Reverse Osmosis with Intermediate Chemical Demineralization: Scale Inhibitor Selection, Degradation, and Seeded Precipitation
Abstract
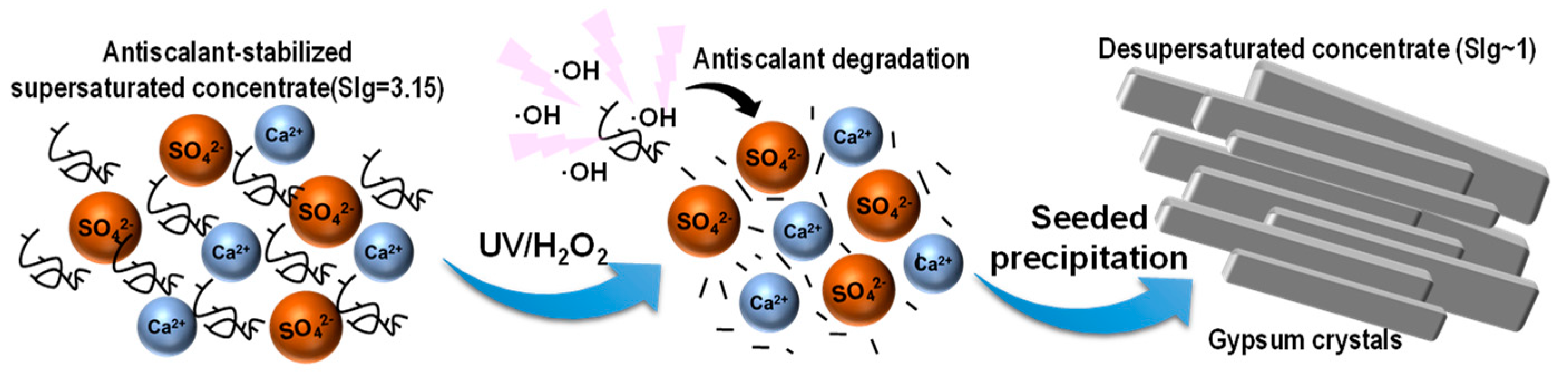
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
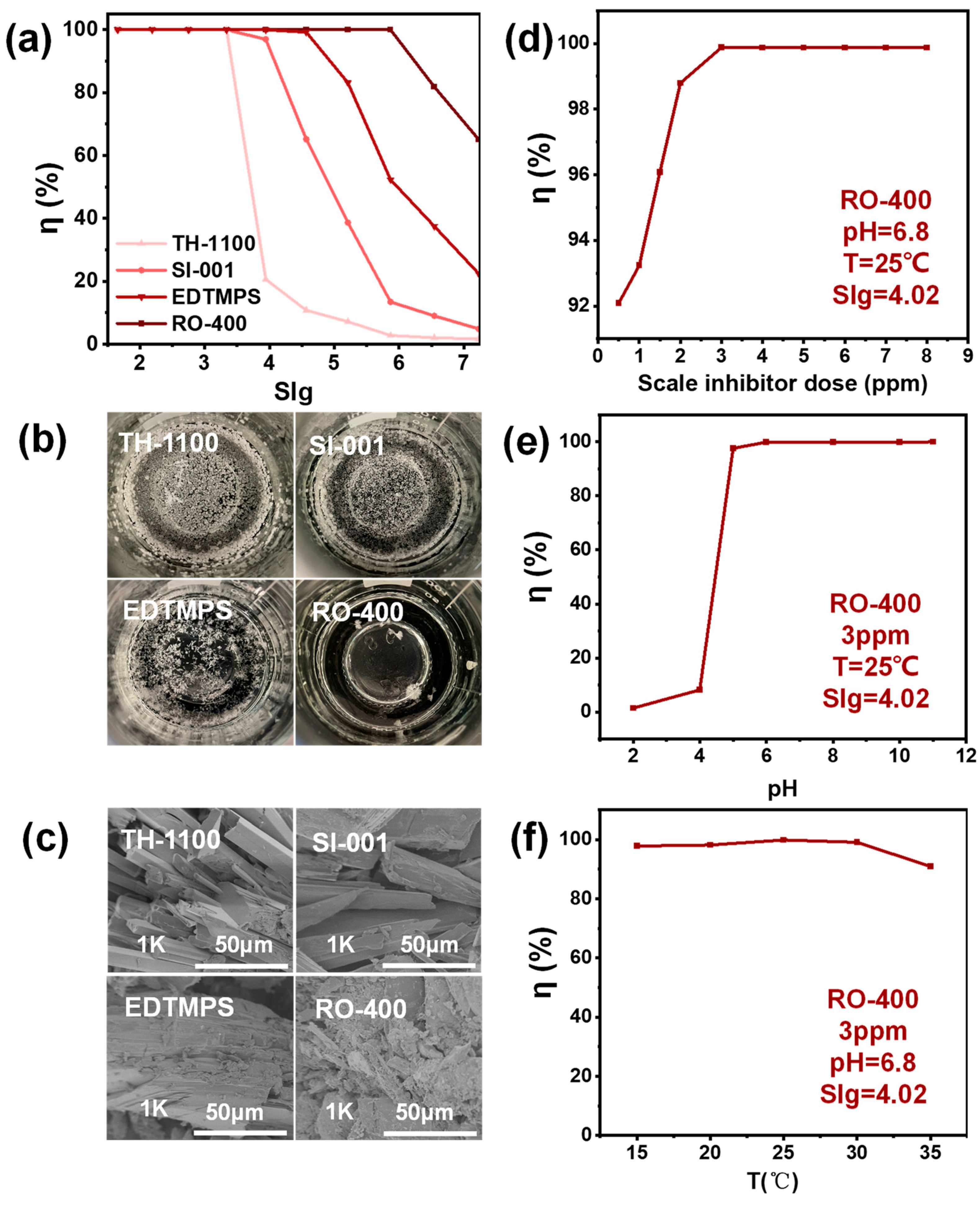
2.1. Static Scale Inhibition Experiment
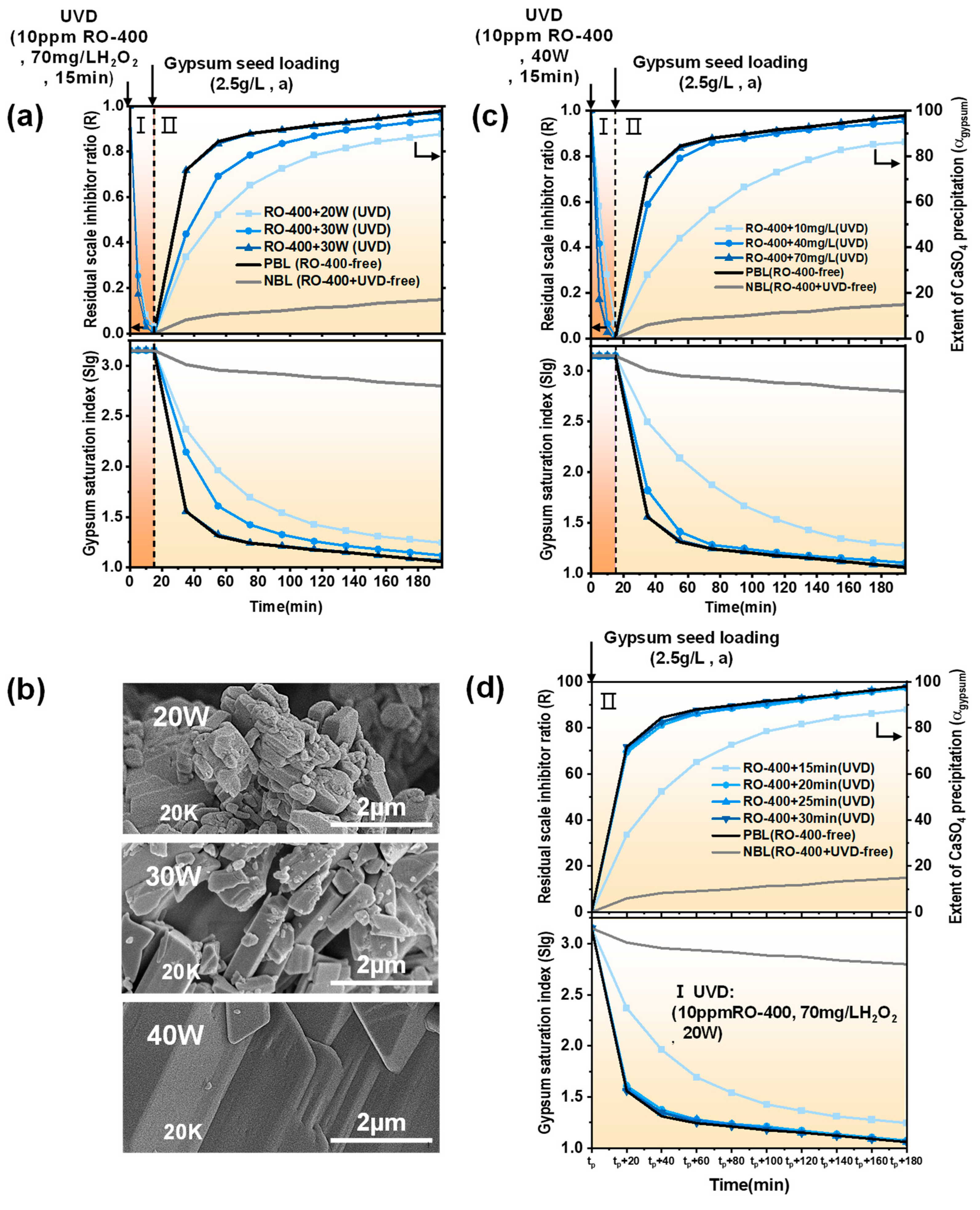
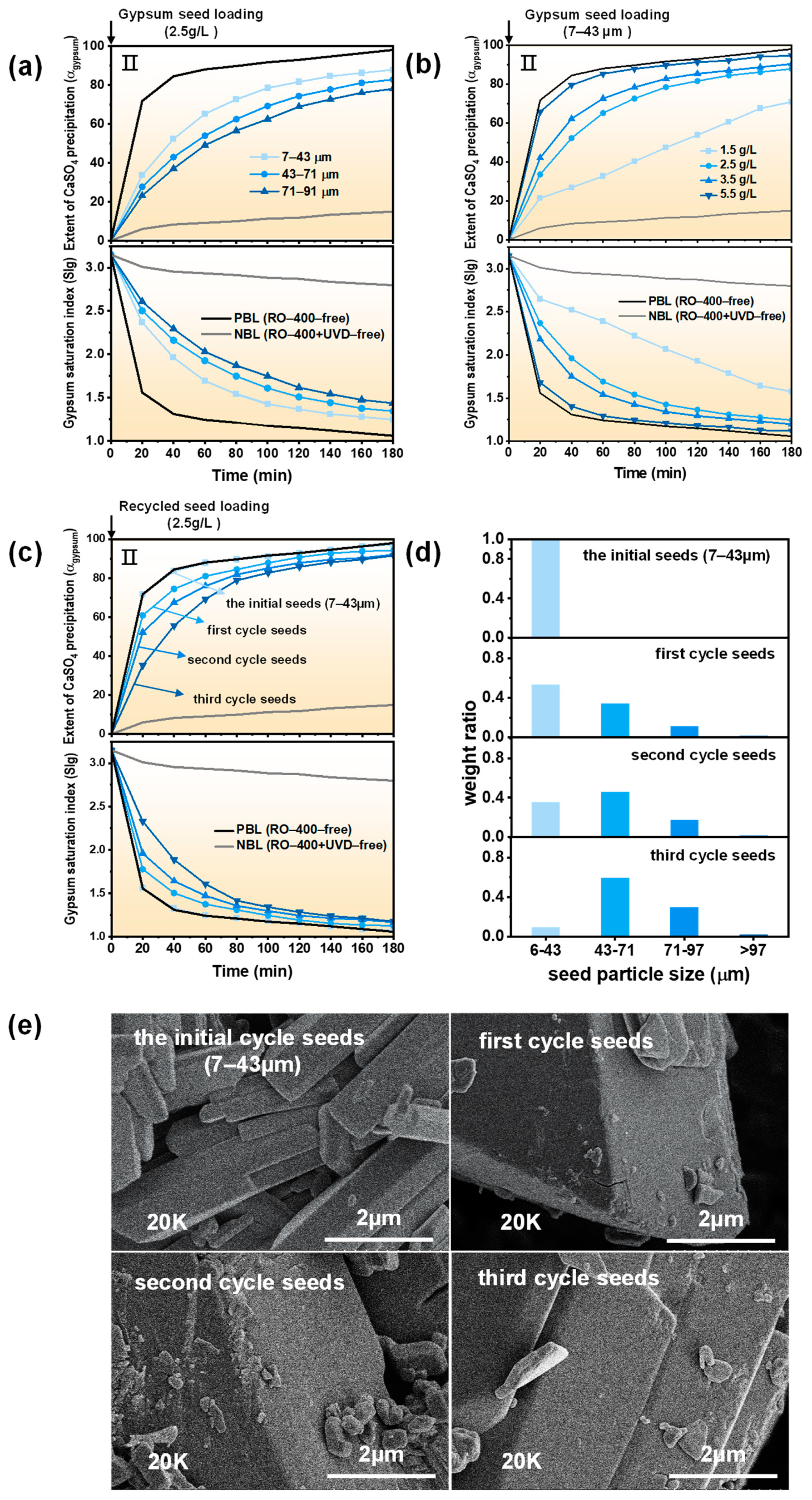
2.2. UVD-GSP Processes
3. Experiment
3.1. Materials and Solutions
3.1.1. Materials
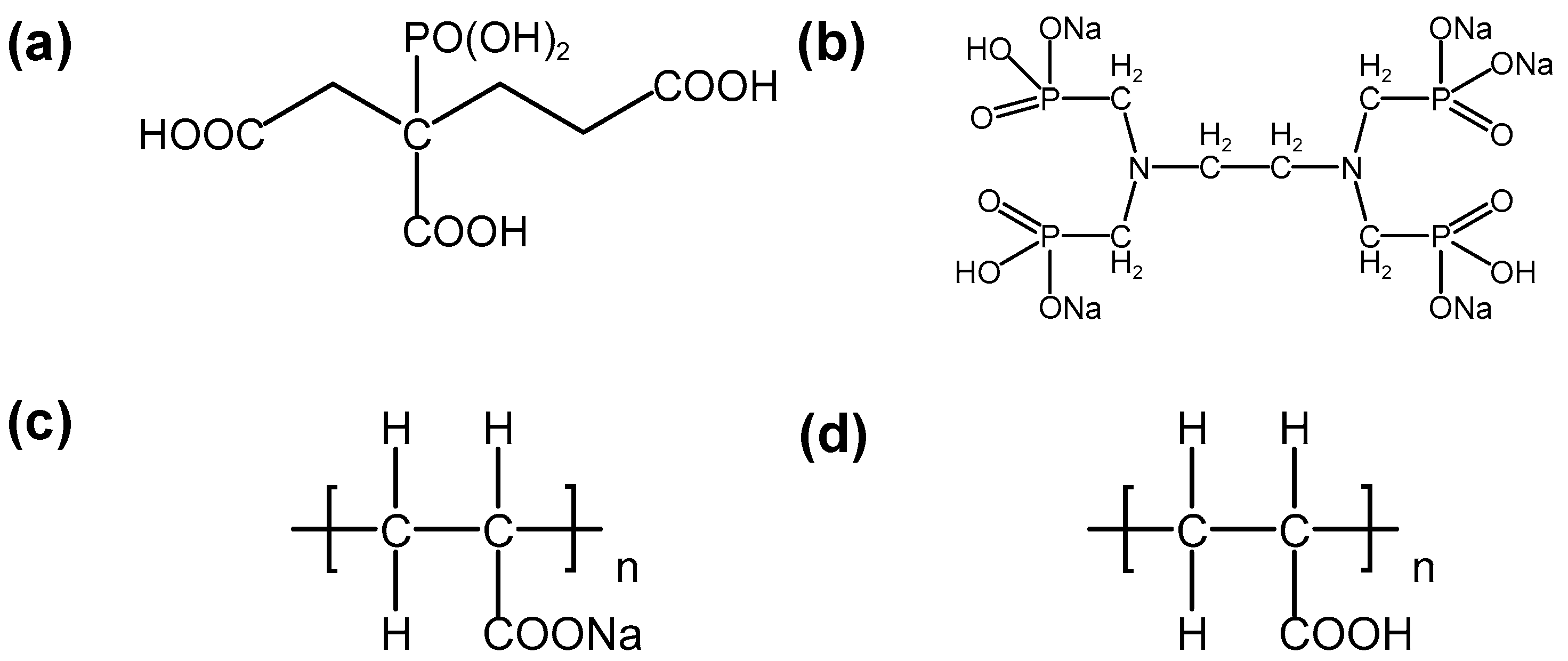
3.1.2. Scale Inhibitors
3.1.3. Preparation of RO Concentrate
3.2. Experimental Details
3.2.1. Static Scale Inhibition Experiments
3.2.2. UVD-GSP Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, L.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhang, W. Treatment of reverse osmosis membrane by sodium hypochlorite and alcohols for enhanced performance using the swelling-fastening effect. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W. Enhanced Anti-Biofouling Properties of BWRO Membranes via the Deposition of Poly (Catechol/Polyamine) and Ag Nanoparticles. Membranes 2023, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhao, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W. Study on the Treatment of Refined Sugar Wastewater by Electrodialysis Coupled with Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket and Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes 2023, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giwa, A.; Dufour, V.; Al Marzooqi, F.; Al Kaabi, M.; Hasan, S.W. Brine management methods: Recent innovations and current status. Desalination 2017, 407, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.M.; Billinge, I.H.; Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Huang, Y.; Winton, R.K.; Yip, N.Y. Drivers, challenges, and emerging technologies for desalination of high-salinity brines: A critical