Current Understanding of the Role of Adenosine Receptors in Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Adenosine Receptors
3. The Structure, Function, Mechanism of Action, Storage, Release, and Synthesis of Adenosine
3.1. Formation of Adenosine
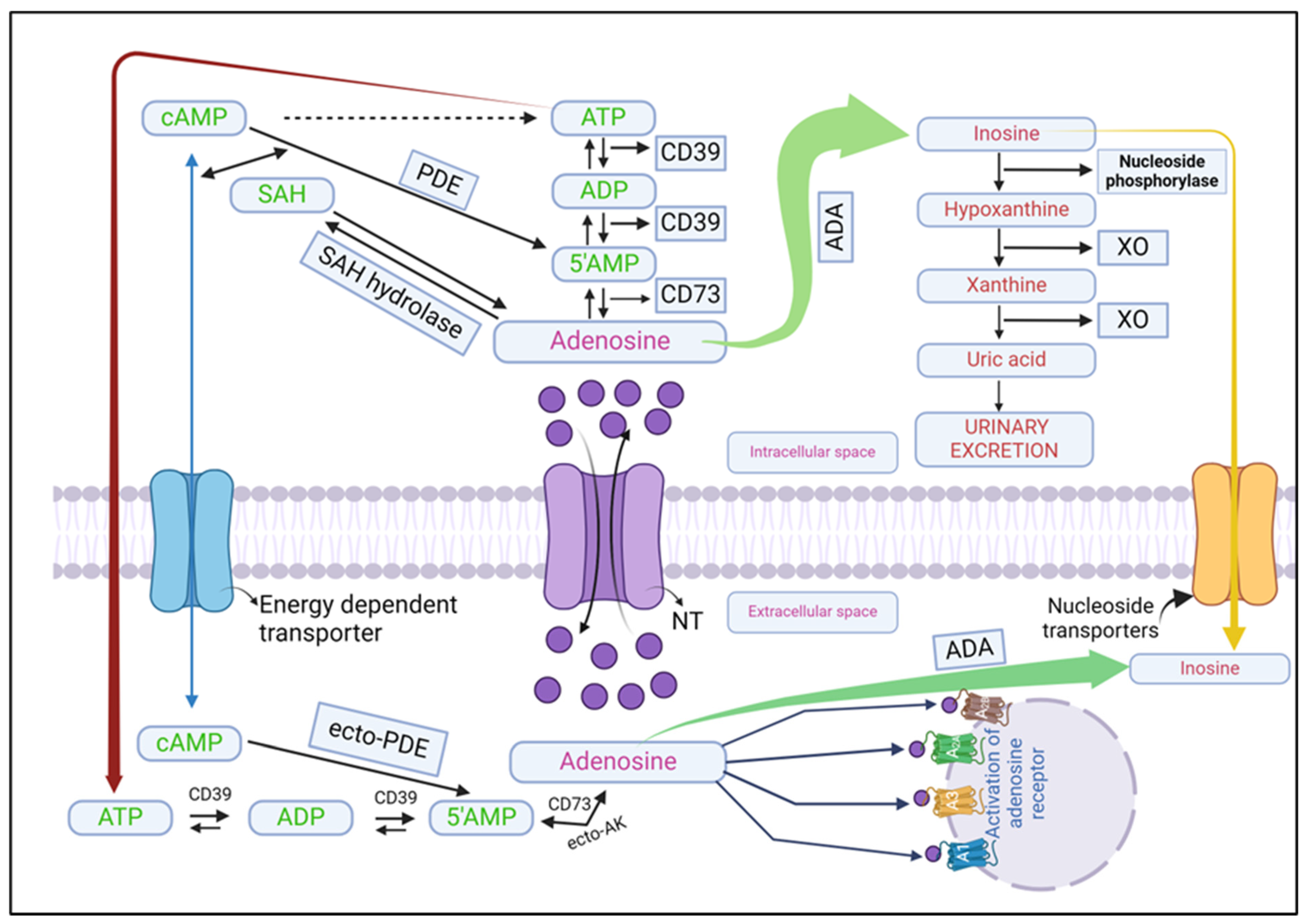
3.1.1. Extracellular Formation
3.1.2. Intracellular Formation
3.2. Adenosine Release
3.3. Adenosine Metabolism
4. The Significance of Adenosine Receptors in Cancer
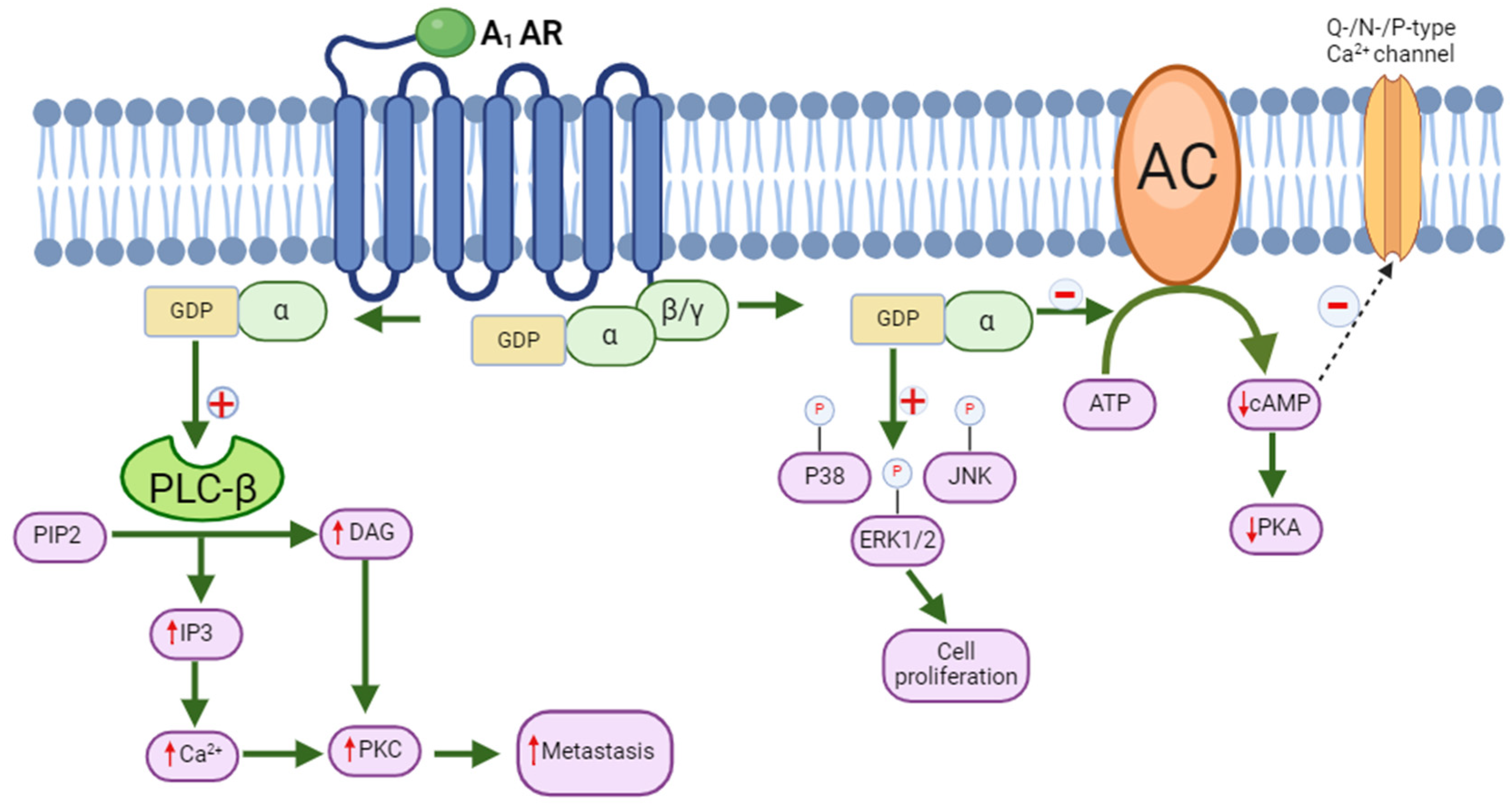
5. Molecular Signaling of A1 Adenosine Receptor and Its Role in Cancer
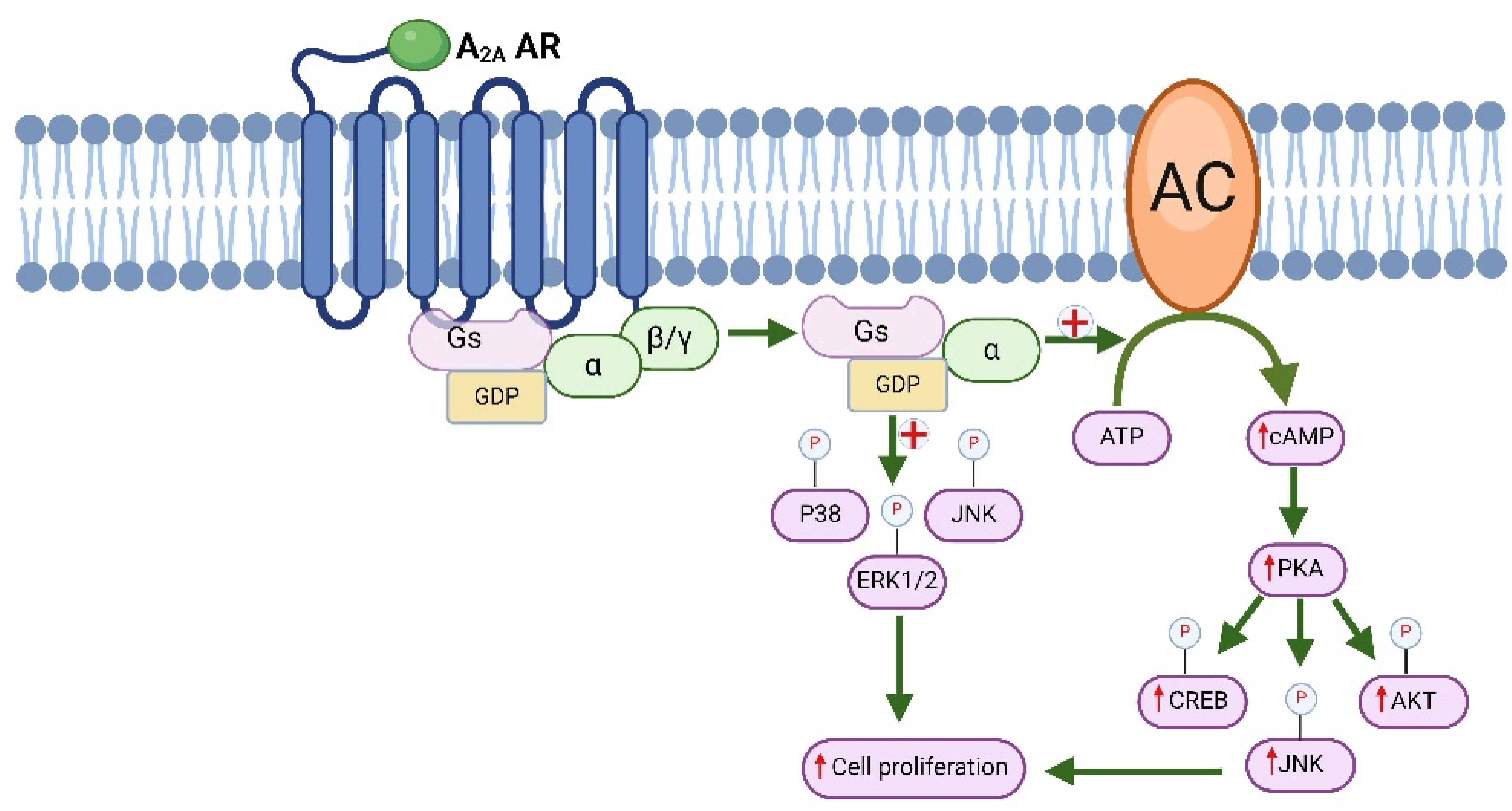
6. The Molecular Signaling Pathways Associated with A2 Adenosine Receptors and Their Involvement in Cancer
6.1. Molecular Signaling of Immunotherapy
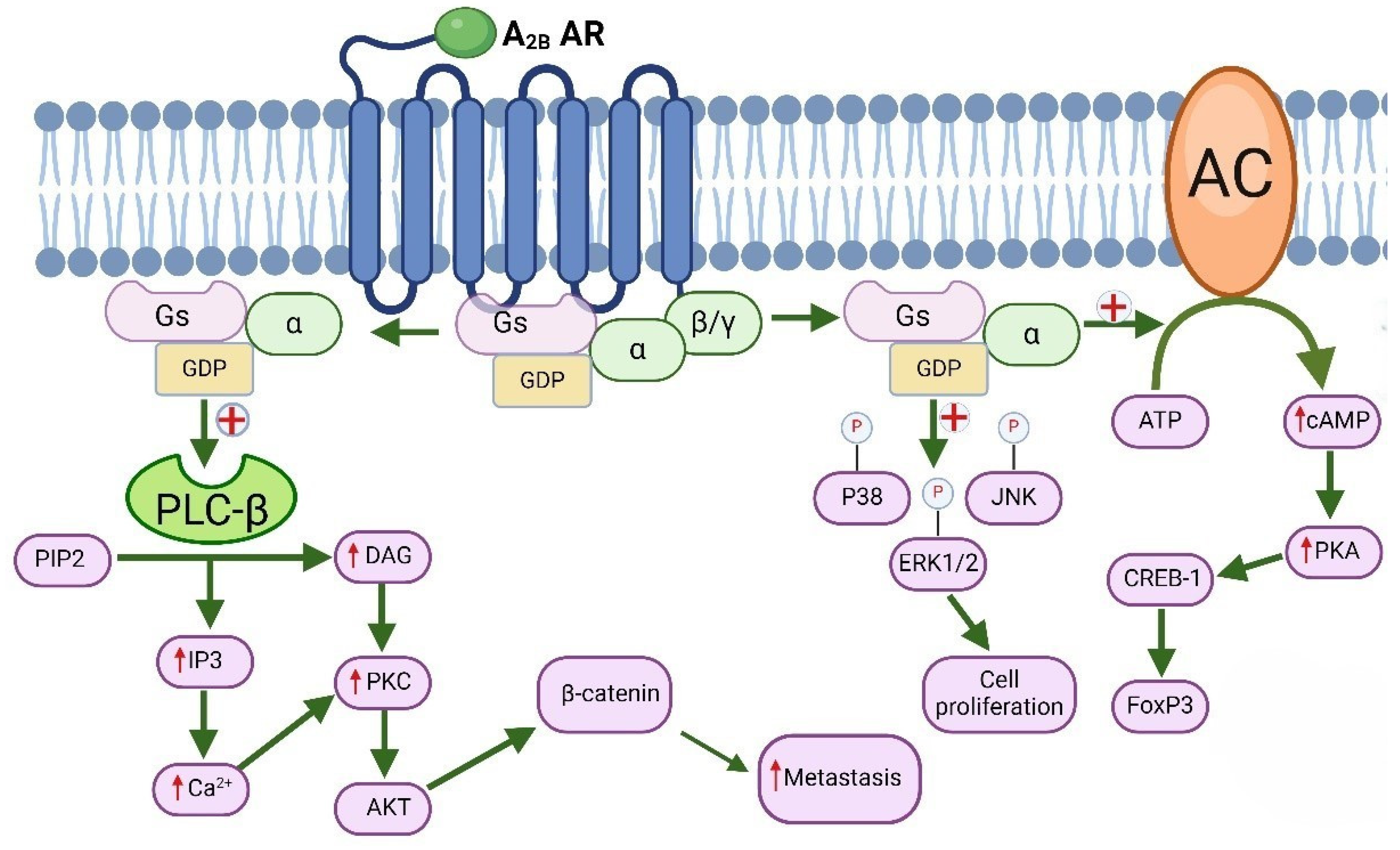
6.2. Molecular Signaling of A2B Adenosine Receptors and Their Role in Cancer
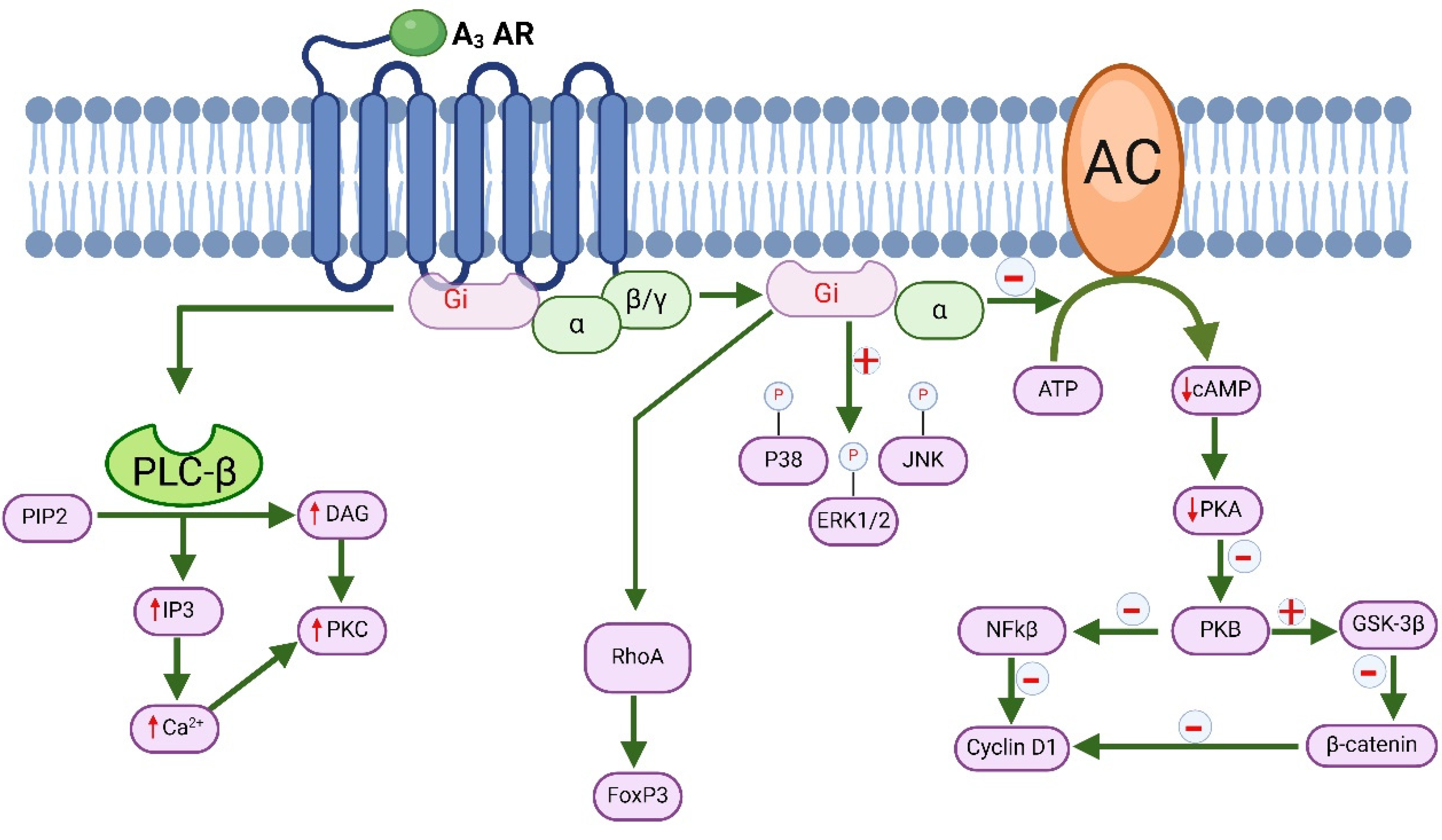
7. Molecular Signaling of A3 Adenosine Receptor and Its Role in Cancer
8. Adenosine Receptor Modulators: Potential Cancer Therapy
8.1. A1 AR Agonists and Antagonist
8.2. A2A Receptor Agonists
8.3. A2A Receptor Antagonists
8.4. A2B Receptor Antagonists
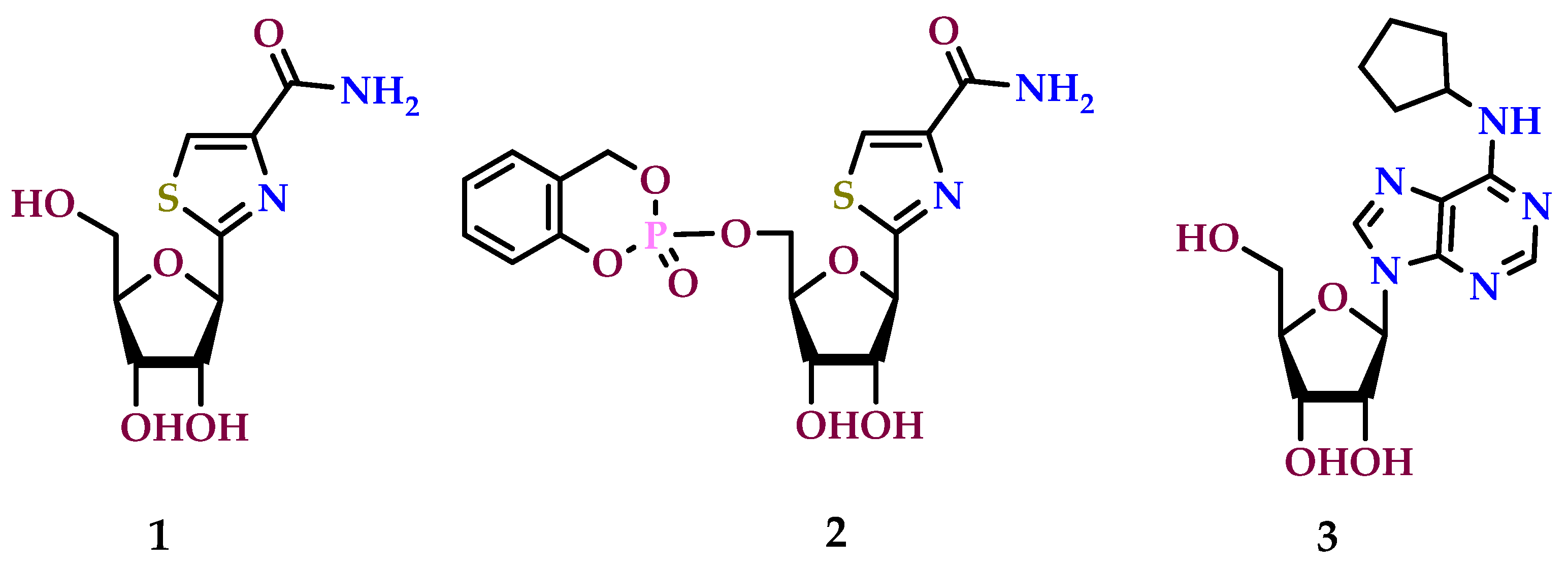
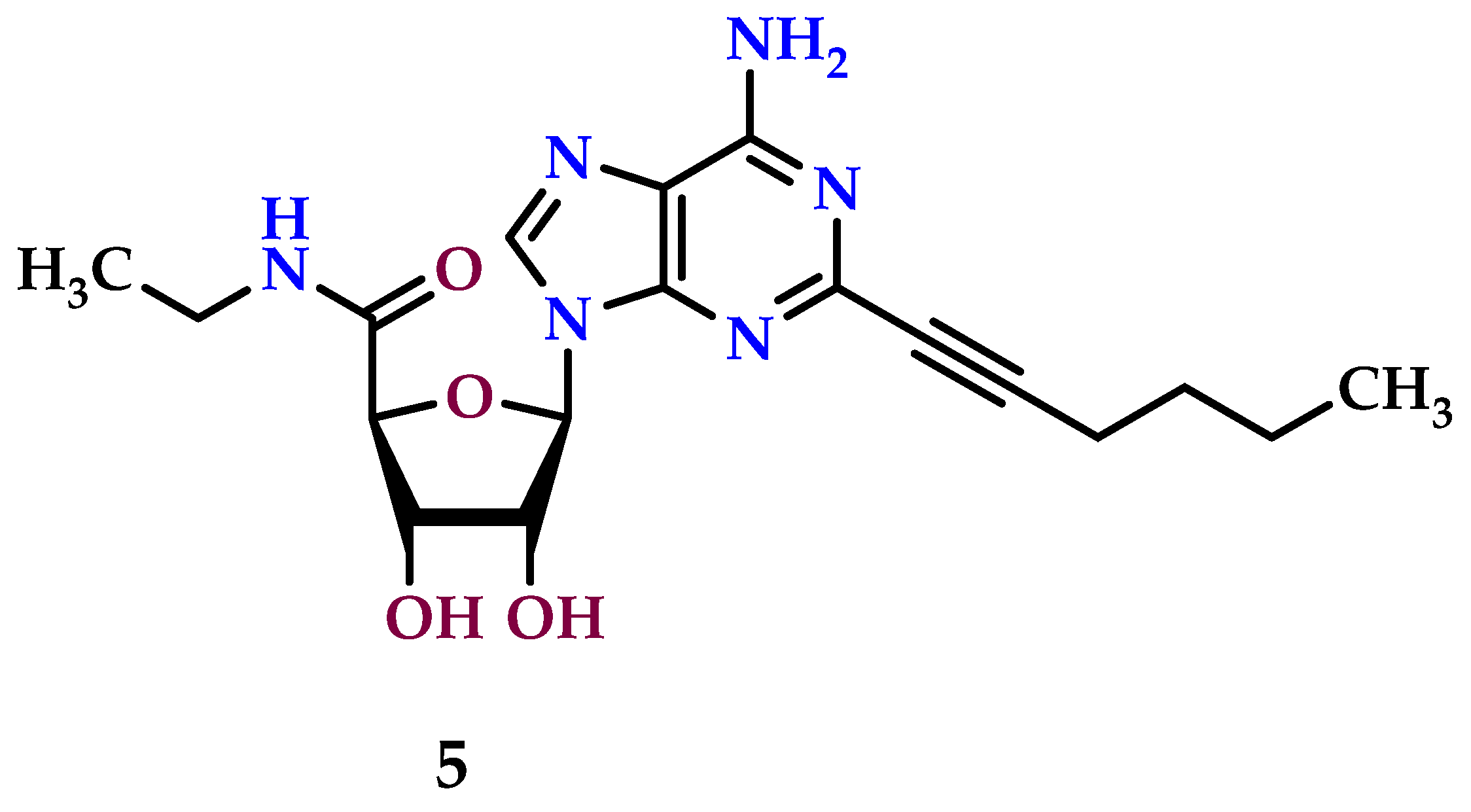
8.5. A3 Receptor Agonists
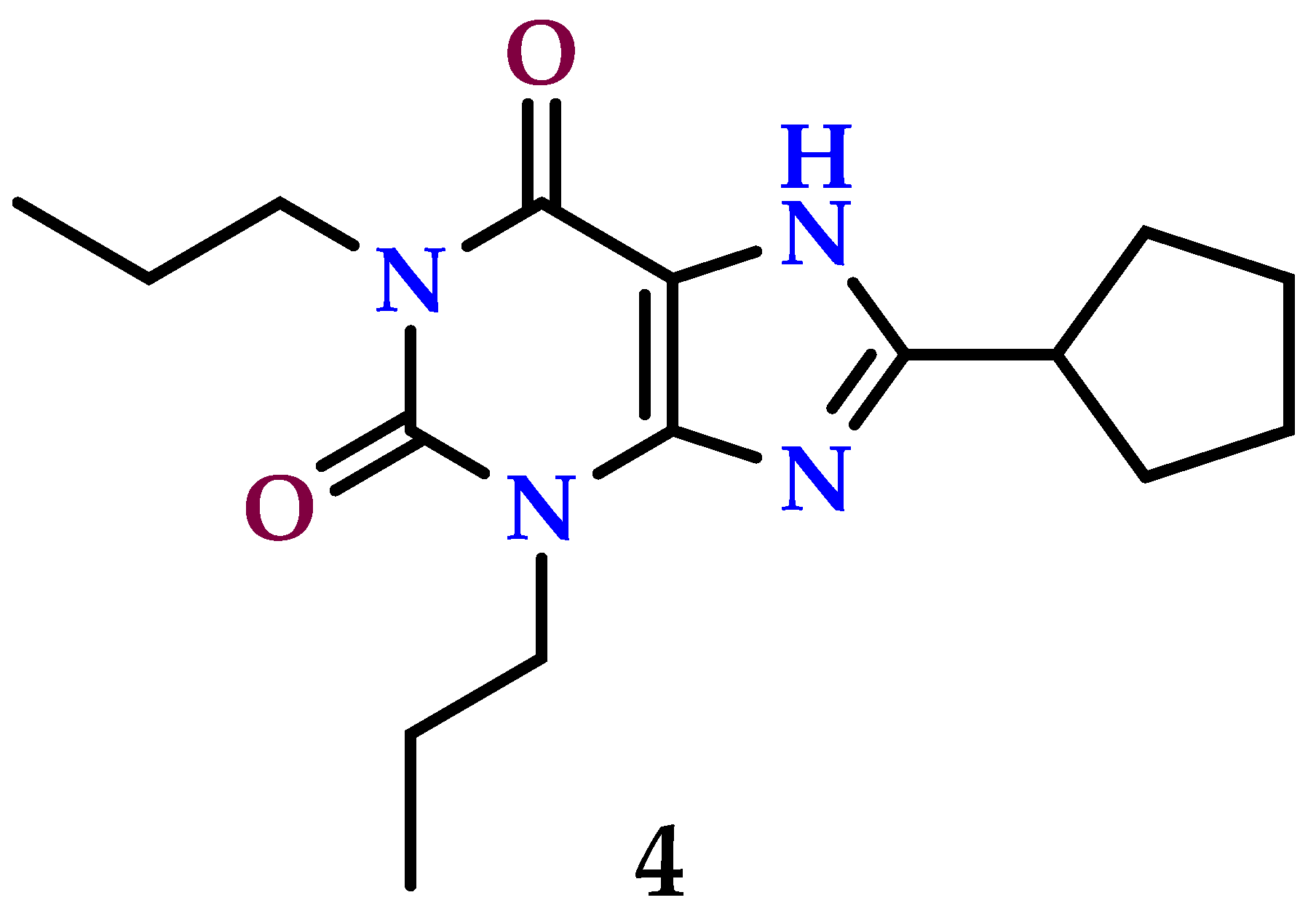
8.6. A3 Receptor Antagonist
9. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| A1 AR | A1 adenosine receptor |
| A2AAR | A2A adenosine receptor |
| A3 AR | A3 adenosine receptor |
| AC | Adenylyl cyclase |
| ADP | Adenosine diphosphate |
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| AK | Adenosine kinase |
| AR | Adenosine receptors |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CD3-AK | CD3-activated killer |
| CIITA | Class-II trans-activator |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CNTs | Concentrative nucleoside transporters |
| CPA | Cyclopentyl adenosine |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| CREB-1 | cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 |
| CVS | Cardiovascular system |
| CXCL10 | C-X-C motif chemokine 10 |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ecto-PDE | Ecto-phosphodiesterase |
| ENTs | Equilibrative nucleoside transporters |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| IP3 | Inositol trisphosphate |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| IRI | Ischemia-reperfusion injury |
| LAK | Lymphokine-activated killer |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MMP2 | Matrix metalloproteinase 2 |
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| PGS | Prostaglandins |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PLD | Phospholipase D |
| RCC | Renal cell carcinoma |
| SAH | S-adenosyl-homocysteine |
| SAHH | S-adenosyl-homocysteine hydrolase |
| SAMe | S-adenosylmethionine |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| VEGFs | Vascular endothelial growth factors |
References
- Khalil, D.N.; Smith, E.L.; Brentjens, R.J.; Wolchok, J.D. The future of cancer treatment: Immunomodulation, CARs and combination immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, K.M.; Rennert, P.D.; Freeman, G.J. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Hourani, W.; Darwish, W.; Hudaib, F.; Abu-Irmaileh, B.; Deb, P.K.; Venugopala, K.N.; Mohanlall, V.; Abu-Dahab, R.; Semreen, M.H. Molecular and metabolic alterations of 2, 3-dihydroquinazolin-4 (1 H)-one derivatives in prostate cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Hudaib, F.; Hourani, W.; Darwish, W.; Abu-Irmaileh, B.; Deb, P.K.; Venugopala, K.N.; Mohanlall, V.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Abu-Dahab, R. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach and in vitro assays revealed promising role of 2, 3-dihydroquinazolin-4 (1H)-one derivatives against colorectal cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 182, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Atyabi, F.; Rastegari, A.; Mollarazi, E.; Kiani, M.; Razavi, A.; Yousefi, M.; Kheshtchin, N.; Hassannia, H.; Hadjati, J.; et al. Downregulation of CD73 in 4T1 breast cancer cells through siRNA-loaded chitosan-lactate nanoparticles. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8403–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K. Recent updates in the computer aided drug design strategies for the discovery of agonists and antagonists of adenosine receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. Immunity, inflammation and cancer: A leading role for adenosine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blay, J.; White, T.D.; Hoskin, D.W. The extracellular fluid of solid carcinomas contains immunosuppressive concentrations of adenosine. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2602–2605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S.; Cattabriga, E.; Iannotta, V.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. A(3) adenosine receptors in human neutrophils and promyelocytic HL60 cells: A pharmacological and biochemical study. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Reynolds, T.; Blay, J. Adenosine as a possible inhibitor of killer T-cell activation in the microenvironment of solid tumours. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 59, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Reynolds, T.; Blay, J. Colon adenocarcinoma cells inhibit anti-CD3-activated killer cell induction. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1994, 38, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, W.M.; Hoskin, D.W.; Blay, J. Adenosine suppresses alpha(4)beta(7) integrin-mediated adhesion of T lymphocytes to colon adenocarcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 276, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Atyabi, F.; Rastegari, A.; Kheshtchin, N.; Arab, S.; Hassannia, H.; Ajami, M.; Mirsanei, Z.; Habibi, S.; Masoumi, F.; et al. CD73 specific siRNA loaded chitosan lactate nanoparticles potentiate the antitumor effect of a dendritic cell vaccine in 4T1 breast cancer bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2017, 246, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, P.K.; Deka, S.; Borah, P.; Abed, S.N.; Klotz, K.-N. Medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential of agonists, antagonists and allosteric modulators of A1 adenosine receptor: Current status and perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2697–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, D.P.; Balakumar, C.; Rao, A.R.; Roy, P.P.; Roy, K. QSAR of adenosine receptor antagonists: Exploring physicochemical requirements for binding of pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine derivatives with human adenosine A3 receptor subtype. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Klotz, K.N.; Linden, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 527–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors—An update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boison, D.; Yegutkin, G.G. Adenosine Metabolism: Emerging Concepts for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Fazzi, D.; Stefanelli, A.; Varani, K.