Cascade Hydroxyl Radical-Generating and Ferroptosis-Inducing Nanofiber System for the Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
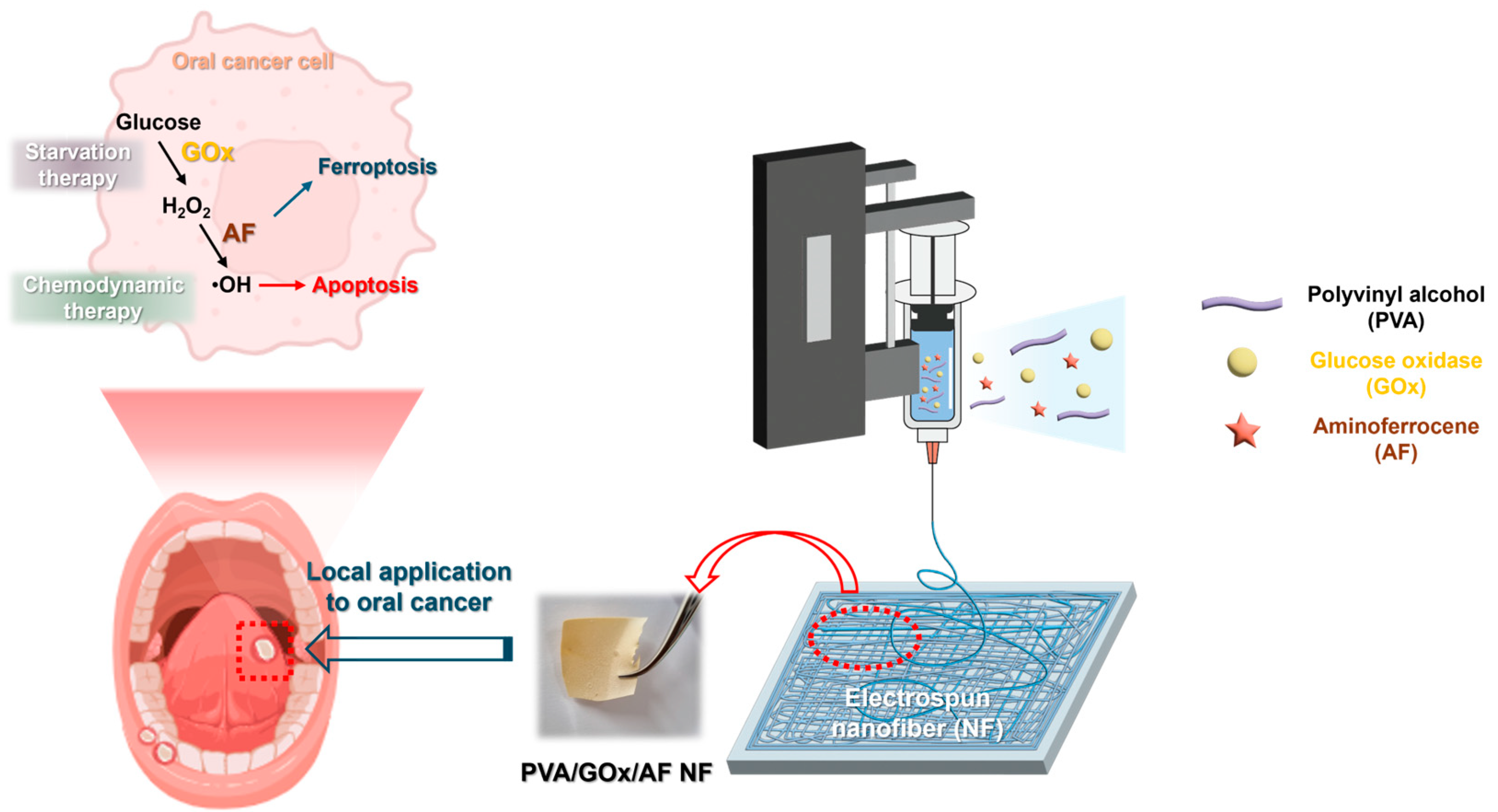
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
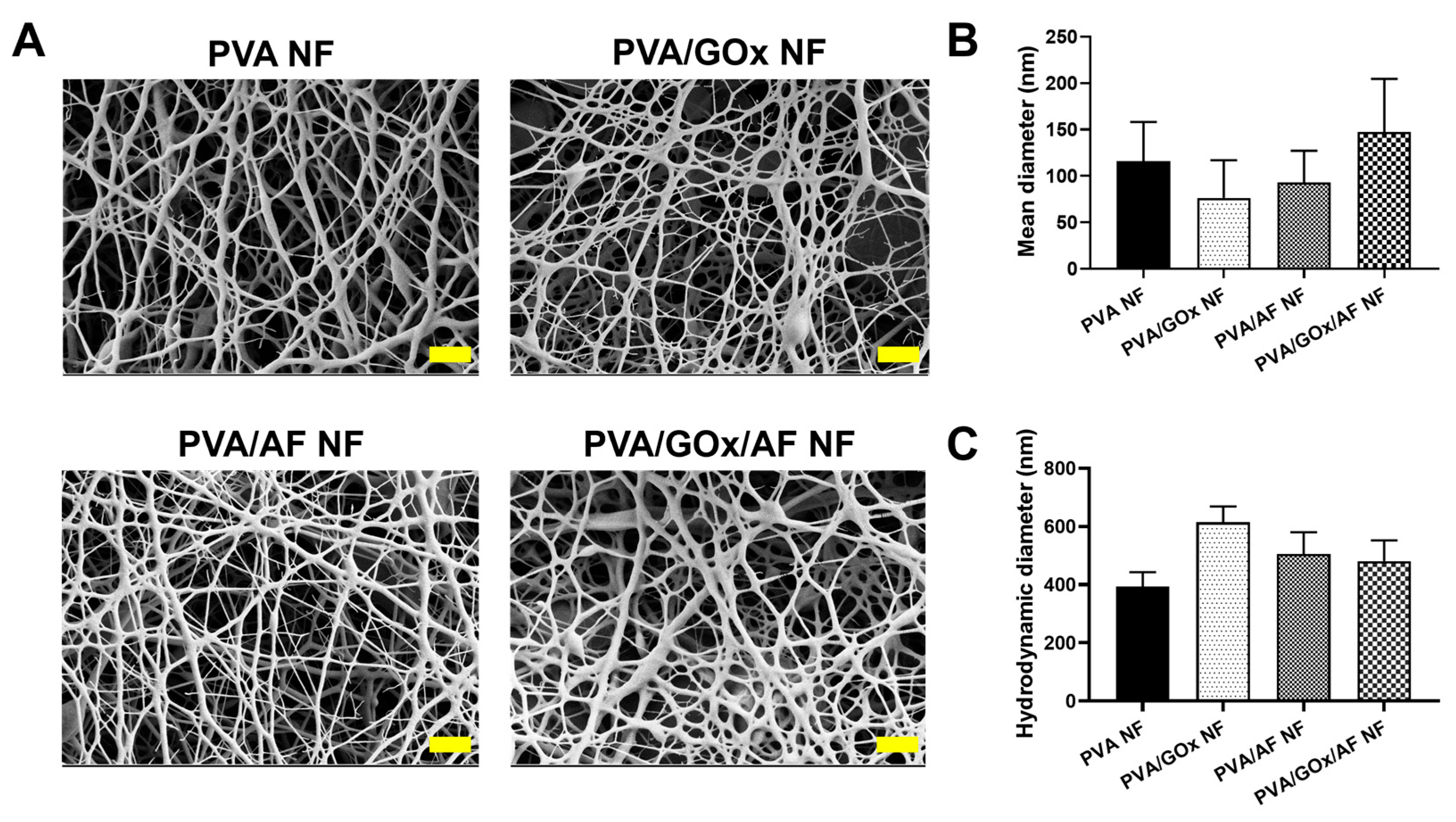
2.1. Fabrication and Physicochemical Evaluation of NF Systems
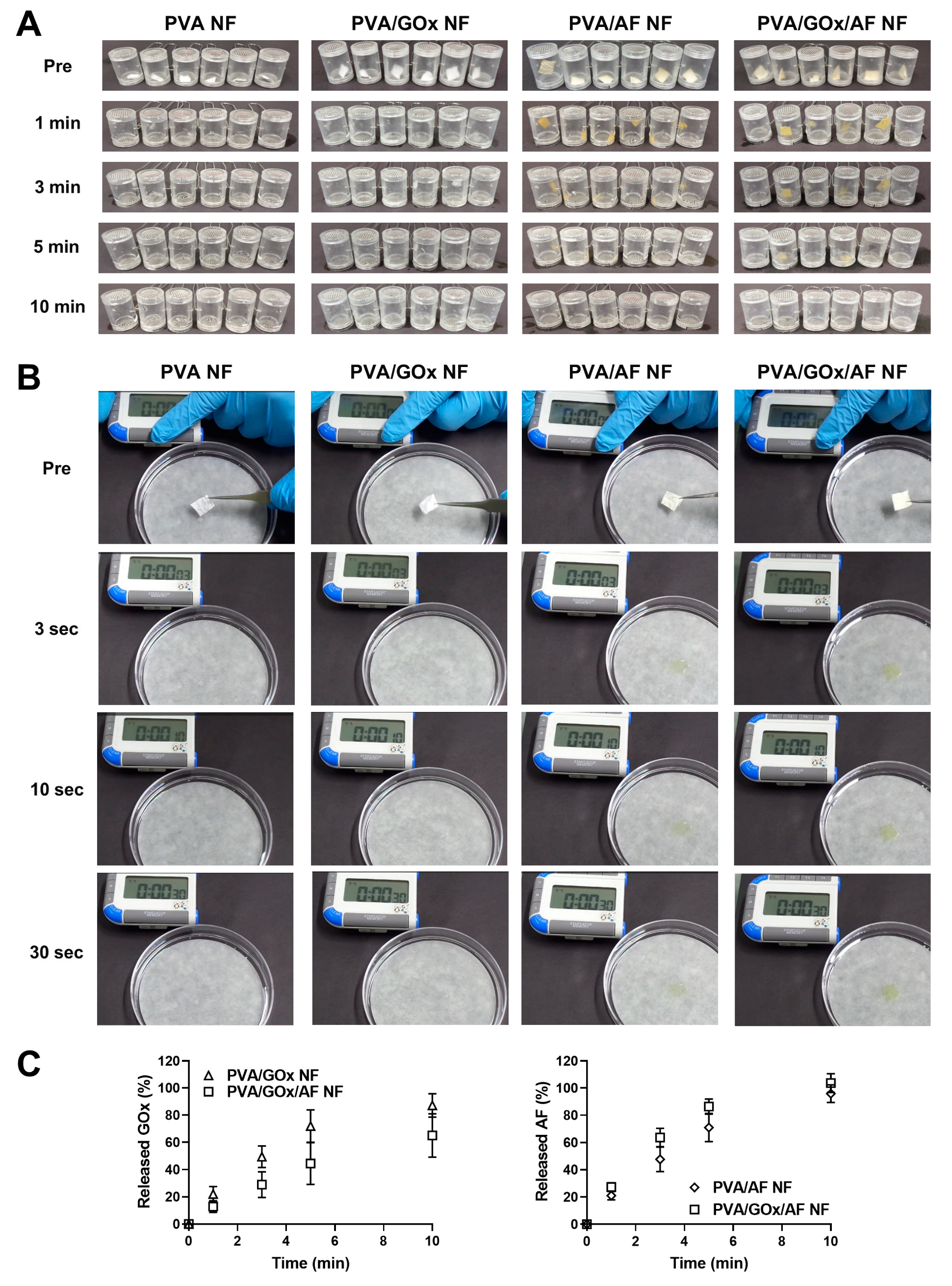
2.2. Disintegration, Wetting, and Dissolution Characteristics
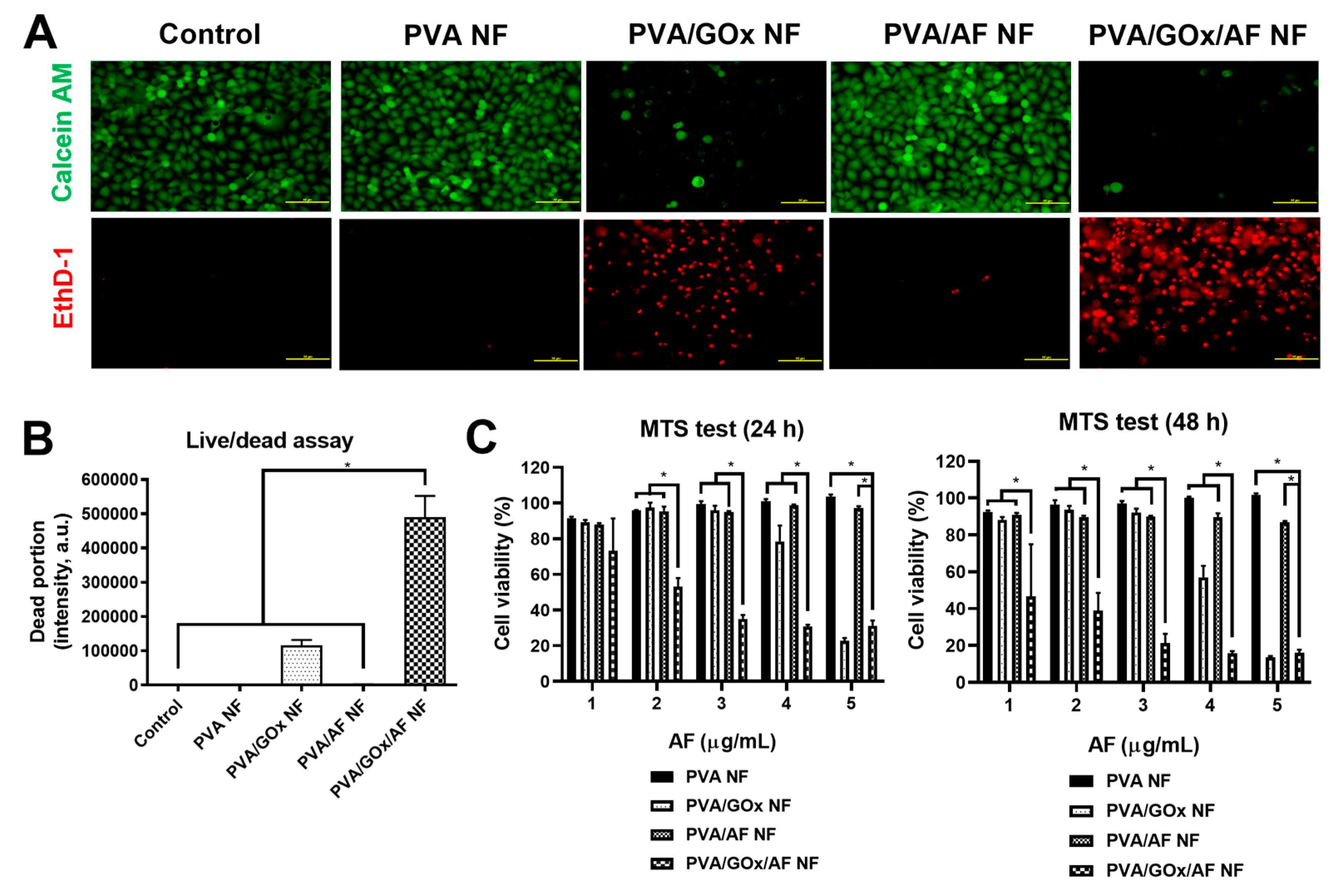
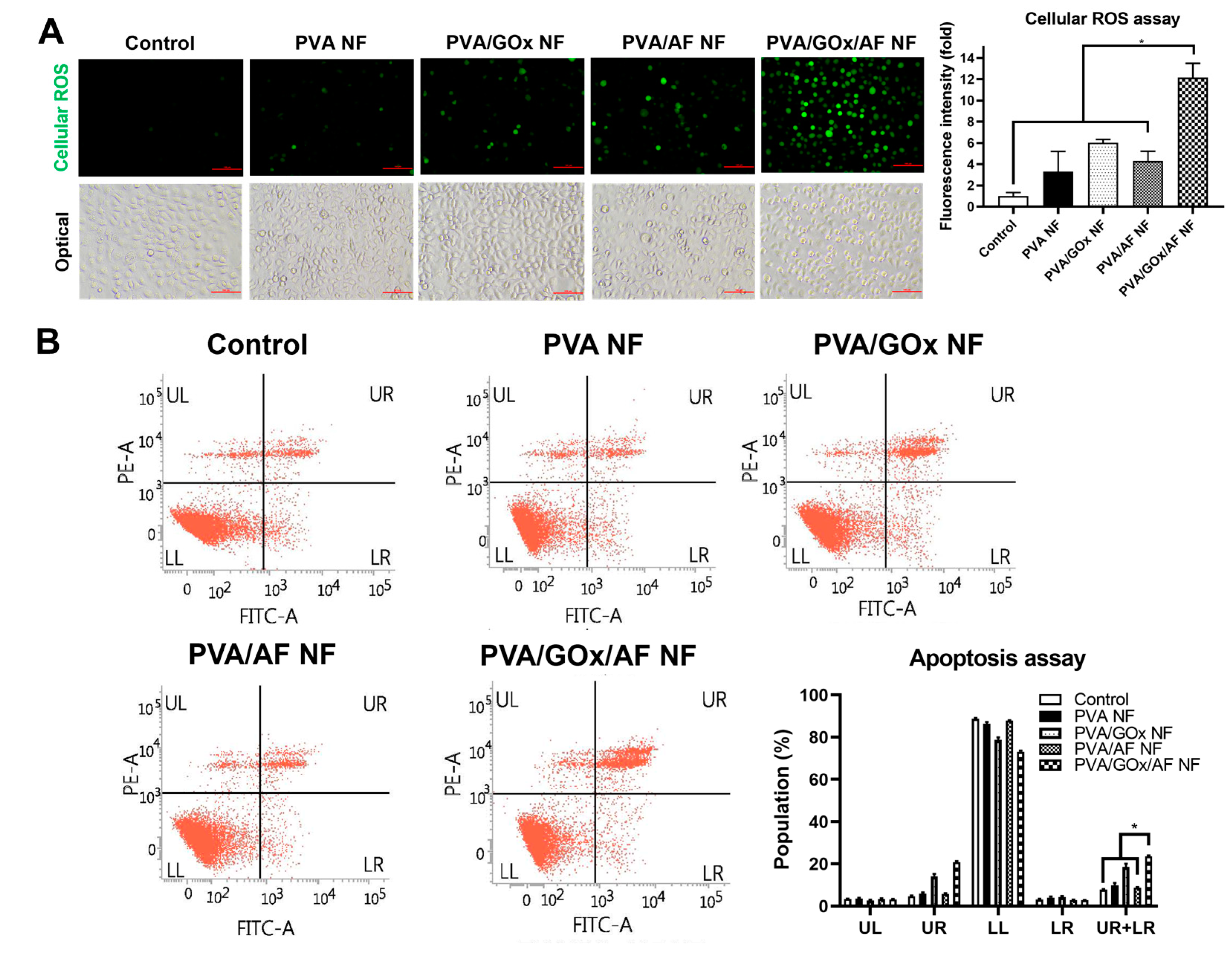
2.3. In Vitro Anticancer Activities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of NF System and Their Physicochemical Assessments
3.3. Disintegration, Wetting, and Dissolution Studies
3.4. In Vitro Anticancer Activity Assays
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, H.; Li, Z.; Bai, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X. Nano-drug delivery systems in oral cancer therapy: Recent developments and prospective. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, D.B.; Rao, R.S.; Hosmani, J.; Khan, S.; Patil, S.; Awan, K.H. Novel therapies in the management of oral cancer: An update. Dis. Mon. 2020, 66, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketabat, F.; Pundir, M.; Mohabatpour, F.; Lobanova, L.; Koutsopoulos, S.; Hadjiiski, L.; Chen, X.; Papagerakis, P.; Papagerakis, S. Controlled drug delivery systems for oral cancer treatment—Current status and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, N.; Song, X.; Dong, X. Recent advances of cancer chemodynamic therapy based on Fenton/Fenton-like chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J. Tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy of oral cancer. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Lee, N.V.; Liu, K.Y.P.; Poh, C.F. Prospects in the application of photodynamic therapy in oral cancer and premalignant lesions. Cancers 2016, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, G.Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, N. Recent advances of sonodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Hao, Q.; Jeong, D.I.; Huh, J.W.; Choi, Y.E.; Cho, H.J. Flash dissolving nanofiber membranes for chemo/cascade chemodynamic therapy of oral cancer. Mater. Des. 2023, 231, 112063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.H.; Qi, C.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Catalytic chemistry of glucose oxidase in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. Rapid synthesis of trimetallic nanozyme for sustainable cascaded catalytic therapy via tumor microenvironment remodulation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2309261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Gupta, D.; Yang, M.; Yang, F.; Feng, N.; Song, J.; Wood, M.J.A.; Qiu, L.; Chen, J. A purposefully designed pH/GSH-responsive MnFe-based metal-organic frameworks as cascade nanoreactor for enhanced chemo-chemodynamic-starvation synergistic therapy. Small 2023, 19, 2303403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Meng, Y.; Li, D.; Yao, L.; Le, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, F.; Chen, X.; Deng, G. Ferroptosis in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.; Jeong, D.I.