Isolation and Purification of Protamine from the Cultured Takifugu flavidus and Its Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Toxicity and Nutritional Analysis of Cultivated Pufferfish Sperm
2.1.1. Toxicity Analysis of Cultivated Pufferfish Sperm
2.1.2. Nutritional Composition Analysis of the Sperm of Pufferfish
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Crude Protamine from Cultured T. flavidus
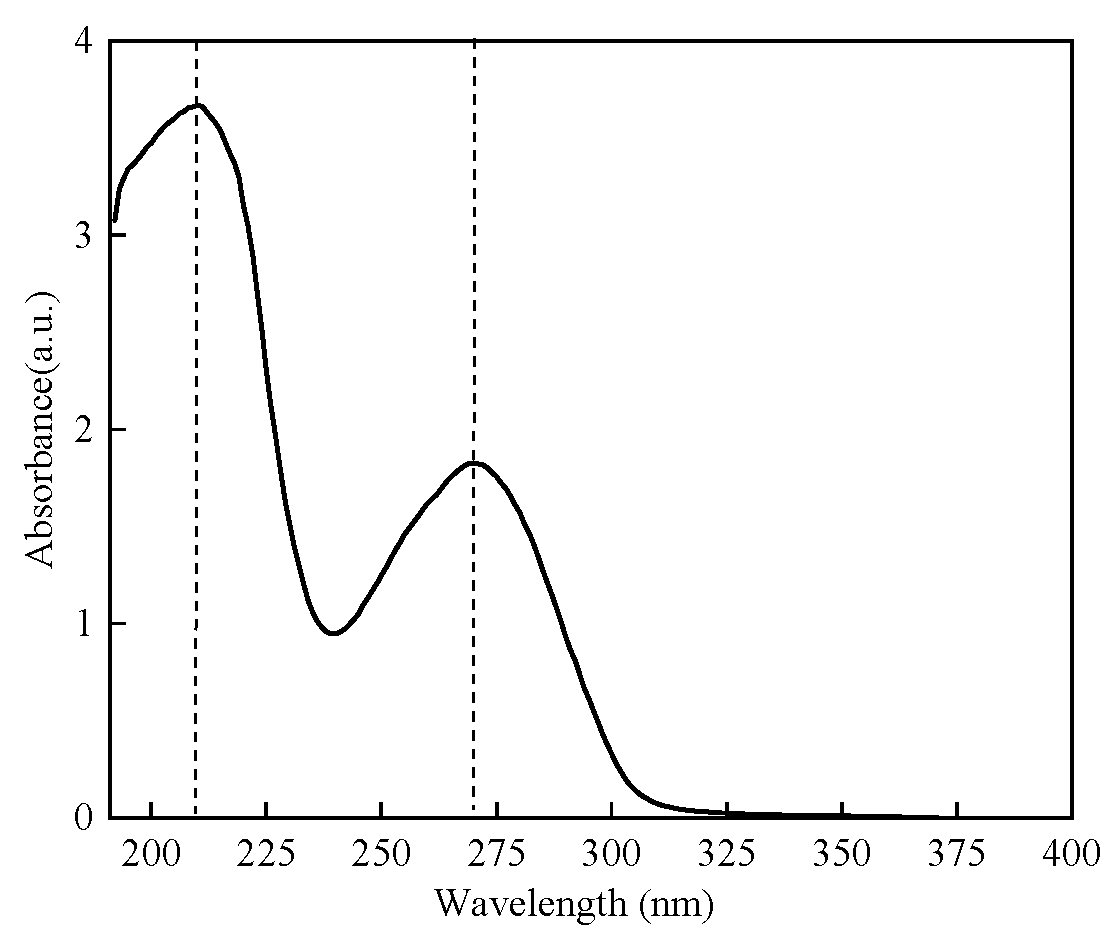
2.2.1. UV Absorption Spectrum of Protamine of T. flavidus
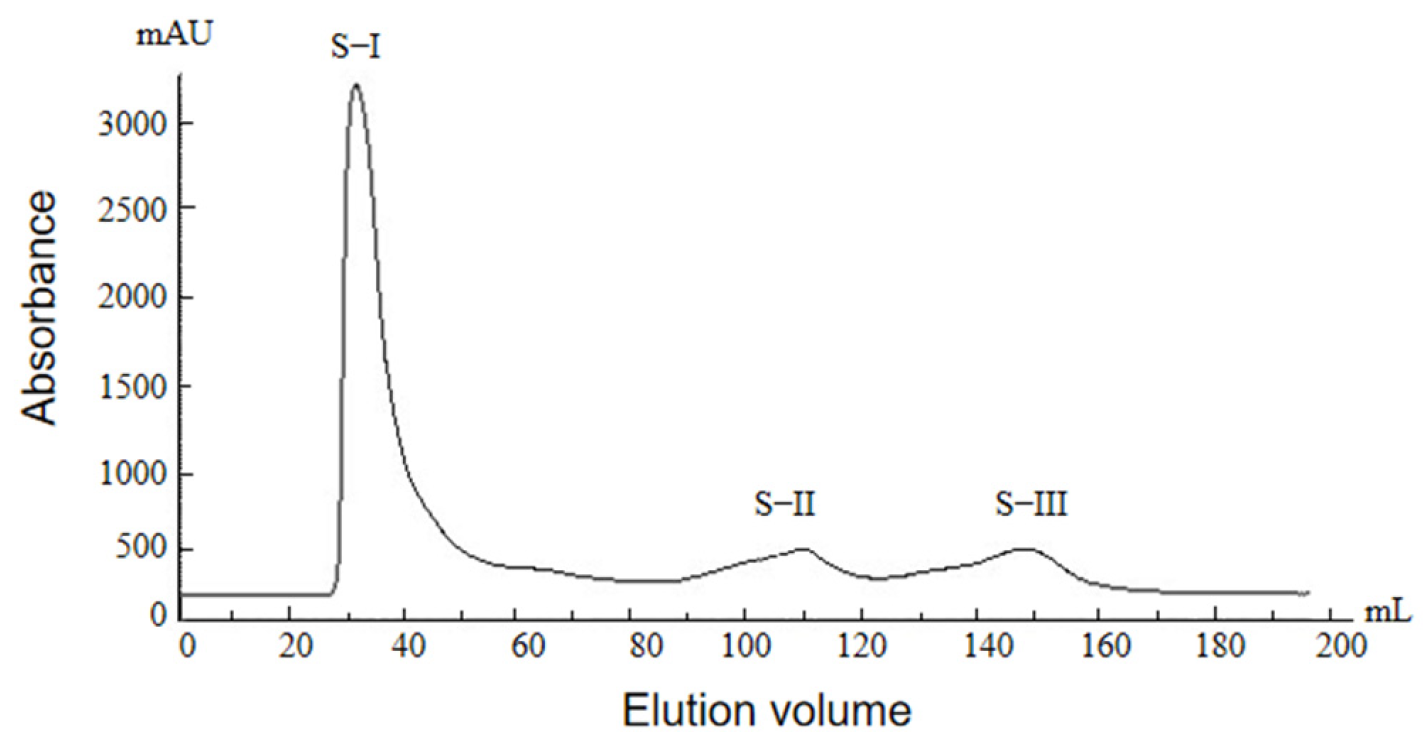
2.2.2. Glucose Gel Column Chromatography Profile of Protamine from T. flavidus
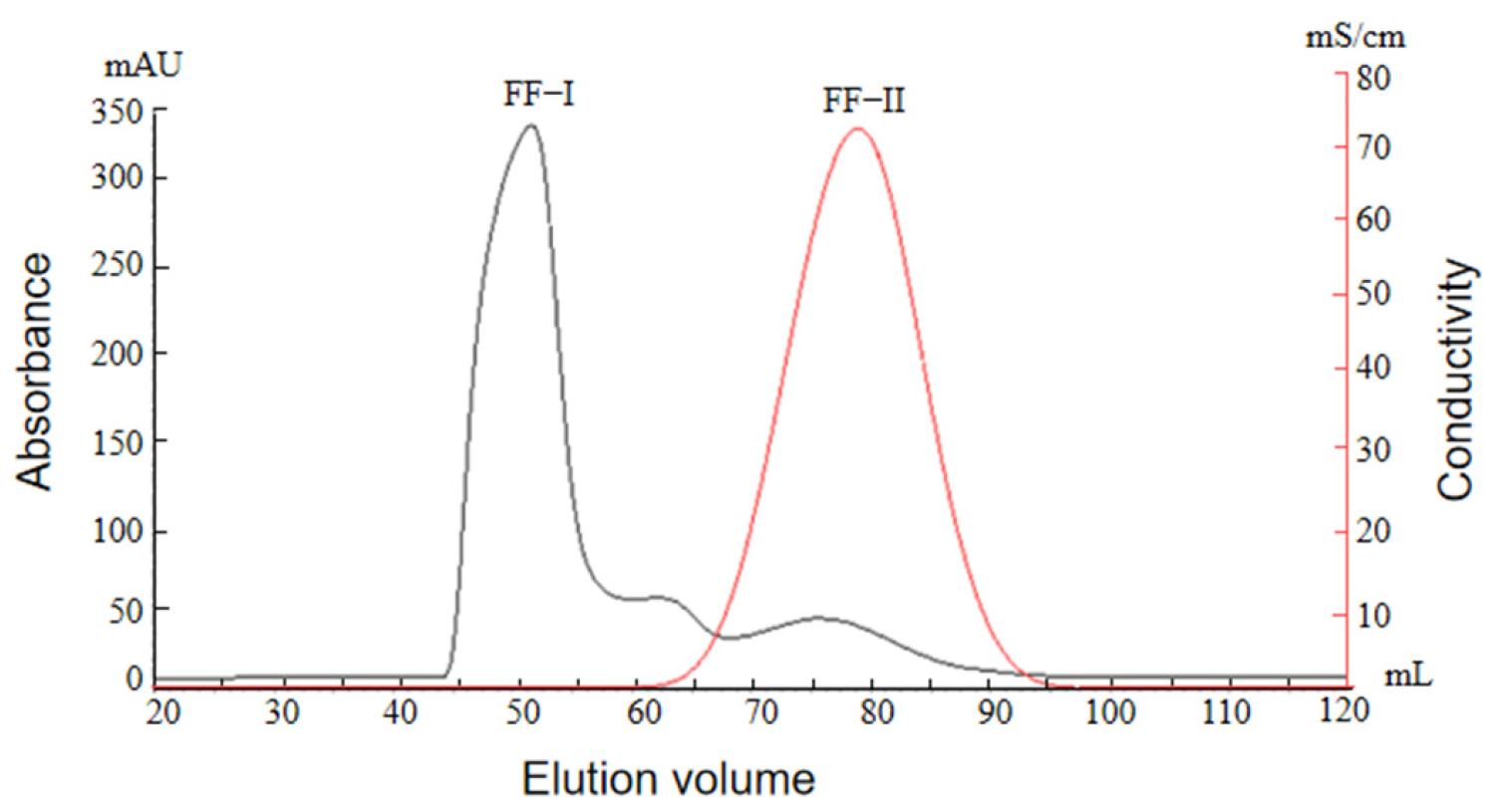
2.2.3. Ion Exchange Chromatography Profile of Protamine from T. flavidus
2.2.4. Desalination Column Chromatography Profile of Protamine from T. flavidus
2.3. Physicochemical Properties of Protamine of Protamine from T. flavidus
2.3.1. Analysis of the Amino Acid Components of Protamine from T. flavidus
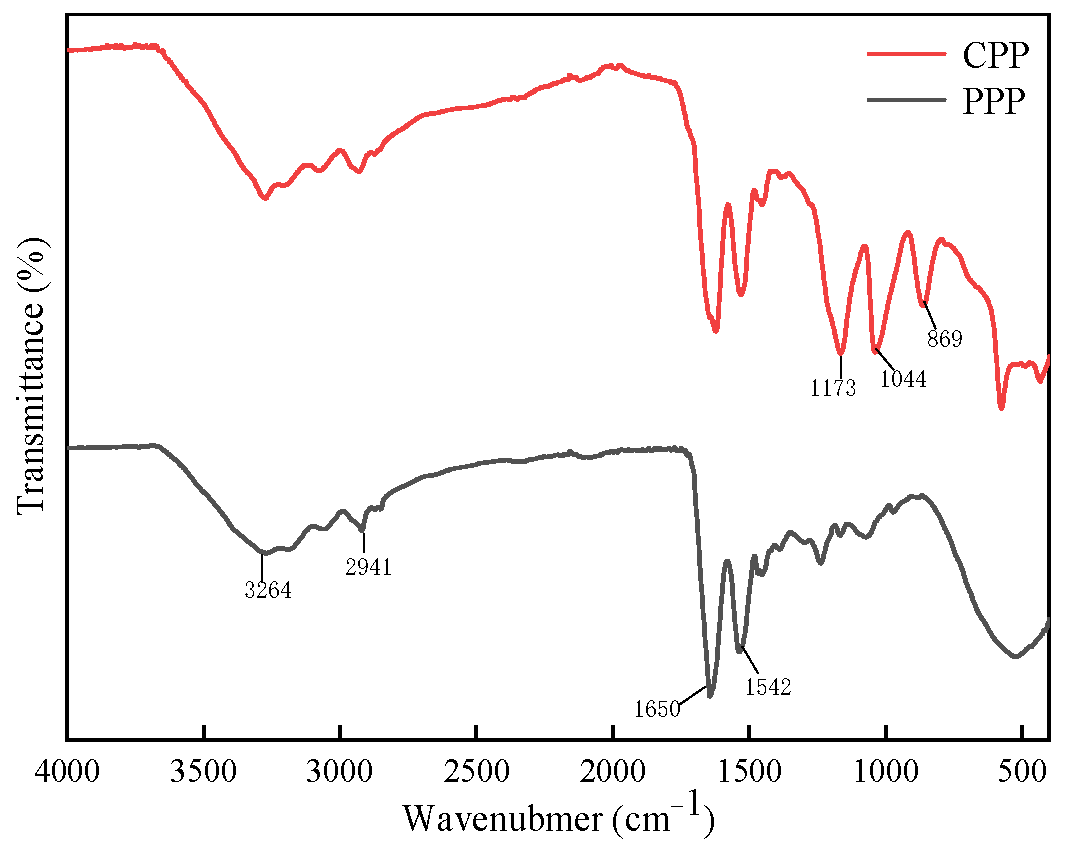
2.3.2. Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis of Protamine
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermal Analysis of Protamine
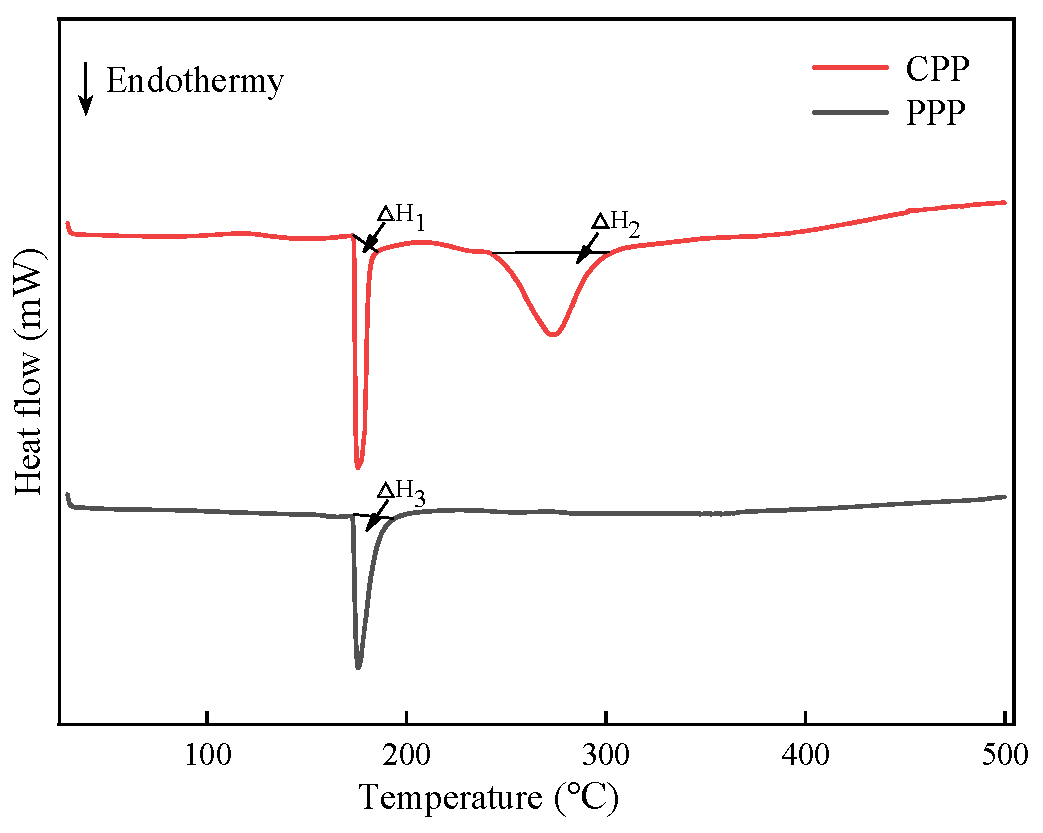
2.3.4. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy Analysis of Protamine
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Instruments
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Nutritional Component Analysis
Determination of the Tetrodotoxin (TTX)
Determination of Essential Nutrients and Mineral Elements
Amino Acid Composition Determination and Evaluation
3.2.2. Extraction of Protamine
3.2.3. Protamine Separated by Sephadex G50 Gel Filtration Chromatography
3.2.4. Protamine Separated by Carboxymethyl Cellulose Gel FF Ion Exchange Chromatography
3.2.5. Protamine Separated by Sephadex G25 Fine Chromatography
3.2.6. Sakaguchi Reaction of Protamine
3.2.7. Detection of the Maximum Ultraviolet Absorption Wavelength of Protamine
3.2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Measurement of Protamine
3.2.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) of Protamine
3.2.10. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy of Protamine
3.2.11. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peniche-Pérez, J.C.; González-Salas, C.; Villegas-Hernández, H.; Díaz-Gamboa, R.; Aguilar-Perera, A.; Guillen-Hernández, G.; Poot-López, G.R. Reproductive biology of the southern pufferfish, Sphoeroides nephelus (Actinopterygii: Tetraodontiformes: Tetraodontidae), in the northern coast off the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2019, 49, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.T.; Chen, B.; Pan, N.; Qiao, K.; Wu, G.; Liu, Z.Y. Collaborative analysis combining headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) and intelligent (electronic) sensory systems to evaluate differences in the flavour of cultured pufferfish. Flavour Fragr. J. 2021, 36, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudong, J.; Qiqi, J.; Zhijun, X.; Xiaoqiang, G.; Jieming, Z.; Changtao, G.; Bin, H. Effects of two different culture systems on the growth performance and physiological metabolism of tiger pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Aquaculture 2018, 495, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Wu, H.; Jiang, T.