Enhancement of the Electric-Force Response of Carbon Black/Silicone Rubber Composites by Silane Coupling Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
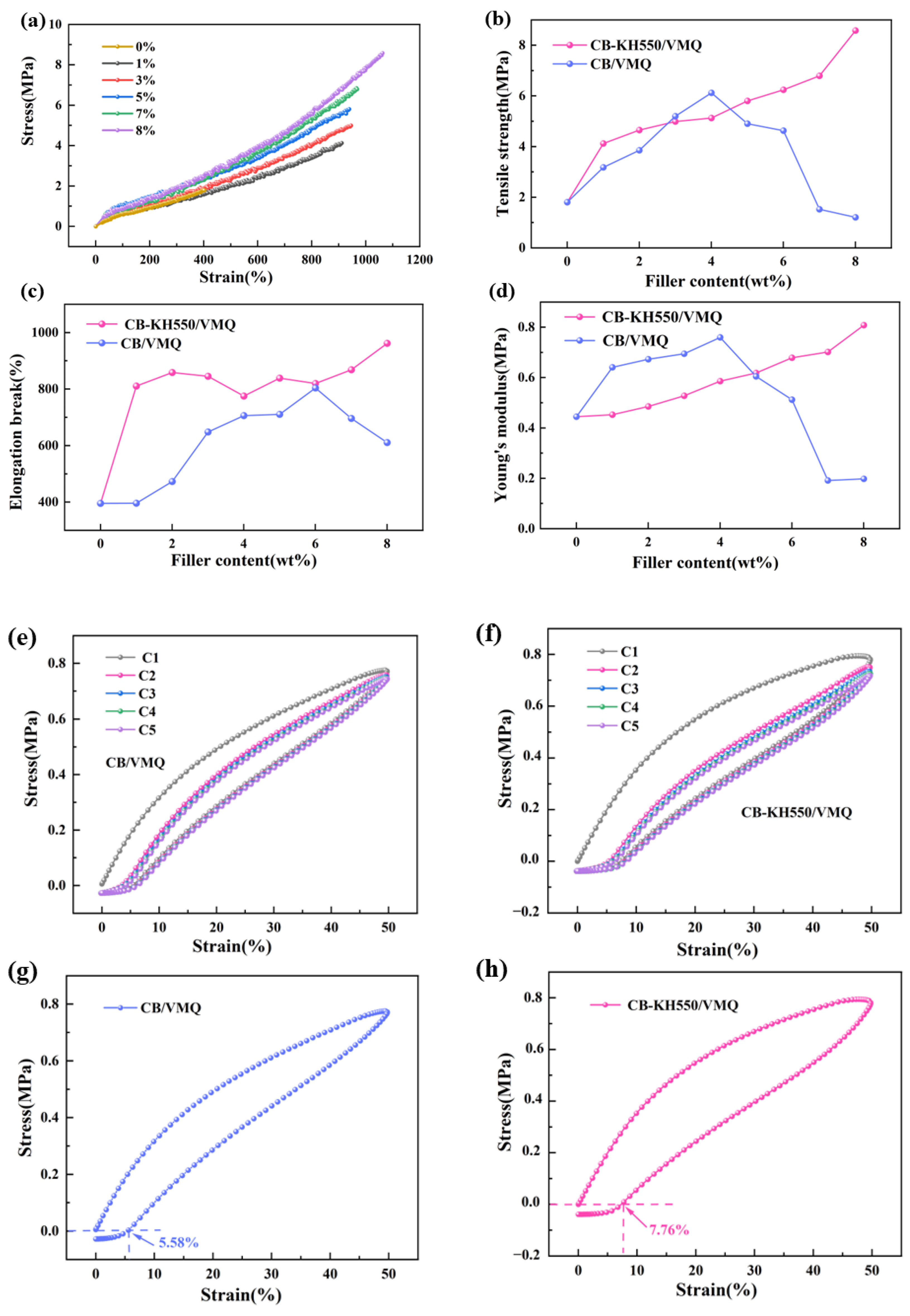
2.1. Mechanical Properties of Two Composites
2.2. Strain Sensing Properties of Composite Materials
2.2.1. Resistance-Strain Response under Static Loading
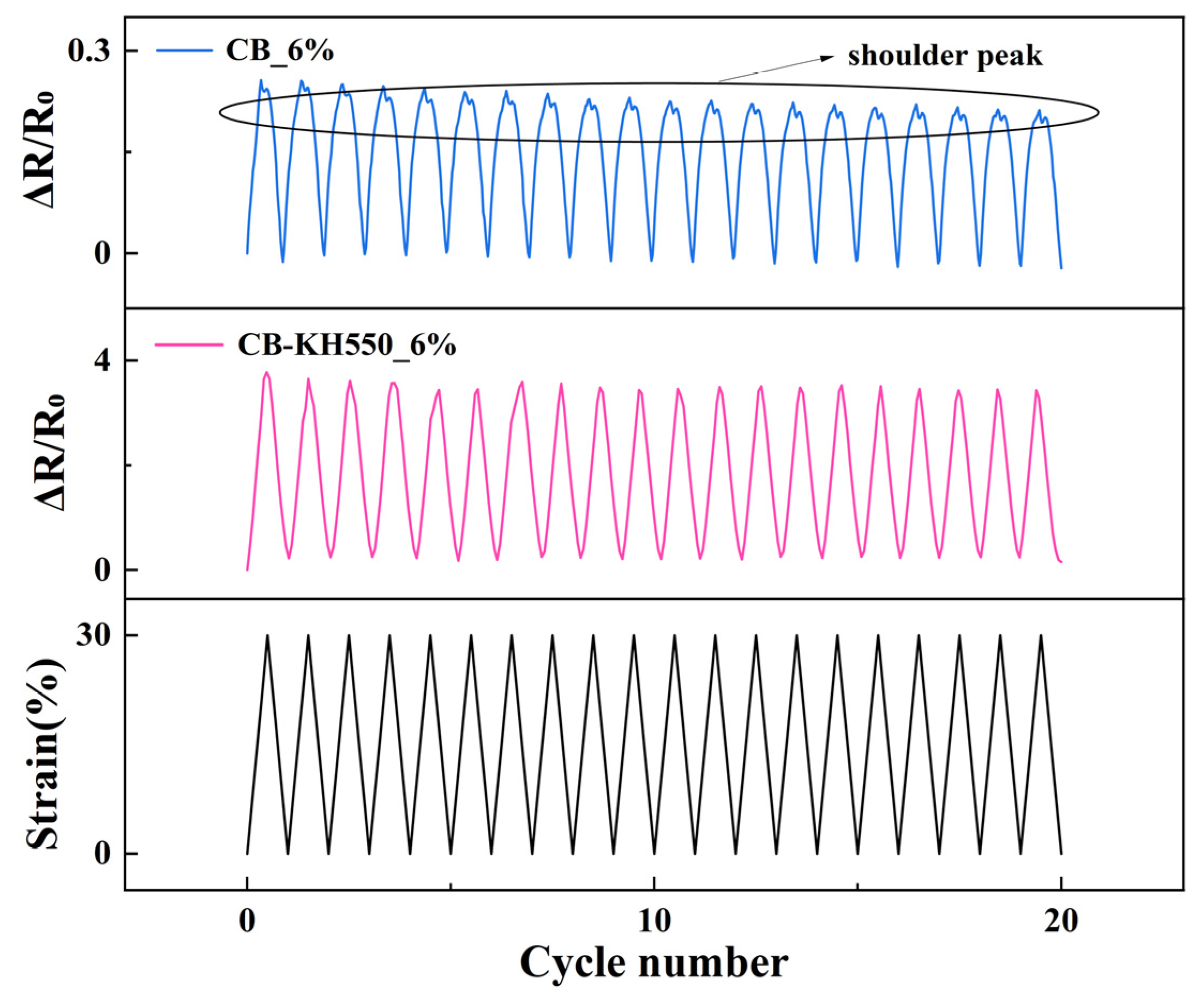
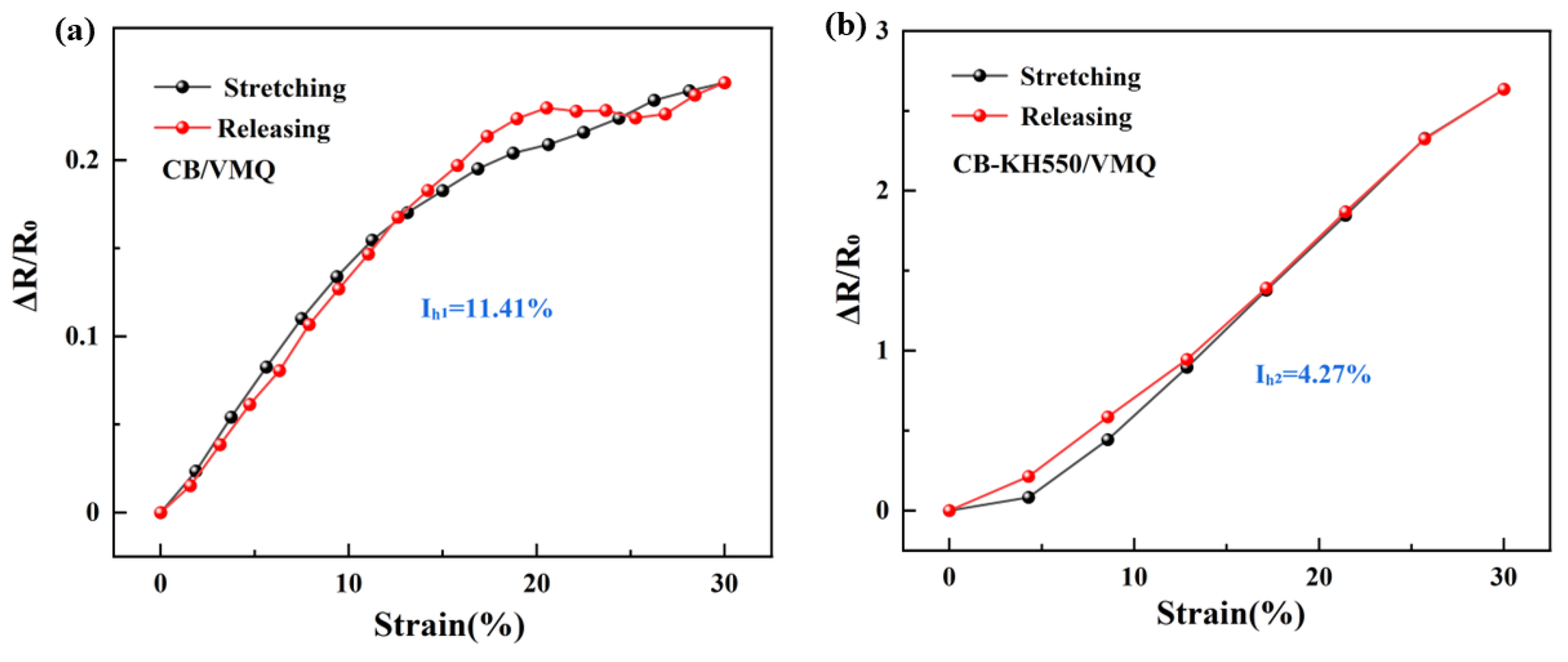
2.2.2. Resistance-Strain Response under Dynamic Loading
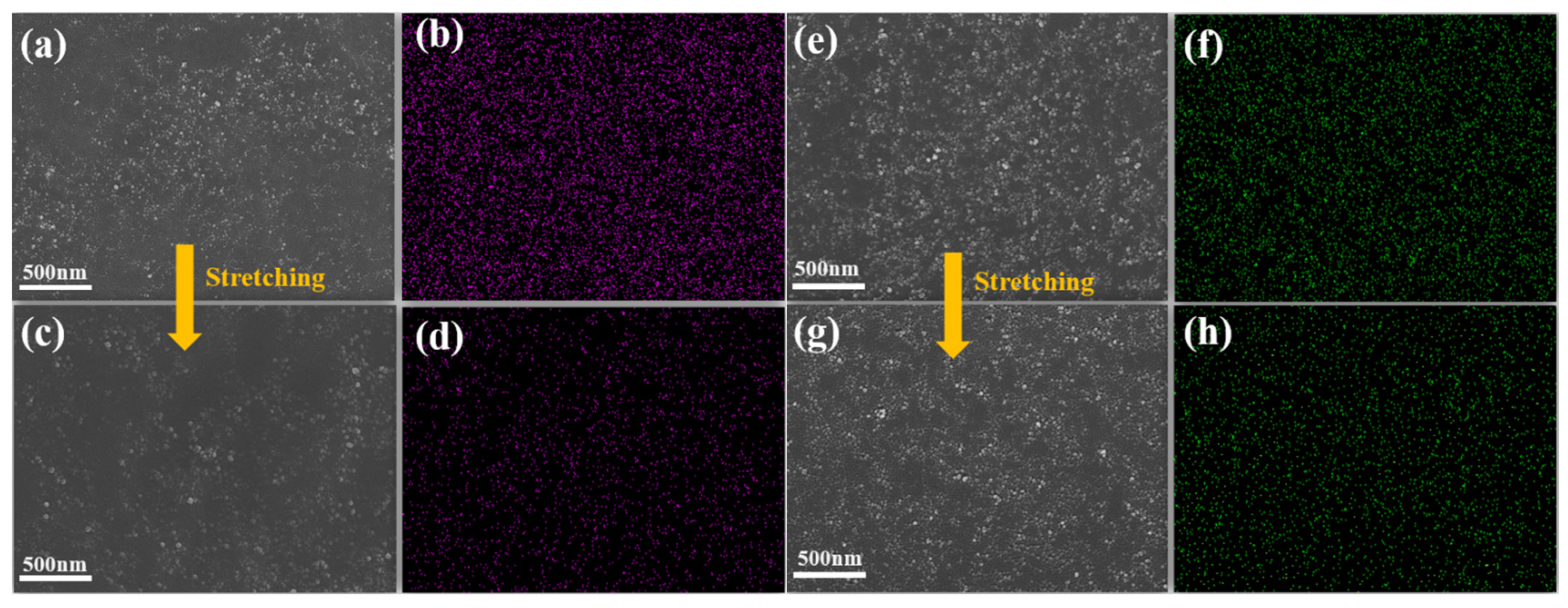
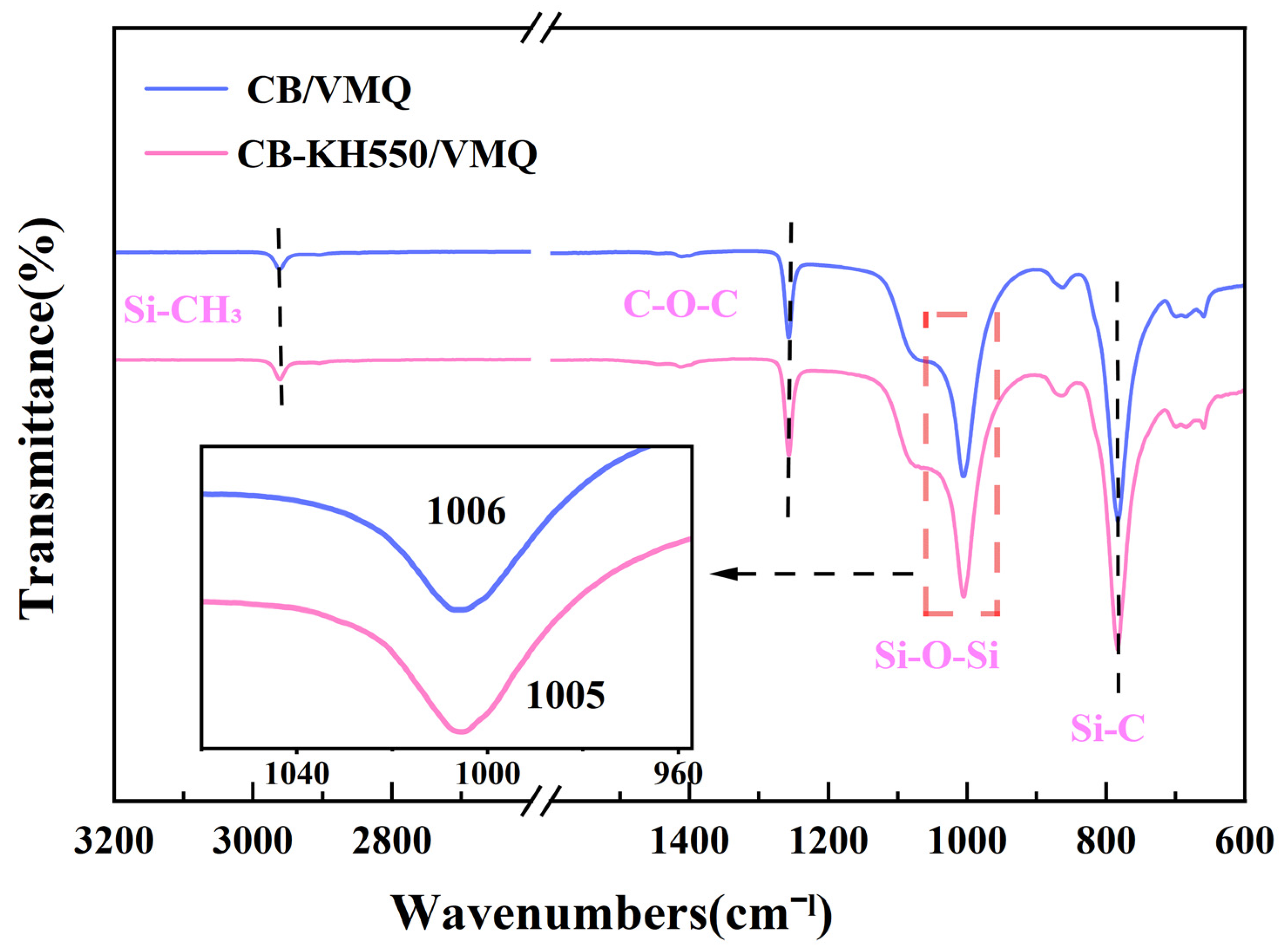
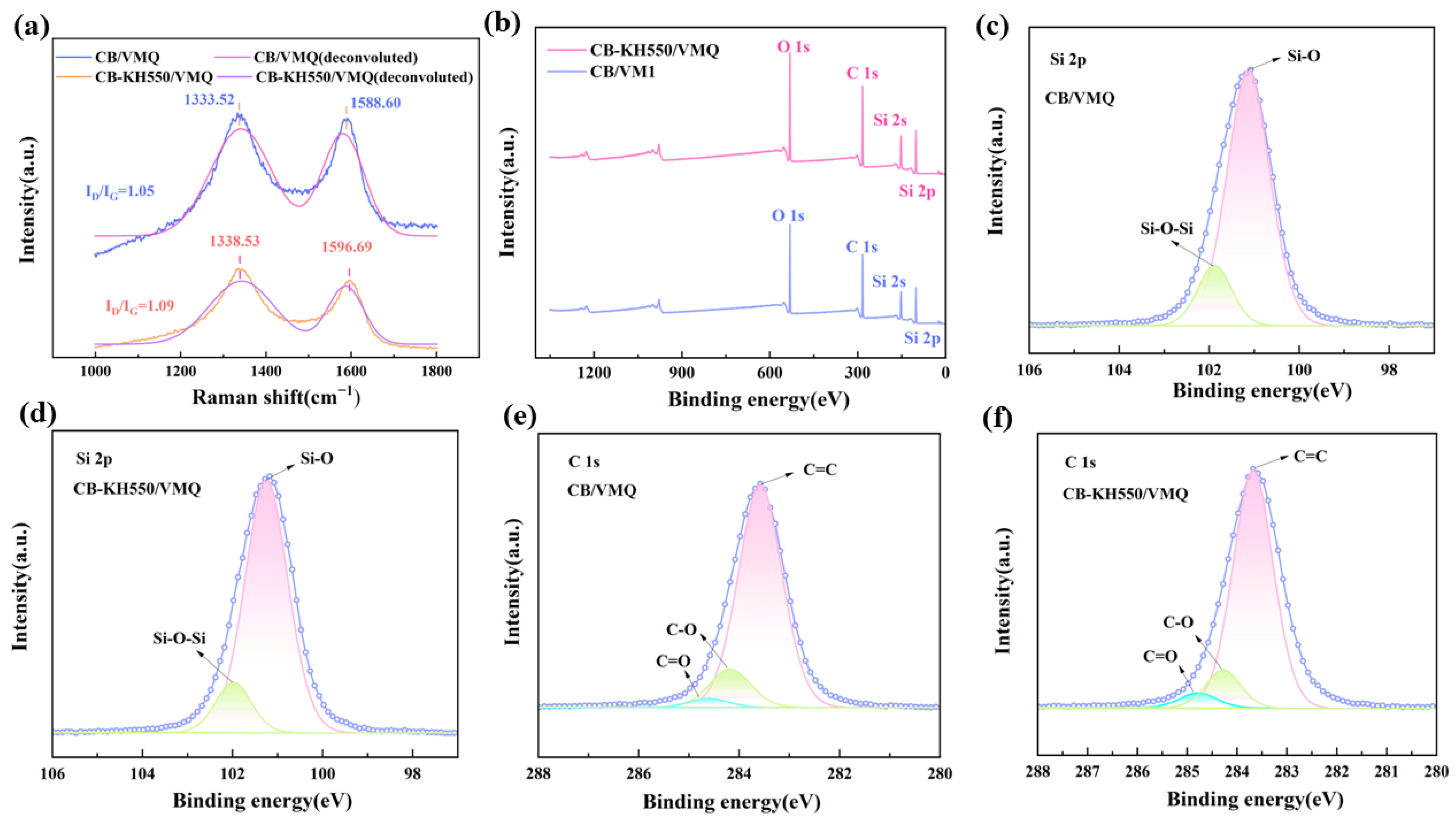
2.3. Dispersion and Interface Effects of Composites
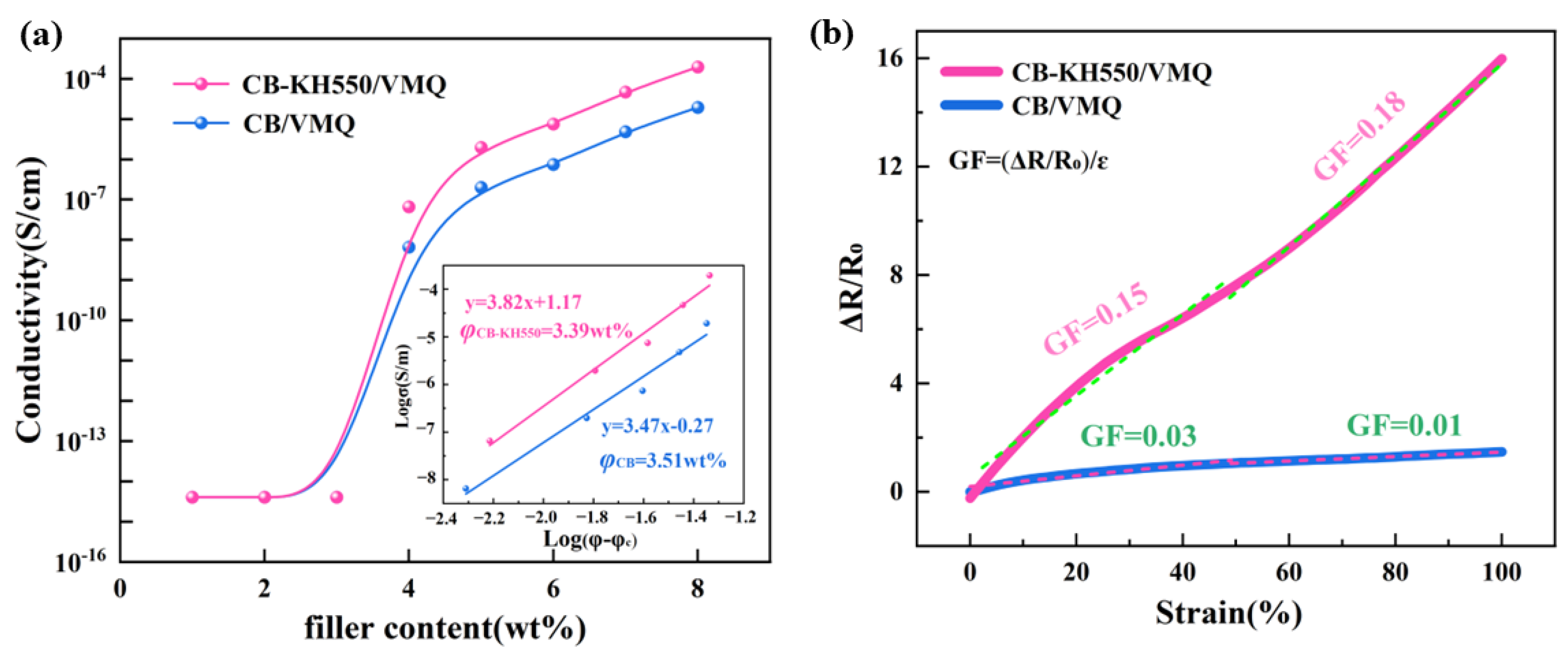
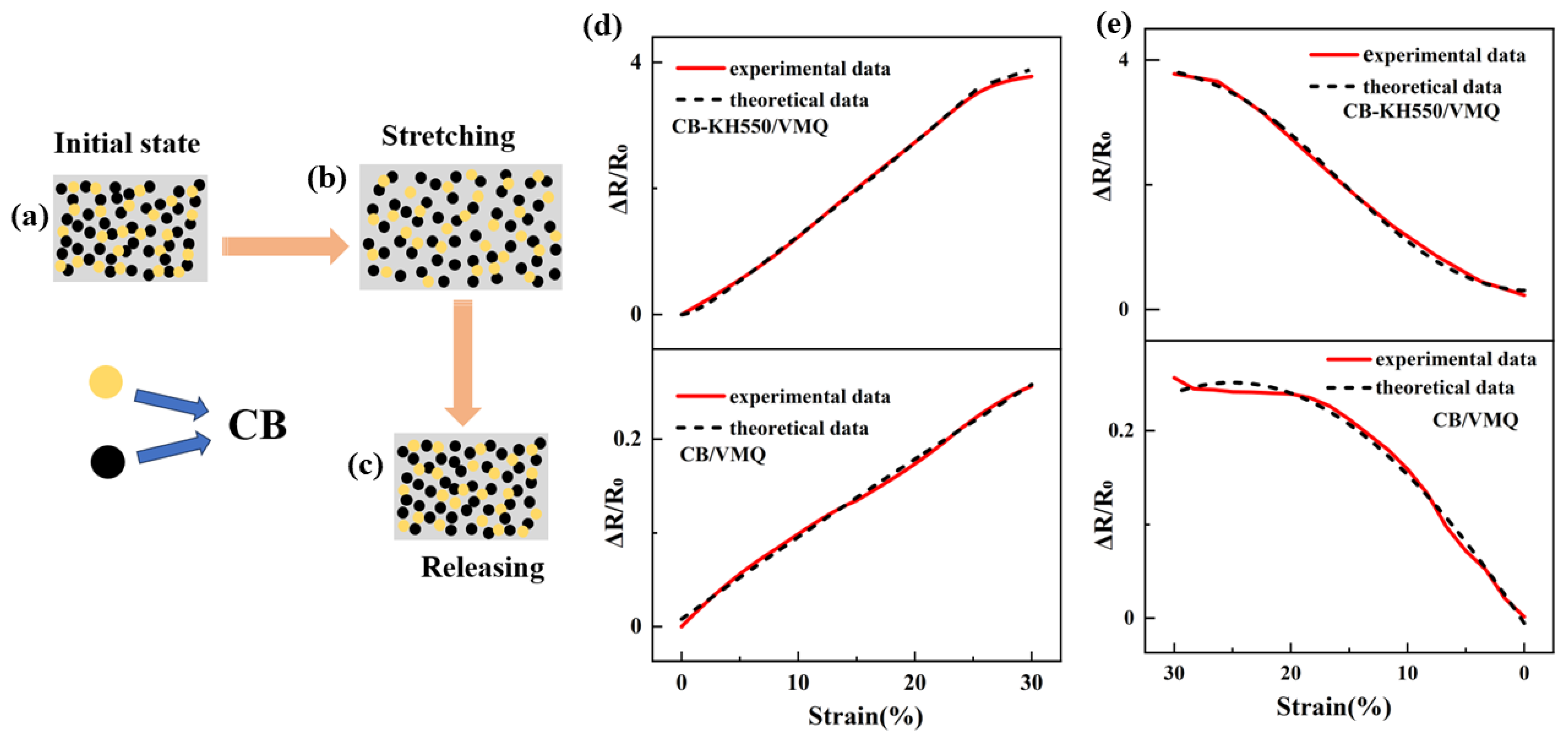
2.4. Strain Sensing Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
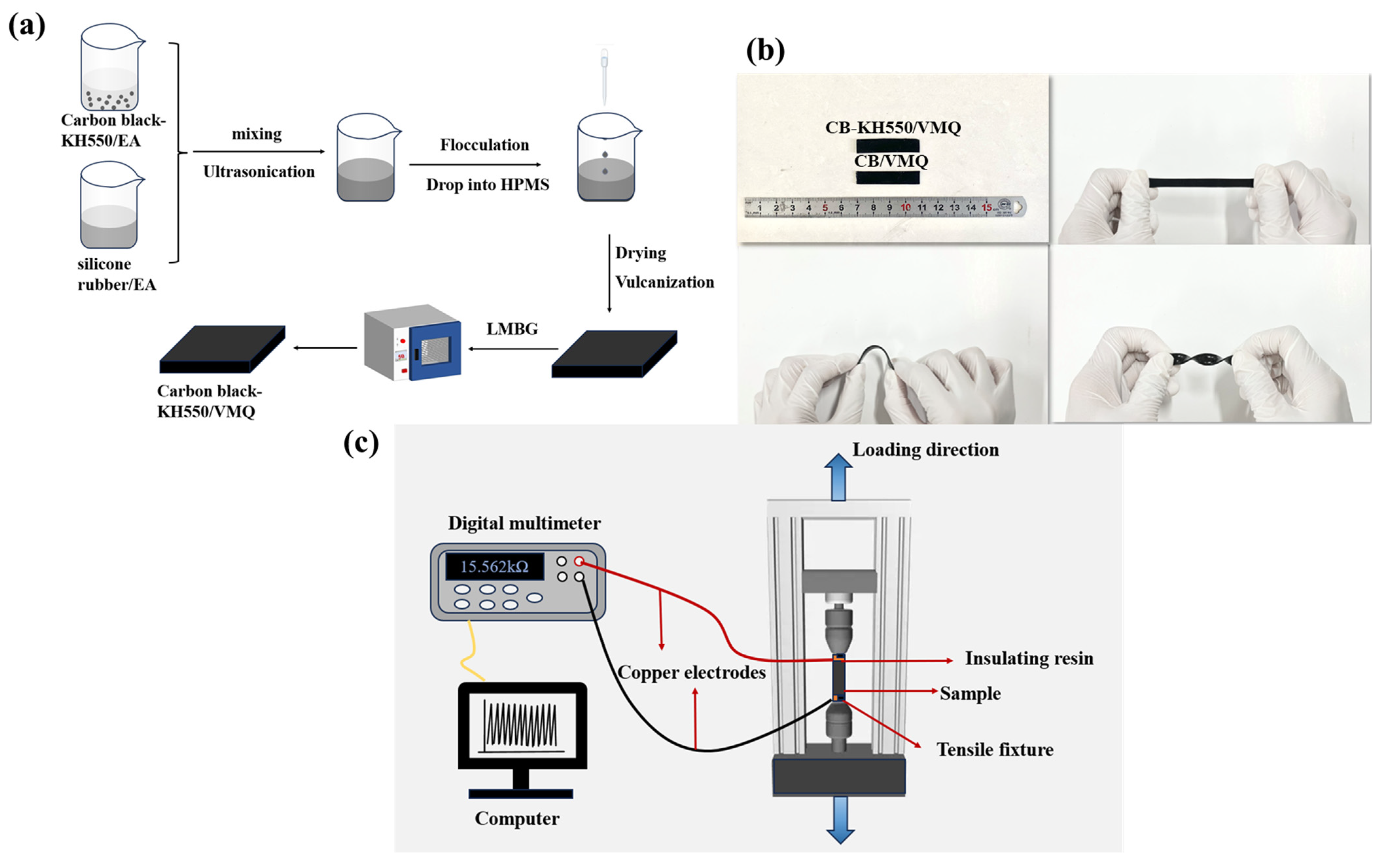
3.2. Preparation of CB-KH550/VMQ Composites
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The percolation thresholds of CB/VMQ and CB-KH550/VMQ composites are 3.51 wt% and 3.39 wt%, respectively, and both composites form three-dimensional tunneling conductive networks;
- (2)
- The addition of KH550 increased the tensile strength, elongation at the break and Young’s modulus of the composites. The tensile strength, elongation at the break and Young’s modulus were increased from 6.12 MPa, 803.7% and 0.75 MPa to 8.58 MPa, 961.7% and 0.81 MPa, respectively;
- (3)
- Compared with the CB/VMQ composites, the shoulder peak phenomenon was not observed in the resistance-strain response properties of CB-KH550/VMQ composites. Meanwhile, the reason for the disappearance of the shoulder phenomenon was explained by the hysteresis effect and the comparison of SEM images and EDS energy spectra before and after stretching;