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, C.; Ahn, S.H.; Ko, H.J.; et al. Fast dissolving nanofiber mat for the local antimicrobial application of roxithromycin in oral cavity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 131, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Cho, H.J. Phloretin-loaded fast dissolving nanofibers for the locoregional therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deadman, B.J.; Hellgardt, K.; Hii, K.K. A colorimetric method for rapid and selective quantification of peroxodisulfate, peroxomonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide. React. Chem. Eng. 2017, 2, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekade, R.K.; Sun, X. The Warburg effect and glucose-derived cancer theranostics. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Peng, Y.; Pan, J.; Niu, X.; Zhao, H.; Lan, M. Colorimetric evaluation of the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of antioxidants using carbon-confined CoOx as a highly active peroxidase mimic. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, H.T.; Tesfaye, W.; Mengstie, T.A. ROS induced lipid peroxidation and their role in ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1226044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; He, Z.; Luo, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Ge, D.; Liu, X.; Shi, W. Ferrocene-liposome-PEG: A robust ˙OH/lipid peroxide nano-converter for inducing tumor ferroptosis. Biomater. Res. 2023, 11, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummen, G.P.C.; van Liebergen, L.C.M.; Op den Kamp, J.A.F.; Post, J.A. C11-BODIPY581/591, an oxidation-sensitive fluorescent lipid peroxidation probe: (micro)spectroscopic characterization and validation of methodology. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Hao, Q.; Jeong, D.I.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Chu, S.; Hyun, U.; Cho, H.-J. Cascade Hydroxyl Radical-Generating and Ferroptosis-Inducing Nanofiber System for the Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Molecules 2024, 29, 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163964
Park J, Hao Q, Jeong DI, Kim H-J, Kim S, Lee SY, Chu S, Hyun U, Cho H-J. Cascade Hydroxyl Radical-Generating and Ferroptosis-Inducing Nanofiber System for the Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Molecules. 2024; 29(16):3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163964
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, JiHye, Qiaojun Hao, Da In Jeong, Hyun-Jin Kim, Sungyun Kim, Song Yi Lee, Seongnam Chu, Usok Hyun, and Hyun-Jong Cho. 2024. "Cascade Hydroxyl Radical-Generating and Ferroptosis-Inducing Nanofiber System for the Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Molecules 29, no. 16: 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163964
APA StylePark, J., Hao, Q., Jeong, D. I., Kim, H.-J., Kim, S., Lee, S. Y., Chu, S., Hyun, U., & Cho, H.-J. (2024). Cascade Hydroxyl Radical-Generating and Ferroptosis-Inducing Nanofiber System for the Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Molecules, 29(16), 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29163964







