Enhanced Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media via Adsorption on Facilely Synthesized Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
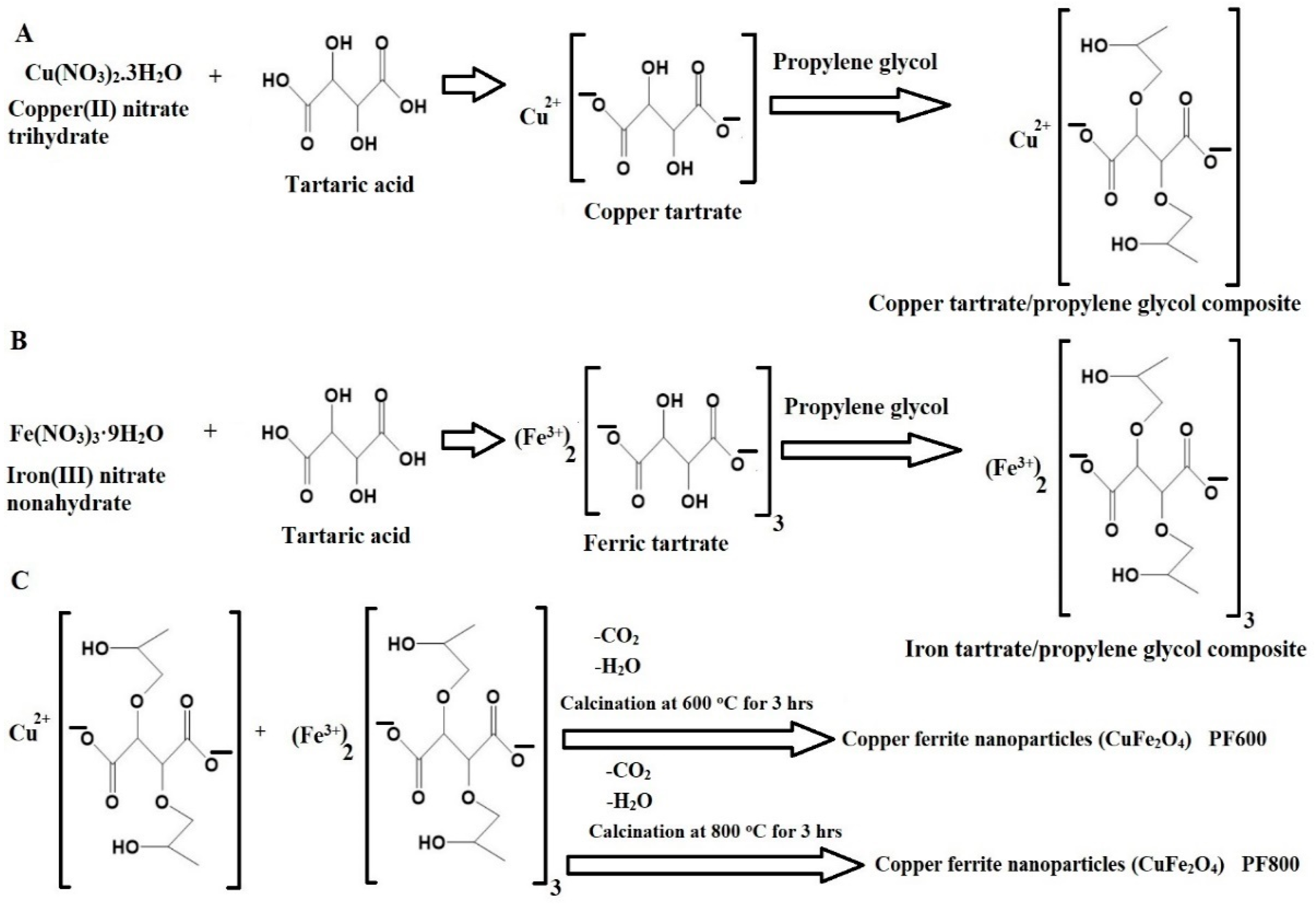
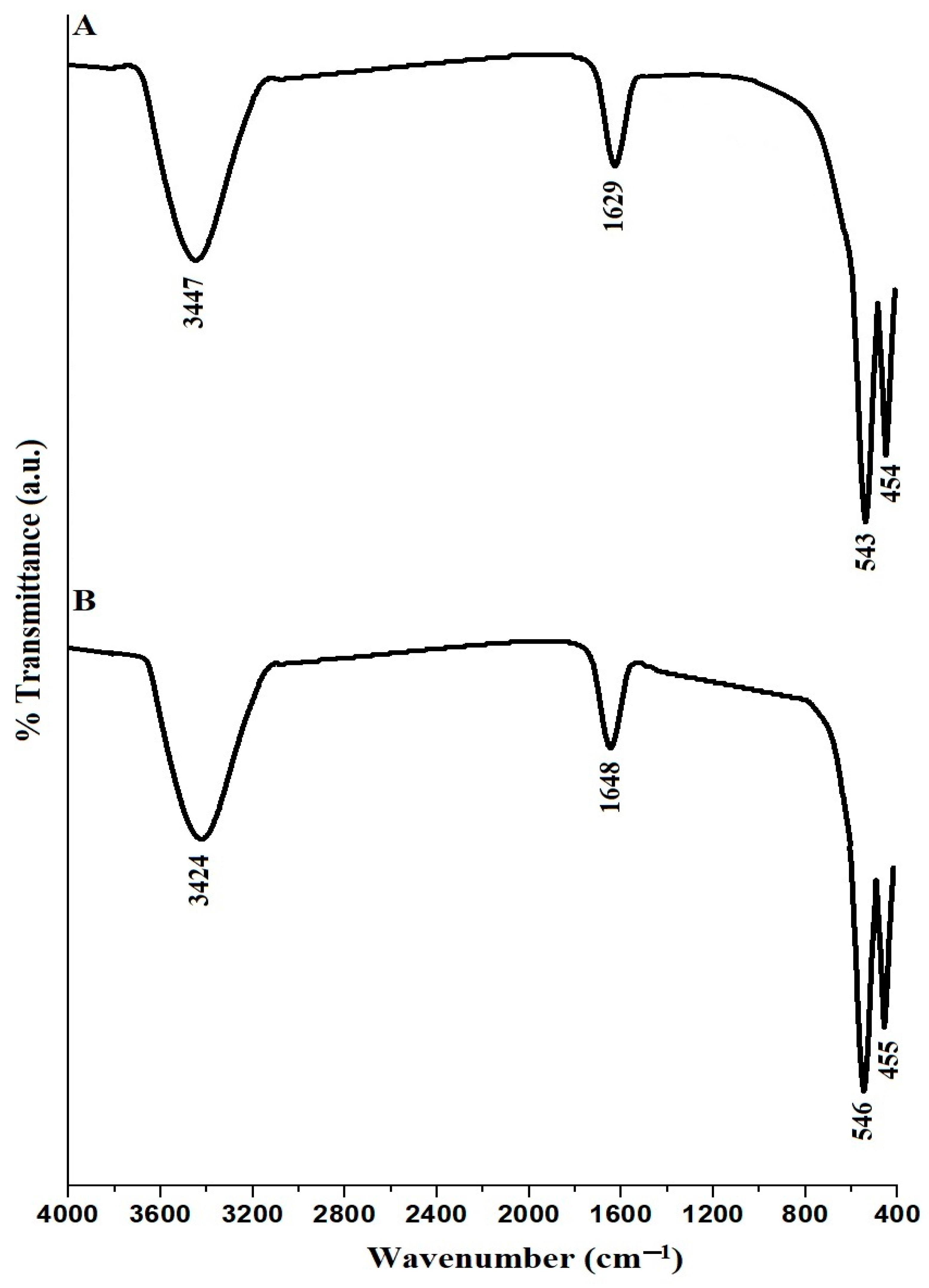
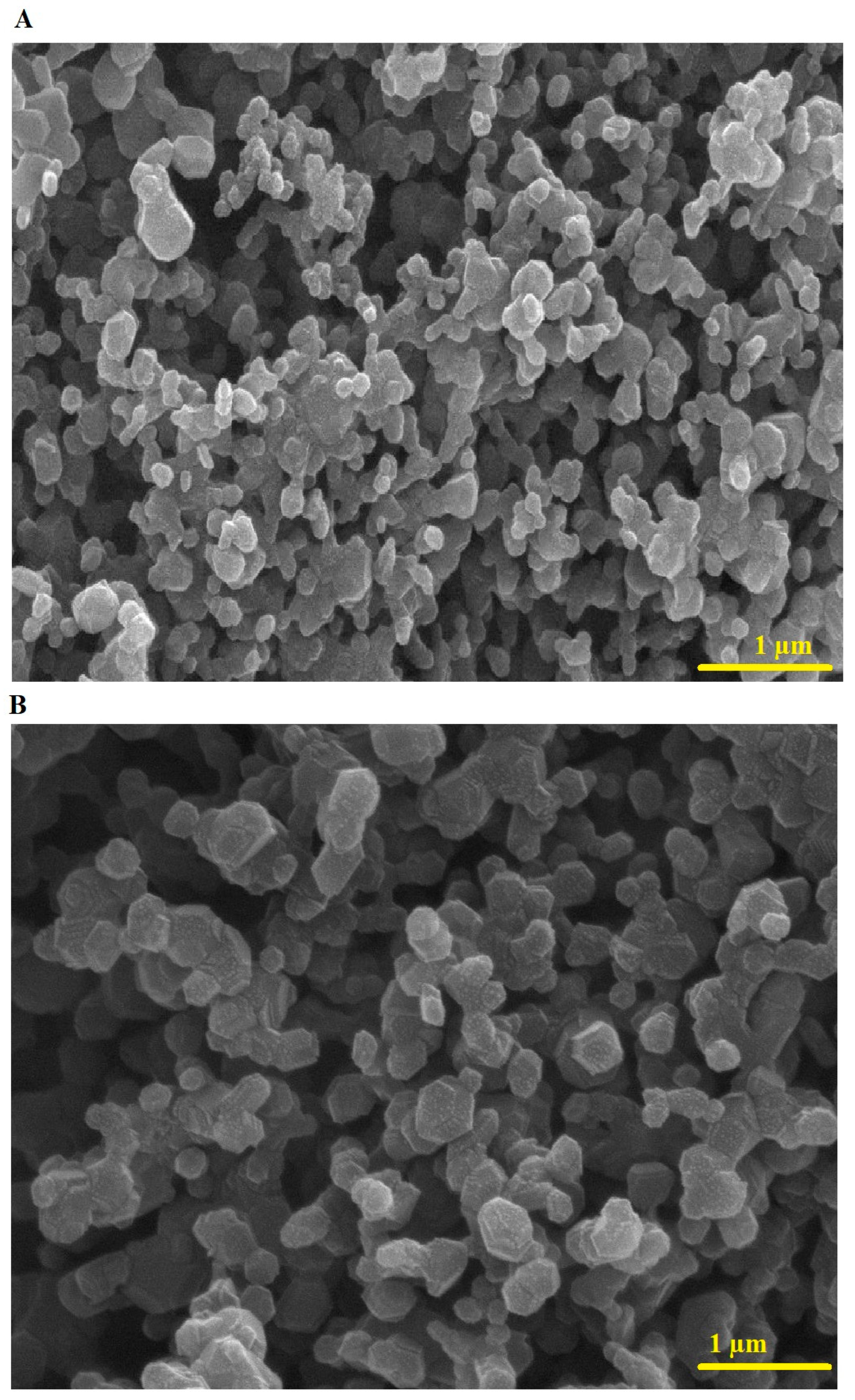
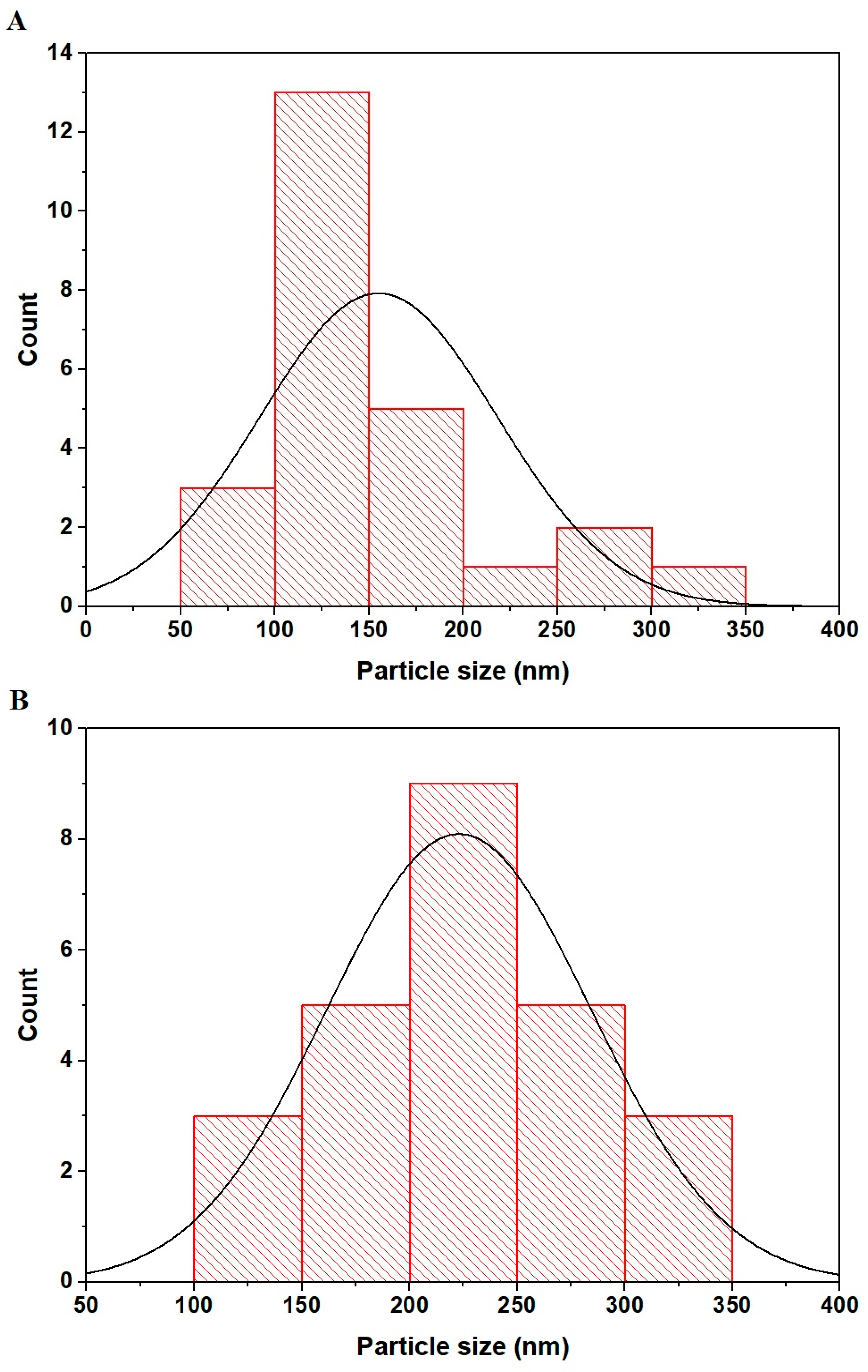
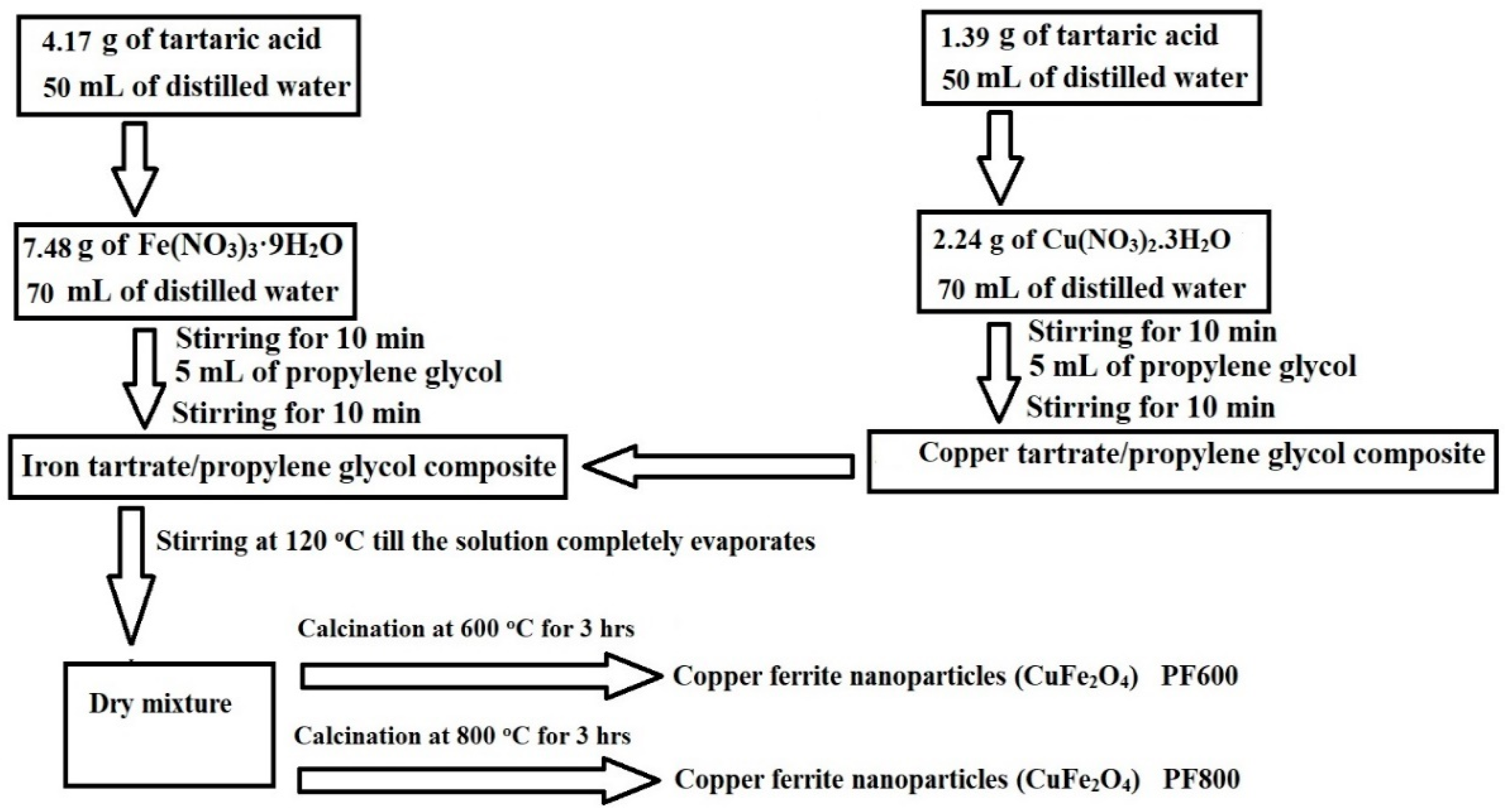
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles
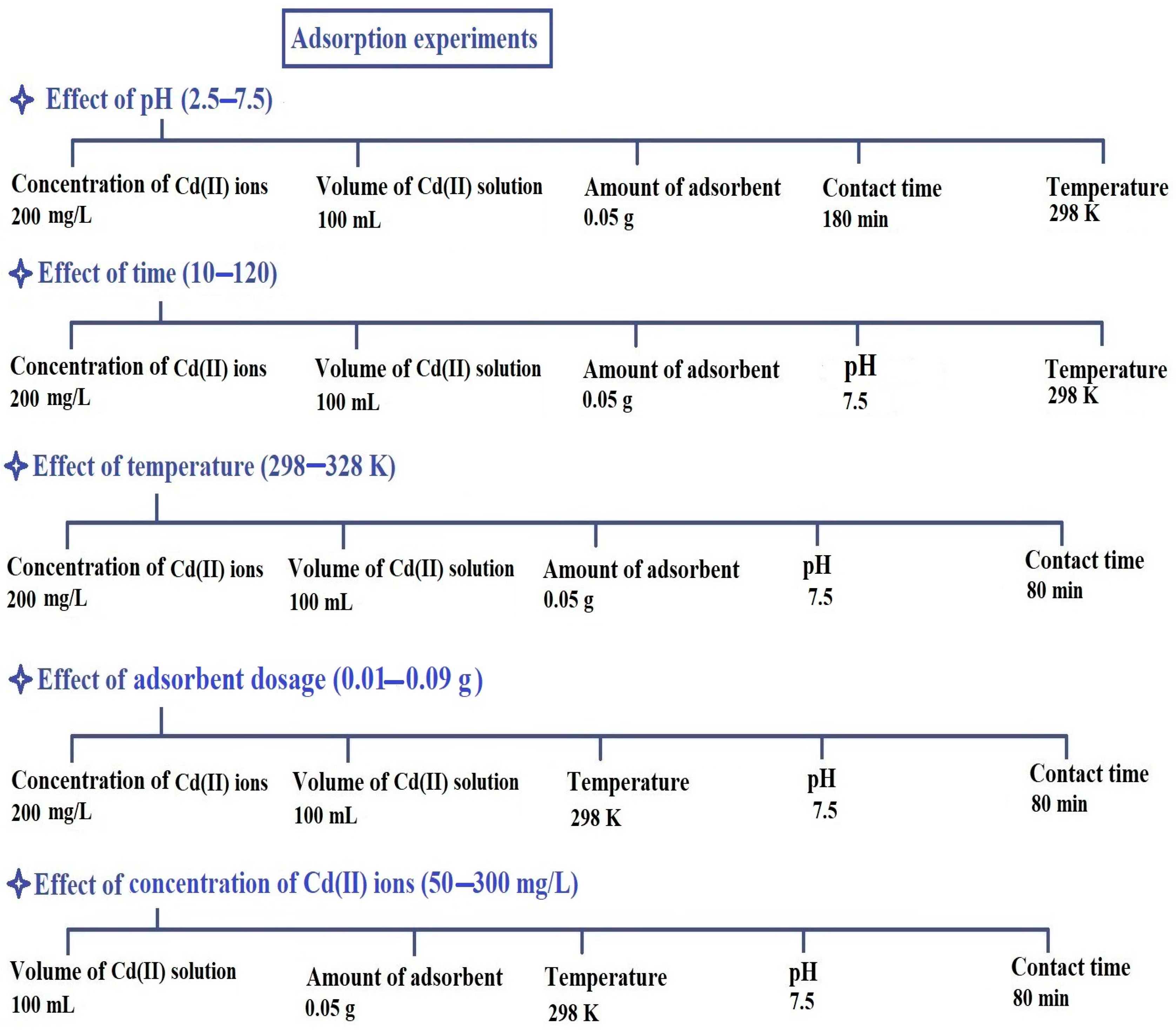
2.2. Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media
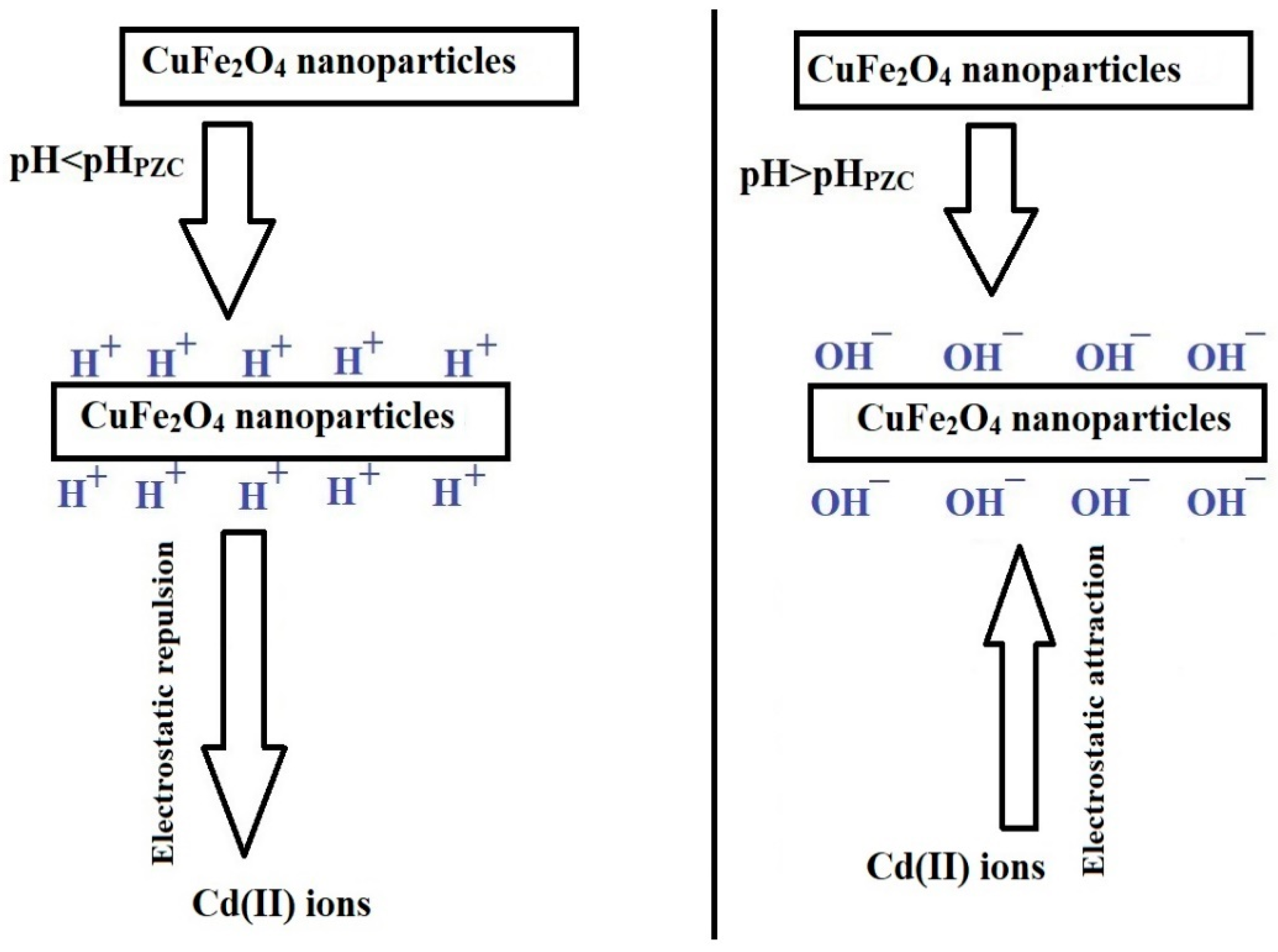
2.2.1. Influence of pH
Adsorption Mechanism
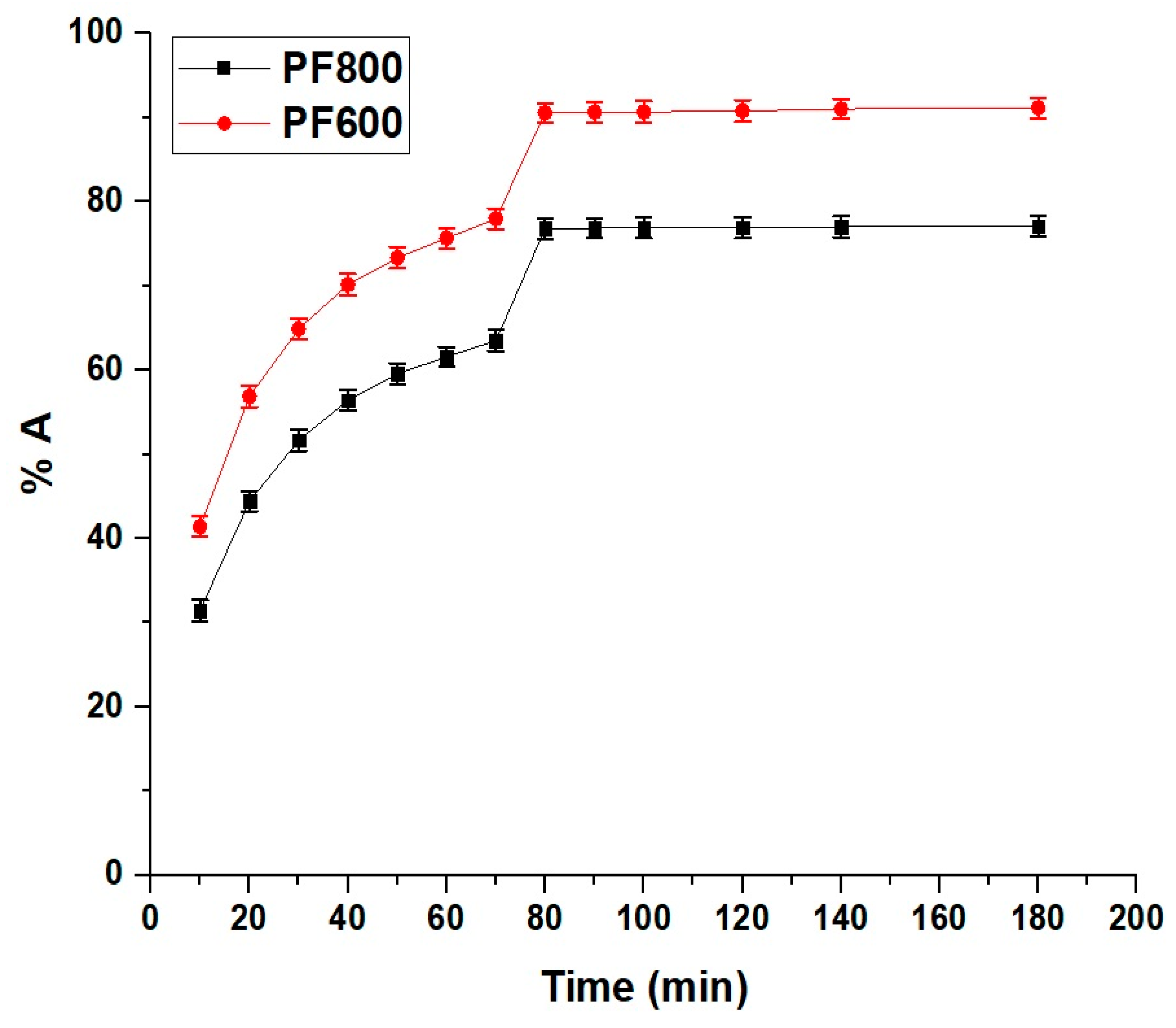
2.2.2. Influence of Contact Time
Adsorption Kinetics
2.2.3. Influence of Temperature
Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.2.4. Influence of Adsorbent Dosage
2.2.5. Influence of Concentration
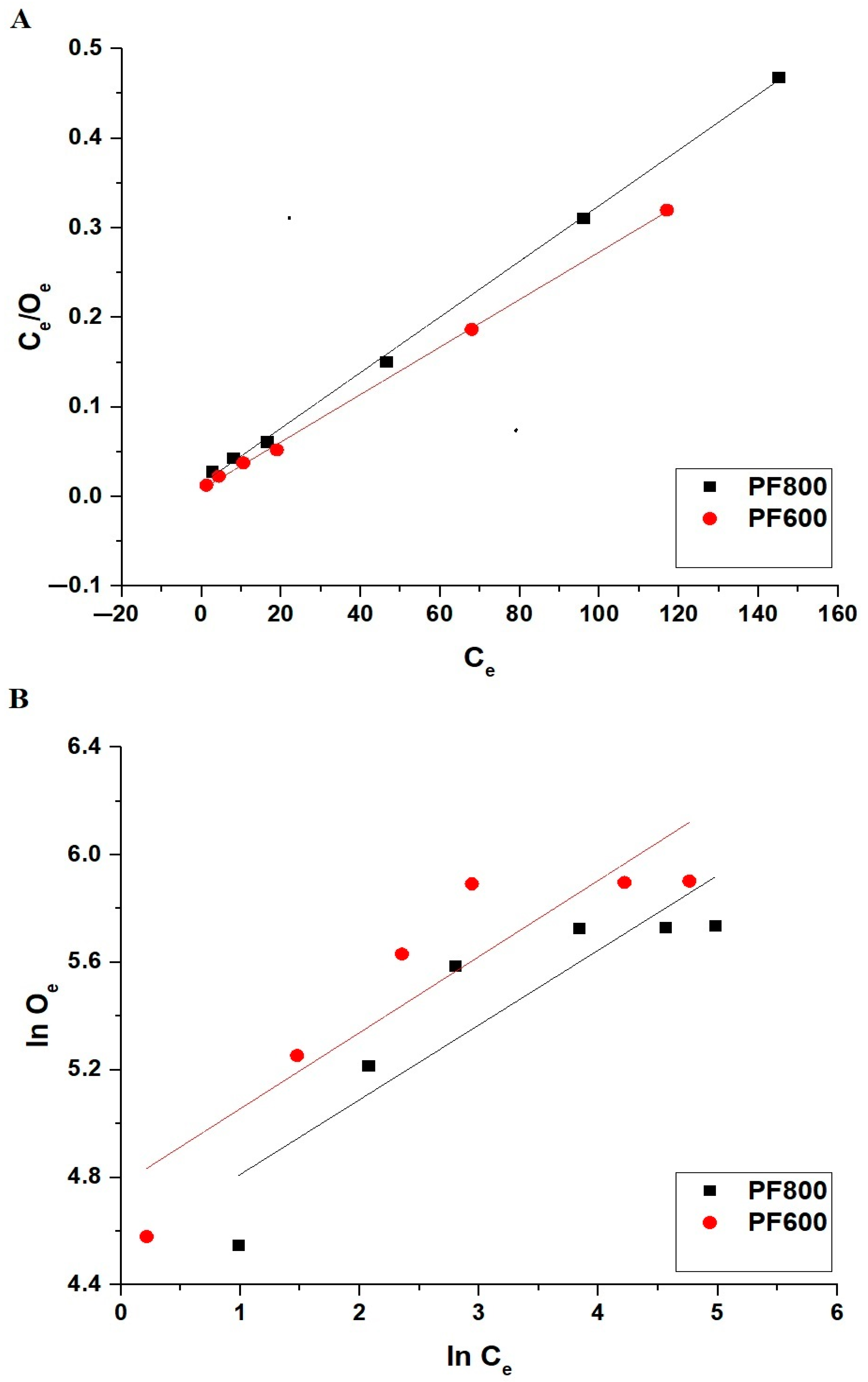
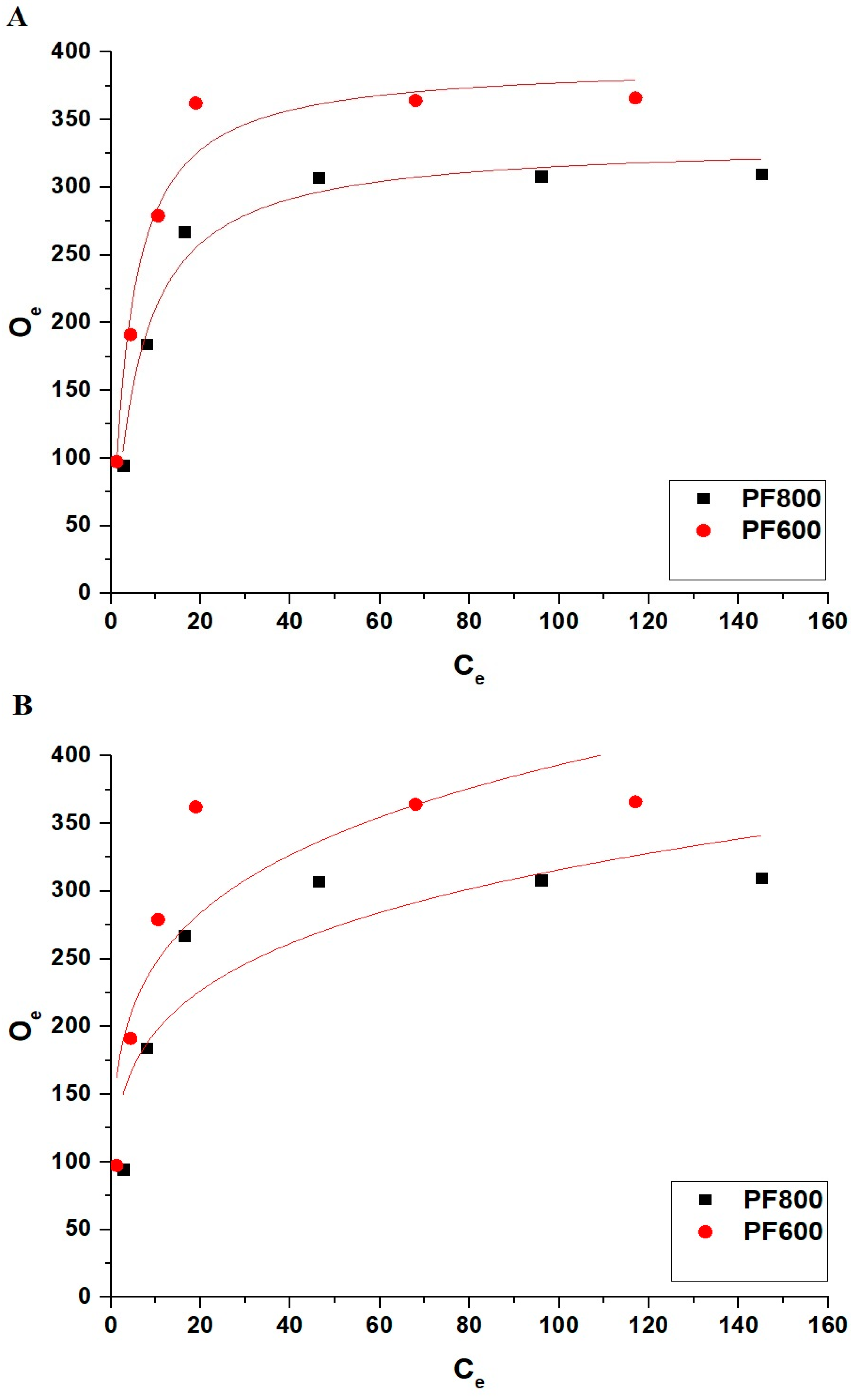
Adsorption Isotherms
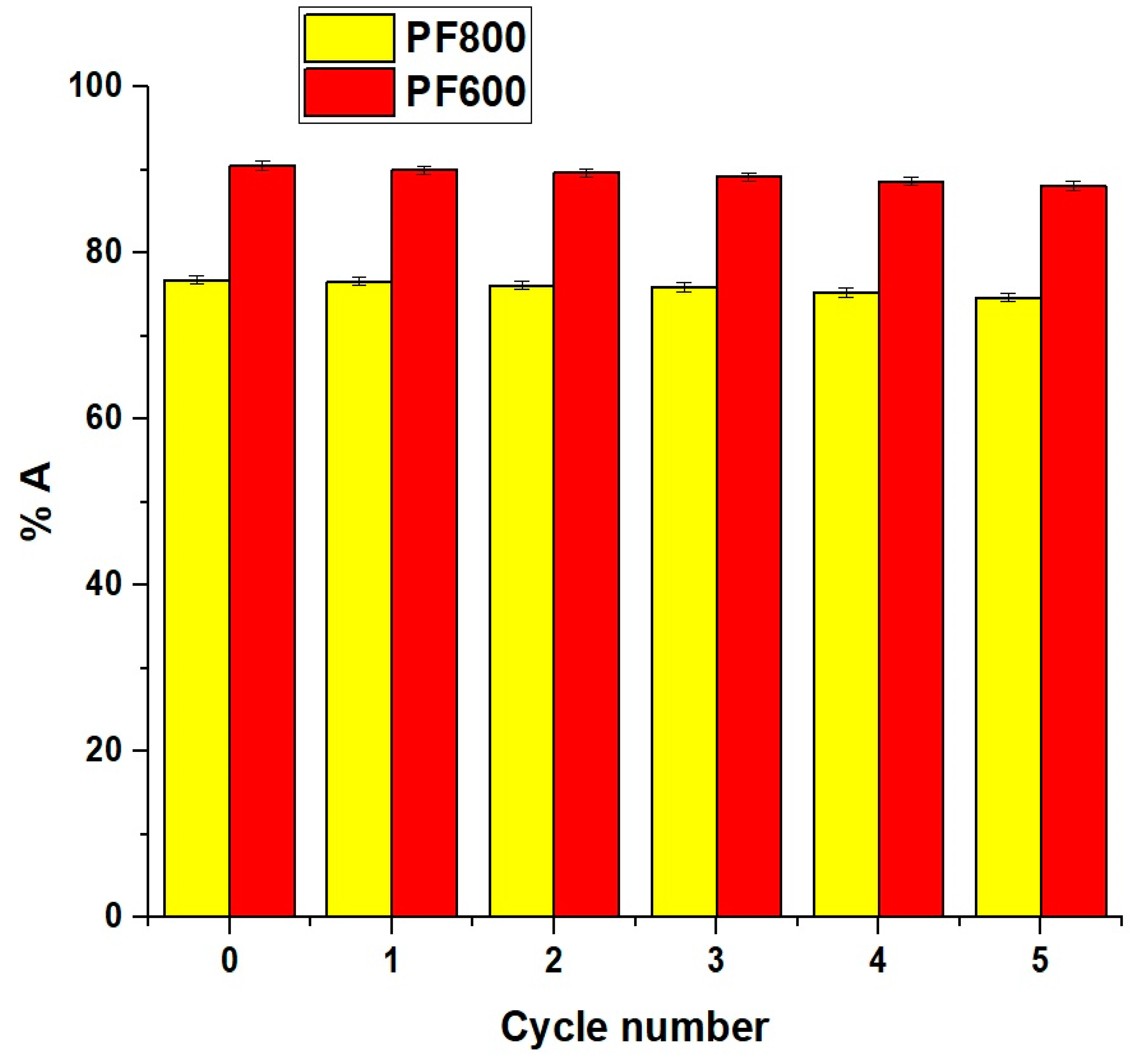
2.2.6. Effect of Regeneration and Reusability
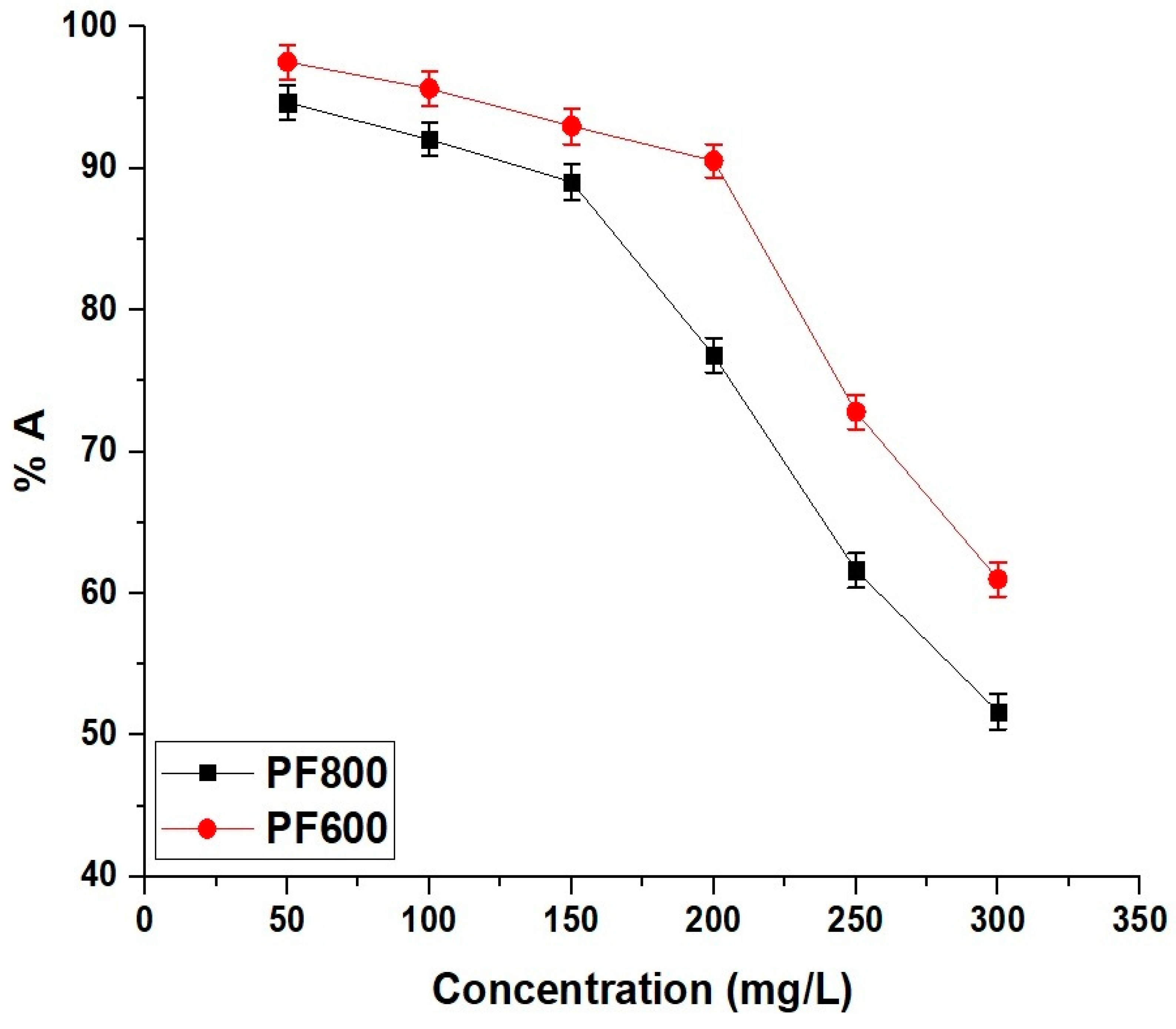
2.2.7. Selectivity of the Adsorbents
2.2.8. Stability of the PF600 and PF800 Samples under Acidic Medium
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Copper Ferrite (CuFe2O4) Nanoparticles
3.3. Instrumentation
3.4. Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media
3.5. Point of Zero Charge (pHPZC) of the PF600 and PF800 Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joshi, N.C.; Joshi, A.; Mitra, D.; Gururani, P.; Kumar, N.; Joshi, H.K. Removal of Heavy Metals Using Cellulose-Based Materials: A Mini-Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 21, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjiya, M.; Zhang, J.C.; Wu, B.; Yin, M.J.; An, Q.F. Nanofiltration Membranes for Sustainable Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Polluted Water: A Review and Future Perspective. Desalination 2024, 578, 117441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Vohra, M.S.; Onaizi, S.A. Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions: Progress of Adsorbents Development and Their Effectiveness. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, Y.G.; Taher, T.; Khairurrijal, K.; Ramadan, B.S.; Safitri, H.; Sudibyo, S.; Yuliansyah, A.T.; Petrus, H.T.B.M. Recent Advances in the Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metals from Acid Mine Drainage by Conventional and Novel Materials: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K.; Singh, J.; Malik, S.; Saharan, Y.; Goyat, R.; Umar, A.; Akbar, S.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Baskoutas, S. Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Promising Solution for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Pollutants from Industrial Wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, D.I.; Conradie, J. The Use of Bidentate Ligands for Heavy Metal Removal from Contaminated Water. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phouthavong, V.; Hagio, T.; Park, J.H.; Nijpanich, S.; Duangkhai, K.; Rujiravanit, R.; Thaveemas, P.; Chounlamany, V.; Kong, L.; Li, L.; et al. Removal of Heavy Metals by BEA Zeolite/Fe3O4 Composite Prepared via Dry-Gel Conversion Method Using Agrowaste-Derived Raw Material. Solid State Sci. 2024, 149, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Hussain, A.; Priyadarshi, M.; Haider, A. Heavy Metals Removal from Synthetic and Industrial Wastewater Using Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2024, 101, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Maganga, I.; Zeng, L.; Gu, Z. Graphene Crown Pore for Efficient Heavy Metal Ion Removal: Protonated vs. Non-Protonated. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 395, 123819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Naik, T.S.S.K.; Basavaraju, U.; Pavithra, N.; Varshney, R.; Chauhan, V.; Shehata, N.; Thamaraiselvan, C.; Subramanian, S.; Singh, J.; et al. Novel and Sustainable Green Sulfur-Doped Carbon Nanospheres via Hydrothermal Process for Cd (II) Ion Removal. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawy, H.A.; Abdel-Salam, A.H.; Khalil, T.E. The Impact of an Amberlite XAD-16-Based Chelating Resin for the Removal of Aqueous Cd(II) and Pb(II)Ions. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Van, H.; Chu Van, H.; Luu Hoang, T.; Vo Nguyen, D.K.; Ha Thuc, C.N. The Starch Modified Montmorillonite for the Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7212–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z. Comparison of Heavy Metal Removals from Aqueous Solutions by Chemical Precipitation and Characteristics of Precipitates. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Du, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhao, M.; Luo, L.; Cui, T.; Deng, S.; Jin, M.; Lyu, Z.; Long, X. Application of Biosurfactant Surfactin for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Water and Soil via a Micellar-Enhanced Ultrafiltration Process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, H.; Hashemi, M.; Rajabi, S. Removal of Arsenic as a Potentially Toxic Element from Drinking Water by Filtration: A Mini Review of Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Techniques. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smara, A.; Delimi, R.; Chainet, E.; Sandeaux, J. Removal of Heavy Metals from Diluted Mixtures by a Hybrid Ion-Exchange/Electrodialysis Process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; Antti, M.L.; Akhtar, F. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Natural Zeolites: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-wasidi, A.S.; Naglah, A.M.; Saad, F.A.