RuNi/TiZr-MMO Catalysts Derived from Zr-Modified NiTi-LDH for CO-Selective Methanation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Catalysts
3.2.1. Preparation of NiTi-LDH and NiTiZrx-LDH
3.2.2. Preparation of RuNi/Ti-MMO and RuNi/TiZrx-MMO
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Catalyst Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeffry, L.; Ong, M.; Nomanbhay, S.; Mofijur, M.; Mubashir, M.; Show, P. Greenhouse gases utilization: A review. Fuel 2021, 301, 121017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sharda, H.; Dutta, A.; Dahiya, A.; Chaudhary, R.; Singh, A.; Rathi, K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, A.; Maken, S.; et al. Optimizing green hydrogen production: Leveraging load profile simulation and renewable energy integration. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 38015–38026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Fan, Y.; Fan, H.; Yang, X.; Yan, K.; Wang, X.; Ma, L. Photo-assisted rechargeable metal batteries. Nano Energy 2024, 125, 109538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, N.; Molina, M.; Gervasio, D.; Robles, J. Approaches to polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and their cost. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asri, N.; Husaini, T.; Sulong, A.; Majlan, E.; Daud, W. Coating of stainless steel and titanium bipolar plates for anticorrosion in PEMFC: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9135–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrahmani, H.; Moghimi, M.; Siavashi, M. Thermal management in PEMFCs: The respective effects of porous media in the gas flow channel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3121–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Lee, D.; Lee, H. Recent progress in selective CO removal in a H2-rich stream. Catal. Today 2009, 139, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagle, R.; Wang, Y.; Xi, G. Selective CO methanation catalysts for fuel processing applications. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 326, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Guo, J. Recent advances on catalysts for preferential oxidation of CO. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 4399–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.; Park, E. CO and CO2 methanation over supported Ni catalysts. Catal. Today 2017, 293–294, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, P.; Kondarides, D.; Verykios, X. Selective methanation of CO over supported Ru catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 88, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yao, N.; Li, S.; Jing, W.; Lv, D.; Li, X. Methanation of CO in hydrogen-rich gas on Ni–Ru/SiO2 catalyst: The type of active sites and Ni–Ru synergistic effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, A.H.; Jalil, A.A.; Hassan, N.S.; Hamid, M.Y.S.; Rahman, A.F.A.; Teh, L.P.; Prasetyoko, D. A review on recent bimetallic catalyst development for synthetic natural gas production via CO methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 30981–31002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinović, P.; Galletti, C.; Specchia, S.; Specchia, V. CO methanation over Ru–Al2O3 catalysts: Effects of chloride doping on reaction activity and selectivity. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumi, D.O.; Phaahlamohlaka, T.N.; Dlamini, M.W.; Mangezvo, I.T.; Mhlanga, S.D.; Scurrell, M.S.; Coville, N.J. Effect of a titania covering on CNTs as support for the Ru catalysed selective CO methanation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 232, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Dong, X.; Zang, Y.; Feng, X. Highly efficient MOF-templated Ni catalyst towards CO selective methanation in hydrogen-rich reformate gases. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 15551–15556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckle, S.; Anfang, H.-G.; Behm, J. Reaction Intermediates and Side Products in the Methanation of CO and CO2 over Supported Ru Catalysts in H2-Rich Reformate Gases. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaideen, K.; Kim, W.; Koo, K.; Yoon, W. Highly dispersed Ni particles on Ru/NiAl catalyst derived from layered double hydroxide for selective CO methanation. Catal. Commun. 2015, 60, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y. Recent advance on VOCs oxidation over layered double hydroxides derived mixed metal oxides. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukyan, K.V.; Cross, A.J.; Yeghishyan, A.V.; Rouvimov, S.; Miller, J.J.; Mukasyan, A.S.; Wolf, E.E. Highly stable Ni–Al2O3 catalyst prepared from a Ni–Al layered double hydroxide for ethanol decomposition toward hydrogen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 508, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Xie, H.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Tan, Y. Insight into the Nanoparticle Growth in Supported Ni Catalysts during the Early Stage of CO Hydrogenation Reaction: The Important Role of Adsorbed CO Molecules. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6367–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ma, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Dong, C.; Zhang, C.; Ding, M. Enhanced low-temperature performance of CO2 methanation over mesoporous Ni/Al2O3-ZrO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 243, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Geng, J.; Dong, X. Zr-promoted nickel-rich spinel-supported Ni catalysts with enhanced performance for selective CO methanation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 9128–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, D.; Chen, C.; Jiang, L.; Takehira, K. Ni/Al2O3-ZrO2 catalyst for CO2 methanation: The role of γ-(Al, Zr)2O3 formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhao, Y. Effect of ZrO2 promoter on structure and catalytic activity of the Ni/SiO2 catalyst for CO methanation in hydrogen-rich gases. Catal. Today 2010, 158, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, G.; Wang, K.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Han, C.; Liu, J.; Tong, M.; Liang, X.; et al. Mesoporous zirconia-modified clays supported nickel catalysts for CO and CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18894–18907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ren, J.; Qin, X.; Qin, Z.; Lin, J.; Li, Z. Ni/SBA-15 catalysts for CO methanation: Effects of V, Ce, and Zr promoters. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96504–96517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tay, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, J.; Armando, B. Morphology and composition controllable synthesis of Mg–Al–CO3 hydrotalcites by tuning the synthesis pH and the CO2 capture capacity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 55, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, P.; Guinea, I.; Labajos, F.M.; Rives, V. Microwave-assisted reconstruction of Ni, Al hydrotalcite-like compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.; Everett, D.; Haul, R.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttakin, M.; Mitra, S.; Thu, K.; Ito, K.; Saha, B. Theoretical framework to evaluate minimum desorption temperature for IUPAC classified adsorption isotherms. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, B.; Kimura, H.; Ni, C.; Yu, R.; Du, W. Morphology evolution of bimetallic Ni/Zn-MOFs and derived Ni3ZnC0.7/Ni/ZnO used to destabilize MgH2. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Benjamin, K.; Franck, D.; Elisabeth, B.; Sébastien, P. Catalytic selective oxidation of isobutane to methacrylic acid on supported (NH4)3HPMo11VO40 catalysts. J. Catal. 