Synthesis of Boronate Affinity-Based Oriented Dummy Template-Imprinted Magnetic Nanomaterials for Rapid and Efficient Solid-Phase Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Food
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
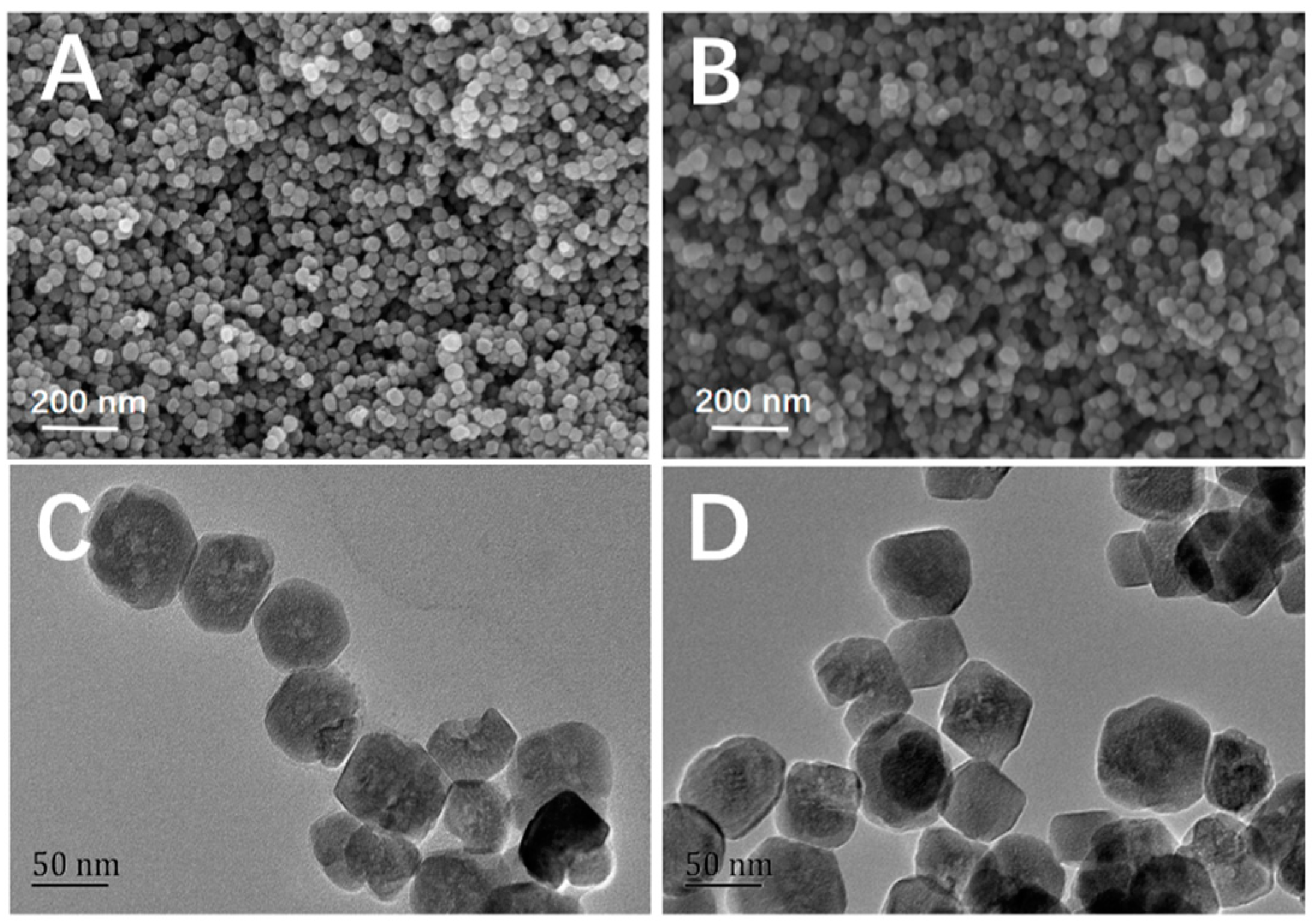
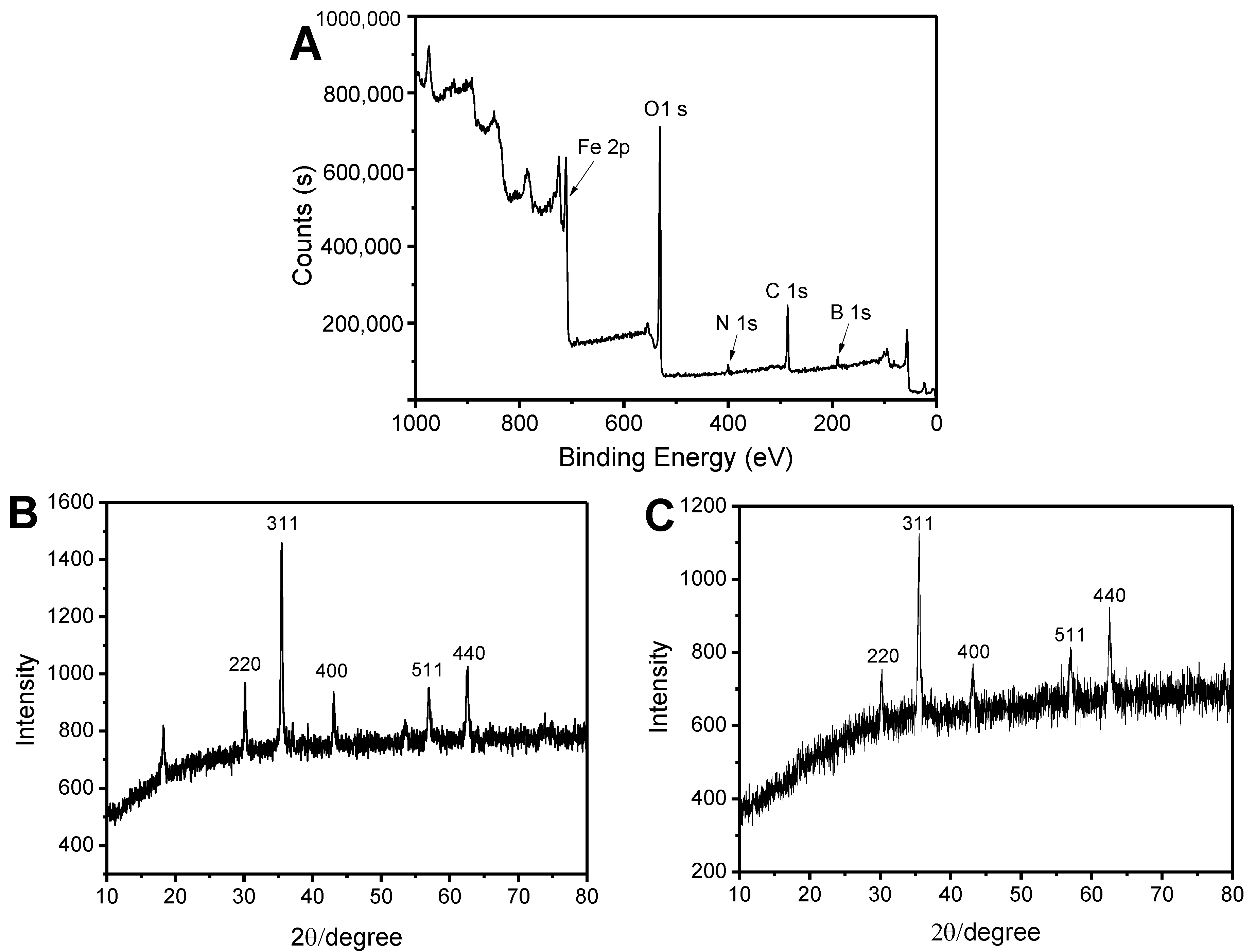
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@FFPBA@MIPs
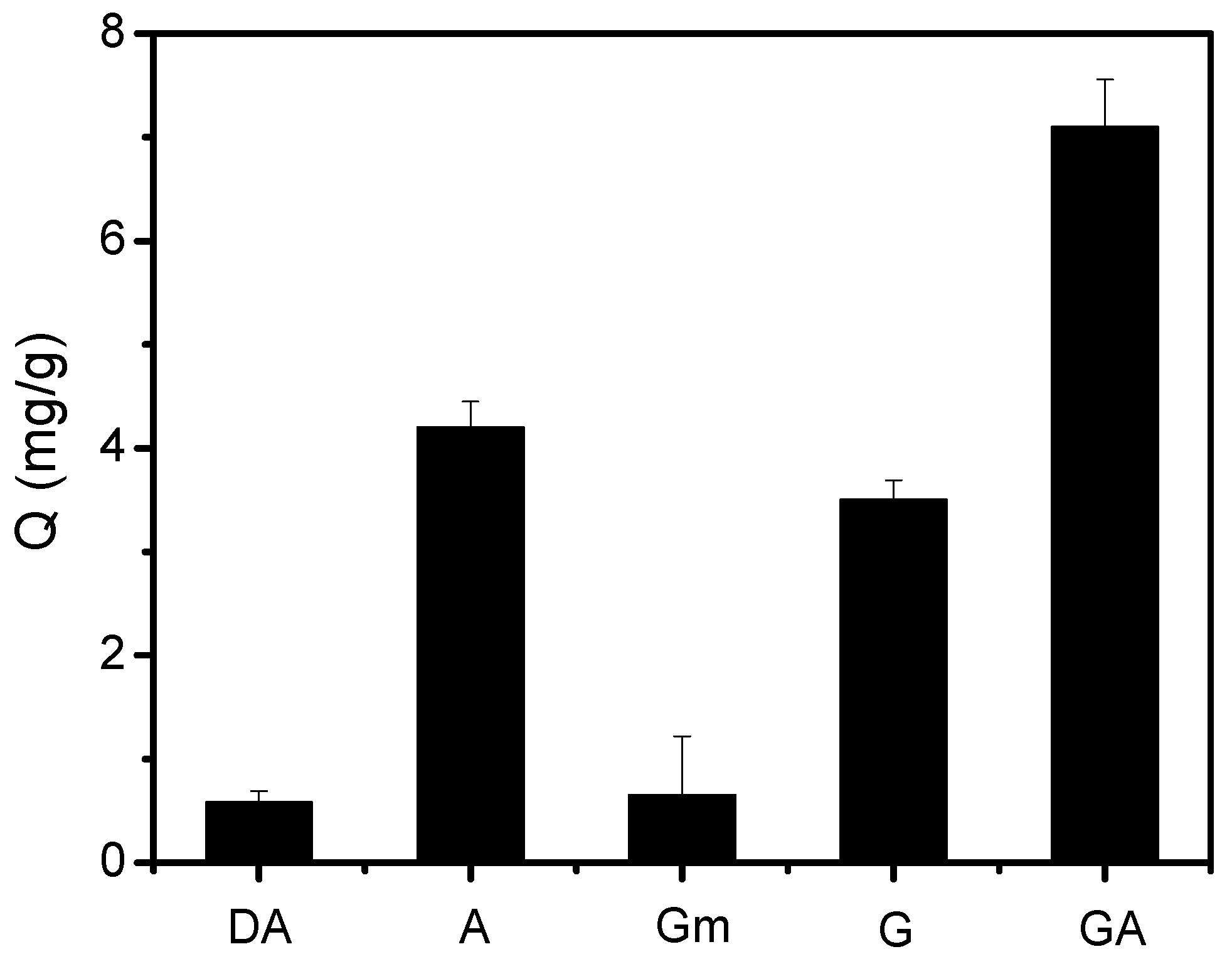
2.2. Selectivity of Fe3O4@FFPBA
2.3. Investigation of Imprinting Conditions
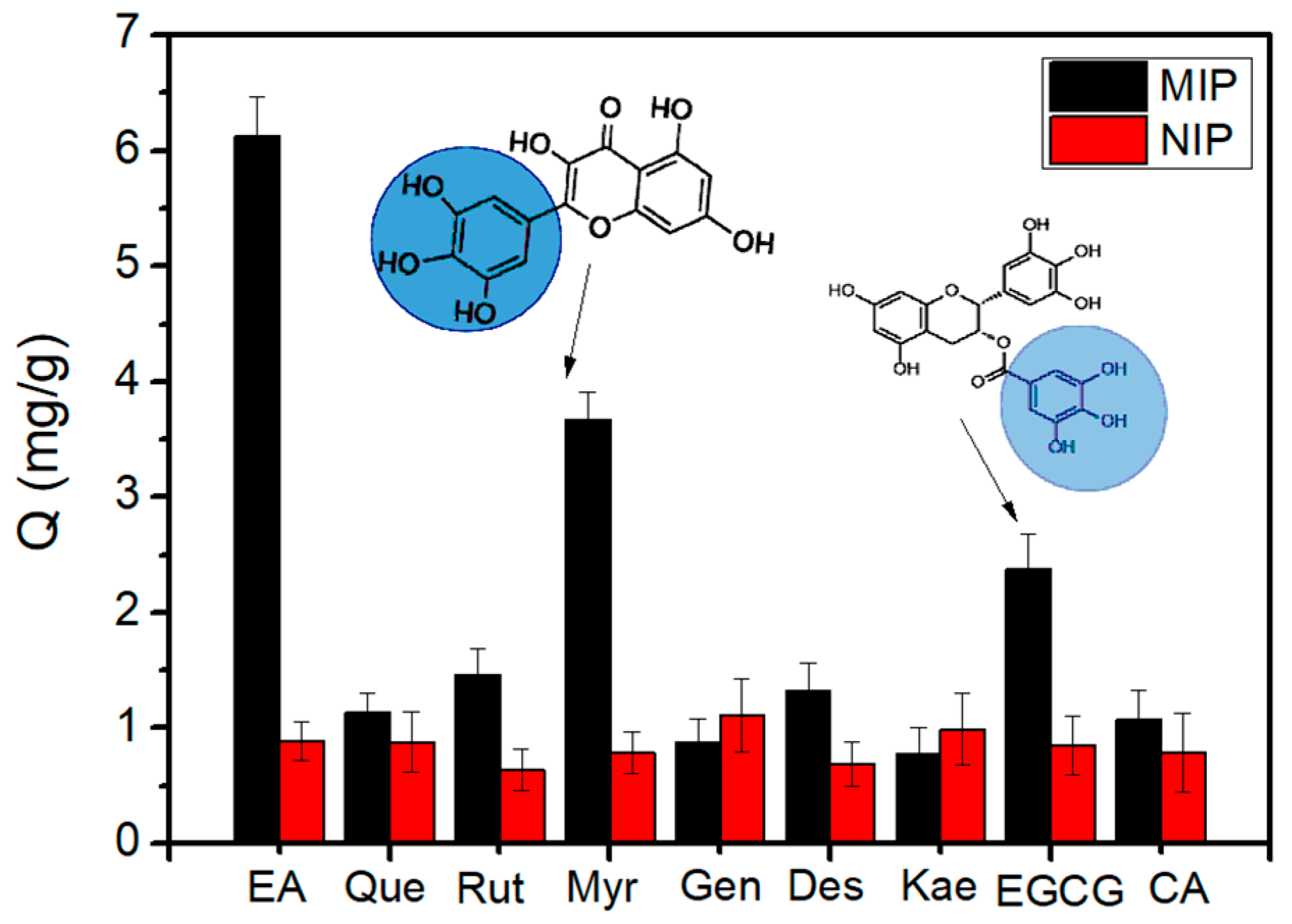
2.4. Specificity of Fe3O4@FFPBA@MIPs
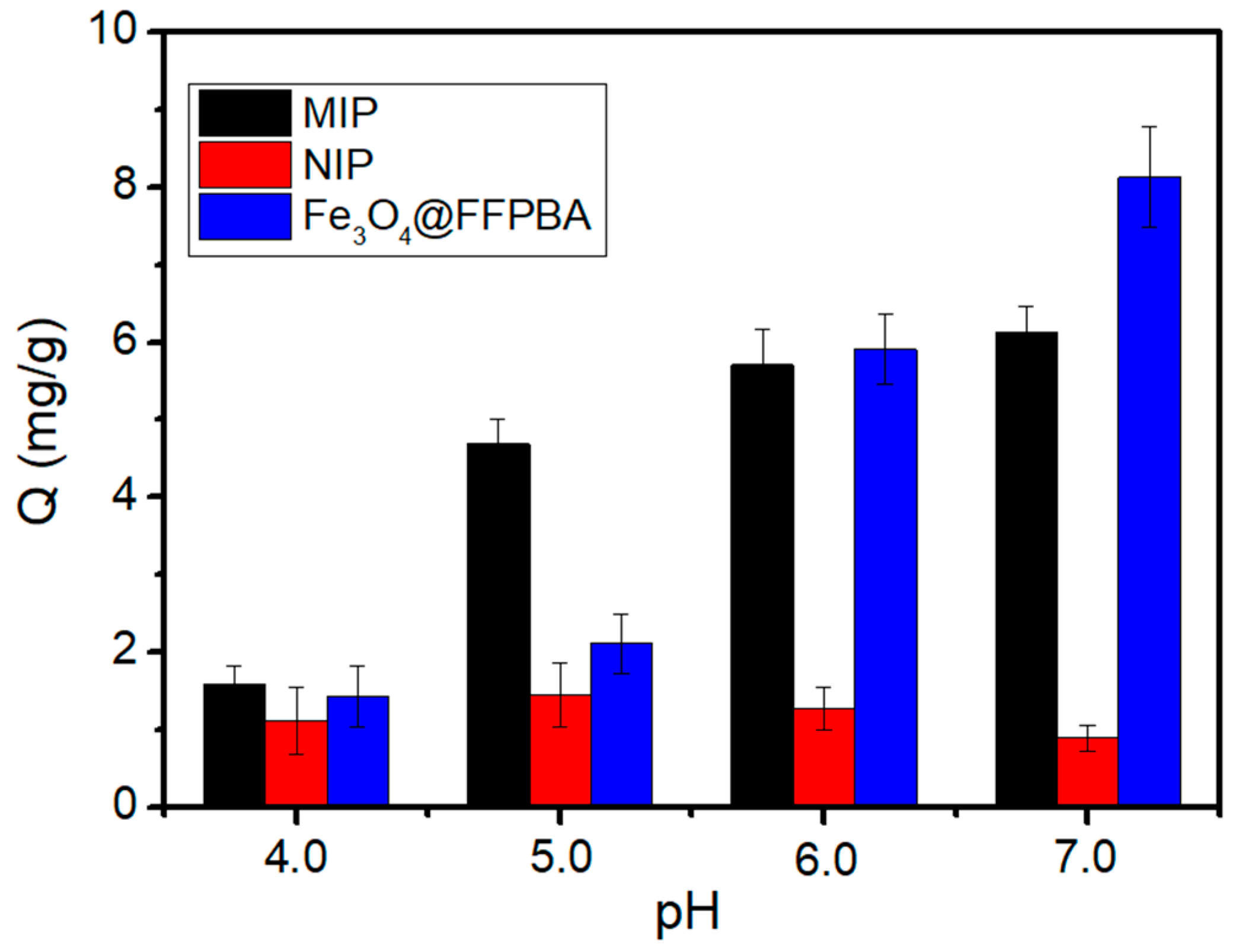
2.5. Binding pH
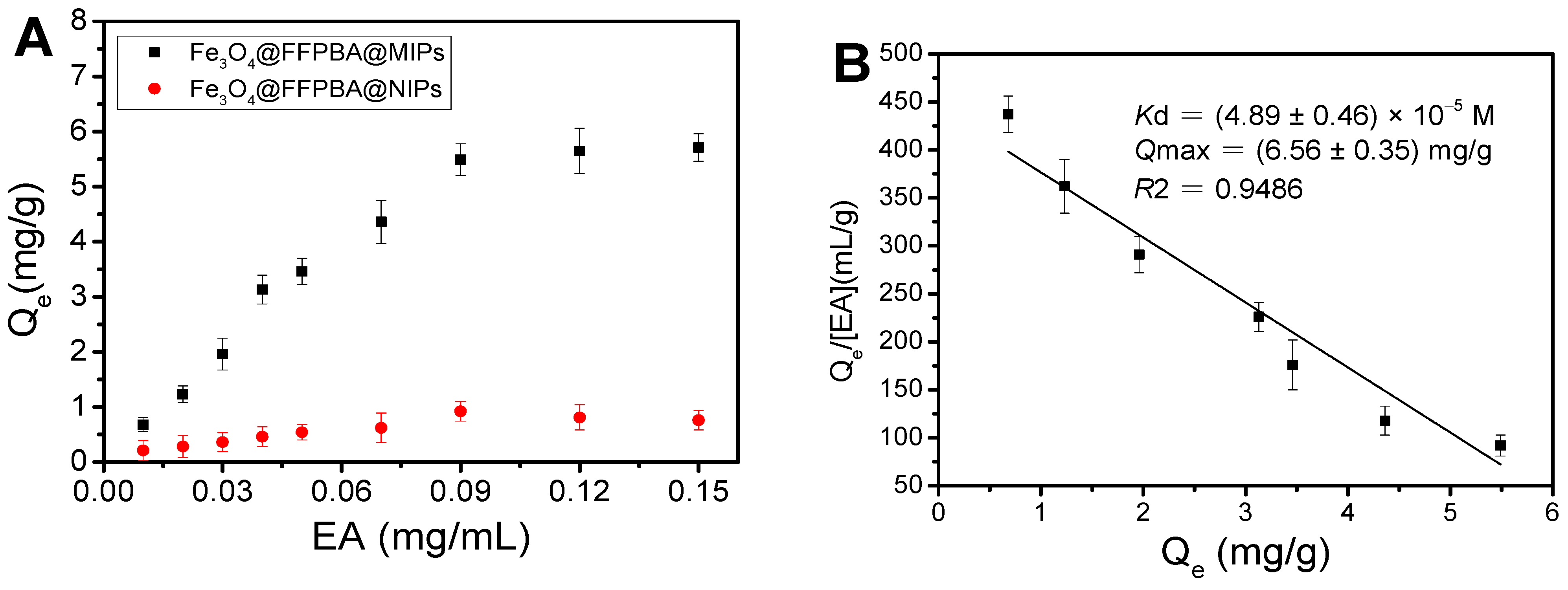
2.6. Binding Equilibrium
2.7. Determination of Kd and Qmax
2.8. Reproducibility and Reusability
2.9. Determination of EA in Real Samples
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Preparation of FFPBA-Functionalized MNPs (Fe3O4@FFPBA)
3.4. Selectivity of the Fe3O4@FFPBA
3.5. Preparation of Fe3O4@FFPBA@MIPs
3.6. Optimization of Imprinting Conditions
3.7. Specificity of Fe3O4@FFPBA@MIPs
3.8. Binding Isotherm and Scatchard Analysis
3.9. Analysis of EA in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Tea Is a Significant Dietary Source of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5394–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J.M. Ellagitannins, ellagic acid and their derived metabolites: A review about source, metabolism, functions and health. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Vinayak, M. Ellagic acid inhibits PKC signaling by improving antioxidant defense system in murine T cell lymphoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4187–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeram, N.P.; Adams, L.S.; Henning, S.M.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nair, M.G.; Heber, D. In Vitro antiproliferative, apoptotic and antioxidant activities of punicalagin, ellagic acid and a total pomegranate tannin extract are enhanced in combination with other polyphenols as found in pomegranate juice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattem, D.A.; Shetty, K. Biological functionality of ellagic acid: A review. Food Biochem. 2005, 29, 234–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo, M.A.