- (4)
- An analytical model of resistance-strain response was developed, and the comparison of experimental results and theoretical predictions shows that the model can better characterize the relationship between resistance and strain in the composite material during the tensile-unloading stage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, L.; Shang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Bhowmick, S.; Nagarajaiah, S. Review of Bridge Structural Health Monitoring Aided by Big Data and Artificial Intelligence: From Condition Assessment to Damage Detection. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidin, S.S.; Jamadin, A.; Abdul Kudus, S.; Mohd Amin, N.; Anuar, M.A. An Overview: The Application of Vibration-Based Techniques in Bridge Structural Health Monitoring. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2022, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayakwad, H.; Thiyagarajan, J.S. Structural Damage Detection through EMI and Wave Propagation Techniques Using Embedded PZT Smart Sensing Units. Sensors 2022, 22, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, K.; Wang, S.; Liang, C.; Zhu, H. A Silanized MCNT/TPU-Based Flexible Strain Sensor with High Stretchability for Deformation Monitoring of Elastomeric Isolators for Bridges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C. Highly Sensitive, Stretchable, and Wash-Durable Strain Sensor Based on Ultrathin Conductive Layer@Polyurethane Yarn for Tiny Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 9936–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q. TiC2: A New Two-Dimensional Sheet beyond MXenes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and Performance of Graphene/Carbon Black Silicone Rubber Composites Used for Highly Sensitive and Flexible Strain Sensors. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2021, 323, 112659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Ye, D.; Zhu, C.; Qiu, L.; Huang, Y. Stretchable, Highly Durable Ternary Nanocomposite Strain Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring of Flexible Aircraft. Sensors 2017, 17, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Xia, Y.; Yang, H. A Flexible and Highly Sensitive Graphene-Based Strain Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 8217–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegan, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Chu, M.; Nguyen, T.; Park, S.-J.; Paul, A.; Kim, J.; Bachman, M.; Khine, M. Skin-Mountable Stretch Sensor for Wearable Health Monitoring. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17295–17303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallares, R.M.; Su, X.; Lim, S.H.; Thanh, N.T.K. Fine-Tuning of Gold Nanorod Dimensions and Plasmonic Properties Using the Hofmeister Effects. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Liu, L.; Jian, A.; Duan, Q.