Effect of the Addition of WO3 on the Structure and Luminescent Properties of ZnO-B2O3:Eu3+ Glass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Thermal Analysis
2.2. Structural Analysis
2.3. Optical Transmission Spectra
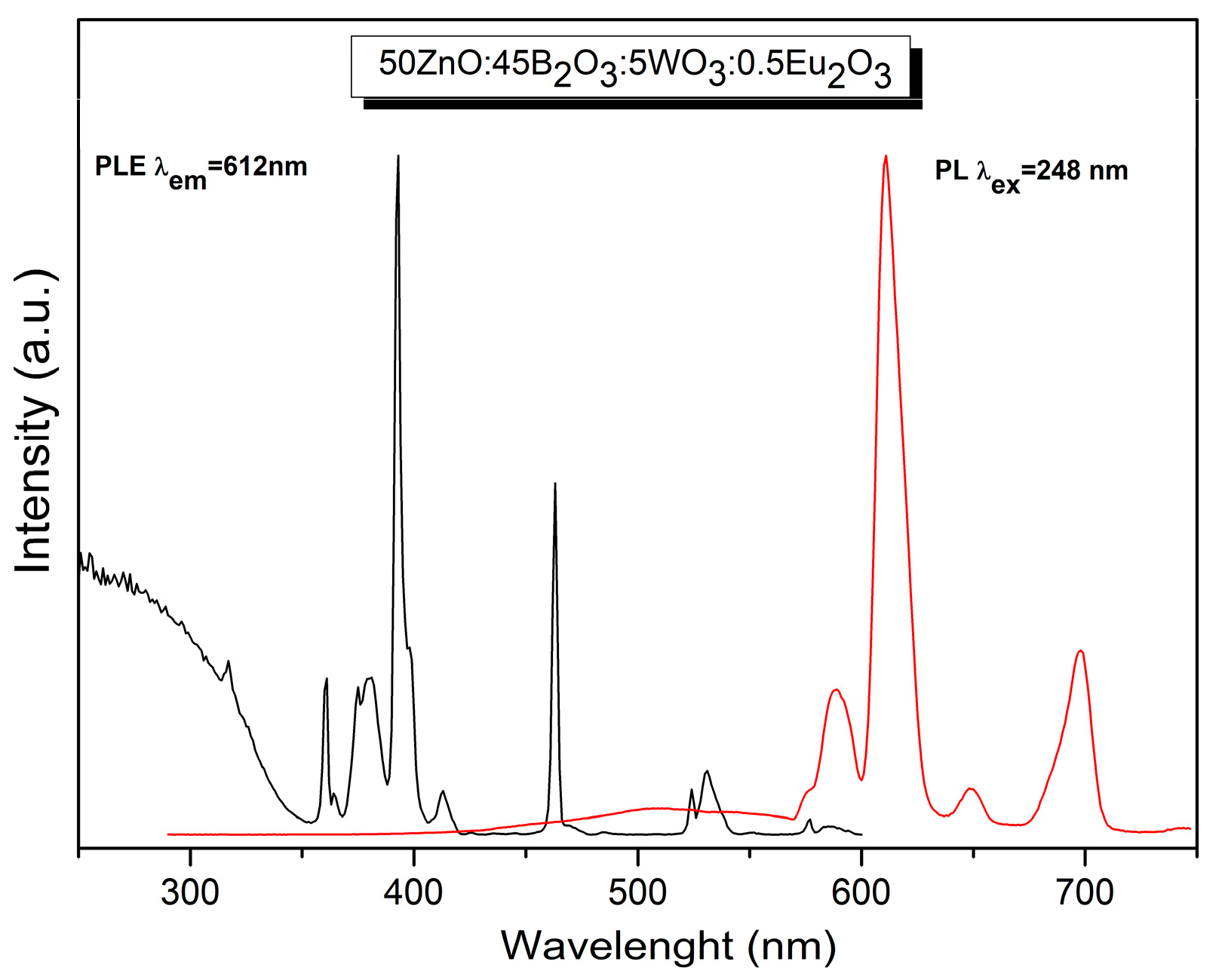
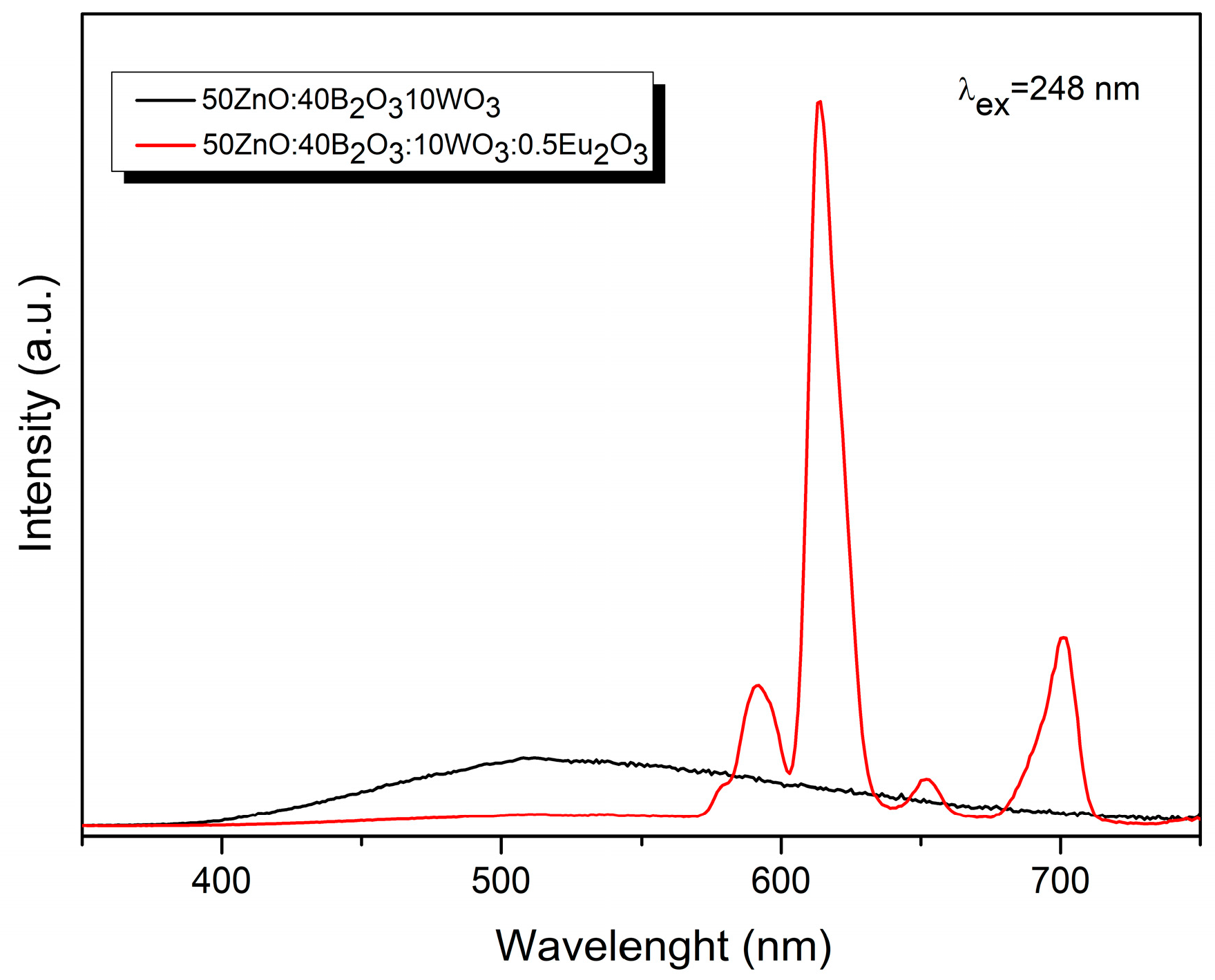
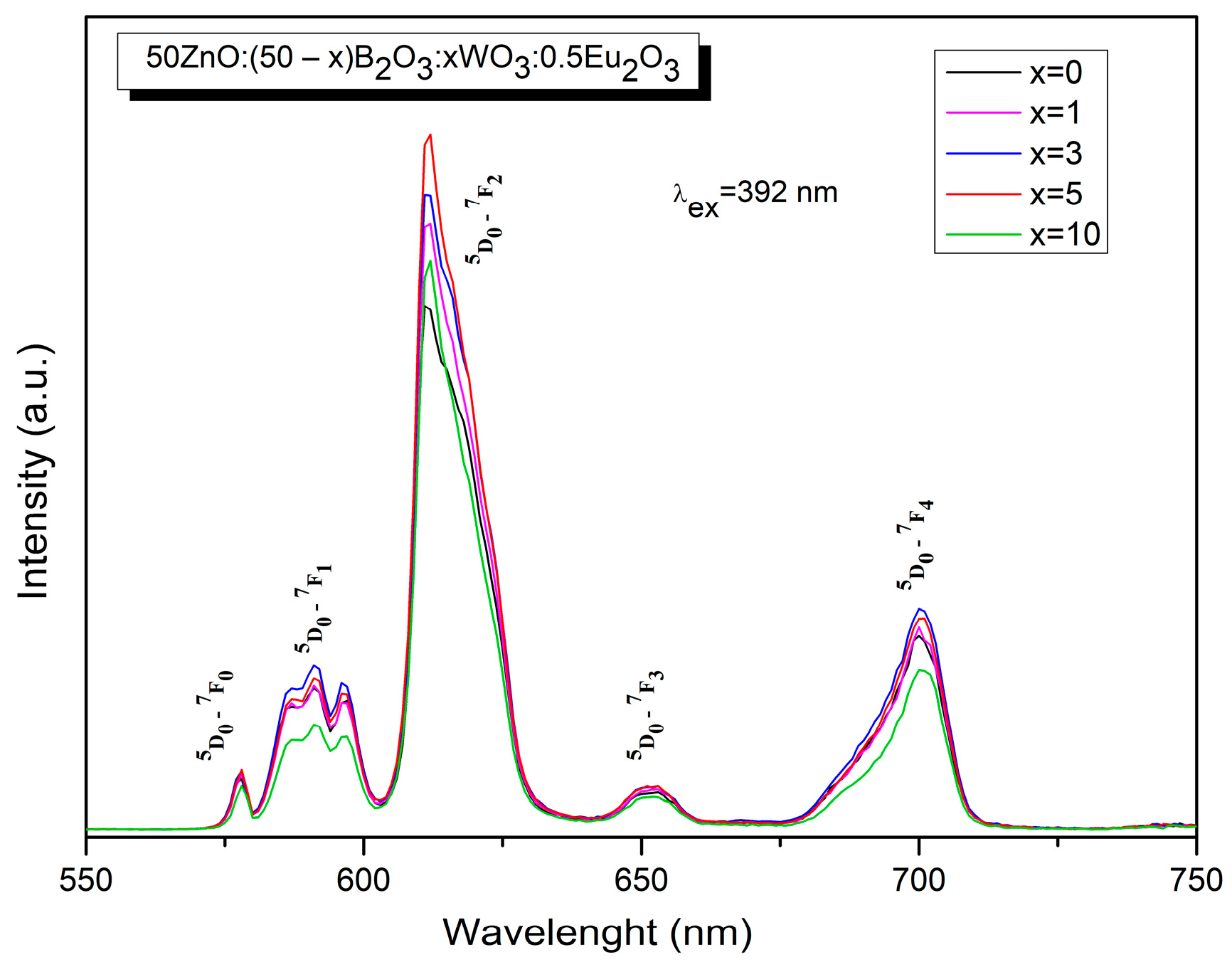
2.4. Luminescent Properties
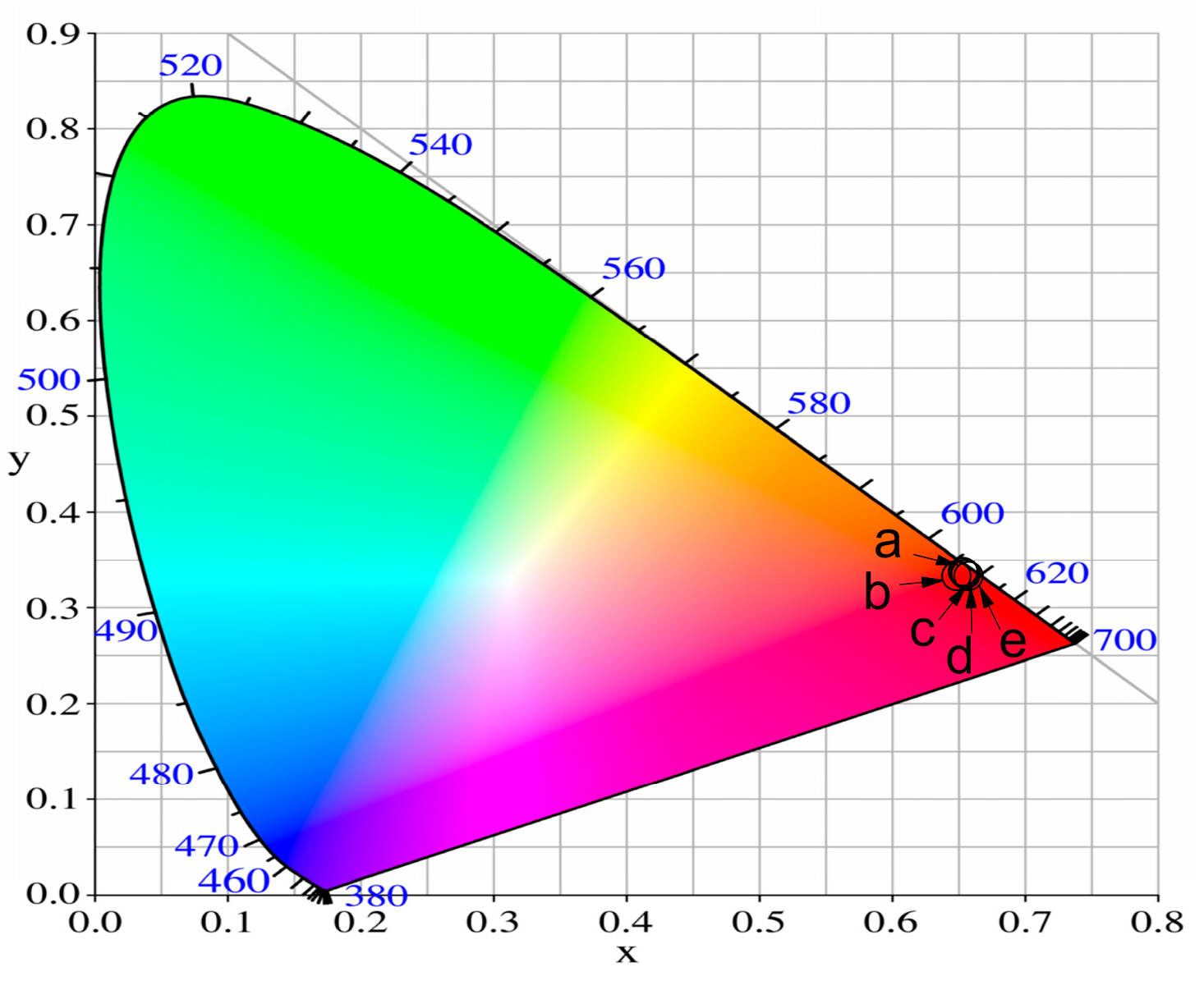
CIE Color Coordinates and CCT (K) Values
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagami, M.; Abe, Y. Properties of sol—Gel-derived Al2O3 SiO2 glasses using Eu3+ ion fluorescence spectra. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 197, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.J. Science and technology of laser glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1990, 123, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengisu, M. Borate glasses for scientific and industrial applications: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2199–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitailipu, M.; Poeppelmeier, K.; Pan, S. Borates: A Rich Source for Optical Materials. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1130–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colak, C.S.; Akyuz, I.; Atay, F. On the dual role of ZnO in zinc-borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 432, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapurna, K.; Das, M.; Kundu, M.; Dwivedhi, R.N.; Buddhudu, S. Spectral properties of Eu3+: ZnO–B2O3–SiO2 glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 741, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D. Concise Inorganic Chemistry; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.N.A.; Siva, B.V.; Neeraja, K.; Mohanq, N.K.; Rojas, J.I. Effect of modifier oxides on spectroscopic and optical properties of Pr3+doped PbO-Ro2O3–WO3–B2O3 glasses (with Ro2O = Sb2O3, Al2O3, and Bi2O3). J. Lumin. 2021, 230, 117666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.N.A.; Siva, B.V.; Neeraja, K.; Mohanq, N.K.; Rojas, J.I. Influence of modifier oxides on spectroscopic features of Nd2O3 doped PbO-Ro2O3–WO3–B2O3 glasses (with Ro2O3 = Sb2O3, Al2O3, and Bi2O3). J. Lumin. 