Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
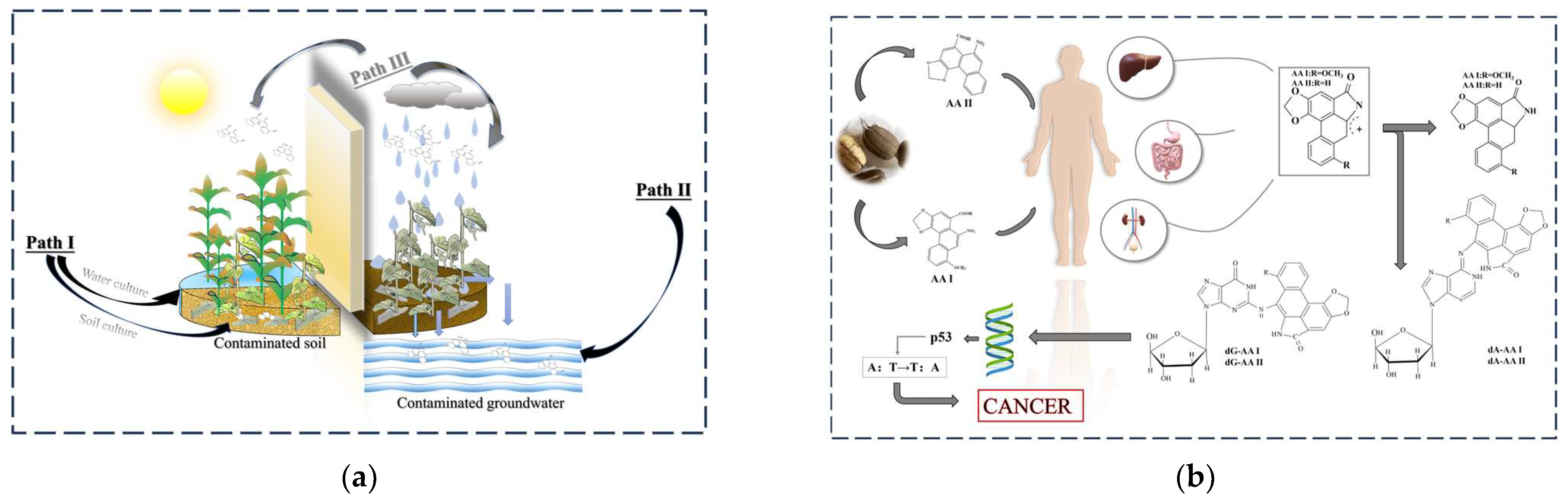
2. AAs Can Cause Cancer and Can Be Exposed to the Environment
2.1. How Do AAs Cause Cancer?
2.2. Exposure to AAs in the Environment
3. Detection Methods of AAs
3.1. Common Detection Methods
3.1.1. HPLC
3.1.2. HPLC-MS
3.2. Other Detection Methods
3.2.1. Sensors
3.2.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
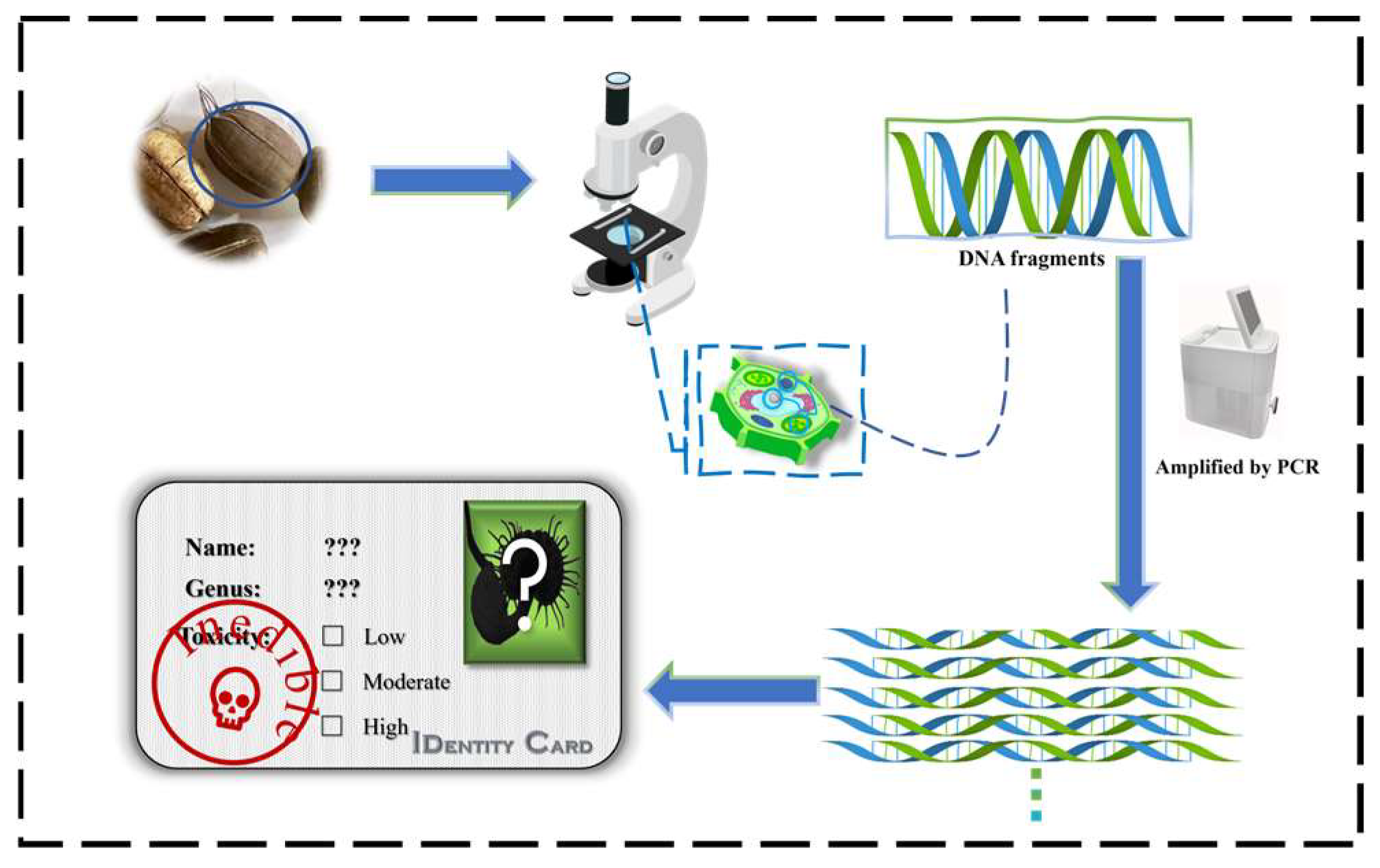
3.2.3. Biological Detection Methods
4. Removal of AAs
4.1. Microbiological Methods
4.2. Adsorption Separation Methods
4.2.1. SPE
- (1)
- MOFs
- (2)
- CNTs
- (3)
- CMCs
- (4)
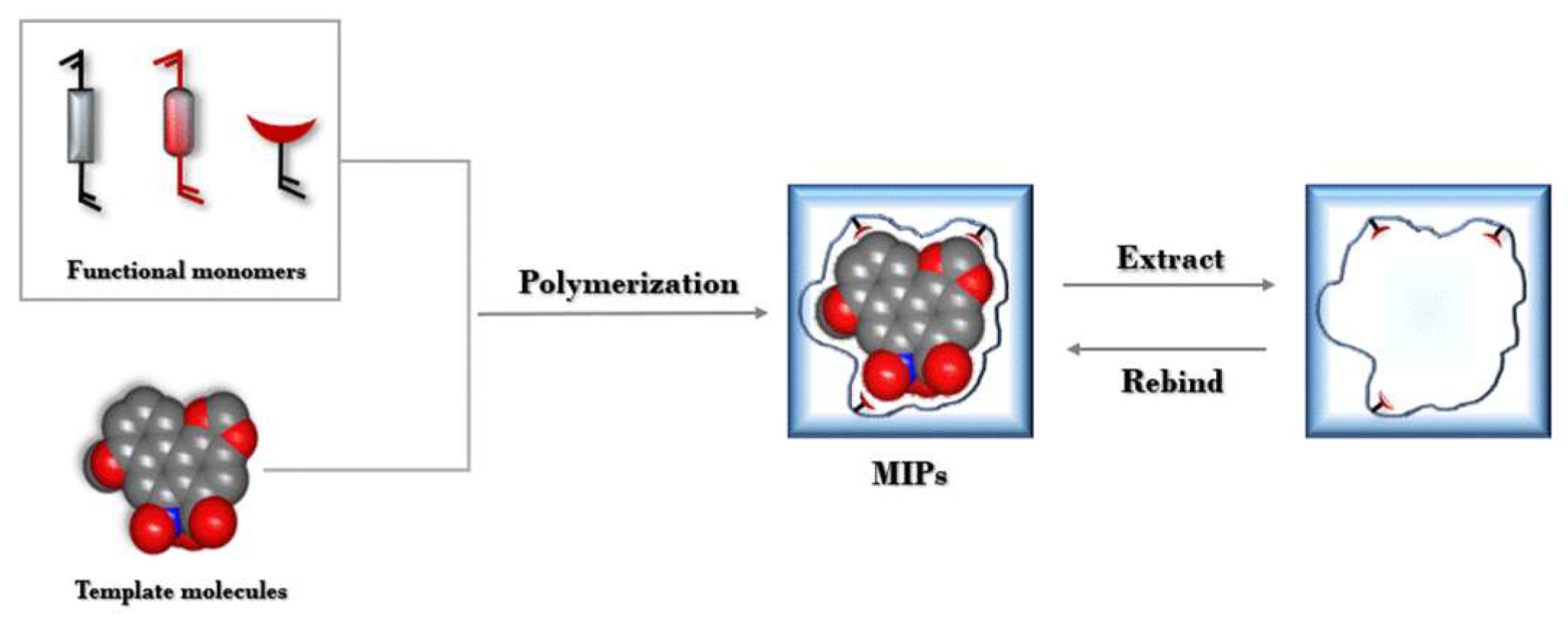
- MIPs
4.2.2. EME
4.2.3. QuEChERS Method
4.2.4. SFE
4.3. Chemical Methods
| Template Molecules | Functional Monomers | Crosslinkers | Initiators | MIPs | Recovery (%) | RSDs (%) | LOD (µg/L) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAI | ZIF-67 | NBS | AIBN | ZIF-67 @EIM-MIM | 96.2–100.0% | 3.5–4.0% | 20 | 50.9 | [114] |
| AAI | acrylic acid | EGDMA | AIBN | MIPs | 91.5% | <4.2% | 60 | 1.3 | [102] |
| AAI | SiO2 | TRIM | — | IL-IL @silicas | 70.0–110.6% | 3.5–9.1% | — | 16.7 | [115] |
| AAI, AAII | CNT | GPTMS | — | SiO2@CNT/Fe3O4 | 92.7–97.5% 92.6–99.4% | <4.0% | 50 | 24.5 | [94] |
| AAI | Chitosan | — | — | CMCs @CS | 73.6–77.7% | 0.8–4.5% | 10 | 77.72 | [97] |
| AAI | PTMOS | TEOS | HAc | MCNTs @AAI-MIPs | 80–110% | 3.27–8.16% | 34 | 23.96 | [93] |
| AAI | ZIF-67 | EGDMA | AIBN | GEIM-ZIF-67 | 97.67–106.98% | — | 24.1 | 34.25 | [88] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiliś-Pstrusińska, K.; Wiela-Hojeńska, A. Nephrotoxicity of Herbal Products in Europe-A Review of an Underestimated Problem. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uber, A.M.; Sutherland, S.M. Nephrotoxins and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debelle, F.D.; Vanherweghem, J.L.; Nortier, J.L. Aristolochic acid nephropathy: A worldwide problem. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.; Chan, J.; Wanke, S.; Neinhuis, C.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Local uses of Aristolochia species and content of nephrotoxic aristolochic acid 1 and 2-A global assessment based on bibliographic sources. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 108–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanherweghem, J.L.; Depierreux, M.; Tielemans, C.; Abramowicz, D.; Dratwa, M.; Jadoul, M.; Richard, C.; Vandervelde, D.; Verbeelen, D.; Vanhaelenfastre, R.; et al. Rapidly progressive interstitial renal fibrosis in young-women—Association with slimming regimen including chinese herbs. Lancet 1993, 341, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Broe, M.E. On a nephratoxic and carcinogenic slimming regimen. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 33, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeiser, H.H.; Bieler, C.A.; Wiessler, M.; Strihou, C.v.Y.d.; Cosyns, J.-P. Detection of DNA Adducts Formed by Aristolochic Acid in Renal Tissue from Patients with Chinese Herbs Nephropathy. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2025–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, G.; Porth, J.; Stahl, R.A. Thrombosis associated with cytomegalovirus infection in patients with ANCA-positive vasculitis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 38, E27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, M.; Ismail, A.; Zakaria, A.; Elmansy, H.; Shahrour, W.; Prowse, O.; Kotb, A. Aristolochic acid: What urologists should know. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2022, 94, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Xian, Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, J.; Liang, A.H. Systematic Overview of Aristolochic Acids: Nephrotoxicity, Carcinogenicity, and Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.; Alhusainy, W.; Woutersen, J.; Rietjens, I.M.; Punt, A. Predicting points of departure for risk assessment based on in vitro cytotoxicity data and physiologically based kinetic (PBK) modeling: The case of kidney toxicity induced by aristolochic acid I. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 92, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, S.L.; Pang, S.T.; McPherson, J.R.; Yu, W.; Huang, K.K.; Guan, P.; Weng, W.H.; Siew, E.Y.; Liu, Y.; Heng, H.L.; et al. Genome-Wide Mutational Signatures of Aristolochic Acid and Its Application as a Screening Tool. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 197ra101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, Y.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Galichet, L.; Cogliano, V.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part A: Pharmaceuticals. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.W.T.; Poon, S.L.; Huang, M.N.; Lim, J.Q.; Boot, A.; Yu, W.; Suzuki, Y.; Thangaraju, S.; Ng, C.C.Y.; Tan, P.; et al. Aristolochic acids and their derivatives are widely implicated in liver cancers in Taiwan and throughout Asia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.N.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, L.N.; Shi, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Han, Z.G. The Mutational Features of Aristolochic Acid-Induced Mouse and Human Liver Cancers. Hepatology 2020, 71, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.E.; Wang, C.Y.; Niu, M.; Liu, T.T.; Ren, L.T.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Lin, L.; Mu, W.Q.; et al. Integration of Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Data to Compare the Hepatotoxicity of Neonatal and Adult Mice Exposed to Aristolochic AcidⅠ. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 840961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamias, G.; Boletis, J. Balkan nephropathy: Evolution of our knowledge. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, A.M.; Lukinich-Gruia, A.T.; Paunescu, V.; Ilia, G. A Theoretical Study of the Molecular Coupled Structures of Aristolochic Acids and Humic Acid, Potential Environmental Contaminants. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokmen, M.R.; Cosyns, J.P.; Arlt, V.M.; Stiborova, M.; Phillips, D.H.; Schmeiser, H.H.; Simmonds, M.S.J.; Cook, H.T.; Vanherweghem, J.L.; Nortier, J.L.; et al. The Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Aristolochic Acid Nephropathy A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelaković, B.; Dika, Ž.; Arlt, V.M.; Stiborova, M.; Pavlović, N.M.; Nikolić, J.; Colet, J.M.; Vanherweghem, J.L.; Nortier, J.L. Balkan Endemic Nephropathy and the Causative Role of Aristolochic Acid. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.C.; Chen, M.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, Y.T. Aristolochic acid-associated urinary tract cancers: An updated meta-analysis of risk and oncologic outcomes after surgery and systematic review of molecular alterations observed in human studies. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anger, E.E.; Yu, F.; Li, J. Aristolochic Acid-Induced Nephrotoxicity: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Protective Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nortier, J.L.; Vanherweghem, J.-L.; Jelakovic, B. Aristolochic Acid Nephropathy and Balkan Nephropathy. In Tubulointerstitial Nephritis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeiser, H.H.; Stiborova, M.; Arlt, V.M. Chemical and molecular basis of the carcinogenicity of Aristolochia plants. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2009, 12, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.V.; Randerath, K. Nudease Pl-mediated enhancement of sensitivity of 32P-postlabeling test for structurally diverse DNA adducts. Carcinogenesis 1986, 7, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfau, W.; Schmeiser, H.H.; Wiessler, M. AristolocMc acid binds covafleettly to tlhe exocycMc ammo gromp off perime emclleoitides mDNA. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfau, W.; Schmeiser, H.H.; Wiessler, M. 32P-PostIlaIbeIlMinig amalysns off tihe DNA addmdts ffonnnied by aristoIocMc acid I and II. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaluri, S.; Bonala, R.R.; Yang, I.Y.; Lukin, M.A.; Wen, Y.J.; Grollman, A.P.; Moriya, M.; Iden, C.R.; Johnson, F. DNA adducts of aristolochic acid II: Total synthesis and site-specific mutagenesis studies in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grollman, A.P.; Shibutani, S.; Moriya, M.; Miller, F.; Wu, L.; Moll, U.; Suzuki, N.; Fernandes, A.; Rosenquist, T.; Medverec, Z.; et al. Aristolochic acid and the etiology of endemic (Balkan) nephropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12129–12134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlt, V.M.; Stiborova, M.; Schmeiser, H.H. Aristolochic acid as a probable human cancer hazard in herbal remedies: A review. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadot, I.; Decleves, A.E.; Nortier, J.; Caron, N. An Integrated View of Aristolochic Acid Nephropathy: Update of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Z.; Tian, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Meng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Yi, Y.; Han, J.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, L.M.; et al. Study on the potential nephrotoxicity and mutagenicity of aristolochic acid IVa and its mechanism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Thakur, S.; Korenjak, M.; Sidorenko, V.S.; Chung, F.F.L.; Zavadil, J. Aristolochic acid-associated cancers: A public health risk in need of global action. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voice, T.C.; McElMurry, S.P.; Long, D.T.; Dimitrov, P.; Ganev, V.S.; Petropoulos, E.A. Evaluation of the hypothesis that Balkan endemic nephropathy is caused by drinking water exposure to contaminants leaching from Pliocene coal deposits. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.W.; Hu, Q.; Chan, W. Uptake and Accumulation of Nephrotoxic and Carcinogenic Aristolochic Acids in Food Crops Grown in Aristolochia clematitis-Contaminated Soil and Water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.W.; Chan, C.K.; Liu, Y.S.; Yao, J.; Mitic, B.; Kostic, E.N.; Milosavljevic, B.; Davinic, I.; Orem, W.H.; Tatu, C.A.; et al. Aristolochic Acids as Persistent Soil Pollutants: Determination of Risk for Human Exposure and Nephropathy from Plant Uptake. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11468–11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Li, W.W.; Chan, C.K.; Liu, J.J.; Deng, K.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Milosavljevic, B.; Kostic, E.N. Quantitation of Aristolochic Acids in Corn, Wheat Grain, and Soil Samples Collected in Serbia: Identifying a Novel Exposure Pathway in the Etiology of Balkan Endemic Nephropathy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5928–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, N.M.; Maksimovic, V.; Maksimovic, J.D.; Orem, W.H.; Tatu, C.A.; Lerch, H.E.; Bunnell, J.E.; Kostic, E.N.; Szilagyi, D.N.; Paunescu, V. Possible health impacts of naturally occurring uptake of aristolochic acids by maize and cucumber roots: Links to the etiology of endemic (Balkan) nephropathy. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-K.; Xiong, L.; Pavlović, N.M.; Chan, W. Determination of Aristolochic Acids in Soil, Water, and Herbal Plants in Medicinal Plant Cultivation Areas: An Emerging Environmental Contaminant Worth Concerning. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, K.; Tang, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, X. Uptake, Translocation, and Fate of Carcinogenic Aristolochic Acid in Typical Vegetables in Soil-Plant Systems. Molecules 2022, 27, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, S.V.M.; Orem, W.H.; Tatu, C.A.; Lerch, H.E.; Szilagyi, D.N. Organic compounds in water extracts of coal: Links to Balkan endemic nephropathy. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, K.K.; Chan, C.K.; Zhao, Y.; Chan, K.K.J.; Liu, G.R.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Chan, W. Occurrence and Environmental Stability of Aristolochic Acids in Groundwater Collected from Serbia: Links to Human Exposure and Balkan Endemic Nephropathy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukinich-Gruia, A.T.; Nortier, J.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Milovanovic, D.; Popovic, M.; Draghia, L.P.; Paunescu, V.; Tatu, C.A. Aristolochic acid I as an emerging biogenic contaminant involved in chronic kidney diseases: A comprehensive review on exposure pathways, environmental health issues and future challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-Y.; Wu, M.-L.; Deng, J.-F.; Hwang, D.-F. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination for aristolochic acid in medicinal plants and slimming products. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 766, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, A.; Kotani, T.; Kojima, S.; Hakamata, H.; Kusu, F. Determination of Aristolochic Acids I and II in Herbal Medicines by High-performance Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection. Electrochemistry 2014, 82, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Lee, K.C.; Liu, N.; Cai, Z.W. A sensitivity enhanced high-performance liquid chromatography fluorescence method for the detection of nephrotoxic and carcinogenic aristolochic acid in herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1164, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Chan, W.; Guo, L.; Cai, Z. Determination of aristolochic acid I in rat urine and plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.A.; Chan, W. Determination of Aristolochic Acids by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5859–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Chan, C.K.; Wong, Y.L.; Chan, K.K.J.; Chan, H.W.; Chan, W. Cooking methods employing natural anti-oxidant food additives effectively reduced concentration of nephrotoxic and carcinogenic aristolochic acids in contaminated food grains. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.L.; Au, C.K.; Chan, C.K.; Jin, L.; Zivkovic Stosic, M.Z.; Dordevic Zlatkovic, M.R.; Zlatkovic, D.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Chan, W. Fabrication of a Simple and Efficient HPLC Reduction Column for Online Conversion of Aristolochic Acids to Aristolactams Prior to Sensitive Fluorescence Detection. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 12365–12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, D.W.; Liu, J.X.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. Phytochemical profiling in single plant cell by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2016, 141, 6338–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Zheng, Y.F.; Cai, Z.W. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of the DNA adducts of aristolochic acids. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leung, E.M.; Chan, W. Quantification of aristolochic acid-RNA adducts in the urine of aristolochic acid-treated rats by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghia, L.P.; Lukinich-Gruia, A.T.; Oprean, C.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Paunescu, V.; Tatu, C.A. Aristolochic acid I: An investigation into the role of food crops contamination, as a potential natural exposure pathway. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4163–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.K.; Chan, K.K.J.; Liu, N.; Chan, W. Quantitation of Protein Adducts of Aristolochic Acid I by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Novel Method for Biomonitoring Aristolochic Acid Exposure. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kite, G.C.; Yule, M.A.; Leon, C.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Detecting aristolochic acids in herbal remedies by liquid chromatography/serial mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, T.T.; Lee, M.R.; Hsiao, S.S.; Hsai, J.L.; Wu, T.S.; Chiang, S.T.; Cai, S.Q. Analysis of aristolochic acid in nine sources of Xixin, a traditional Chinese medicine, by liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 33, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.H.; Chan, W.; Li, J.H.; Cai, Z.W. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for investigating the biochemical effects induced by aristolochic acid in rats: The plasma metabolome. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Lin, A.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Ou, R.M.; Huang, H.D. A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of aristolochic acid-I in rat plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.H.; Rosenquist, T.A.; Sidorenko, V.; Iden, C.R.; Chen, C.H.; Pu, Y.S.; Bonala, R.; Johnson, F.; Dickman, K.G.; Grollman, A.P.; et al. Biomonitoring of Aristolactam-DNA Adducts in Human Tissues Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Ion-Trap Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaclavik, L.; Krynitsky, A.J.; Rader, J.I. Quantification of aristolochic acids I and II in herbal dietary supplements by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-multistage fragmentation mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A—Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2014, 31, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Chan, W. Development of a novel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for aristolochic acids detection: Application in food and agricultural soil analyses. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Chan, K.K.J.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Chan, W. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of aristolochic acids in soil samples collected from Serbia: Link to Balkan endemic nephropathy. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.X.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S.C. Rapid Analysis of Aristolochic Acid Analogues in Traditional Chinese Patent Medicine by LC-MS/MS. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8823596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Pan, G.R.; Chan, W. Analysis of aristolochic acids in Houttuynia cordataby liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Guo, L.; Tan, T.; Liu, F.; Wan, Y.Q. Study of the Contents of Analogues of Aristolochic Acid in Houttuynia cordata by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2022, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, X. Rapid simultaneous determination of thirteen aristolochic acids analogs in Aristolochiaceae plants by Ultra-High-Performance liquid Chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in dynamic multiple reaction monitoring mode. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2023, 1225, 123753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Guan, H.; Wang, C. Rapid and Simultaneous Quantification of Six Aristolochic Acids and Two Lignans in Asari Radix et Rhizoma Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 5269545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Xu, C.L.; Yang, T.; Hu, Z.R.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Feng, G.D. Developed a novel sensor based on fluorescent graft conjugated polymer for the determination of aristolochic acid in traditional Chinese medicine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A—Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.J.; Liu, M.Y.; Tian, F.L.; Liu, Z.L. A Novel Luminescent Metal-Organic Framework as a Remarkable Sensor for Detecting Aristolochic Acids in Biological Fluids. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yan, B. Europium chelate-anionic exchange functionalized covalent organic frameworks for the sensing of aristolochic acid a in humans and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim in surface water. Talanta 2023, 265, 124869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gong, S.; Wen, D.; Che, B.; Liao, Y.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Hu, S. Rapid determination of aristolochic acid I and II in Aristolochia plants from different regions by β-cyclodextrin-modified capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1049, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mamat, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, P.; Dong, Y.; Hu, G. Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified via Molybdenum Disulfide Decorated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Sensitive Voltammetric Detection of Aristolochic Acids. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, M.F.; Baikeli, Y.; Mamat, X.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Dong, Y.M.; Chang, F.Q.; Zhang, H.C.; Hu, G.Z. Soft-templated mesoporous carbon-modified glassy carbon electrode for sensitive and selective detection of aristolochic acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Fernández Pierna, J.A.; Dardenne, P.; Baeten, V. Detection of Melamine in Soybean Meal Using Near-Infrared Microscopy Imaging with Pure Component Spectra as the Evaluation Criteria. J. Spectrosc. 2016, 2016, 5868170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Chai, Q.Q.; Lin, N.; Li, X.H.; Wang, W. 1D convolutional neural network for the discrimination of aristolochic acids and their analogues based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5118–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.L.; Wong, K.L.; Shaw, P.C. Rapid authentication of Cordyceps by lateral flow dipstick. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Pang, X.; Song, J.; Shi, L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.; Leon, C. A renaissance in herbal medicine identification: From morphology to DNA. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Cai, S.Q.; Xiang, L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Yao, H.; Song, J.Y.; et al. An integrated system for identifying the hidden assassins in traditional medicines containing aristolochic acids. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.; Xu, Z.; Jia, J.; Leon, C.; Hu, S.; Lin, Y.; Ragupathy, S.; Song, J.; Newmaster, S.G. Biomonitoring for traditional herbal medicinal products using DNA metabarcoding and single molecule, real-time sequencing. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongkhao, K.; Tungphatthong, C.; Sukrong, S. A PCR-lateral flow immunochromatographic assay (PCR-LFA) for detecting Aristolochia species, the plants responsible for aristolochic acid nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Huang, Z. Development of two immunochromatographic test strips based on gold nanospheres and gold nanoflowers for the rapid and simultaneous detection of aflatoxin B1 and aristolochic acid a in dual-use medicinal and food ingredients. Microchem. J. 2023, 186, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Tang, W.; Guo, R.L.; Li, J.Q.; Yang, W.; He, Z.G. Research progress on Chinese herbal medicine fermentation and profile of active substances derived. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019, 44, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ren, G.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, N.; Kong, X.; Jiang, D.; Liu, C. Identification of a Novel Coumarins Biosynthetic Pathway in the Endophytic Fungus Fusarium oxysporum GU-7 with Antioxidant Activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, 1098–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikmundova, M.; Drandarov, K.; Bigler, L.; Hesse, M.; Werner, C. Biotransformation of 2-benzoxazolinone and 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one by endophytic fungi isolated from Aphelandra tetragona. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4863–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, R.; Sanhueza, L.; Mendoza, L.; Cotoras, M. Characterization of the fungitoxic activity on Botrytis cinerea of the aristolochic acids I and II. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, D.; Shi, Q.; Ren, G.; Liu, C. Microbial degradation of aristolochic acid I by endophytic fungus A.h-Fs-1 of Asarum heterotropoides. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 917117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.W.; Tian, M.L.; Row, K.H.; Yan, X.M.; Xiao, W. Isolation of aristolochic acid I from herbal plant using molecular imprinted polymer composited ionic liquid-based zeolitic imidazolate framework-67. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3047–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Liu, H.Y.; Han, Y.M.; Bai, L.G.; Yan, H.Y. On-line enrichment and determination of aristolochic acid in medicinal plants using a MOF-based composite monolith as adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. B—Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1159, 122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, M.M.; Dai, L.C. Interaction between chlortetracycline and calcium-rich biochar: Enhanced removal by adsorption coupled with flocculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Chen, G.N.; Wang, L.; Cui, X.; Luo, Z.M.; Jing, W.H.; Chang, C.; Zeng, A.G.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q. Metal-organic framework grafted with melamine for the selective recognition and miniaturized solid phase extraction of aristolochic acid I from traditional Chinese medicine. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1647, 462155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, F.; Guo, L.; Luo, D.; Wan, Y. A dispersive solid-phase extraction method for the determination of Aristolochic acids in Houttuynia cordata based on MIL-101(Fe): An analytes-oriented adsorbent selection design. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Gao, J.; Li, X.X.; Li, Y.J.; He, X.W.; Chen, L.X.; Zhang, Y.K. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized carbon nanotubes for highly selective removal of aristolochic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1602, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.; Chen, G.N.; Wang, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Chang, C.; Guo, Q.; Luo, Z.M.; Fu, Q. Adenine-coated magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the selective extraction of aristolochic acids based on multiple interactions. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghubanshi, H.; Dikio, E.D.; Naidoo, E.B. The properties and applications of helical carbon fibers and related materials: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 44, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Yu, P.; Luo, Z.M.; Bai, X.F.; Li, X.Q.; Fu, Q. Single-helix carbon microcoils prepared via Fe(III)-osmotically induced shape transformation of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) for enhanced adsorption and antibacterial activities. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Ge, Y.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Guo, P.Q.; Luo, Z.M.; Du, W.; Chang, C.; Liu, R.L.; Fu, Q. Hybrid-type carbon microcoil-chitosan composite for selective extraction of aristolochic acid I from Aristolochiaceae medicinal plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1561, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Soni, D.; Pratiwi, R.; Rahayu, D.; Megantara, S.; Mutakin. Synthesis of Diazepam-Imprinted Polymers with Two Functional Monomers in Chloroform Using a Bulk Polymerization Method. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 7282415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phungpanya, C.; Chaipuang, A.; Machan, T.; Watla-iad, K.; Thongpoon, C.; Suwantong, O. Synthesis of prednisolone molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles by precipitation polymerization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, A.-M.; Maior, I.; Nicolae, C.A.; Bocăneală, F.L. Novel Pva Proton Conducting Membranes Doped with Polyaniline Generated by in-Situ Polymerization. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 211, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.H.; Xiao, R.; Tang, J.; Zhu, Q.K.; Li, X.M.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, X.W. Preparation and adsorption properties of molecularly imprinted polymer via RAFT precipitation polymerization for selective removal of aristolochic acid I. Talanta 2017, 162, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.H.; Fan, Y.; Mao, X.J.; Guo, L.; Yan, A.P.; Guo, X.; Wan, Y.Q.; Wan, H. Thermosensitive and magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective recognition and extraction of aristolochic acid. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.H.; Shu, H.; Xu, X.Y.; Guo, P.Q.; Liu, R.L.; Luo, Z.M.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Combined magnetic porous molecularly imprinted polymers and deep eutectic solvents for efficient and selective extraction of aristolochic acid I and II from rat urine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C—Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 97, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.H.; Guo, P.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, G.N.; Zhang, X.M.; Shu, H.; Zhang, B.L.; Luo, Z.M.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Selective analysis of aristolochic acid I in herbal medicines by dummy molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2791–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Deng, Q.L.; Wang, S. Dummy molecularly imprinted silica materials for effective removal of aristolochic acid I from kaempfer dutchmanspipe root extract. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjelstad, A.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S. Electromembrane extraction--three-phase electrophoresis for future preparative applications. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, C.; Shen, X. Electromembrane extraction of aristolochic acids: New insights in separation of bioactive ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1608, 460424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M. Fast and Easy Multiresidue Method Employing Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and “Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction” for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X. Correction: QuEChERS pretreatment combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of aristolochic acids I and II in Chinese herbal patent medicines. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35597–35599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattiram, P.D.; Abas, F.; Suleiman, N.; Mohamad Azman, E.; Chong, G.H. Edible oils as a co-extractant for the supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of flavonoids from propolis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chow, A.H.L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Zheng, Y. Removal of toxic aristolochic acid components from Aristolochia plants by supercritical fluid extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Tung, K.K.; Pavlovic, N.M.; Chan, W. Remediation of aristolochic acid-contaminated soil by an effective advanced oxidation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Tian, M. Solid-Phase Extraction of Aristolochic Acid I from Natural Plant Using Dual Ionic Liquid-Immobilized ZIF-67 as Sorbent. Separations 2021, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.W.; Tian, M.L.; Yan, X.M.; Xiao, W.; Row, K.H. Dual ionic liquid-immobilized silicas for multi-phase extraction of aristolochic acid from plants and herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1592, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analysis Method | Sample | Mass Spectrometer Type | Detection Pattern | Components | Scan Mode | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS/MS | serum albumin | triple quadrupole | positive ion mode | protein adducts of AAI | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [55] |
| LC-MS/MS | herbal | quadrupole ion-trap | positive or negative ion mode | AAI, AAII | — | [56] |
| LC-MS/MS | Chinese medicine | — | positive ion mode | AAI, AAII | full scan (SCAN) | [57] |
| LC-MS/MS | plasma metabolome | quadrupole time-of-flight | positive or negative ion mode | AAI, AAII | — | [58] |
| LC-MS/MS | rat plasma | triple quadrupole | positive ion mode | AAI | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [59] |
| UHPLC-MSn | Human Tissues | quadrupole ion-trap | — | Aristolactam-DNA Adducts | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [60] |
| UHPLC-MS3 | herbal | quadrupole ion-trap | positive ion mode | AAI, AAII | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [61] |
| LC-MS/MS | food and agricultural soil | — | positive ion mode | Aristolactams | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [62] |
| LC-MS/MS | over 130 soil samples | — | positive ion mode | AAI | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [63] |
| LC-MS/MS | Chinese patent medicine | triple quadrupole | positive ion mode | Aristolochic acid analogues | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [64] |
| LC-MS/MS | Houttuynia cordata | — | positive ion mode | AAI, AAII | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [65] |
| UHPLC-MS | Houttuynia cordata | quadrupole time-of-flight | — | Aristolochic acid analogues | — | [66] |
| UHPLC-MS/MS | Aristolochiaceae plants | — | positive ion mode | Aristolochic acids analogs | dynamic multiple reaction monitoring (dMRM) | [67] |
| UHPLC-MS | Asari Radix et Rhizoma | triple quadrupole | positive ion mode | Aristolochic acids derivatives | multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) | [68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010081
Wang C, Liu Y, Han J, Li W, Sun J, Wang Y. Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Changhong, Yunchao Liu, Jintai Han, Wenying Li, Jing Sun, and Yinan Wang. 2024. "Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review" Molecules 29, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010081
APA StyleWang, C., Liu, Y., Han, J., Li, W., Sun, J., & Wang, Y. (2024). Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review. Molecules, 29(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010081






