Performance of Rod-Shaped Ce Metal–Organic Frameworks for Defluoridation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
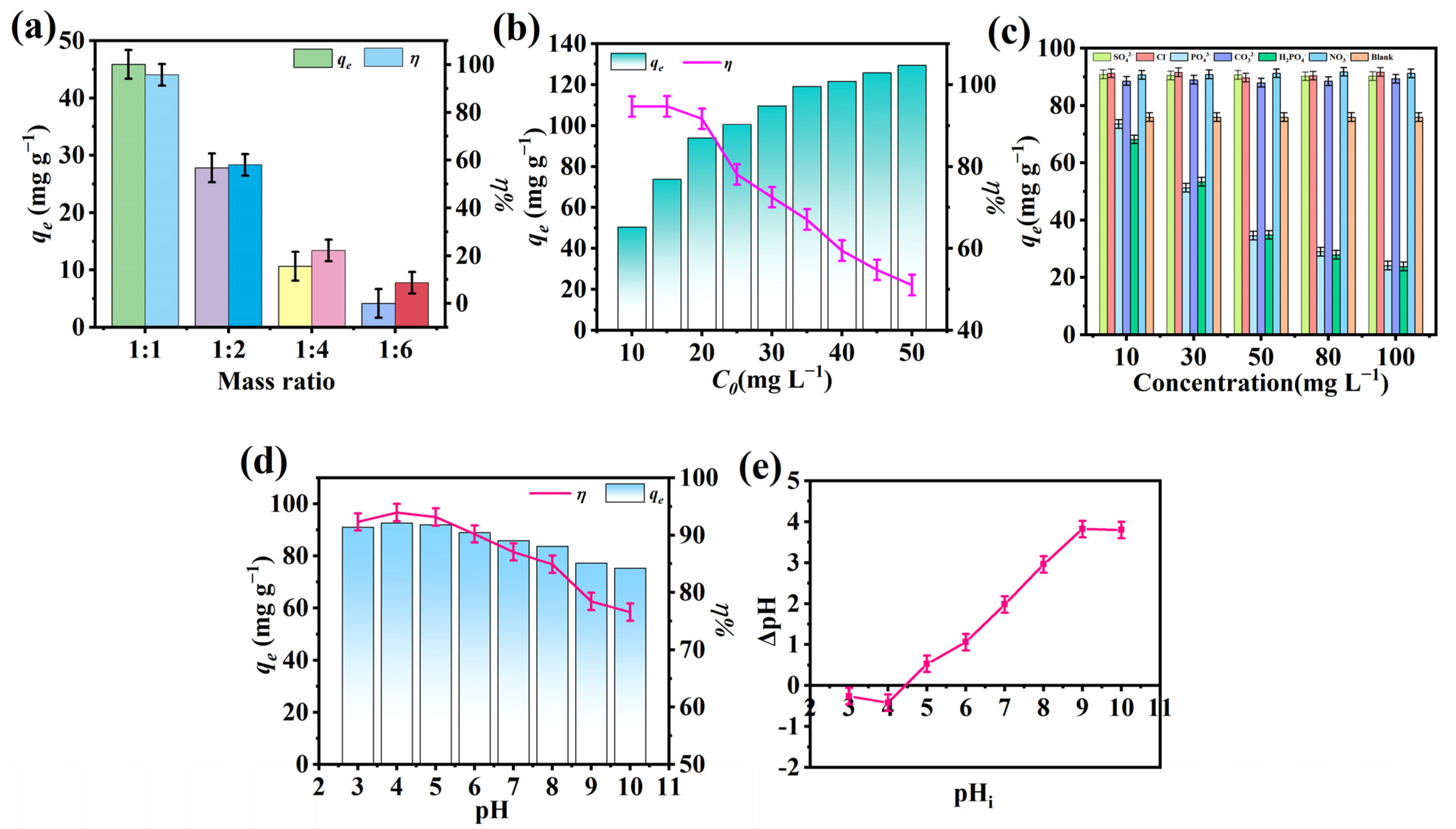
2.1. Influence of the Molar Ratio of Precursors
2.2. Influence of Initial F− Concentration
2.3. Effect of Co-Existing Ions
2.4. Effect of pH
2.5. Characterization
2.5.1. XRD
2.5.2. FTIR
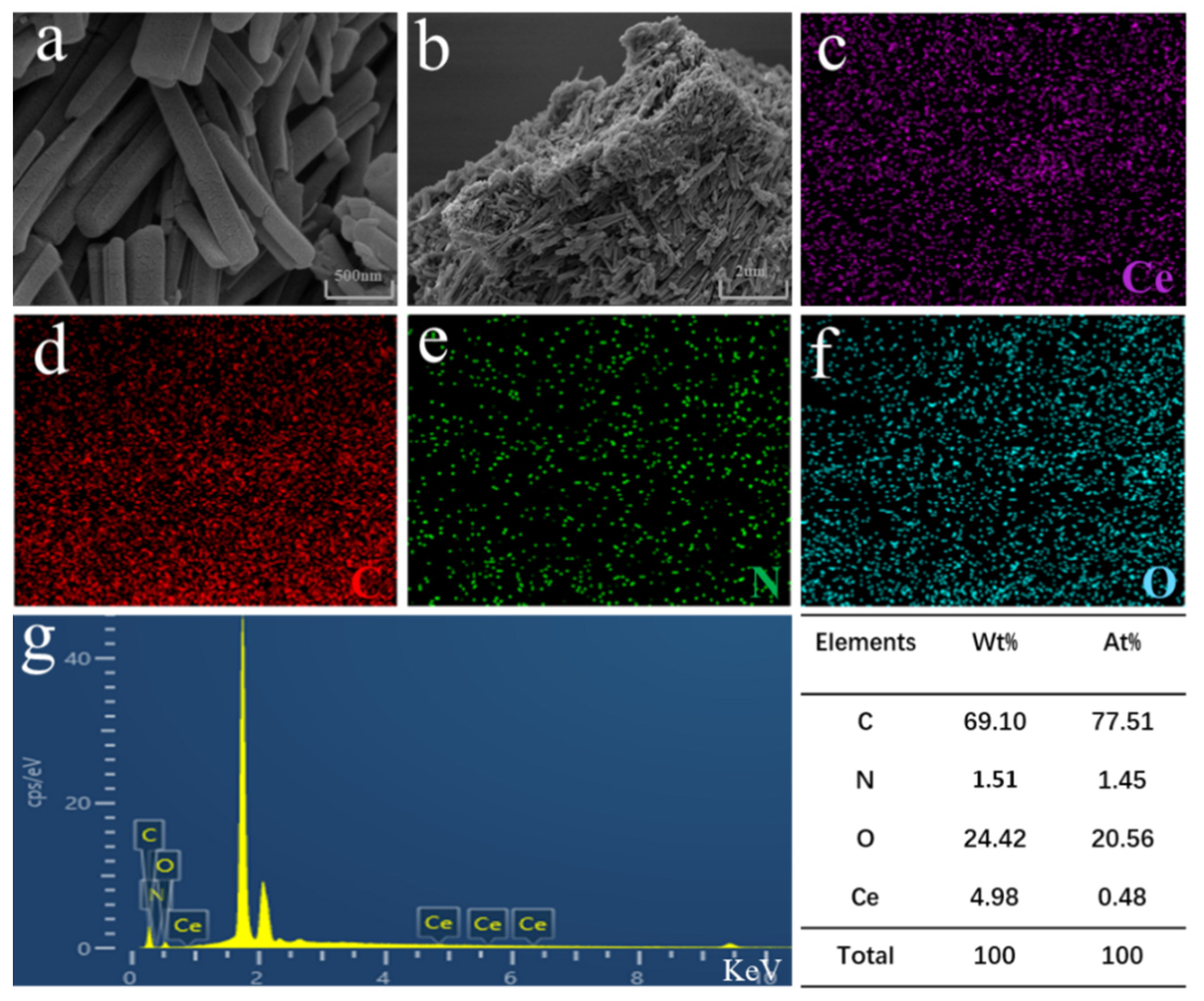
2.5.3. SEM and Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) Analyses
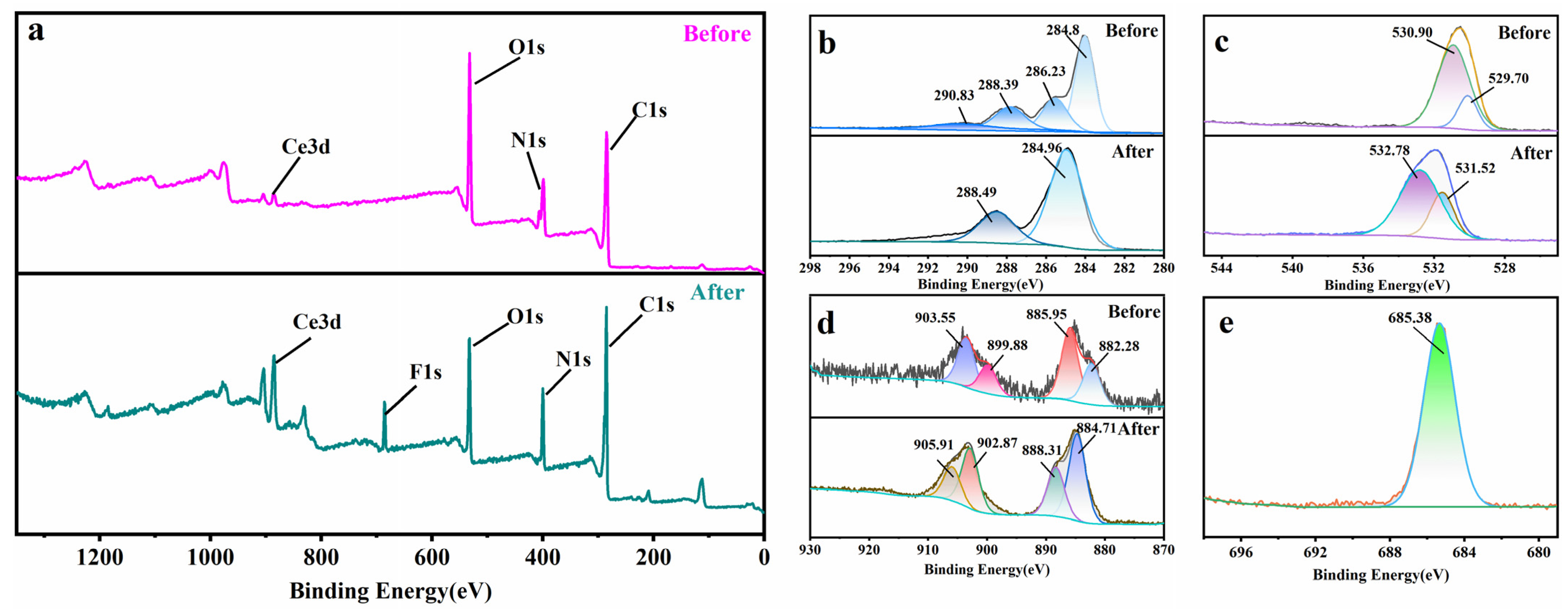
2.5.4. XPS
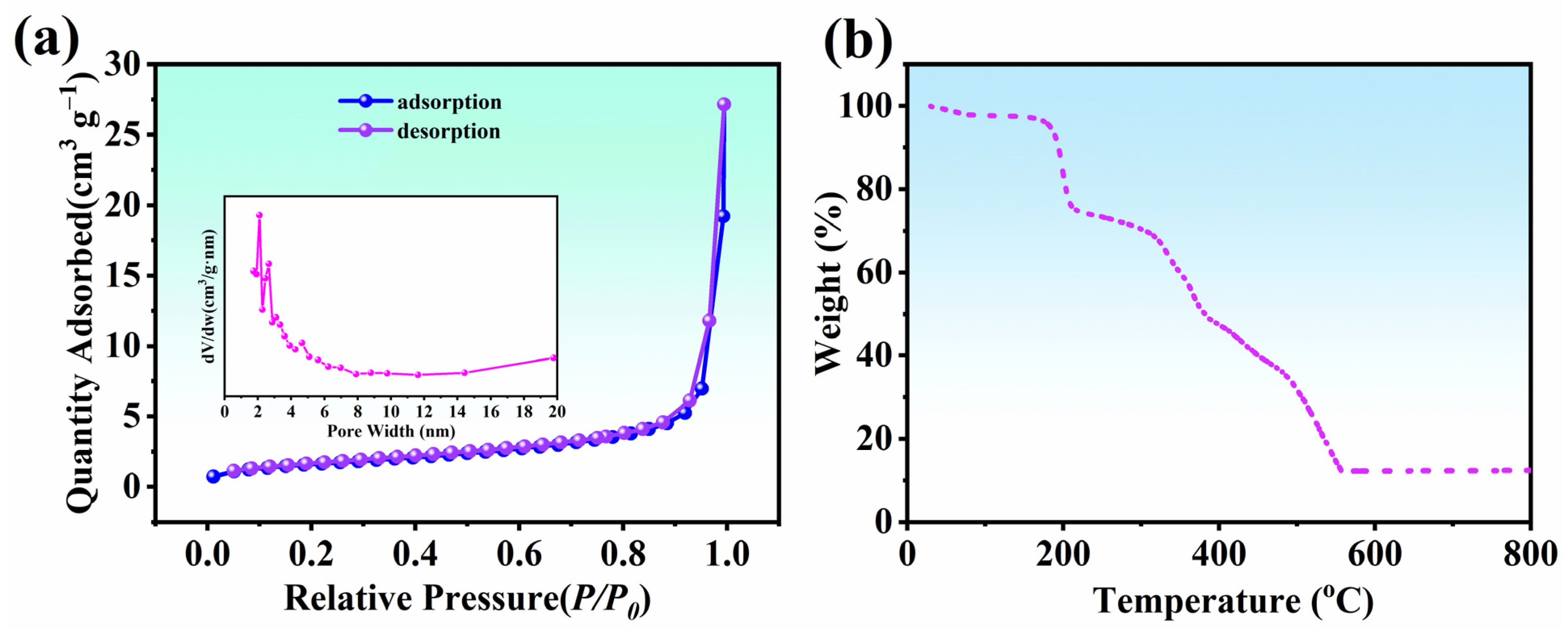
2.5.5. N2 Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
2.5.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.7. Thermodynamic and Isothermal Research on Adsorption
2.8. Field Application
2.9. Performance Comparation of Ce-Based Adsorbents for Fluoride Removal
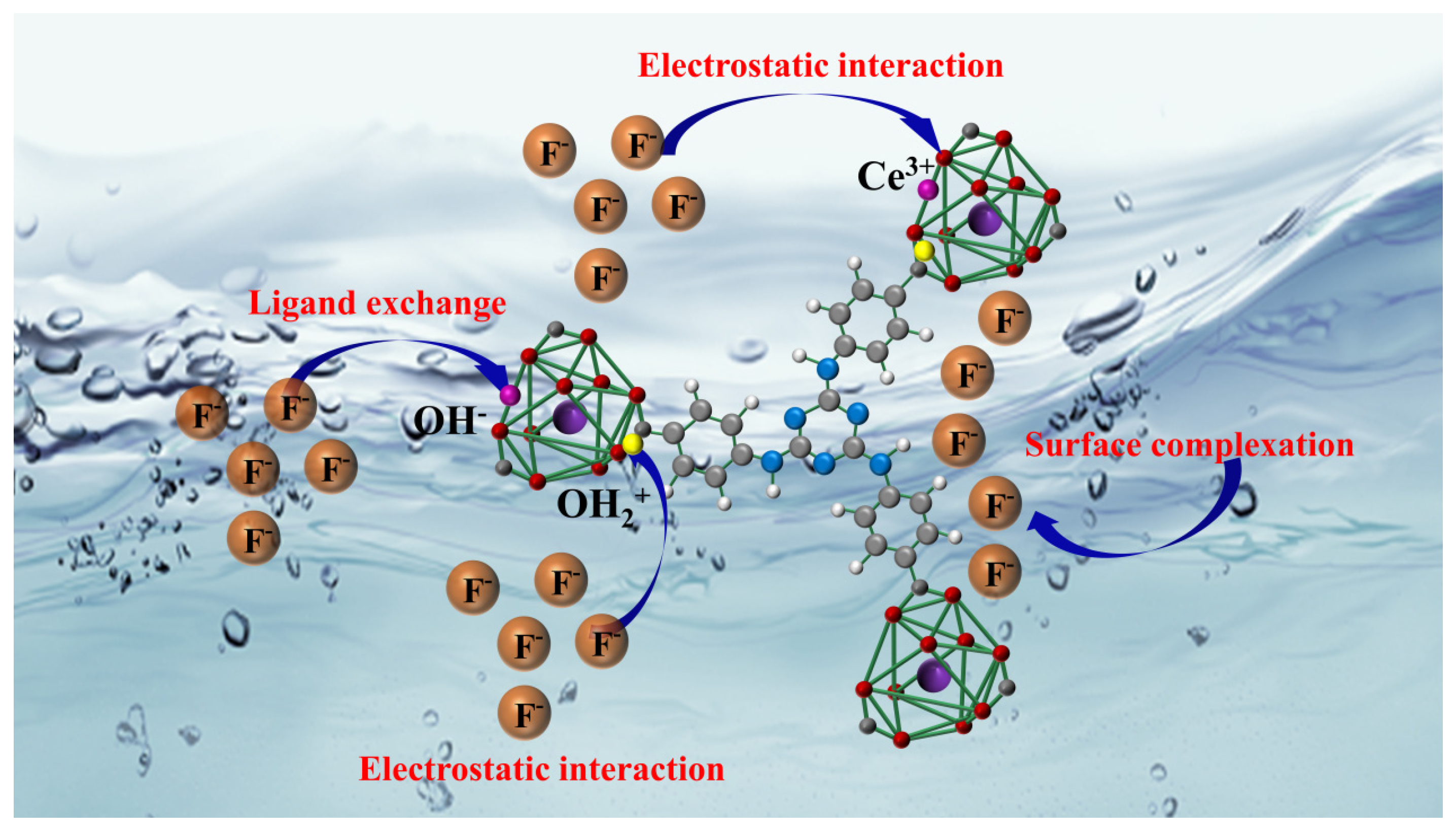
2.10. Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Ce-H3TATAB-MOFs
3.3. Material Characterization
3.4. Batch Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ghosh, S.; Malloum, A.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Ahmadi, S.; Dehghani, M.H.; Othmani, A.; Gökkuş, Ö.; Mubarak, N.M. New generation adsorbents for the removal of fluoride from water and wastewater: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 118257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Qian, H.; Qu, W.; Zheng, L.; Feng, W.; Ren, W. Fluoride Occurrence and Human Health Risk in Drinking Water Wells from Southern Edge of Chinese Loess Plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzu, M.; Tanda, A.; Cappai, C.; Roggero, P.P.; Seddaiu, G. Impacts of soil and water fluoride contamination on the safety and productivity of food and feed crops: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husejnovic, M.S.; Turkic, A.; Halilcevic, A.; Hadzic, N.; Mahmutbegovic, H. Deterministic and probabilistic human health risk assessment for fluorides in drinking groundwater from Lukavac, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2022, 