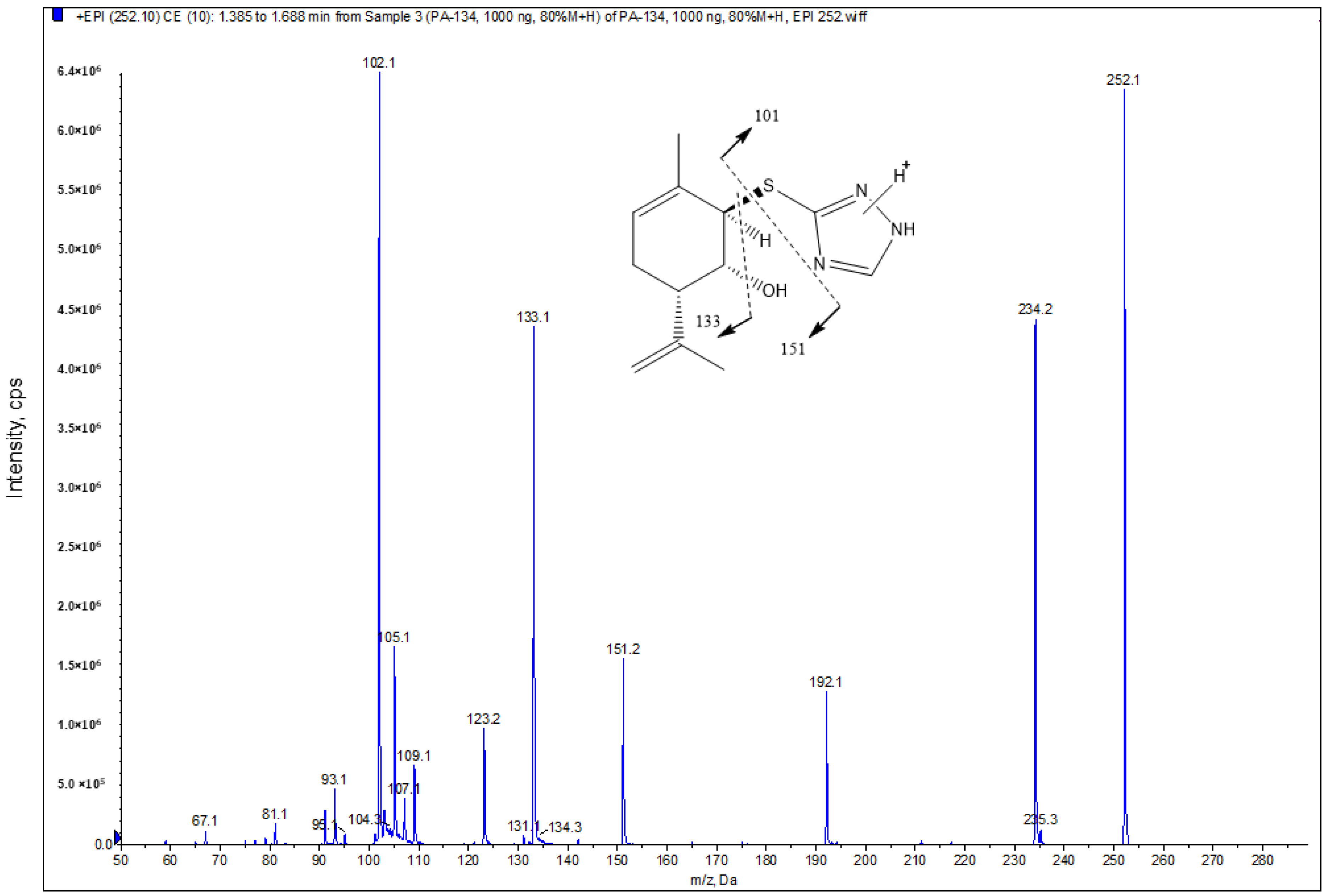
2.1. Mass Spectrometric and Chromatographic Conditions
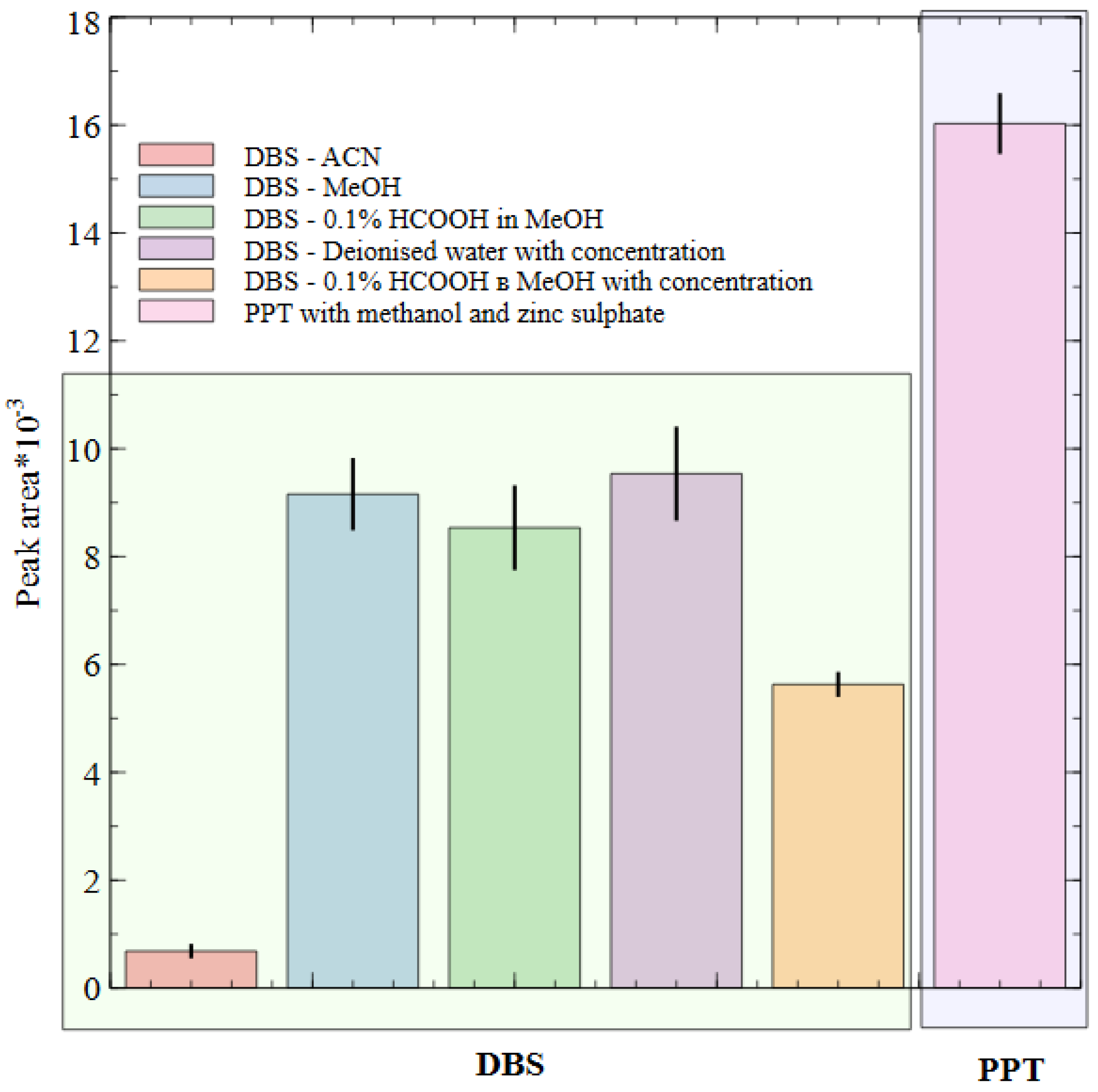
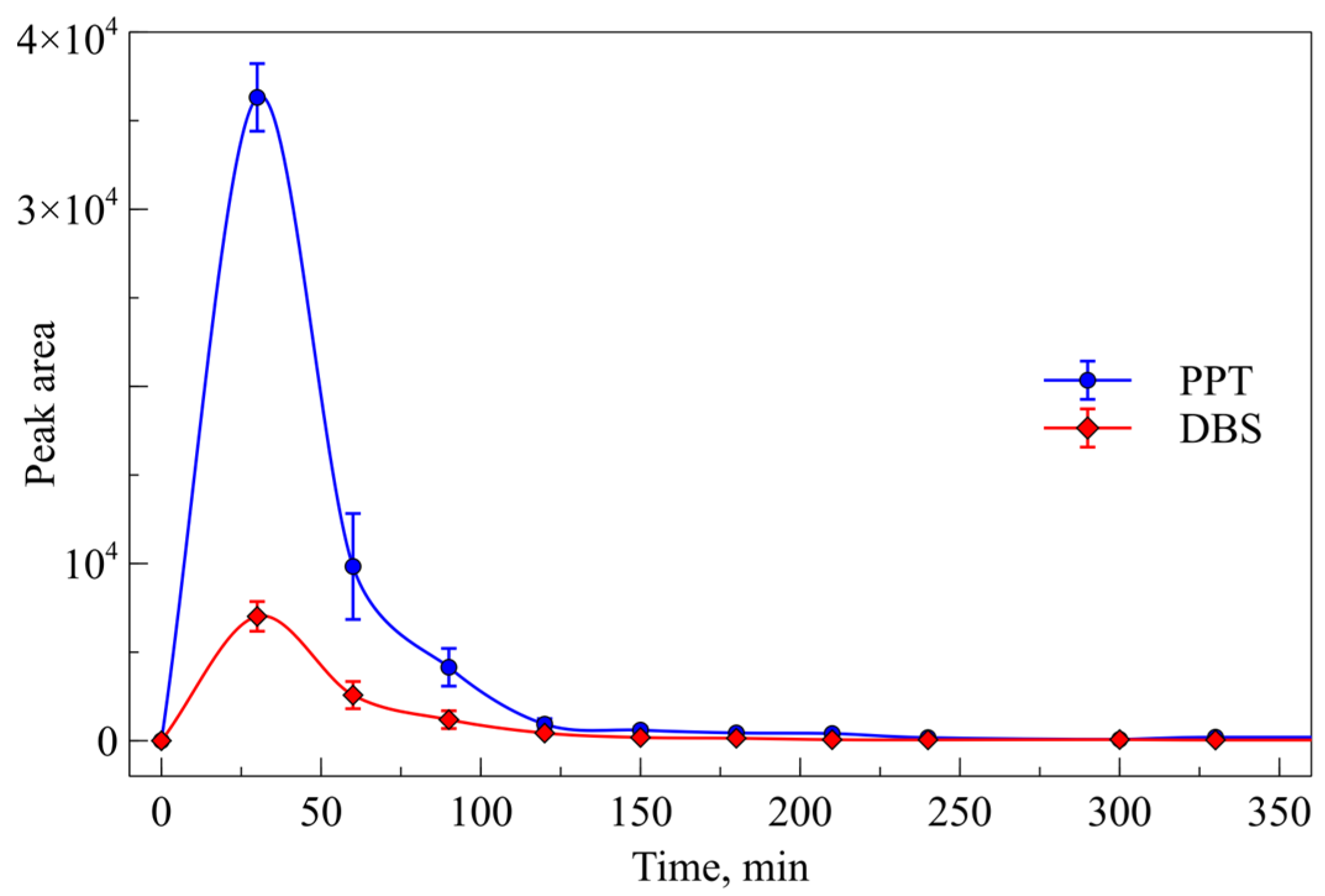
2.2. Sample Preparation Method and Biostability Study
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Selectivity
2.3.2. Calibration Curve
2.3.3. Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.3.4. Accuracy and Precision
2.3.5. Carryover
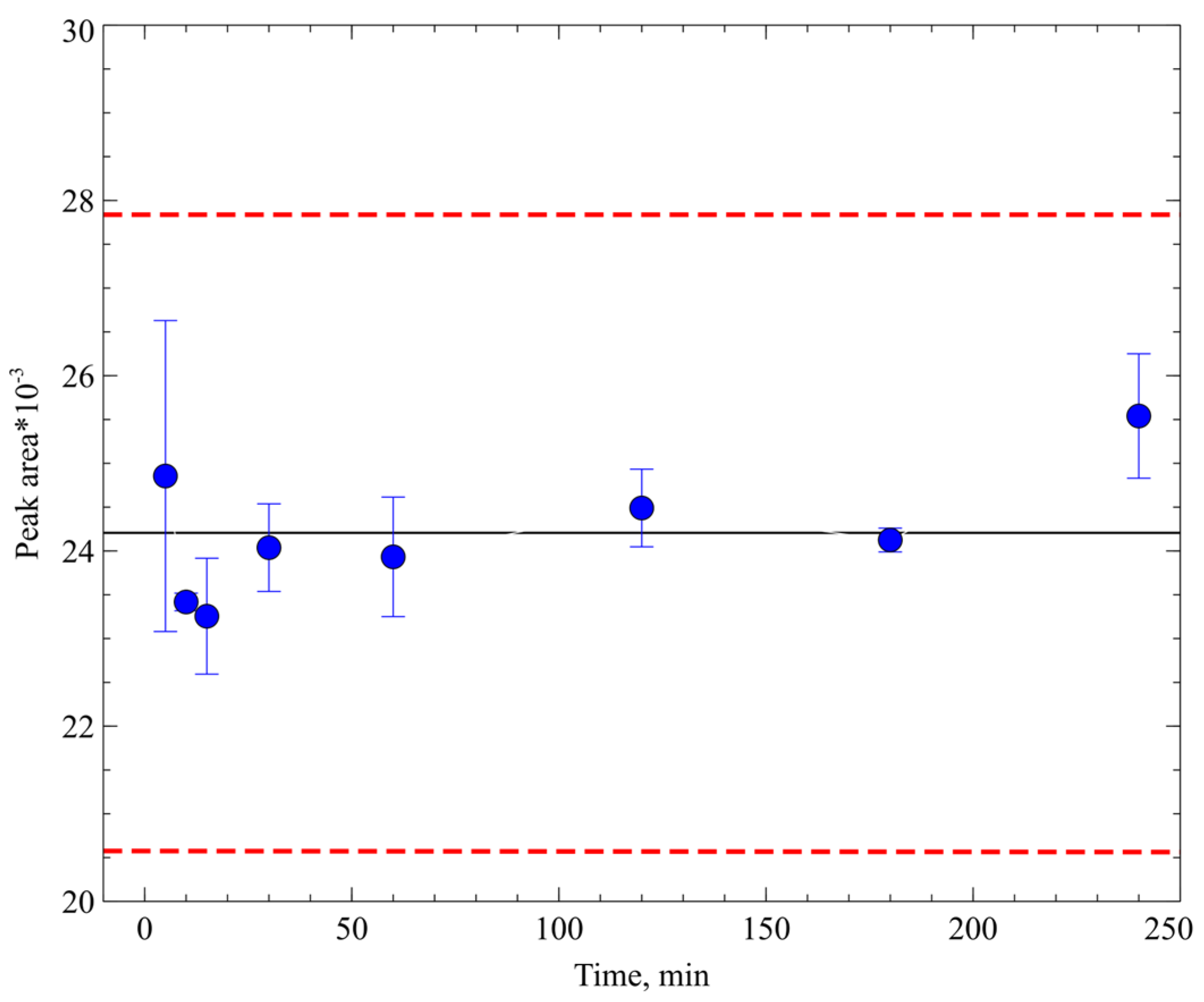
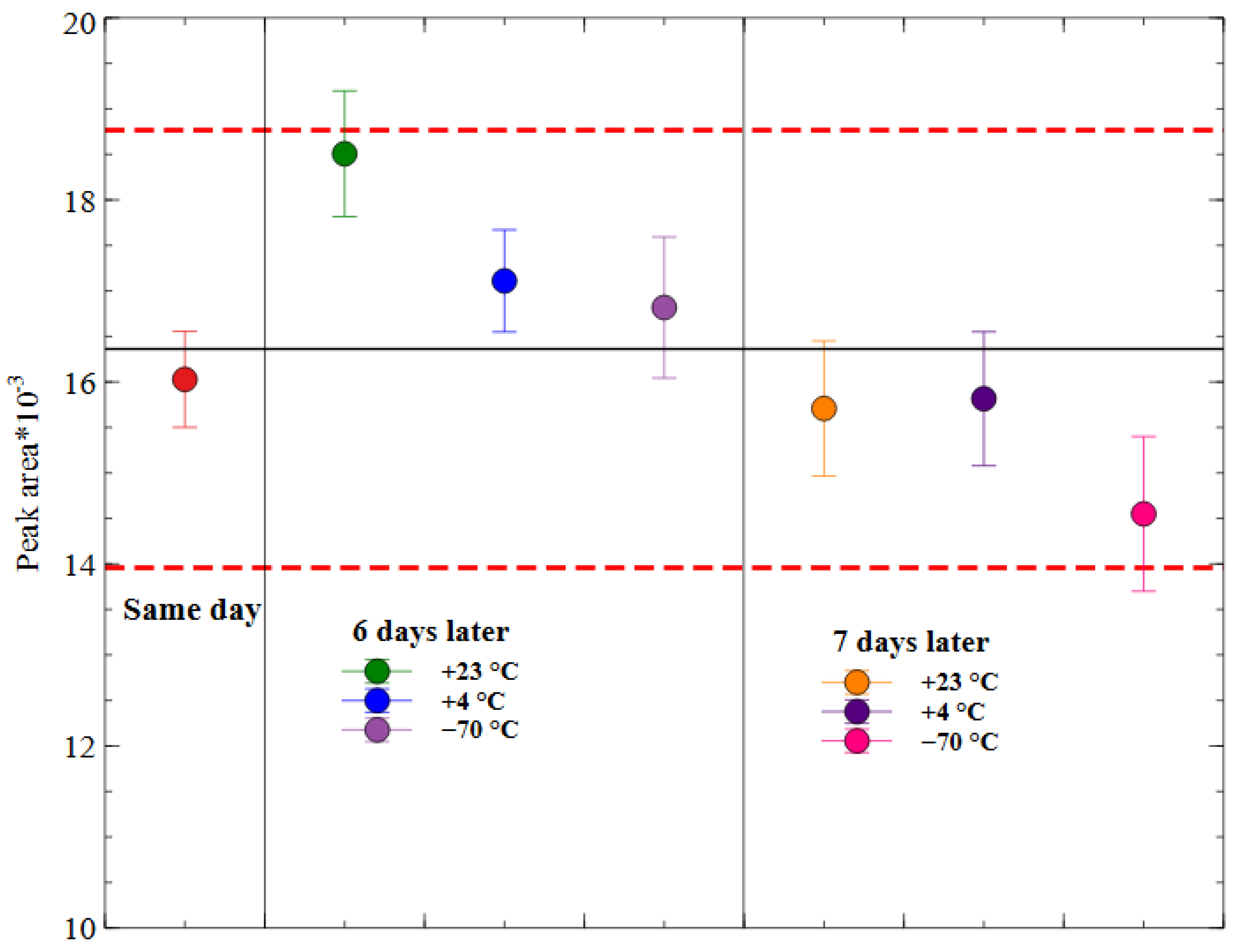
2.3.6. Stability of Prepared Samples
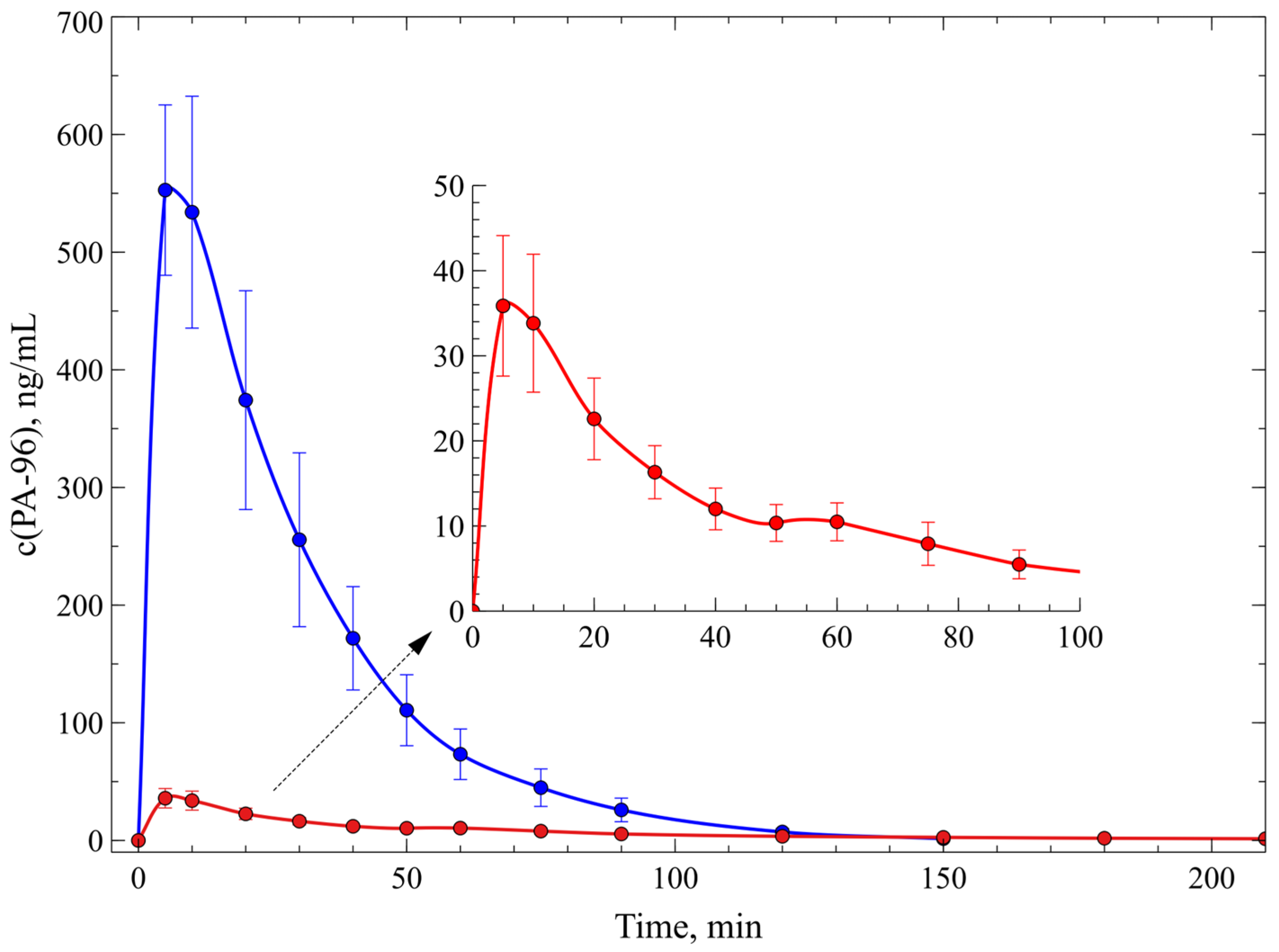
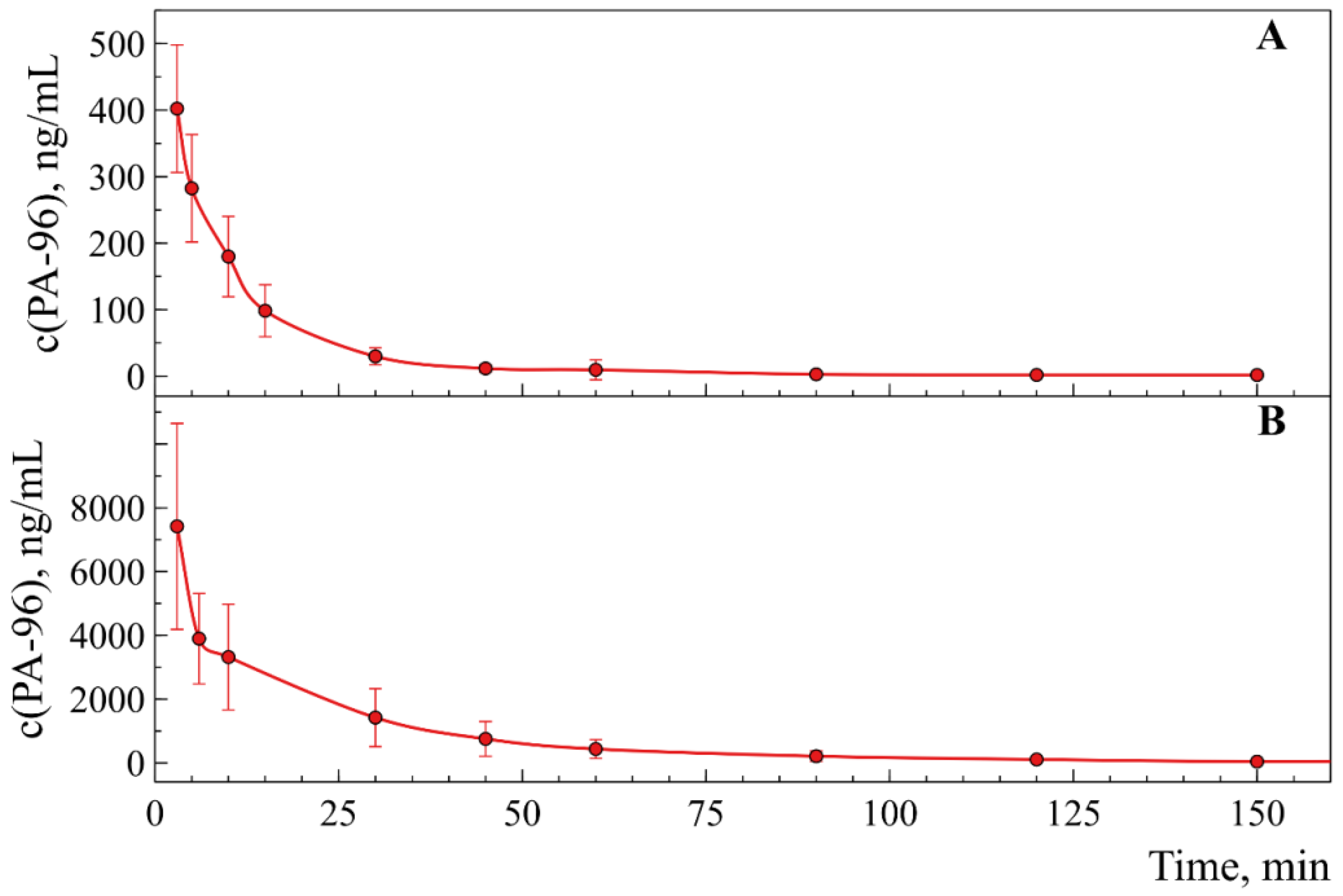
2.4. Investigation of Pharmacokinetics of PA-96
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation and LC–MS/MS Conditions
3.3. Working Solutions and Calibrators
3.4. Sample Preparation. Blood Preparation Protocol
3.4.1. Protein Precipitation (PPT)
3.4.2. Dried Blood Spots (DBS) Preparation and Processing
3.5. Validation
3.5.1. Selectivity and Specificity
3.5.2. Linearity
3.5.3. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
3.5.4. Extraction Recovery
3.5.5. Matrix Effect (ME)
3.5.6. Precision and Accuracy
3.5.7. Carryover
3.5.8. Stability of PA-96 in Mice Whole Blood and in Prepared Samples
3.6. Animals and Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Sherer, T.; Okun, M.S.; Bloem, B.R. The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson Pandemic. J. Park. Dis. 2018, 8, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, A.; Högl, B. Sleep in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Sue, C.M.; Williams-Gray, C.H. The pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, R.; Cereda, E.; Akpalu, A.; Sarfo, F.S.; Cham, M.; Laryea, R.; Obese, V.; Oppon, K.; Del