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Highly Sensitive Wearable Strain Sensor Based on Silver Nanowires and Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 255202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Yao, Y.; Montes-García, V.; Stoeckel, M.; Von Holst, M.; Ciesielski, A.; Samorì, P. Highly Sensitive Strain Sensors Based on Molecules–Gold Nanoparticles Networks for High-Resolution Human Pulse Analysis. Small 2021, 17, 2007593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ma, S.; Yan, T.; Pan, Z. Flexible Strain Sensor Based on CNT/TPU Composite Nanofiber Yarn for Smart Sports Bandage. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 232, 109605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sheng, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Tian, M.; Chen, S.; Jerrams, S.; Zhou, F.; Yu, J. Highly Stretchable and Sensitive SBS/Gr/CNTs Fibers with Hierarchical Structure for Strain Sensors. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 164, 107296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, L.; Gao, L.; Pan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P. Highly Stretchable Strain Sensor Based on SWCNTs/CB Synergistic Conductive Network for Wearable Human-Activity Monitoring and Recognition. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, S.; Zhu, M.; Xu, G.; Sun, L. High-Performance Strain Sensors Based on Bilayer Carbon Black/PDMS Hybrids. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ying, C.; Gao, H.; Liu, Q.; Fu, X.; Hu, S. Highly Flexible Strain Sensors Based on Polydimethylsiloxane/Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Prepared by a Swelling/Permeating Method and Enhanced Sensitivity by CNTs Surface Modification. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 171, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Choi, Y.; Chen, T.