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Modification of Sodium Aluminum Silicate Hydrate by Thioglycolic Acid as a New Composite Capable of Removing and Preconcentrating Pb (II), Cu (II), and Zn (II) Ions from Food and Water Samples. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Naglah, A.M.; Saad, F.A.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Modification of Silica Nanoparticles with 1-Hydroxy-2-Acetonaphthone as a Novel Composite for the Efficient Removal of Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Hg(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Joshi, P.; Gusain, R.; Khatri, O.P. Recent Advances in Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal and Metalloid Ions by Metal Oxide-Based Nanomaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Q. Heavy Metal Removal from Water/Wastewater by Nanosized Metal Oxides: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, W.A.; Haleem, N.; Baig, M.A.; Jamal, Y. Synthesis, Characterization and Heavy Metal Removal Efficiency of Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles (NFN’s). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, C.; Kollu, P.; Felix, S.; Velmurugan, V.; Jeong, S.K.; Grace, A.N. CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4@graphene Adsorbents for Heavy Metal Ions-Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28965–28972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Algethami, F.K.; AlSalem, H.S.; Binkadem, M.S.; Khairy, M.; Saad, F.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Alqahtani, Z. Efficient Disposal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/CdMn2O4/CdO as Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposites. Inorganics 2023, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Al-Farraj, E.S. Facile Synthesis and Characterizations of Mixed Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for the Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B and Congo Red Dyes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deep, N.C.; Ghosh, S.; Tanna, A.R. Green Synthesis for Fabrication of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles with Photocatalytic Dye Degrading Potential as a Sustainable Effluent Treatment Strategy. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Simple Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Adsorption of Indigo Carmine Dye from Aqueous Media. Inorganics 2023, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farraj, E.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Congo Red Dye Using Facilely Synthesized and Characterized MgAl2O4 Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 4870–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhalili, Z.