Sorbo, F.; Bonvegna, S.; et al. Natural history of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease and the long-duration response to levodopa. Brain 2020, 143, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaoui, M.A.; Geoffroy, P.A.; Roze, E.; Degos, B.; Garcin, B. Functional Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease and Functional Parkinsonism: A Systematic Review. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 32, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.; Mao, Z.-H. Progression of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Progression of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2012, 28, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Shukla, S. Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: Opening new avenues in treatment. Curr. Res. Behav. 2021, 2, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Foffani, G.; Dehay, B.; Bezard, E.; Obeso, J.A. Motor and non-motor circuit disturbances in early Parkinson disease: Which happens first? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Unmet needs in Parkinson disease: Motor and non-motor. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 80, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinus, J.; Zhu, K.; Marras, C.; Aarsland, D.; van Hilten, J.J. Risk factors for non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Nichols, E.; Abd-Allah, F. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Vélez, G.E.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Parkinson’s Disease Genetics and Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 8, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, N.; Teo, W.-P.; Chandra, S.; Chapman, J. Parkinson’s Disease and the Environment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.N.; Esteves, A.R.; Empadinhas, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Parkinson’s Disease: A Multisystem Disorder. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 39, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, B.R.; Goldman, S.M.; Miller, G.W.; Greenamyre, J.T.; Dorsey, E.R. Preventing Parkinson’s Disease: An Environmental Agenda. J. Park. Dis. 2022, 12, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, K.; Ullah, A.; Shkodina, A.D.; Boiko, D.I.; Rafique, Z.; Alghamdi, B.S.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Ashraf, G.M. Drug reprofiling history and potential therapies against Parkinson’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1028356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, I.; Cacabelos, R. Current Drugs and Potential Future Neuroprotective Compounds for Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; Satake, Y.; Hiraga, K.; Yokoi, K.; Hattori, M.; Suzuki, M.; Hara, K.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Okun, M.S.; Katsuno, M. Effects of MAO-B inhibitors on non-motor symptoms and quality of life in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jia, C.; Li, T.; Le, W. Hot Topics in Recent Parkinson’s Disease Research: Where We are and Where We Should Go. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woitalla, D.; Buhmann, C.; Hilker-Roggendorf, R.; Höglinger, G.; Koschel, J.; Müller, T.; Weise, D. Role of dopamine agonists in Parkinson’s disease therapy. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, A.C.; Moore, B.T.; Daniels, R.N. Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Levodopa. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogetofte, H.; Alamyar, A.; Blaabjerg, M.; Meyer, M. Levodopa Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: History, Current Status and Perspectives. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; Jo, S.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, Y.S.; Lee, D.; Ryu, H.-S.; Chung, S.J. Therapeutic Effect of Levodopa/Carbidopa/Entacapone on Sleep Disturbance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Mov. Disord. 2020, 13, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.K.; Kwatra, M.; Wang, J.; Ko, H.S. Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Emerging Treatment Strategies. Cells 2022, 11, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvey, P.M.; Hendey, B.; Monahan, A.J. The Blood Brain Barrier in Neurodegenerative Disease: A Rhetorical Perspective. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Sig Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Kotzur, R.; Richter, F. Blood–brain barrier alterations and their impact on Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis and therapy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W. Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier: Molecular Mechanism of Transport of Drugs and Physiologically Important Compounds. J. Membr. Biol. 2015, 248, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration, Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/bioanalytical-method-validation-scientific-guideline (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Ardashov, O.V.; Pavlova, A.V.; Il’ina, I.V.; Morozova, E.A.; Korchagina, D.V.; Karpova, E.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Highly potent activity of (1R,2R,6S)-3-methyl-6-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-diol in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3866–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdman, E.; Kapitsa, I.; Ivanova, E.; Voronina, T.; Ardashov, O.; Volcho, K.; Khazanov, V.; Salakhutdinov, N. Evolution of anti-parkinsonian activity of monoterpenoid (1R,2R,6S)-3-methyl-6-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-diol in various in vivo models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 815, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstikova, T.G.; Pavlova, A.V.; Dolgikh, M.P.; Il’ina, I.V.; Ardashov, O.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Tolstikov, G.A. (4S,5R,6R)-para-Mentha-1,8-dien-5,6-diol is a new highly effective anticonvulsant agent. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2009, 429, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Base of Clinical Trials in Russia. Available online: https://grlsbase.ru/clinicaltrails/clintrail/581 (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Ardashov, O.V.; Pavlova, A.V.; Korchagina, D.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Antiparkinsonian activity of some 9-N-, O-, S- and C-derivatives of 3-methyl-6-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohex-3-ene-1,2-diol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotliarova, A.; Podturkina, A.V.; Pavlova, A.V.; Gorina, D.S.; Lastovka, A.V.; Ardashov, O.V.; Rogachev, A.D.; Izyurov, A.E.; Arefieva, A.B.; Kulikov, A.V.; et