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.S.; Kang, J.; Lyu, L.; Gao, J.; Piao, Y. Superhydrophobic and Wearable TPU Based Nanofiber Strain Sensor with Outstanding Sensitivity for High-Quality Body Motion Monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Lu, S. Highly Sensitive and Stretchable MXene/CNTs/TPU Composite Strain Sensor with Bilayer Conductive Structure for Human Motion Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 15504–15516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Niu, K.; Fan, Z.; Guo, R. Resistance Sensing Response Optimization and Interval Loading Continuity of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Natural Rubber Composites: Experiment and Simulation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yuan, L.; Yao, X.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, D. Monotonic Strain Sensing Behavior of Self-Assembled Carbon Nanotubes/Graphene Silicone Rubber Composites under Cyclic Loading. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, D.; Cui, X.; Shi, D.; Zhu, Y. Three-Dimensional Light-Weight Piezoresistive Sensors Based on Conductive Polyurethane Sponges Coated with Hybrid CNT/CB Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 548, 149268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Dai, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. A Highly Stretchable and Stable Strain Sensor Based on Hybrid Carbon Nanofillers/Polydimethylsiloxane Conductive Composites for Large Human Motions Monitoring. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wan, K.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Feng, Q.; Zhaofang, D. Thermospun Conductive Composites with a Wide Strain Range, Excellent Fatigue Resistance, and High Linearity for Fibrous Strain Sensors. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2023, 1, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W. Design of Flexible Strain Sensor with Both Ultralow Detection Limit and Wide Sensing Range via the Multiple Sensing Mechanisms. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 213, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, A.J.; Papageorgiou, D.G.; Vallés, C.; Liscio, A.; Palermo, V.; Bissett, M.A.; Young, R.J.; Kinloch, I.A. Electrical Percolation in Graphene–Polymer Composites. 2D Mater. 2018, 5, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-C. Carbon Black Filled Conducting Polymers and Polymer Blends. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2002, 21, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Lin, L.; Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Fu, Q. Progress on the Morphological Control of Conductive Network in Conductive Polymer Composites and the Use as Electroactive Multifunctional Materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 627–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yao, X.; Zheng, Z.; Gong, L.; Yuan, L.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y. Highly Sensitive and Stretchable Graphene-Silicone Rubber Composites for Strain Sensing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 167, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.T. Highly Sensitive Metal-Grid Strain Sensors via Water-Based Solution Processing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42153–42159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, K.