2020, 223, 117171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousti, M.R.; Poirier, G.Y.; Camargo, A.S.S. Structural and spectroscopic characteristics of Eu3+-doped tungsten phosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2015, 45, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataalla, M.A.; Afify, S.; Hassan, M.; Abdallah, M.; Milanova, M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Mohamed, A. Tungsten-based glasses for photochromic, electrochromic, gas sensors, and related applications: A. review. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 491, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanova, M.; Aleksandrov, L.; Iordanova, R. Structure and luminescence properties of tungsten modified zinc borate glasses doped with Eu3+ ions. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 61, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanova, M.; Aleksandrov, L.; Yordanova, A.; Iordanova, R.; Tagiara, N.S.; Herrmann, A.; Gao, G.; Wondraczek, L.; Kamitsos, E.I. Structural and luminescence behavior of Eu3+ ions in ZnO-B2O3-WO3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 600, 122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, A.; Milanova, M.; Iordanova, R.; Fabian, M.; Aleksandrov, L.; Petrova, P. Network Structure and Luminescent Properties of ZnO–B2O3–Bi2O3–WO3:Eu3+ Glasses. Materials 2023, 16, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swapna, G.; Upender, M.; Prasad, M. Raman FTIR, thermal and optical properties of TeO2-Nb2O5-B2O3-V2O5 quaternary glass system. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, N.H. Composition-properties relationship in Inorganic Oxide Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1974, 15, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddeek, Y.; Azooz, M.; Saddek, A. Ultrasonic investigations of some bismuth borate glasses doped with Al2O3. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddeek, Y. Effect of B2O3 on the structure and properties of tungsten-tellurite glasses. Philos. Mag. 2009, 89, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Khanna, A.; González-Barriuso, M.; González, F.; Chen, B. Short-range structure and thermal properties of alumino-tellurite glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 470, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, T.L. The Strength of Chemical Bonds, 2nd ed.; Butterworth: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Topper, B.; Möncke, D.; Youngman, R.E.; Valvi, C.; Kamitsos, E.I.; Varsamis, C.P. Zinc borate glasses: Properties, structure and modelling of the composition-dependence of borate speciation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 5967–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Y.; Möncke, D.; Kamitsos, E.I.; Houizot, P.; Célarié, F.; Rouxel, T.; Wondraczek, L. Structure and mechanical properties of copper–lead and copper–zinc borate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 435, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamitsos, E.I.; Karakassides, M.A.; Chryssikos, G.D. Vibrational Spectra of Magnesium-Sodium-Borate Glasses. 2. Raman and Mid-Infrared Investigation of the Network Structure. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Dimitriev, Y. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnWO4 at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, L.; Komatsu, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Honma, T.; Iordanova, R. Structure of MoO3–WO3–La2O3–B2O3 glasses and crystallization of LaMo1 − xWxBO6 solid solutions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 429, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.S.; Khanna, A. Eu3+ activated molybdate and tungstate based red phosphors with charge transfer band in blue region. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, R3153–R3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimpoeno, W.A.; Lintang, H.O.; Yuliati, L. Zinc oxide with visible light photocatalytic activity originated from oxygen vacancy defects. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 833, 012080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasse, G.; Grabmaier, B.C. Luminescent Materials, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelber, Germany, 1994; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefdraad, H.E. The charge-transfer absorption band of Eu3+ in oxides. J. Solid State Chem. 1975, 15, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchur, A.K.; Ningthoujam, R.S. Behaviour of electric and magnetic dipole transitions of Eu3+, 5D0-7F0 and Eu-O charge transfer band in Li+ co-doped YPO4:Eu3+. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10859–10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariselvam, K.; Liu, J. Synthesis and luminescence properties of Eu3+ doped potassium titano telluroborate (KTTB) glasses for red laser applications. J. Lumin. 2021, 230, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Interpretation of europium (III) spectra. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 295, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, C.; Herrmann, A.; Kracker, M.; Patzig, C.; H¨oche, T.; Rüssel, C. Microstructure investigation and fluorescence properties of europium-doped scheelite crystals in glass-ceramics made under different synthesis conditions. J. Lumin. 2021, 238, 118244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, L.; Milanova, M.; Yordanova, A.; Iordanova, R.; Nedyalkov, N.; Petrova, P.; Tagiara, N.S.; Palles, D.; Kamitsos, E.I. Synthesis, structure and luminescence properties of Eu3+-doped 50ZnO.40B2O3.5WO3.5Nb2O5 glass. Phys. Chem. Glas. Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. B 2023, 64, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sreena, T.S.; Raj, A.K.; Rao, P.P. Effects of charge transfer band position and intensity on the photoluminescence properties of Ca1.9M2O7: 0.1Eu3+ (M = Nb, Sb and Ta). Solid State Sci. 2022, 123, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Yan, B.; Chen, H.H. Solid-state synthesis, characterization and luminescent properties of Eu3+-doped gadolinium tungstate and molybdate phosphors: Gd(2−x)MO6:Eux3+(M = W, Mo). J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Jiang, D.G.; Chen, S.W.; Zheng, G.T.; Huang, S.M.; Gu, M.; Zhao, J.T. Eu3+- activated borogermanate scintillating glass with a high Gd2O3 content. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Liu, X.; Lin, J. Luminescence properties of R2MoO6: Eu3+ (R= Gd, Y, La) phosphors prepared by Pechini sol-gel process. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 2676–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungpanich, J.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Large-scale synthesis of WO3 nanoplates by a microwave-hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasse, G. On the Eu3+ fluorescence of mixed metal oxides. IV. The photoluminescent efficiency of Eu3+-activated oxides. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 45, 2356–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejneka, M.; Snitzer, E.; Riman, R.E. Blue, green and red fluorescence and energy transfer of Eu3+ in fluoride glasses. J. Lumin. 1995, 65, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanova, R.; Milanova, M.; Yordanova, A.; Aleksandrov, L.; Nedylkov, N.; Kukeva, R.; Petrova, P. Structure and Luminescent Properties of Niobium Modified ZnO-B2O3: Eu3+ Glass. Materials 2024, 17, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinelli, M.; Speghini, A.; Ferrari, M.; Montagna, M. Spectroscopic investigation of zinc borate glasses doped with trivalent europium ions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 201, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Jang, K.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, H.; Jayasankar, C.K. Thermal, structural and optical properties of Eu3+-doped zinc-tellurite glasses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, S.B.; Halimah, M.K.; Chan, K.T.; Muhammad, F.D.; Nazrin, S.N.; Tafida, R.A. Eu3+ ions doped zinc borotellurite glass system for white light laser application: Structural, physical, optical properties, and Judd-Ofelt theory. J. Lumin. 