Thermophysical Investigation of Multiform NiO Nanowalls@carbon Foam/1-Octadecanol Composite Phase Change Materials for Thermal Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Microstructure
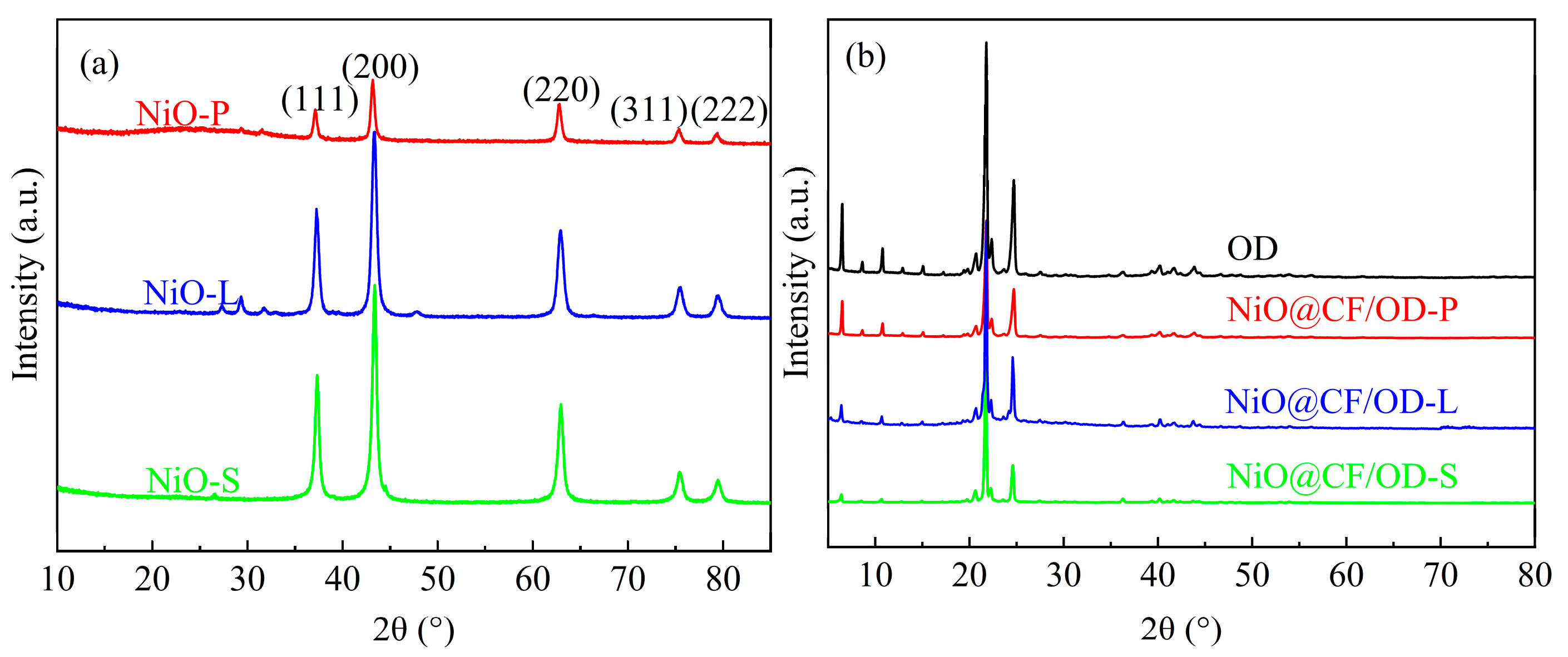
2.2. Component
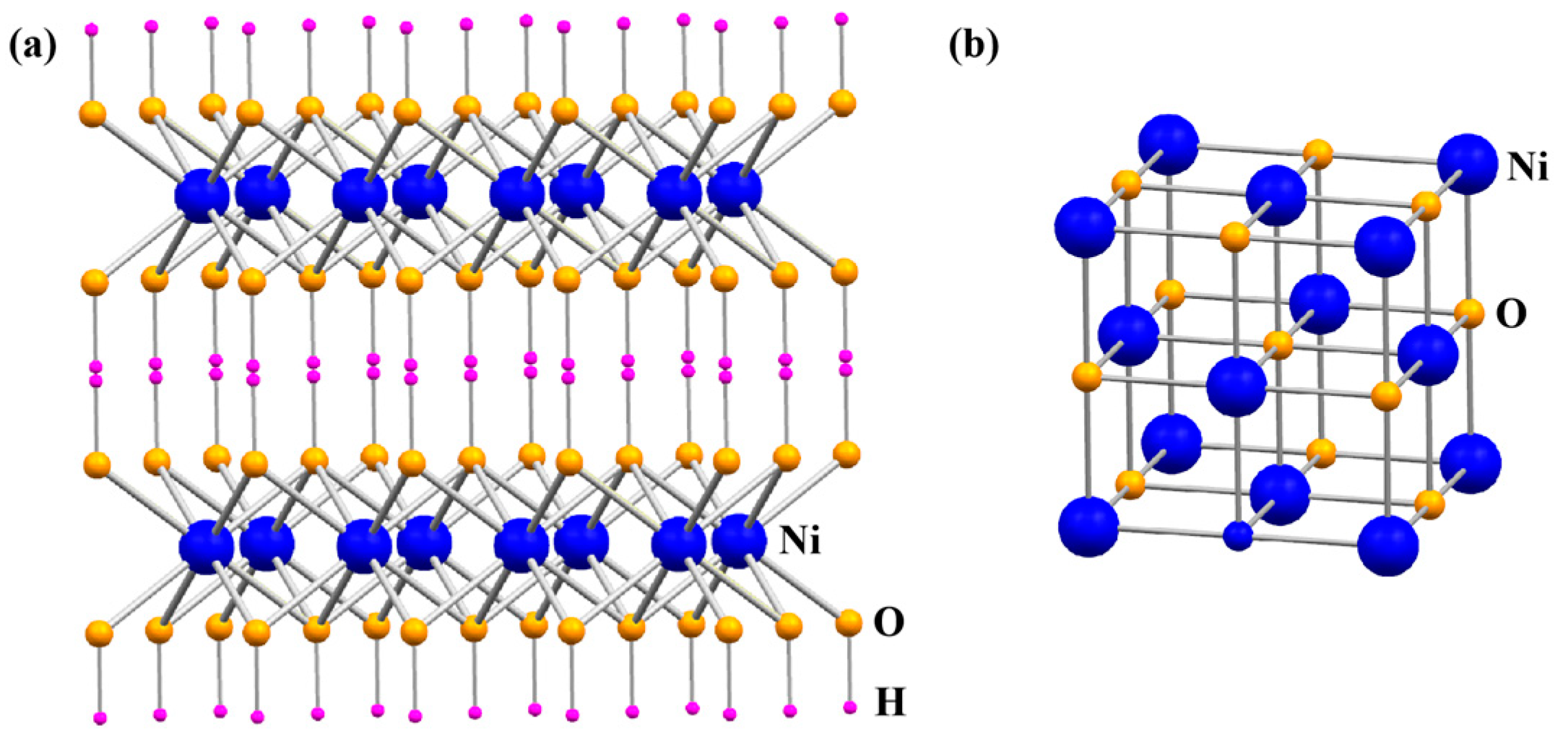
2.3. Mechanism Analysis of In Situ Generation of NiO Nanowalls
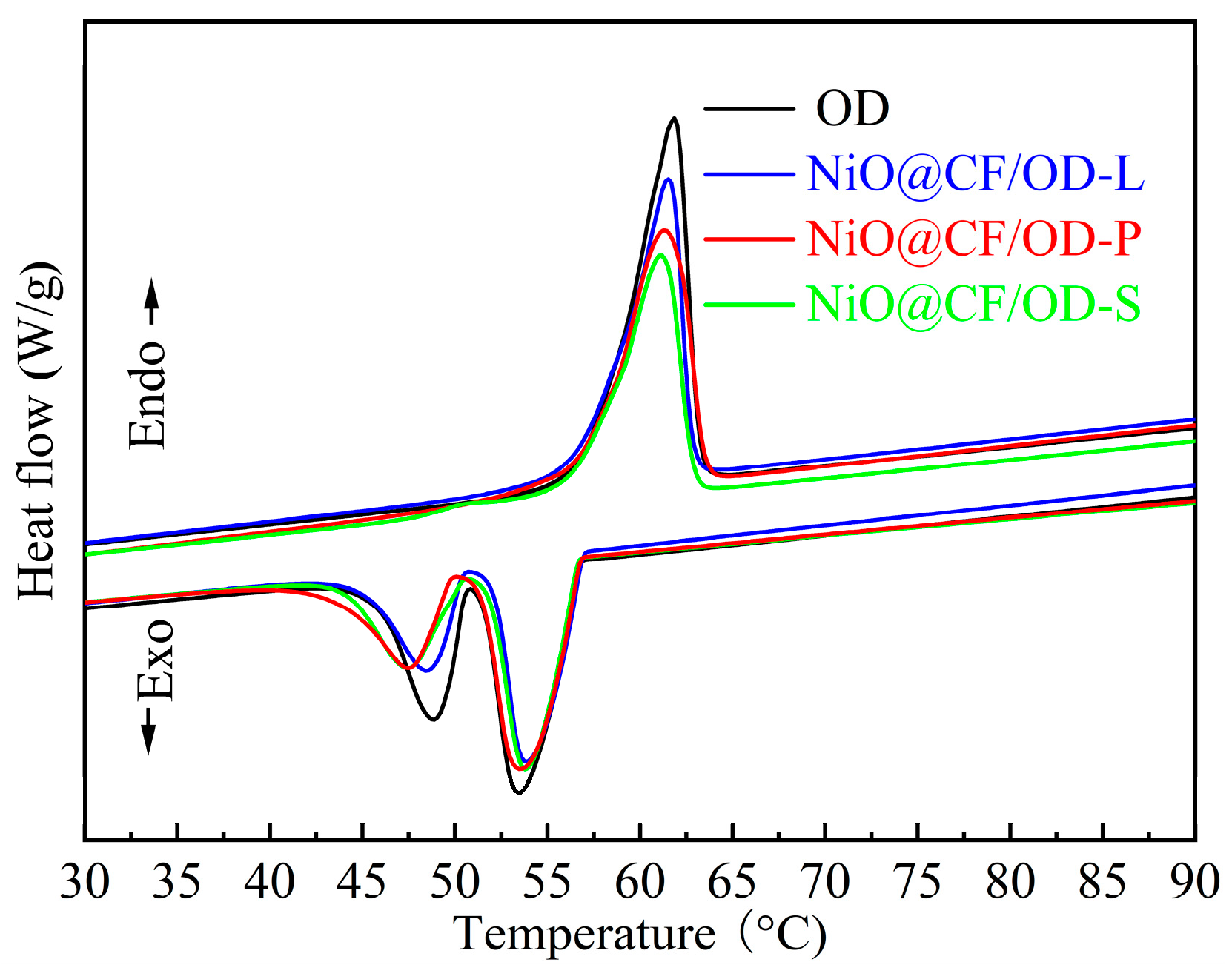
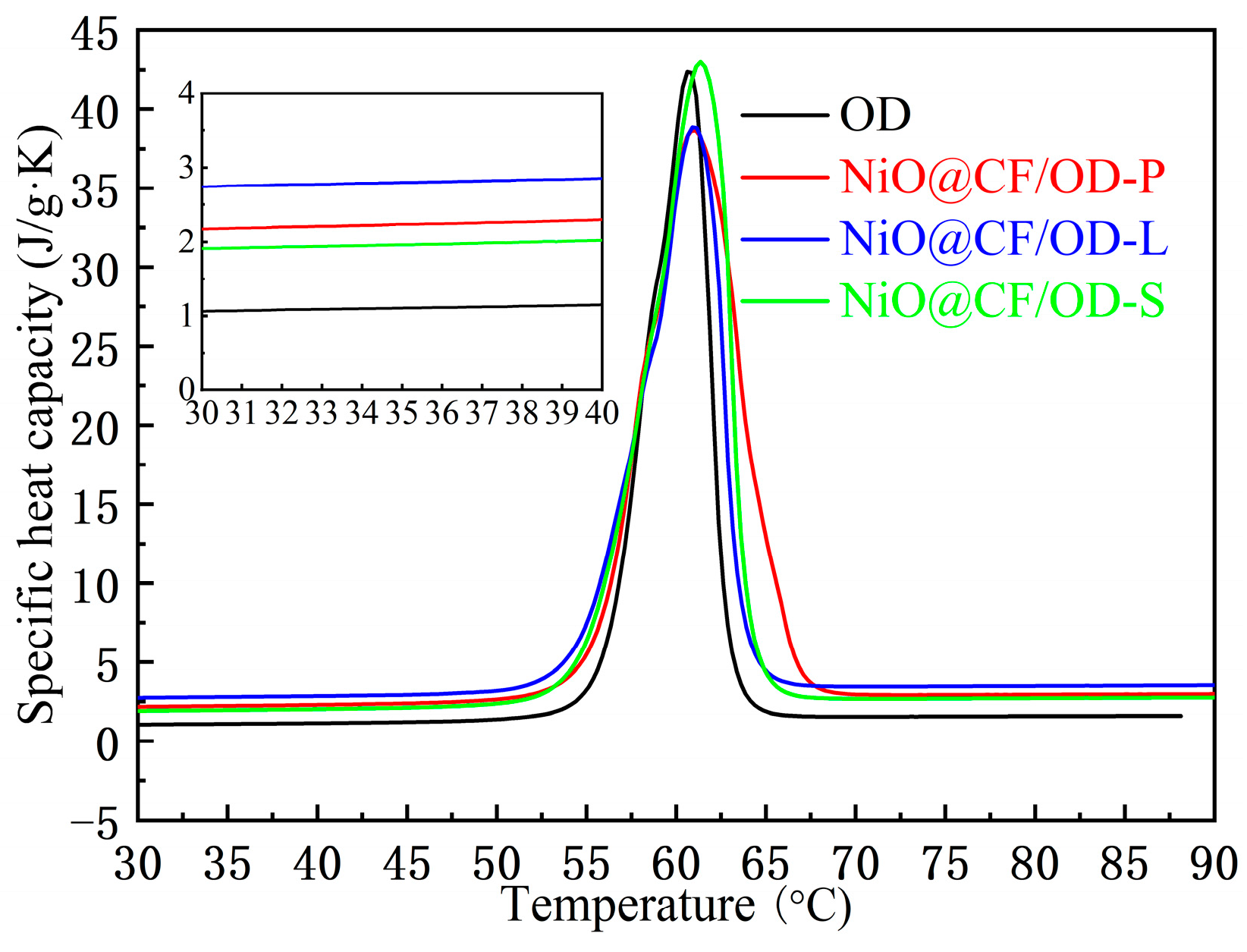
2.4. Thermal Storage Properties
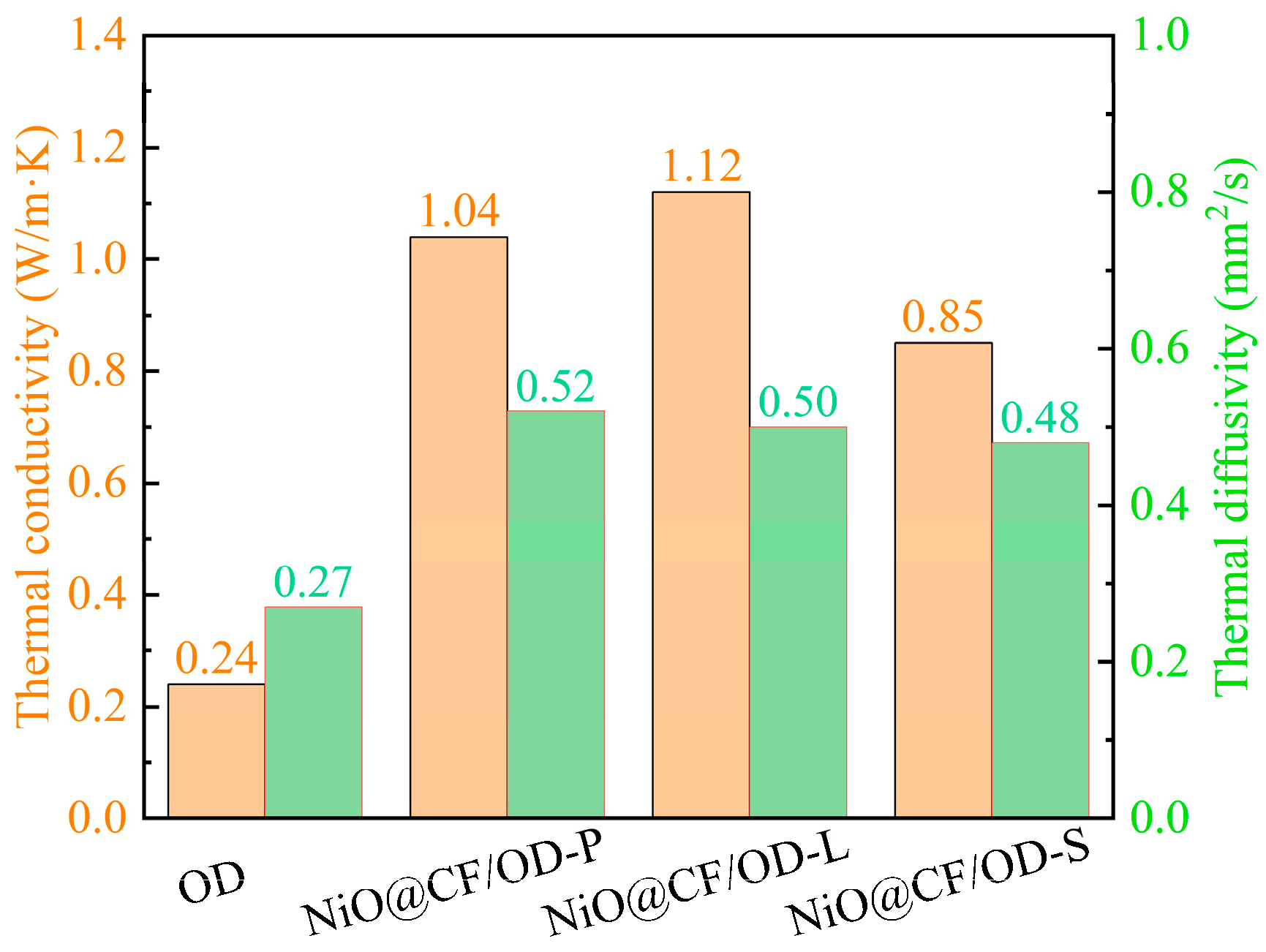
2.5. Heat-Conducting Properties
2.6. Thermal Reliability
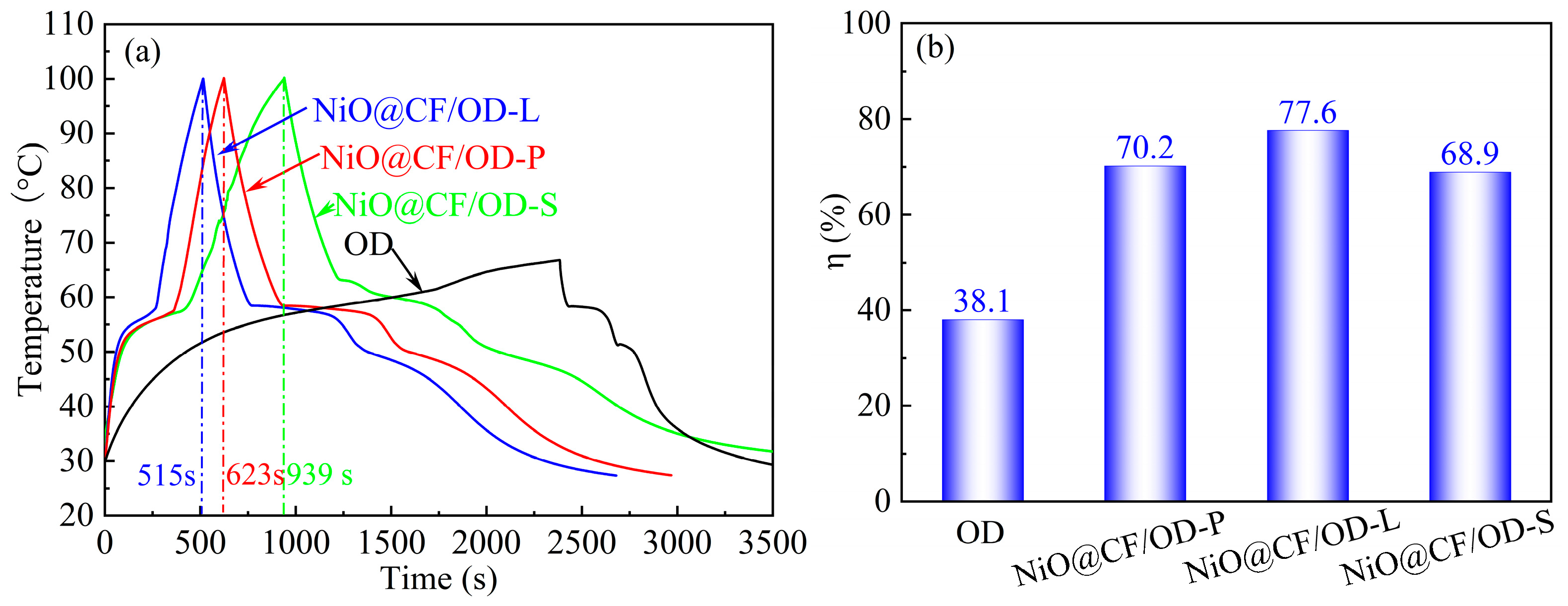
2.7. Photothermal Conversion
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
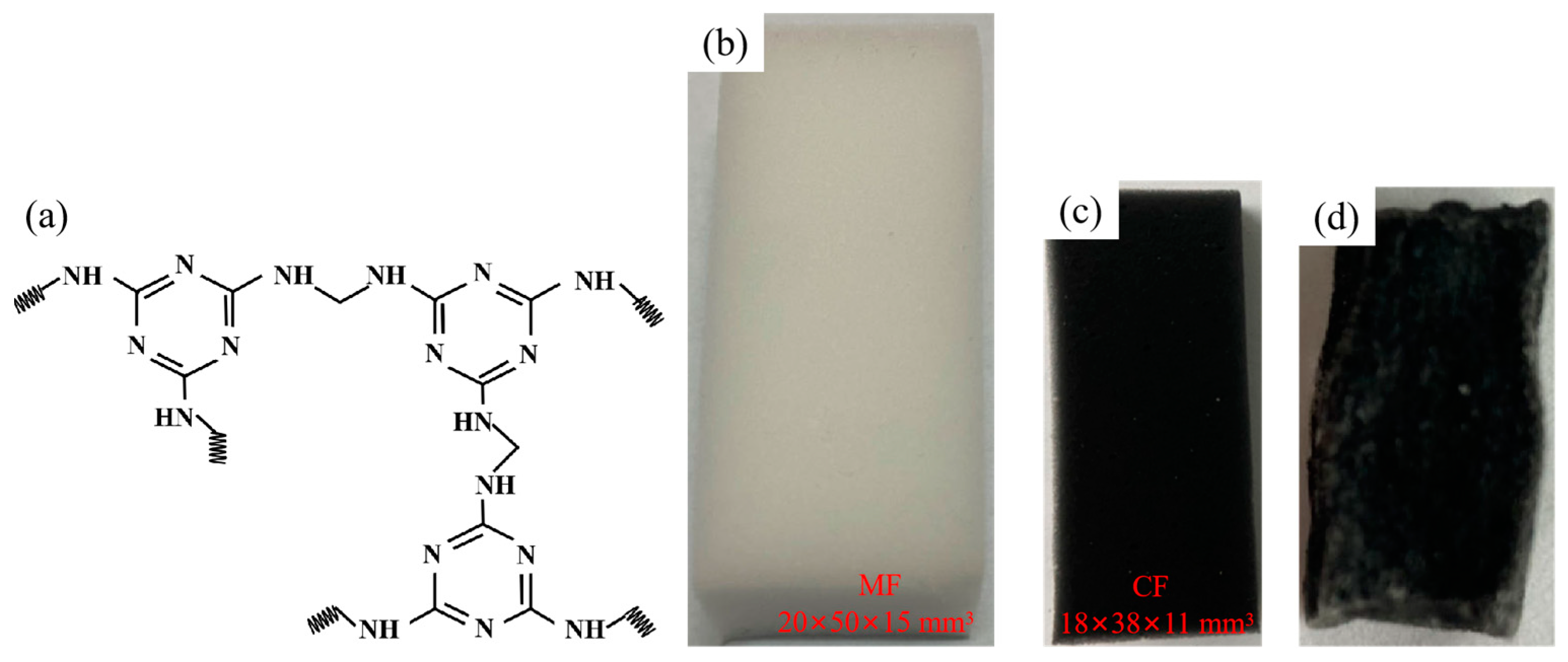
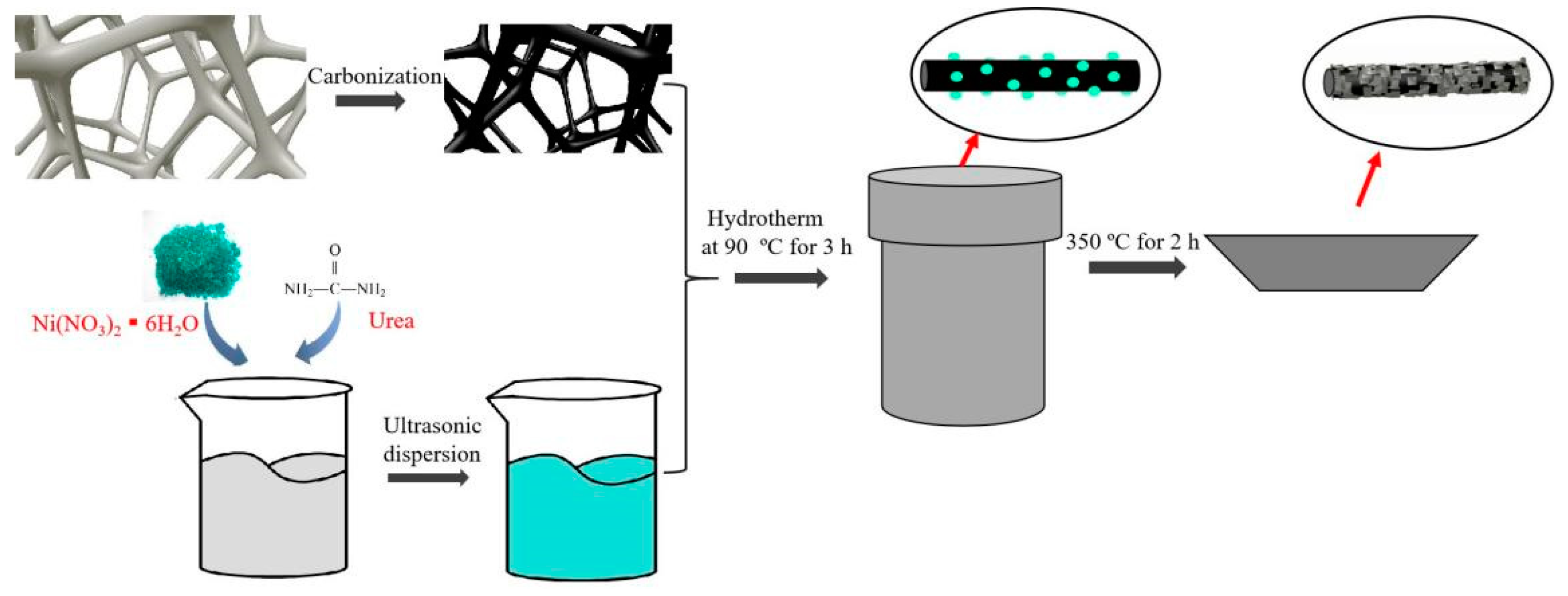
3.2. Preparation of Carbon Foam
3.3. Preparation of NiO@CF/OD CPCMs
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, J.; Singh, P. Review on phase change materials for spacecraft avionics thermal management. J. Energy Storage 2024, 87, 111369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, C.; Wu, D.; Zhong, K.; Kong, Z. Highly stable solid-solid phase change materials for battery thermal management systems. J. Energy Storage 2024, 88, 111495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curà, F.; Sesana, R.; Corsaro, L.; Dugand, M. An Active Thermography approach for materials characterisation of thermal management systems for Lithium-ion batteries. Heliyon 2024, 10, 28587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Li, C.; He, Y. Advanced electro-heat