Chemical Synthesis and Insecticidal Activity Research Based on α-Conotoxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Screening of α-Conotoxins from C. quercinus
2.2. Synthesis of Linear Conopeptides
2.3. Optimization of Oxidative Folding Conditions
2.4. Oxidative Folding
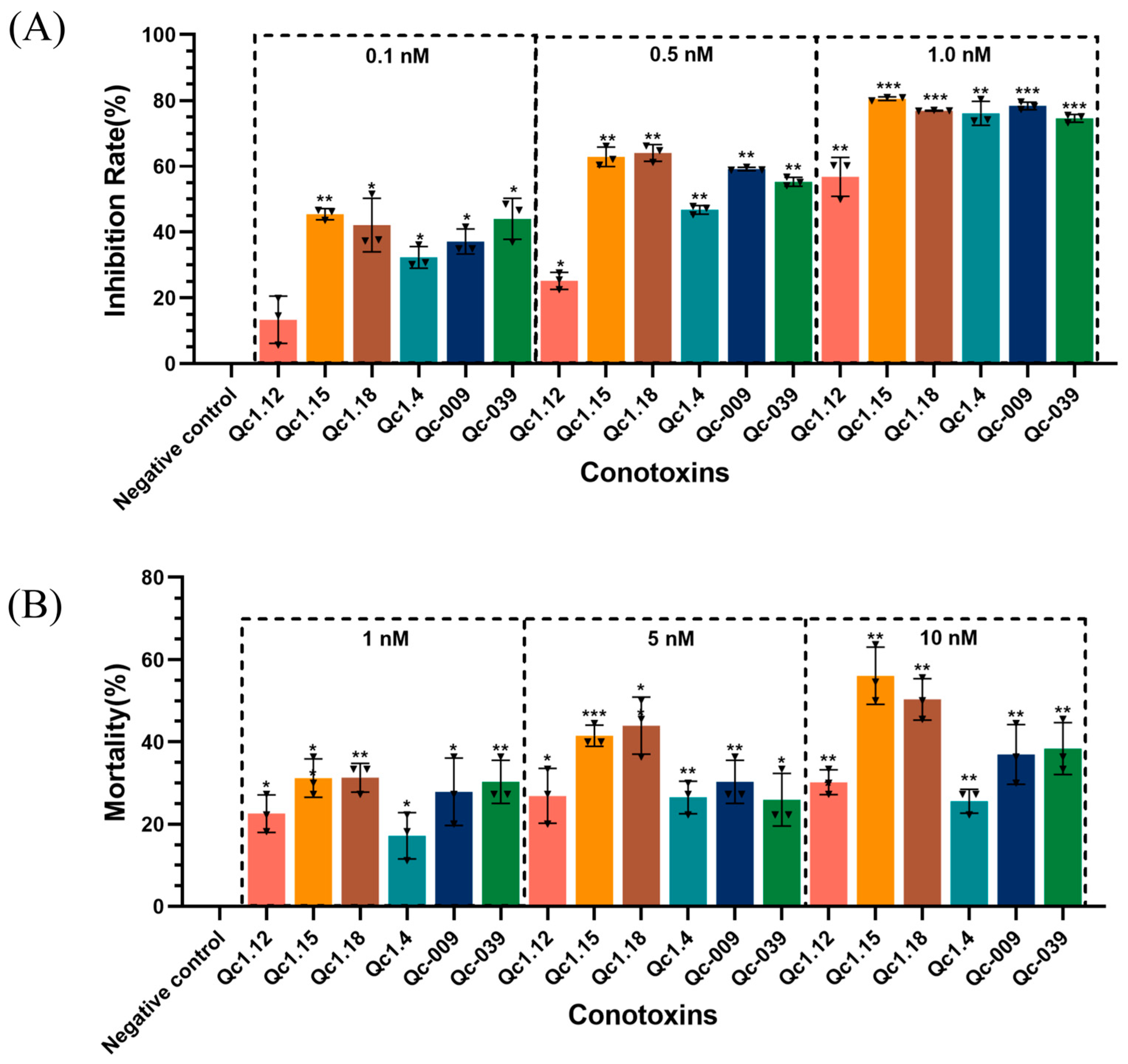
2.5. Cytotoxic Activity of α-Conotoxins from C. quercinus
2.6. Insect Toxicity Test of α-Conotoxins from C. quercinus
2.7. Electrostatic Surface
2.8. Predicting the Binding Mode of α-Conotoxins at nAChR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Screening of α-Conotoxins from C. quercinus
4.2. Synthesis of Linear Conopeptides
4.3. Optimization of Oxidative Folding Conditions
4.4. Oxidative Folding
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. Insect Bioassay
4.7. Electrostatic Surface
4.8. Molecular Docking
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, H.; Deng, B.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Zou, B.; Chen, H.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Programmed Aptamer Screening, Characterization, and Rapid Detection for α-Conotoxin MI. Toxins 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Li, R.; Ren, J.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S. Alanine-Scanning Mutagenesis of α-Conotoxin GI Reveals the Residues Crucial for Activity at the Muscle Acetylcholine Receptor. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosti, E.; Boni, R.; Gallo, A. µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Diversity of Conopeptides and Their Precursor Genes of Conus Litteratus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackieh, R.; Abou-Nader, R.; Wehbe, R.; Mattei, C.; Legros, C.; Fajloun, Z.; Sabatier, J.M. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: A Prominent Target of Marine Toxins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.W.; Wu, W.L.; Hwang, D.F. The complete mitochondrial genome of Conus quercinus (Neogastropoda: Conidae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018, 3, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, G.R.; da Silva, D.L.; Beraldo-Neto, E.; Vigerelli, H.; de Oliveira, L.A.; Sciani, J.M.; Pimenta, D.C. Neglected Venomous Animals and Toxins: Underrated Biotechnological Tools in Drug Development. Toxins 2021, 13, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, J.L.B.; Imperial, J.S.; Morgenstern, D.; Ueberheide, B.; Gajewiak, J.; Antunes, A.; Robinson, S.D.; Espino, S.; Watkins, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; et al. Characterization of the First Conotoxin from Conus ateralbus, a Vermivorous Cone Snail from the Cabo Verde Archipelago. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.B.; Bullock, C.W.; Andersen, T.; McDougal, O.M. DockoMatic: Automated peptide analog creation for high throughput virtual screening. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.X.; He, P.M.; Jia, R. Effects of µ-Conotoxin GIIIB on the cellular activity of mouse skeletal musculoblast: Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis. Proteome Sci. 2023, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Li, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S. α-Conotoxin TxIB: A Uniquely Selective Ligand for α6/α3β2β3 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Attenuates Nicotine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xiong, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. DSPE-PEG Modification of α-Conotoxin TxID. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Q. High Throughput Identification of Novel Conotoxins from the Vermivorous Oak Cone Snail (Conus quercinus) by Transcriptome Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Antunes, A. Biomedical Potential of the Neglected Molluscivorous and Vermivorous Conus Species. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul George, A.A.; Heimer, P.; Maaß, A.; Hamaekers, J.; Hofmann-Apitius, M.; Biswas, A.; Imhof, D. Insights into the Folding of Disulfide-Rich μ-Conotoxins. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12330–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardisson-Araújo, D.M.; Morgado Fda, S.; Schwartz, E.F.; Corzo, G.; Ribeiro, B.M. A new theraphosid spider toxin causes early insect cell death by necrosis when expressed in vitro during recombinant baculovirus infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armishaw, C.J. Synthetic α-conotoxin mutants as probes for studying nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and in the development of novel drug leads. Toxins 2010, 2, 1471–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Watkins, M.; Olivera, B.M. Evolution of Conus peptide genes: Duplication and positive selection in the A-superfamily. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 70, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q. Mitochondrial genome sequencing of a vermivorous cone snail Conus quercinus supports the correlative analysis between phylogenetic relationships and dietary types of Conus species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Almeida, M.; Varela Coelho, A.; Cutignano, A.; Gonçalves, L.G.; Hansen, E.; Khnykin, D.; Mass, T.; Ramšak, A.; Rocha, M.S.; et al. Biomaterials and Bioactive Natural Products from Marine Invertebrates: From Basic Research to Innovative Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, H.C.; Kaas, Q.; Muttenthaler, M. Neuropeptide signalling systems—An underexplored target for venom drug discovery. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Lin, B.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q. Screening and Validation of Highly-Efficient Insecticidal Conotoxins from a Transcriptome-Based Dataset of Chinese Tubular Cone Snail. Toxins 2017, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiezia, M.C.; Chiarabelli, C.; Polticelli, F. Recombinant expression and insecticidal properties of a Conus ventricosus conotoxin-GST fusion protein. Toxicon 2012, 60, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Gao, B. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of cysteine-free conopeptides from Conus betulinus. Toxicon 2023, 233, 107253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Liu, D.; Dai, J.K.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.R. Synthesis and In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Quaternized 10-Methoxycanthin-6-one Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Li, W.; Yan, X.; Qiao, J.; Caiyin, Q. Research Progress on the Synthetic Biology of Botanical Biopesticides. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinkar, O.U.; Prashar, A.; Kumar, A.; Hadapad, A.B.; Hire, R.S.; Makde, R.D. Txp40, an insecticidal toxin protein from Xenorhabdus nematophila: Purification, toxicity assessment and biophysical characterization. Toxicon 2022, 218, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bai, H.; Song, P.; Nangong, Z.; Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q. Insecticidal Activity of Chitinases from Xenorhabdus nematophila HB310 and Its Relationship with the Toxin Complex. Toxins 2022, 14, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liang, S.