37, e2022016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggeborn, L.; Ohman, M. The Effects of Fluoride in Drinking Water. J. Polit. Econ. 2021, 129, 465–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štepec, D.; Ponikvar-Svet, M. Fluoride in Human Health and Nutrition. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, F. Indoor air quality and health: Empirical evidence from fluoride pollution in China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 63, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bolisetty, S.; Cao, Y.; Handschin, S.; Adamcik, J.; Peng, Q.; Mezzenga, R. Selective and Efficient Removal of Fluoride from Water: In Situ Engineered Amyloid Fibril/ZrO2 Hybrid Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 6012–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Agyeman, I.; Shen, J.; Schafer, A.I. Renewable energy powered membrane technology: Impact of pH and ionic strength on fluoride and natural organic matter removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Zhang, G. Efficient removal of fluoride by hierarchical Ce–Fe bimetal oxides adsorbent: Thermodynamics, kinetics and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossien Saghi, M.; Chabot, B.; Rezania, S.; Sillanpää, M.; Akbar Mohammadi, A.; Shams, M.; Alahabadi, A. Water-stable zirconium and iron-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as fluoride scavengers in aqueous medium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, X.; Pan, B. Fluoride uptake by three lanthanum based nanomaterials: Behavior and mechanism dependent upon lanthanum species. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, A.; Hettithanthri, O.; Sandanayake, S.; Mahatantila, K.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Vithanage, M. Essence of hydroxyapatite in defluoridation of drinking water: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.B.; Yang, R.