conversion properties of microcrystalline graphite-based composite phase change material with the three-dimensional framework. J. Energy Storage 2023, 59, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Ding, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, J. Shape-stable Bi-Sn-In alloy/Ag/copper foam composite phase change material for thermal storage and management. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, N.; Sobhan, C. Thermophysical characterization and melting heat transfer analysis of an organic phase change material dispersed with GNP-Ag hybrid nanoparticles. Heat Mass Transfer. 2022, 58, 1811–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadiran, T.; Hussein, M.; Zainal, Z.; Rafeadah, R. Encapsulation techniques for organic phase change materials as thermal energy storage medium: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 143, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiyeol, B.; Suho, K.; Kwangsoo, K.; Soyoung, B. Impregnation of Activated Carbon with Organic Phase-Change Material. Materials 2024, 17, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Latibari, S.; Sadrameli, S. Carbon based material included-shaped stabilized phase change materials for sunlight-driven energy conversion and storage: An extensive review. Sol. Energy 2018, 170, 1130–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, T.; Wang, B.; Fan, C.; Liu, C. Porous carbon network-based composite phase change materials with heat storage capacity and thermal management functions. Carbon 2024, 226, 119174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sharma, R.; Khalid, M.; Goyal, R.; Sari, A.; Tyagi, V. Evaluation of carbon based-supporting materials for developing form-stable organic phase change materials for thermal energy storage: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 246, 111896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Min, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, M. Graphene aerogel stabilized phase change material for thermal energy storage. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 40, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nagar, D.; Emam, M.; El-Betar, A.; Nada, S. Performance improvement of building-integrated photovoltaic panels using a composite phase change material-carbon foam heat sink: An experimental study. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Li, Z.; PAN, W. 3D network structural shape-stabilized composite PCMs for integrated enhancement of thermal conductivity and photothermal properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 240, 111645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljafari, B.; Kareri, T.; Kalidasan, B.; Bhutto, Y.; Pandey, A.; Alqaed, S. Organic/carbon and organic/carbon-metal composite phase change material for thermoelectric generator: Experimental evaluation. J. Energy Storage 2024, 78, 110082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B. Silica-based aerogels encapsulate organic/inorganic composite phase change materials for building thermal management. J. Energy Storage 2024, 