N-Heterocycles as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pyrazole Derivatives
3. Imidazole Derivatives
4. Thiazole Derivatives
5. Thiazolidinone Derivatives
6. Thiadiazole Derivatives
7. Triazole Derivatives
8. Oxazole and Oxadiazole Derivatives
9. Pyrrole Derivatives
10. Pyrrolidine Derivatives
11. Indole Derivatives
12. Isatin Derivatives
13. Indolizidine Derivatives
14. Imidazo-Pyrimidine Derivatives
15. Pyrimidine Derivatives
16. Triazine Derivatives
17. Quinazoline/Quinazolin-ones Derivatives
18. Pyrazine Derivatives
19. Quinoxaline Derivatives
20. Piperazine Derivatives
21. Piperidine Derivatives
22. Pyridine Derivatives
23. Quinolines Derivatives
24. Miscellaneous N-Heterocyclic Derivatives
25. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, P.; Arora, V.; Lamba, H.; Wadhwa, D. Importance of heterocyclic chemistry: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 2947–2954. [Google Scholar]
- Gribble, G.; Joule, J. Progress in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dua, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Sonwane, S.; Srivastava, S. Pharmacological significance of synthetic heterocycles scaffold: A review. Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 120–144. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Dwivedi, J.; Singh, R. A review: Biological significances of heterocyclic compounds. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- Franzén, R.G. Recent advances in the preparation of heterocycles on solid support: A review of the literature. J. Comb. Chem. 2000, 2, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.P.; Robinson, R.P.; Fobian, Y.M.; Blakemore, D.C.; Jones, L.H.; Fadeyi, O. Modern advances in heterocyclic chemistry in drug discovery. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 6611–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, X.-H.; Wang, S.-Q.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X.-B.; Yu, B. FDA-approved pyrimidine-fused bicyclic heterocycles for cancer therapy: Synthesis and clinical application. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 214, 113218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermer, A.; Faiz, O.; Demirbas, A.; Demirbas, N.; Alagumuthu, M.; Arumugam, S. Piperazine-azole-fluoroquinolone hybrids: Conventional and microwave irradiated synthesis, biological activity screening and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 85, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermer, A.; Demirbas, N.; Demirbas, A.; Colak, N.; Ayaz, F.A.; Alagumuthu, M.; Arumugam, S. Synthesis, biological activity and structure activity relationship studies of novel conazole Egues via conventional, microwave and ultrasound mediated techniques. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermer, A.; Demirbaş, N.; Şirin, Y.; Uslu, H.; Özdemir, Z.; Demirbaş, A. Conventional and microwave prompted synthesis, antioxidant, anticholinesterase activity screening and molecular docking studies of new quinolone-triazole hybrids. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 78, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherief, H.A.; Youssif, B.G.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M. Novel 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as potential anticancer agents: Design, synthesis, molecular docking and mechanistic studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkin, A.V.; Curreli, F.; Iusupov, I.R.; Spiridonov, E.A.; Ahmed, S.; Markov, P.O.; Manasova, E.V.; Altieri, A.; Debnath, A.K. Design, Synthesis, and Antiviral Activity of the Thiazole Positional Isomers of a Potent HIV-1 Entry Inhibitor NBD-14270. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, M.; Ingarra, A.M.; Raimondi, M.V.; Spanò, V.; Piccionello, A.P.; De Franco, M.; Menilli, L.; Gandin, V.; Miolo, G.; Barraja, P. New tricyclic systems as photosensitizers towards triple negative breast cancer cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2022, 45, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra, D.; Abonia, R.; Castillo, J.-C. Recent applications of the multicomponent synthesis for bioactive pyrazole derivatives. Molecules 2022, 27, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillone, K.; Riillo, C.; Rocca, R.; Ascrizzi, S.; Spanò, V.; Scionti, F.; Polerà, N.; Maruca, A.; Barreca, M.; Juli, G. The new microtubule-targeting agent SIX2G induces immunogenic cell death in multiple myeloma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniciuc, L.; Amăriucăi-Mantu, D.; Diaconu, D.; Mangalagiu, V.; Danac, R.; Antoci, V.; Mangalagiu, I.I. Benzoquinoline Derivatives: An Attractive Approach to Newly Small Molecules with Anticancer Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhon, E.; Cox, S.; Buontempo, P.; O’Connell, J.; Slater, W.; De Martino, J.; Schwartz, J.; Miller, G.; Arnold, E.; Zhang, A. SCH 38057: A picornavirus capsid-binding molecule with antiviral activity after the initial stage of viral uncoating. Antivir. Res. 1993, 21, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Symons, J.A.; Deval, J. Innovation and trends in the development and approval of antiviral medicines: 1987–2017 and beyond. Antivir. Res. 2018, 155, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundala, R.; Balutia, H.; Lavanya, R.; Velayutham, R.; Roy, K.K. HCV NS3 serine protease as a drug target for the development of drugs against hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). In Cancer-Leading Proteases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 243–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kappus, M.R.; Wolfe, C.R.; Muir, A.J. Direct-Acting Antivirals and Organ Transplantation: Is There Anything We Can’t Do? J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222 (Suppl. S9), S794–S801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Lockart, I.; Alavi, M.; Danta, M.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Dore, G.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Effectiveness of direct-acting antiviral treatment for hepatitis C in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deval, J.; Symons, J.A.; Beigelman, L. Inhibition of viral RNA polymerases by nucleoside and nucleotide analogs: Therapeutic applications against positive-strand RNA viruses beyond hepatitis C virus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.M.; da Silva, D.L.; Modolo, L.V.; Alves, R.B.; de Resende, M.A.; Martins, C.V.; de Fátima, Â. Schiff bases: A short review of their antimicrobial activities. J. Adv. Res. 2011, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, D.; Yogeeswari, P.; Myneedu, N.S.; Saraswat, V. Abacavir prodrugs: Microwave-assisted synthesis and their evaluation of anti-HIV activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2127–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Lee, P.W.; Cao, S. China: Forward to the Green Pesticides via a Basic Research Program; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Seiber, J.N. Sustainability and Agricultural and Food Chemistry; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Rice, C.M. Structure of the zinc-binding domain of an essential component of the hepatitis C virus replicase. Nature 2005, 435, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, S.; Gamal, N.; Andreone, P. NS 5A inhibitors for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Akagi, Y.; Terui, T.; Fujioka, S.; Komoda, Y.; Kinoshita, W.; Maeda, K.; Ukaji, Y.; Inaba, T. Discovery of a novel unsymmetrical structural class of HCV NS5A inhibitors with low picomolar antiviral activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, D.D. Antiviral drug resistance. Antivir. Res. 2006, 71, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, P.M. New antivirals and drug resistance. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, G.C.; Martins, L.M.; Bregadiolli, B.A.; Moreno, V.F.; da Silva-Filho, L.C.; da Silva, B.H.S.T. Heterocyclic compounds as antiviral drugs: Synthesis, structure–activity relationship and traditional applications. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2021, 58, 2226–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; Aljohani, G.; Alhaddad, O.A. Investigation of some antiviral N-heterocycles as COVID 19 drug: Molecular docking and DFT calculations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinodia, M. N-heterocycles: Recent Advances in Biological Applications. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2023, 20, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermer, A.; Keles, T.; Sirin, Y. Recent studies of nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds as novel antiviral agents: A review. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutalabisin, F.; Ghafarikhaligh, M.; Mihankhah, P.; Khaligh, N.G. Recent developed nitrogen/sulfur heterocyclic compounds with marked and selective antiviral activities (microreview). Curr. Org. Chem. 2023, 27, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Henary, M. Synthesis and applications of nitrogen-containing heterocycles as antiviral agents. Molecules 2022, 27, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Sharma, P.; Kaushik, N. Pyrazole: A versatile moiety. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2011, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, S.K.; Abou-Elmagd, W.S. Synthesis and anti H5N1 activities of some novel fused heterocycles bearing pyrazolyl moiety. Synth. Commun. 2018, 48, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Elmagd, W.S.; EL-Ziaty, A.K.; Elzahar, M.I.; Ramadan, S.K.; Hashem, A.I. Synthesis and antitumor activity evaluation of some N-heterocycles derived from pyrazolyl-substituted 2 (3 H)-furanone. Synth. Commun. 2016, 46, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.-R.; Chu, T.-Y.; Reddy, G.R.; Tseng, S.-N.; Chen, H.-L.; Tang, W.-F.; Wu, M.-s.; Yeh, J.-Y.; Chao, Y.-S.; Hsu, J.T. Pyrazole compound BPR1P0034 with potent and selective anti-influenza virus activity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sabbagh, O.I.; Baraka, M.M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Pannecouque, C.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Balzarini, J.; Rashad, A.A. Synthesis and antiviral activity of new pyrazole and thiazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.E.; Hegab, M.I.; Abdel-Megeid, R.E.; Micky, J.A.; Abdel-Megeid, F.M. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of some new pyrazole and fused pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7102–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.I.; Youssef, A.S.; Kandeel, K.A.; Abou-Elmagd, W.S. Conversion of some 2 (3H)-furanones bearing a pyrazolyl group into other heterocyclic systems with a study of their antiviral activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cai, X.-J.; Song, B.-A.; Bhadury, P.S.; Yang, S.; Jin, L.-H.; Xue, W.; Hu, D.-Y.; Zeng, S. Synthesis and antiviral activity of novel pyrazole derivatives containing oxime esters group. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9699–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadh, S.M.; Farghaly, T.A.; Abdallah, M.A.; Abdalla, M.M.; El-Aziz, M.R.A. New pyrazoles incorporating pyrazolylpyrazole moiety: Synthesis, anti-HCV and antitumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Fernandez, R.; Goya, P.; Elguero, J. A review of recent progress (2002–2012) on the biological activities of pyrazoles. ARKIVOC 2013, 2014, 233–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, S.; Bazzanini, R.; Baraldi, P.G.; Guarneri, M.; Simoni, D.; Marongiu, M.E.; Pani, A.; La Colla, P.; Tramontano, E. Pyrazole-related nucleosides. Synthesis and antiviral/antitumor activity of some substituted pyrazole and pyrazolo [4,3-d]-1,2,3-triazin-4-one nucleosides. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schneller, S.W.; Ikeda, S.; Snoeck, R.; Andrei, G.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 5′-deoxypyrazofurin. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 3727–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, R.; Ashton, C.J.; Baxter, A.D.; Hann, M.M.; Marr, C.L.; Mason, A.M.; Mo, C.-L.; Myers, P.L.; Noble, S.A.; Penn, C.R. The synthesis and antiviral activity of 4-fluoro-1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucl. Acids 1999, 18, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genin, M.J.; Biles, C.; Keiser, B.J.; Poppe, S.M.; Swaney, S.M.; Tarpley, W.G.; Yagi, Y.; Romero, D.L. Novel 1, 5-diphenylpyrazole nonnucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors with enhanced activity versus the delavirdine-resistant P236L mutant: Lead identification and SAR of 3-and 4-substituted derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostom, S.A.; Shalaby, M.A.; El-Demellawy, M.A. Polysubstituted pyrazoles, part 5. Synthesis of new 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid hydrazide analogs and some derived ring systems. A novel class of potential antitumor and anti-HCV agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Chandrakumar, N.; Yoon, J.-J.; Plemper, R.K.; Snyder, J.P. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of the measles virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complex activity: Synthesis and in vitro evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5199–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.-F.; Zhang, H.-S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Sanchez, T.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Neamati, N.; Long, Y.-Q. Efficient synthesis and utilization of phenyl-substituted heteroaromatic carboxylic acids as aryl diketo acid isosteres in the design of novel HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4521–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowbray, C.E.; Burt, C.; Corbau, R.; Gayton, S.; Hawes, M.; Perros, M.; Tran, I.; Price, D.A.; Quinton, F.J.; Selby, M.D. Pyrazole NNRTIs 4: Selection of UK-453,061 (lersivirine) as a development candidate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5857–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowbray, C.E.; Burt, C.; Corbau, R.; Perros, M.; Tran, I.; Stupple, P.A.; Webster, R.; Wood, A. Pyrazole NNRTIs 1: Design and initial optimisation of a novel template. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5599–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidique, S.; Shiryaev, S.A.; Ratnikov, B.I.; Herath, A.; Su, Y.; Strongin, A.Y.; Cosford, N.D. Structure–activity relationship and improved hydrolytic stability of pyrazole derivatives that are allosteric inhibitors of West Nile Virus NS2B-NS3 proteinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5773–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, K.; Shanthi, G.; Selvam, N.P.; Manoharan, S.; Perumal, P.T.; Rajendran, M. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 4, 4′-(arylmethylene) bis (1H-pyrazol-5-ols) against peste des petits ruminant virus (PPRV). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4501–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09 Revision D. 01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, K.M.; Abdel-Gawad, H.; Mohamed, H.A.; Badria, F.A. Synthesis, anti-HSV-1, and cytotoxic activities of some new pyrazole-and isoxazole-based heterocycles. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Song, B.; Bhadury, P.S.; Yang, S.; Hu, D.; Jin, L. Synthesis and antiviral activity of novel pyrazole amides containing α-aminophosphonate moiety. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2011, 48, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, C.; So, W.; Jo, M.; Ok, T.; Kwon, J.; Kong, S.; Jo, S.; Kim, Y. Discovery of phenylaminopyridine derivatives as novel HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndungu, J.M.; Krumm, S.A.; Yan, D.; Arrendale, R.F.; Reddy, G.P.; Evers, T.; Howard, R.; Natchus, M.G.; Saindane, M.T.; Liotta, D.C. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of the measles virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: Synthesis, structure–activity relationships, and pharmacokinetics. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4220–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, A.S.; Nasr, M.N.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Tawfik, S.S. Synthesis and antiviral activity of new 3-methyl-1, 5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 4139–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Xu, G.F.; Fan, Z.J.; Wang, D.Q.; Yang, X.L. Synthesis and anti-TMV activity of novel N-(3-alkyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-3-alkyl-4-substituted-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamides. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, H.-Y.; Park, D.-S.; Choi, J.; Baek, S.M.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Seong, S.; Choi, I.; Lee, H.-g. Identification of a series of 1, 3, 4-trisubstituted pyrazoles as novel hepatitis C virus entry inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6467–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuhara, T.; Kato, T.; Hirai, A.; Kurihara, H.; Shimada, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Maeta, H.; Togami, H.; Shimura, K.; Matsuoka, M. Structure–activity relationship study of phenylpyrazole derivatives as a novel class of anti-HIV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4557–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsy, A.R.; Ramadan, S.K.; Elsafty, M.M. Synthesis and antiviral activity of some pyrrolonyl substituted heterocycles as additives to enhance inactivated Newcastle disease vaccine. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadoriya, K.S.; Sharma, M.C.; Jain, S.V. 2,4-Dihydropyrano [2,3-c] pyrazole: Discovery of new lead as through pharmacophore modelling, atom-based 3D-QSAR, virtual screening and docking strategies for improved anti-HIV-1 chemotherapy. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, R.; Desideri, N.; Biava, M.; Droghini, P.; Atzori, E.M.; Ibba, C.; Collu, G.; Sanna, G.; Delogu, I.; Loddo, R. N-((1,3-Diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) methyl) anilines: A novel class of anti-RSV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2401–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Guo, Y.-C.; Wang, D.-D.; Dai, X.-J.; Wu, F.-J.; Liu, H.-F.; Dai, G.-F.; Tao, J.-C. Novel pyrazole fused heterocyclic ligands: Synthesis, characterization, DNA binding/cleavage activity and anti-BVDV activity. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manvar, D.; Pelliccia, S.; La Regina, G.; Famiglini, V.; Coluccia, A.; Ruggieri, A.; Anticoli, S.; Lee, J.-C.; Basu, A.; Cevik, O. New 1-phenyl-5-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamides inhibit hepatitis C virus replication via suppression of cyclooxygenase-2. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, H.; Huang, L.-C.S.; Kapoor, M.; Liao, Y.-J.; Yang, C.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Hwu, J.R.; Huang, T.-J.; Hsu, M.-H. Design and synthesis of pyridine-pyrazole-sulfonate derivatives as potential anti-HBV agents. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Cai, X.-J.; Chen, Z.; Song, B.-A.; Bhadury, P.S.; Yang, S.; Jin, L.-H.; Xue, W.; Hu, D.-Y.; Zeng, S. Synthesis and antiviral activities of pyrazole derivatives containing an oxime moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10160–10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-N.; Luo, R.-H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, J.; Yang, L.-M.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Liu, H. Synthesis and anti-HIV-1 activity evaluation for novel 3a,6a-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[3,4-c] pyrazole-4,6-dione derivatives. Molecules 2016, 21, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Q.; Chen, Z.; He, M.; Jin, L.; Hu, D. Synthesis and bioactivity of pyrazole acyl thiourea derivatives. Molecules 2012, 17, 5139–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, B.A.; Gudmundsson, K.S.; Allen, S.H. Pyrazolo [1,5-a] pyridine antiherpetics: Effects of the C3 substituent on antiviral activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2858–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.-L.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Chan, W.L.; Wang, G.; Ng, R.H.; Lim, J.Y.; Lee, W.Y.; Jeyaraj, D.A.; Niyomrattanakit, P. N-sulfonylanthranilic acid derivatives as allosteric inhibitors of dengue viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7934–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, A.; Ali, S.S.; Alanazi, A.M.; Mashwani, M.A.; Al-Obaid, A.M. Synthesis, Antiviral, and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Benzyl Protected Diversified C-nucleosides. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, K.; Suzuki, T.; Negishi, K.; Graci, J.D.; Thompson, C.N.; Cameron, C.E.; Watanabe, M. Effects of introduction of hydrophobic group on ribavirin base on mutation induction and anti-RNA viral activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, C.R., III; Revankar, G.R.; Dalley, N.K.; George, R.D.; McKernan, P.A.; Hamill, R.L.; Robins, R.K. Synthesis and biological activity of certain nucleoside and nucleotide derivatives of pyrazofurin. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, W.M. Selective inhibition of RNA tumor virus replication in vitro and evaluation of candidate antiviral agents in vivo. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1977, 284, 472–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Nanda, A.K. A review on heterocyclic: Synthesis and their application in medicinal chemistry of imidazole moiety. Science 2018, 6, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Narasimhan, B.; Kumar, P.; Judge, V.; Narang, R.; De Clercq, E.; Balzarini, J. Synthesis, antimicrobial and antiviral evaluation of substituted imidazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2347–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baures, P.W. Heterocyclic HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi, M.; Zmurko, J.; Kaptein, S.; Rozenski, J.; Neyts, J.; Van Aerschot, A. Synthesis and evaluation of imidazole-4, 5-and pyrazine-2, 3-dicarboxamides targeting dengue and yellow fever virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E.; Cools, M.; Balzarini, J.; Snoeck, R.; Andrei, G.; Hosoya, M.; Shigeta, S.; Ueda, T.; Minakawa, N.; Matsuda, A. Antiviral activities of 5-ethynyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide and related compounds. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielsen, B.; Phelan, M.J.; Barthel-Rosa, L.; See, C.; Huggins, J.W.; Kefauver, D.F.; Monath, T.P.; Ussery, M.A.; Chmurny, G.N. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of N-carboxamidine-substituted analogs of 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamidine hydrochloride. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 3231–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, J.; Pizarro, H.; Jashes, M.; De Clercq, E.; Sandino, A. In vivo effect of EICAR (5-ethynyl-1-β-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-carboxamide) on experimental infected rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) fry with infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. Antivir. Res. 2000, 48, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Pozzo, F.; Galligioni, V.; Vaccari, F.; Gallina, L.; Battilani, M.; Scagliarini, A. Antiviral efficacy of EICAR against canine distemper virus (CDV) in vitro. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 88, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzarini, J.; Karlsson, A.; Wang, L.; Bohman, C.; Horska, K.; Votruba, I.; Fridland, A.; Van Aerschot, A.; Herdewijn, P.; De Clercq, E. Eicar (5-ethynyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide). A novel potent inhibitor of inosinate dehydrogenase activity and guanylate biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24591–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, M.; Gonzales, S.R.; Kumarapperuma, S.C.; Jeselnik, M.; Arterburn, J.B.; Hanley, K.A. A novel nucleoside analog, 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-3-ethynyl-[1,2,4] triazole (ETAR), exhibits efficacy against a broad range of flaviviruses in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2010, 87, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starčević, K.; Kralj, M.; Ester, K.; Sabol, I.; Grce, M.; Pavelić, K.; Karminski-Zamola, G. Synthesis, antiviral and antitumor activity of 2-substituted-5-amidino-benzimidazoles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, S.-C.; Hwu, J.R.; Singha, R.; Huang, W.-C.; Chang, Y.H.; Hsu, M.-H.; Shieh, F.-k.; Lin, C.-C.; Hwang, K.C.; Horng, J.-C. Coumarins hinged directly on benzimidazoles and their ribofuranosides to inhibit hepatitis C virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Wang, G.-F.; Luo, Y.; Huang, W.-G.; Tang, W.; Feng, C.-L.; Shi, L.-P.; Ren, Y.-D.; Zuo, J.-P.; Lu, W. Identification of 1-isopropylsulfonyl-2-amine benzimidazoles as a new class of inhibitors of hepatitis B virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, Y.M.; Omar, M.A.; Mahmoud, K.; Elhallouty, S.M.; El-Senousy, W.M.; Ali, M.M.; Mahmoud, A.E.; Abdel-Halim, A.H.; Soliman, S.M.; El Diwani, H.I. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo antitumor and antiviral activity of novel 1-substituted benzimidazole derivatives. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 826–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, M.; Simone, M.; Tasso, B.; Novelli, F.; Boido, V.; Sparatore, F.; Paglietti, G.; Pricl, S.; Giliberti, G.; Blois, S. Antiviral activity of benzimidazole derivatives. II. Antiviral activity of 2-phenylbenzimidazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2937–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wei, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q. Design, synthesis, antiviral activity and mode of action of phenanthrene-containing N-heterocyclic compounds inspired by the phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid antofine. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashima, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ishida, T.; Noji, S.; Yata, S.; Ando, I.; Komatsu, M.; Ikeda, S.; Hashimoto, H. Benzimidazole derivatives bearing substituted biphenyls as hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors: Structure− activity relationship studies and identification of a potent and highly selective inhibitor JTK-109. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4721–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashima, S.; Oka, T.; Ikegashira, K.; Noji, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Hara, Y.; Goto, H.; Mizojiri, R.; Niwa, Y.; Noguchi, T. Further studies on hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors toward improved replicon cell activities: Benzimidazole and structurally related compounds bearing the 2-morpholinophenyl moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwu, J.R.; Singha, R.; Hong, S.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Das, A.R.; Vliegen, I.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J. Synthesis of new benzimidazole–coumarin conjugates as anti-hepatitis C virus agents. Antivir. Res. 2008, 77, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Xie, J.; Luo, X. Synthesis and antiviral activity against Coxsackie virus B3 of some novel benzimidazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, T.; Gigante, B.; Marques, M.M.; Gilchrist, T.L.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of benzimidazoles, quinoxalines and indoles from dehydroabietic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monforte, A.-M.; Ferro, S.; De Luca, L.; Surdo, G.L.; Morreale, F.; Pannecouque, C.; Balzarini, J.; Chimirri, A. Design and synthesis of N1-aryl-benzimidazoles 2-substituted as novel HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Sun, Z.J.; Xue, F.; Luo, X.J.; Xiu, N.Y.; Teng, L.; Peng, Z.G. Design, synthesis and biological activity of some novel benzimidazole derivatives against Coxsackie virus B3. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yao, J.-P.; Yang, L.; Feng, C.-L.; Tang, W.; Wang, G.-F.; Zuo, J.-P.; Lu, W. Design and synthesis of novel benzimidazole derivatives as inhibitors of hepatitis B virus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5048–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.W.; Cantrell, A.S.; Hoegberg, M.; Jaskunas, S.R.; Johansson, N.G.; Jordan, C.L.; Kinnick, M.D.; Lind, P.; Morin, J.M., Jr. Phenethylthiazolethiourea (PETT) compounds, a new class of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. 1. Synthesis and basic structure-activity relationship studies of PETT analogs. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 4929–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwatashi, S.; Arikawa, Y.; Kotani, E.; Miyamoto, M.; Naruo, K.-i.; Kimura, H.; Tanaka, T.; Asahi, S.; Ohkawa, S. Novel inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase as an anti-TNF-α drug: Discovery of N-[4-[2-ethyl-4-(3-methylphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-5-yl]-2-pyridyl] benzamide (TAK-715) as a potent and orally active anti-rheumatoid arthritis agent. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5966–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Muijlwijk-Koezen, J.E.; Timmerman, H.; Vollinga, R.C.; Frijtag von Drabbe Künzel, J.; de Groote, M.; Visser, S.; IJzerman, A.P. Thiazole and thiadiazole analogues as a novel class of adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Khaliq, M.; Zhou, Z.; Post, C.B.; Kuhn, R.J.; Cushman, M. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of antiviral agents targeting flavivirus envelope proteins. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crute, J.J.; Grygon, C.A.; Hargrave, K.D.; Simoneau, B.; Faucher, A.-M.; Bolger, G.; Kibler, P.; Liuzzi, M.; Cordingley, M.G. Herpes simplex virus helicase-primase inhibitors are active in animal models of human disease. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Smith, K.L.; Varaprasad, C.V.; Chang, E.; Alexander, J.; Yao, N. Synthesis of thiazolone-based sulfonamides as inhibitors of HCV NS5B polymerase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraher, C.E., Jr.; Roner, M.R. Organotin polymers as anticancer and antiviral agents. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 751, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. A novel benzo-heterocyclic amine derivative N30 inhibits influenza virus replication by depression of Inosine-5′-Monophospate Dehydrogenase activity. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-J.; Sun, W.-F.; Zhong, Z.-J.; Gao, R.-M.; Yi, H.; Li, Y.-H.; Peng, Z.-G.; Li, Z.-R. Synthesis and broad-spectrum antiviral activity of some novel benzo-heterocyclic amine compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamama, W.S.; El-Bana, G.G.; Shaaban, S.; Habib, O.; Zoorob, H.H. Advances in the domain of 4-amino-3-mercapto-1, 2, 4-triazine-5-ones. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 24010–24049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, R.K.; Tripathi, R.; Katti, S.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and evaluation of 2-(2,6-dihalophenyl)-3-pyrimidinyl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one analogues as anti-HIV-1 agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3134–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, R.K.; Katti, S.B.; Kaushik-Basu, N.; Arora, P.; Pan, Z. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependant RNA polymerase: 2-Aryl-3-heteroaryl-1, 3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6110–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaushik-Basu, N.; Bopda-Waffo, A.; Talele, T.T.; Basu, A.; Chen, Y.; Kucukguzel, S.G. 4-Thiazolidinones: A novel class of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitors. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 3857–3868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawal, R.K.; Tripathi, R.; Katti, S.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 2-aryl-3-heteroaryl-1, 3-thiazolidin-4-ones as anti-HIV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Carbone, A.; Chimirri, A.; De Clercq, E.; Monforte, A.M.; Monforte, P.; Pannecouque, C.; Zappalà, M. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of 2,3-diaryl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones. IL Farm. 2003, 58, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Balzarini, J.; Carbone, A.; Chimirri, A.; De Clercq, E.; Monforte, A.; Monforte, P.; Pannecouque, C.; Zappala, M. 2-(2,6-Dihalophenyl)-3-(pyrimidin-2-yl)-1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones as non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2004, 63, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzioglu, N.; Karali, N.; Gursoy, A.; Pannecouque, C.; Leysen, P.; Paeshuyse, J.; Neyts, J.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and primary antiviral activity evaluation of 3-hydrazono-5-nitro-2-indolinone derivatives. Arkivoc 2006, 1, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarini, J.; Orzeszko, B.; Maurin, J.K.; Orzeszko, A. Synthesis and anti-HIV studies of 2-adamantyl-substituted thiazolidin-4-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bai, J.; Jiao, L.; Guo, Z.; Yin, Q.; Li, X. Design, microwave-assisted synthesis and HIV-RT inhibitory activity of 2-(2,6-dihalophenyl)-3-(4,6-dimethyl-5-(un)substituted-pyrimidin-2-yl) thiazolidin-4-ones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3980–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, K.; Yarovenko, V.N.; Nikitina, A.S.; Zavarzin, I.V.; Krayushkin, M.M.; Kovalenko, L.V.; Esqueda, A.; Odde, S.; Neamati, N. Design, synthesis and structure-activity studies of rhodanine derivatives as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Molecules 2010, 15, 3958–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Guo, Z.; Yin, Q.; Duan, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, X. Design, synthesis and HIV-RT inhibitory activity of novel thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, R.K.; Tripathi, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Paranjape, R.; Katti, S.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E. 2-(2,6-Dihalo-phenyl)-3-heteroaryl-2-ylmethyl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones: Anti-HIV agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2008, 72, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, R.K.; Tripathi, R.; Katti, S.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E. Design and synthesis of 2-(2,6-dibromophenyl)-3-heteroaryl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones as anti-HIV agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 2800–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, V.; Jain, A.; Kumar, K.S.; Rajak, H.; Agrawal, R.K. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Thiazolidinone Derivatives as Antimicrobial and Anti-viral Agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahab, B.F.; Shaaban, S. Thiazolothiadiazoles and thiazolooxadiazoles: Synthesis and biological applications. Synthesis 2014, 46, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shaaban, S.; Liu, N.-W.; Hofman, K.; Manolikakes, G. Recent advances in the synthesis of C–S bonds via metal-catalyzed or-mediated functionalization of C–H bonds. Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 69, 135–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.; Hu, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, B. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of novel 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole-chalcone conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4298–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, P.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Fang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E. Novel 1,2,3-thiadiazole derivatives as HIV-1 NNRTIs with improved potency: Synthesis and preliminary SAR studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5920–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, N.S.; Al-Haidery, N.H.; Al-Masoudi, I.A.; Sabri, M.; Sabri, L.; Al-Masoudi, N.A. Amino Acid Derivatives, Part 4: Synthesis and Anti-HIV Activity of New Naphthalene Derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2010, 343, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Wei, Y.; Drach, J.C.; Townsend, L.B. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of trisubstituted indole N-nucleosides as analogues of 2,5,6-trichloro-1-(β-D-ribofuranosyl) benzimidazole (TCRB). J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manvar, D.; Küçükgüzel, İ.; Erensoy, G.; Tatar, E.; Deryabaşoğulları, G.; Reddy, H.; Talele, T.T.; Cevik, O.; Kaushik-Basu, N. Discovery of conjugated thiazolidinone-thiadiazole scaffold as anti-dengue virus polymerase inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Li, X.-Y.; Dong, Y.-W.; Qin, Y.-G.; Li, X.-L.; Song, B.-A.; Yang, X.-L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-carboxaldehyde benzoyl hydrazone derivatives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buemi, M.R.; Gitto, R.; Ielo, L.; Pannecouque, C.; De Luca, L. Inhibition of HIV-1 RT activity by a new series of 3-(1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl) thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fascio, M.L.; Sepúlveda, C.S.; Damonte, E.B.; D’Accorso, N.B. Synthesis and antiviral activity of some imidazo [1,2-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole carbohydrate derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 480, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuzem, S.; Poordad, F. Pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin therapy in the treatment of CHC: Individualization of treatment duration according to on-treatment virologic response. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crance, J.M.; Scaramozzino, N.; Jouan, A.; Garin, D. Interferon, ribavirin, 6-azauridine and glycyrrhizin: Antiviral compounds active against pathogenic flaviviruses. Antivir. Res. 2003, 58, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, I.; Briese, T.; Fischer, N.; Lau, J.Y.-N.; Lipkin, W.I. Ribavirin inhibits West Nile virus replication and cytopathic effect in neural cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Meng, F. Antiviral Composition Containing Fucoidan and Ribavirin for Preventing and Treating Plant Viral Diseases. CN 101869111A, 27 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell, R.W.; Huffman, J.H.; Khare, G.P.; Allen, L.B.; Witkowski, J.T.; Robins, R.K. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of virazole: 1-f8-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. Science 1972, 177, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, J.; Robins, R.K.; Sidwell, R.W.; Simon, L.N. Design, synthesis, and broad spectrum antiviral activity of 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and related nucleosides. J. Med. Chem. 1972, 15, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krilov, L.R. Respiratory syncytial virus disease: Update on treatment and prevention. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetano, J.N.; Reau, N. Hepatitis C: Management of side effects in the era of direct-acting antivirals. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2013, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smee, D.F.; Bray, M.; Huggins, J.W. Antiviral activity and mode of action studies of ribavirin and mycophenolic acid against orthopoxviruses in vitro. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2001, 12, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyssen, P.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J. The predominant mechanism by which ribavirin exerts its antiviral activity in vitro against flaviviruses and paramyxoviruses is mediated by inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. RNA virus error catastrophe: Direct molecular test by using ribavirin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6895–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.-H.; Kumarapperuma, S.C.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Chu, Y.-K.; Arterburn, J.B.; Parker, W.B.; Smith, J.; Spik, K.; Ramanathan, H.N. Synthesis of 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-3-ethynyl-[1,2,4] triazole and its in vitro and in vivo efficacy against Hantavirus. Antivir. Res. 2008, 79, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Rocchi, P.; Yao, J.; Qu, F.; Neyts, J.; Iovanna, J.L.; Peng, L. Discovery of novel arylethynyltriazole ribonucleosides with selective and effective antiviral and antiproliferative activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajczyk, A.; Kulinska, K.; Kulinski, T.; Hurst, B.L.; Day, C.W.; Smee, D.F.; Ostrowski, T.; Januszczyk, P.; Zeidler, J. Antivirally active ribavirin analogues–4,5-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole nucleosides: Biological evaluation against certain respiratory viruses and computational modelling. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2014, 23, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudinov, M.V.; Matveev, A.V.; Prutkov, A.N.; Konstantinova, I.D.; Fateev, I.V.; Prasolov, V.S.; Smirnova, O.A.; Ivanov, A.V.; Galegov, G.A.; Deryabin, P.G. Novel 5-alkyl(aryl)-substituted ribavirine analogues: Synthesis and antiviral evaluation. Mendeleev Commun. 2016, 26, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernekar, S.K.V.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, J.; Kankanala, J.; Li, H.; Geraghty, R.J.; Wang, Z. 5′-Silylated 3′-1, 2, 3-triazolyl thymidine analogues as inhibitors of West Nile virus and dengue virus. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4016–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyushin, O.I.; Sharova, E.V.; Vinogradova, N.M.; Genkina, G.K.; Moiseeva, A.A.; Klemenkova, Z.S.; Orshanskaya, I.R.; Shtro, A.A.; Kadyrova, R.A.; Zarubaev, V.V. Synthesis of camphecene derivatives using click chemistry methodology and study of their antiviral activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2181–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macan, A.M.; Harej, A.; Cazin, I.; Klobučar, M.; Stepanić, V.; Pavelić, K.; Pavelić, S.K.; Schols, D.; Snoeck, R.; Andrei, G. Antitumor and antiviral activities of 4-substituted 1,2,3-triazolyl-2,3-dibenzyl-L-ascorbic acid derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 184, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, T.; Dick, A.; Meuser, M.E.; Zalloum, W.A.; Chen, C.-H.; Ding, X.; Gao, P.; Cocklin, S.; Lee, K.-H. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 4-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole phenylalanine derivatives as novel HIV-1 capsid inhibitors with promising antiviral activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 190, 112085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keaney, E.P.; Connolly, M.; Dobler, M.; Karki, R.; Honda, A.; Sokup, S.; Karur, S.; Britt, S.; Patnaik, A.; Raman, P. 2-Alkyloxazoles as potent and selective PI4KIIIβ inhibitors demonstrating inhibition of HCV replication. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3714–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belema, M.; Nguyen, V.N.; Romine, J.L.; St. Laurent, D.R.; Lopez, O.D.; Goodrich, J.T.; Nower, P.T.; O’Boyle, D.R.; Lemm, J.A.; Fridell, R.A. Hepatitis C virus NS5A replication complex inhibitors. Part 6: Discovery of a novel and highly potent biarylimidazole chemotype with inhibitory activity toward genotypes 1a and 1b replicons. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1995–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Markovitz, B.; Trovato, R.; Murphy, B.R.; Austin, H.; Willardsen, A.J.; Baichwal, V.; Morham, S.; Bajji, A. Discovery of a new HIV-1 inhibitor scaffold and synthesis of potential prodrugs of indazoles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2888–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draffan, A.G.; Frey, B.; Fraser, B.H.; Pool, B.; Gannon, C.; Tyndall, E.M.; Cianci, J.; Harding, M.; Lilly, M.; Hufton, R. Derivatives of imidazotriazine and pyrrolotriazine C-nucleosides as potential new anti-HCV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4984–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, Y.-F.; Riccardi, K.A.; Lin, P.-F.; Parker, D.D.; Rahematpura, S.; Mathew, M.; Zheng, M. Inhibitors of HIV-1 attachment. Part 10. The discovery and structure–activity relationships of 4-azaindole cores. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-J.; Zhang, D.-J.; Peng, Z.-G.; Li, Y.-H.; Shan, G.-Z.; Zuo, L.-M.; Wu, L.-T.; Li, S.-Y.; Gao, R.-M.; Li, Z.-R. Synthesis and antiviral activity of a novel class of (5-oxazolyl) phenyl amines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rynearson, K.D.; Charrette, B.; Gabriel, C.; Moreno, J.; Boerneke, M.A.; Dibrov, S.M.; Hermann, T. 2-Aminobenzoxazole ligands of the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3521–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.M.; Cabiddu, M.G.; De Montis, S.; Mura, R.; Pompei, R. Synthesis of new compounds with promising antiviral properties against group A and B Human Rhinoviruses. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4061–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.A.; Bilimoria, D.; Bubenik, M.; Cadilhac, C.; Cottrell, K.M.; Denis, F.; Dietrich, E.; Ewing, N.; Falardeau, G.; Giroux, S. Synthesis and evaluation of NS5A inhibitors containing diverse heteroaromatic cores. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Gever, J.R.; Rao, S.; Widjaja, K.; Prusiner, S.B.; Silber, B.M. Discovery and preliminary structure–activity relationship of arylpiperazines as novel, brain-penetrant antiprion compounds. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryde, D.C.; Tran, T.-D.; Gardner, I.; Bright, H.; Stupple, P.; Galan, S.; Alsop, L.; Watson, L.; Middleton, D.S.; Dayal, S. Non-benzimidazole containing inhibitors of respiratory syncytial virus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ma, C.; DeGrado, W.F.; Wang, J. Discovery of highly potent inhibitors targeting the predominant drug-resistant S31N mutant of the influenza A virus M2 proton channel. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarla, R.; Liu, J.; Naduthambi, D.; Chang, W.; Mosley, R.T.; Bao, D.; Steuer, H.M.M.; Keilman, M.; Bansal, S.; Lam, A.M. Discovery of a novel class of potent HCV NS4B inhibitors: SAR studies on piperazinone derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2136–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Tai, A.; Jiang, G.; Ouyang, G. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 2-substituted methylthio-5-(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, K.-S.; Qiu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Trehan, A.; Fang, H.; Pearce, B.; Yang, Z.; Zadjura, L.; D’Arienzo, C.J.; Riccardi, K. Inhibitors of HIV-1 attachment. Part 8: The effect of C7-heteroaryl substitution on the potency, and in vitro and in vivo profiles of indole-based inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, K.J.; Parcella, K.; Yeung, K.-S.; Grant-Young, K.A.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Beno, B.R.; Sheriff, S. The discovery of a pan-genotypic, primer grip inhibitor of HCV NS5B polymerase. MedChemComm 2017, 8, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmansour, F.; Eydoux, C.; Querat, G.; De Lamballerie, X.; Canard, B.; Alvarez, K.; Guillemot, J.-C.; Barral, K. Novel 2-phenyl-5-[(E)-2-(thiophen-2-yl) ethenyl]-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole and 3-phenyl-5-[(E)-2-(thiophen-2-yl) ethenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives as dengue virus inhibitors targeting NS5 polymerase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamati, N.; Mazumder, A.; Sunder, S.; Owen, J.M.; Tandon, M.; Lown, J.W.; Pommier, Y. Highly potent synthetic polyamides, bisdistamycins, and lexitropsins as inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamontagne, J.; Mills, C.; Mao, R.; Goddard, C.; Cai, D.; Guo, H.; Cuconati, A.; Block, T.; Lu, X. Screening and identification of compounds with antiviral activity against hepatitis B virus using a safe compound library and novel real-time immune-absorbance PCR-based high throughput system. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmy, K.M.; Soliman, D.H.; Shahin, E.B.; Abd Alhameed, R. Synthesis and molecular modeling study of novel pyrrole Schiff Bases as anti-HSV-1 agents. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 736–745. [Google Scholar]
- Curreli, F.; Kwon, Y.D.; Belov, D.S.; Ramesh, R.R.; Kurkin, A.V.; Altieri, A.; Kwong, P.D.; Debnath, A.K. Synthesis, antiviral potency, in vitro ADMET, and X-ray structure of potent CD4 mimics as entry inhibitors that target the Phe43 cavity of HIV-1 gp120. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3124–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-I.; Su, B.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Wang, S.-T.; Wu, W.-C.; Dangate, P.; Wang, S.-Y.; Huang, W.-I.; Cheng, T.-J.; Lin, O.A. Synthesis and inhibitory effects of novel pyrimido-pyrrolo-quinoxalinedione analogues targeting nucleoproteins of influenza A virus H1N1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, A.C.C.; Panciera, M.; Simao dos Santos, E.F.; Singh, M.K.; Garcia, M.L.; de Souza, G.E.; Nakabashi, M.; Costa, J.L.; Garcia, C.l.R.; Oliva, G. Discovery of Marinoquinolines as Potent and Fast-Acting Plasmodium falciparum Inhibitors with in Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5547–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswat, P.; Jeyabalan, G.; Hassan, M.Z.; Rahman, M.U.; Nyola, N.K. Review of synthesis and various biological activities of spiro heterocyclic compounds comprising oxindole and pyrrolidine moities. Synth. Commun. 2016, 46, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesel, A.J. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity including human immunodeficiency and hepatitis C viruses mediated by a novel retinoid thiosemicarbazone derivative. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.; Sulkowski, M.; Jacobson, I.; Kraft, W.K.; Maliakkal, B.; Al-Ibrahim, M.; Gordon, S.C.; Kwo, P.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Panorchan, P. Characterization of vaniprevir, a hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor, in patients with HCV genotype 1 infection: Safety, antiviral activity, resistance, and pharmacokinetics. Antivir. Res. 2013, 99, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatiou, G.; Foscolos, G.B.; Fytas, G.; Kolocouris, A.; Kolocouris, N.; Pannecouque, C.; Witvrouw, M.; Padalko, E.; Neyts, J.; De Clercq, E. Heterocyclic rimantadine analogues with antiviral activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 5485–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifan, A.; Stanciu, C.; Iliescu, L.; Sporea, I.; Baroiu, L.; Diculescu, M.; Luca, M.-C.; Miftode, E.; Cijeveschi, C.; Mihai, C. Effectiveness of 8-and 12-Week Treatment with Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir and Dasabuvir in Treatment-Naïve HCV Patients in a Real-Life Setting in Romania: The AMETHYST Study. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2021, 30, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.; Shukla, A.; Parmar, P.; Rawal, R.M.; Patel, B.; Saraf, M.; Goswami, D. Reckoning a fungal metabolite, Pyranonigrin A as a potential Main protease (Mpro) inhibitor of novel SARS-CoV-2 virus identified using docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys. Chem. 2020, 264, 106425–106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhar, Z.; Khan, S.; AlOmar, S.Y.; Alkhuriji, A.; Ahmad, A. ABBV-744 as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease enzyme against COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, N.; Silakari, O. Indoles as therapeutics of interest in medicinal chemistry: Bird’s eye view. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 134, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ölgen, S.; Altanlar, N.; Karataylı, E.; Bozdayı, M. Antimicrobial and antiviral screening of novel indole carboxamide and propanamide derivatives. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2008, 63, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampieri, M.; Balbi, A.; Mazzei, M.; La Colla, P.; Ibba, C.; Loddo, R. Antiviral activity of indole derivatives. Antivir. Res. 2009, 83, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sawy, A.E.R.; Abo-Salem, H.M.; Zarie, E.S.; Abd-Alla, H.I.; El-Safty, M.M.; Mandour, A. Synthesis and antiviral activity of novel ethyl 2-(3-heterocycle-1h-indol-1-yl) acetate derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bag, P.; Ojha, D.; Mukherjee, H.; Halder, U.C.; Mondal, S.; Biswas, A.; Sharon, A.; Van Kaer, L.; Chakrabarty, S.; Das, G. A dihydro-pyrido-indole potently inhibits HSV-1 infection by interfering the viral immediate early transcriptional events. Antivir. Res. 2014, 105, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delogu, I.; Pastorino, B.; Baronti, C.; Nougairède, A.; Bonnet, E.; de Lamballerie, X. In vitro antiviral activity of arbidol against Chikungunya virus and characteristics of a selected resistant mutant. Antivir. Res. 2011, 90, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P. Synthesis and in vitro anti-hepatitis B virus activities of some ethyl 5-hydroxy-1H-indole-3-carboxylates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriskin, Y.S.; Pécheur, E.-I.; Polyak, S.J. Arbidol: A broad-spectrum antiviral that inhibits acute and chronic HCV infection. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Song, Y.; Yang, P.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Design, synthesis, and antiviral, fungicidal, and insecticidal activities of tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carbohydrazide derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9987–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V.; Pandeya, S.; DeClercq, E.; Pannecouque, C.; Witvrouw, M. Synthesis of aryl semicarbazone of 4-aminoacetophenone and their anti-HIV activity. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1998, 73, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitz, Y.; Barko, N.; Abmmoff, M.; Ronen, D. Relationships between structure and antiretroviral activity of thiosemicarbazone derivatives. Chemotherapy 1994, 40, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Hall, R.; Moyer, R. The effect of inhibitors on the growth of the entomopoxvirus from Amsacta moorei in Lymantria dispar (gypsy moth) cells. Virology 1995, 211, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sethi, M. Foye’s Principles of Medicinal Chemistry; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.-H.; Lemm, J.A.; O’Boyle, D.R.; Racela, J.; Colonno, R.; Gao, M. Specific inhibition of bovine viral diarrhea virus replicase. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6753–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, N.; Venables, B.L.; Combrink, K.D.; Gulgeze, H.B.; Yu, K.-L.; Civiello, R.L.; Thuring, J.; Wang, X.A.; Yang, Z.; Zadjura, L. Respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitors. Part 7: Structure–activity relationships associated with a series of isatin oximes that demonstrate antiviral activity in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4857–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NP, S.; Sriram, D.; Nath, G.; Clercq, E.D. Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-HIV activity of Schiff and Mannich bases of isatin with N-[6-chlorobenzothiazol-2-yl] thiosemicarbazide. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 61, 358. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, Q.; Liang, H.; Li, C.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y.; Lai, L. Potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease derived from N-substituted isatin compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-R.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.W.; Chou, S.-Y.; Chen, S.-F.; Liu, L.T.; Wu, Y.-T.; Kuo, C.-J.; Chen, T.S.-S.; Juang, S.-H. Synthesis and evaluation of isatin derivatives as effective SARS coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3058–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Kumar, A.; Mamidi, P.; Kumar, S.; Basantray, I.; Saswat, T.; Das, I.; Nayak, T.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Subudhi, B.B. Inhibition of chikungunya virus replication by 1-[(2-methylbenzimidazol-1-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-indolin-3-ylidene]amino] thiourea (MBZM-N-IBT). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.A.; Cianci, C.W.; Yu, K.-L.; Combrink, K.D.; Thuring, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Civiello, R.L.; Kadow, K.F.; Roach, J.; Li, Z. Respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitors. Part 5: Optimization of benzimidazole substitution patterns towards derivatives with improved activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4592–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, D.; Yogeeswari, P.; Gopal, G. Synthesis, anti-HIV and antitubercular activities of lamivudine prodrugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, I.-J.; Wang, L.-W.; Hsu, T.-A.; Yueh, A.; Lee, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chao, Y.-S.; Shih, S.-R.; Chern, J.-H. Isatin-β-thiosemicarbazones as potent herpes simplex virus inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1948–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Chan, W.L.; Ding, M.; Leong, S.Y.; Nilar, S.; Seah, P.G.; Liu, W.; Karuna, R.; Blasco, F.; Yip, A. Lead optimization of spiropyrazolopyridones: A new and potent class of dengue virus inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, E.I.; Hui, D.S.; Memish, Z.A.; Drosten, C.; Zumla, A. The middle east respiratory syndrome (MERS). Infect. Dis. Clin. 2019, 33, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.-Y.; Huang, R.-Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.-K.; Li, G.-R.; Yao, Y.-C.; Gao, J. Alkaloids from Cynanchum komarovii with inhibitory activity against the tobacco mosaic virus. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-Q.; Liu, Y.