2022, 250, 119099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.; Jayasankar, C.K. Optical spectroscopy of Eu3+ ions in lithium borate and lithium fluoroborate glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2000, 279, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageno, Y.; Takebe, H.; Morinaga, K.; Izumitani, T.J. Effect of modifier ions on fluorescence and absorption of Eu3+ in alkali and alkaline earth silicate glasses. Non-Cryst. Solids 1994, 169, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, N.; Shinozaki, K.; Kato, T.; Onoda, D.; Takebuchi, Y.; Fukushima, H.; Yanagida, T. Scintillation characteristics of Eu2O3-doped WO3–Al2O3–TeO2 glasses. J. Lumin. 2022, 249, 119003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Yi, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Structure refinement and one-center luminescence of Eu3+ activated ZnBi2B2O7 under UV excitation. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Görller-Walrand, C. Application of the Eu3+ ion for site symmetry determination. J. Rare Earths 1996, 14, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.; Guild, J. The CIE colorimetric standards and their use. Trans. Opt. Soc. 1931, 33, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, T.B. SpectraChroma (Version 1.0.1) [Computer Software]. 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/4906590 (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Trond, S.S.; Martin, J.S.; Stanavage, J.P.; Smith, A.L. Properties of Some Selected Europium—Activated Red Phosphors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1969, 116, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCamy, C.S. Correlated color temperature as an explicit function of chromaticity coordinates. Color Res. Appl. 1992, 17, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Noh, H.; Choi, B.; Park, S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, J. Molybdenum substitution induced luminescence enhancement in Gd2W1-xMoxO6Eu3+ phosphors for near ultraviolet based solid state lighting. J. Lunin. 2018, 202, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
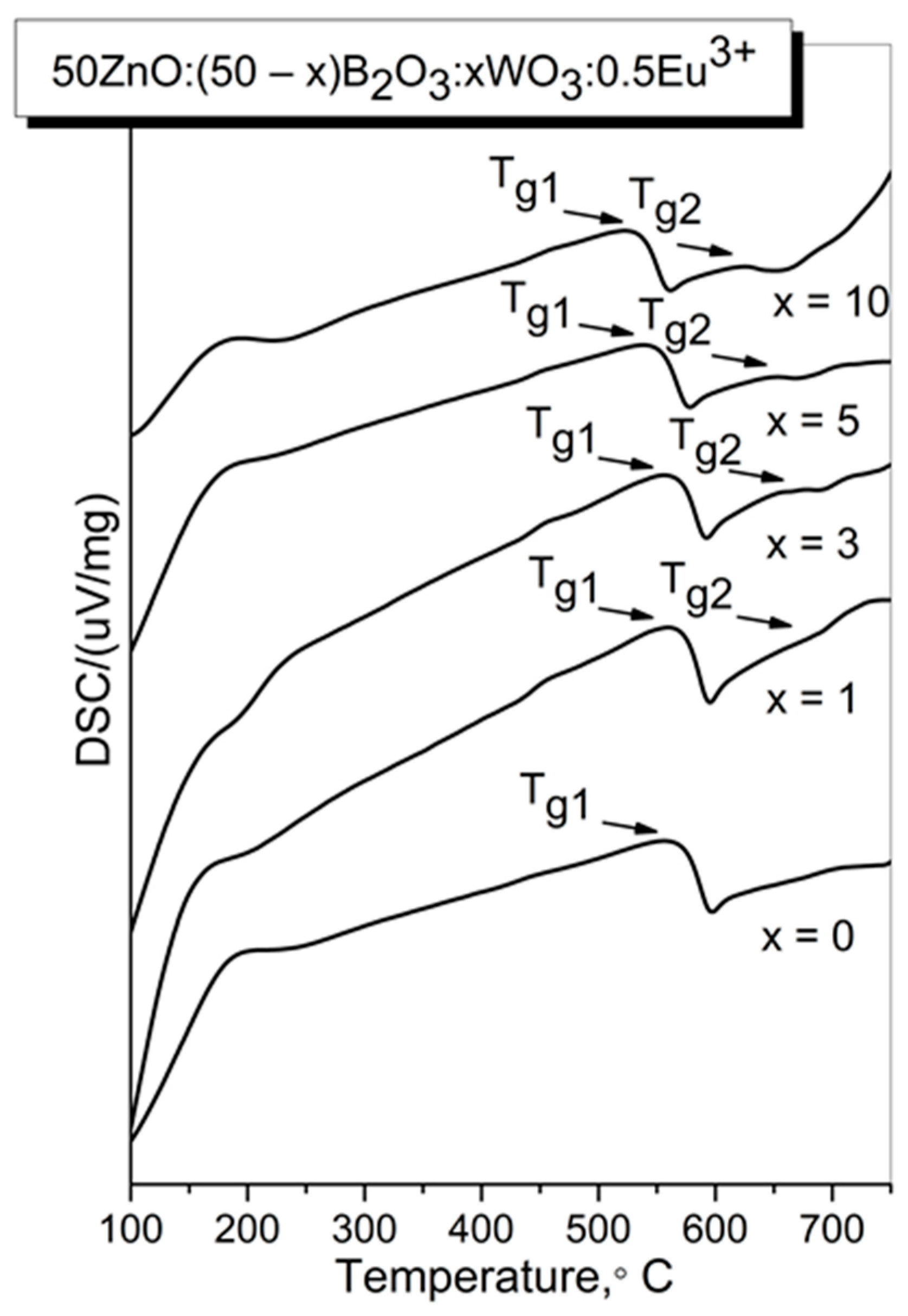
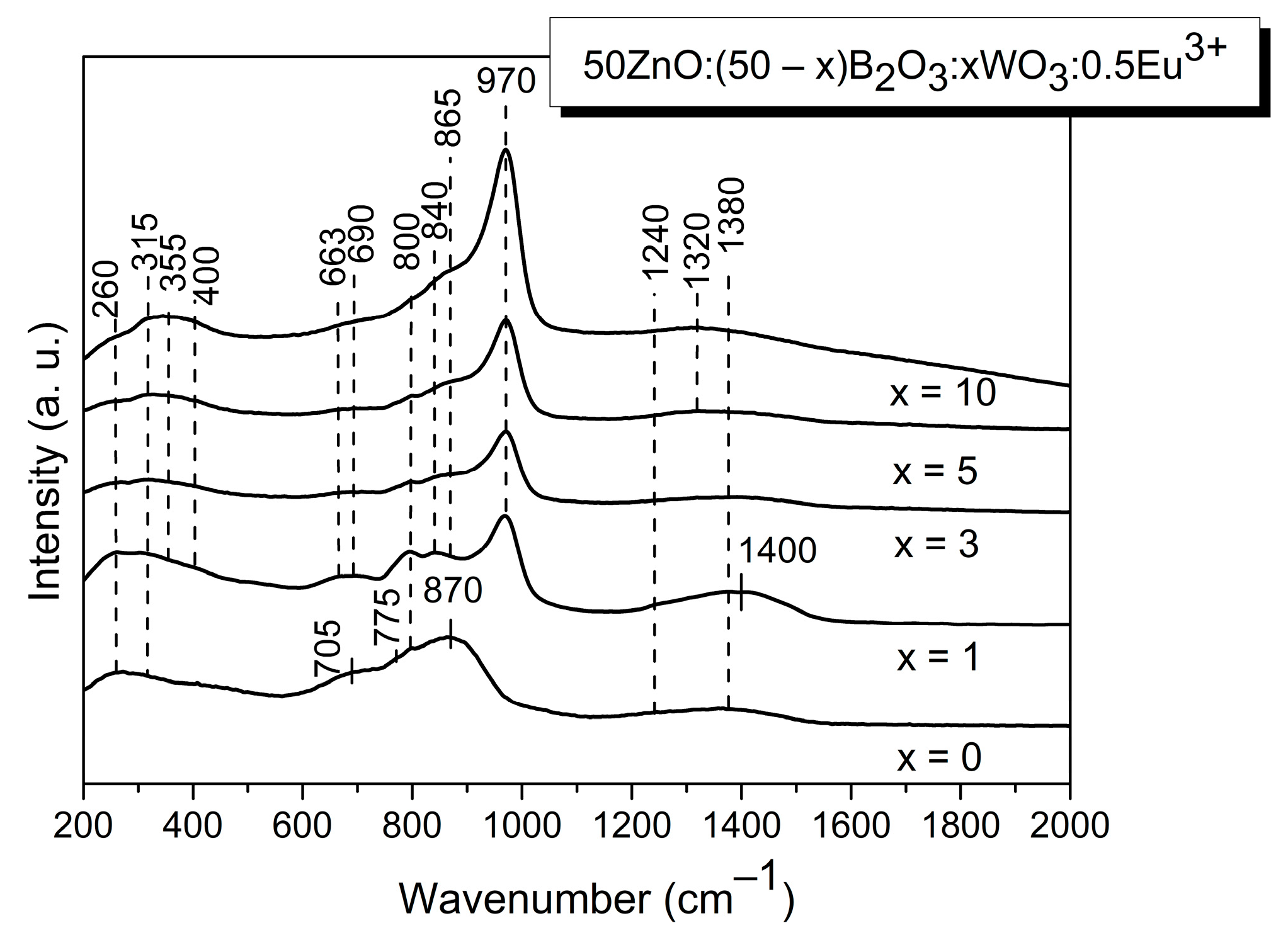
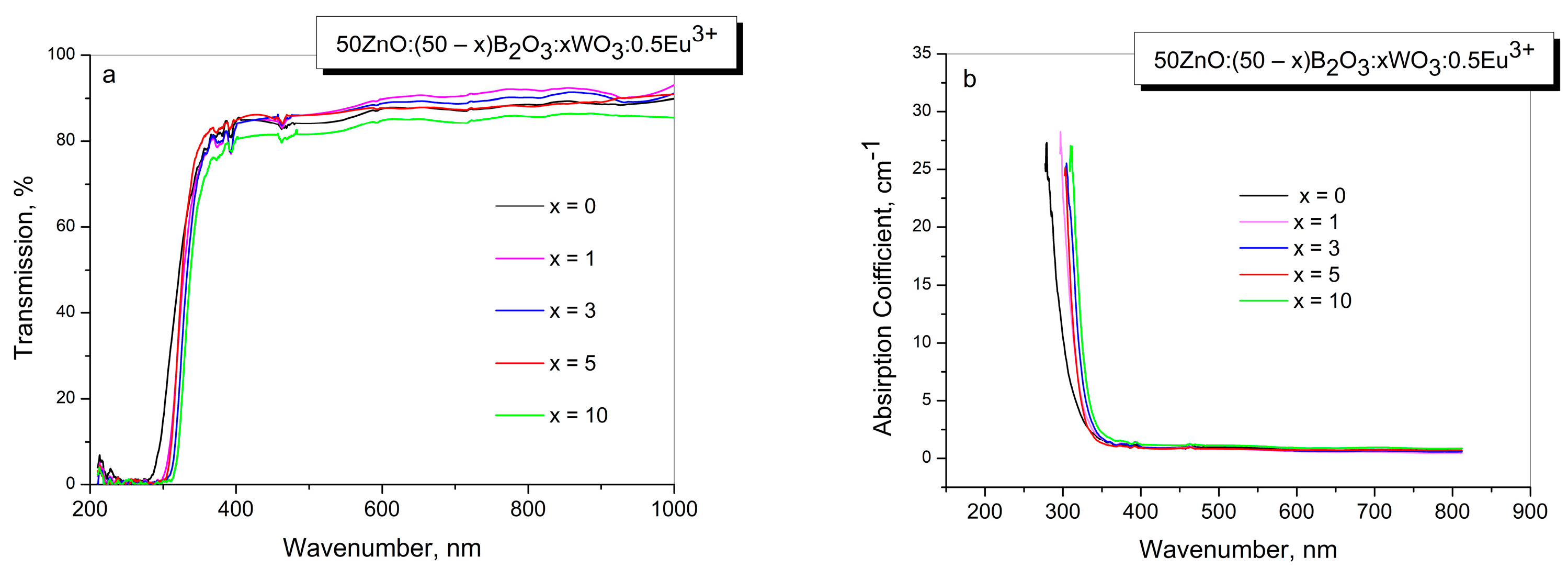
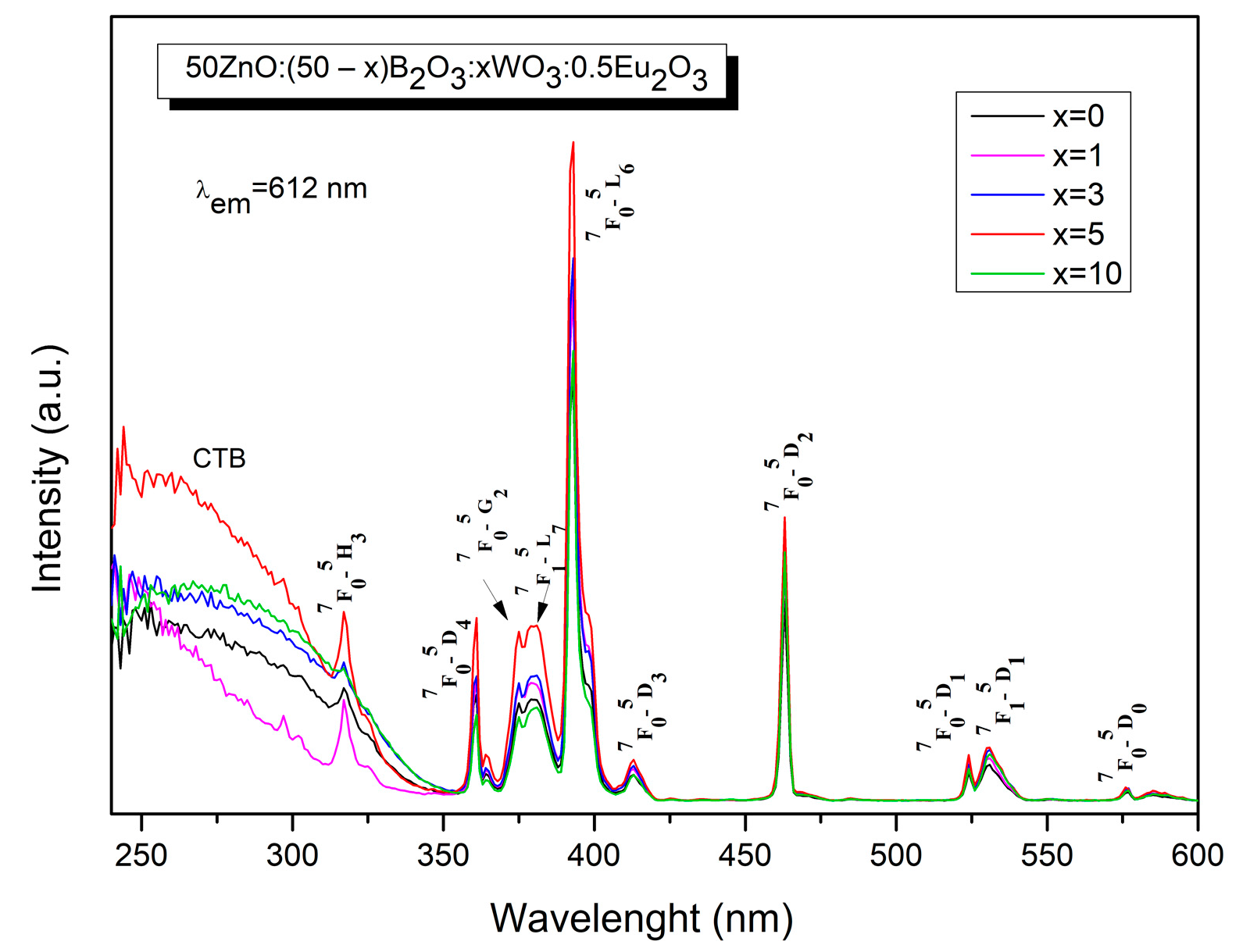