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Cárdeno, A.; Aparicio-Soto, M.; Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Villegas, I.; de la Lastra, C.A. Dietary supplementation of an ellagic acid-enriched pomegranate extract attenuates chronic colonic inflammation in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shitany, N.A.; El-Bastawissy, E.A.; El-desoky, K. Ellagic acid protects against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B, inducible cyclooxygenase and proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of interleukin-10 via an antioxidant mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, A.; Grossi, M.R.; Pepe, G.; Filippi, S.; Muthukumar, S.; Papeschi, C.; Natarajan, A.T.; Palitti, F. Protective effect of ellagic acid (EA) on micronucleus formation induced by N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) in mammalian cells, in in vitro assays and in vivo. Mutat. Res. 2012, 746, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, H.; Aytekin, I.; Esen, H.; Alp, A.; Buyukbas, S.; Basarali, K.; Hatipoglu, N.K.; Kul, S. Protective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester, ellagic acid, sulforaphan and curcuma on malathion induced damage in lungs, liver and kidneys in an acute toxicity rat model. Rev. Med. Vet. 2011, 162, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Shimogaki, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Tamai, H.; Masuda, M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis inhibition. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2000, 22, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Ji, Y.M.; Luo, C.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Shih, Y. Quantification of ellagic acid in cosmetic products by using a partially preanodized screen-printed carbon electrode coupled with flow injection analysis. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, e205–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zou, Z.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Fluorescent metal-organic frameworks MIL-101(Al)-NH2 for rapid and sensitive detection of ellagic acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2020, 242, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, K.C. Determination of Ellagic Acid in Strawberry by UPLC—MS/MS. J. Instrum. Anal. 2016, 35, 1591–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Panichayupakarananta, P.; Issuriya, A.; Sirikatitham, A.; Wang, W. Antioxidant assay-guided purification and LC determination of ellagic acid in pomegranate peel. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2010, 48, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenil, N.; Yemis, F.; Guler, A. In different maturation stages of arum italicum miler (araceae) fruits, determination of the ellagic acid, hesperidin, resvaratrol and quercetin quantities by HPLC-DAD. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2019, 10, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Spisso, A.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Fernanda Silva, M. Determination of ellagic acid by capillary electrophoresis in Argentinian wines. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.V.; Lima, D.L.D.; Evtyugin, D.V.; Esteves, V.I. Development and application of a capillary electrophoresis method for the determination of ellagic acid in E-globulus wood and in filtrates from E-globulus kraft pulp. Wood Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Ye, C.; Yu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, S. Seed-mediated growth of Au@Ag core-shell nanorods for the detection of ellagic acid in whitening cosmetics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1002, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, V.H.; Lista, A.G. Micellar nanotubes dispersed electrokinetic chromatography for the simultaneous determination of antibiotics in bovine milk. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopico-García, M.S.; Fique, A.; Guerra, L.; Afonso, J.M.; Pereira, O.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.M. Principal components of phenolics to characterize red Vinho Verde grapes: Anthocyanins or non-coloured compounds? Talanta 2008, 75, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Boronate affinity materials for separation and molecular recognition: Structure, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8097–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematollahzadeh, A.; Sun, W.; Aureliano, C.S.