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y. Removal of fluoride from water using aluminum hydroxide-loaded zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsido, A.W.; Kumar, A.; Tekola, B.; Mogessie, B.; Alemayehu, E. Evaluation of bentonite clay in modified and unmodified forms to remove fluoride from water. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 2661–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q.; Xie, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, D.; He, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, N.; Ge, C. Removal of fluoride using platanus acerifoli leaves biochar—An efficient and low-cost application in wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, I.; Rizwan, M.; Ullman, J.L.; Haroon, H.; Qayyum, A.; Ahmed, N.; Elesawy, B.H.; Askary, A.E.; Gharib, A.F.; Ismail, K.A. Lignocellulosic Based Biochar Adsorbents for the Removal of Fluoride and Arsenic from Aqueous Solution: Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling. Polymers 2022, 14, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhang, K.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Review of fluoride removal from water environment by adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, L.H.; Meledina, M.; Turner, S.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Zhang, K.; Rodriguez-Albelo, L.M.; Masala, A.; Bordiga, S.; Jiang, J.; Navarro, J.A.; et al. 1D-2D-3D Transformation Synthesis of Hierarchical Metal-Organic Framework Adsorbent for Multicomponent Alkane Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Bon, V.; Senkovska, I.; Lee, H.C.; Kaskel, S. Four-dimensional metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drout, R.J.; Robison, L.; Chen, Z.; Islamoglu, T.; Farha, O.K. Zirconium Metal–Organic Frameworks for Organic Pollutant Adsorption. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, S.; Kumar, R.; Deep, A.; Kurade, M.B.; Ji, S.-W.; Jeon, B.-H. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of emerging contaminants from aquatic environments. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials as chemical sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Luo, J.; Xiang, K.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H. High-performance monoclinic WO3 nanospheres with the novel NH4+ diffusion behaviors for aqueous ammonium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. A defect-free MOF composite membrane prepared via in-situ binder-controlled restrained second-growth method for energy storage device. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 35, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Peng, S.; Ma, C.; Duan, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; et al. A poly(amidoxime)-modified MOF macroporous membrane for high-efficient uranium extraction from seawater. e-Polymers 2022, 22, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Gao, M.; Huang, X.; Xu, D. Recent Advances and Applications of Magnetic Metal-Organic Frameworks in Adsorption and Enrichment Removal of Food and Environmental Pollutants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz Khan, M.; Khalid, M.; Shahid, M. What triggers dye adsorption by metal organic frameworks? The current perspectives. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 1575–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Song, J.; Han, X.; Wen, Q.; Yang, W.; Pan, W.; Jian, S.; Jiang, S. Fabrication of Ce-La-MOFs for defluoridation in aquatic systems: A kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanisms study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Lai, B.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L. The enhanced removal of phosphate by structural defects and competitive fluoride adsorption on cerium-based adsorbent. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaseelan, A.; Viswanathan, N. Design of Amino-Functionalized Benzene-1,4-Dicarboxylic Acid-Fabricated Lanthanum-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Defluoridation of Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 5328–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, G.A.; Saghi, M.H.; Anastopoulos, I.; Javid, A.; Roudbari, A.; Talebi, S.S.; Ghadiri, S.K.