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; Zhai, Y. Simultaneous identification and quantification of tetrodotoxin in fresh pufferfish and pufferfish-based products using immunoaffinity columns and liquid chromatography/quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2017, 35, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tao, N. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional composition of farmed male puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, T.A.; Singer, D.S.; Thompson, J.W. Purification and analysis of protamine. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.T.; Austin, J.W.; Gill, T.A. Antibacterial effect of protamine in combination with EDTA and refrigeration. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 66, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, T.; P Venkatesh, Y. Occurrence, functions and biological significance of arginine-rich proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2016, 17, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaques, L. Protamine—Antagonist to heparin. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1973, 108, 1291. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, D.-S.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kang, H.-J.; Jin, D.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of protamine prepared from salmon sperm. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 902–907. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.; Dixon, G.; Ferrier, L.; Gedamu, L.; Iatrou, K. The structure and function of protamine mRNA from developing trout testis. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1977, 19, 135–155. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Recent advances on protein separation and purification methods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, J.; Rodríguez, L.P.; Blanco, L.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Tetrodotoxin, an extremely potent marine neurotoxin: Distribution, toxicity, origin and therapeutical uses. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6384–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christidis, G.; Mandalakis, M.; Anastasiou, T.I.; Tserpes, G.; Peristeraki, P.; Somarakis, S. Keeping Lagocephalus sceleratus off the Table: Sources of Variation in the Quantity of TTX, TTX Analogues, and Risk of Tetrodotoxication. Toxins 2021, 13, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.-L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.-P. Toxicity of cultured puffer fish and seasonal variations in China. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Emoto, Y.; Tatsuno, R.; Wang, J.J.; Ngy, L.; Taniyama, S.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Maturation-associated changes in toxicity of the pufferfish Takifugu poecilonotus. Toxicon 2010, 55, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, S.; Ishizuka, K.; Mitsuoka, R.; Takimoto, N.; Yokoyama, N.; Detake, A.; Takayanagi, C.; Yoshikawa, S.; Sugita, H. Seasonal changes in the tetrodotoxin content of the pufferfish Takifugu niphobles. Toxicon 2016, 114, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaba, N.; Çorapcı, B.; Eryaşar, K. Determination of some quality properties and nutritional composition of Turkish raw meat ball produced with marinated Atlantic bonito. Gida 2014, 39, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.T.; Wu, J.N.; Xu, M.; Liu, S.J.; Su, Y.C.; Qiao, K.; Liu, Z.Y. Analysis and Evaluation of the Nutritional Components in Different Parts of Four Species of Puffer Fish. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, N.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, Y. Comparison of nutritional composition of farmed pufferfish muscles among Fugu obscurus, Fugu flavidus and Fugu rubripes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacik, A.; Tirpak, F.; Tomka, M.; Miskeje, M.; Tvrda, E.; Arvay, J.; Andreji, J.; Slanina, T.; Gabor, M.; Hleba, L. Trace elements content in semen and their interactions with sperm quality and RedOx status in freshwater fish Cyprinus carpio: A correlation study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M.K.; Gupta, J.; Gupta, R. Mineral Nutraceuticals and Immunity Enhancement. Nutraceuticals Funct. Foods Immunomodul. 2022, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybodi, N.M.; Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Sheidaei, Z.; Mortazavian, A.M. Wheat bread: Potential approach to fortify its lysine content. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 15, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, B.P.; Milani, D.; Cross, J.L.; Clark, V.W.; Edwards, A.B.; Anderton, R.S.; Blacker, D.J.; Knuckey, N.W. Assessment of the ueuroprotective effects of arginine-rich protamine peptides, poly-arginine peptides (R12-Cyclic, R22) and arginine–tryptophan-containing peptides following: In vitro excitotoxicity and/or permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. NeuroMol. Med. 2017, 19, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.R.; Wu, H.W.; He, Y. Preparation and heparin antagonistic effect of protamine from Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Milts. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2020, 40, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S.; Wang, L.L.; Li, X.Y.; Huang, H.L.; Chi, H. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional compositions of Dosidicus gigas and Onychoteuthis borealijaponicus okada. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 2247–2251+2293. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Feng, W.; Xiong, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F. Impact of drying method on the nutritional value of the edible insect protein from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae: Amino acid composition, nutritional value evaluation, in vitro digestibility, and thermal properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leser, S. The 2013 FAO report on dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition: Recommendations and implications. Nutr. Bull. 2013, 38, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomičić, Z.; Pezo, L.; Spasevski, N.; Lazarević, J.; Čabarkapa, I.; Tomičić, R. Diversity of amino acids composition in cereals. Food Feed Res. 2022, 49, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Bao, D.P.; Wang, R.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, H.M. Amino acid composition and nutritional evaluation of proteins in six samples of cultivated Flammulina velutipes. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Meherunnahar, M.; Ahmed, T.; Chowdhury, R.S.; Miah, M.A.S.; Sridhar, K.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Hoque, M.M.; Sharma, M. Development of novel foxtail millet-based nutri-rich instant noodles: Chemical and quality characteristics. Foods 2023, 12, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Harvey, P.J. Effect of light intensity and wavelength on biomass growth and protein and amino acid composition of Dunaliella salina. Foods 2021, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiayuan, Z.; Hongcai, Z.; Shunsheng, C. Optimization of extraction process of protamine from Takifugu obscurus. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2020, 41, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.R.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Gong, Y.D.; Tang, J.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G.F. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagens and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin and bone of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Suzuki, K. Protamines: Isolation characterization structure and function. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 81, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Su, R.-Q.; Zhang, W.-T.; Chen, J. Purification and the secondary structure of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the alcalase hydrolysate of seahorse protein. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3927–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiary, R.; Middaugh, C.R. Ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy. Anal. Aggreg. Part. Protein Pharm. 2012, 40, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Purification and characterization of a novel bacteriocin from Lactobacillus paracasei ZFM54. LWT 2021, 143, 111125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.L.; Thacker, J.B.; Schug, K.A.; Maráková, K. Sample preparation and fractionation techniques for intact proteins for mass spectrometric analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 211–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junjie, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Shiwang, S.; Huadong, L. Purification and identification of chub Aristichthys nobilis protamine. Jiangxi Sci. 2001, 19, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.L.; Liu, S.J.; Wu, C.Y. The extraction process research of squid protamine. J. Fish. Res. 2013, 35, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Motohiro, T.; Nishi, N.; Muta, E.; Ota, S. Primary structure of scombrine γ, protamine isolated from spotted mackerel (Scomber australasicus). J. Biochem. 1993, 113, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Han, F.; Wang, H. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides from salmon protamine hydrolysate. J. Food Biochem. 2008, 32, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.S. Basic proteins: 1. The nitrogen and the percentages of some amino acids in the protamine of the sardine, Sardina caerulea. J. Biol. Chem. 1926, 70, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W. Protamine and protamine reactions. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2004, 42, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali Sarvestani, M.R.; Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions in food samples by a silver nanoparticle/COF composite modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 3505–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriglieri, J.; Salvioli-Mariani, E.; Mantovani, L.; Tribaudino, M.; Lottici, P.; Laporte-Magoni, C.; Bersani, D. Micro-raman mapping of the polymorphs of serpentine. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offeman, R.D.; Stephenson, S.K.; Franqui, D.; Cline, J.L.; Robertson, G.H.; Orts, W.J. Extraction of ethanol with higher alcohol solvents and their toxicity to yeast. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, N.; Xiang, S.; Guan, N. IR and raman investigation of one-dimensional and three-dimensional aluminophosphite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 18361–18366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesov, B.A. Raman spectra of crystalline secondary amides. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 179, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanganathan, U.; Nogami, M. Investigations on effects of the incorporation of various ionic liquids on PVA based hybrid membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuguang, S. The investigation of chemical structure of coal macerals via transmitted-light FT-IR microspectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 62, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, V.; Bloisi, F.; Perretta, G.; Aronne, A.; Ausanio, G.; Costantini, A.; Vicari, L. Frozen microemulsions for MAPLE immobilization of lipase. Molecules 2017, 22, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adochitei, A.; Drochioiu, G. Rapid characterization of peptide secondary structure by FT-IR spectroscopy. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2011, 56, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Sukprasert, J.; Thumanu, K.; Phung-On, I.; Jirarungsatean, C.; Erickson, L.E.; Tuitemwong, P.; Tuitemwong, K. Synchrotron FTIR light reveals signal changes of biofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticle attachment on Salmonella sp. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 6149713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Ribotta, P.D.; LEOn, A.E. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies on the thermal properties of peanut proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4434–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Boggs, I.; Weeks, M.; Li, Q.; Wu, H.; Harris, P.; Ma, Y.; Day, L. Kinetic modelling of the heat stability of bovine lactoferrin in raw whole milk. J. Food Eng. 2020, 280, 109977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.L.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, H. Identification of thermophilic proteins by incorporating evolutionary and acid dissociation information into Chou’s general pseudo amino acid composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 407, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugrahadi, P.P.; Hinrichs, W.L.; Frijlink, H.W.; Schöneich, C.; Avanti, C. Designing formulation strategies for enhanced stability of therapeutic peptides in aqueous solutions: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.D.; Ryu, H.J.; Cho, H.I.