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Inorganics 2024, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghanmi, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Simple Production and Characterization of ZnO/MgO Nanocomposite as a Highly Effective Adsorbent for Eliminating Congo Red Dye from Water-Based Solutions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-wasidi, A.S.; Shah, R.K.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous. Inorganics 2024, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazey, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Kotp, Y.H.; Hameed, A.M.; Subaihi, A. Facile Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles from Egyptian Insecticide Cans for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, B.R.; Hari Krishna, R.; Kottam, N.; Nagabhushana, B.M.; Sharath, R.; Darukaprasad, B. Removal of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution by Magnetic CuFe2O4 Nano-Adsorbent Synthesized by One Pot Solution Combustion Method. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Krishnaiah, A.; Ghosh, T.K.; Viswanath, D.S.; Boddu, V.M.; Smith, E.D. Adsorption of Divalent Cadmium (Cd(II)) from Aqueous Solutions onto Chitosan-Coated Perlite Beads. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 5066–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution Using Polyaniline Grafted Chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Saad, F.A.; Shah, R.K.; Al-Farraj, E.S.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. A Facile Sol-Gel Synthesis and Characterization of MgCO3/MnCO3 and MgMn2O4/Mn2O3 Novel Nanostructures With Remarkably High Adsorption Activity Toward Eriochrome Black T Dye. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 33, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Khalil, M.M.H.; Algethami, F.K.; Khairy, M.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G.; Saad, F.A.; Shah, R.K.; Ammar, A.M. Facile Synthesis of MgO/CuO and MgO/Cu3MgO4 Binary Nanocomposites as Promising Adsorbents for the Disposal of Zn(II) Ions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 34, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhao, J.S.; Rathod, N.V.; Rao, A.; Ghugare, C.D.; Chavan, S.M.; Kubade, A.V.; Kalyani, V.S.; Patil, A.B. Efficient Removal of Toxic Cd(II) Ions from Waste Streams by a Novel Modified Biodegradable Magnetic Sorbent. Chem. Inorg. Mater. 2023, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczajowska-Zadrożna, M.; Filipkowska, U.; Jóźwiak, T. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Cd (II) from Aqueous Solutions by Chitosan Immobilized in Alginate Beads. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Al-Senani, G.M.; Algethami, F.K.; Shah, R.K.; Saad, F.A.; ur Rehman, K.; Khezami, L.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis of MgO/ZnO Nanocomposite for Efficient Removal of Alizarin Red S Dye from Aqueous Media. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 162, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Al-Senani, G.M.; Algethami, F.K.; Shah, R.K.; Saad, F.A.; Munshi, A.M.; Rehman, K.U.; Khezami, L.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Calcium Ferrite Nanoparticles: A Simple Synthesis Approach for the Effective Disposal of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Environments. Inorganics 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Algethami, F.K.; Alsalem, H.S.; Binkadem, M.S. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Nanostructures for the Efficient Disposal of Crystal Violet Dye from Aqueous Media. Inorganics 2023, 11, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farraj, E.S.; Alotaibi, A.N.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Saad, F.A.; Rehman, K.U.; Algethami, F.K.; Shah, R.K. Functionalization of Na2Ca2Si3O9/Ca8Si5O18 Nanostructures with Chitosan and Terephthalaldehyde Crosslinked Chitosan for Effective Elimination of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Inorganics 2024, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafeeq, K.; Rayes, S.M.E.; Khalil, M.M.H.; Shah, R.K.; Saad, F.A.; Khairy, M.; Algethami, F.K.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Functionalization of Calcium Silicate/Sodium Calcium Silicate Nanostructures with Chitosan and Chitosan/Glutaraldehyde as Novel Nanocomposites for the Efficient Adsorption of Cd(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Silicon 2024, 16, 1713–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdat, S.; Tokay, F.; Demirci, S.; Yilmaz, S.; Sahiner, N. Removal of Cd(II), Co(II), Cr(III), Ni(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) Ions from Wastewater Using Polyethyleneimine (PEI) Cryogels. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouotou, D.; Gharibi, E.K.; Bailón-García, E.; Ghalit, M. Improved Cd (II) Ions Removal Performance from Aqueous Solution Using Cerium Doped Activated Carbon. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 51, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, I.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W.; Aubry, C.; Suresh, S.; Sillanpää, M.; Haija, M.A. Facile Preparation of Magnetic CuFe2O4 on Sepiolite/GO Nanocomposites for Efficient Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from Aqueous Solution. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 38828–38838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, M.E.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Hassanien, M.M.; Ibrahim, W.A. Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Modified with Dibenzoylmethane as a Novel Composite for Efficient Removal of Cd(II), Hg(II), and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2182–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, C.T.A.; Tho, P.T.; Xuan, N.D.; Ho, T.A.; Ha, P.T.V.; Trang, L.T.Q.; Tuan, N.Q.; Manh, D.H.; Thanh, T.D.; Tran, N. Microwave Absorption Properties for Composites of CoFe2O4/Carbonaceous-Based Materials: A Comprehensive Review. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 990, 174429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Saud Abdulhameed, A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Yong, S.K.; Wilson, L.D.; Jawad, A.H.; Algburi, S. Chitosan-Schiff Base Nano Silica Hybrid System for Azo Acid Dye Removal: Multivariable Optimization, Desirability Function, and Adsorption Mechanism. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 162, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.H.A.; Gad ElRab, E.K.M.; Kamel, R.M.; Elshaarawy, R.F.M. Cost-Effective Removal of Toxic Methylene Blue Dye from Textile Effluents by New Integrated Crosslinked Chitosan/Aspartic Acid Hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, H.; Kumar, A.; Ishaque, A.; Parveen, M.; Nami, S.A.A. Synthesis, Morphology and Dye Removal Studies of Ternary Hydrogels Bearing Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Chitosan and Glutamic Acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1298, 137003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; El-Dougdoug, W.; Kotp, Y.H. Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Novel Zeolite Nanostructures for the Efficient Removal of Pb(II) and Hg(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Silicon 2023, 15, 7453–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Saad, F.A.; Munshi, A.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium and Manganese Mixed Oxides for the Efficient Removal of Tartrazine Dye from Aqueous Media. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5656–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Algethami, F.K.; Saad, F.A.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Remarkable High Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Facilely Synthesized MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 33, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, I.M.M.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G.; Hassanien, M.M.; Alnagar, N.R.; Mortada, W.I. Use of Microwave Irradiation for Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Thioglycolic Acid for Removal of Cadmium and Mercury. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 258, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Basha, M.T.; Alghanmi, R.M.; Al-Farraj, E.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Functionalization of Sodium Magnesium Silicate Hydroxide/Sodium Magnesium Silicate Hydrate Nanostructures Using 2,3-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde as a Novel Nanocomposite for the Efficient Removal of Cd(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Separations 2023, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-wasidi, A.S.; Katouah, H.A.; Saad, F.A.