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Shams, M. Aminated graphitic carbon derived from corn stover biomass as adsorbent against antibiotic tetracycline: Optimizing the physicochemical parameters. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 313, 113523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Han, R. Preparation of Novel Magnetic Microspheres with the La and Ce-Bimetal Oxide Shell for Excellent Adsorption of Fluoride and Phosphate from Solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 3641–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, K.; Viswanathan, N. A facile synthesis of metal ion-imprinted graphene oxide/alginate hybrid biopolymeric beads for enhanced fluoride sorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 75905–75915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Ding, W.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, M. Fluoride Removal by Lanthanum Alginate Bead: Adsorbent Characterization and Adsorption Mechanism. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 19, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaseelan, A.; Kumar, I.A.; Naushad, M.; Viswanathan, N. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite embedded cerium-organic frameworks for fluoride capture from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and Application of Granular Activated Carbon from Biomass Waste Materials for Water Treatment: A Review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 299–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, L.; An, X.; Wan, G.; Zhu, W.; Luo, Y. Enhanced fluoride removal from water by rare earth (La and Ce) modified alumina: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Deng, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, G.; Huang, J. Preparation of Al-Ce hybrid adsorbent and its application for defluoridation of drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xing, Y.H.; Bai, F.Y. A Uranyl-Organic Framework Featuring Two-Dimensional Graphene-like Layered Topology for Efficient Iodine and Dyes Capture. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 6866–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, L.-X.; Xing, Y.-H.; Bai, F.-Y. A Double-Walled Thorium-Based Metal–Organic Framework as a Promising Dual-Function Absorbent for Efficiently Capturing Iodine and Dyes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 5686–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaseelan, A.; Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Viswanathan, N. Fabrication of amino functionalized benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid facilitated cerium based metal organic frameworks for efficient removal of fluoride from water environment. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, B.; Song, J.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Zhan, W.; Liu, D. Defluoridation of water using calcined magnesia/pullulan composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Bai, Y. Efficient oxidation of o-xylene over CeO2 catalyst prepared from a Ce-MOF template: The promotion of K+ embedding substitution. Mol. Catal. 2017, 436, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, M. In situ preparation of palladium nanoclusters in cerium metal-organic frameworks Ce-MOF-808, Ce-UiO-66 and Ce-BTC as nanoreactors for room temperature Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 312, 110783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Q.; Li, G.Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, T.L.; Bu, X.H. A Water-Stable Luminescent Zn-II Metal-Organic Framework as Chemosensor for High-Efficiency Detection of Cr-VI-Anions (Cr2O72− and CrO42−) in Aqueous Solution. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 3192–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Chen, N.; Dai, w.; Zheng, M.; Wang, M.; Qian, Y.; Xu, P. Preparation and adsorption properties of aminated magnetic carbon nanotubes. J. For. Eng. 2022, 7, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, S.; Dechnik, J.; Janiak, C.; De, S. Aluminium fumarate metal-organic framework: A super adsorbent for fluoride from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 303, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Zha, Y.; Gao, H. Study on Congo red adsorption property of activated carben from bamboo leaf residue. J. For. Eng. 2022, 7, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Obey, G.; Adelaide, M.; Ramaraj, R. Biochar derived from non-customized matamba fruit shell as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, M.; Jin, B. Adsorption characteristics, isotherm, kinetics, and diffusion of modified natural bentonite for removing diazo dye. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Bhunia, A.; Jana, P.P.; Dey, S.; Mollmer, J.; Janiak, C.; Nayek, H.P. Microporous La-metal-organic framework (MOF) with large surface area. Chemistry 2015, 21, 2789–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yan, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W. Effects of the washing treatment using diluted acid and base on the structure of biochar and its adsorption performance on tetracycline. J. For. Eng. 2021, 6, 87–93. [Google Scholar]

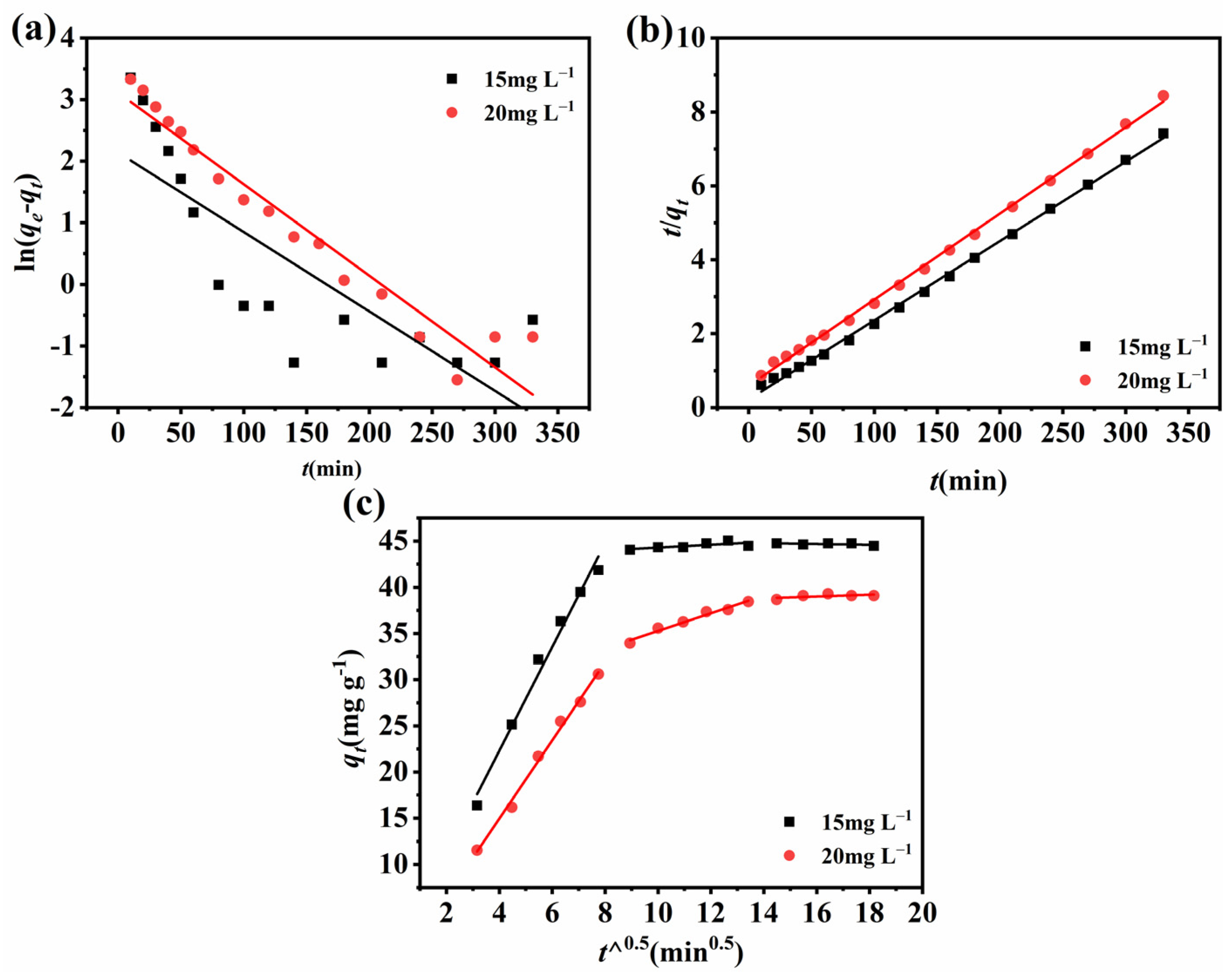

| Models | C0 (mg L−1) | K | qe | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| quasi-first order | 15 | 0.0129 | 8.5071 | 0.6754 |
| 20 | 0.0149 | 22.5042 | 0.9399 | |
| quasi-second order | 15 | 0.0021 | 46.5100 | 0.9983 |
| 20 | 0.0009 | 42.9184 | 0.9985 |
| C0 (mg L−1) | Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | y = −0.1611 + 5.615x | 0.9843 |
| y = 42.7577 + 0.1544x | 0.5380 | |
| y = 45.4148 − 0.0449x | 0.2672 | |
| 20 | y = −1.9843 + 4. 2339x | 0.9941 |
| y = 25.7361 + 0. 9544x | 0.9729 | |
| y = 37.4474 + 0. 0973x | 0.3633 |
| T (K) | ΔGo (kJ mol−1) | ΔHo (kJ mol−1) | ΔSo (J (mol·K)−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | −9.5039 | 48.0881 | 193.2618 |