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Stute, J.; Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Shojaei, A.; Sellergren, B. High-capacity hierarchically imprinted polymer beads for protein recognition and capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, D.; He, G.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z. A facile and general approach for preparation of glycoprotein-imprinted magnetic nanoparticles with synergistic selectivity. Talanta 2016, 153, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Hong, M.; Miao, M.; Bin, Q.; Lin, Z.Y.; Cai, Z.W.; Chen, G.N. Novel composites of multifunctional Fe3O4@Au nanofibers for highly efficient glycoprotein imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Han, C.; Yu, Z.; Sun, X.; Chen, J.; Dhanjai; Shao, X.; Wang, D. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers for class-selective extraction of amphetamine-type stimulants from alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverages. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1663, 462759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Qi, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q. Ultrasensitive, label-free voltammetric determination of norfloxacin based on molecularly imprinted polymers and Au nanoparticle-functionalized black phosphorus nanosheet nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, M.; Cui, R.; Chen, L. Dual-template molecularly imprinted polymers for dispersive solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in water samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 2019, 144, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Wang, A.; Chen, L.; Han, S. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8146–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.G.; Zhang, L.; Han, B.; Yao, X.C.; Chen, W.; Hu, Y.L. Preparation of ellagic acid molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres based on distillation-precipitation polymerization for the efficient purification of a crude extract. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.X.; Duan, R.; Yang, Y.S.; Peng, C.; Dong, L.Y.; Wang, X.H. Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of ellagic acid by integrating boronate-affinity controllable-oriented imprinted magnetic nanoparticle and boronic acid-modified/polyethylene glycol-coated allochroic-graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2021, 345, 130400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Lang, J.Y.; Bai, C.C.; Yu, S.S.; Kong, X.J.; Dong, L.Y.; Wang, X.H. Construction of PEGylated boronate-affinity-oriented imprinting magnetic nanoparticles for ultrasensitive detection of ellagic acid from beverages. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 6557–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucel, N.; Gulen, H.; Hatir, P.C. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the recognition of ellagic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bi, S.; Chai, J.; Tong, Y.; Tian, M. ZIF-based boronic acid modified molecular imprinted polymers in combination with silver nanoparticles/glutathione coated graphene oxide adsorbent for the selective enrichment of ellagic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1714, 464579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, Z.; Xing, R.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Precision Imprinting of Glycopeptides for Facile Preparation of Glycan-Specific Artificial Antibodies. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9845–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Ye, J.; Bie, Z.J.; Liu, Z. Affinity-tunable specific recognition of glycoproteins via boronate affinity-based controllable oriented surface imprinting. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Liu, Z. Facile preparation of glycoprotein-imprinted 96-well microplates for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay by boronate affinity-based oriented surface imprinting. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Bie, Z. Branched polyethyleneimine-assisted boronic acid-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for the selective enrichment of trace glycoproteins. Analyst 2017, 142, 4494–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Tu, T.; Yang, M.; Xu, C. Efficient preparation of surface imprinted magnetic nanoparticles using poly (2-anilinoethanol) as imprinting coating for the selective recognition of glycoprotein. Talanta 2018, 184, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, N.