Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Assessment of New Haloperidol Analogues as Potential Anticancer Compounds Targeting Sigma Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology and Computational
2.2.1. SR Binding Affinities, SAR Discussion
2.2.2. Cytotoxic Profiles
2.2.3. Molecular Docking
2.2.4. In Silico ADME Properties and Toxicity Prediction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Chemical Reagents and Instruments
3.1.2. Synthetic Procedure
General Synthesis of Compounds 4a–j
3.2. Computational
Docking
3.3. Biology
3.3.1. S1R and S2R Binding Assays
3.3.2. Viability Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanner, M.; Moebius, F.F.; Flandorfer, A.; Knaus, H.G.; Striessnig, J.; Kempner, E.; Glossmann, H. Purification, molecular cloning, and expression of sigma1-binding site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8072–8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.P. Evidence for sigma opioid receptor: Binding of [3H]SKF-10047 to etorphine-inaccessible sites in guinea-pig brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1982, 223, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quirion, R.; Bowen, W.D.; Itzhak, Y.; Junien, Y.L.; Musacchio, J.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Su, T.P.; Tam, S.W.; Taylor, D.P. A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1992, 13, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M.; Bowen, W.D.; Goldstein, S.R.; Roberts, A.H.; Patrick, S.L.; Hohmann, A.G.; De Costa, B. Autoradiographic distribution of [3H](+)-pentazocine and [3H]1,3-di-o-tolylguanidine (DTG) binding sites in guinea pig brain: A comparative study. Brain Res. 1992, 581, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, P.; Quirion, R. [3H]1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine and [3H](+)pentazocine binding sites in the rat brain: Autoradiographic visualization of the putative sigma1 and sigma2 receptor subtypes. Neuroscience 1997, 76, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.R.; Zheng, S.; Gurpinar, E.; Koehl, A.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C. Crystal structure of the human σ1 receptor. Nature 2016, 532, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashy, T.; Su, T. Regulating ankyrin dynamics: Roles of sigma-1 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Bowen, W.D. Role of sigma-1 receptor C-terminal segment in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor activation: Constitutive enhancement of calcium signaling in MCF-7 tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 28198–28215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobos, E.J.; Entrena, J.M.; Nieto, F.R.; Cendan, C.M.; Pozo, E.D. Pharmacology and therapeutic potential of sigma-1 ligands. Curr. Neuropharmocol. 2008, 6, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, T.; Lockhart, B.P. Neuroprotective and anti-amnesic potentials of σ (sigma) receptor ligands, Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 21, 69–102. [Google Scholar]
- King, M.; Pan, Y.X.; Mei, J.; Chang, J.; Xu, J.; Pasternak, G.W. Enhanced kappa-opioid receptor-mediated analgesia by antisense targeting the sigma1 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 331, R5–R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, K.A.; Bowen, W.D.; Walker, F.O.; De Costa, B.; Matsumoto, R.R. Two novel sigma receptor ligands, BD1047 and LR172, attenuate cocaine-induced toxicity and locomotor activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 370, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, F.J.; Maher, C.M. Sigma1 Pharmacology in the Context of Cancer. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 244, pp. 237–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K. Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: Targeting the sigma-1 receptor. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, A.; Schmidt, H.R.; Wood, M.D.; Sahn, J.J.; Martin, S.F.; Kruse, A.C. Identification of the gene that codes for the σ2 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7160–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartz, F.; Kern, L.; Erz, D.; Zhu, M.; Gilbert, D.; Meinhof, T.; Wirkner, U.; Erfle, H.; Muckenthaler, M.; Pepperkok, R.; et al. Identification of cholesterol-regulating genes by targeted RNAi screening. Cell. Metab. 2009, 10, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riad, A.; Zeng, C.; Weng, C.C.; Winters, H.; Xu, K.; Makvandi, M.; Metz, T.; Carlin, S.; Mach, R.H. Sigma-2 Receptor/TMEM97 and PGRMC-1 Increase the Rate of Internalization of LDL, by LDL Receptor through the Formation of a Ternary Complex. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, A.; Lyu, J.; Braz, J.M.; Tummino, T.A.; Craik, V.; O’Meara, M.J.; Webb, C.M.; Radchenko, D.S.; Moroz, Y.S.; Huang, X.P.; et al. Structures of the σ2 receptor enable docking for bioactive ligand discovery. Nature 2021, 600, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cratteri, P.; Romanelli, M.N.; Cruciani, G.; Bonaccini, C.; Melani, F. Grind-derived pharmacopore model for a series of alfa-trophanyl derivative ligands of the sigma-2 receptor. J. Comuput. Aided Mol. Des. 2004, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurini, E.; Zampieri, D.; Mamolo, M.G.; Vio, L.; Zanette, C.; Florio, C.; Posocco, P.; Fermeglia, M.; Pricl, S. A 3D-Pharmacophore model for σ2 receptors based on a series of substituted benzo[d]oxazol-2(3H)-one derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2954–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, D.J.; Kinder, D.H.; Mahfouz, T.M. A Comprehensive Ligand Based Mapping of the σ2 Receptor Binding Pocket. Med. Chem. 2014, 10, 98–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, H.R.; Liu, D.; Lv, F.Z.; Li, J.N. Overexpression of MAC30 is associated with poor clinical outcome in human non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Gui, X.H.; Lin, X.B.; Chen, R.H.; Cai, H.R.; Fen, Y.; Sheng, Y.L. Prognostic value of MAC30 expression in human pure squamous cell carcinomas of the lung. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 2705–2710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, Y.; Jia, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Expression of AC30 protein is related to survival and clinicopathological variables in breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Ning, X.; Meng, F.; Xiao, M.; Wang, D.; Lou, G.; Zhang, Y. Elevated expression of MAC30 predicts lymph node metastasis and unfavorable prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Yu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.T.; Huang, W.J.; Nie, X.C.; Song, C.Q. Downregulated MAC30 expression inhibits proliferation and mobility of human gastric cancer cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayed, H.; Kleeff, J.; Ding, J.; Hammer, J.; Giese, T.; Zentgraf, H.; Büchler, M.W.; Friess, H. Expression analysis of MAC30 in human pancreatic cancer and tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Histol. Histopathol. 2004, 19, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.; Pykett, M.J.; Harnish, P.; Zang, K.D.; George, D.L. Identification and characterization of genes differentially expressed in meningiomas. Cell Growth Differ. 1993, 4, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseaux, C.G.; Greene, S.F. Sigma receptors [σRs]: Biology in normal and diseased states. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2016, 36, 327–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanillo, D.; Romero, L.; Merlos, M.; Vela, J.M. Sigma1 receptor: A new therapeutic target for pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahn, J.J.; Mejia, G.L.; Ray, P.R.; Martin, S.F.; Price, T.J. Sigma 2 Receptor/Tmem97 Agonists Produce Long Lasting Antineuropathic Pain Effects in Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, D.R.; Monsma, F.J., Jr. Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1992, 13, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravliova, E.; Barbakadze, T.; Natsvlishvili, N.; Mikeladze, D.G. Haloperidol induces neurotoxicity by the NMDA receptor downstream signaling pathway, alternative from glutamate excitotoxicity. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 50, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalwadi, D.A.; Kim, S.; Schetz, J.A. Activation of the sigma-1 receptor by haloperidol metabolites facilitates brain-derived neurotrophic factor secretion from human astroglia. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 105, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrazzo, A.; Fiorito, J.; Zappalà, L.; Prezzavento, O.; Ronsisvalle, S.; Pasquinucci, L.; Scoto, G.M.; Bernardini, R.; Ronsisvalle, G. Antiproliferative activity of phenylbutyrate ester of haloperidol metabolite II [(±)-MRJF4. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Pore, S.K.; Sinha, S.; Janardhanan, R.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Banerjee, R. Structure-Activity Study To Develop Cationic Lipid-Conjugated Haloperidol Derivatives as a New Class of Anticancer Therapeutics. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2378–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozio, P.; Fiorito, J.; Di Giacomo, V.; Di Stefano, A.; Marinelli, L.; Cacciatore, I.; Cataldi, A.; Pacella, S.; Turkez, H.; Parenti, C.; et al. Haloperidol metabolite II prodrug: Asymmetric synthesis and biological evaluation on rat C6 glioma cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amata, E.; Dichiara, M.; Arena, E.; Pittalà, V.; Pistarà, V.; Cardile, V.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Fraix, A.; Marrazzo, A.; Sortino, S.; et al. Novel Sigma Receptor Ligand-Nitric Oxide Photodonors: Molecular Hybrids for Double-Targeted Antiproliferative Effect. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9531–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennon, R.A.; Ablordeppey, S.Y.; Ismaiel, A.M.; El-Ashmawy, M.B.; Fischer, J.B.; Howie, K.B. Structural features important for sigma1 receptor binding. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, D.; Mamolo, M.G.; Laurini, E.; Florio, C.; Zanette, C.; Fermeglia, M.; Posocco, P.; Paneni, M.S.; Pricl, S.; Vio, L. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and three-dimensional in silico pharmacophore model for σ1 receptor ligand based on a series of benzo[d]oxazol-2(3H)-one derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5380–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, D.; Fortuna, S.; Calabretti, A.; Romano, M.; Menegazzi, R.; Schepmann, D.; Wünsch, B.; Collina, S.; Zanon, D.; Mamolo, M.G. Discovery of new potent dual sigma receptor/GluN2b ligands with antioxidant property as neuroprotective agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niso, M.; Abate, C.; Conti, M.; Ferorelli, S.; Azzariti, A.; Perrone, R.; Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F. Sigma-2 receptor agonists as possible antitumor agents in resistant tumors: Hints for collateral sensitivity. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lee, P.W.; Tang, Y. admetSAR: A comprehensive source and free tool for evaluating chemical ADMET properties. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lou, C.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. admetSAR 2.0: Web-service for prediction and optimization of chemical ADMET properties. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, G.P.; Day, C.P.; Kesteven, P.J.L.; Daly, A.K. Association of polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 with warfarin dose requirement and risk of bleeding complications. Lancet 1999, 353, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, D.; Fortuna, S.; Romano, M.; Amata, E.; Dichiara, M.; Marrazzo, A.; Pasquinucci, L.; Turnaturi, R.; Mamolo, M.G. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel aminopropylcarboxamide derivative sas sigma ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 72, 128860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheeseright, T.; Mackey, M.; Rose, S.; Vinter, A. Molecular Field Extrema as Descriptors of Biological Activity: Definition and Validation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.R.; Mackey, M.D. Electrostatic Complementarity as a Fast and Effective Tool to Optimize Binding and Selectivity of Protein–Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3036–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Stuart Firth-Clark, S.; Tosco, P.; Mey Antonia, S.J.S.; Mackey, M.; Michel, J. Assessment of Binding Affinity via Alchemical Free-Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amata, E.; Rescifina, A.; Prezzavento, O.; Arene, E.; Dichiara, M.; Pittalà, V.; Montilla-Gargia, A.; Punzo, F.; Merini, P.; Cobos, E.J.; et al. (+)-Methyl (1R,2S)-2-{[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]methyl}-1-phenylcyclopropanecarboxylate [(+)-MR200] Derivatives as Potent and Selective Sigma Receptor Ligands: Stereochemistry and Pharmacological Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrazzo, A.; Dichiara, M.; Cosentino, G.; Amata, E.; Gitto, R. Discovery and computational studies of piperidine/piperazine-based compounds endowed with sigma receptor affinity. RCS Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Dichiara, M.; Ambrosio, F.A.; Barbaraci, C.; Gonzalez-Cano, R.; Costa, G.; Parenti, C.; Marrazzo, A.; Pasquinucci, L.; Cobos, E.J.; Alcaro, S.; et al. Synthesis, Computational Insights, and Evaluation of Novel Sigma Receptors Ligands. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1845–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encinas, M.; Iglesias, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Muhaisen, A.; Ceña, V.; Gallego, C.; Comella, J.X. Sequential treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor gives rise to fully differentiated, neurotrophic factor-dependent, human neuron-like cells. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, M.; Yamaji, T.; Saito, K.; Shirasago, Y.; Satomura, K.; Endo, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Hanada, K.; Osada, N. Identification of Characteristic Genomic Markers in Human Hepatoma HuH-7 and Huh7.5.1-8 Cell Lines. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 546106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, D.; Calabretti, A.; Romano, M.; Fortuna, S.; Collina, S.; Amata, E.; Dichiara, M.; Marrazzo, A.; Mamolo, M.G. Cytotoxicity Profiles and Neuroprotective Properties of the Novel Ifenprodil Analogues as Sigma Ligands. Molecules 2023, 28, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmpd |  | Ki S1R (nM) a | Ki S2R (nM) a | S2R/S1R | S1R/S2R |
| 4a |  | 21.58 ± 3.44 | 210.38 ± 21.37 | 10 | 0.5 |
