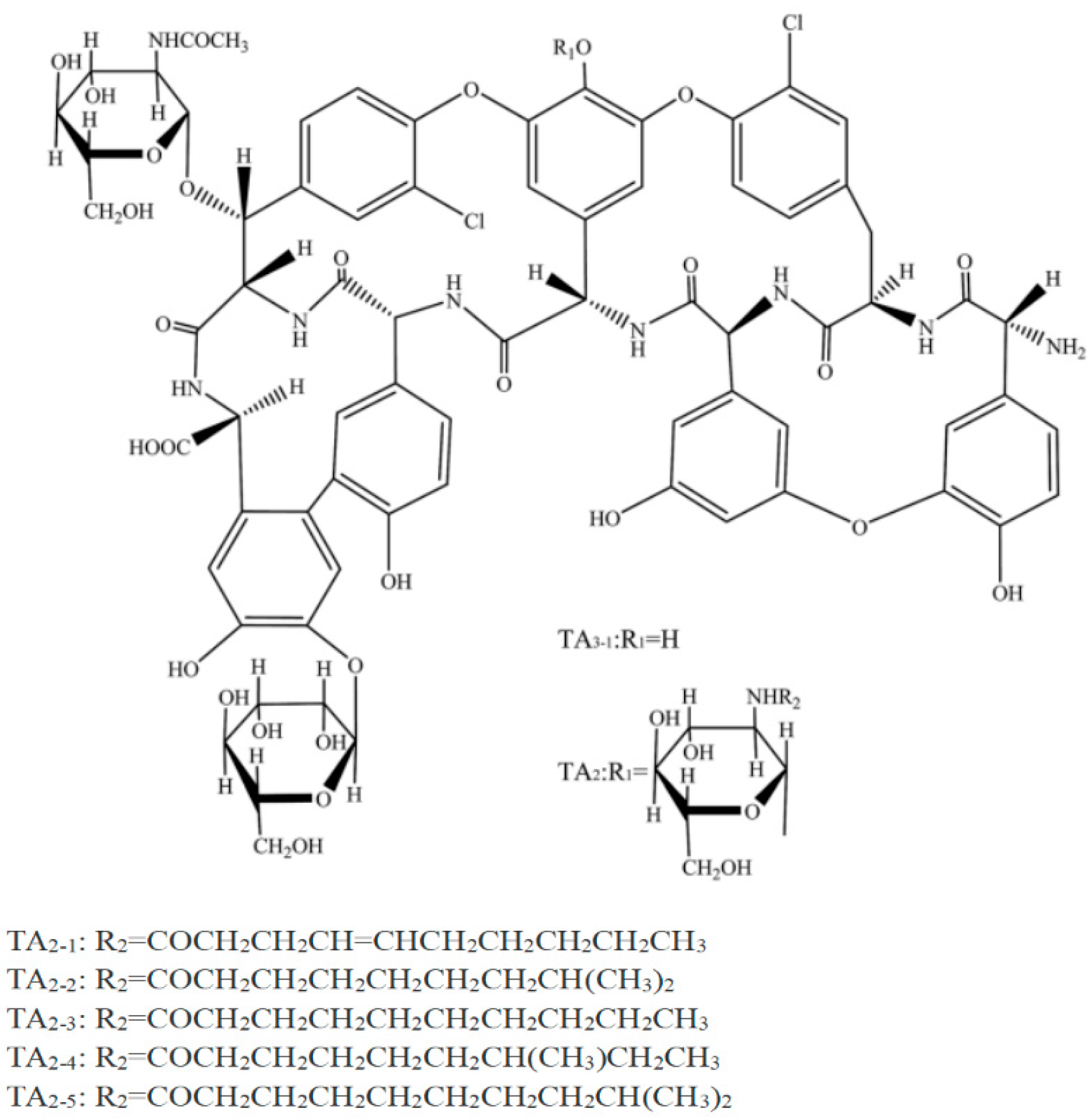
A Highly Efficient Fluorescent Turn-Off Nanosensor for Quantitative Detection of Teicoplanin Antibiotic from Humans, Food, and Water Based on the Electron Transfer between Imprinted Quantum Dots and the Five-Membered Cyclic Boronate Esters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
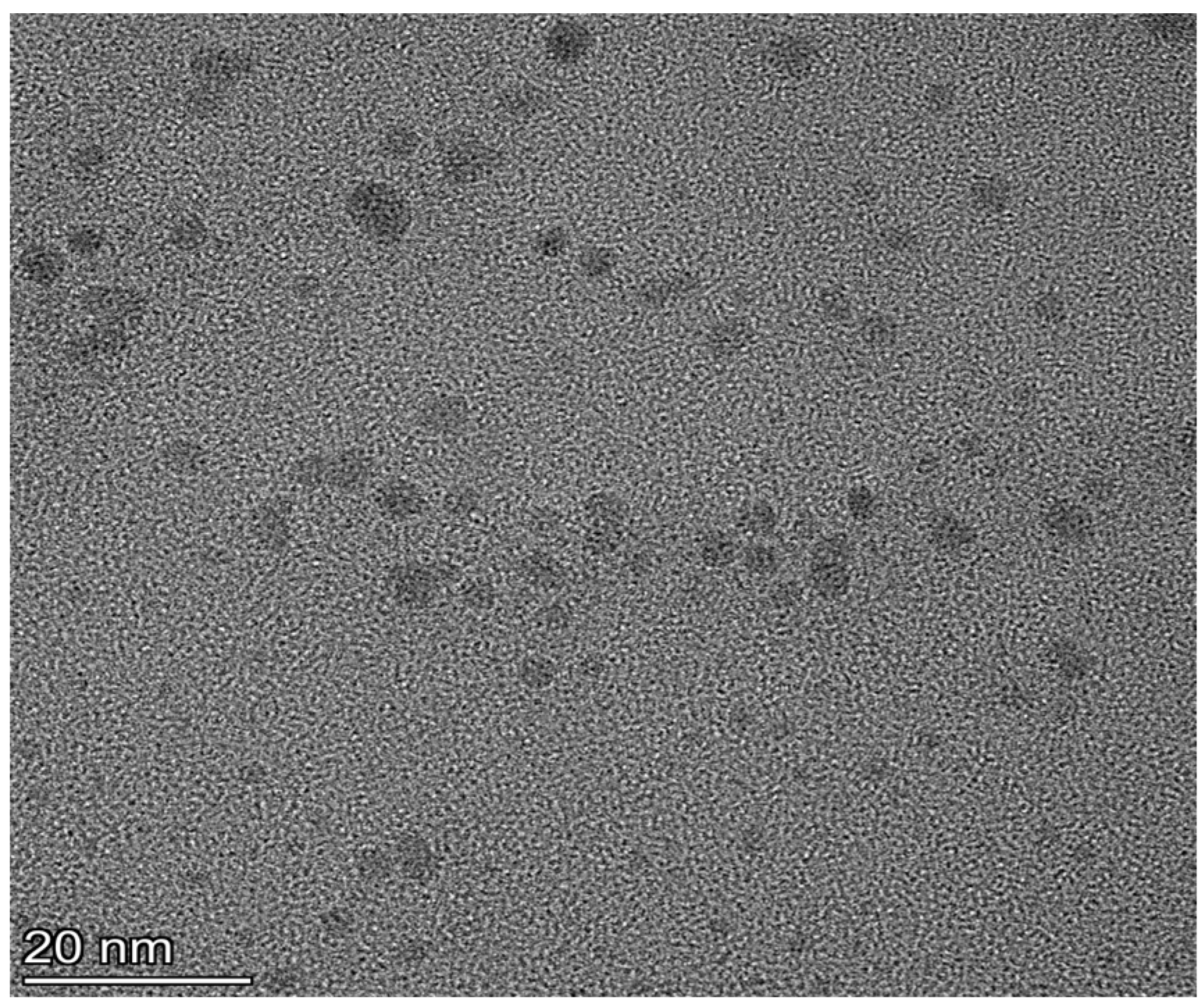
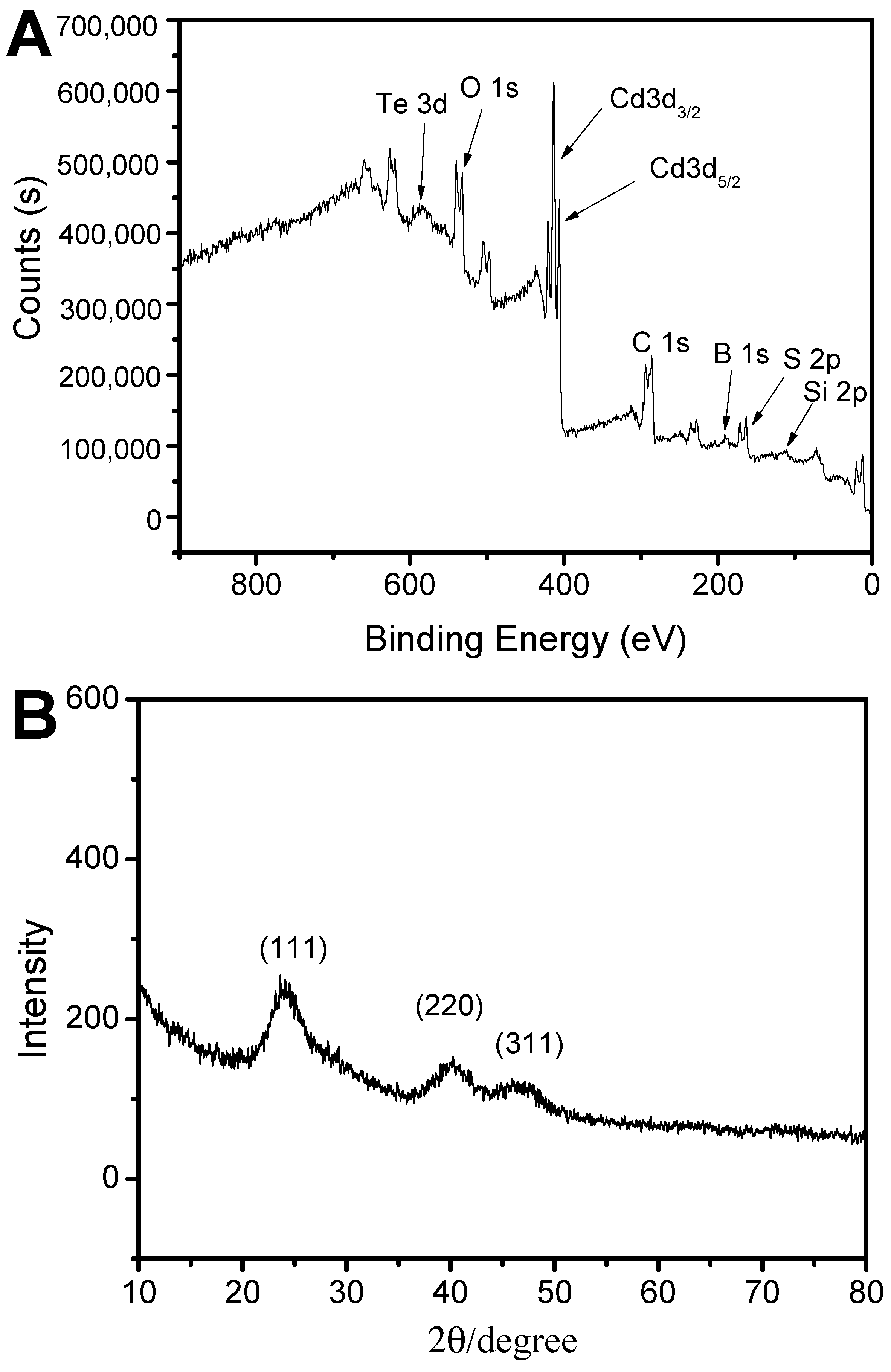
2.1. Characterization of QDs@APBA and QDs@APBA@MIPs
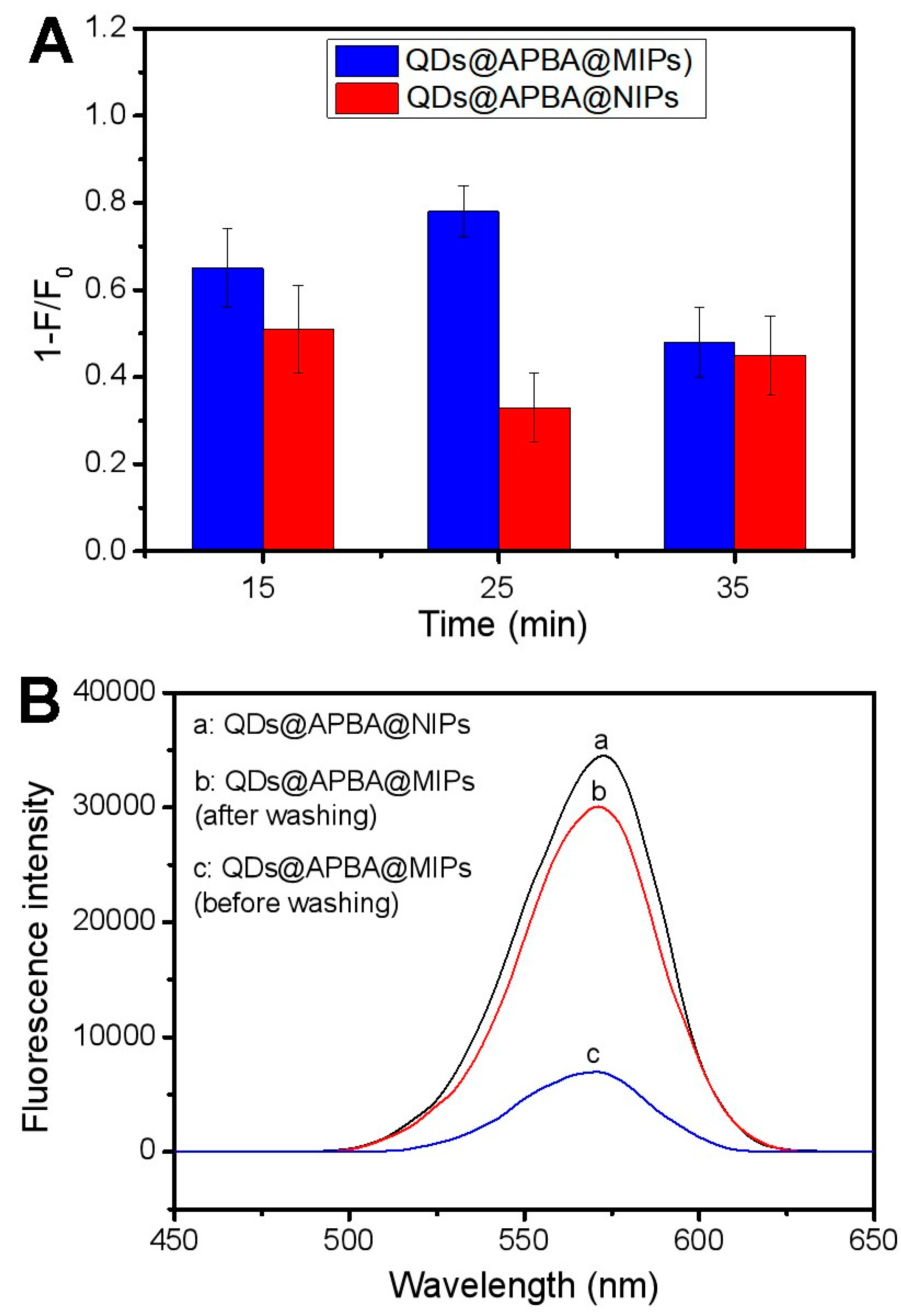
2.2. Optimization of the Polymerization Time
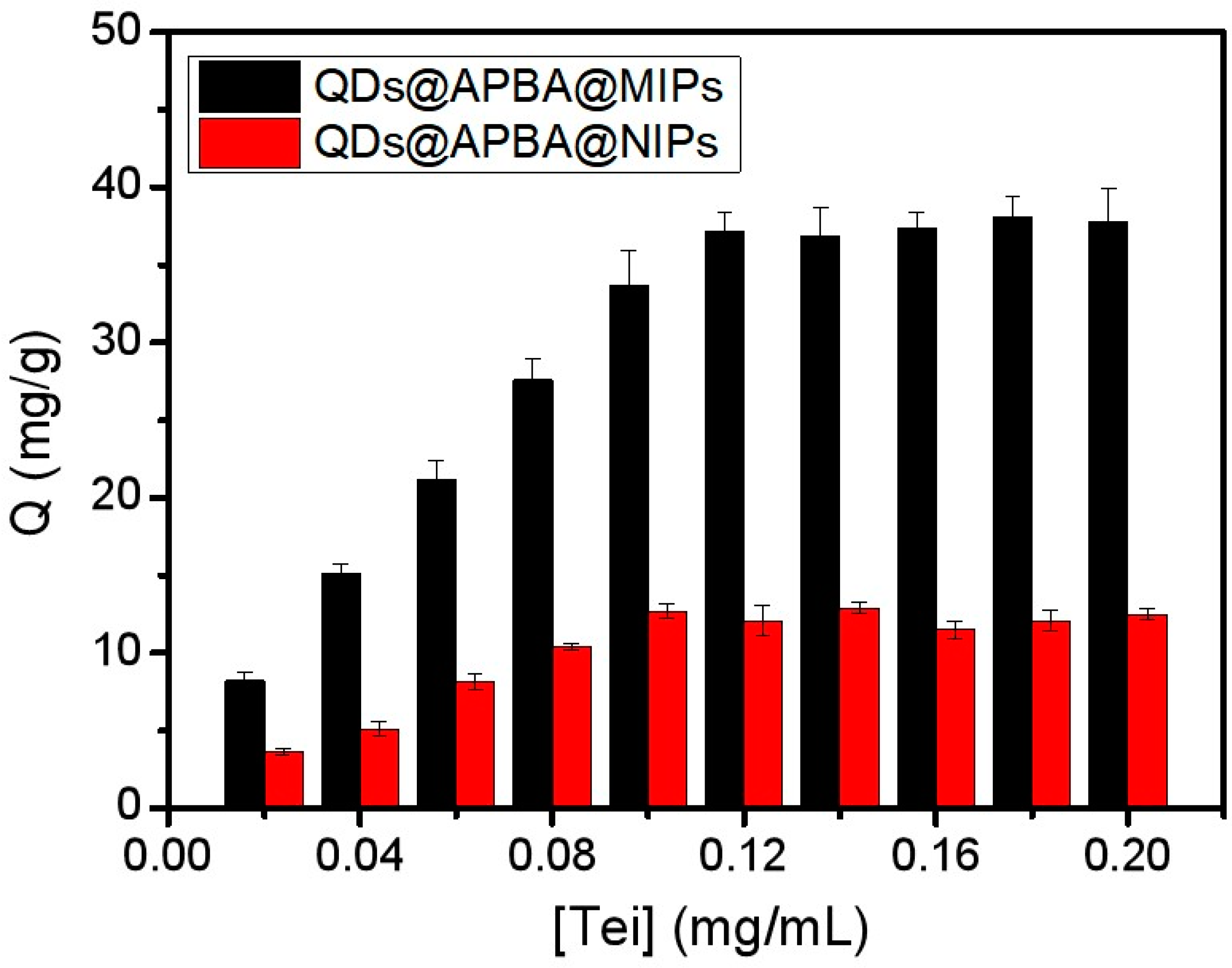
2.3. Static Adsorption Test
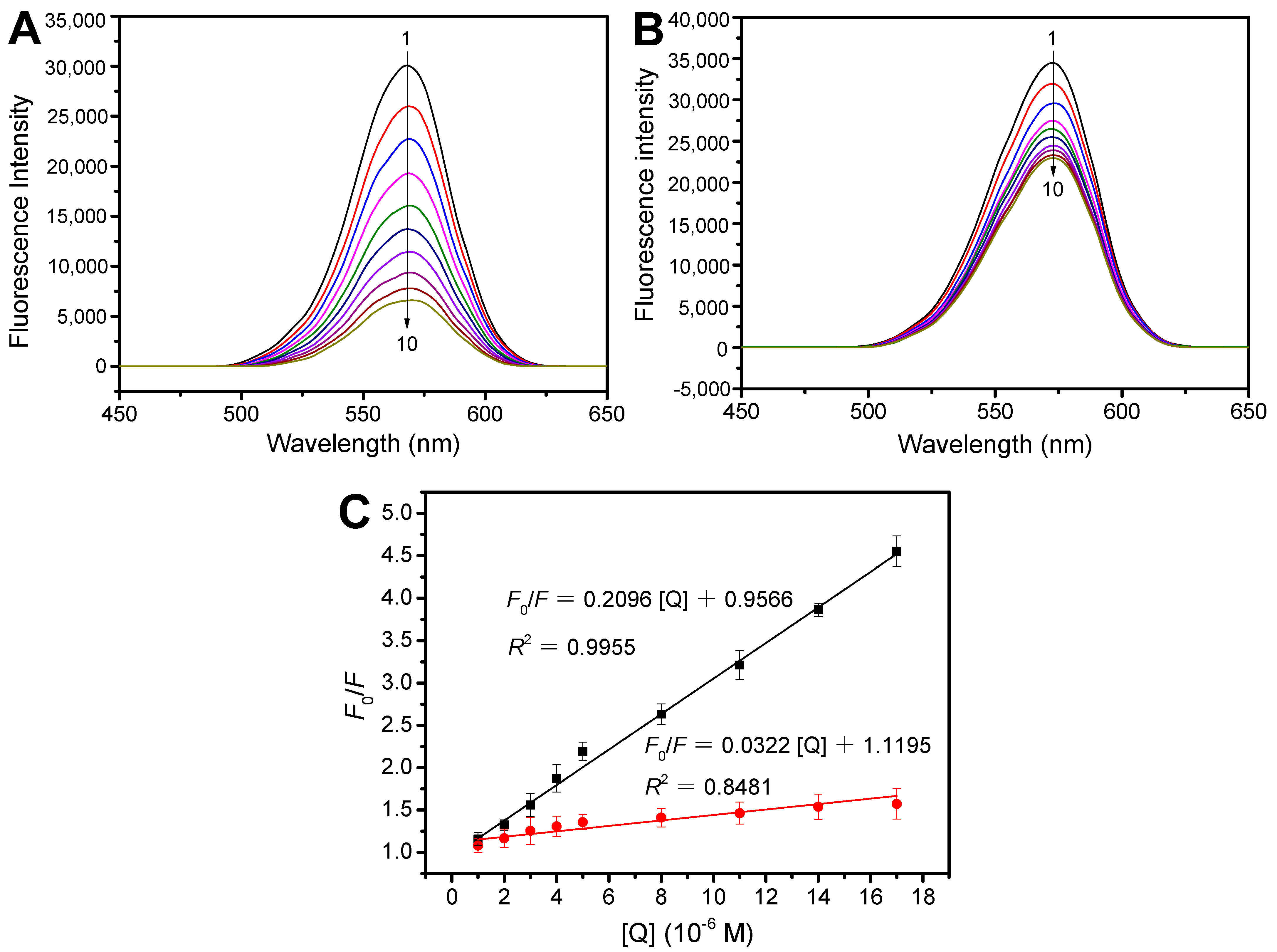
2.4. Fluorescence Quenching of QDs@APBA@MIPs by Tei
2.5. The Operative Mechanism of Static Fluorescence Quenching
2.6. Effect of Binding pH on the Imprinting Effect
2.7. Binding Specificity of QDs@APBA@MIPs
2.8. Reproducibility and Chemical Stability
2.9. Determination of Tei in Real Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Preparation of APBA-Functionalized CdTe QDs (QDs@APBA)
3.4. Preparation of QDs@APBA@MIPs
3.5. Adsorption Performance Test of QDs@APBA@MIPs
3.6. Specificity of the QDs@APBA@MIPs for Tei
3.7. Application to Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Zheng, X.-J.; Tian, J.; Hu, S.; Bai, X.-H.; Chen, X. Determination of teicoplanin in human plasma by reverse micelle mediated dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1643, 462058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, N. Sir Alexander Fleming. J. Med. Biogr. 2007, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Tatsumura, Y. Alexander Fleming (1881–1955): Discoverer of penicillin. Singap. Med. J. 2015, 56, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolhouse, M.E.J.; Ward, M.J. Sources of antimicrobial resistance. Science 2013, 341, 1460–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.W.; Dolfing, J.; Ehlert, P.A.I.; Graham, D.W. Evidence of increasing antibiotic resistance gene abundances in archived soils since 1940. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, E.; Marinelli, F.; Marcone, G.L. Old and New Glycopeptide Antibiotics: Action and Resistance. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 572–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhong, M.; Wei, Y. Direct fluorescence polarization assay for the detection of glycopeptide antibiotics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7044–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, S.J.; White, L.O.; Keevil, B. Assay of teicoplanin in serum: Comparison of high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence polarization immunoassay. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hanada, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Okamori, Y.; Kimura, T.; Ogata, H. Improved quantitative determination of total and unbound concentrations of six teicoplanin components in human plasma by high performance liquid chromatography. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, N.; Ohno, K.; Shimamura, T.; Furukawa, H.; Todo, S.; Kishino, S. Quantitative determination of individual teicoplanin components in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 847, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.-L.; Sun, H.-Y.; Chen, G.-Y.; Lin, S.-W.; Kuo, C.-H. Simultaneous quantification of antimicrobial agents for multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in human plasma by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 116, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-Y.; Cho, S.-H.; Song, Y.-H.; Nam, M.-S.; Kim, C.-W. Direct injection LC–MS/MS method for the determination of teicoplanin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1008, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltombe, O.; Mertens, T.; Eloot, S.; Verstraete, A.G. Development and validation of an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography—High resolution mass spectrometry method for the quantification of total and free teicoplanin in human plasma. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 65, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Hu, G.; Wang, Q.; Peng, R.; Tan, L.; Yang, Z. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of five glycopeptide antibiotics in food and biological samples using solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1538, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live Cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Boronate affinity materials for separation and molecular recognition: Structure, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8097–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tsai, W.-B.; Garrison, M.D.; Ferrari, S.; Ratner, B.D. Template-imprinted nanostructured surfaces for protein recognition. Nature 1999, 398, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantada-Vázquez, M.P.; Sánchez-González, J.; Peña-Vázquez, E.; Tabernero, M.J.; Bermejo, A.M.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel molecularly imprinted polymer—Coated Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for specific fluorescent recognition of cocaine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Kazemifard, N.; Rezaei, B. Development of a selective prilocaine optical sensor based on molecularly imprinted shell on CdTe quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Wang, D.-N.; Yin, Y.-M.; Wang, L.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Xie, M.