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Highly Stretchable and Durable Fiber-Shaped Strain Sensor with Porous Core-Sheath Structure for Human Motion Monitoring. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 189, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yue, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Multifunctional Stretchable Strain Sensor Based on Polydopamine/Reduced Graphene Oxide/Electrospun Thermoplastic Polyurethane Fibrous Mats for Human Motion Detection and Environment Monitoring. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, M.; Shang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-Sensitive and Durable Strain Sensor with Sandwich Structure and Excellent Anti-Interference Ability for Wearable Electronic Skins. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, K.; Yan, C.; Zheng, G.; Huang, J.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-Stretchable, Durable and Conductive Hydrogel with Hybrid Double Network as High Performance Strain Sensor and Stretchable Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ang, M.H. Effect of Different Prestretching Index and Preloading on Actuation Behaviors of Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4064–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Yang, Y.; Guo, R.; Fan, Z.; Deng, P.; Zhang, S. Effect of Vulcanization on the Electro-Mechanical Sensing Characteristics of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Silicone Rubber Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Filler | m | k1 | k2 | K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CB-KH550 | 1.834 | 0.047 | 0.283 | 0.119 | 0.177 | 0.134 |
| CB | 48.127 | 67.158 | 25.225 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.043 |
| Materials | Content |
|---|---|
| VMQ | 100 |
| CB | Variable X (X = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) |
| KH550 | Variable Y (Y = X/4) |
| SiO2 | 20 |
| HPMS | 4 |
| DCP | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wan, B.; Ding, T.; Sha, X. Enhancement of the Electric-Force Response of Carbon Black/Silicone Rubber Composites by Silane Coupling Agents. Molecules 2024, 29, 2740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122740
Zhao Y, Yang Y, Wan B, Ding T, Sha X. Enhancement of the Electric-Force Response of Carbon Black/Silicone Rubber Composites by Silane Coupling Agents. Molecules. 2024; 29(12):2740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122740
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yanfang, Yang Yang, Bangwei Wan, Tianyu Ding, and Xun Sha. 2024. "Enhancement of the Electric-Force Response of Carbon Black/Silicone Rubber Composites by Silane Coupling Agents" Molecules 29, no. 12: 2740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122740
APA StyleZhao, Y., Yang, Y., Wan, B., Ding, T., & Sha, X. (2024). Enhancement of the Electric-Force Response of Carbon Black/Silicone Rubber Composites by Silane Coupling Agents. Molecules, 29(12), 2740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122740