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Insecticidal Toxin, μ-sparatoxin-Hv2, from the Venom of the Spider Heteropoda venatoria. Toxins 2018, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.; Fitches, E.C.; Chougule, N.; Bell, H.A.; Gatehouse, J.A. Recombinant conotoxin, TxVIA, produced in yeast has insecticidal activity. Toxicon 2011, 58, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, P.; Xie, J.; Xie, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhangsun, D.; Yu, J.; Luo, S. Loop2 Size Modification Reveals Significant Impacts on the Potency of α-Conotoxin TxID. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.D.; Han, Y.H.; Wang, C.G.; Chi, C.W. From the identification of gene organization of alpha conotoxins to the cloning of novel toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.N.; Nunes, K.P.; Dourado, L.F.N.; Vieira, T.O.; Mariano, X.M.; Cunha Junior, A.D.S.; de Lima, M.E. From the PnTx2-6 Toxin to the PnPP-19 Engineered Peptide: Therapeutic Potential in Erectile Dysfunction, Nociception, and Glaucoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 831823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, M. Synthesis and evaluation of a novel analgesic conotoxin Lt7b that inhibits calcium currents and increases sodium currents. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5330–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, H.; Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Garcia-Bustos, J.; Taki, A.C.; Addison, R.S.; Hayes, S.; Beattie, K.D.; McGee, S.L.; Martin, S.D.; et al. Identification of Fromiamycalin and Halaminol A from Australian Marine Sponge Extracts with Anthelmintic Activity against Haemonchus contortus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.P.C.; Li, B.; Kwok, H.F. Venom Peptides and Toxins—A Prospective Spearhead in Cancer Treatment. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2017, 20, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Seukep, A.J.; Guo, M. Recent Advances in Molecular Docking for the Research and Discovery of Potential Marine Drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Peng, C.; Yi, Y.; Gao, B.; Shi, Q. A Transcriptomic Survey of Ion Channel-Based Conotoxins in the Chinese Tubular Cone Snail (Conus betulinus). Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Yang, J.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q. Cone Snails: A Big Store of Conotoxins for Novel Drug Discovery. Toxins 2017, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, H.; Flores, V.; Diego-Garcia, E.; Corrales-Garcia, L.; Villegas, E.; Corzo, G. A comparison between the recombinant expression and chemical synthesis of a short cysteine-rich insecticidal spider peptide. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.J.; Holding, M.L.; Rautsaw, R.M.; Rokyta, D.R.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gibbs, H.L. Venom Gene Sequence Diversity and Expression Jointly Shape Diet Adaptation in Pitvipers. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Nicke, A.; Tsetlin, V.I. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor inhibitors derived from snake and snail venoms. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Ren, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhangsun, M.; Zhangsun, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S. Identification of Crucial Residues in α-Conotoxin EI Inhibiting Muscle Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Toxins 2019, 11, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, N.; Lewis, R.J. Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Modulators from Cone Snails. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giribaldi, J.; Wilson, D.; Nicke, A.; El Hamdaoui, Y.; Laconde, G.; Faucherre, A.; Moha Ou Maati, H.; Daly, N.L.; Enjalbal, C.; Dutertre, S. Synthesis, Structure and Biological Activity of CIA and CIB, Two α-Conotoxins from the Predation-Evoked Venom of Conus catus. Toxins 2018, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Duque, H.; Campos Dias, S.; Franco, O.L. Structural and Functional Analyses of Cone Snail Toxins. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasheverov, I.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Shelukhina, I.; Nikolaev, G.; Utkin, Y.; Tsetlin, V. Marine Origin Ligands of Nicotinic Receptors: Low Molecular Compounds, Peptides and Proteins for Fundamental Research and Practical Applications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, R.B.; Stewart, J.M.; Jernberg, N. Instrument for automated synthesis of peptides. Anal. Chem. 1966, 38, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marglin, A.; Merrifield, R.B. The synthesis of bovine insulin by the solid phase method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 5051–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, L.C.; Kuo, H.Y.; Mrksich, M. Peptide Arrays: Development and Application. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oca, S.A.-M.; Montes-De-Oca-Jiménez, R.; Vázquez-Chagoyán, J.C.; Barbabosa-Pliego, A.; Rivadeneira-Barreiro, P.E.; Zambrano-Rodríguez, P.C. The Use of Peptides in Veterinary Serodiagnosis of Infectious Diseases: A Review. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumruck, A.C.; Tietze, D.; Steinacker, L.K.; Tietze, A.A. Chemical synthesis of membrane proteins: A model study on the influenza virus B proton channel. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, S.L.; Raabe, M. Solid-Phase Protein Modifications: Towards Precision Protein Hybrids for Biological Applications. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yao, G.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wan, X.; Jiang, H. Structural and Functional Characterization of Conotoxins from Conus achatinus Targeting NMDAR. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; He, T.; Saleem, M.; He, G. Metalloprotein-Specific or Critical Amino Acid Residues: Perspectives on Plant-Precise Detoxification and Recognition Mechanisms under Cadmium Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Huang, X.; Guo, D.; Lou, H.; Hou, Z.; Su, M.; Liang, R.; Xie, C.; You, M.; et al. Differential effects of a post-anthesis heat stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain proteome determined by iTRAQ. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.T.; Taichi, M.; Nishio, H.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Tam, J.P. Optimal oxidative folding of the novel antimicrobial cyclotide from Hedyotis biflora requires high alcohol concentrations. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 7275–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.C.; Yen, C.F.; Lin, C.C.; Lung, F.T. Designing the antimicrobial peptide with centrosymmetric and amphipathic characterizations for improving antimicrobial activity. J. Pept. Sci. 2023, 29, e3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.P.; Hancock, R.E. The relationship between peptide structure and antibacterial activity. Peptides 2003, 24, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.A.; Jin, A.H.; Braga Emidio, N.