97, 112858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Organic-inorganic hybrid phase change materials with high energy storage density based on porous shaped paraffin/hydrated salt/expanded graphite composites. Energy 2024, 304, 132169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amudhalapalli, G.; Devanuri, J. Synthesis, characterization, thermophysical properties, stability and applications of nanoparticle enhanced phase change materials—A comprehensive review. Therm. Sci. Eng. Progress. 2022, 28, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Ma, Z.; Ding, M.; Li, Y.; Dang, L.; Yang, K.; Li, F.; Xue, B. Preparation and characterization of expanded dickite/decanoic acid phase-change materials. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2024, 13, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B. Thermally-induced flexible composite phase change material with enhanced thermal conductivity. J. Power Sources 2024, 603, 234447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Miao, L.F.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.H. Hollow Ni/NiO@N-doped porous carbon for lithium ion battery anode based on dual-buffering strategy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 176080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Huo, X.T.; Guo, M.; Zhang, M. A review of NiO-based electrochromic-energy storage bifunctional material and integrated device. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Leng, S. Electrical conductivity and electrical stability of Bi/Mg modified NiO ceramics for NTC thermistors. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2023, 10, 2302712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, M.; Wei, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Core-shell NiO/C@NiFe-LDH nanocomposite as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 024501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, D.; Song, J.; Jiao, Z.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, B.; Chu, Y. A facile hydrothermal synthesis of graphene porous NiO nanocomposite and its application in electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Xu, R.; Williams, O.; Wang, Z.; Sievers, C. Reaction paths of methane activation and oxidation of surface intermediates over NiO on ceria-zirconia catalysts studied by in-situ FTIR spectroscopy. J. Catal. 2021, 404, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, H.; Tam, L.; Nguyen, G. Methylated mesoporous silica loaded with 1-octadecanol as a new shape-stabilized phase change material for enhanced thermal energy storage efficiency. Can. J. Chem. 2023, 101, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X. Preparation and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)-g-octadecanol copolymers based solid–solid phase change materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 131, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wen, G. NiO@C and Ni@C nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties. Nano 2020, 15, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Kishore, R.A.; Kolari, P.