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. Boronate affinity-based template-immobilization surface imprinted quantum dots as fluorescent nanosensors for selective and sensitive detection of myricetin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2022, 272, 121023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, L.Y.; He, Y.L.; Niu, Y.Y.; Hussain, S.; Gao, R.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Shahid, M.; Wang, S. Amphiphilic core-shell magnetic adsorbents for efficient removal and detection of phthalate esters. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 129817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Tang, X.; Tang, Y. Novel bayberry-and-honeycomb-like magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective enrichment of rutin from Sophora japonica. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.V.; Kim Do, O.T.; Nguyen, N.D.; Huynh, C.D. Synthesis of amorphous carbon functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a smart nanosorbent for organic dyes removal. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 10644–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Pascual, A.M.; Rahdar, A. Functional Nanomaterials in Biomedicine: Current Uses and Potential Applications. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Wu, J.Y.; Luo, X.B. Facile preparation of a novel Hg(II)-ion-imprinted polymer based on magnetic hybrids for rapid and highly selective removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14916–14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberdeen, S.; Cali, E.; Vandeperre, L.; Ryan, M.P. Selective radionuclide and heavy metal sorption using functionalised magnetic nanoparticles for environmental remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 15855–15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Bie, Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, Z. Photolithographic boronate affinity molecular imprinting: A general and facile approach for glycoprotein imprinting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7451–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.J.; Tu, X.Y.; Ye, J.; Bie, Z.J.; Bi, X.D.; Liu, Z. Nanoconfining affinity materials for pH-mediated protein capture-release. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Ding, Y.H.; Ma, Y.D.