-X.; Fan, Z.-J.; Wang, Q.-M.; Li, G.-R.; Yao, Y.-C.; Yu, X.-S.; Huang, R.-Q. Antiviral activity of alkaloids from Cynanchum komarovii. Fine Chem. Intermed. 2007, 37, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.-M.; Yao, Y.-C.; Huang, R.-Q.; Fan, Z.; Li, G.; Yu, X. Antiviral activity of antofine from Cynanchum komarovii. Pesticides 2007, 46, 425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, M.; Wang, K.; Huang, R. Concise synthesis of benzoindolizidine derivatives and bioactivity evaluation. Lett. Org. Chem. 2008, 5, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Su, B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Mi, N.; Wang, Q. Synthesis and antiviral activities of phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids and their derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2703–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q. Design, synthesis, and anti-tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) activity of phenanthroindolizidines and their analogues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10212–10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Z.; Ouyang, D. The interaction between tylophorine B and TMV RNA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4300–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Cai, C.; Deng, M.; Liang, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q. Design, synthesis, antiviral activity, and SARs of 13a-substituted phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2881–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitby, K.; Pierson, T.C.; Geiss, B.; Lane, K.; Engle, M.; Zhou, Y.; Doms, R.W.; Diamond, M.S. Castanospermine, a potent inhibitor of dengue virus infection in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8698–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, C.G.; Ahmed, S.P.; Kang, M.S.; Nash, R.J.; Porter, E.A.; Tyms, A.S. The effect of oral treatment with 6-O-butanoyl castanospermine (MDL 28,574) in the murine zosteriform model of HSV-1 infection. Glycobiology 1995, 5, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieven, M.; Vlietinick, A.; Berghe, D.V.; Totte, J.; Dommisse, R.; Esmans, E.; Alderweireldt, F. Plant antiviral agents. III. Isolation of alkaloids from Clivia miniata Regel (Amaryl-lidaceae). J. Nat. Prod. 1982, 45, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, S.; Abdel-Wahab, B.F. Groebke–Blackburn–Bienaymé multicomponent reaction: Emerging chemistry for drug discovery. Mol. Divers. 2016, 20, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraher, C.E.; Sabir, T.S.; Roner, M.R.; Shahi, K.; Bleicher, R.E.; Roehr, J.L.; Bassett, K.D. Synthesis of organotin polyamine ethers containing acyclovir and their preliminary anticancer and antiviral activity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2006, 16, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A. Monosaccharidic push-pull Butadienes: Versatile synthetic intermediates. Z. Für Naturforschung B 2014, 69, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E.; Field, H.J. Antiviral prodrugs–the development of successful prodrug strategies for antiviral chemotherapy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E.; Holý, A. Acyclic nucleoside phosphonates: A key class of antiviral drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilay, K.P.V.; Jasamai, M.; Thayan, R.; Santhanam, J.; Hassan, S.S.; Yap, W.B. Nucleoside analogs as potential antiviral agents for dengue virus infections. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamou, Y.; Tubiana, R.; Thibault, V. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in patients with HIV and lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.S.; Fordyce, M.W.; Hitchcock, M.J. Tenofovir alafenamide: A novel prodrug of tenofovir for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus. Antivir. Res. 2016, 125, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Chang, S.-Y.; Sheng, W.-H.; Sun, H.-Y.; Lee, K.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Su, Y.-C.; Liu, W.-C.; Hung, C.-C.; Chang, S.-C. Virological response to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in HIV-positive patients with lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus coinfection in an area hyperendemic for hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lam, Y.-F.; Seto, W.-K.; Wong, D.; Cheung, K.-S.; Fung, J.; Mak, L.-Y.; Yuen, J.; Chong, C.-K.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Seven-year treatment outcome of entecavir in a real-world cohort: Effects on clinical parameters, HBsAg and HBcrAg levels. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, K.; Joshi, D.; Byrne, R.; Bruce, M.; Carey, I.; Agarwal, K.; Taylor, C. Tenofovir-based combination therapy for HIV/HBV co-infection: Factors associated with a partial HBV virological response in patients with undetectable HIV viraemia. AIDS 2013, 27, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, L.; Šmídková, M.; Nencka, R.; Neča, J.; Kastl, T.; Palus, M.; De Clercq, E.; Růžek, D. Structure-activity relationships of nucleoside analogues for inhibition of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Yin, Z.; Duraiswamy, J.; Schul, W.; Lim, C.C.; Liu, B.; Xu, H.Y.; Qing, M.; Yip, A.; Wang, G. Inhibition of dengue virus RNA synthesis by an adenosine nucleoside. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Yin, Z.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Qing, M.; Schul, W.; Duraiswamy, J.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Goh, A.; Xu, H.Y.; Yip, A. Inhibition of dengue virus by an ester prodrug of an adenosine analog. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3255–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Yokokawa, F.; Shi, P.-Y. The search for nucleoside/nucleotide analog inhibitors of dengue virus. Antivir. Res. 2015, 122, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latour, D.R.; Jekle, A.; Javanbakht, H.; Henningsen, R.; Gee, P.; Lee, I.; Tran, P.; Ren, S.; Kutach, A.K.; Harris, S.F. Biochemical characterization of the inhibition of the dengue virus RNA polymerase by beta-d-2′-ethynyl-7-deaza-adenosine triphosphate. Antivir. Res. 2010, 87, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Schneller, S.W. 1-Deaza-5′-noraisteromycin. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucl. Acids 2004, 23, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamuy, R.; Berman, B. Topical antiviral agents for herpes simplex virus infections. Drugs Today 1998, 34, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, G.J.; Weller, S.; Pakes, G.E. A review of the pharmacokinetics of abacavir. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 47, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Bhadti, V.; Doboszewski, B.; Gu, Z.; Kosugi, Y.; Pullaiah, K.; Van Roey, P. General syntheses of 2′, 3′-dideoxynucleosides and 2′, 3′-didehydro-2′, 3′-dideoxynucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenichev, M.S.; Oslovsky, V.E.; Sun, L.; Tijsma, A.; Kurochkin, N.N.; Tararov, V.I.; Chizhov, A.O.; Neyts, J.; Pannecouque, C.; Leyssen, P. Modification of the length and structure of the linker of N6-benzyladenosine modulates its selective antiviral activity against enterovirus 71. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 111, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tararov, V.I.; Tijsma, A.; Kolyachkina, S.V.; Oslovsky, V.E.; Neyts, J.; Drenichev, M.S.; Leyssen, P.; Mikhailov, S.N. Chemical modification of the plant isoprenoid cytokinin N6-isopentenyladenosine yields a selective inhibitor of human enterovirus 71 replication. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlov, A.A.; Drenichev, M.S.; Oslovsky, V.E.; Kurochkin, N.N.; Solyev, P.N.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Palyulin, V.A.; Karganova, G.G.; Mikhailov, S.N.; Osolodkin, D.I. New tools in nucleoside toolbox of tick-borne encephalitis virus reproduction inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angusti, A.; Manfredini, S.; Durini, E.; Ciliberti, N.; Vertuani, S.; Solaroli, N.; Pricl, S.; Ferrone, M.; Fermeglia, M.; Loddo, R. Design, Synthesis and Anti Flaviviridae Activity of N6-,5′,3′-O-and 5′,2′-O-Substituted Adenine Nucleoside Analogs. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Amr, A.E.-G.E.; Sabry, N.M.; Abdulla, M.M. Synthesis, reactions, and anti-inflammatory activity of heterocyclic systems fused to a thiophene moiety using citrazinic acid as synthon. Monatsh. Chem. 2007, 138, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, M.N.; Quenelle, D.C.; Hartline, C.B.; Harden, E.A.; Jefferson, G.; Frederick, S.L.; Daily, S.L.; Whitley, R.J.; Tiwari, K.N.; Maddry, J.A. Inhibition of herpesvirus replication by 5-substituted 4′-thiopyrimidine nucleosides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5251–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Todome, Y. Inhibition of poliovirus by effect of a methylthiopyrimidine derivative. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1970, 133, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaka, T.; Tanaka, H.; Baba, M.; Hayakawa, H.; Walker, R.T.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E. A novel lead for specific anti-HIV-1 agents: 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy) methyl]-6-(phenylthio) thymine. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 2507–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Takashima, H.; Ubasawa, M.; Sekiya, K.; Nitta, I.; Baba, M.; Shigeta, S.; Walker, R.T.; De Clercq, E.; Miyasaka, T. Structure-activity relationships of 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy) methyl]-6-(phenylthio) thymine analogs: Effect of substitutions at the C-6 phenyl ring and at the C-5 position on anti-HIV-1 activity. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarini, J.; Baba, M.; De Clercq, E. Differential activities of 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy) methyl]-6-(phenylthio) thymine derivatives against different human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutant strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocková, D.; Holý, A.n.; Masojídková, M.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; De Clercq, E.; Balzarini, J. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 2, 4-diamino-5-cyano-6-[2-(phosphonomethoxy) ethoxy] pyrimidine and related compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 3197–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holý, A.; Votruba, I.; Masojídková, M.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Naesens, L.; De Clercq, E.; Balzarini, J. 6-[2-(Phosphonomethoxy) alkoxy] pyrimidines with antiviral activity. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, A.; Artico, M.; Sbardella, G.; Massa, S.; Novellino, E.; Greco, G.; Loi, A.G.; Tramontano, E.; Marongiu, M.E.; La Colla, P. 5-Alkyl-2-(alkylthio)-6-(2,6-dihalophenylmethyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-4(3H)-ones: Novel potent and selective dihydro-alkoxy-benzyl-oxopyrimidine derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, P.; Chandramohan, M.; De Clercq, E.; Witvrouw, M.; Pannecouque, C. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of 4-[(1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene) amino]-N(4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinyl)-benzene sulfonamide and its derivatives. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.F.; Flefel, E.M.; Amr, A.E.-G.E.; El-Shafy, D.N.A. Anti-HSV-1 activity and mechanism of action of some new synthesized substituted pyrimidine, thiopyrimidine and thiazolopyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, V.; Petrocchi, A.; Matassa, V.G.; Taliani, M.; Laufer, R.; De Francesco, R.; Altamura, S.; Pace, P. HCV NS5b RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors: From α, γ-diketoacids to 4,5-dihydroxypyrimidine-or 3-methyl-5-hydroxypyrimidinonecarboxylic acids. Design and synthesis. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5336–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekupec, S.; Makuc, D.; Plavec, J.; Šuman, L.; Kralj, M.; Pavelić, K.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E.; Mintas, M.; Raić-Malić, S. Novel C-6 fluorinated acyclic side chain pyrimidine derivatives: Synthesis, 1H and 13C NMR conformational studies, and antiviral and cytostatic evaluations. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, U.; Attenni, B.; Malancona, S.; Colarusso, S.; Conte, I.; Di Filippo, M.; Harper, S.; Pacini, B.; Giomini, C.; Thomas, S. 2-(2-Thienyl)-5, 6-dihydroxy-4-carboxypyrimidines as inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase: Discovery, SAR, modeling, and mutagenesis. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, F.; Esté, J.A.; Clotet-Codina, I.; Armand-Ugón, M.; Maga, G.; Crespan, E.; Cancio, R.; Mugnaini, C.; Bernardini, C.; Togninelli, A. Parallel solution-phase and microwave-assisted synthesis of new S-DABO derivatives endowed with subnanomolar anti-HIV-1 activity. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 8000–8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrozkij, M.B.; Rotili, D.; Tarantino, D.; Botta, G.; Eremiychuk, A.S.; Musmuca, I.; Ragno, R.; Samuele, A.; Zanoli, S.; Armand-Ugón, M. 5-Alkyl-6-benzyl-2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethylsulfanyl) pyrimidin-4 (3 H)-ones, a Series of Anti-HIV-1 Agents of the Dihydro-alkoxy-benzyl-oxopyrimidine Family with Peculiar Structure−Activity Relationship Profile. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4641–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, R.; Katlama, C.; Kitchen, V.; Boucher, C.A.; Tubiana, R.; McBride, M.; Ingrand, D.; Weber, J.; Hill, A.; McDade, H. Evaluation of safety and efficacy of 3TC (lamivudine) in patients with asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection: A phase I/II study. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lai, C.L. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaminza, P.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Chisari, F.V. Unbiased probing of the entire hepatitis C virus life cycle identifies clinical compounds that target multiple aspects of the infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordheim, L.P.; Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F.; Dumontet, C. Advances in the development of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues for cancer and viral diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, E.C., Jr. Plaque inhibition test for detection of specific inhibitors of DNA containing viruses. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1961, 107, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Antiviral drugs in current clinical use. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costin, D.; Dogaru, M.; Popa, A.; Cijevschi, I. Trifluridine therapy in herpetic in keratitis. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 2004, 108, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabasseda, X. Brivudine: A herpes virostatic with rapid antiviral activity and once-daily dosing. Drugs Today 2003, 39, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E.; Férir, G.; Kaptein, S.; Neyts, J. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections. Viruses 2010, 2, 1279–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foye, W.O. Foye’s Principles of Medicinal Chemistry; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya, H. Anti-HIV Nucleosides: Past, Present, and Future; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya, H.; Weinhold, K.J.; Furman, P.A.; St Clair, M.H.; Lehrman, S.N.; Gallo, R.C.; Bolognesi, D.; Barry, D.W.; Broder, S. 3′-Azido-3′-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): An antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7096–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.A.; Lewi, P.J.; Arnold, E.; Daeyaert, F.; De Jonge, M.; Heeres, J.; Koymans, L.; Vinkers, M.; Guillemont, J.; Pasquier, E. In search of a novel anti-HIV drug: Multidisciplinary coordination in the discovery of 4-[[4-[[4-[(1 E)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile (R278474, rilpivirine). J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovici, D.W.; De Corte, B.L.; Kukla, M.J.; Ye, H.; Ho, C.Y.; Lichtenstein, M.A.; Kavash, R.W.; Andries, K.; de Bethune, M.-P.; Azijn, H. Evolution of anti-HIV drug candidates. Part 3: Diarylpyrimidine (DAPY) analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Clark, A.D.; Lewi, P.J.; Heeres, J.; De Jonge, M.R.; Koymans, L.M.; Vinkers, H.M.; Daeyaert, F.; Ludovici, D.W.; Kukla, M.J. Roles of conformational and positional adaptability in structure-based design of TMC125-R165335 (etravirine) and related non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors that are highly potent and effective against wild-type and drug-resistant HIV-1 variants. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, M.F.; Beavis, A. Triorganotins inhibit the mitochondrial inner membrane anion channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17250–17256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatelain, G.; Debing, Y.; De Burghgraeve, T.; Zmurko, J.; Saudi, M.; Rozenski, J.; Neyts, J.; Van Aerschot, A. In search of flavivirus inhibitors: Evaluation of different tritylated nucleoside analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Burghgraeve, T.; Selisko, B.; Kaptein, S.; Chatelain, G.; Leyssen, P.; Debing, Y.; Jacobs, M.; Van Aerschot, A.; Canard, B.; Neyts, J. 3′,5′ Di-O-trityluridine inhibits in vitro flavivirus replication. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, C.; Serpi, M.; Slusarczyk, M.; Ferrari, V.; Pertusati, F.; Meneghesso, S.; Derudas, M.; Farleigh, L.; Zanetta, P.; Bugert, J. Anti-flavivirus Activity of Different Tritylated Pyrimidine and Purine Nucleoside Analogues. ChemistryOpen 2016, 5, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M.; Vaidya, A. Sofosbuvir: First global approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofia, M.J.; Bao, D.; Chang, W.; Du, J.; Nagarathnam, D.; Rachakonda, S.; Reddy, P.G.; Ross, B.S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.-R. Discovery of a β-d-2′-deoxy-2′-α-fluoro-2′-β-C-methyluridine nucleotide prodrug (PSI-7977) for the treatment of hepatitis C virus. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7202–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stedman, C. Sofosbuvir, a NS5B polymerase inhibitor in the treatment of hepatitis C: A review of its clinical potential. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.J.; Sharma, S.D.; Feng, J.Y.; Ray, A.S.; Smidansky, E.D.; Kireeva, M.L.; Cho, A.; Perry, J.; Vela, J.E.; Park, Y. Sensitivity of mitochondrial transcription and resistance of RNA polymerase II dependent nuclear transcription to antiviral ribonucleosides. PLoS Path. 2012, 8, e1003030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.Y.; Xu, Y.; Barauskas, O.; Perry, J.K.; Ahmadyar, S.; Stepan, G.; Yu, H.; Babusis, D.; Park, Y.; McCutcheon, K. Role of mitochondrial RNA polymerase in the toxicity of nucleotide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, L.; Nencka, R.; Huvarová, I.; Palus, M.; Joao Alves, M.; Gould, E.A.; De Clercq, E.; Růžek, D. Nucleoside inhibitors of Zika virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.-w.; Tao, S.; Bassit, L.; Whitaker, T.; McBrayer, T.R.; Ehteshami, M.; Amiralaei, S.; Pradere, U.; Cho, J.H. β-D-2′-C-methyl-2,6-diaminopurine ribonucleoside phosphoramidates are potent and selective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and are bioconverted intracellularly to bioactive 2,6-diaminopurine and guanosine 5′-triphosphate forms. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3445–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalezari, J.; Poordad, F.; Mehra, P.; Nguyen, T.; Dejesus, E.; Godofsky, E.; Patrick, G.D.; Chen, J.; Pietropaolo, K.; Zhou, X.-J. Antiviral Activity, Pharmacokinetics and Safety of IDX184 In Combination With Pegylated Interferon (Pegifn) And Ribavirin (Rbv) In Treatment-Naive Hcv Genotype 1-Infected Subjects. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, S469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan-Zhou, X.-R.; Mayes, B.A.; Rashidzadeh, H.; Gasparac, R.; Smith, S.; Bhadresa, S.; Gupta, K.; Cohen, M.L.; Bu, C.; Good, S.S. Pharmacokinetics of IDX184, a liver-targeted oral prodrug of 2′-methylguanosine-5′-monophosphate, in the monkey and formulation optimization for human exposure. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 41, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Jiang, W.-R.; Robledo, N.; Leveque, V.; Ali, S.; Lara-Jaime, T.; Masjedizadeh, M.; Smith, D.B.; Cammack, N.; Klumpp, K. Characterization of the metabolic activation of hepatitis C virus nucleoside inhibitor β-d-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methylcytidine (PSI-6130) and identification of a novel active 5′-triphosphate species. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29812–29820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.L.; Hollecker, L.; Mason, J.C.; Stuyver, L.J.; Tharnish, P.M.; Lostia, S.; McBrayer, T.R.; Schinazi, R.F.; Watanabe, K.A.; Otto, M.J. Design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of 2’-deoxy-2’-fluoro-2’-C-methylcytidine, a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5504–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Leveque, V.; Le Pogam, S.; Ma, H.; Philipp, F.; Inocencio, N.; Smith, M.; Alker, A.; Kang, H.; Najera, I. Selected replicon variants with low-level in vitro resistance to the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor PSI-6130 lack cross-resistance with R1479. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4356–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chun, B.-K.; Rachakonda, S.; Du, J.; Khan, N.; Shi, J.; Stec, W.; Cleary, D.; Ross, B.S.; Sofia, M.J. An efficient and diastereoselective synthesis of PSI-6130: A clinically efficacious inhibitor of HCV NS5B polymerase. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 6819–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Forns, X.; Hézode, C.; Lee, S.S.; Scalori, A.; Voulgari, A.; Le Pogam, S.; Nájera, I.; Thommes, J.A. Mericitabine and either Boceprevir or Telaprevir in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection and prior null response: The randomized DYNAMO 1 and DYNAMO 2 studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pockros, P.; Jensen, D.; Tsai, N.; Taylor, R.; Ramji, A.; Cooper, C.; Dickson, R.; Tice, A.; Stancic, S.; Ipe, D. First SVR data with the nucleoside analogue polymerase inhibitor mericitabine (RG7128) combined with peginterferon/ribavirin in treatment-naive HCV G1/4 patients: Interim analysis from the JUMP-C trial. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, S538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierra, C.; Benzaria, S.; Amador, A.; Moussa, A.; Mathieu, S.; Storer, R.; Gosselin, G. Nm 283, an efficient prodrug of the potent anti-HCV agent 2′-C-methylcytidine. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucl. Acids 2005, 24, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, D.; Lawitz, E.; Nguyen, T.; Younes, Z.; Santoro, J.; Gitlin, N.; McEniry, D.; Chasen, R.; Goff, J.; Knox, S. 736 Early clearance of HCV RNA with valopicitabine (NM283) plus PEG-Interferon in treatment-naïve patients with HCV-1 infection: First results from a phase IIb trial. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, S271–S272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.K.; Cooksley, G.; Dore, G.J.; Robson, R.; Shaw, D.; Berns, H.; Hill, G.; Klumpp, K.; Najera, I.; Washington, C. Robust antiviral activity of R1626, a novel nucleoside analog: A randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2008, 48, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.R.; Zeuzem, S.; Andreone, P.; Ferenci, P.; Herring, R.; Jensen, D.M.; Asselah, T.; Dieterich, D.; Foster, G.R.; Marcellin, P. Balapiravir plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD)/ribavirin in a randomized trial of hepatitis C genotype 1 patients. Ann. Hepatol. 2012, 11, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.M.; Tran, C.N.B.; Phung, L.K.; Duong, K.T.H.; Huynh, H.L.A.; Farrar, J.; Nguyen, Q.T.H.; Tran, H.T.; Nguyen, C.V.V.; Merson, L. A randomized, double-blind placebo controlled trial of balapiravir, a polymerase inhibitor, in adult dengue patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afdhal, N.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Lawitz, E.; Godofsky, E.; Chao, G.; Fielman, B.; Knox, S.; Brown, N. Enhanced Antiviral Efficacy for Valopicitabine (NM283) Plus Peg-Interferon in Hepatitis C Patients with HCV Genotype-1 Infection: Results of a Phase lla Multicenter Trial. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, S.; Cooksley, G.; Shaw, D.; Berns, H.; Brandl, M.; Fettner, S.; Hill, G.; Ipe, D.; Klumpp, K.; Mannino, M. 731 Interim results of a multiple ascending dose study of R1626, a novel nucleoside analog targeting hcv polymerase in chronic HCV patients. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, P.L.; Llinas-Brunet, M. Therapies for hepatitis C infection: Targeting the non-structural proteins of HCV. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Infect. Agents 2002, 1, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.P.; Keller, P.A. Control of hepatitis C: A medicinal chemistry perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, R.; Migliaccio, G. Challenges and successes in developing new therapies for hepatitis C. Nature 2005, 436, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondla, R.; Coats, S.J.; McBrayer, T.R.; Grier, J.; Johns, M.; Tharnish, P.M.; Whitaker, T.; Zhou, L.; Schinazi, R.F. Anti-hepatitis C virus activity of novel β-D-2′-C-methyl-4′-azido pyrimidine nucleoside phosphoramidate prodrugs. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2009, 20, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Kalayanov, G.; Winqvist, A.; Pinho, P.; Sund, C.; Zhou, X.-X.; Wähling, H.; Belfrage, A.-K.; Pelcman, M.; Agback, T. Discovery of 4′-azido-2′-deoxy-2′-C-methyl cytidine and prodrugs thereof: A potent inhibitor of Hepatitis C virus replication. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3265–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, L.; Kondo, H.; Zouharova, D.; Hirano, M.; Valdés, J.J.; Muto, M.; Kastl, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Haviernik, J.; Igarashi, M. Escape of tick-borne flavivirus from 2′-C-methylated nucleoside antivirals is mediated by a single conservative mutation in NS5 that has a dramatic effect on viral fitness. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01028-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julander, J.G.; Jha, A.K.; Choi, J.-A.; Jung, K.-H.; Smee, D.F.; Morrey, J.D.; Chu, C.K. Efficacy of 2′-C-methylcytidine against yellow fever virus in cell culture and in a hamster model. Antivir. Res. 2010, 86, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toots, M.; Yoon, J.-J.; Cox, R.M.; Hart, M.; Sticher, Z.M.; Makhsous, N.; Plesker, R.; Barrena, A.H.; Reddy, P.G.; Mitchell, D.G. Characterization of orally efficacious influenza drug with high resistance barrier in ferrets and human airway epithelia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, G.; Maeda, K.; Umezawa, H.; Iitaka, Y. The structural studies of formycin and formycin B. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966, 7, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, J.G.; Edgar, A.R.; Hutchison, R.J.; Stobie, A.; Wightman, R.H. A new synthesis of formycin via nitropyrazole derivatives. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1980, 5, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanko, K.; Eggermont, K.; Patel, A.; Kaptein, S.; Delang, L.; Verfaillie, C.M.; Neyts, J. Replication of the Zika virus in different iPSC-derived neuronal cells and implications to assess efficacy of antivirals. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hercik, K.; Brynda, J.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E. Structural basis of Zika virus methyltransferase inhibition by sinefungin. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukhan, D.; Leroy, F.; Peyronnet, J.; Bosc, E.; Chaves, D.; Durka, M.; Storer, R.; La Colla, P.; Seela, F.; Gosselin, G. Synthesis of 5-aza-7-deazaguanine nucleoside derivatives as potential anti-flavivirus agents. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucl. Acids 2005, 24, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.-L.; Schul, W.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Gu, F.; Duraiswamy, J.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Niyomrattanakit, P.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Goh, A. An adenosine nucleoside inhibitor of dengue virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20435–20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-Q.; Zhang, N.-N.; Li, C.-F.; Tian, M.; Hao, J.-N.; Xie, X.-P.; Shi, P.-Y.; Qin, C.-F. Adenosine Analog NITD008 Is a Potent Inhibitor of Zika Virus; Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; p. ofw175. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, M.K.; Shi, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Flint, M.; Spiropoulou, C.F. In vitro antiviral activity of adenosine analog NITD008 against tick-borne flaviviruses. Antivir. Res. 2016, 130, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.K.; Wells, J.; Panchal, R.G.; Stuthman, K.S.; Garza, N.L.; Van Tongeren, S.A.; Dong, L.; Retterer, C.J.; Eaton, B.P.; Pegoraro, G. Protection against filovirus diseases by a novel broad-spectrum nucleoside analogue BCX4430. Nature 2014, 508, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Kotian, P.; Warren, T.; Panchal, R.; Bavari, S.; Julander, J.; Dobo, S.; Rose, A.; El-Kattan, Y.; Taubenheim, B. BCX4430–a broad-spectrum antiviral adenosine nucleoside analog under development for the treatment of Ebola virus disease. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.U. Ebola hemorrhagic fever-recent outbreak. Int. J. Biol. Med. Res. 2015, 6, 4916–4919. [Google Scholar]