| Sample ID | Tg1/°C | Tg2/°C | EB/kJ mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| x = 0 | 570 (843 K) | - | 548 |
| x = 1 | 568 (841 K) | 688 (961 K) | 546 |
| x = 3 | 565 (838 K) | 680 (953 K) | 543 |
| x = 5 | 543 (816 K) | 653 (926 K) | 540 |
| x = 10 | 532 (805 K) | 626 (899 K) | 532 |
| Peak Positions | Assignments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| 260 | ν (Zn-O) | [21,22] |
| 315 | ν (Eu-O) + ν2 [WO4]2 | [13] |
| 355 | ν4 [WO4]2− | [13] |
| 400 | νs[W2O4]n | [13] |
| 663 | νas[W2O4]n | [13] |
| 690 | νas[W2O4]n | [13] |
| 705 | δ[BØ2O]− + in-plane and out-of-plane bending modes of both polymerized (BØ0) species and isolated orthoborate units (BO3)3-+ bending of the B-O-B connection in the pyroborate dimers, [B2O5]4− | [21,22,23] |
| 800 | ring breathing of the boroxol rings+ ν3[WO4]2− | [13,21,22,23] |
| 840 | νas(WO2) + B-O-B stretching of [B2O5]4− | [13] |
| 865 | νs(WO2) | [13] |
| 870 | B-O-B bridges in pyroborate dimers, [B2O5]4− | [21,22,23] |
| 970 | ν1[WO4]2− | [13] |
| 1240 | B-O− stretch in pyroborate units | [21,22,23] |
| 1380–1320 | B-O− stretch in metaborate units | [21,22,23] |
| 1400 | B-O− stretch in metaborate units | [21,22,23] |
| Glass Composition | Relative Luminescent Intensity Ratio, R | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 50ZnO:50B2O3:0.5Eu2O3 | 4.34 | Current work |
| 50ZnO:49B2O3:1WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 5.67 | Current work |
| 50ZnO:47B2O3:3WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 5.71 | Current work |
| 50ZnO:45B2O3:5WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 5.82 | Current work |
| 50ZnO:40B2O3:10WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 5.57 | Current work + [13] |
| 50ZnO:(50 − x)B2O3: xNb2O5:0.5Eu2O3:, x = 0, 1, 3 and 5 mol % | 4.31–5.16 | [42] |
| 50ZnO:40B2O3:10WO3:xEu2O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 10) | 4.54÷5.77 | [13] |
| 50ZnO:40B2O3:5WO3:5Nb2O5:xEu2O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 10) | 5.09÷5.76 | [34] |
| 4ZnO:3B2O3 0.5–2.5 mol % Eu2O3 | 2.74–3.94 | [43] |
| 60TeO2:39ZnO:1Eu2O3 | 3.25 | [44] |
| 60TeO2:20ZnO:19LiF:1Eu2O3 | 3.70 | [44] |