al. A Newly Identified Monoterpenoid-Based Small Molecule Able to Support the Survival of Primary Cultured Dopamine Neurons and Alleviate MPTP-Induced Toxicity In Vivo. Molecules 2022, 27, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhina, A.A.; Rogachev, A.D.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Pokrovsky, A.G.; Khazanov, V.A.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantitative analysis of the anti-influenza agent camphecene in rat plasma and its application to study the blood-to-plasma distribution of the agent. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 180, 113039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhina, A.A.; Rogachev, A.D.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Pokrovsky, A.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Stability study of the antiviral agent camphecene in dried blood spots at different temperatures. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogachev, A.D.; Putilova, V.P.; Zaykovskaya, A.V.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Sokolova, A.S.; Fomenko, V.V.; Pyankov, O.V.; Maksyutov, R.A.; Pokrovsky, A.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Biostability study, quantitation method and preliminary pharmacokinetics of a new antifilovirus agent based on borneol and 3-(piperidin-1-yl)propanoic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 199, 114062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessborn, D.; Sköld, K.; Zeeberg, D.; Kaewkhao, K.; Sköld, O.; Ahnoff, M. Heat stabilization of blood spot samples for determination of metabolically unstable drug compounds. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PK Parameter and Dose | 5 mg/kg (n = 4) | 10 mg/kg (n = 4) |