-X. Quantum dots capped with dummy molecularly imprinted film as luminescent sensor for the determination of tetrabromobisphenol A in water and soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10472–10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Tao, Y.; Shen, X.; Jin, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Luo, D.; Mei, S.; Lee, Y.-I. Highly sensitive and selective fluorescent sensor for tetrabromobisphenol-A in electronic waste samples using molecularly imprinted polymer coated quantum dots. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. SPR nanosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer film with gold nanoparticles for sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Talanta 2020, 219, 121219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Y.; Tian, X.; Liang, Y.; He, X.; Gao, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Multi-stimuli responsive molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with tailorable affinity for modulated specific recognition of human serum albumin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6634–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. A self-assembled polydopamine film on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for specific capture of protein. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Recent progress and application of boronate affinity materials in bioanalysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 140, 116271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ye, J.; Bie, Z.; Liu, Z. Affinity-tunable specific recognition of glycoproteins via boronate affinity-based controllable oriented surface imprinting. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. Pattern Recognition of Cells via Multiplexed Imaging with Monosaccharide-Imprinted Quantum Dots. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5646–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bie, Z.; Wang, F.; Guo, E. Efficient synthesis of riboflavin-imprinted magnetic nanoparticles by boronate affinity-based surface imprinting for the selective recognition of riboflavin. Analyst 2018, 143, 4936–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tu, T.; Yang, M.; Xu, C. Efficient preparation of surface imprinted magnetic nanoparticles using poly (2-anilinoethanol) as imprinting coating for the selective recognition of glycoprotein. Talanta 2018, 184, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, B. The preparation of a boronate affinity-based controlled oriented imprinting coating on a silica nanoparticle surface for the separation and purification of shikimic acid in herbal medicine. Anal. Methods Adv. Methods Appl. 2024, 16, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, N.; Tian, X. Synthesis of Boronate Affinity-Based Oriented Dummy Template-Imprinted Magnetic Nanomaterials for Rapid and Efficient Solid-Phase Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Food. Molecules 2024, 29, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, X.; Su, J.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. A strategy of utilizing Cu2+-mediating interaction to prepare magnetic imprinted polymers for the selective detection of celastrol in traditional Chinese medicines. Talanta 2021, 231, 122339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, Z.; Xing, R.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Precision Imprinting of Glycopeptides for Facile Preparation of Glycan-Specific Artificial Antibodies. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9845–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Pang, J.; Xu, S.; He, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. A Glycoform-Resolved Dual-Modal Ratiometric Immunoassay Improves the Diagnostic Precision for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Ye, Q.; Chi, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Fan, B.; Li, B.; Qin, C.; et al. Rational Development of Hypervalent Glycan Shield-Binding Nanoparticles with Broad-Spectrum Inhibition against Fatal Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2202689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Mercaptophenylboronic acid-capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive fluorescence detection of glycoproteins. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Wang, S.; Bie, Z.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable–oriented surface imprinting. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 964–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Jalili, R.; Manzoori, J.L. A sensitive fluorescent nanosensor for chloramphenicol based on molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Lumin. J. Biol. Chem. Lumin. 2016, 31, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Q. Boronate affinity-based surface-imprinted quantum dots as novel fluorescent nanosensors for the rapid and efficient detection of rutin. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3212–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiao, H.-F.; Shi, X.-Z.; Sun, A.; Wang, X.; Chai, J.; Li, D.-X.; Chen, J. Development and application of a novel fluorescent nanosensor based on FeSe quantum dots embedded silica molecularly imprinted polymer for the rapid optosensing of cyfluthrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Kang, Q.; Shen, D.; Chen, L. Quantum dots based imprinting fluorescent nanosensor for the selective and sensitive detection of phycocyanin: A general imprinting strategy toward proteins. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad-Samarin, M.; Faridbod, F.; Dezfuli, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R. A novel metronidazole fluorescent nanosensor based on graphene quantum dots embedded silica molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, D.; Cingolani, M.; Rampazzo, E.; Prodi, L.; Zaccheroni, N. Static quenching upon adduct formation: A treatment without shortcuts and approximations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8414–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Huo, J.-Z.; Zhao, X.-J. Facile synthesis of red emitting 3-aminophenylboronic acid functionalized copper nanoclusters for rapid, selective and highly sensitive detection of glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, H.; Qian, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, A. A fluorometric biosensor based on functional Au/Ag nanoclusters for real-time monitoring of tyrosinase activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Žídek, K.; Abdellah, M.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Zheng, K.; Pullerits, T. Surface plasmon inhibited photo-luminescence activation in CdSe/ZnS core–shell quantum dots. J. Phys. Condens. Matter Inst. Phys. J. 2016, 28, 254001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Dou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. A simple and economical one-pot method to synthesize high-quality water soluble CdTe QDs. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14573–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | Added Quantity (µM) | Detected Quantity a (µM) | Recoveries (%, n = 3) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine | 0 | 0 | ---- | ---- |
| 3.00 | 2.86 | 95.33 | 5.12 | |
| 6.00 | 6.25 | 104.17 | 3.64 | |