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Rosengren, K.J. Chemical Synthesis and NMR Solution Structure of Conotoxin GXIA from Conus geographus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoids and Other Insect Nicotinic Receptor Competitive Modulators: Progress and Prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Xia, S.; Durkin, K.A.; Casida, J.E. Insect nicotinic receptor interactions in vivo with neonicotinoid, organophosphorus, and methylcarbamate insecticides and a synergist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17273–17277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillebois, E.; Thany, S.H. The use of insecticide mixtures containing neonicotinoids as a strategy to limit insect pests: Efficiency and mode of action. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 184, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, S.; Sciocco-Cap, A.; Romanowski, V. Baculovirus insecticides in Latin America: Historical overview, current status and future perspectives. Viruses 2015, 7, 2230–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X. History and current status of development and use of viral insecticides in China. Viruses 2015, 7, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windley, M.J.; Herzig, V.; Dziemborowicz, S.A.; Hardy, M.C.; King, G.F.; Nicholson, G.M. Spider-venom peptides as bioinsecticides. Toxins 2012, 4, 191–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Menofy, W.; Osman, G.; Assaeedi, A.; Salama, M. A novel recombinant baculovirus overexpressing a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin enhances insecticidal activity. Biol. Proced. Online 2014, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Harvey, P.J.; Kaas, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Christensen, S.; et al. Cloning, synthesis, and characterization of αO-conotoxin GeXIVA, a potent α9α10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4026–E4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gieter, S.; Gallagher, C.I.; Wijckmans, E.; Pasini, D.; Ulens, C.; Efremov, R.G. Sterol derivative binding to the orthosteric site causes conformational changes in an invertebrate Cys-loop receptor. eLife 2023, 12, e86029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
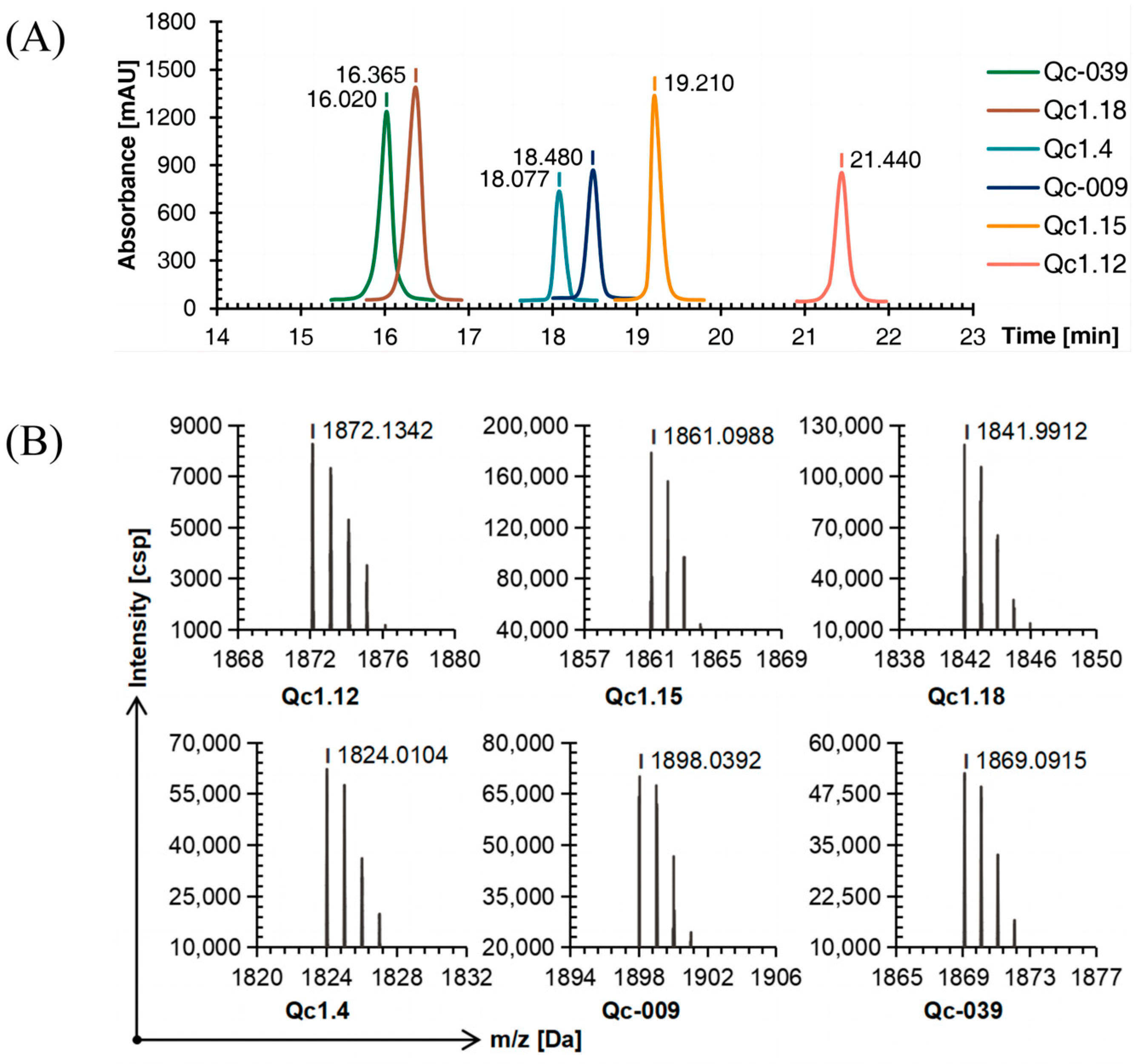



| Name | Conotoxin Sequences | Cysteine Binding Mode | Theoretical Mass (Da) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qc1.12 | QGCCSYPACAVSNPDIC | Cys1-Cys3 and Cys2-Cys4 | 1871.13 |
| Qc1.15 | DGCCSDPACAVNHPDIC | Cys1-Cys3 and Cys2-Cys4 | 1860.10 |
| Qc1.18 | DGCCSSPSCSVNNPDIC | Cys1-Cys3 and Cys2-Cys4 | 1840.99 |
| Qc1.4 | QGCCSDPACAVSNPDIC | Cys1-Cys4 and Cys2-Cys3 | 1823.01 |
| Qc-009 | DECCSNPSCAVSNPDIC | Cys1-Cys3 and Cys2-Cys4 | 1897.04 |
| Qc-039 | DGCCSNPSCSVNNPDIC | Cys1-Cys3 and Cys2-Cys4 | 1868.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Qin, H.; Liao, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, B. Chemical Synthesis and Insecticidal Activity Research Based on α-Conotoxins. Molecules 2024, 29, 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122846
Lin C, Qin H, Liao Y, Chen J, Gao B. Chemical Synthesis and Insecticidal Activity Research Based on α-Conotoxins. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122846
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chengzhang, Hailong Qin, Yanling Liao, Jiao Chen, and Bingmiao Gao. 2024. "Chemical Synthesis and Insecticidal Activity Research Based on α-Conotoxins" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122846
APA StyleLin, C., Qin, H., Liao, Y., Chen, J., & Gao, B. (2024). Chemical Synthesis and Insecticidal Activity Research Based on α-Conotoxins. Molecules, 29(12), 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122846