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Kaur, S.; Vidal, J.; Jackson, R. Model-driven development of durable and scalable thermal energy storage materials for buildings. Energy 2023, 265, 126339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.D.; Feng, Q.G.; Ni, W.L.; Li, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wu, Q.H.; Huang, Z.Y. Stable and reliable PEG/TiO2 phase change composite with enhanced thermal conductivity based on a facile sol-gel method without deionized water. J. Energy Storage 2024, 89, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.Q.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Cheng, X.M. Composite phase change materials with carbon-mesh/CuS/ZnO interface biocarbon skeleton for solar energy storage, solar photocatalysis and electromagnetic shielding. J. Energy Storage 2024, 90, 111937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafoji, P.; Mariappan, V.; Anish, R.; Karthikeyan, K.; Kalidoss, P. Characterization and thermal properties of Lauryl alcohol- Capric acid with CuO and TiO2 nanoparticles as phase change material for cold storage system. Mater. Lett. 2022, 316, 132052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Shi, J. Synthesis and properties of phase change microcapsule with SiO2-TiO2 hybrid shell. Sol. Energy 2018, 167, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cheng, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Zou, G.Y.; Li, G.; Huang, Y. Effect of MOF derived hierarchical Co3O4/expanded graphite on thermal performance of stearic acid phase change material. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Fang, G. Synthesis and thermal properties of 1-octadecanol/nano-TiO2/carbon nanofiber composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 272, 125041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Mou, F.; Yu, G. In-situ calcination of NiO nanowalls@ carbon foam with hybrid 2D/3D framework to reinforce 1-octadecanol phase change materials. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
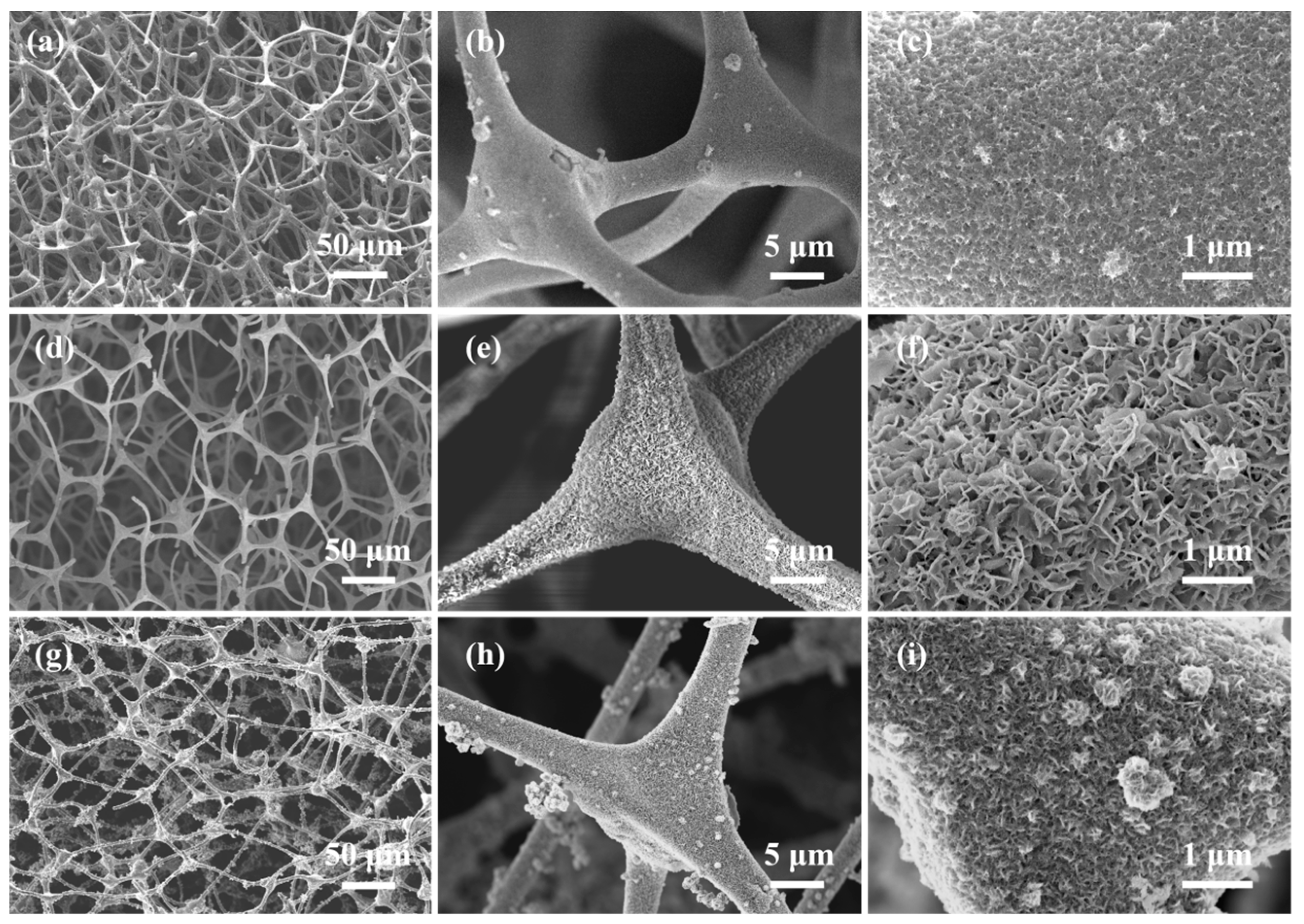
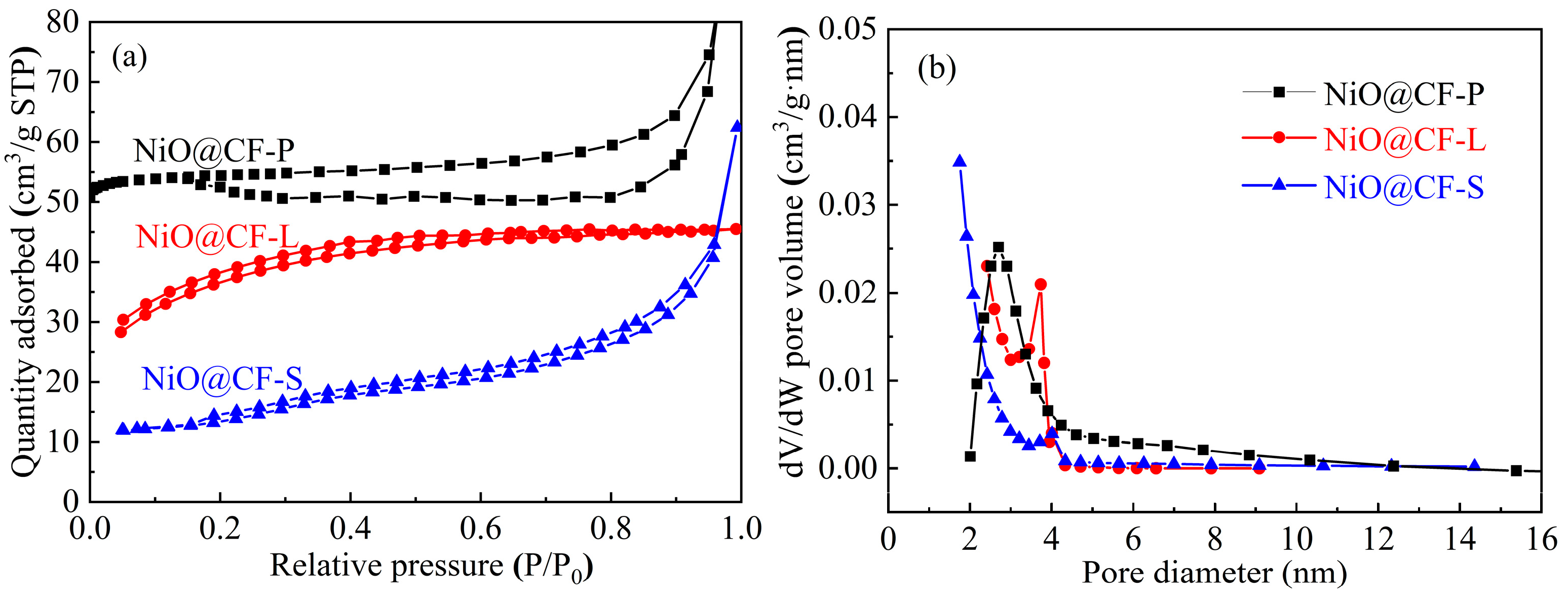



| Samples | Specific Surface Area m2/g | Pore Volume cm3/g | Average Pore Size nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiO@CF-P | 176.2 | 0.09 | 5.69 |
| NiO@CF-L | 101.9 | 0.07 | 2.86 |
| NiO@CF-S | 80.5 | 0.05 | 2.41 |
| Samples | Melting | Solidifying | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Ts (°C) | ΔHs (J/g) | |
| OD | 57.7 | 242.2 | 56.7 | 210.1 |
| NiO@CF/OD-P | 57.9 | 218.9 | 56.5 | 189.0 |
| NiO@CF/OD-L | 57.5 | 220.7 | 57.6 | 185.3 |
| NiO@CF/OD-S | 56.9 | 180.2 | 57.1 | 160.3 |
| Filler | Methods | Matrix | Tm °C | Thermal Enthalpy (J/g) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m K) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesoporous MgO | Evaporative pyrolysis | PEG1000 | 31.5 | 100.7 | -- | [30] |
| TiO2 | Sol–gel | PEG | 55 | 123.3 | 0.39 | [31] |
| CuS/ZnO | Calcination | PA | 75.2 | 155 | 0.45 | [32] |
| CuO | Direct addition | Lauryl alcohol-Capric acid | 8.7 | 159.1 | 0.17 | [33] |