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Functionalization of Silica Nanoparticles by 5-Chloro-8-Quinolinol as a New Nanocomposite for the Efficient Removal and Preconcentration of Al3+ Ions from Water Samples. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 15276–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Khairy, M.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Efficient Disposal of Basic Fuchsin Dye from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/MgMn2O4/Mg(Mg0.333Mn1.333)O4 as a Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposite. Inorganics 2023, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El, N.; Abdalla, S.; Ikhlas, M.K.; Ehab, A.M. Facile Synthesis of Sodium Iron Silicate/Sodium Iron Oxide Silicate Nanostructures from Canned Beans and Rice Husk Wastes for Efficient Removal of Cd (II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Silicon 2024, 16, 2955–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






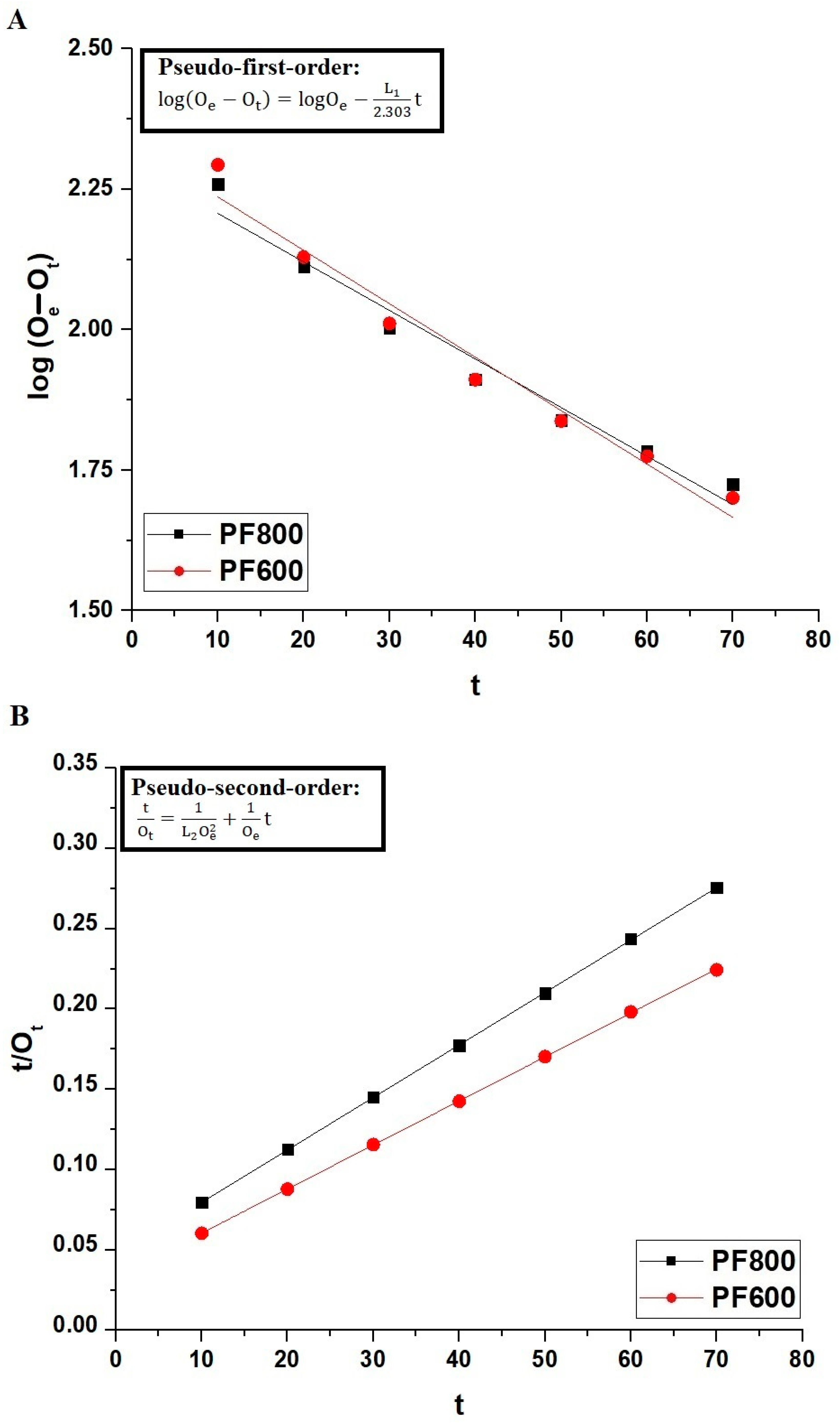
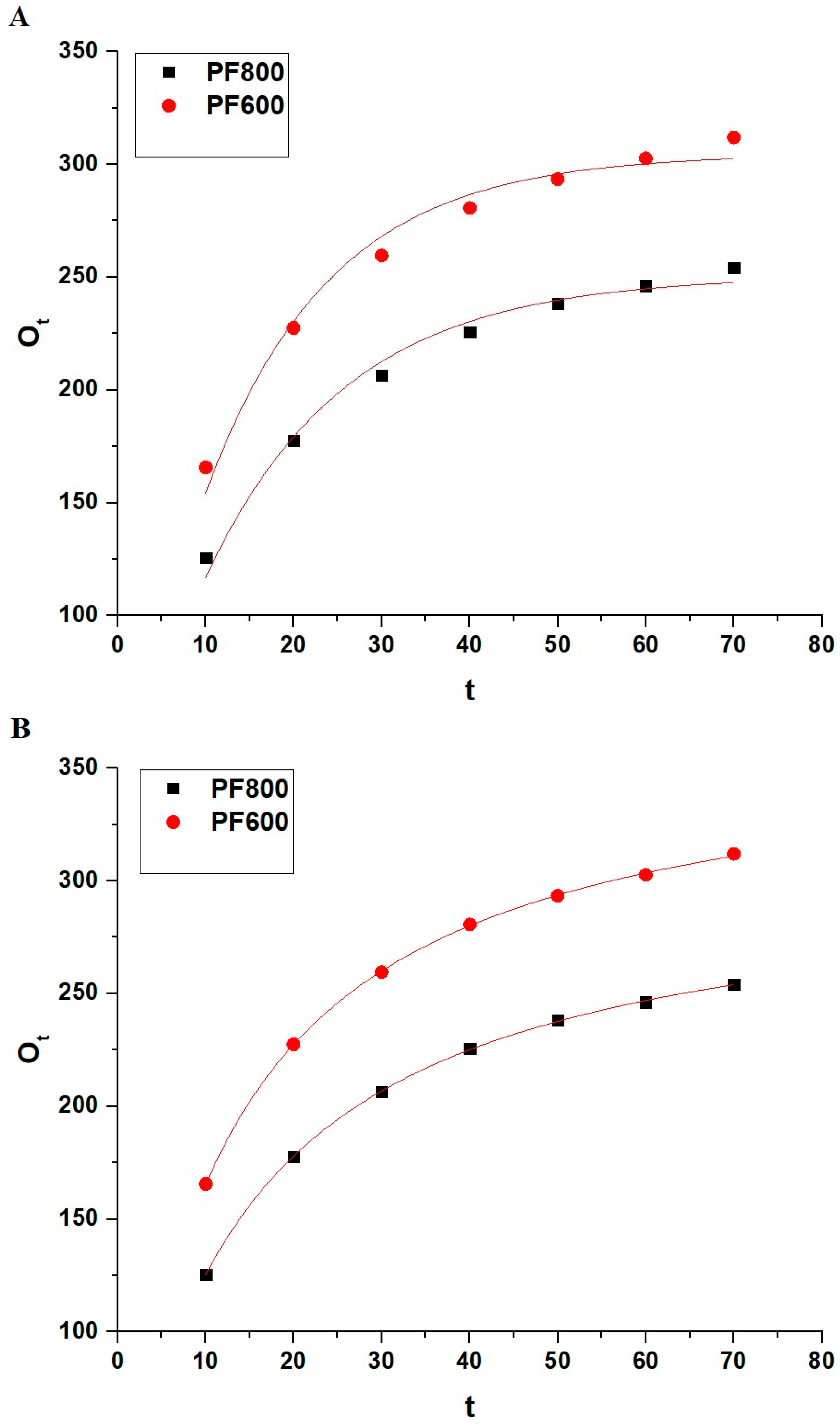



| Samples | OExp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 (1/min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | RSS | L2 (g/mg.min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | RSS | ||
| PF800 | 307.24 | 0.0199 | 196.53 | 0.9609 | 0.00703 | 0.000228 | 305.81 | 0.9999 | 0.00327 |
| PF600 | 362.16 | 0.0219 | 214.43 | 0.9635 | 0.00794 | 0.000230 | 364.96 | 0.9999 | 0.00274 |
| Samples | OExp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 (1/min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | χ2 | L2 (g/mg.min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | χ2 | ||
| PF800 | 307.24 | 0.0628 | 250.64 | 0.9823 | 36.87 | 2.27 × 10−4 | 306.21 | 0.9999 | 0.22563 |
| PF600 | 362.16 | 0.0707 | 304.59 | 0.9739 | 69.22 | 2.28 × 10−4 | 364.39 | 0.9998 | 0.4998 |
| Samples | ΔS° (KJ/molK) | ΔH° (KJ/mol) | ΔG° (KJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 328 | |||
| PF800 | 0.0449 | −18.16 | −31.56 | −32.01 | −32.46 | −32.91 |
| PF600 | 0.0699 | −28.26 | −49.12 | −49.82 | −50.52 | −51.22 |
| Samples | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omax (mg/g) | L4 (L/mg) | R2 | RSS | Omax (mg/g) | L3 (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | 1/Z | R2 | RSS | |
| PF800 | 322.58 | 0.2135 | 0.9989 | 1.29 × 10−4 | 406.11 | 93.11 | 0.2779 | 0.7680 | 0.2074 |
| PF600 | 377.36 | 0.3239 | 0.9991 | 5.56 × 10−5 | 529.85 | 118.28 | 0.2830 | 0.7848 | 0.2400 |
| Samples | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omax (mg/g) | L4 (L/mg) | R2 | χ2 | Omax (mg/g) | L3 (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | 1/Z | R2 | χ2 | |