| 9.00 | 8.72 | 96.89 | 4.21 | |
| Milk | 0 | 0 | ---- | ---- |
| 3.00 | 2.92 | 97.33 | 3.98 | |
| 6.00 | 5.51 | 91.83 | 4.89 | |
| 9.00 | 8.56 | 95.11 | 4.12 | |
| Water | 0 | 0 | ---- | ---- |
| 3.00 | 3.20 | 106.67 | 2.87 | |
| 6.00 | 5.89 | 98.17 | 3.46 | |
| 9.00 | 8.48 | 94.22 | 3.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Tian, X. A Highly Efficient Fluorescent Turn-Off Nanosensor for Quantitative Detection of Teicoplanin Antibiotic from Humans, Food, and Water Based on the Electron Transfer between Imprinted Quantum Dots and the Five-Membered Cyclic Boronate Esters. Molecules 2024, 29, 4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174115
Zhang Y, Li D, Tian X. A Highly Efficient Fluorescent Turn-Off Nanosensor for Quantitative Detection of Teicoplanin Antibiotic from Humans, Food, and Water Based on the Electron Transfer between Imprinted Quantum Dots and the Five-Membered Cyclic Boronate Esters. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174115
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yansong, Daojin Li, and Xiping Tian. 2024. "A Highly Efficient Fluorescent Turn-Off Nanosensor for Quantitative Detection of Teicoplanin Antibiotic from Humans, Food, and Water Based on the Electron Transfer between Imprinted Quantum Dots and the Five-Membered Cyclic Boronate Esters" Molecules 29, no. 17: 4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174115
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, D., & Tian, X. (2024). A Highly Efficient Fluorescent Turn-Off Nanosensor for Quantitative Detection of Teicoplanin Antibiotic from Humans, Food, and Water Based on the Electron Transfer between Imprinted Quantum Dots and the Five-Membered Cyclic Boronate Esters. Molecules, 29(17), 4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174115