| SiO2/TiO2 | Sol–gel | Paraffin | 29.0 | 93.7 | 0.2 | [34] |
| Hollow porous Co3O4-EG | In-suit | Steric acid | 69.4 | 192.8 | 1.26 | [35] |
| Nano TiO2/carbon nanofiber | Direct addition | OD | 57.6 | 209.3 | 0.43 | [36] |
| NiO@CF | Calcination | OD | 56.5 | 208.3 | 1.12 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Xiong, W.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Q. Thermophysical Investigation of Multiform NiO Nanowalls@carbon Foam/1-Octadecanol Composite Phase Change Materials for Thermal Management. Molecules 2024, 29, 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184453
Wang X, Wang Q, Cheng X, Xiong W, Chen X, Cheng Q. Thermophysical Investigation of Multiform NiO Nanowalls@carbon Foam/1-Octadecanol Composite Phase Change Materials for Thermal Management. Molecules. 2024; 29(18):4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184453
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiuli, Qingmeng Wang, Xiaomin Cheng, Wen Xiong, Xiaolan Chen, and Qianju Cheng. 2024. "Thermophysical Investigation of Multiform NiO Nanowalls@carbon Foam/1-Octadecanol Composite Phase Change Materials for Thermal Management" Molecules 29, no. 18: 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184453
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, Q., Cheng, X., Xiong, W., Chen, X., & Cheng, Q. (2024). Thermophysical Investigation of Multiform NiO Nanowalls@carbon Foam/1-Octadecanol Composite Phase Change Materials for Thermal Management. Molecules, 29(18), 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184453