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, J. Thermal behavior of proteins: Heat-resistant proteins and their heat-induced secondary structural changes. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14839–14846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Kaur, P.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Application of circular dichroism spectroscopy in studying protein folding, stability, and interaction. In Advances in Protein Molecular and Structural Biology Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Vila, J.A.; Ripoll, D.R.; Scheraga, H.A. Physical reasons for the unusual α-helix stabilization afforded by charged or neutral polar residues in alanine-rich peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 13075–13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bane, V.; Hutchinson, S.; Sheehan, A.; Brosnan, B.; Barnes, P.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A. LC-MS/MS method for the determination of tetrodotoxin (TTX) on a triple quadruple mass spectrometer. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Li, L.; Fan, X. Preparation and evaluation of certified reference materials for crude protein, crude fat, and crude ash in feed. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.3-2016; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Moisture in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.4-2016; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Ash in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.5-2016; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Protein in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.6-2016; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Fat in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.92-2016; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Calcium in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.91-2017; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Potassium, Sodium in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009 241-2017; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Magnesium in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.87-2016; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Phosphorus in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.14-2017; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Zinc in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Standardization Administration of China, GB 5009.93-2017; National Standards for Food Safety Determination of Selenium in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Doğan, G.; Ertan, Ö.O. Determination of amino acid and fatty acid composition of goldband goatfish [Upeneus moluccensis (Bleeker, 1855)] fishing from the Gulf of Antalya (Turkey). Int. Aquat. Res. 2017, 9, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karray, A.; Alonazi, M.; Smaoui, S.; Michaud, P.; Soliman, D.; Ben Bacha, A. Purification and biochemical characterization of a new protease inhibitor from conyza dioscoridis with antimicrobial, antifungal and cytotoxic effects. Molecules 2020, 25, 5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.S.; Yin, L.J.; Jiang, S.T. Purification and characterization of the amylase from a small abalone Haliotis sieboldii. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.; Jung, W.K.; Mendis, E.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, S.K. A novel anticoagulant purified from fish protein hydrolysate inhibits factor XIIa and platelet aggregation. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Lin, D.; Gao, Y.; Wu, L.; Fu, J.; Galaa, K.; Lin, X.; Lin, L. Ultrasensitive off-on-off fluorescent nanosensor for protamine and trypsin detection based on inner-filter effect between N,S-CDs and gold nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirison, J.; Matsumiya, K.; Samoto, M.; Hidaka, H.; Kouno, M.; Matsumura, Y. Solubility of soy lipophilic proteins: Comparison with other soy protein fractions. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucinski, A.C.; Boyne, M.T.; Keire, D.A. Modern analytics for naturally derived complex drug substances: NMR and MS tests for protamine sulfate from chum salmon. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, L.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Bergia, R.; Dhital, S. Structural and thermal characterization of protein isolates from Australian lupin varieties as affected by processing conditions. Foods 2023, 12, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Takifugu obscurus | Takifugu rubripes | Takifugu bimaculatus | Takifugu flavidus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetrodotoxin content (μg/g) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Toxicity level | D | D | D | D |
| Items | Content | Items | Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients (%) | Crude protein | 17.47 ± 0.49 a | Amino acids (g/100 g) | Lysine (Lys) | 0.67 ± 0.01 c |
| Crude fat | 1.71 ± 0.12 c | ∑EAA | 2.34 | ||
| Crude ash | 1.80 ± 0.06 b | Aspartic acid (Asp **) | 0.63 ± 0.01 b | ||
| Moisture | 79.01 ± 0.45 c | Serine(Ser) | 0.34 ± 0.00 d | ||
| Minerals (mg/kg) | Calcium (Ca) | 42.63 ± 1.12 b | Glutamic acid (Glu **) | 0.90 ± 0.01 c | |
| Potassium (K) | 3336.67 ± 25.17 c | Glycine (Gly **) | 0.44 ± 0.00 c | ||
| Sodium (Na) | 652.67 ± 4.04 d | Alanine (Ala **) | 0.41 ± 0.00 d | ||
| Magnesium (Mg) | 150.09 ± 1.73 c | Cysteine (Cys) | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | ||
| Phosphorus (P) | 2660.00 ± 32.06 b | Tyrosine (Tyr) | 0.15 ± 0.00 b | ||
| Zinc (Zn) | 4.67 ± 0.21 d | Histidine (His) | 0.14 ± 0.00 c | ||
| Selenium (Se) | 0.18 ± 0.06 d | Arginine (Arg) | 0.60 ± 0.01 d | ||
| Amino Acids (g/100 g) | Threonine (Thr) | 0.33 ± 0.00 c | Proline (Pro) | 0.26 ± 0.00 c | |
| Valine (Val) | 0.34 ± 0.00 c | ∑NEAA | 3.88 | ||
| Methionine (Met) | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | ∑TAA | 6.21 | ||
| Isoleucine (Ile) | 0.20 ± 0.01 c | ∑FAA | 2.75 | ||
| Leucine (Leu) | 0.49 ± 0.01 c | ∑EAA/∑TAA | 37.57% | ||
| Phenylalanine (Phe) | 0.22 ± 0.01 c | ||||
| Scoring Pattern | Thr | Val | Ile | Leu | Phe + Tyr | Met + Cys | Lys | Total | EAAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAS | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.70 | 2.76 | 0.27 |
| CS | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 2.11 |
| Sephadex G50 Gel Chromatography | CM Sepharose Fast Flow Ion Exchange Chromatography | Sephadex G25 Gel Chromatography | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-I | S-II | S-III | FF-I | FF-II | FF-III | G-I | G-II | |