|---|---|---|
| Tmax, min | 6.3 ± 1.3 | 8.8 ± 1.3 |
| Cmax, ng/mL | 36 ± 8 | 588 ± 71 |
| t1/2, min | 44 ± 13 | 15.2 ± 1.2 |
| AUC0-t, ng/mL·min | (1.7 ± 0.3) × 103 | (1.8 ± 0.4) × 104 |
| Vz/F_obs, (mg)/(ng/mL) | (1.9 ± 0.5) × 10−1 | (13.7 ± 2.7) × 10−3 |
| Cl/F_obs, (mg)/(ng/mL)/min | (3.3 ± 0.7) × 10−3 | (6.4 ± 1.5) × 10−4 |
| PK Parameter | 1st Administration | 2nd Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Tmax, min | 10.0 ± 2.2 | 248.3 ± 2.5 |
| Cmax, ng/mL | 60 ± 15 | 58 ± 13 |
| t1/2, min | 21 ± 4 | 19 ± 3 |
| AUC0-t, ng/mL·min | (1.5 ± 0.3) × 103 | (8.1 ± 2.3) × 103 |
| Vz/F_obs, (mg)/(ng/mL) | 0.108 ± 0.025 | 0.025 ± 0.004 |
| Cl/F_obs, (mg)/(ng/mL)/min | (4.0 ± 0.8) × 10−3 | (0.79 ± 0.14) × 10−3 |
| PK Parameter and Dose | 1 mg/kg (n = 6) | 10 mg/kg (n = 2) |
|---|---|---|
| Tmax, min | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 3 |
| Cmax, ng/mL | (3.9 ± 0.3) × 102 | (7 ± 3) × 103 |
| t1/2, min | 37 ± 10 | 26.1 ± 2.9 |
| AUC0-t, ng/mL·min | (5.1 ± 0.6) × 103 | (1.3 ± 0.7) × 105 |
| Vz/F_obs, (mg)/(ng/mL) | (1.1 ± 0.4) × 10−2 | (0.40 ± 0.24) × 10−2 |
| Cl/F_obs, (mg)/(ng/mL)/min | (2.01 ± 0.19) × 10−4 | (0.10 ± 0.05) × 10−3 |
| Analyte and Precursor Ion (Q1 m/z) | Product Ion (Q3 m/z) | DP * (V) | CE (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA96 (252.2) | 102.1 (quantifier) | 21 | 23 | 4 |
| 133.2 (qualifier) | 21 | 21 | 4 | |
| 151.3 (qualifier) | 21 | 17 | 4 | |
| 2-Ad (152.3) | 93.1 (quantifier) | 16 | 35 | 14 |