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, Y.P.; Li, D.J.; Wang, S.S. High-capacity boronate affinity-based template-immobilized surface imprinted silica nanoparticles for rapid, selective, and efficient extraction and determination of lincomycin in milk and chicken. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1271921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, G.; Yao, J.; Yang, P.; Lu, H. Highly specific revelation of rat serum glycopeptidome by boronic acid-functionalized mesoporous silica. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 753, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Boronic Acid functionalized core-shell polymer nanoparticles prepared by distillation precipitation polymerization for glycopeptide enrichment. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 9056–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.F.; Uddin, K.M.A.; Ye, L. Boronic Acid Terminated Thermo-Responsive and Fluorogenic Polymer: Controlling Polymer Architecture for Chemical Sensing and Affinity Separation. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 6464–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Pang, J.; Xu, S.; He, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. A Glycoform-Resolved Dual-Modal Ratiometric Immunoassay Improves the Diagnostic Precision for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.P.; Xu, W.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Yan, Y.S. A surface-imprinted polymer for removing dibenzothiophene from gasoline. Microchim. Acta 2010, 171, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Zheng, J.; Tong, Y.; Chai, F.; Tian, M. Construction of the molecularly imprinted adsorbent based on shaddock peel biochar sphere for highly sensitive detection of ribavirin in food and water resources. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, Z.; Fu, M.; Huang, R.; Chen, W. Facile synthesis of flower-like sandwich-structured molecularly imprinted polymers for efficient recognition of target protein from egg white. Food Chem. 2023, 421, 136165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Gong, H.; Pang, Y.; Ge, X.; Li, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers based on calcined rape pollen and deep eutectic solvents for efficient sinapic acid extraction from rapeseed meal extract. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Heinlein, J.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Tian, X. Strategic preparation of porous magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers via a simple and green method for high-performance adsorption and removal of meropenem. Talanta 2023, 258, 124419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.C.; Sun, Y.; Guo, D.Z.; Lu, R.H.; Mao, Y.Y.; Ou, H.X. Porous boronate imprinted microsphere prepared based on new RAFT functioned cellulose nanocrystalline with multiple H-bonding at the emulsion droplet interface for highly specific separation of Naringin. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | Spiked Levels (μg/g) | Found (μg/g) | Recoveries (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strawberry | 0.0 | 12.6 | -- | -- |
| 20.0 | 30.8 | 91.0 | 4.3 | |
| 40.0 | 55.3 | 106.8 | 2.7 | |
| 60.0 | 69.8 | 95.3 | 5.6 | |
| Pineapple | 0.0 | 1.6 | -- | -- |
| 20.0 | 22.4 | 104.0 | 3.8 | |
| 40.0 | 39.1 | 93.8 | 2.9 | |
| 60.0 | 5.84 | 94.7 | 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Tang, N.; Tian, X. Synthesis of Boronate Affinity-Based Oriented Dummy Template-Imprinted Magnetic Nanomaterials for Rapid and Efficient Solid-Phase Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Food. Molecules 2024, 29, 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112500
Li D, Tang N, Tian X. Synthesis of Boronate Affinity-Based Oriented Dummy Template-Imprinted Magnetic Nanomaterials for Rapid and Efficient Solid-Phase Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Food. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112500
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Daojin, Na Tang, and Xiping Tian. 2024. "Synthesis of Boronate Affinity-Based Oriented Dummy Template-Imprinted Magnetic Nanomaterials for Rapid and Efficient Solid-Phase Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Food" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112500
APA StyleLi, D., Tang, N., & Tian, X. (2024). Synthesis of Boronate Affinity-Based Oriented Dummy Template-Imprinted Magnetic Nanomaterials for Rapid and Efficient Solid-Phase Extraction of Ellagic Acid from Food. Molecules, 29(11), 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112500