| 60TeO2:19ZnO:10Na2O:10Li2O:1Eu2O3 | 3.73 | [44] |
| 60ZnO:20B2O3:(20 − x)SiO2−xEu2O3 (x = 0 and 1) | 3.166 | [6] |
| [{(TeO2)0.7:(B2O3)0.3}0.7:(ZnO)0.3](1−y)(Eu2O3)y with 0.01 = y ≤ 0.05 | 2.15–3.08 | [45] |
| 59.5Li2O:39.5B2O3:1Eu2O3 | 4.18 | [46] |
| 19.5Na2O:20MgO:59.5SiO2:1Eu2O3 | 4.43 | [47] |
| (15 − x)WO3–5Al2O3–80TeO2–xEu2O3; x = 0.1÷5 mol % | 5.4÷6 | [48] |
| Glass Composition | Chromaticity Coordinates (x, y) | CCT (K) |
|---|---|---|
| 50ZnO:50B2O3:0.5Eu2O3 | 0.645, 0.346 | 2301.26 |
| 50ZnO:49B2O3:1WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 0.651, 0.348 | 2324.59 |
| 50ZnO:47B2O3:3WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 0.650, 0.350 | 2270.30 |
| 50ZnO:45B2O3:5WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 0.652, 0.347 | 2359.79 |
| 50ZnO:40B2O3:10WO3:0.5Eu2O3 | 0.654, 0.345 | 2439.74 |
| NTSC standard for red phosphors | 0.670, 0.330 | |
| Y2O2S:Eu3+ | 0.658, 0.340 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yordanova, A.; Aleksandrov, L.; Milanova, M.; Iordanova, R.; Petrova, P.; Nedyalkov, N. Effect of the Addition of WO3 on the Structure and Luminescent Properties of ZnO-B2O3:Eu3+ Glass. Molecules 2024, 29, 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112470
Yordanova A, Aleksandrov L, Milanova M, Iordanova R, Petrova P, Nedyalkov N. Effect of the Addition of WO3 on the Structure and Luminescent Properties of ZnO-B2O3:Eu3+ Glass. Molecules. 2024; 29(11):2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112470
Chicago/Turabian StyleYordanova, Aneliya, Lyubomir Aleksandrov, Margarita Milanova, Reni Iordanova, Petia Petrova, and Nikolay Nedyalkov. 2024. "Effect of the Addition of WO3 on the Structure and Luminescent Properties of ZnO-B2O3:Eu3+ Glass" Molecules 29, no. 11: 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112470
APA StyleYordanova, A., Aleksandrov, L., Milanova, M., Iordanova, R., Petrova, P., & Nedyalkov, N. (2024). Effect of the Addition of WO3 on the Structure and Luminescent Properties of ZnO-B2O3:Eu3+ Glass. Molecules, 29(11), 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29112470