- Eyer, L.; Zouharová, D.; Širmarová, J.; Fojtíková, M.; Štefánik, M.; Haviernik, J.; Nencka, R.; De Clercq, E.; Růžek, D. Antiviral activity of the adenosine analogue BCX4430 against West Nile virus and tick-borne flaviviruses. Antivir. Res. 2017, 142, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julander, J.G.; Siddharthan, V.; Evans, J.; Taylor, R.; Tolbert, K.; Apuli, C.; Stewart, J.; Collins, P.; Gebre, M.; Neilson, S. Efficacy of the broad-spectrum antiviral compound BCX4430 against Zika virus in cell culture and in a mouse model. Antivir. Res. 2017, 137, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Smidansky, E.D.; Oh, H.S.; Takhampunya, R.; Padmanabhan, R.; Cameron, C.E.; Peterson, B.R. Synthesis of a 6-methyl-7-deaza analogue of adenosine that potently inhibits replication of polio and dengue viruses. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7958–7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrey, J.D.; Smee, D.F.; Sidwell, R.W.; Tseng, C. Identification of active antiviral compounds against a New York isolate of West Nile virus. Antivir. Res. 2002, 55, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, M.; McMullan, L.K.; Dodd, K.A.; Bird, B.H.; Khristova, M.L.; Nichol, S.T.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Inhibitors of the tick-borne, hemorrhagic fever-associated flaviviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3206–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, L.; Valdés, J.J.; Gil, V.A.; Nencka, R.; Hřebabecký, H.; Šála, M.; Salát, J.; Černý, J.; Palus, M.; De Clercq, E. Nucleoside inhibitors of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5483–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, A.A.; Chistov, A.A.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Ustinov, A.V.; Korshun, V.A.; Karganova, G.G.; Osolodkin, D.I. Rigid amphipathic nucleosides suppress reproduction of the tick-borne encephalitis virus. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinov, V.; Egorov, I.; Chupakhin, O.; Belanov, E.; Bormotov, N.; Serova, O. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 1, 2, 4-triazine derivatives. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 45, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, N.; Balboni, G.; Congiu, C.; Onnis, V.; Demizu, Y.; Misawa, T.; Kurihara, M.; Kato, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Toyama, M. Design, synthesis, and anti-HIV-1 activity of 1-substituted 3-(3,5-dimethylbenzyl) triazine derivatives. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2015, 24, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mibu, N.; Yokomizo, K.; Koga, A.; Honda, M.; Mizokami, K.; Fujii, H.; Ota, N.; Yuzuriha, A.; Ishimaru, K.; Zhou, J. Synthesis and antiviral activities of some 2,4,6-trisubstituted 1,3,5-triazines. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krečmerová, M.; Holý, A.; Pískala, A.; Masojídková, M.; Andrei, G.; Naesens, L.; Neyts, J.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E.; Snoeck, R. Antiviral activity of triazine analogues of 1-(S)-[3-hydroxy-2-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]cytosine(cidofovir) and related compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutterer, C.; Hamilton, S.; Steingruber, M.; Zeitträger, I.; Bahsi, H.; Thuma, N.; Naing, Z.; Örfi, Z.; Örfi, L.; Socher, E. The chemical class of quinazoline compounds provides a core structure for the design of anticytomegaloviral kinase inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2016, 134, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakaran, M.; Selvam, P.; DeClercq, E.; Sridhar, S.K. Synthesis, antiviral and cytotoxic activity of 6-bromo-2,3-disubstituted-4(3H)-quinazolinones. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleiss, M.; Eickhoff, J.; Auerochs, S.; Leis, M.; Abele, S.; Rechter, S.; Choi, Y.; Anderson, J.; Scott, G.; Rawlinson, W. Protein kinase inhibitors of the quinazoline class exert anti-cytomegaloviral activity in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2008, 79, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, P.; Vijayalakshimi, P.; Smee, D.F.; Gowen, B.B.; Julander, J.G.; Day, C.W.; Barnard, D.L. Novel 3-sulphonamido-quinazolin-4 (3 H)-One Derivatives: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiviral Activities against Respiratory and Biodefense Viruses. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2007, 18, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, P.; Babu, K.; Padamraj, R.; Persoons, L.; de Clercq, E. Synthesis, antiviral and cytotoxic activities of some novel 2-phenyl-3-disubstituted quinazolin-4(3H)-ones. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 2, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.S.; Ganguly, S.; Veerasamy, R.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis, antiviral activity and cytotoxicity evaluation of Schiff bases of some 2-phenyl quinazoline-4(3) H-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5474–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, F.E.; Guryev, A.A.; Fröhlich, T.; Hampel, F.; Kahnt, A.; Hutterer, C.; Steingruber, M.; Bahsi, H.; von Bojničić-Kninski, C.; Mattes, D.S. Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, B.; Tong, X.-K.; Tang, W.; Li, D.-W.; He, P.-L.; Garcia, J.-M.; Zeng, L.-M.; Gao, A.-H.; Yang, L.; Li, J. Discovery and optimization of 2, 4-diaminoquinazoline derivatives as a new class of potent dengue virus inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3135–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, B.; Naesens, L.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. First discovery of novel 3-hydroxy-quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones as specific anti-vaccinia and adenovirus agents via ‘privileged scaffold’refining approach. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5182–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Cen, S.; Wang, Y. Design, synthesis and in vitro anti-influenza A virus evaluation of novel quinazoline derivatives containing S-acetamide and NH-acetamide moieties at C-4. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Hu, D.; Li, P.; Xie, D.; Gan, X. Synthesis, antiviral bioactivity of novel 4-thioquinazoline derivatives containing chalcone moiety. Molecules 2015, 20, 11861–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Ganguly, S.; Veerasamy, R.; Jan, B. Synthesis, antiviral and cytotoxic investigation of 2-phenyl-3-substituted quinazolin-4 (3H)-ones. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desai, D.; Lauver, M.; Ostman, A.; Cruz, L.; Ferguson, K.; Jin, G.; Roper, B.; Brosius, D.; Lukacher, A.; Amin, S. Inhibition of diverse opportunistic viruses by structurally optimized retrograde trafficking inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi, M.; Zmurko, J.; Kaptein, S.; Rozenski, J.; Gadakh, B.; Chaltin, P.; Marchand, A.; Neyts, J.; Van Aerschot, A. Synthetic strategy and antiviral evaluation of diamide containing heterocycles targeting dengue and yellow fever virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shah, U.; Jayne, C.; Chackalamannil, S.; Velázquez, F.; Guo, Z.; Buevich, A.; Howe, J.A.; Chase, R.; Soriano, A.; Agrawal, S. Novel quinoline-based P2–P4 macrocyclic derivatives as pan-genotypic HCV NS3/4a protease inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schiering, N.; D’Arcy, A.; Villard, F.; Simić, O.; Kamke, M.; Monnet, G.; Hassiepen, U.; Svergun, D.I.; Pulfer, R.; Eder, J. A macrocyclic HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor interacts with protease and helicase residues in the complex with its full-length target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21052–21056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilot-Matias, T.; Tripathi, R.; Cohen, D.; Gaultier, I.; Dekhtyar, T.; Lu, L.; Reisch, T.; Irvin, M.; Hopkins, T.; Pithawalla, R. In vitro and in vivo antiviral activity and resistance profile of the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor ABT-450. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revill, P.; Serradell, N.; Bolos, J.; Rosa, E. Telaprevir. Drugs Future 2007, 32, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranovich, T.; Wong, S.-S.; Armstrong, J.; Marjuki, H.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. T-705 (favipiravir) induces lethal mutagenesis in influenza A H1N1 viruses in vitro. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrey, J.D.; Taro, B.S.; Siddharthan, V.; Wang, H.; Smee, D.F.; Christensen, A.J.; Furuta, Y. Efficacy of orally administered T-705 pyrazine analog on lethal West Nile virus infection in rodents. Antivir. Res. 2008, 80, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julander, J.; Shafer, K.; Smee, D.; Morrey, J.; Furuta, Y. Efficacy of T-1106 or T-705, alone or in combination with ribavirin, in the treatment of hamsters infected with yellow fever virus. Antivir. Res. 2008, 2, A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeres, J.; De Jonge, M.R.; Koymans, L.M.; Daeyaert, F.F.; Vinkers, M.; Van Aken, K.J.; Arnold, E.; Das, K.; Kilonda, A.; Hoornaert, G.J. Design, synthesis, and SAR of a novel pyrazinone series with non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, L.; Porro, M.T.; Gomez, N.; Salvatori, M.; Turk, G.; Estrin, D.; Moglioni, A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of quinoxaline compounds as anti-HIV agents targeting reverse transcriptase enzyme. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 188, 111987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, A.; Sanna, G.; Briguglio, I.; Madeddu, S.; Vitale, G.; Piras, S.; Corona, P.; Peana, A.T.; Laurini, E.; Fermeglia, M. Quinoxaline derivatives as new inhibitors of coxsackievirus B5. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 145, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmenberg, J.; Wahren, B.; Bergman, J.; Akerfeldt, S.; Lundblad, L. Antiherpesvirus activity and mechanism of action of indolo-(2, 3-b) quinoxaline and analogs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Kingi, N.; Bergman, J. Interactions of antiviral indolo [2, 3-b] quinoxaline derivatives with DNA. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7744–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, P.; Lakra, D.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis, antiviral and cytotoxicity studies of novel N-substituted indophenazine derivatives. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 74, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H. Progress of bis (heteroaryl) piperazines (BHAPs) as non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Yogeeswari, P.; Bhat, P.; Thomas, A.; Srividya, M.; Sriram, D. Novel isatinyl thiosemicarbazones derivatives as potential molecule to combat HIV-TB co-infection. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Kadow, J.F.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Gao, Q.; Wu, D.; Parker, D.D.; Yang, Z.; Zadjura, L.; Robinson, B.A. Inhibitors of HIV-1 attachment. Part 4: A study of the effect of piperazine substitution patterns on antiviral potency in the context of indole-based derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5140–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabarrini, O.; Stevens, M.; Cecchetti, V.; Sabatini, S.; Dell’Uomo, M.; Manfroni, G.; Palumbo, M.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Fravolini, A. Structure modifications of 6-aminoquinolones with potent anti-HIV activity. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5567–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kempf, D.J.; Sham, H.L.; Green, B.E.; Molla, A.; Korneyeva, M.; Vasavanonda, S.; Wideburg, N.E.; Saldivar, A.; Marsh, K.C. Potent piperazine hydroxyethylamine HIV protease inhibitors containing novel P3 ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 3531–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, M.; Kashiwase, H.; Katsube, T.; Kimura, T.; Komai, T.; Momota, K.; Ohmine, T.; Nishigaki, T.; Kimura, S.; Shimada, K. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of arylpiperazinyl fluoroquinolones: A new class of anti-HIV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 3063–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, D.; He, G.; Mandadapu, S.R.; Aravapalli, S.; Kim, Y.; Chang, K.-O.; Groutas, W.C. Inhibition of noroviruses by piperazine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, J.; Gao, D.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Gong, Z.; Sun, T.; Li, S. Pharmacophore-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel chloro-pyridazine piperazines as human rhinovirus (HRV-3) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1057–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wan, J.; Lin, M.-I.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Tu, Z.; Cheng, Y.-S.E. Design, synthesis, and in vitro biological evaluation of 1 H-1, 2, 3-triazole-4-carboxamide derivatives as new anti-influenza A agents targeting virus nucleoprotein. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.H.; Holsinger, L.J.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell 1992, 69, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, C.S.; Shuck, K.; Lear, J.D.; Dieckmann, G.R.; DeGrado, W.F.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H. Cu (II) inhibition of the proton translocation machinery of the influenza A virus M2 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5474–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughlin, C. Antiviral agents, RNA viruses other than HIV. Burg. Med. Chem. Drug Disc. 1997, 5, 565–576. [Google Scholar]