2014, 309, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; Dong, X. RuNi/MMO Catalysts Derived from a NiAl-NO3-LDH Precursor for CO Selective Methanation in H2-Rich Gases. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Xing, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Cao, J.; Lv, B. Rapid synthesis of Cu2O hollow spheres at low temperature and their catalytic performance for the decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. CrystEngComm 2021, 23, 7985–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X. Highly efficient Ru/TiO2-NiAl mixed oxide catalysts for CO selective methanation in hydrogen-rich gas. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Feng, J.; Dong, X. Ru–Ni/GA-MMO composites as highly active catalysts for CO selective methanation in H2-rich gases. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 24640–24651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Jiang, X.; Hu, J.; Song, J.; Sun, N.; Zhang, D.; Kuai, L. Ru Nanoworms Loaded TiO2 for Their Catalytic Performances toward CO Oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5079–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Ji, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Hybrid nanostructures of pit-rich TiO2 nanocrystals with Ru loading and N doping for enhanced solar water splitting. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2781–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zou, S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, K.; Sarina, S.; Huang, J. RuCu bimetallic catalyst on N-doped mesoporous carbon for high-performance CO2 methanation. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Wang, W. Stability and activity maintenance of Ni catalysts supported on La-, Ce-, and Mg-promoted Al2O3 and ZrO2 for H2 production from steam reforming of glycerol. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 9369–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, J.; Li, Z. Silica/titania composite-supported Ni catalysts for CO methanation: Effects of Ti species on the activity, anti-sintering, and anti-coking properties. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 201, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Dong, C.; Zhao, H.; Dong, X. A Novel Hierarchical RuNi/Al2O3–Carbon Nanotubes/Ni Foam Catalyst for Selective Removal of CO in H2-Rich Fuels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 5558–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalachew, M.; Salvatore, A.; Siglinda, P.; Chen, S.; Gabriele, C. CO2 methanation over Ni catalysts based on ternary and quaternary mixed oxide: A comparison and analysis of the structure-activity relationships. Catal. Today 2018, 304, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, S.; Barbera, K.; Giglio, E.; Deorsola, F.; Bensaid, S.; Perathoner, S.; Pirone, R.; Centi, G. Synthesis, Characterization, and Activity Pattern of Ni–Al Hydrotalcite Catalysts in CO2 Methanation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8299–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alstrup, I. On the Kinetics of Co Methanation on Nickel Surfaces. J. Catal. 1995, 151, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Meng, X.; Lv, Y.; Bian, Z.; Xin, Z. Effect of impregnation solvent on Ni dispersion and catalytic properties of Ni/SBA-15 for CO methanation reaction. Fuel 2016, 165, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Behzad, N.; Mehran, R.; Ebrahim, N. CO methanation over Ni catalysts supported on high surface area mesoporous nanocrystalline γ-Al2O3 for CO removal in H2-rich stream. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Kikuchi, R.; Takagaki, A.; Sugawara, T.; Ted Oyama, S.; Satokawa, S. Effect of metal addition to Ru/TiO2 catalyst on selective CO methanation. Catal. Today 2014, 232, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, G.; Bei, K.; Zhang, G.; Lv, Y. Insight into the role of lanthanide metal oxides on the carbon deposition resistance of Ni/MSS catalysts for dry reforming of methane. Fuel 2024, 367, 131562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, G.; Yu, J.; Yang, L.; Li, F. Defect-rich Ni–Ti layered double hydroxide as a highly efficient support for Au nanoparticles in base-free and solvent-free selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5226–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; He, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, D. Partial hydrogenation of acetylene over a NiTi-layered double hydroxide supported PdAg catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Meng, F.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Solution-combusted nanosized Ni-Al2O3 catalyst for slurry CO methanation: Effects of alkali/alkaline earth metal chlorides. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16510–16521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cui, L.; Ma, H. Selective methanation of CO over Ni/Al2O3 catalyst: Effects of preparation method and Ru addition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 5484–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Shoji, D.; Urasaki, K.; Shimoda, N.; Satokawa, S. Physical mixing of TiO2 with sponge nickel creates new active sites for selective CO methanation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Kikuchi, R.; Wada, K.; Osada, K.; Akiyama, K.; Satokawa, S.; Kawashima, Y. Long-term durability of Ni/TiO2 and Ru–Ni/TiO2 catalysts for selective CO methanation. J. Power Sources 2014, 264, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Liang, J.; Ma, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, B.; Guo, Z.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S. Large-pore mesoporous RuNi-doped TiO2–Al2O3 nanocomposites for highly efficient selective CO methanation in hydrogen-rich reformate gases. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, D.; Zhao, H.; Dong, X. Ni-doped TiO2 nanotubes supported Ru catalysts for CO selective methanation in H2-rich reformate gases. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2018, 124, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ping, D.; Dong, X.; Dong, Y.; Zang, Y. Construction of Ru/Ni-Al-oxide/Ni-foam monolithic catalyst for deep-removing CO in hydrogen-rich gas via selective methanation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 148, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
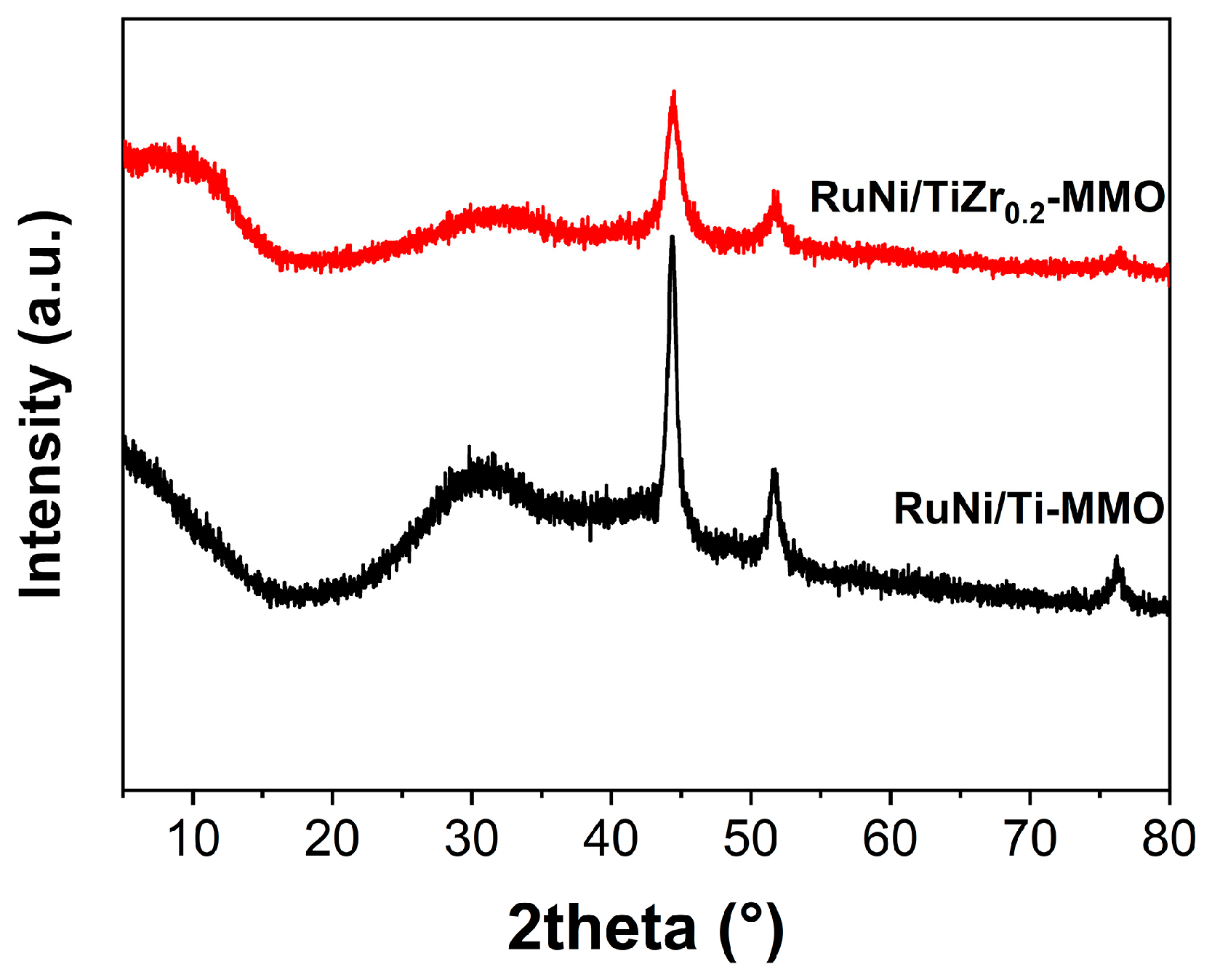
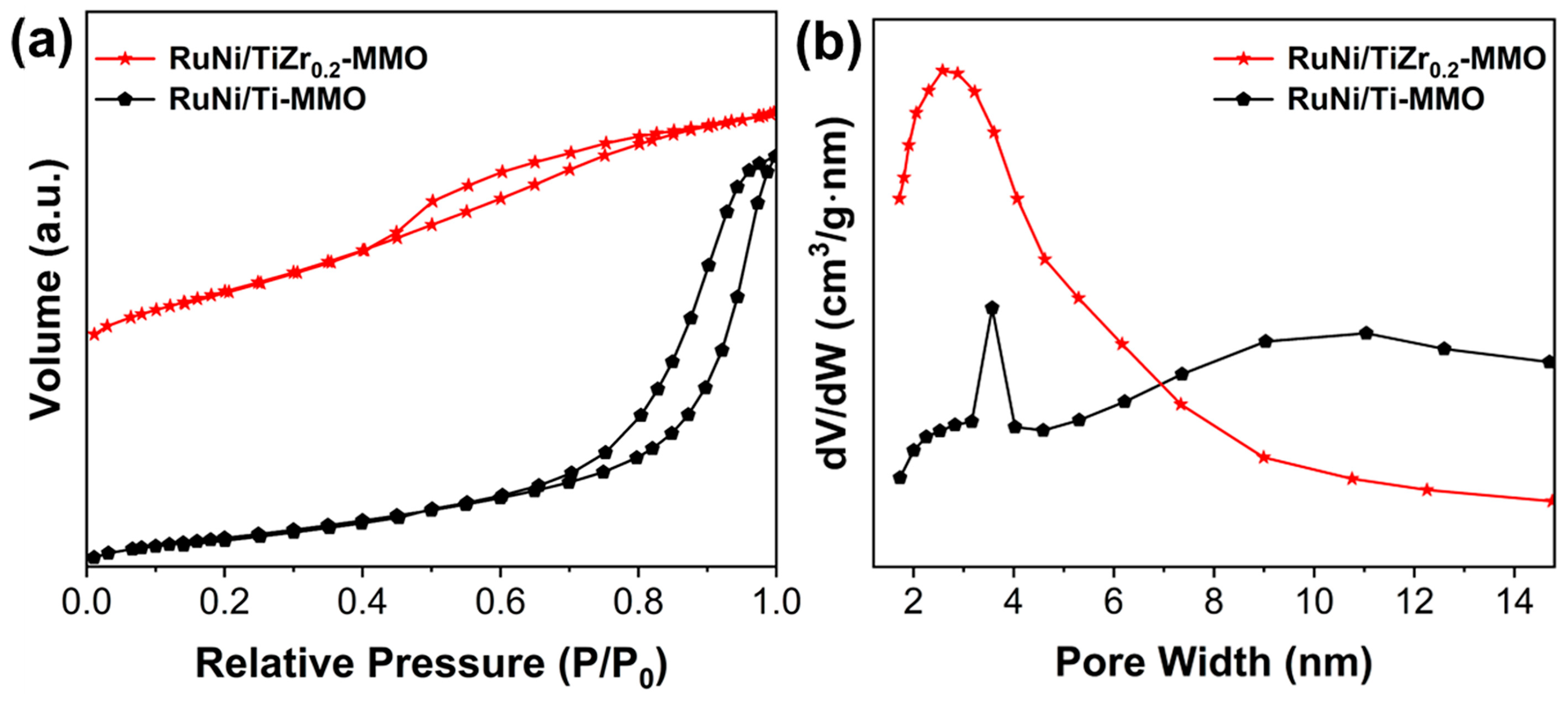
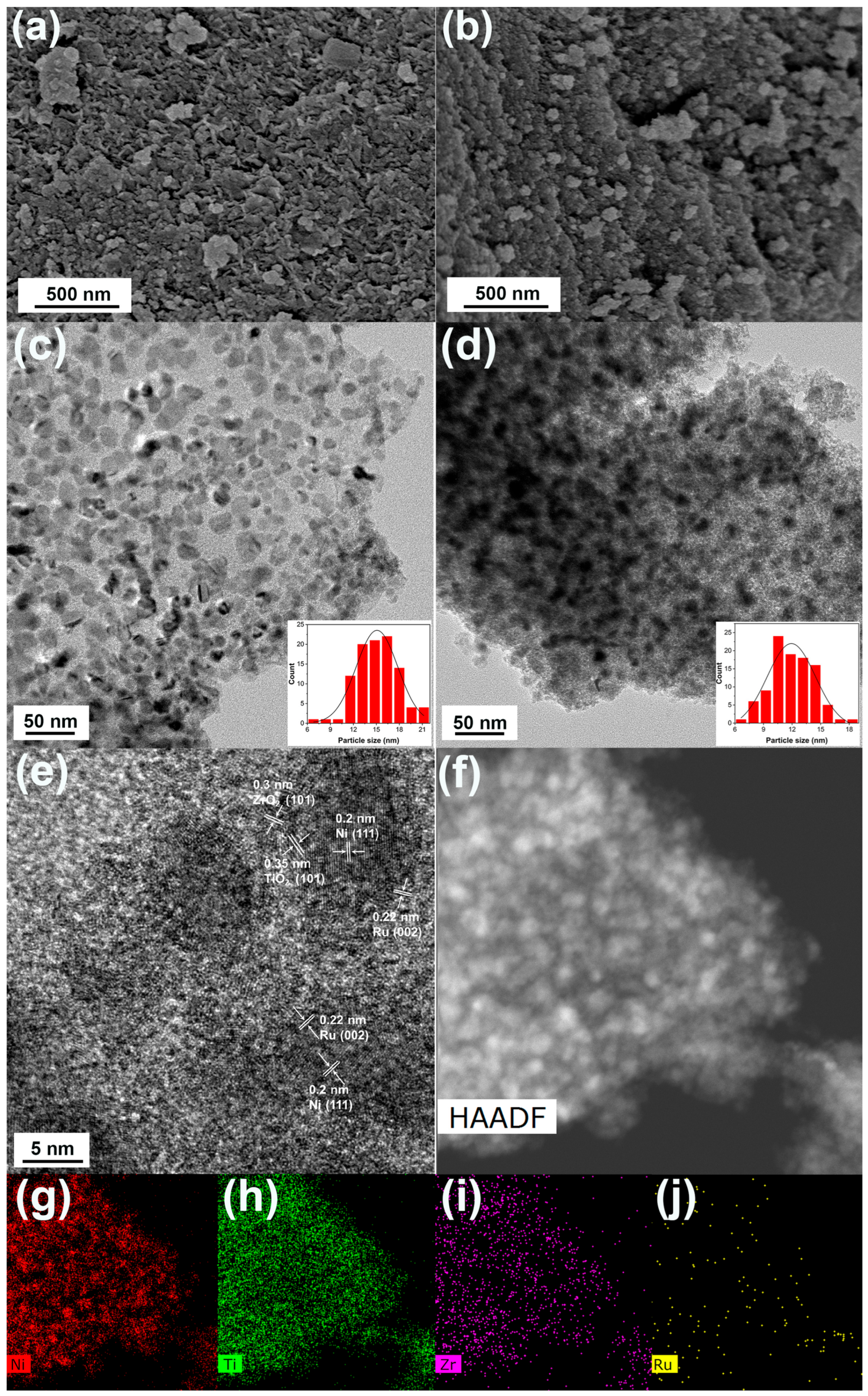
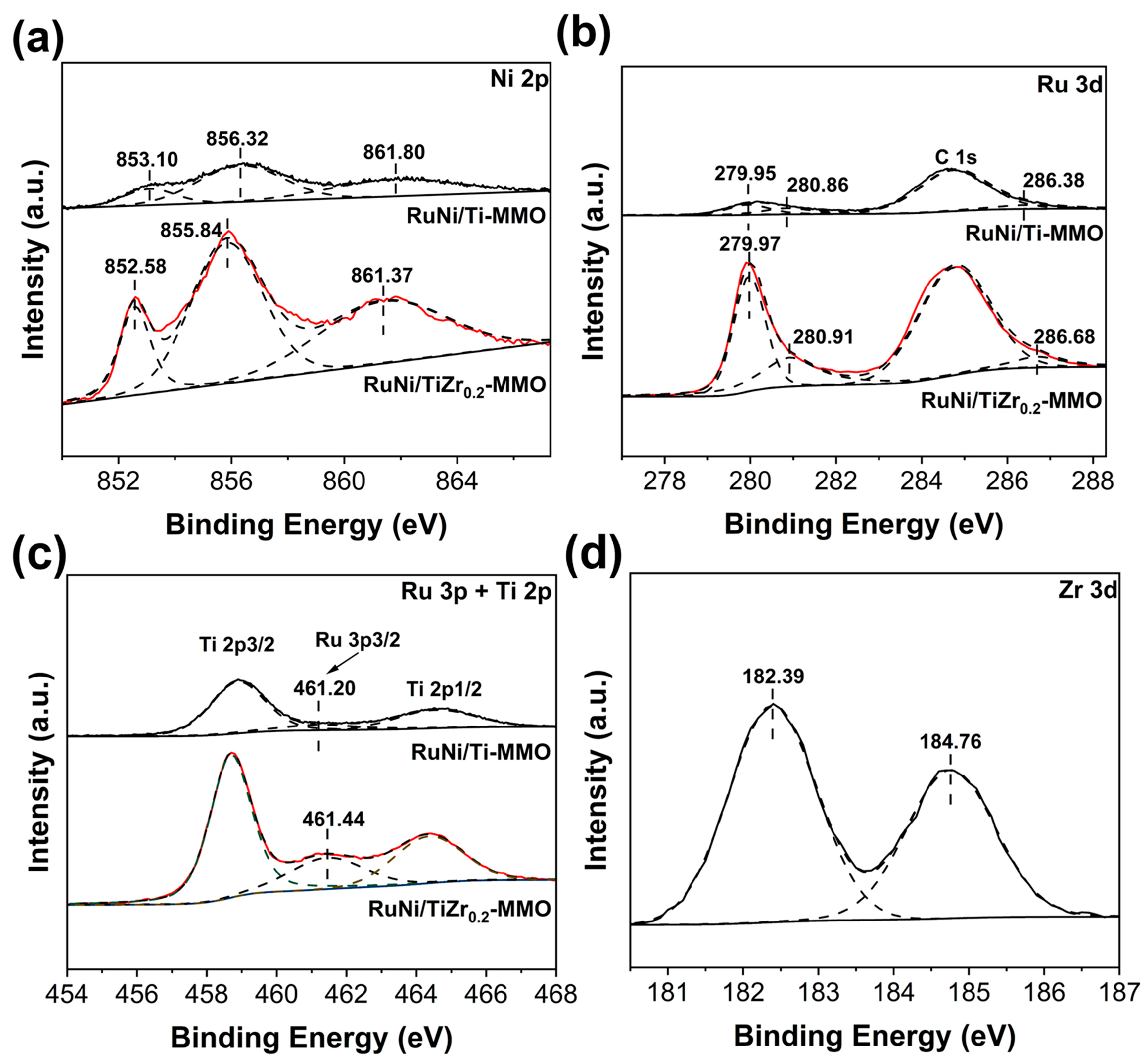

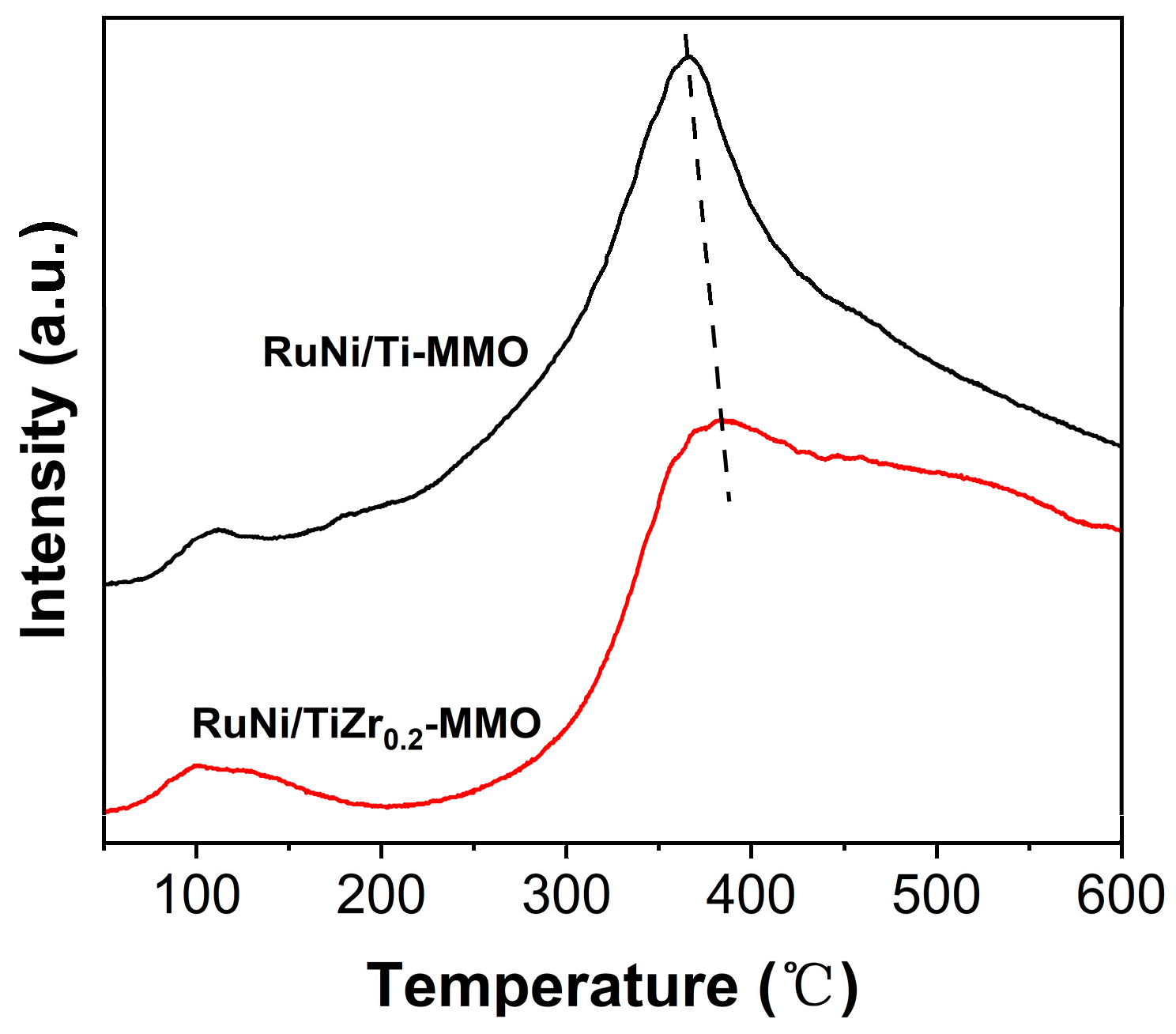
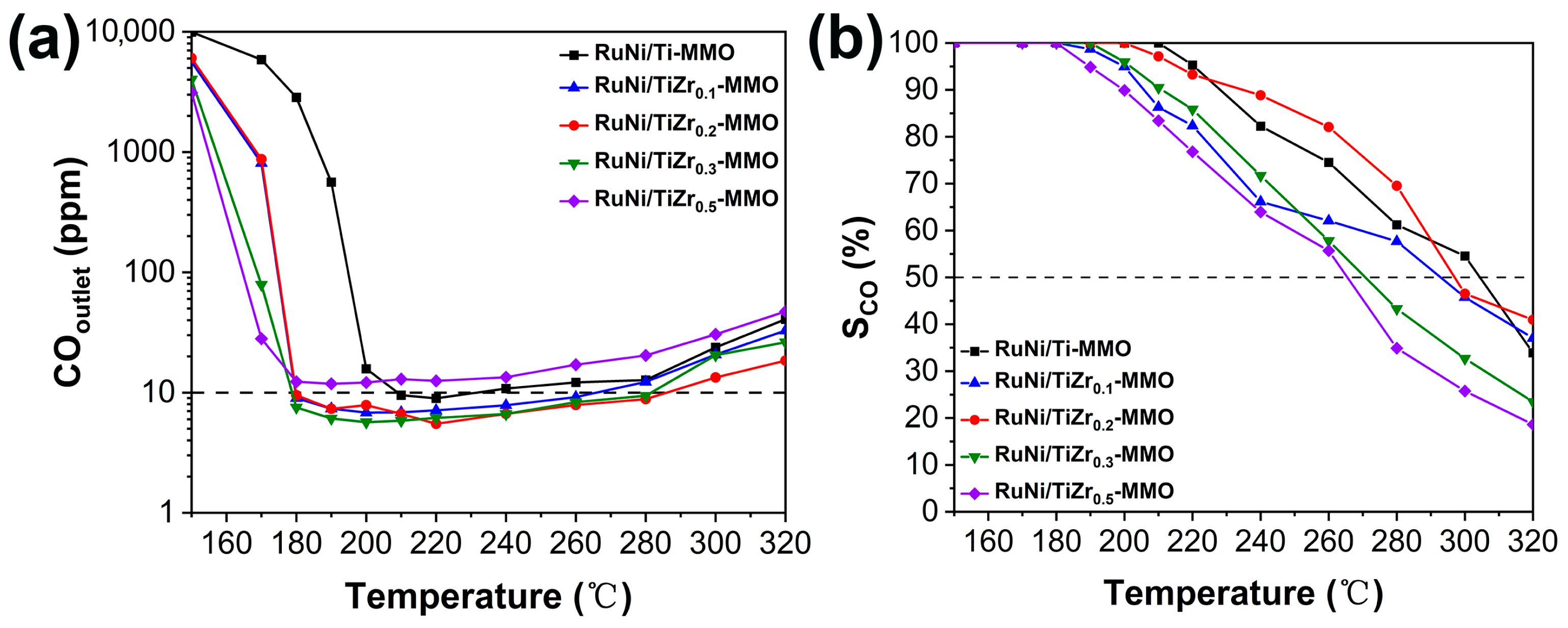
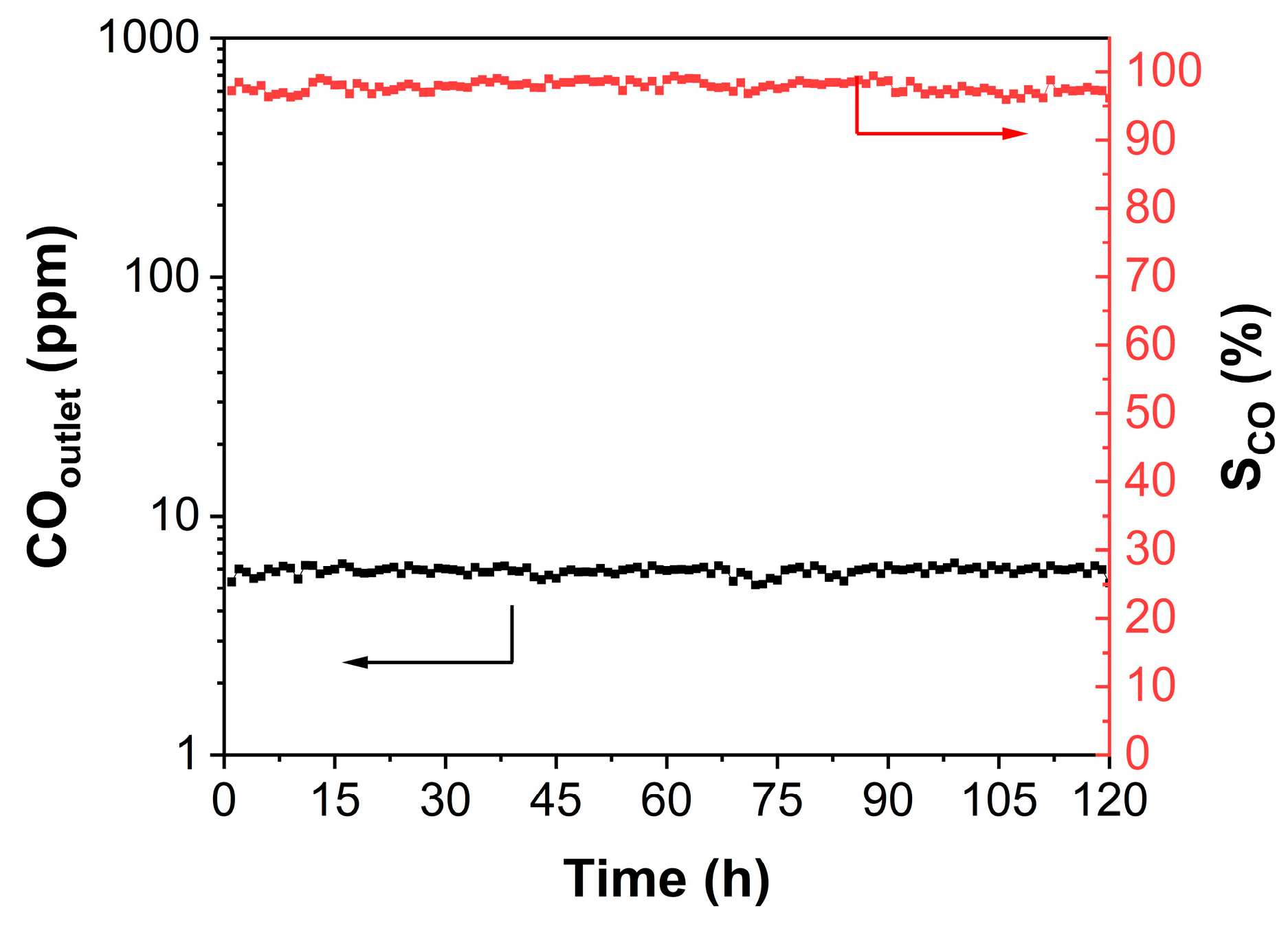
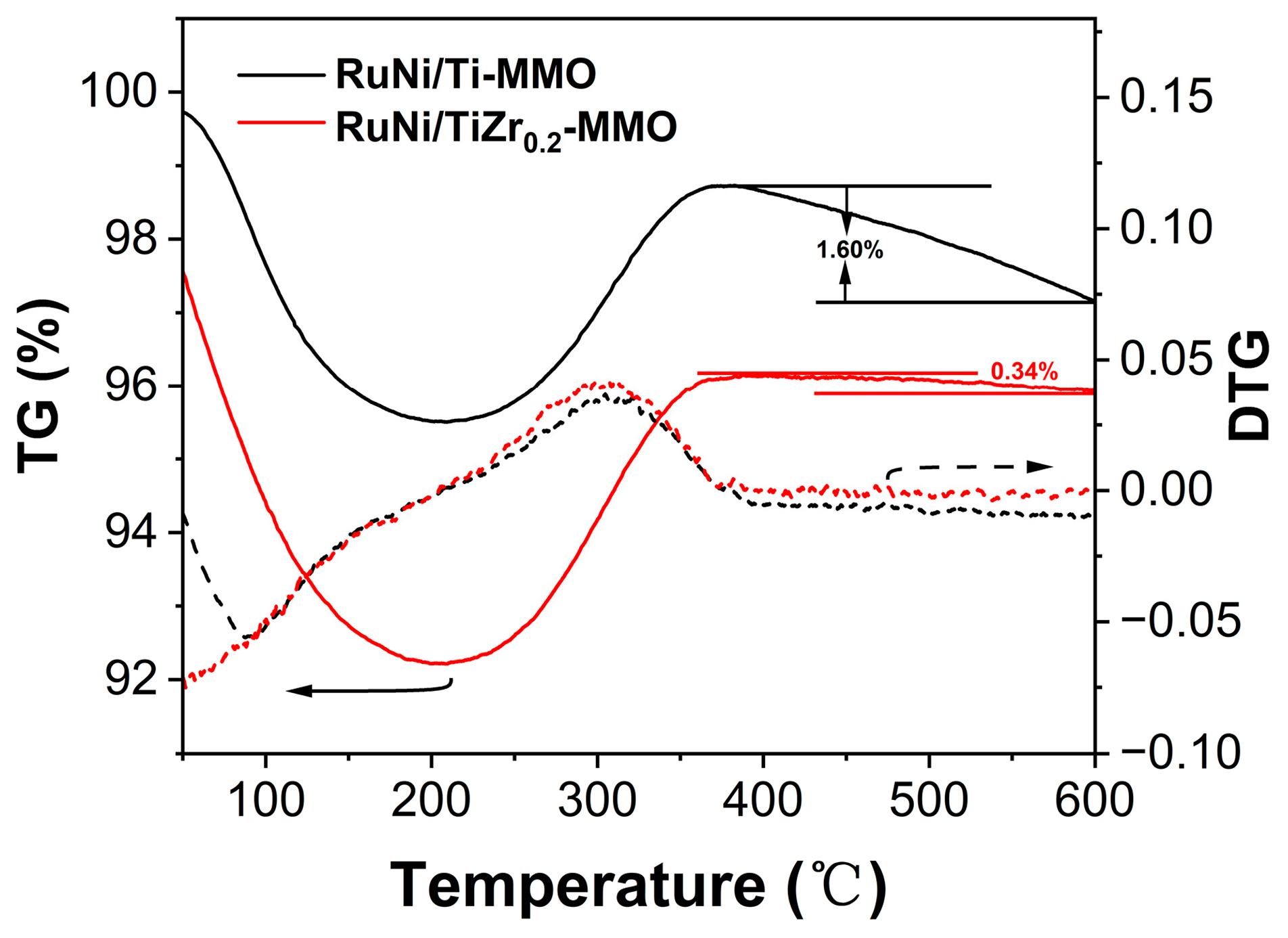

| Catalyst | Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| RuNi/Ti-MMO | 90 | 7.4 |
| RuNi/TiZr0.2-MMO | 191 | 3.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Dong, X. RuNi/TiZr-MMO Catalysts Derived from Zr-Modified NiTi-LDH for CO-Selective Methanation. Molecules 2024, 29, 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143309
Li Z, Ma J, Dong X. RuNi/TiZr-MMO Catalysts Derived from Zr-Modified NiTi-LDH for CO-Selective Methanation. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143309
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhihui, Jiteng Ma, and Xinfa Dong. 2024. "RuNi/TiZr-MMO Catalysts Derived from Zr-Modified NiTi-LDH for CO-Selective Methanation" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143309
APA StyleLi, Z., Ma, J., & Dong, X. (2024). RuNi/TiZr-MMO Catalysts Derived from Zr-Modified NiTi-LDH for CO-Selective Methanation. Molecules, 29(14), 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143309