| PF800 | 333.72 | 0.1719 | 0.9715 | 221.36 | 364.39 | 122.08 | 0.2064 | 0.7460 | 1974.51 |
| PF600 | 391.84 | 0.2555 | 0.9616 | 478.57 | 452.48 | 154.96 | 0.2023 | 0.7286 | 3382.44 |
| Adsorbent | Omax (mg/g) | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Cerium-doped activated carbon | 5.88 | [46] |
| Polyaniline grafted chitosan | 14.33 | [35] |
| Copper ferrite/sepiolite/graphene oxide composite | 19.01 | [47] |
| Nickel ferrite | 21.11 | [22] |
| Polyethyleneimine | 22.73 | [45] |
| Nickel ferrite/graphene oxide composite | 74.62 | [23] |
| Cobalt ferrite/graphene oxide composite | 105.26 | [23] |
| Chitosan-Coated perlite beads | 178.6 | [34] |
| Chitosan-alginate beads | 207.00 | [39] |
| Modified biodegradable magnetic sorbent | 251.88 | [38] |
| PF800 | 322.58 | This study |
| PF600 | 377.36 | This study |
| Binary System | Adsorbent | Cd(II) | Pb(II) | Zn(II) | Cu(II) | Ca(II) | Mg(II) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(II)-Pb(II) | PF600 | 275.02 | 102.34 | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| PF800 | 229.02 | 93.56 | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | |
| Cd(II)-Zn(II) | PF600 | 287.24 | ---- | 90.12 | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| PF800 | 242.04 | ---- | 80.54 | ---- | ---- | ---- | |
| Cd(II)-Cu(II) | PF600 | 266.82 | ---- | ---- | 110.54 | ---- | ---- |
| PF800 | 216.35 | ---- | ---- | 106.23 | ---- | ---- | |
| Cd(II)-Ca(II) | PF600 | 207.13 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 170.23 | ---- |
| PF800 | 178.91 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 143.67 | ---- | |
| Cd(II)-Mg(II) | PF600 | 214.13 | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | 163.23 |
| PF800 | 184.35 | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | 138.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Basha, M.T. Enhanced Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media via Adsorption on Facilely Synthesized Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles. Molecules 2024, 29, 3711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153711
Al-Kadhi NS, Basha MT. Enhanced Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media via Adsorption on Facilely Synthesized Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153711
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Kadhi, Nada S., and Maram T. Basha. 2024. "Enhanced Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media via Adsorption on Facilely Synthesized Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153711
APA StyleAl-Kadhi, N. S., & Basha, M. T. (2024). Enhanced Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Media via Adsorption on Facilely Synthesized Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles. Molecules, 29(15), 3711. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153711