| 4b |  | 44.46 ± 7.39 | 124.17 ± 16.27 | 2.8 | 0.35 |
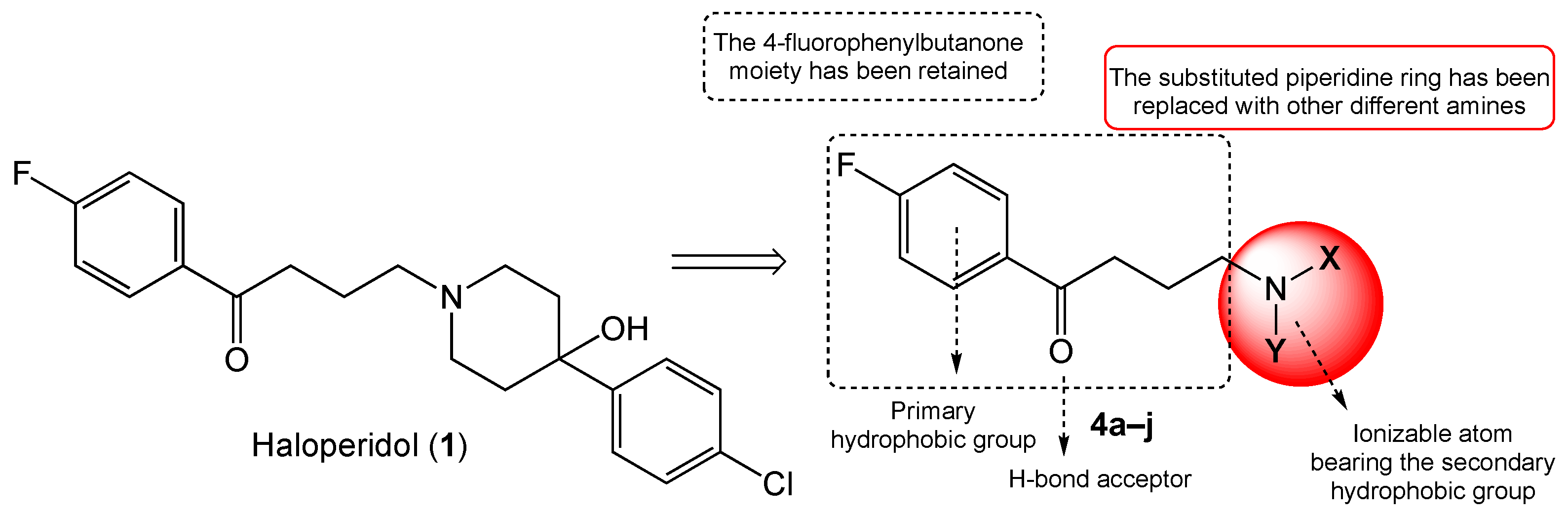
| 4c | 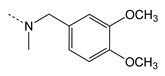 | 301.30 ± 74.73 | 148.25 ± 10.34 | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| 4d |  | 18.79 ± 2.91 | 13.15 ± 2.78 | 0.7 | 1.4 |
| 4e | 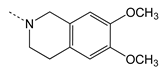 | 1663.41 ± 118.09 | 6.93 ± 0.76 | 0.004 | 241 |
| 4f |  | 70.15 ± 23.19 | 16.37 ± 3.17 | 0.23 | 4.3 |
| 4g | 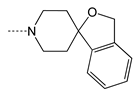 | 6.30 ± 1.40 | 9.23 ± 0.95 | 1.46 | 0.7 |
| 4h | 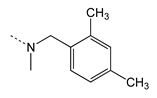 | 59.70 ± 7.60 | 27.73 ± 3.03 | 0.46 | 2.1 |
| 4i |  | 13.90 ± 3.11 | 28.31 ± 3.33 | 2.03 | 0.5 |
| 4j |  | 6.10 ± 0.58 | 152.76 ± 30.31 | 25 | 0.04 |
| HAL b | - | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 16 ± 1.7 | 30 | 0.03 |
| (+)-PTZ c | - | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 1465 ± 224 | 312 | 0.003 |
| DTG d | - | 124 ± 19 | 18 ± 1 | 0.14 | 6.9 |
| SRM e | - | 10.5 ± 2.6 | 12.6 ± 0.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| Cmpd | IC50 (μM) | |
|---|---|---|
| SH-SY5Y | HUH-7 | |
| 4d | 0 | 163 ± 18 |
| 4e | 120 ± 13 | 40 ± 5 |
| 4g | 57 ± 6 | 16 ± 2 |
| 4j | 58 ± 7 | 37 ± 6 |
| HAL | 41 ± 6 | 19 ± 2 |
| SRM | 5.0 ± 1 | 2.0 ± 0.25 |
| Cmpd | clogP | clogS | Skin Permeant | RO5 Violation | BBB Permeant | GI Abs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Coctanol]/[Cwater] | (mol/L)water | cm/s | ≤1 | - | - | |
| 4d | 3.64 | −4.00 | −5.73 | 0 | Yes | High |
| 4e | 3.72 | −4.15 | −5.99 | 0 | Yes | High |
| 4g | 3.91 | −4.12 | −6.11 | 0 | Yes | High |
| 4j | 4.54 | −4.98 | −5.41 | 0 | Yes | High |
| HAL | 4.22 | −4.82 | −5.54 | 0 | Yes | High |
| SRM | 5.85 | −6.52 | −4.78 | 1 | No | Low |
| Cmpd | CYP2C8 | CYP1A2 | CYP2C19 | CYP2C9 | CYP2D6 | CYP3A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition | ||||||
| 4d | −0.8113 | +0.6893 | +0.5571 | −0.7488 | +0.8636 | −0.8616 |
| 4e | −0.5596 | −0.5000 | −0.6131 | −0.7220 | +0.6847 | −0.8254 |
| 4g | −0.7173 | −0.6239 | −0.7124 | −1.0000 | +0.5507 | −0.6430 |
| 4j | +0.7192 | −0.7398 | −0.6508 | −0.6607 | +0.6378 | −0.8955 |
| HAL | −0.6600 | −0.9045 | −0.9248 | −1.0000 | +0.5101 | +0.6899 |
| SRM | −0.7403 | +0.7752 | +0.5786 | −0.7062 | −0.5673 | +0.5827 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zampieri, D.; Romano, M.; Fortuna, S.; Amata, E.; Dichiara, M.; Cosentino, G.; Marrazzo, A.; Mamolo, M.G. Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Assessment of New Haloperidol Analogues as Potential Anticancer Compounds Targeting Sigma Receptors. Molecules 2024, 29, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112697
Zampieri D, Romano M, Fortuna S, Amata E, Dichiara M, Cosentino G, Marrazzo A, Mamolo MG. Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Assessment of New Haloperidol Analogues as Potential Anticancer Compounds Targeting Sigma Receptors. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112697
Chicago/Turabian StyleZampieri, Daniele, Maurizio Romano, Sara Fortuna, Emanuele Amata, Maria Dichiara, Giuseppe Cosentino, Agostino Marrazzo, and Maria Grazia Mamolo. 2024. "Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Assessment of New Haloperidol Analogues as Potential Anticancer Compounds Targeting Sigma Receptors" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112697
APA StyleZampieri, D., Romano, M., Fortuna, S., Amata, E., Dichiara, M., Cosentino, G., Marrazzo, A., & Mamolo, M. G. (2024). Design, Synthesis, and Cytotoxic Assessment of New Haloperidol Analogues as Potential Anticancer Compounds Targeting Sigma Receptors. Molecules, 29(11), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112697








