Fast Detection of Heavy Metal Content in Fritillaria thunbergii by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy with PSO-BP and SSA-BP Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Determination of the Best Preprocessing Algorithm
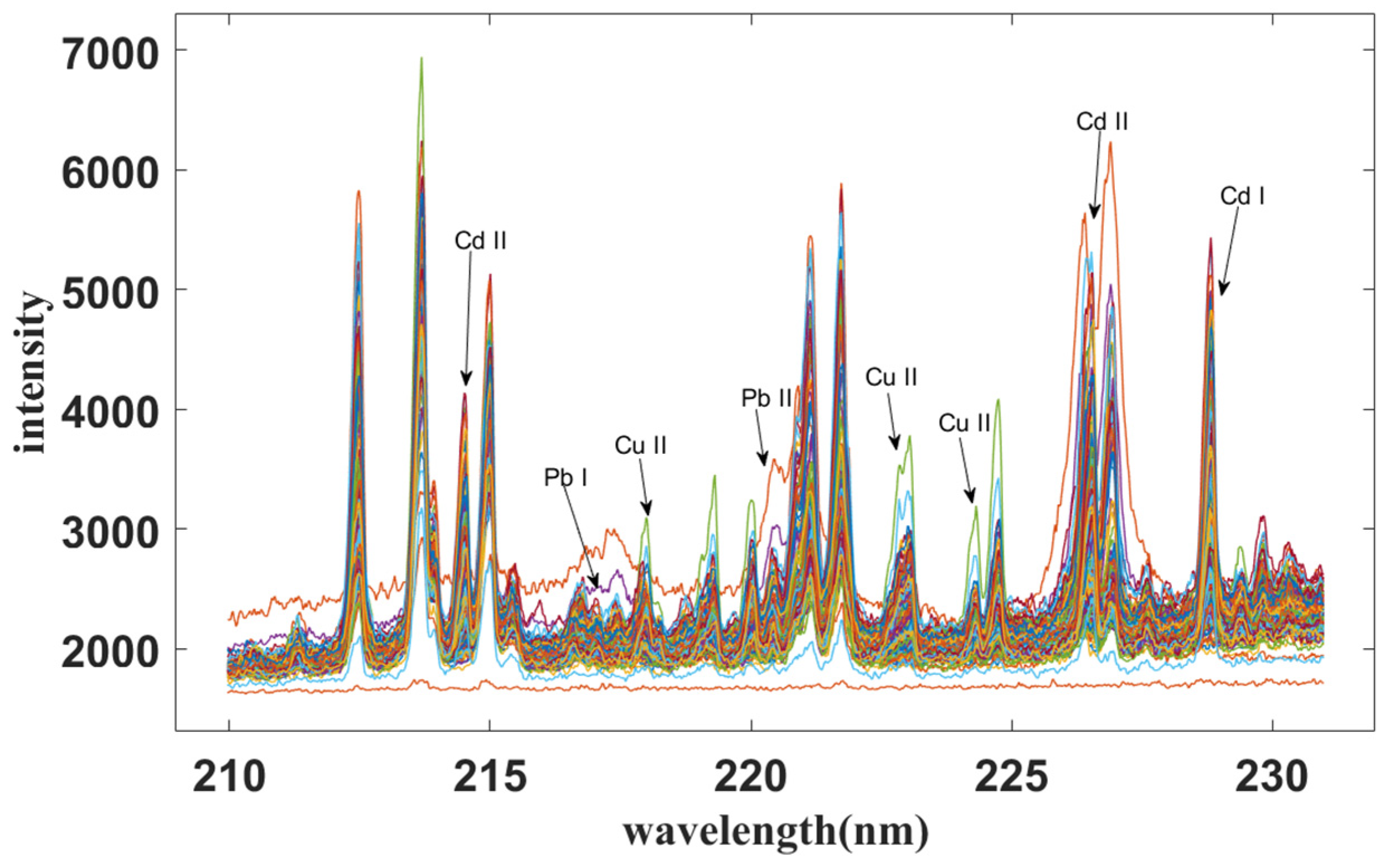
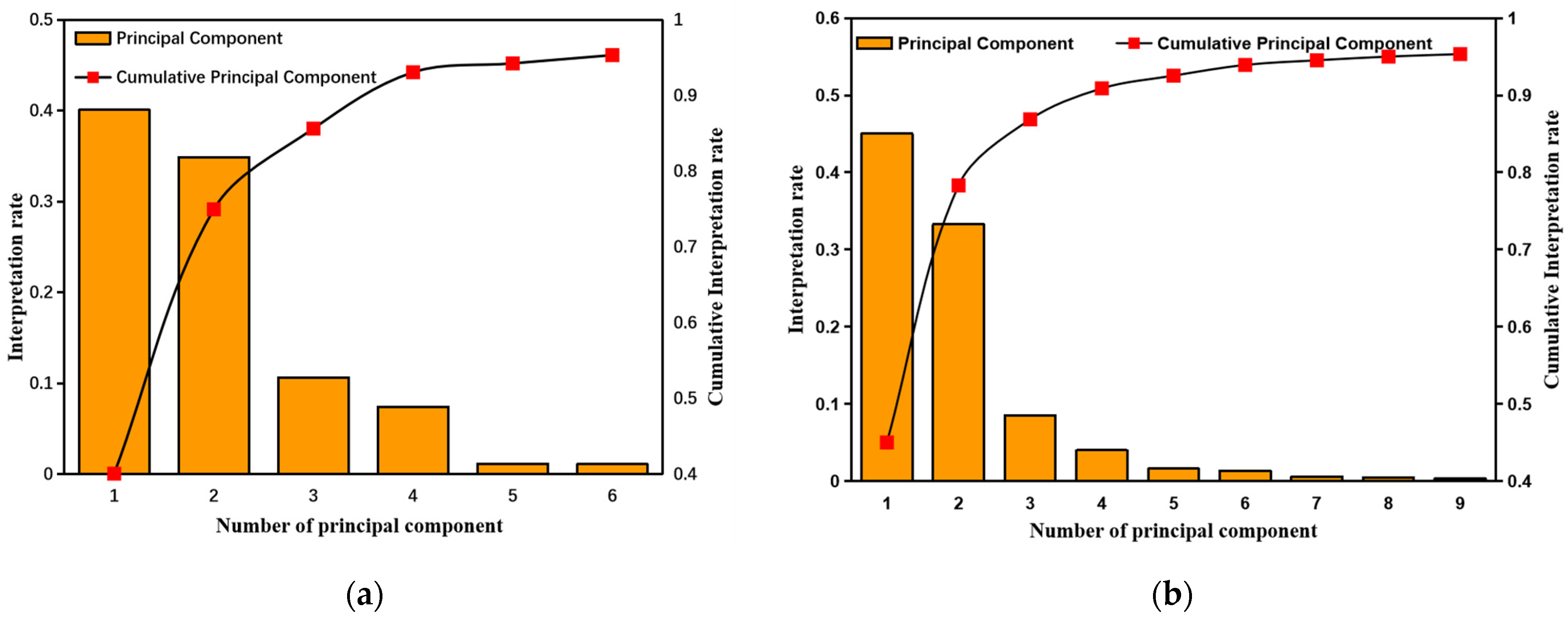
2.2. Sensitive Variable Selection
2.3. Model Estimations and Comparisons
2.3.1. BPNN Model Prediction Results
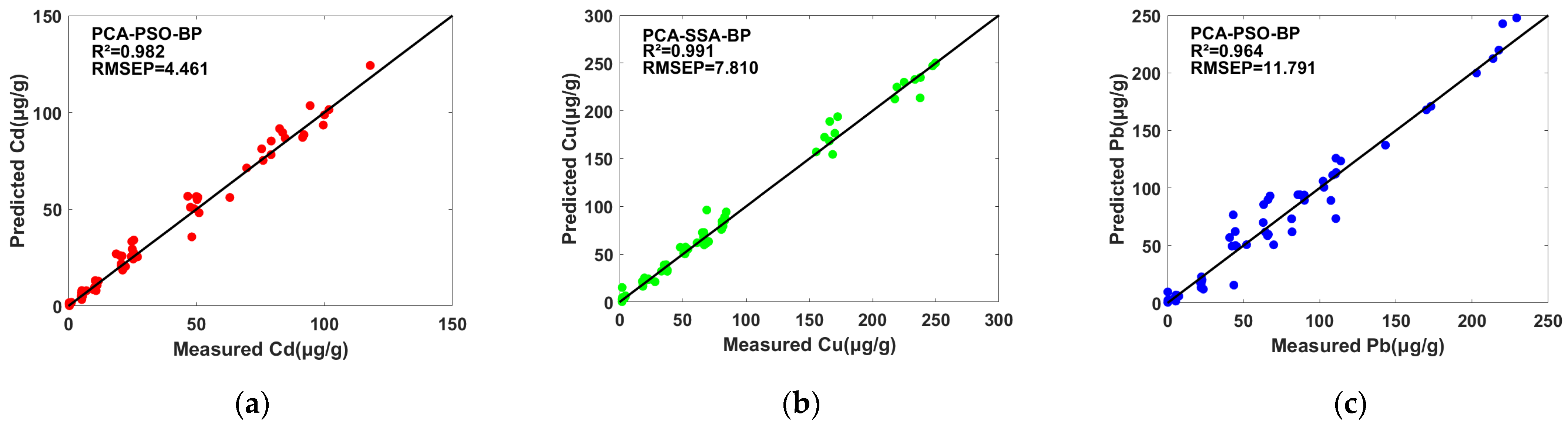
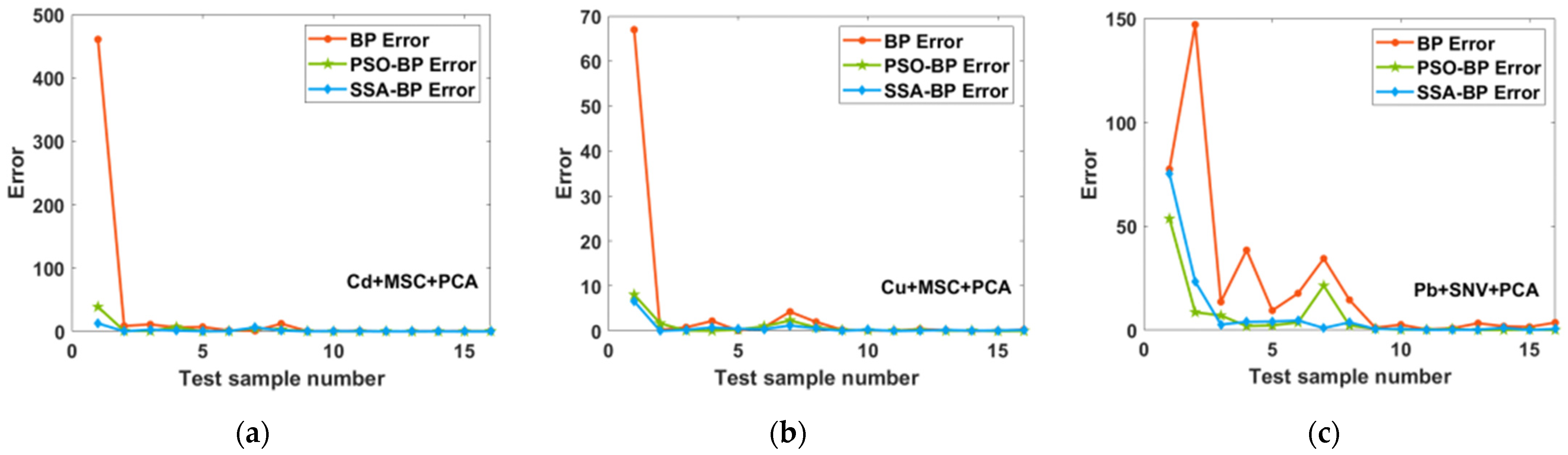
2.3.2. PSO-BP and SSA-BP Models’ Prediction Results
2.3.3. Comparison with a Conventional Method (PLSR)
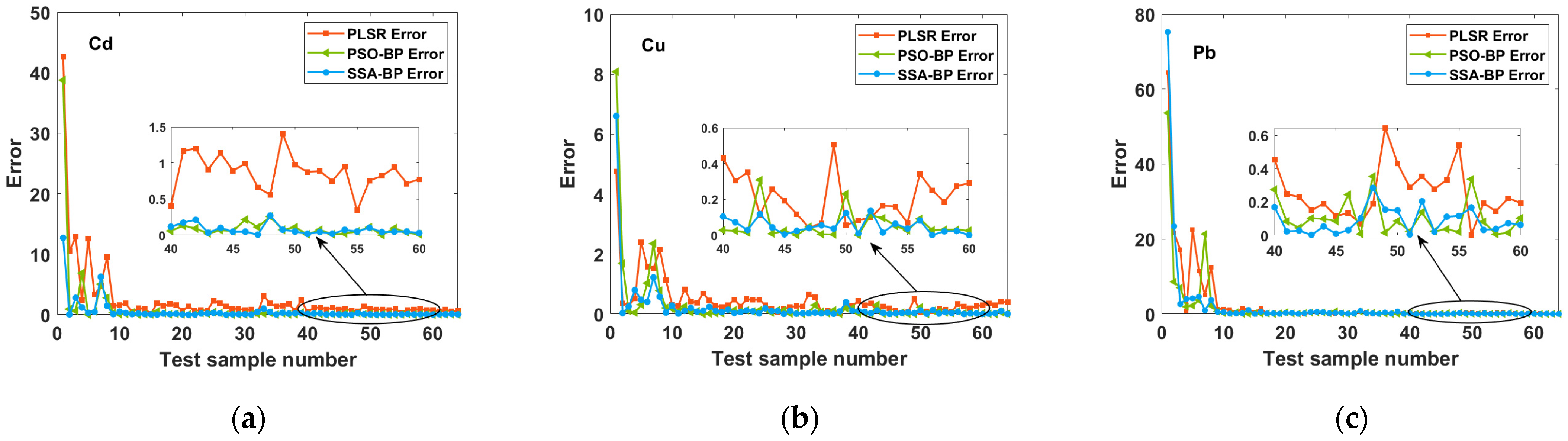
2.3.4. Comparison of PSO-BP and SSA-BP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Fritillaria thunbergii Material and Sampling
3.2. LIBS Experimental
3.3. Reference Method for Heavy Metal Content Determination
3.4. Sample Division and Spectral Preprocessing
3.5. Sensitive Variable Selection
3.6. Discriminant Analysis Method
3.6.1. BPNN
3.6.2. PSO-BP
3.6.3. SSA-BP
3.7. Model Evaluation and Software
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wu, F.; Tian, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X. Efficacy, chemical composition, and pharmacological effects of herbal drugs derived from Fritillaria cirrhosa D. Don and Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 985935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.C.; Gu, X.J.; Xiao, X.G. Phytochemical and biological research of Fritillaria medicine resources. Pharmacol. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.T. Review: Drug therapy in Chinese traditional medicine. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiner, M.; Cindrić, I.J. Review–trace determination of potentially toxic elements in (medicinal) plant materials. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1550–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.C.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, H.H. Metabolic profiling investigation of Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.W.; Omenetto, N. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part I: Review of basic diagnostics and plasma-particle interactions: Still-challenging issues within the analytical plasma community. Appl. Spectrosc. 2010, 64, 335–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALOthman, Z.A.; Habila, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Solid phase extraction of Cd (II), Pb (II), Zn (II) and Ni (II) from food samples using multiwalled carbon nanotubes impregnated with 4-(2-thiazolylazo) resorcinol. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.L.; Ciocan, A.C.; Borisov, O.V.; Russo, R.E. Laser ablation processes investigated using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP–AES). Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 127, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skordas, K.; Papastergios, G.; Filippidis, A. Major and trace element contents in apples from a cultivated area of central Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8465–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ye, L.; Peng, J.; Song, K.; Shen, T.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. Fast detection of copper content in rice by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with uni- and multivariate analysis. Sensors 2018, 18, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Saleem, S. Online in situ detection and rapid distinguishing of saffron. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 032020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Rao, H.; Huang, L. Effect of Cu stress on minerals in rice by analyzing husk based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B 2020, 126, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Altuwiriqi, R.; Gondal, M.A.; Aldakheel, R.K.; Alotaibi, H.F. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of human nails to find correlation between nutri-ents and vitamin D deficiency using LIBS and ICP–AES. Talanta 2018, 185, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, E.M.; Imam, H.; Song, H. Detection of heavy metals using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technique for both horse hair and goat hair. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, A.Y.; Sun, X.C.; Lin, C.X. Trend in research on characterization, environmental impacts and treatment of oily sludge: A systematic review. Molecules 2022, 27, 7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, Z.A.; Ahmed, N.; Ahmed, R.; Liaqat, U.; Baig, M.A. Elemental composition analysis of granite rocks using LIBS and LA-TOF-MS. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4985–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedarnig, J.D.; Trautner, S.; Grünberger, S.; Giannakaris, N.; Eschlböck-Fuchs, S.; Hofstadler, J. Review of element analysis of industrial materials by in-line laser—induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Wang, Y.; Cui, W.; Zou, B.; Zou, Z.; Tu, Y. A transferable spectroscopic diagnosis model for predicting arsenic contamination in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.W.; Fu, H.B.; Hou, Z.Y.; Wang, H.D.; Ni, Z.B.; Dong, F.Z. Calibration curve and support vector regression methods applied for quantification of cement raw meal