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine receptor targeting in health and disease. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1591–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Varani, K. Adenosine as a Multi-Signalling Guardian Angel in Human Diseases: When, Where and How Does it Exert its Protective Effects? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: The State of the Art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Deb, P.K. Frontiers in Pharmacology of Neurotransmitters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, P.; Deka, S.; Mailavaram, R.P.; Deb, P.K. P1 receptor agonists/antagonists in clinical trials-potential drug candidates of the future. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2792–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, P.K. Therapeutic Potentials of Adenosine Receptors: The State of The Art. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2789–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K. Progress in the Development of Agonists, Antagonists and Allosteric Modulators of Adenosine Receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2695–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Samarneh, S.; Jaber, A.M.Y.; Kassab, G.; Agrawal, N. Therapeutic Potentials of A2B Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Current Status and Perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2741–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; Kokaz, S.F.; Abed, S.N.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Hourani, W.; Jaber, A.Y.; Mailavaram, R.P.; Kumar, P.; Venugopala, K.N. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors. In Frontiers in Pharmacology of Neurotransmitters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 325–359. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Michela, B.; Marucci, G.; Deb, P.K.; Morsy, M.A.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; Nair, A.B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; et al. Adenosine Receptor Activity of Methyl/ethyl 3-(substituted benzoyl)-6,8-dimethylindolizine-2-substituted-1-carboxylates. U.S. Patent 11974991B1, 7 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Deb, P.K.; Michela, B.; Marucci, G.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Venugopala, R. 7-Isopropyl 1,2-dimethyl 3-(substitutedbenzoyl)indolizine-1,2,7-tricarboxylates as Adenosine Receptor Active Compounds. U.S. Patent 11981673B1, 14 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine, an endogenous distress signal, modulates tissue damage and repair. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Navarro, G.; Reyes-Resina, I. Adenosine Receptor Antagonists to Combat Cancer and to Boost Anti-Cancer Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. Cells 2021, 10, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskovalova, T.; Huang, X.; Sitkovsky, M.; Zacharia, L.C.; Jackson, E.K.; Gorelik, E. Gs protein-coupled adenosine receptor signaling and lytic function of activated NK cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciruela, F.; Albergaria, C.; Soriano, A.; Cuffí, L.; Carbonell, L.; Sánchez, S.; Gandía, J.; Fernández-Dueñas, V. Adenosine receptors interacting proteins (ARIPs): Behind the biology of adenosine signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Irenius, E.; Kull, B.; Schulte, G. Comparison of the potency of adenosine as an agonist at human adenosine receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.; Chen, W.; Cobb, M.H. Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3100–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, Z.G.; Dhanasekaran, D.N. G Protein regulation of MAPK networks. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3122–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glukhova, A.; Thal, D.M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Vecchio, E.A.; Jörg, M.; Scammells, P.J.; May, L.T.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Structure of the Adenosine A(1) Receptor Reveals the Basis for Subtype Selectivity. Cell 2017, 168, 867–877.e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Deb, P.K.; Kachler, S.; Akkinepalli, R.R.; Mailavaram, R.; Klotz, K.-N. Synthesis and adenosine receptors binding studies of new fluorinated analogues of pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines and quinazolines. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offermanns, S.; Simon, M.I. G alpha 15 and G alpha 16 couple a wide variety of receptors to phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15175–15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco, P.; Diniz, C.; Gonçalves, J. Facilitation of noradrenaline release by activation of adenosine A(2A) receptors triggers both phospholipase C and adenylate cyclase pathways in rat tail artery. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Mailavaram, R.; Tekade, R.K.; Jaber, A.M.Y. Molecular modeling approaches for the discovery of adenosine A2B receptor antagonists: Current status and future perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1854–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Gupta, M. Adenosine and its receptors as therapeutic targets: An overview. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlágh, B.; Vizi, E.S. The role of extracellular adenosine in chemical neurotransmission in the hippocampus and Basal Ganglia: Pharmacological and clinical aspects. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dux, E.; Fastbom, J.; Ungerstedt, U.; Rudolphi, K.; Fredholm, B.B. Protective effect of adenosine and a novel xanthine derivative propentofylline on the cell damage after bilateral carotid occlusion in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 1990, 516, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Trivedi, B.K.; Churchill, P.C.; Williams, M. Novel therapeutics acting via purine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 41, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layland, J.; Carrick, D.; Lee, M.; Oldroyd, K.; Berry, C. Adenosine: Physiology, pharmacology, and clinical applications. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latini, S.; Pedata, F. Adenosine in the central nervous system: Release mechanisms and extracellular concentrations. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-F.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine receptors as drug targets—What are the challenges? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, J.B.; Diniz, C. The Adenosinergic System as a Therapeutic Target in the Vasculature: New Ligands and Challenges. Molecules 2017, 22, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H. Extracellular metabolism of ATP and other nucleotides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinho, R.O.; Duarte, T.; Pacini, E.S. New perspectives in signaling mediated by receptors coupled to stimulatory G protein: The emerging significance of cAMP efflux and extracellular cAMP-adenosine pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleli, M.; Fredholm, B.B.; Sobrevia, L.; Carlström, M. Pharmacological targeting of adenosine receptor signaling. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 55, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, R.F. Adenosine receptors. Roles and pharmacology. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 603, 211–225, discussion 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkovsky, M.V.; Lukashev, D.; Apasov, S.; Kojima, H.; Koshiba, M.; Caldwell, C.; Ohta, A.; Thiel, M. Physiological control of immune response and inflammatory tissue damage by hypoxia-inducible factors and adenosine A2A receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 657–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitkovsky, M.; Lukashev, D. Regulation of immune cells by local-tissue oxygen tension: HIF1α and adenosine receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.H.; Raoofi Mohseni, S.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Anvari, E.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2032–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Elsaadi, S.; Misund, K.; Abdollahi, P.; Vandsemb, E.N.; Moen, S.H.; Kusnierczyk, A.; Slupphaug, G.; Standal, T.; Waage, A.; et al. Conversion of ATP to adenosine by CD39 and CD73 in multiple myeloma can be successfully targeted together with adenosine receptor A2A blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A. Adenosine receptors. In Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Boison, D. Regulation of Extracellular Adenosine. In The Adenosine Receptors; Borea, P.A., Varani, K., Gessi, S., Merighi, S., Vincenzi, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizterlands, 2018; pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bjursell, M.K.; Blom, H.J.; Cayuela, J.A.; Engvall, M.L.; Lesko, N.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Brandberg, G.; Halldin, M.; Falkenberg, M.; Jakobs, C.; et al. Adenosine kinase deficiency disrupts the methionine cycle and causes hypermethioninemia, encephalopathy, and abnormal liver function. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, J.D. The metabolism of homocysteine: Pathways and regulation. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1998, 157 (Suppl. S2), S40–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; Mailavaram, R.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Kaki, V.R.; Kaur, R.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.N.; Akkinepally, R.R. Synthesis, adenosine receptor binding and molecular modelling studies of novel thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, N.T.; Elliott, M.B.; Oshinsky, M.L. The Role of Adenosine Signaling in Headache: A Review. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bynoe, M.S.; Viret, C.; Yan, A.; Kim, D.-G. Adenosine receptor signaling: A key to opening the blood–brain door. Fluids Barriers CNS 2015, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deussen, A.; Bading, B.; Kelm, M.; Schrader, J. Formation and salvage of adenosine by macrovascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264, H692–H700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deussen, A. Metabolic flux rates of adenosine in the heart. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deussen, A.; Stappert, M.; Schäfer, S.; Kelm, M. Quantification of extracellular and intracellular adenosine production: Understanding the transmembranous concentration gradient. Circulation 1999, 99, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boison, D. Adenosine kinase: Exploitation for therapeutic gain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 906–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia, E.; Farré, D.; Cortés, A.; Ferrer-Costa, C.; Orozco, M.; Mallol, J.; Lluís, C.; Canela, E.I.; McCormick, P.J.; Franco, R.; et al. The catalytic site structural gate of adenosine deaminase allosterically modulates ligand binding to adenosine receptors. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, R.; Martinez-Navio, J.M.; Lejeune, M.; Climent, N.; Oliva, H.; Gatell, J.M.; Gallart, T.; Mallol, J.; Lluis, C.; Franco, R. CD26, adenosine deaminase, and adenosine receptors mediate costimulatory signals in the immunological synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9583–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, S.; Mirandola, P.; Varani, K.; Gessi, S.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Borea, P.A. A glance at adenosine receptors: Novel target for antitumor therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 100, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Reynolds, T.; Blay, J. 2-Chloroadenosine inhibits the MHC-unrestricted cytolytic activity of anti-CD3-activated killer cells: Evidence for the involvement of a non-A1/A2 cell-surface adenosine receptor. Cell. Immunol. 1994, 159, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Butler, J.J.; Drapeau, D.; Haeryfar, S.M.M.; Blay, J. Adenosine acts through an A3 receptor to prevent the induction of murine anti-CD3-activated killer T cells. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P.; Kallinowski, F.; Okunieff, P. Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic microenvironment of human tumors: A review. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 6449–6465. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarella, A.M.; Ryu, Y.K.; Manji, G.A.; Rustgi, A.K. Extracellular ATP and Adenosine in Cancer Pathogenesis and Treatment. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 731–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegutkin, G.G.; Boison, D. ATP and Adenosine Metabolism in Cancer: Exploitation for Therapeutic Gain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 797–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signaling and vascular cell proliferation and death. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Daele, P.; Van Coevorden, A.; Roger, P.P.; Boeynaems, J.M. Effects of adenine nucleotides on the proliferation of aortic endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 1992, 70, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Arslan, G.; Halldner, L.; Kull, B.; Schulte, G.; Wasserman, W. Structure and function of adenosine receptors and their genes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.J.; Lindon, A.C.; Flint, K.J.; Jones, N.C.; Goodbourn, S. Activating transcription factor-1 is a specific antagonist of the cyclic adenosine 3′.5′-monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding protein-1-mediated response to cAMP. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Basheer, R.; Arrigoni, E.; Thatte, H.S.; Greene, R.W.; Ambudkar, I.S.; McCarley, R.W. Adenosine induces inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-mediated mobilization of intracellular calcium stores in basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7680–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, G.E.; Codina, J.; Birnbaumer, L.; Brown, A.M. Coupling of ATP-sensitive K+ channels to A1 receptors by G proteins in rat ventricular myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, H820–H826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduri, S.; Dick, G.; Nayeem, M.; Mustafa, S. Adenosine A(1) receptor signaling inhibits BK channels through a PKCα-dependent mechanism in mouse aortic smooth muscle. Physiol. Rep. 2013, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, I.; Grün, M.; Böhmer, F.D.; Rubio, I. Role of cAMP in the promotion of colorectal cancer cell growth by prostaglandin E2. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Frank, D.A. CREB in the pathophysiology of cancer: Implications for targeting transcription factors for cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettcher, M.; Lawson, A.; Ladenburger, V.; Fredebohm, J.; Wolf, J.; Hoheisel, J.D.; Frezza, C.; Shlomi, T. High throughput synthetic lethality screen reveals a tumorigenic role of adenylate cyclase in fumarate hydratase-deficient cancer cells. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.J.; Yu, J.K.; Ge, W.T.; Hu, H.G.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, S. SPARCL1, Shp2, MSH2, E-cadherin, p53, ADCY-2 and MAPK are prognosis-related in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Goh, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Hwang, J.A.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.J.; Seo, H.; Park, J.H.; Suzuki, H.; Yamamoto, E.; et al. Upregulation of adenylate cyclase 3 (ADCY3) increases the tumorigenic potential of cells by activating the CREB pathway. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1791–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Smith, R.A.; Stone, T.W. Purine suppression of proliferation of Sertoli-like TM4 cells in culture. Cell Prolif. 1995, 28, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synowitz, M.; Glass, R.; Färber, K.; Markovic, D.; Kronenberg, G.; Herrmann, K.; Schnermann, J.; Nolte, C.; van Rooijen, N.; Kiwit, J.; et al. A1 adenosine receptors in microglia control glioblastoma-host interaction. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8550–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Yee, G.S.; Bhattamisra, S.K. Adenosine Receptors as Novel Targets for the Treatment of Various Cancers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2828–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; King, G.L.; Robinson, G.S.; Ferrara, N.; Aiello, L.P. Adenosine mediates hypoxic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor in retinal pericytes and endothelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Gebicke-Haerter, P.J.; Christoffel, F.; Timmer, J.; Northoff, H.; Berger, M.; Van Calker, D. Both adenosine A1- and A2-receptors are required to stimulate microglial proliferation. Neurochem. Int. 1996, 29, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, T.; Borse, V.; Sheth, S.; Sheehan, K.; Ghosh, S.; Tupal, S.; Jajoo, S.; Mukherjea, D.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Adenosine A1 Receptor Protects Against Cisplatin Ototoxicity by Suppressing the NOX3/STAT1 Inflammatory Pathway in the Cochlea. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3962–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blay, J. Adenosine and Tumor Microenvironment. In Encyclopedia of Cancer; Schwab, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Bruchard, M.; Chalmin, F.; Rébé, C. Production of adenosine by ectonucleotidases: A key factor in tumor immunoescape. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 473712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Basso, A.; Black, S.; Malkowski, M.; Kwee, L.; Pachter, J.A.; Lachowicz, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. RNA interference targeting of A1 receptor-overexpressing breast carcinoma cells leads to diminished rates of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, L.; Chu, X.; Deng, F.; Tang, J.; Tang, Y.; Dai, Y. The Adenosine A1 Receptor Antagonist DPCPX Inhibits Tumor Progression via the ERK/JNK Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, D.; Baraldi, P.G.; Moorman, A.R.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. History and perspectives of A2A adenosine receptor antagonists as potential therapeutic agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2015, 35, 790–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.A.; Agha, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.; Nassar, N.N. Role of adenosine A2A receptor in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury: Signaling to phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (pERK1/2). Neuroscience 2016, 314, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessi, S.; Bencivenni, S.; Battistello, E.; Vincenzi, F.; Colotta, V.; Catarzi, D.; Varano, F.; Merighi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Inhibition of A(2A) Adenosine Receptor Signaling in Cancer Cells Proliferation by the Novel Antagonist TP455. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, H. Adenosine in cancer immunotherapy: Taking off on a new plane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 189005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterfreund, R.A.; MacCollin, M.; Gusella, J.; Fink, J.S. Characterization and expression of the human A2a adenosine receptor gene. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.J.; Li, W.; Chen, J.F. Normal and abnormal functions of adenosine receptors in the central nervous system revealed by genetic knockout studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 1358–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskó, G.; Linden, J.; Cronstein, B.; Pacher, P. Adenosine receptors: Therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and immune diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, J.; Toselli, P.; Bhawan, J.; Sudireddy, V.; Taylor, L.; Polgar, P. Angiotensin II type 1 and bradykinin B2 receptors expressed in early stage epithelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pathological overproduction: The bad side of adenosine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Haegele, S.; Muller, L.; Whiteside, T.L. Immunoregulatory activity of adenosine and its role in human cancer progression. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etique, N.; Grillier-Vuissoz, I.; Lecomte, J.; Flament, S. Crosstalk between adenosine receptor (A2A isoform) and ERalpha mediates ethanol action in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszałka, P.; Gołuńska, M.; Urban, A.; Stasiłojć, G.; Stanisławowski, M.; Majewski, M.; Składanowski, A.C.; Bigda, J. Specific Activation of A3, A2A and A1 Adenosine Receptors in CD73-Knockout Mice Affects B16F10 Melanoma Growth, Neovascularization, Angiogenesis and Macrophage Infiltration. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Aso, M.; Mediero, A.; Low, Y.C.; Levine, J.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A2A receptor plays an important role in radiation-induced dermal injury. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavis, P.A.; Divisekera, U.; Paget, C.; Chow, M.T.; John, L.B.; Devaud, C.; Dwyer, K.; Stagg, J.; Smyth, M.J.; Darcy, P.K. Blockade of A2A receptors potently suppresses the metastasis of CD73+ tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14711–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waickman, A.T.; Alme, A.; Senaldi, L.; Zarek, P.E.; Horton, M.; Powell, J.D. Enhancement of tumor immunotherapy by deletion of the A2A adenosine receptor. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Olah, M.E. Cyclic AMP-dependent, protein kinase A-independent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 following adenosine receptor stimulation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Role of exchange protein activated by cAMP 1 (Epac1). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, P.; Hinze, A.V.; Harst, A.; von Kügelgen, I. A₂B receptors mediate the induction of early genes and inhibition of arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation via Epac. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Benini, A.; Mirandola, P.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Leung, E.; Maclennan, S.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. Hypoxia inhibits paclitaxel-induced apoptosis through adenosine-mediated phosphorylation of bad in glioblastoma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, P. Adenosine A2B Receptor: From Cell Biology to Human Diseases. Front. Chem. 2016, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-G.; Jacobson, K.A. A2B Adenosine Receptor and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, E.A.; White, P.J.; May, L.T. The adenosine A(2B) G protein-coupled receptor: Recent advances and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 198, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, N.K. The Inactivation of ERK1/2, p38 and NF-kB Is Involved in the Down-Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis and Function by A2B Adenosine Receptor Stimulation. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscsó, B.; Csóka, B.; Selmeczy, Z.; Himer, L.; Pacher, P.; Virág, L.; Haskó, G. Adenosine augments IL-10 production by microglial cells through an A2B adenosine receptor-mediated process. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Bencivenni, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K.; Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S. A(2B) adenosine receptors stimulate IL-6 production in primary murine microglia through p38 MAPK kinase pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.; Svejda, B.; Gustafsson, B.I.; Granlund, A.B.; Sandvik, A.K.; Timberlake, A.; Sumpio, B.; Pfragner, R.; Modlin, I.M.; Kidd, M. The role of mechanical forces and adenosine in the regulation of intestinal enterochromaffin cell serotonin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G397–G405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xin, W.; Yang, X.M.; Kuno, A.; Rich, T.C.; Cohen, M.V.; Downey, J.M. A2B adenosine receptors inhibit superoxide production from mitochondrial complex I in rabbit cardiomyocytes via a mechanism sensitive to Pertussis toxin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phosri, S.; Arieyawong, A.; Bunrukchai, K.; Parichatikanond, W.; Nishimura, A.; Nishida, M.; Mangmool, S. Stimulation of Adenosine A(2B) Receptor Inhibits Endothelin-1-Induced Cardiac Fibroblast Proliferation and α-Smooth Muscle Actin Synthesis Through the cAMP/Epac/PI3K/Akt-Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phosri, S.; Bunrukchai, K.; Parichatikanond, W.; Sato, V.H.; Mangmool, S. Epac is required for exogenous and endogenous stimulation of adenosine A(2B) receptor for inhibition of angiotensin II-induced collagen synthesis and myofibroblast differentiation. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Du, C.; Lv, J.; Zhao, G.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Haskó, G.; Xie, X. Blocking A2B adenosine receptor alleviates pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via inhibition of IL-6 production and Th17 differentiation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D.; Turcotte, M.; Stagg, J. Targeting A2 adenosine receptors in cancer. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigano, S.; Alatzoglou, D.; Irving, M.; Ménétrier-Caux, C.; Caux, C.; Romero, P.; Coukos, G. Targeting Adenosine in Cancer Immunotherapy to Enhance T-Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chu, X.; Deng, F.; Tong, L.; Tong, G.; Yi, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Tang, Y.; Xia, Y.; et al. The adenosine A2b receptor promotes tumor progression of bladder urothelial carcinoma by enhancing MAPK signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48755–48768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, G.; Fredholm, B.B. Signalling from adenosine receptors to mitogen-activated protein kinases. Cell. Signal. 2003, 15, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntantie, E.; Gonyo, P.; Lorimer, E.L.; Hauser, A.D.; Schuld, N.; McAllister, D.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Dwinell, M.B.; Auchampach, J.A.; Williams, C.L. An adenosine-mediated signaling pathway suppresses prenylation of the GTPase Rap1B and promotes cell scattering. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmet, C.J.; Gallenne, T.; Prieur, A.; Reyal, F.; Visser, N.L.; Wittner, B.S.; Smit, M.A.; Geiger, T.R.; Laoukili, J.; Iskit, S.; et al. Identification of a pharmacologically tractable Fra-1/ADORA2B axis promoting breast cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5139–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Xia, J.; Wu, X.; Kong, H.; Wang, H.; Xie, W.; Xu, Y. Adenosine signaling inhibits CIITA-mediated MHC class II transactivation in lung fibroblast cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekic, C.; Sag, D.; Li, Y.; Theodorescu, D.; Strieter, R.M.; Linden, J. Adenosine A2B receptor blockade slows growth of bladder and breast tumors. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Madi, L.; Cohn, I. A3 adenosine receptor as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer. Drugs 2002, 13, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Ohana, G.; Barer, F.; Ochaion, A.; Erlanger, A.; Madi, L. An agonist to the A3 adenosine receptor inhibits colon carcinoma growth in mice via modulation of GSK-3 beta and NF-kappa B. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Liang, B.T.; Jacobson, K.A. Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of A3 adenosine receptor agonists. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarberg, C.; Schulte, G.; Fredholm, B.B. Evidence for functional adenosine A3 receptors in microglia cells. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neary, J.T.; McCarthy, M.; Kang, Y.; Zuniga, S. Mitogenic signaling from P1 and P2 purinergic receptors to mitogen-activated protein kinase in human fetal astrocyte cultures. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 242, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Woo, J.S. The adenosine A3 receptor agonist Cl-IB-MECA induces cell death through Ca²⁺/ROS-dependent down regulation of ERK and Akt in A172 human glioma cells. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.; Pingle, S.C.; Hallam, D.M.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Activation of the adenosine A3 receptor in RAW 264.7 cells inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha release by reducing calcium-dependent activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessi, S.; Sacchetto, V.; Fogli, E.; Merighi, S.; Varani, K.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Leung, E.; Maclennan, S.; Borea, P.A. Modulation of metalloproteinase-9 in U87MG glioblastoma cells by A3 adenosine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S. The A3 adenosine receptor: History and perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 74–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, L.; Ochaion, A.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Erlanger, A.; Ohana, G.; Harish, A.; Merimski, O.; Barer, F.; Fishman, P. The A3 adenosine receptor is highly expressed in tumor versus normal cells: Potential target for tumor growth inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4472–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Rotondo, J.C.; Lanzillotti, C.; Campione, G.; Martini, F.; Tognon, M. Cancer biology and molecular genetics of A3 adenosine receptor. Oncogene 2022, 41, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Benini, A.; Mirandola, P.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Leung, E.; Maclennan, S.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine modulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in human glioblastoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madi, L.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Barer, F.; Ardon, E.; Ochaion, A.; Fishman, P. A3 adenosine receptor activation in melanoma cells: Association between receptor fate and tumor growth inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42121–42130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S.; Morelli, A.; Ferrari, D.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Spalluto, G.; Borea, P.A. Pharmacological and biochemical characterization of A3 adenosine receptors in Jurkat T cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Makaritsis, K.; Francis, C.E.; Gavras, H.; Ravid, K. A role for the A3 adenosine receptor in determining tissue levels of cAMP and blood pressure: Studies in knock-out mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1500, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajoo, S.; Mukherjea, D.; Watabe, K.; Ramkumar, V. Adenosine A(3) receptor suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by inhibiting NADPH oxidase activity. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Stemmer, S.M.; Zozulya, G.; Ochaion, A.; Patoka, R.; Barer, F.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Jacobson, K.A.; Fishman, P. CF102 an A3 adenosine receptor agonist mediates anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory effects in the liver. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, K.; Maniero, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Targa, M.; Stefanelli, A.; Maniscalco, P.; Martini, F.; Tognon, M.; Borea, P.A. A₃ receptors are overexpressed in pleura from patients with mesothelioma and reduce cell growth via Akt/nuclear factor-κB pathway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Min, H.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Park, E.J.; Shin, D.H.; Jeong, L.S.; Lee, S.K. A novel adenosine analog, thio-Cl-IB-MECA, induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Barer, F.; Madi, L.; Multani, A.S.; Pathak, S. The A3 adenosine receptor as a new target for cancer therapy and chemoprotection. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 269, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naffouje, R.; Grover, P.; Yu, H.; Sendilnathan, A.; Wolfe, K.; Majd, N.; Smith, E.P.; Takeuchi, K.; Senda, T.; Kofuji, S.; et al. Anti-Tumor Potential of IMP Dehydrogenase Inhibitors: A Century-Long Story. Cancers 2019, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwein, S.; Mishra, B.; De, U.C.; Acharya, P.C. Recent Progress of Adenosine Receptor Modulators in the Development of Anticancer Chemotherapeutic Agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2842–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellacci, L.; Barboni, G.; Franchetti, P.; Martini, C.; Jayaram, H.N.; Grifantini, M. A new tiazofurin pronucleotide: Synthesis and biological evaluation of cyclosaligenyl-tiazofurin monophosphate. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2003, 22, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Synowitz, M.; Powell, J.D.; Klotz, K.N.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine receptors and cancer. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 1808, 399–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, K.N. Adenosine receptors and their ligands. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, K.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Klotz, K.N.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Cacciari, B.; Romagnoli, R.; Spalluto, G.; Borea, P.A. [(3)H]MRE 3008F20: A novel antagonist radioligand for the pharmacological and biochemical characterization of human A(3) adenosine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 968–975. [Google Scholar]
- Merighi, S.; Mirandola, P.; Milani, D.; Varani, K.; Gessi, S.; Klotz, K.N.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine receptors as mediators of both cell proliferation and cell death of cultured human melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkovsky, M.V.; Kjaergaard, J.; Lukashev, D.; Ohta, A. Hypoxia-adenosinergic immunosuppression: Tumor protection by T regulatory cells and cancerous tissue hypoxia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5947–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Sult, E.; Hay, C.; Blake, S.J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Takeda, K.; Teng, M.W.L.; et al. Co-inhibition of CD73 and A2AR Adenosine Signaling Improves Anti-tumor Immune Responses. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.; Gorelik, E.; Prasad, S.J.; Ronchese, F.; Lukashev, D.; Wong, M.K.K.; Huang, X.; Caldwell, S.; Liu, K.; Smith, P.; et al. A2A adenosine receptor protects tumors from antitumor T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13132–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, R.; Miele, L.; Maiolino, P.