- Stylianakis, I.; Kolocouris, A.; Kolocouris, N.; Fytas, G.; Foscolos, G.B.; Padalko, E.; Neyts, J.; De Clercq, E. Spiro [pyrrolidine-2, 2′-adamantanes]: Synthesis, anti-influenza virus activity and conformational properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoidis, G.; Kolocouris, N.; Foscolos, G.B.; Kolocouris, A.; Fytas, G.; Karayannis, P.; Padalko, E.; Neyts, J.; De Clercq, E. Are the 2-isomers of the drug rimantadine active anti-influenza A agents? Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2003, 14, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, L.; Dong, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Cen, S.; Wang, Y. Design and evaluation of novel piperidine HIV-1 protease inhibitors with potency against DRV-resistant variants. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 220, 113450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Xian, T.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Luo, M. Discovery and SAR study of piperidine-based derivatives as novel influenza virus inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8048–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononova, A.; Sokolova, A.; Cheresiz, S.; Yarovaya, O.; Nikitina, R.; Chepurnov, A.; Pokrovsky, A.; Salakhutdinov, N. N-Heterocyclic borneol derivatives as inhibitors of Marburg virus glycoprotein-mediated VSIV pseudotype entry. MedChemComm 2017, 8, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seck, R.; Gassama, A.; Cojean, S.; Cavé, C. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of 1, 4-disubstituted piperidine derivatives. Molecules 2020, 25, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ghosh, A.K.; Miller, H.; Knox, K.; Kundu, M.; Peterson, F.; Meyers, D.J.; Arav-Boger, R. Inhibition of Human Coronaviruses by Piperidine-4-Carboxamides. Infect. Dis. Diagn. Treat. 2022, 6, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, E.; Abele, R.; Lukevics, E. Pyridine oximes: Synthesis, reactions, and biological activity. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2003, 39, 825–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gualda, B.; Pu, S.-Y.; Froeyen, M.; Herdewijn, P.; Einav, S.; De Jonghe, S. Structure-activity relationship study of the pyridine moiety of isothiazolo [4,3-b] pyridines as antiviral agents targeting cyclin G-associated kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hawash, S.A.; Abdel Wahab, A.E.; El-Demellawy, M.A. Cyanoacetic acid hydrazones of 3-(and 4-)Acetylpyridine and some derived ring systems as potential antitumor and anti-HCV agents. Int. J. Pharm. Med. Chem. 2006, 339, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrabel, M.; Hocek, M.; Havran, L.; Fojta, M.; Votruba, I.; Klepetarova, B.; Pohl, R.; Rulisek, L.; Zendlova, L.; Hobza, P. Purines bearing phenanthroline or bipyridine ligands and their RuII complexes in position 8 as model compounds for electrochemical DNA labeling-: Synthesis, crystal structure, electrochemistry, quantum chemical calculations, cytostatic and antiviral activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 1752–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardino, A.M.R.; da Silva Pinheiro, L.C.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Loureiro, N.I.; Castro, H.C.; Lanfredi-Rangel, A.; Sabatini-Lopes, J.; Borges, J.C.; Carvalho, J.M.; Romeiro, G.A. Design, synthesis, SAR, and biological evaluation of new 4-(phenylamino) thieno [2, 3-b] pyridine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5765–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attla, A.M.; Mansour, H.A.; Almehdi, A.A.; Abbasi, M.M. Synthesis of some pyridine ribosides and their biological activity. Nucleosides Nucleotides 1999, 18, 2301–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.S.; Sakr, S.I.; El-Senousy, W.M.; Madkour, H.M. Synthesis, antibacterial, and antiviral evaluation of new heterocycles containing the pyridine moiety. Arch. Pharm. 2013, 346, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chezal, J.-M.; Paeshuyse, J.; Gaumet, V.; Canitrot, D.; Maisonial, A.; Lartigue, C.; Gueiffier, A.; Moreau, E.; Teulade, J.-C.; Chavignon, O. Synthesis and antiviral activity of an imidazo [1,2-a]pyrrolo[2,3-c] pyridine series against the bovine viral diarrhea virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2044–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, S. Safety of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Focus on molecular structure. Infect. Urol. 2000, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzucco, M.B.; Talarico, L.B.; Vatansever, S.; Carro, A.C.; Fascio, M.L.; D’Accorso, N.B.; García, C.C.; Damonte, E.B. Antiviral activity of an N-allyl acridone against dengue virus. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Lin, C.-K.; Chen, Y.-L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Wu, H.-N.; Tseng, C.-K.; Lee, J.-C. Synthesis, antiproliferative and anti-dengue virus evaluations of 2-aroyl-3-arylquinoline derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 79, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yin, R.; Zhang, M.; Yu, R.; Hao, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, T. Boronic acid modifications enhance the anti-influenza A virus activities of novel quindoline derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2840–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschman, S.Z.; Garfinkel, E. Inhibition of hepatitis B DNA polymerase by intercalating agents. Nature 1978, 271, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, A.; Boelaert, J.R.; Cassone, A.; Majori, G.; Cauda, R. Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: An old drug against today’s diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, N.E. Examination of potential inhibitors of hepatitis A virus uncoating. Intervirology 1998, 41, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-C.; Tseng, C.-K.; Lin, C.-K.; Tseng, C.-H. Discovery of novel diarylpyrazolylquinoline derivatives as potent anti-dengue virus agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overacker, R.D.; Banerjee, S.; Neuhaus, G.F.; Sephton, S.M.; Herrmann, A.; Strother, J.A.; Brack-Werner, R.; Blakemore, P.R.; Loesgen, S. Biological evaluation of molecules of the azaBINOL class as antiviral agents: Inhibition of HIV-1 RNase H activity by 7-isopropoxy-8-(naphth-1-yl) quinoline. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Naik, D.; Jariwala, N.; Bhadane, D.; Kumar, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Bhutani, K.K.; Singh, I.P. Synthesis of C-2 and C-3 substituted quinolines and their evaluation as anti-HIV-1 agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobori, H.; Uemura, K.; Toba, S.; Sanaki, T.; Shishido, T.; Hall, W.W.; Orba, Y.; Sawa, H.; Sato, A. Identification of quinolone derivatives as effective anti-Dengue virus agents. Antivir. Res. 2020, 184, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Lima, G.; Moraes, A.M.; Araújo, A.d.S.; da Silva, E.T.; de Freitas, C.S.; Vieira, Y.R.; Marttorelli, A.; Neto, J.C.; Bozza, P.T.; de Souza, M.V. 2,8-bis (trifluoromethyl) quinoline analogs show improved anti-Zika virus activity, compared to mefloquine. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamroukh, A.H.; Zaki, M.E.; Morsy, E.M.; Abdel-Motti, F.M.; Abdel-Megeid, F.M. Synthesis of Pyrazolo[4′,3′:5,6] pyrano [2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives for Antiviral Evaluation. Arch. Pharm. J. Pharm. Med. Chem. 2007, 340, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, M.E.; Avolio, S.; Pompei, M.; Pesci, S.; Monteagudo, E.; Pucci, V.; Giuliano, C.; Fiore, F.; Rowley, M.; Summa, V. Synthesis and antiviral properties of novel 7-heterocyclic substituted 7-deaza-adenine nucleoside inhibitors of Hepatitis C NS5B polymerase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4801–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Bai, F.; Liu, N.; Liang, X.; Zhan, P.; Ma, C.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X. Design, synthesis and evaluation of pyrazole derivatives as non-nucleoside hepatitis B virus inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andries, K.; Moeremans, M.; Gevers, T.; Willebrords, R.; Sommen, C.; Lacrampe, J.; Janssens, F.; Wyde, P.R. Substituted benzimidazoles with nanomolar activity against respiratory syncytial virus. Antivir. Res. 2003, 60, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavurala, S.; Vaarla, K.; Kesharwani, R.; Naesens, L.; Liekens, S.; Vedula, R.R. Bis coumarinyl bis triazolothiadiazinyl ethane derivatives: Synthesis, antiviral activity evaluation, and molecular docking studies. Synth. Commun. 2018, 48, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. 1H-1,2,3-Triazole-tethered isatin-7-chloroquinoline and 3-hydroxy-indole-7-chloroquinoline conjugates: Synthesis and antimalarial evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, D.; Bal, T.R.; Yogeeswari, P. Aminopyrimidinimino isatin analogues: Design of novel non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors with broad-spectrum chemotherapeutic properties. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 8, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.V.; Kumari, P.; Rajani, D.P.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Chikhalia, K.H. Antimicrobial, anti-TB, anticancer and anti-HIV evaluation of new s-triazine-based heterocycles. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.V.; Kumari, P.; Rajani, D.P.; Chikhalia, K.H. A new class of 2-(4-cyanophenyl amino)-4-(6-bromo-4-quinolinyloxy)-6-piperazinyl (piperidinyl)-1, 3, 5-triazine analogues with antimicrobial/antimycobacterial activity. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.V.; Kumari, P.; Rajani, D.P.; Chikhalia, K.H. Synthesis and Antimycobacterial Activity of Various 1-(8-Quinolinyloxy)-3-piperazinyl (piperidinyl)-5-(4-cyano-3-trifluoromethylphenylamino)-s-triazines. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, R.V.; Kumari, P.; Rajani, D.P.; Chikhalia, K.H. Synthesis and studies of novel 2-(4-cyano-3-trifluoromethylphenyl amino)-4-(quinoline-4-yloxy)-6-(piperazinyl/piperidinyl)-s-triazines as potential antimicrobial, antimycobacterial and anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4354–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.L.; Chen, Y.-L.; Xu, H.Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Yokokawa, F.; Shi, P.-Y. Synergistic suppression of dengue virus replication using a combination of nucleoside analogs and nucleoside synthesis inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, J.-H.; Shia, K.-S.; Hsu, T.-A.; Tai, C.-L.; Lee, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-S.; Tseng, S.-N.; Shih, S.-R. Design, synthesis, and structure–activity relationships of pyrazolo [3,4-d] pyrimidines: A novel class of potent enterovirus inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2519–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.K.; Jordan, R.; Arvey, A.; Sudhamsu, J.; Shrivastava-Ranjan, P.; Hotard, A.L.; Flint, M.; McMullan, L.K.; Siegel, D.; Clarke, M.O. GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghigo, D.; Aldieri, E.; Todde, R.; Costamagna, C.; Garbarino, G.; Pescarmona, G.; Bosia, A. Chloroquine stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in murine, porcine, and human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiza, R.; Freitas, A.C.; Nanayakkara, D.; McChesney, J.D.; Walker, L. New Chloroquine Analogues as Antiviral Agents. Acta Farm. Bonaer. 2006, 25, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, B.; O’Meara, J.A.; Bordeleau, J.e.; Garneau, M.; Godbout, C.; Gorys, V.; Leblanc, M.l.; Villemure, E.; White, P.W.; Llinàs-Brunet, M. Discovery of hepatitis C virus NS3-4A protease inhibitors with improved barrier to resistance and favorable liver distribution. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massari, S.; Daelemans, D.; Barreca, M.L.; Knezevich, A.; Sabatini, S.; Cecchetti, V.; Marcello, A.; Pannecouque, C.; Tabarrini, O. A 1,8-naphthyridone derivative targets the HIV-1 Tat-mediated transcription and potently inhibits the HIV-1 replication. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.F.; Turner, E.M.; Gudmundsson, K.S.; Jenkinson, S.; Spaltenstein, A.; Thomson, M.; Wheelan, P. Novel N-substituted benzimidazole CXCR4 antagonists as potential anti-HIV agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, A.; Saunders, O.L.; Butler, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Vela, J.E.; Feng, J.Y.; Ray, A.S.; Kim, C.U. Synthesis and antiviral activity of a series of 1′-substituted 4-aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-nucleosides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2705–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, A.; Saxena, V. Synthesis and antiviral activity of some new 6-aryl-7-arylazo-4-phenyl-2H-thiazolo (3,2-alpha)-1,3,5-triazine-2-thiones. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 1985, 47, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
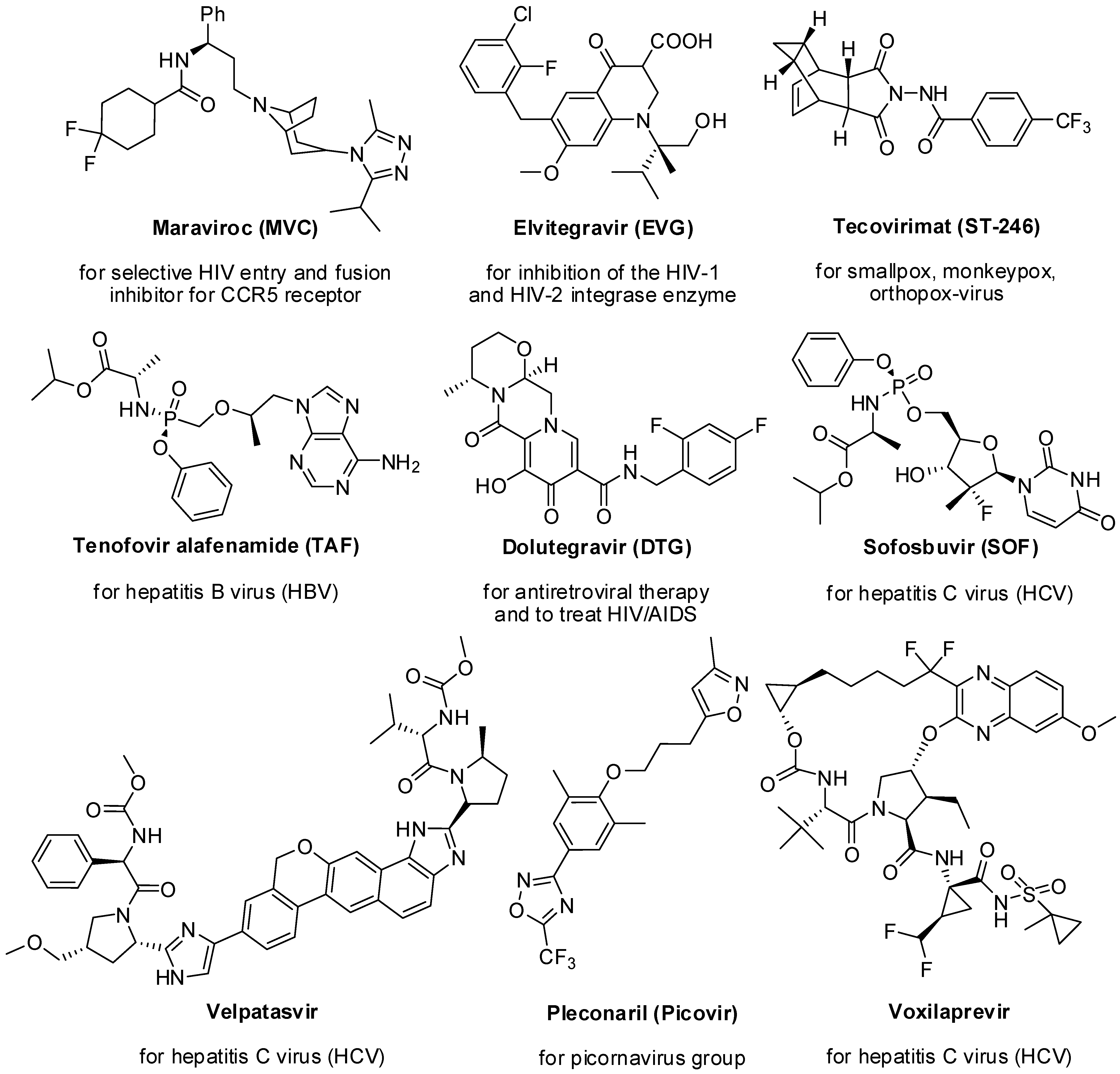
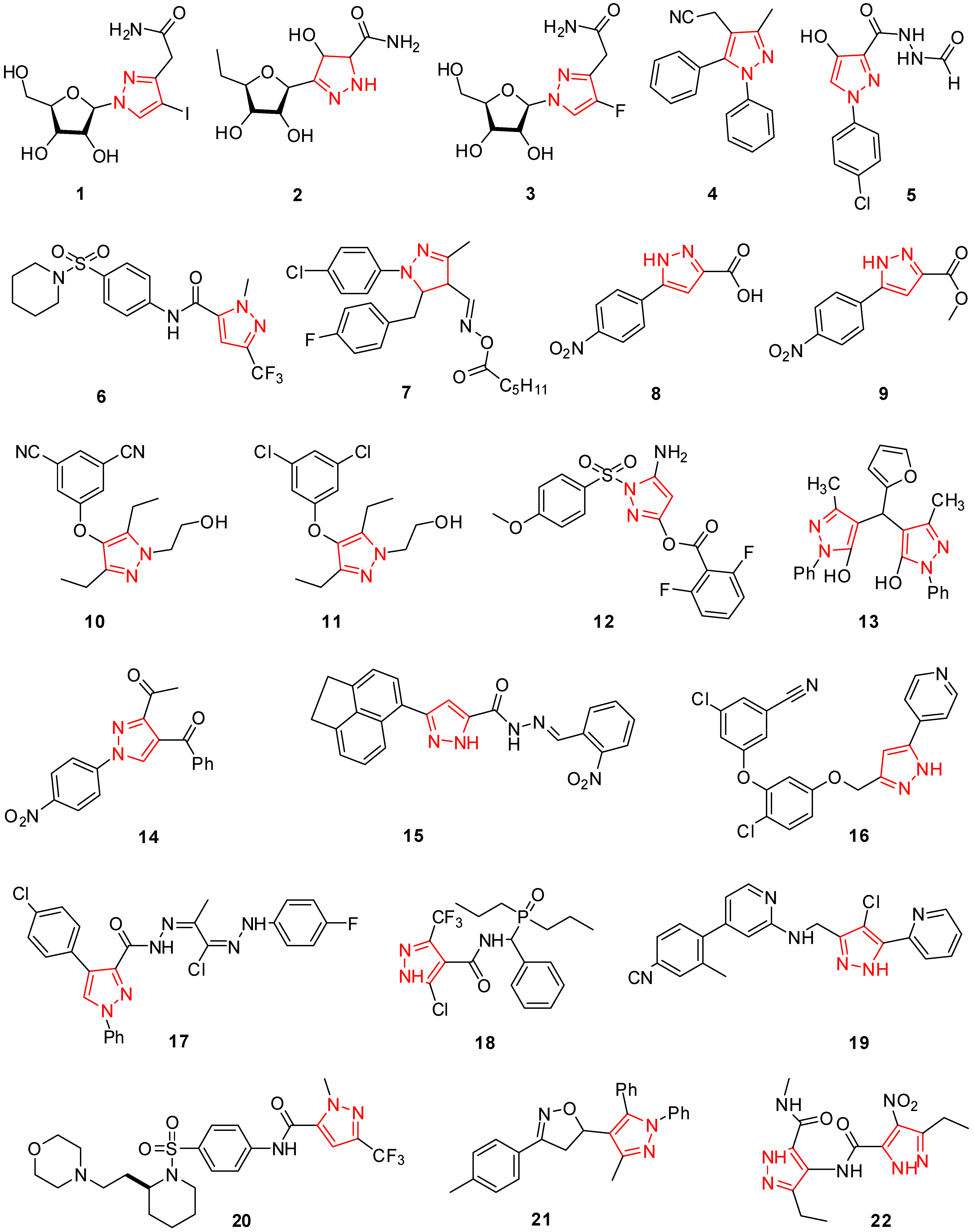
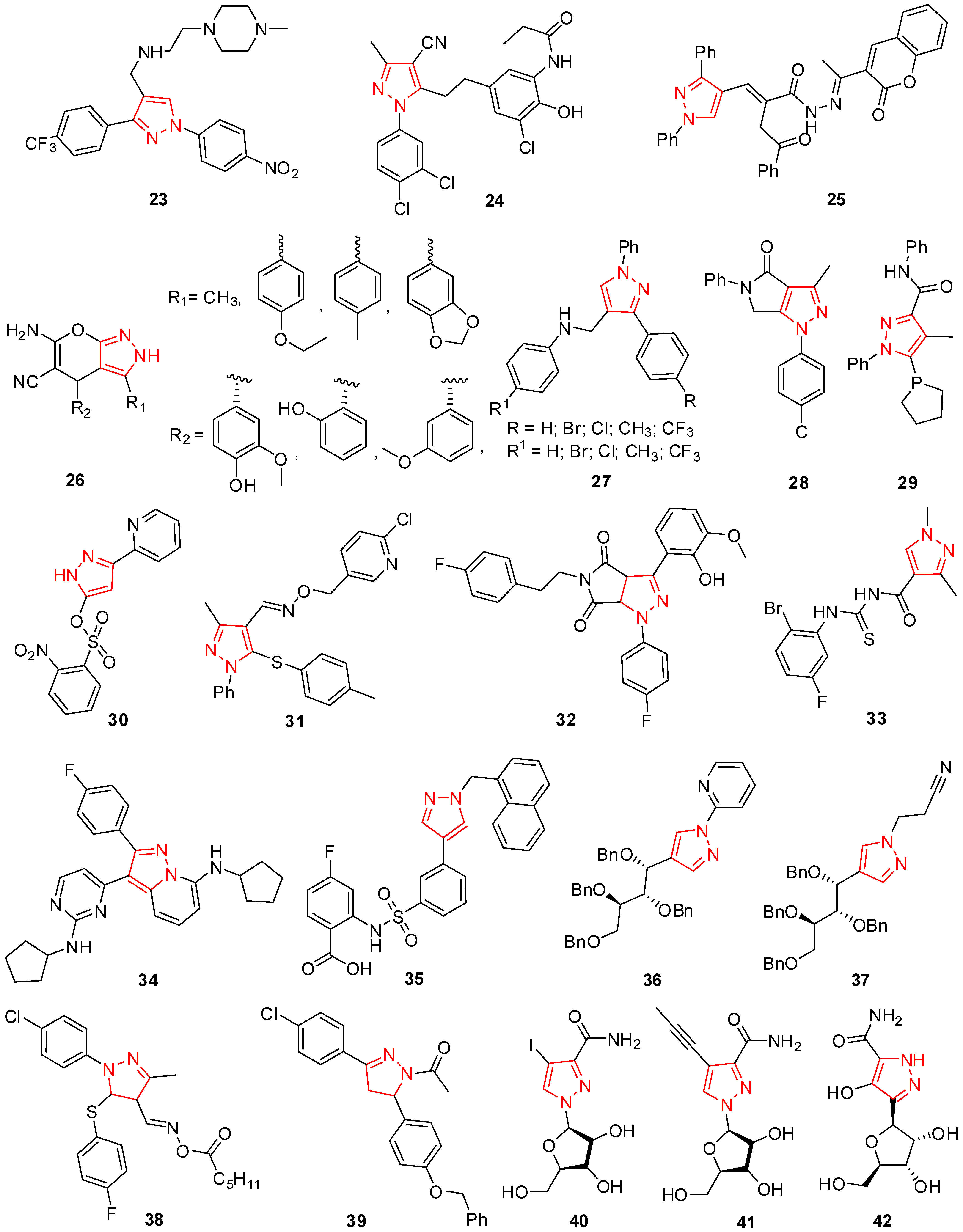

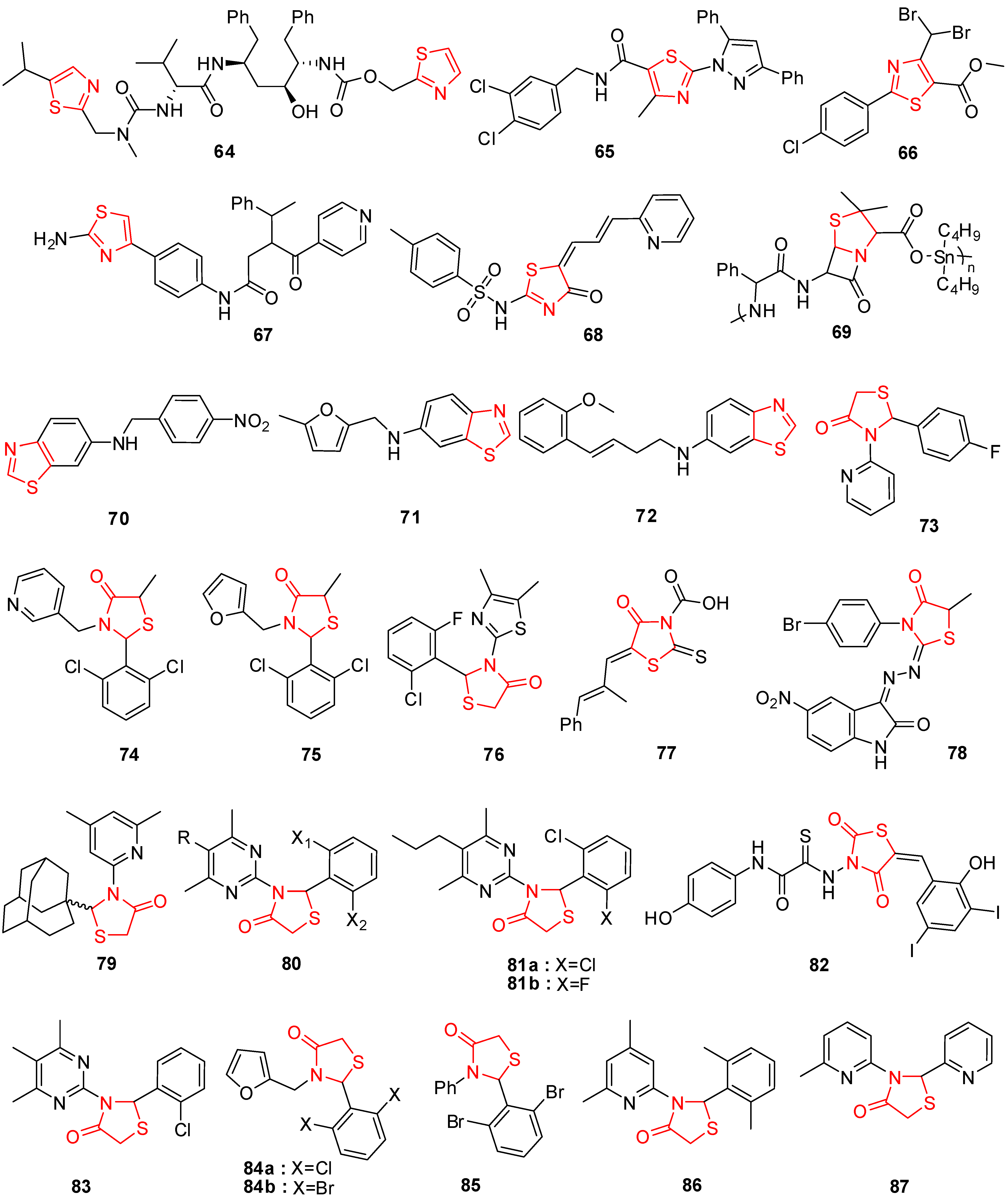
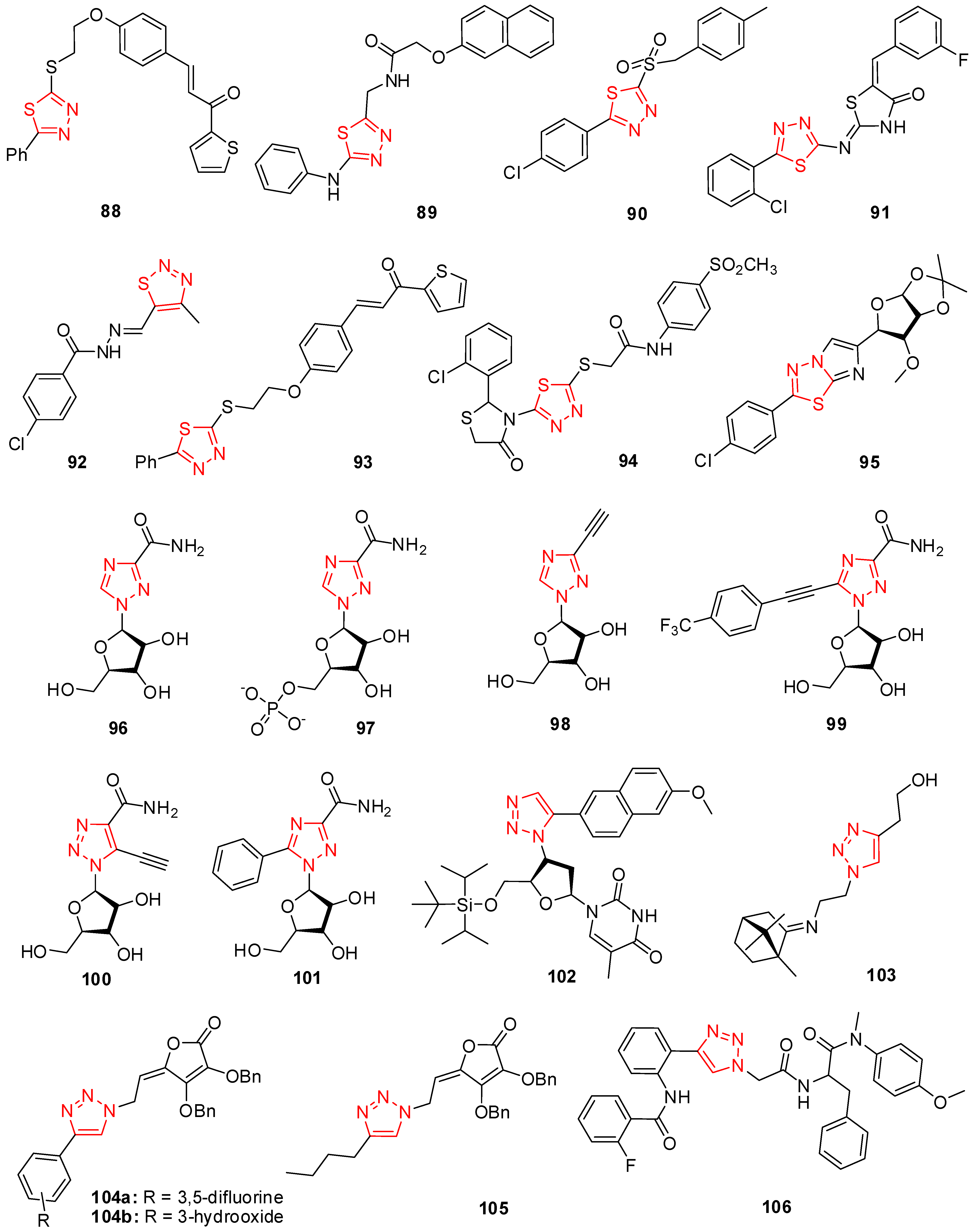




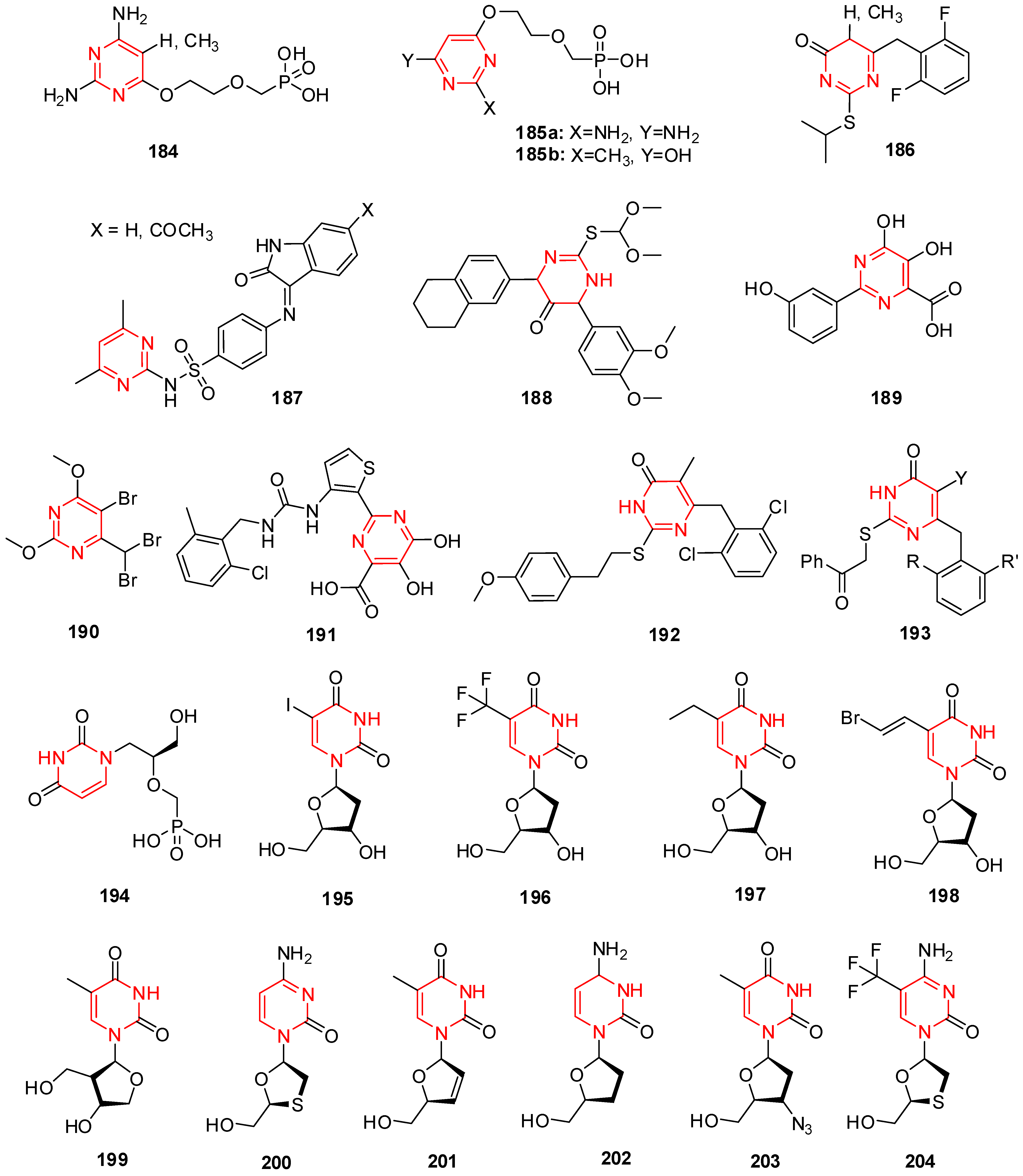

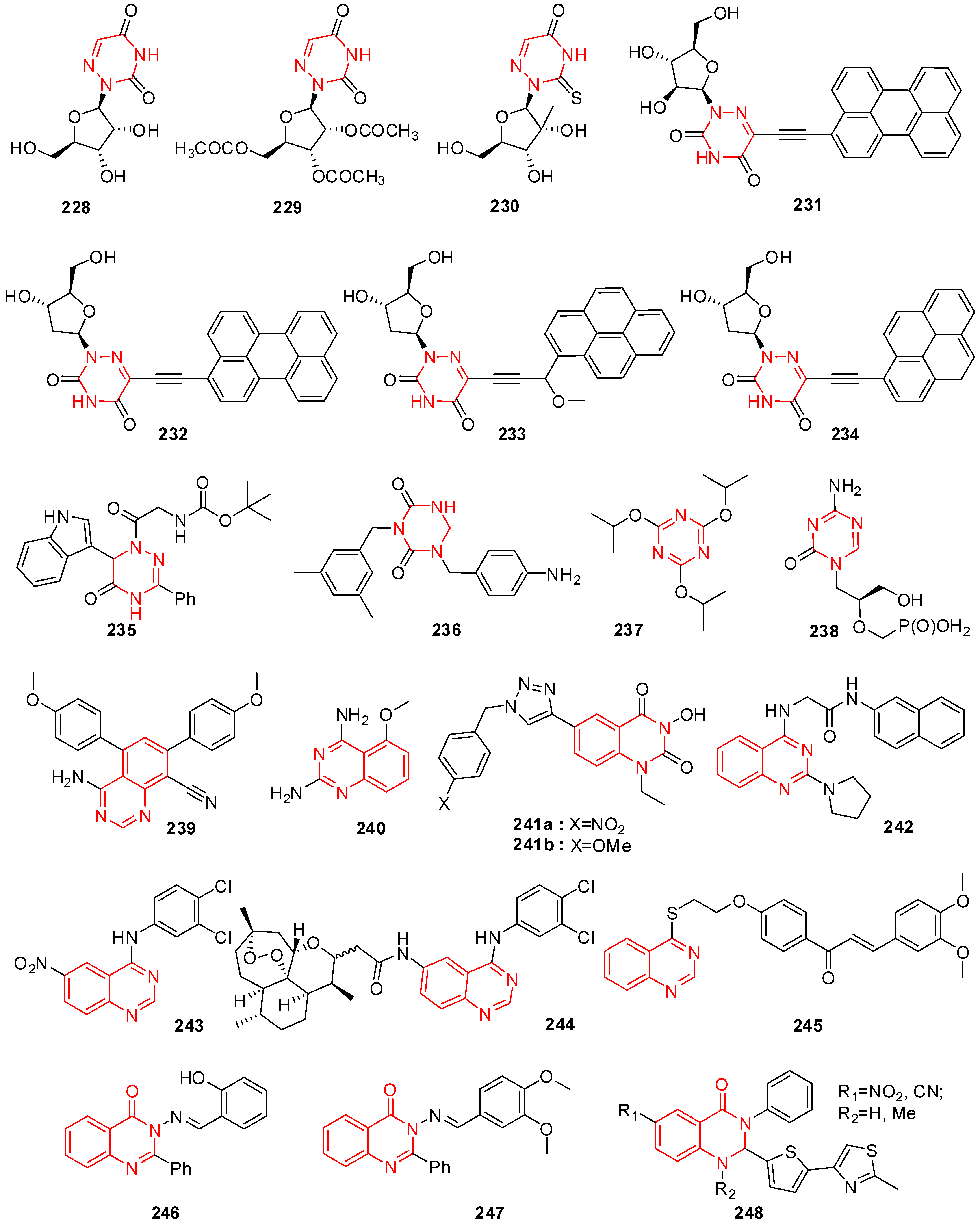
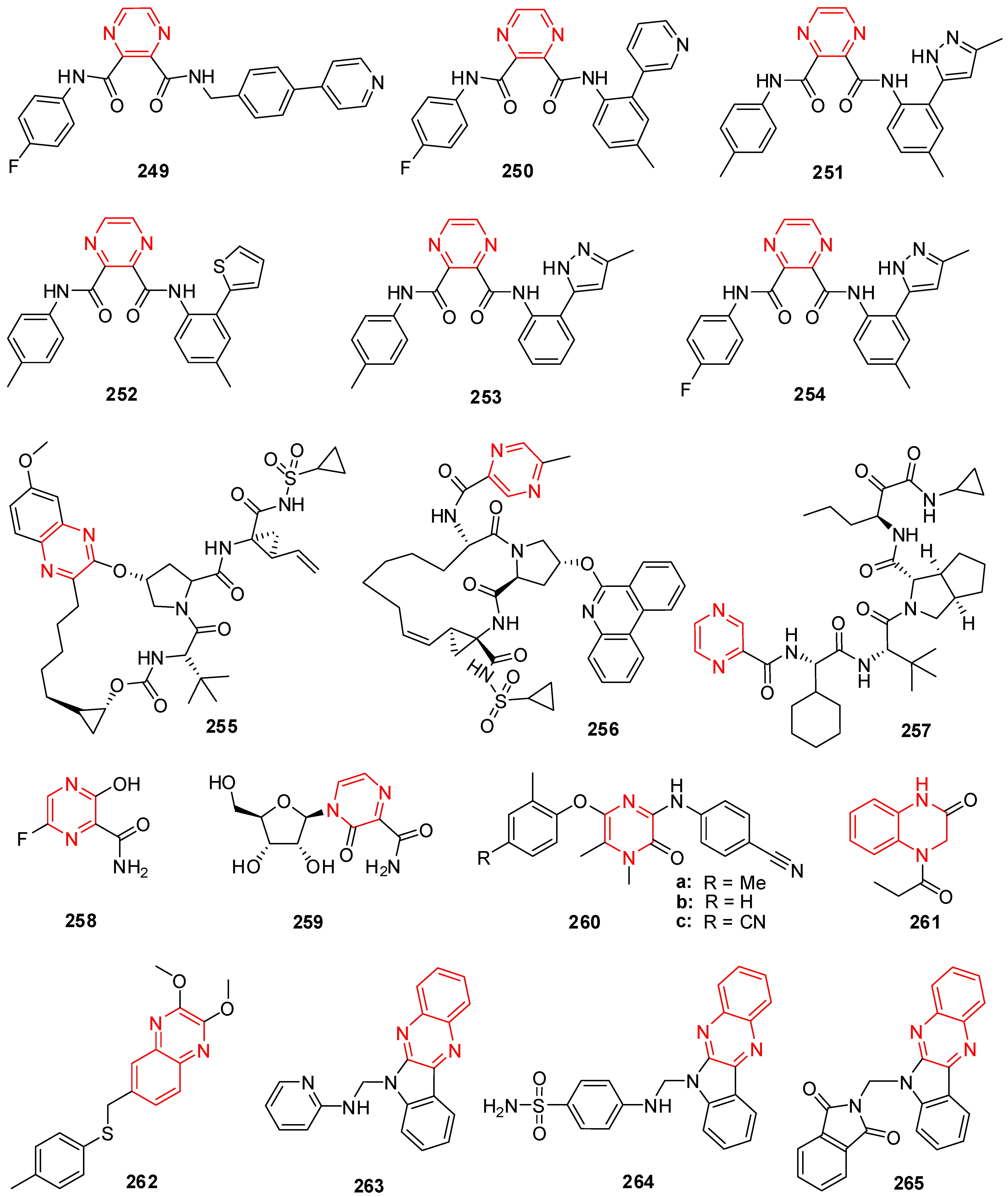
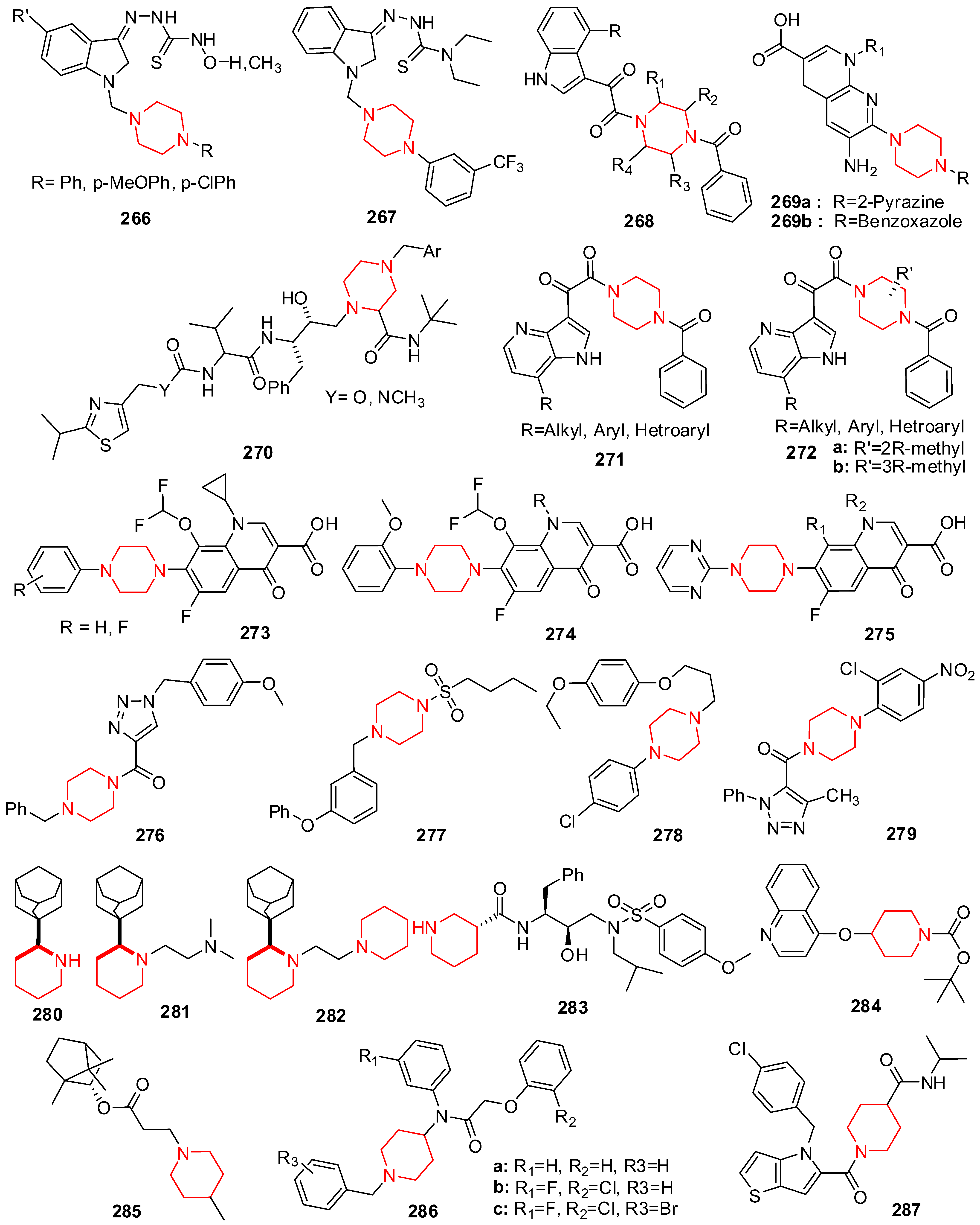

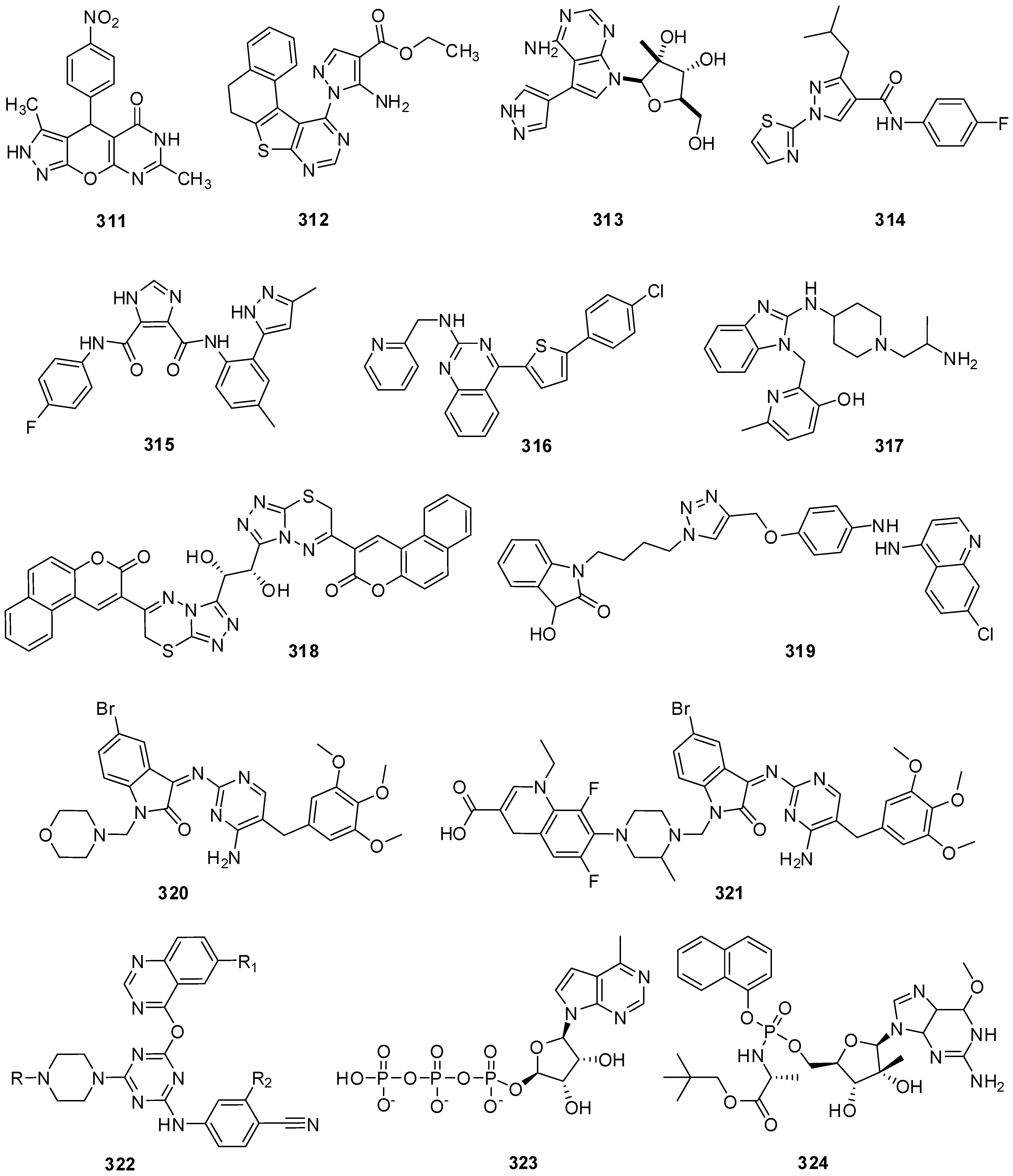

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, G.; Sohail, M.; Bilal, M.; Rasool, N.; Qamar, M.U.; Ciurea, C.; Marceanu, L.G.; Misarca, C. N-Heterocycles as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Overview. Molecules 2024, 29, 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102232
Ahmad G, Sohail M, Bilal M, Rasool N, Qamar MU, Ciurea C, Marceanu LG, Misarca C. N-Heterocycles as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Overview. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102232
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Gulraiz, Maria Sohail, Muhammad Bilal, Nasir Rasool, Muhammad Usman Qamar, Codrut Ciurea, Luigi Geo Marceanu, and Catalin Misarca. 2024. "N-Heterocycles as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Overview" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102232
APA StyleAhmad, G., Sohail, M., Bilal, M., Rasool, N., Qamar, M. U., Ciurea, C., Marceanu, L. G., & Misarca, C. (2024). N-Heterocycles as Promising Antiviral Agents: A Comprehensive Overview. Molecules, 29(10), 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102232