| 107.2 (qualifier) | 21 | 37 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorina, D.S.; Lastovka, A.V.; Rogachev, A.D.; Podturkina, A.V.; Pavlova, A.V.; Ardashov, O.V.; Li-Zhulanov, N.S.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Pharmacokinetics and Dose Proportionality Study of a Novel Antiparkinsonian Agent, a 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-ylthio-conjugate of Prottremine. Molecules 2024, 29, 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184498
Gorina DS, Lastovka AV, Rogachev AD, Podturkina AV, Pavlova AV, Ardashov OV, Li-Zhulanov NS, Tolstikova TG, Volcho KP, Salakhutdinov NF. Pharmacokinetics and Dose Proportionality Study of a Novel Antiparkinsonian Agent, a 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-ylthio-conjugate of Prottremine. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184498
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorina, Daria S., Anastasiya V. Lastovka, Artem D. Rogachev, Alexandra V. Podturkina, Alla V. Pavlova, Oleg V. Ardashov, Nikolai S. Li-Zhulanov, Tatyana G. Tolstikova, Konstantin P. Volcho, and Nariman F. Salakhutdinov. 2024. "Pharmacokinetics and Dose Proportionality Study of a Novel Antiparkinsonian Agent, a 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-ylthio-conjugate of Prottremine" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184498
APA StyleGorina, D. S., Lastovka, A. V., Rogachev, A. D., Podturkina, A. V., Pavlova, A. V., Ardashov, O. V., Li-Zhulanov, N. S., Tolstikova, T. G., Volcho, K. P., & Salakhutdinov, N. F. (2024). Pharmacokinetics and Dose Proportionality Study of a Novel Antiparkinsonian Agent, a 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-ylthio-conjugate of Prottremine. Molecules, 29(18), 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184498