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. Adenosine limits the therapeutic effectiveness of anti-CTLA4 mAb in a mouse melanoma model. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Fan, J.; Wang, L.; Thompson, L.F.; Liu, A.; Daniel, B.J.; Shin, T.; Curiel, T.J.; Zhang, B. CD73 on tumor cells impairs antitumor T-cell responses: A novel mechanism of tumor-induced immune suppression. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavis, P.A.; Milenkovski, N.; Henderson, M.A.; John, L.B.; Allard, B.; Loi, S.; Kershaw, M.H.; Stagg, J.; Darcy, P.K. Adenosine Receptor 2A Blockade Increases the Efficacy of Anti-PD-1 through Enhanced Antitumor T-cell Responses. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, B.; Hao, S. Adenosine-A2A Receptor Pathway in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 837230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willingham, S.B.; Ho, P.Y.; Hotson, A.; Hill, C.; Piccione, E.C.; Hsieh, J.; Liu, L.; Buggy, J.J.; McCaffery, I.; Miller, R.A. A2AR Antagonism with CPI-444 Induces Antitumor Responses and Augments Efficacy to Anti-PD-(L)1 and Anti-CTLA-4 in Preclinical Models. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaffery, I.; Laport, G.; Hotson, A.; Willingham, S.; Patnaik, A.; Beeram, M.; Miller, R. Biomarker and clinical activity of CPI-444, a novel small molecule inhibitor of A2A receptor (A2AR), in a Ph1b study in advanced cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, vi124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Venugopala, K.N. Targeting the DNA damage response machinery for lung cancer treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churov, A.; Zhulai, G. Targeting adenosine and regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediavilla-Varela, M.; Castro, J.; Chiappori, A.; Noyes, D.; Hernandez, D.C.; Allard, B.; Stagg, J.; Antonia, S.J. A Novel Antagonist of the Immune Checkpoint Protein Adenosine A2a Receptor Restores Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Activity in the Context of the Tumor Microenvironment. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Battistello, E.; Giacomelli, L.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S. Targeting A3 and A2A adenosine receptors in the fight against cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappori, A.; Williams, C.; Creelan, B.; Tanvetyanon, T.; Gray, J.; Haura, E.; Thapa, R.; Chen, D.-T.; Beg, A.; Boyle, T.; et al. Phase I/II study of the A2AR antagonist NIR178 (PBF-509), an oral immunotherapy, in patients (pts) with advanced NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, A.; Andrews, S.P.; Marshall, F.H. Structurally Enabled Discovery of Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, L.; Hotson, A.; Powderly, J.D.; Sznol, M.; Heist, R.S.; Choueiri, T.K.; George, S.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Shepard, D.R.; et al. Adenosine 2A Receptor Blockade as an Immunotherapy for Treatment-Refractory Renal Cell Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Maa, T.; Wang, U.; Feoktistov, I.; Biaggioni, I.; Belardinelli, L. Expression and function of A2B adenosine receptors in the U87MG tumor cells. Drug Dev. Res. 2003, 58, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.; Ward, E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, D.; Sinha, D.; Barkauskas, D.; Young, A.; Kalimutho, M.; Stannard, K.; Caramia, F.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Stagg, J.; Khanna, K.K.; et al. Adenosine 2B Receptor Expression on Cancer Cells Promotes Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, W.; Tanaka, S.; Tsukimoto, M.; Kojima, S. Adenosine A2B receptor antagonist PSB603 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting induction of regulatory T cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mølck, C.; Ryall, J.; Failla, L.M.; Coates, J.L.; Pascussi, J.-M.; Heath, J.K.; Stewart, G.; Hollande, F. The A2b adenosine receptor antagonist PSB-603 promotes oxidative phosphorylation and ROS production in colorectal cancer cells via adenosine receptor-independent mechanism. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, S.; Miele, L. Targeting the adenosine A2b receptor in the tumor microenvironment overcomes local immunosuppression by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e27989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, L.; Jin, L.; Leleti, M.; Ashok, D.; Jeffrey, J.; Rieger, A.; Tiessen, R.G.; Arold, G.; Tan, J.B.L.; Powers, J.P.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacology of AB928, a novel dual adenosine receptor antagonist, in a randomized, phase 1 study in healthy volunteers. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.V.; Suman, S.; Goruganthu, M.U.L.; Tchekneva, E.E.; Guan, S.; Arasada, R.R.; Antonucci, A.; Piao, L.; Ilgisonis, I.; Bobko, A.A.; et al. Improving combination therapies: Targeting A2B-adenosine receptor to modulate metabolic tumor microenvironment and immunosuppression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 1404–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Ochaion, A.; Cohen, S.; Bar-Yehuda, S. The Anti-Cancer Effect of A(3) Adenosine Receptor Agonists: A Novel, Targeted Therapy. Immunol. Endocr. Metab. Agents. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, L.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.O.; Gao, Z.G.; Kim, S.K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Chun, M.W. Design and synthesis of 3′-ureidoadenosine-5′-uronamides: Effects of the 3′-ureido group on binding to the A3 adenosine receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4851–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, B.V.; Jacobson, K.A. Purine derivatives as ligands for A3 adenosine receptors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 1275–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Yehuda, S.; Madi, L.; Silberman, D.; Gery, S.; Shkapenuk, M.; Fishman, P. CF101, an agonist to the A3 adenosine receptor, enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in a colon carcinoma murine model. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Benini, A.; Mirandola, P.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Leung, E.; Maclennan, S.; Borea, P.A. A3 adenosine receptor activation inhibits cell proliferation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in A375 human melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 19516–19526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Pierron, A.; Ravid, K. An adenosine analogue, IB-MECA, down-regulates estrogen receptor alpha and suppresses human breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6413–6423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohana, G.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Arich, A.; Madi, L.; Dreznick, Z.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Silberman, D.; Slosman, G.; Fishman, P. Inhibition of primary colon carcinoma growth and liver metastasis by the A3 adenosine receptor agonist CF101. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucci, G.; Santinelli, C.; Buccioni, M.; Navia, A.M.; Lambertucci, C.; Zhurina, A.; Yli-Harja, O.; Volpini, R.; Kandhavelu, M. Anticancer activity study of A(3) adenosine receptor agonists. Life Sci. 2018, 205, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Yoshikawa, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kagota, S.; Shinozuka, K.; Kunitomo, M. Antitumor effect of cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) on mouse melanoma and lung carcinoma cells involves adenosine A3 receptor stimulation. Anticancer. Res. 2006, 26, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Varani, K.; Leung, E.; Mac Lennan, S.; Borea, P.A. The A3 adenosine receptor: An enigmatic player in cell biology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Klutz, A.M.; Tosh, D.K.; Ivanov, A.A.; Preti, D.; Baraldi, P.G. Medicinal chemistry of the A3 adenosine receptor: Agonists, antagonists, and receptor engineering. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 193, 123–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, S.; Choi, W.J.; Jeong, L.S.; Yang, Y.; Hong, J.T.; Yoon, D.Y. A3 adenosine receptor antagonist, truncated Thio-Cl-IB-MECA, induces apoptosis in T24 human bladder cancer cells. Anticancer. Res. 2010, 30, 2823–2830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spinaci, A.; Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Maggi, F.; Marucci, G.; Francucci, B.; Santoni, G.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R. A3 Adenosine Receptor Antagonists with Nucleoside Structures and Their Anticancer Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, S.; Persico, M.; Trevisan, L.; Biasinutto, C.; Bolcato, G.; Salmaso, V.; Da Ros, T.; Gianferrara, T.; Prencipe, F.; Kachler, S.; et al. [1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidines as Tools to Investigate A3 Adenosine Receptors in Cancer Cell Lines. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202300299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Hou, X.; Byun, W.S.; Kim, G.; Jarhad, D.B.; Lee, G.; Hyun, Y.E.; Yu, J.; Lee, C.S.; Qu, S.; et al. Structure–Activity Relationship of Truncated 2,8-Disubstituted-Adenosine Derivatives as Dual A2A/A3 Adenosine Receptor Antagonists and Their Cancer Immunotherapeutic Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 12249–12265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


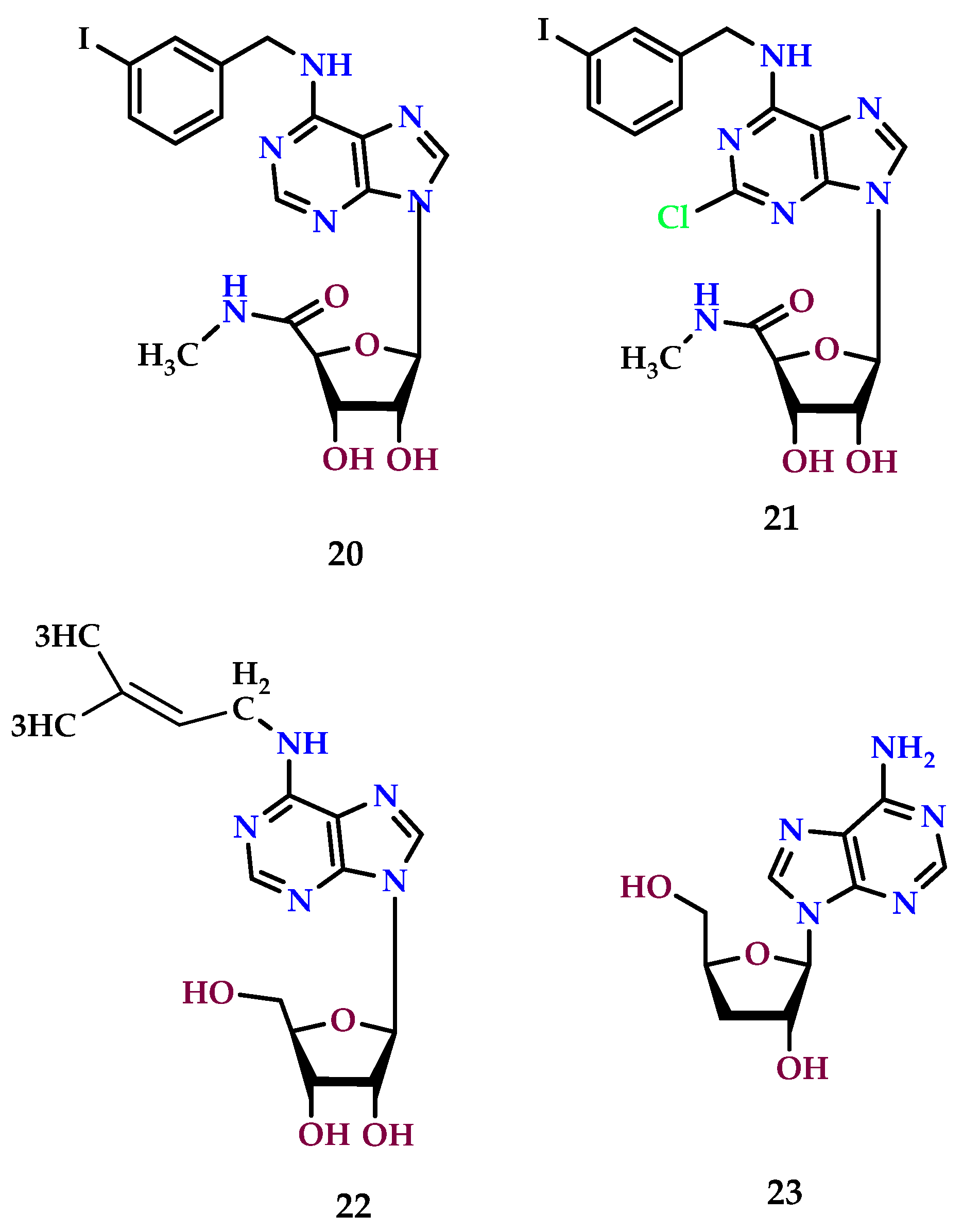
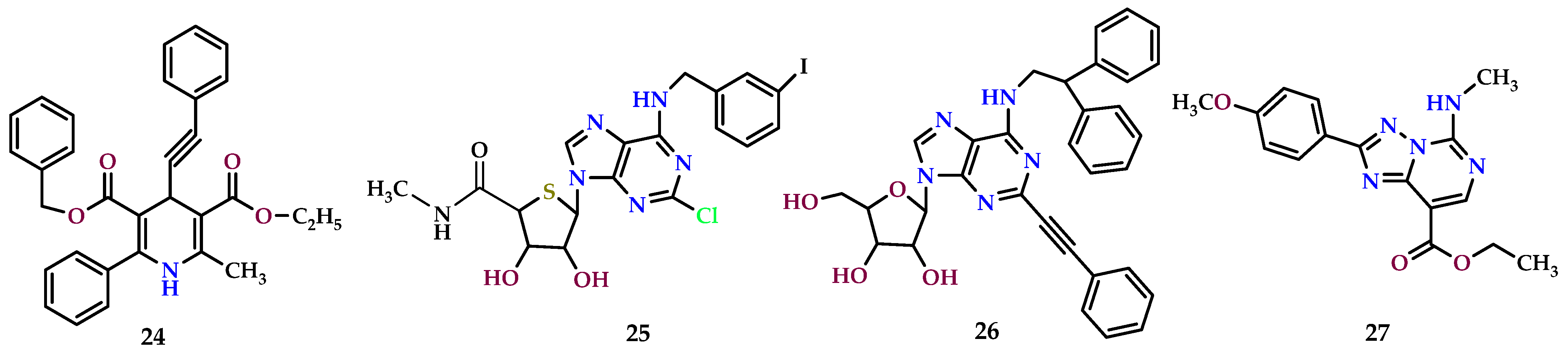
| Receptors | Affinity for Adenosine (nM) | G Protein Coupling | Signaling System |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 AR | 1–10 | Gi/o | ↓AC, ↑PLC, ↑PI3 kinase, ↑MAPK, ↑K+, Ca2+ |
| A2A AR | 30 | Gs | ↑AC, ↑MAPK |
| A2B AR | 1000 | GsGq/11 | ↑AC, ↑PLC, ↑MAPK |
| A3 AR | 100 | GsGq/11 | ↓AC, ↑PLC, ↑PI3 kinase, ↑MAPK |
| Compounds | Target | Agonist/Antagonist | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tiazofurin | A1 receptor | Agonist | Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) inhibitor |
| Cyclosaligenyl-tiazofurin monophosphate | A1 receptor | Agonist | Inhibition of inosine Monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) |
| N6-cyclopentyladenosine | A1 receptor | Agonist | Inhibition of adenylate cyclase |
| 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine | A1 receptor | Antagonist | Binds and blocks the stimulation of A1 AR |
| HENECA (2-hexynyl-NECA) | A2A receptor | Agonist | Stimulation of adenylate cyclase |
| ZM241385 (4-(2-((7-amino-2-(furan-2-yl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-5-yl)amino)ethyl)phenol) | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Prevents A2A receptor response |
| SCH58261 (2-(furan-2-yl)-7-phenethyl-7H-pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-5-amine) | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Blocks A2A receptor response |
| SYN115 (tozadenant) | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Binds A2A receptor and prevents the receptor from responding to its natural ligand (adenosine) or other agonists |
| TP455 (2-(furan-2-yl)-N5-(2-methoxybenzyl)thiazolo [5,4-d]pyrimidine-5,7-diamine) | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Binds A2A receptor and prevents the receptor from responding to its natural ligand (adenosine) or other agonists |
| CGS21680 | A2A receptor | Antagonist (in the presence of SYN115) | Blocks A2A receptor |
| (NECA) 5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Blocks A2A receptor |
| PBF-509 (5-bromo-2,6-di(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyrimidin-4-amine) | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Binds A2A receptor and prevents the receptor from responding to its natural ligand (adenosine) or other agonists |
| Preladenant | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Blocks the adenosine A2A receptor |
| AZD4365 (6-(2-chloro-6-methylpyridin-4-yl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-3-amine) | A2A receptor | Antagonist | A2A receptor inhibitor |
| Ciforadenant | A2A receptor | Antagonist | Blocks A2A receptor |
| PSB1115 (4-(2,6-dioxo-1-propyl-3,7-dihydropurin-8-yl)benzenesulfonic acid) | A2B receptor | Antagonist | Blocks A2B receptor |
| PSB603 (8-[4-[4-(4-chlorophenzyl)piperazide-1-sulfonyl)phenyl]]-1-propylxanthine) | A2B receptor | Antagonist | A2B receptor inhibitor |
| ATL801 | A2B receptor | Antagonist | A2B receptor inhibitor |
| AB928 | A2B receptor | Antagonist | Adenosine A2A and A2B receptor blocker |
| Piclidenoson (IB-MECA) | A3 receptor | Agonist | Activation triggers intracellular signaling pathways mediated by G proteins, resulting in various downstream effects |
| (Cl-IB-MECA) | A3 receptor | Agonist | Activates the adenosine A3 receptor and triggers intracellular signaling pathways mediated by G proteins |
| N6-(2-isopentenyl)) adenosine | A3 receptor | Agonist | Activates A3 receptor |
| Cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) | A3 receptor | Agonist | Activates A3 receptor |
| MRS1523 | A3 receptor | Antagonist | Blocks the A3 receptor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venugopala, K.N.; Buccioni, M. Current Understanding of the Role of Adenosine Receptors in Cancer. Molecules 2024, 29, 3501. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153501
Venugopala KN, Buccioni M. Current Understanding of the Role of Adenosine Receptors in Cancer. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3501. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153501
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenugopala, Katharigatta Narayanaswamy, and Michela Buccioni. 2024. "Current Understanding of the Role of Adenosine Receptors in Cancer" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3501. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153501
APA StyleVenugopala, K. N., & Buccioni, M. (2024). Current Understanding of the Role of Adenosine Receptors in Cancer. Molecules, 29(15), 3501. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153501