review. Desalination 2022, 538, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hasson, D.; Semiat, R.; Shemer, H. Intermediate concentrate demineralization techniques for enhanced brackish water reverse osmosis water recovery—A review. Desalination 2019, 466, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Kaufmann, F.; Rahardianto, A.; Cohen, Y. Desupersaturation of RO concentrate and gypsum removal via seeded precipitation in a fluidized bed crystallizer. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelich, C.J.; Williams, M.D.; Rahardianto, A.; Franklin, J.C.; Cohen, Y. High-recovery reverse osmosis desalination using intermediate chemical demineralization. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 301, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-S.; Wu, J.-H. Municipal-to-Industrial Water Reuse via Multi-Stage and Multi-Pass Reverse Osmosis Systems: A Step from Water Scarcity towards Sustainable Development. Water 2022, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, H.; Maghram Al Shaiae, M.; Green, T.N.; Ito, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Onishi, M.; Fusaoka, Y.; Farooque Ayumantakath, M.; Saleh Al Amoudi, A. Reliable Sea Water Ro Operation with High Water Recovery and No-Chlorine/No-Sbs Dosing in Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Membranes 2021, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penteado de Almeida, J.; Stoll, Z.; Xu, P. An Alternating, Current-Induced Electromagnetic Field for Membrane Fouling and Scaling Control during Desalination of Secondary Effluent from Municipal Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisciandaro, M.; Innocenzi, V.; Tortora, F.; Mazziotti di Celso, G. Reduction of Fouling and Scaling by Calcium Ions on an UF Membrane Surface for an Enhanced Water Pre-Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Wei, C. Experimental study on seeded precipitation assisted reverse osmosis for industrial wastewater reuse. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 20, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, N.; Chaudhuri, A.; Das, S.P. Numerical modelling and analysis of concentration polarization and scaling of gypsum over RO membrane during seawater desalination. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 190, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydranautics. Chemical Pretreatment for RO and NF. In Technical Application Bulletin No 111; Hydranautics: Oceanside, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chuan Yee Lee, B.; Tan, E.; Lu, Y.; Komori, H.; Pietsch, S.; Goodlett, R.; James, M. Antiscalant and its deactivation in zero/minimized liquid discharge (ZLD/MLD) application in the mining sector—Opportunities, challenges and prospective. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Testa, F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Moulin, P. The effect of antiscalant addition on calcium carbonate precipitation for a simplified synthetic brackish water reverse osmosis concentrate. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F. Calcium sulfate precipitation studies with scale inhibitors for reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination 2013, 319, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, S.; Tang, X.; Liu, H. Treatment of brackish water inland desalination brine via antiscalant removal using persulfate photolysis. Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, B.C.; Rahardianto, A.; Cohen, Y. Antiscalant removal in accelerated desupersaturation of RO concentrate via chemically-enhanced seeded precipitation (CESP). Water Res. 2012, 46, 4261–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardianto, A.; McCool, B.C.; Cohen, Y. Accelerated desupersaturation of reverse osmosis concentrate by chemically-enhanced seeded precipitation. Desalination 2010, 264, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lisitsin, D.; Liu, Y.; David, H.; Semiat, R. Desupersaturation of RO Concentrates by Addition of Coagulant and Surfactant. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2007, 40, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halleb, A.; Nakajima, M.; Yokoyama, F.; Neves, M.A. Effect of Surfactants on Reverse Osmosis Membrane Performance. Separations 2023, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, X.; Huo, M.; Geng, Z. The Influence of Residual Coagulant Al on the Biofilm EPS and Membrane Fouling Potential in Wastewater Reclamation. Water 2020, 12, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A.; et al. Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek, A.; Puszczało, E. Effect of Photooxidation on Nanofiltration Membrane Fouling During Wastewater Treatment from the Confectionery Industry. Water 2020, 12, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Maafa, I.M.; Qudsieh, I.Y. Photodegradation of Methylene Blue Using a UV/H2O2 Irradiation System. Water 2024, 16, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pelaez, M.; Westrick, J.A.; O’Shea, K.E.; Hiskia, A.; Triantis, T.; Kaloudis, T.; Stefan, M.I.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. Efficient removal of microcystin-LR by UV-C/H(2)O(2) in synthetic and natural water samples. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Degradation of Bezafibrate with UV/H2O2 in Surface Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2011, 40, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Song, D.; Chen, W.; Yang, H. Antiscalants in RO membrane scaling control. Water Res. 2020, 183, 115985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Qiu, F.; Zhou, X.; Qi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Guo, Q.; Guo, X. Synthesis and application of terpolymer scale inhibitor in the presence of β-cyclodextrins. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 109, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Testa, F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Moulin, P. Effect of antiscalants on precipitation of an RO concentrate: Metals precipitated and particle characteristics for several water compositions. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2672–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Han, J.; Su, M.; Wu, Q. Synthesis of modified polyaspartic acid and evaluation of its scale inhibition and dispersion capacity. Desalination 2015, 358, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, C. Inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores using various combinations of ultraviolet treatment with addition of hydrogen peroxide. Photochem. Photobiol. 2014, 90, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kou, J.; Sun, C. Combing Seeding Crystallization with Flotation for Recovery of Fluorine from Wastewater: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Studies. Molecules 2023, 28, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Evaluation of the structural morphology of starch-graft-poly(acrylic acid) on its scale-inhibition efficiency. Water Res. 2018, 141, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qu, H.; Yang, Z.; Fu, C.-e.; Tian, Z.; Yang, W. Scale inhibition performance and mechanism of sulfamic/amino acids modified polyaspartic acid against calcium sulfate. Desalination 2017, 419, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimaru, I.W.; Corigliano, A.T.; Zhao, F. Using Classical EDTA Titrations To Measure Calcium and Magnesium in Intravenous Fluid Bags. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 2238–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkrtchyan, K.V.; Pigareva, V.A.; Zezina, E.A.; Kuznetsova, O.A.; Semenova, A.A.; Yushina, Y.K.; Tolordava, E.R.; Grudistova, M.A.; Sybachin, A.V.; Klimov, D.I.; et al. Preparation of Biocidal Nanocomposites in X-ray Irradiated Interpolyelectolyte Complexes of Polyacrylic Acid and Polyethylenimine with Ag-Ions. Polymers 2022, 14, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Salt | PRO Concentrate Model Solution (A) | SRO Concentrate Model Solutions (70%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Solution (B-Bulk) | Solution (B-Membrane Surface) | ||
| CaCl2 | mmol/L | 12.85 | 42.91 | 52.22 |
| Na2SO4 | mmol/L | 20.75 | 69.31 | 84.34 |
| NaCl | mmol/L | 26.40 | 88.20 | 107.33 |
| pH | - | 6.7 | 6.8 | 6.9 |
| SIg | - | 0.70 | 3.15 | 4.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Wang, P.; Xie, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W. Reverse Osmosis with Intermediate Chemical Demineralization: Scale Inhibitor Selection, Degradation, and Seeded Precipitation. Molecules 2024, 29, 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102163
Xu S, Wang P, Xie L, Du Y, Zhang W. Reverse Osmosis with Intermediate Chemical Demineralization: Scale Inhibitor Selection, Degradation, and Seeded Precipitation. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102163
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shichang, Ping Wang, Lixin Xie, Yawei Du, and Wen Zhang. 2024. "Reverse Osmosis with Intermediate Chemical Demineralization: Scale Inhibitor Selection, Degradation, and Seeded Precipitation" Molecules 29, no. 10: 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102163
APA StyleXu, S., Wang, P., Xie, L., Du, Y., & Zhang, W. (2024). Reverse Osmosis with Intermediate Chemical Demineralization: Scale Inhibitor Selection, Degradation, and Seeded Precipitation. Molecules, 29(10), 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29102163