| 308 | −11.4365 | ||
| 318 | −13.3692 |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | Kf (L g−1) | n | R2 | |
| 298 | 101.6260 | 0.9128 | 0.9950 | 72.1855 | 6.0168 | 0.8494 |
| 308 | 115.7407 | 0.8105 | 0.9924 | 66.3315 | 6.0683 | 0.8205 |
| 318 | 129.7017 | 1.7058 | 0.9974 | 60.7813 | 6.5134 | 0.6650 |
| Water Quality Parameters | Before Adsorption | After Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| F– (mg L–1) | 11.3 | 0.56 |
| pH | 3.67 | 3.95 |
| COD (mg L–1) | 125 | 74 |
| Adsorbents | pH | qm (mg g–1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAP-Ce-BTC-MOFs | 6 | 4.46 | [34] |
| Ce-ABDC | 6–7 | 4.88 | [38] |
| Ce-BDC | 6–7 | 4.91 | [38] |
| Ce-UIO-66 MOF | 3 | 66.1 | [44] |
| Ce-bpdc | 7 | 45.5 | [45] |
| Ce-AlOOH | 3 | 62.77 | [46] |
| Ce@BTC MOFs | 7.49 | 4.94 | [47] |
| Ce-BTC | 3–9 | 70.7 | [48] |
| Ce-fum | 4 | 78.94 | [49] |
| Ce-H3TATAB-MOFs | 4 | 129.7 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Yang, W.; Han, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, C.; Pan, W.; Jian, S.; Hu, J. Performance of Rod-Shaped Ce Metal–Organic Frameworks for Defluoridation. Molecules 2023, 28, 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083492
Song J, Yang W, Han X, Jiang S, Zhang C, Pan W, Jian S, Hu J. Performance of Rod-Shaped Ce Metal–Organic Frameworks for Defluoridation. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083492
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jiangyan, Weisen Yang, Xiaoshuai Han, Shaohua Jiang, Chunmei Zhang, Wenbin Pan, Shaoju Jian, and Jiapeng Hu. 2023. "Performance of Rod-Shaped Ce Metal–Organic Frameworks for Defluoridation" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083492
APA StyleSong, J., Yang, W., Han, X., Jiang, S., Zhang, C., Pan, W., Jian, S., & Hu, J. (2023). Performance of Rod-Shaped Ce Metal–Organic Frameworks for Defluoridation. Molecules, 28(8), 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083492