| Sakaguchi reaction | +++ | − | − | − | + | +++ | +++ | − |
| Antibacterial activity | +++ | − | − | − | − | ++ | +++ | − |
| Amino Acid Species | Crude Protamine of Pufferfish (CPP) | Purified Protamine of Pufferfish (PPP) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (g/100 g) | Percentage (%) | Content (g/100 g) | Percentage (%) | ||
| Aspartic acid | Asp | 2.10 ± 0.02 | 4.54 ± 0.04 | 1.78 ± 0.02 | 3.85 ± 0.05 |
| Threonine | Thr | 2.55 ± 0.02 | 5.52 ± 0.05 | 1.79 ± 0.01 | 3.86 ± 0.01 |
| Serine | Ser | 2.71 ± 0.02 | 5.87 ± 0.05 | 2.68 ± 0.01 | 5.79 ± 0.03 |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | 1.88 ± 0.02 | 4.07 ± 0.04 | 1.08 ± 0.02 | 2.33 ± 0.03 |
| Glycine | Gly | 3.80 ± 0.02 | 8.21 ± 0.04 | 2.99 ± 0.01 | 6.46 ± 0.02 |
| Alanine | Ala | 6.01 ± 0.04 | 13.00 ± 0.05 | 6.13 ± 0.04 | 13.25 ± 0.10 |
| Cysteine | Cys | − | − | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.04 |
| Viline | Val | 2.80 ± 0.02 | 6.06 ± 0.03 | 2.42 ± 0.02 | 5.22 ± 0.03 |
| Methionine | Met | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 1.17 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.03 |
| Isoleucine | IIe | 1.37 ± 0.01 | 2.95 ± 0.02 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 1.85 ± 0.03 |
| Leucine | Leu | 2.65 ± 0.02 | 5.72 ± 0.03 | 1.73 ± 0.02 | 3.74 ± 0.04 |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 2.15 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.01 |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 1.81 ± 0.01 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 2.39 ± 0.05 |
| Lysine | Lys * | 6.36 ± 0.01 | 13.75 ± 0.02 | 12.5 ± 0.01 | 27.02 ± 0.19 |
| Hlstidine | His * | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 1.53 ± 0.02 |
| Argnine | Arg * | 9.18 ± 0.01 | 19.85 ± 0.03 | 17.0 ± 0.06 | 36.90 ± 0.17 |
| Proline | Pro | 2.32 ± 0.03 | 5.03 ± 0.06 | 1.53 ± 0.02 | 3.31 ± 0.05 |
| Secondary Structure | A-Helix | Β-Sheet | Β-Turn | Random Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage (%) | 0.00 | 51.40 | 10.40 | 38.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Qiao, K.; Li, S.; Liu, Z. Isolation and Purification of Protamine from the Cultured Takifugu flavidus and Its Physicochemical Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010263
Liu S, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Su Y, Chen B, Wang Y, Xu M, Qiao K, Li S, Liu Z. Isolation and Purification of Protamine from the Cultured Takifugu flavidus and Its Physicochemical Properties. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010263
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuji, Yue Zhang, Yihui Chen, Yongchang Su, Bei Chen, Yin Wang, Min Xu, Kun Qiao, Shuigen Li, and Zhiyu Liu. 2024. "Isolation and Purification of Protamine from the Cultured Takifugu flavidus and Its Physicochemical Properties" Molecules 29, no. 1: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010263
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Su, Y., Chen, B., Wang, Y., Xu, M., Qiao, K., Li, S., & Liu, Z. (2024). Isolation and Purification of Protamine from the Cultured Takifugu flavidus and Its Physicochemical Properties. Molecules, 29(1), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010263