using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 034003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G. Integrating a hybrid back propagation neural network and particle swarm optimization for estimating soil heavy metal contents using hyperspectral data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Zhou, D.; Luo, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Lu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Hyperspectral prediction model of metal content in soil based on the genetic ant colony algorithm. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shen, R.; Chen, Y.; Wan, Q.; Shi, T.; Wang, J.; Wan, Y.; Hong, Y.; Li, X. Estimating heavy metal concentrations in suburban soils with reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 2019, 336, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, B.F.; Feng, M.H.; Chen, K.N.; Pan, J.Z. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter released from biochar at different py-rolysis temperatures. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 2505. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad, E.T.; Armaghani, D.J.; Momeni, E. Rock strength estimation: A PSO-based BP approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.K.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Hou, T. The SSA-BP-based potential threat prediction for aerial tar-get considering commander emotion. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, T.Y.; Bai, D. BP neural network improved by sparrow search algorithm in predicting debonding strain of FRP-strengthened RC beams. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9979028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Meng, X.C.; Zhu, L.Q. Overlapping spectral analysis based on genetic algorithms and BP neural net-works. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 2066. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Wu, Q.; Liao, W.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Adaptive droop-based hierarchical optimal voltage control scheme for VSC-HVDC connected offshore wind farm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2021, 17, 8165–8176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Q.; Zhou, L.; Gao, P.Q.; Yang, B.; Han, Y.M.; Lian, C. Short-term power generation forecasting of a photovoltaic plant based on PSO-BP and GA-BP neural networks. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 824691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X. The backpropagation artificial neural network based on elite particle swam optimization algorithm for stochastic linear bilevel programming problem. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1626182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Chen, Q.R.; Wang, X.G. Comparative study of several new swarm intelligence optimization algorithms. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2020, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Peng, L.; Ji, Z.; Zheng, S.; Tian, Z.; Geng, S. Research on substation project cost prediction based on sparrow search algorithm optimized BP neural net-work. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Preprocessing | Cd | Cu | Pb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rcv2 | RMSECV (mg/kg) | Rcv2 | RMSECV (mg/kg) | Rcv2 | RMSECV (mg/kg) | |
| None | 0.932 | 8.478 | 0.943 | 18.021 | 0.818 | 25.134 |
| SNV | 0.945 | 7.641 | 0.974 | 12.166 | 0.883 | 20.370 |
| MSC | 0.950 | 7.294 | 0.978 | 10.951 | 0.872 | 20.698 |
| WT | 0.937 | 8.205 | 0.942 | 17.970 | 0.823 | 24.763 |
| SG | 0.934 | 8.393 | 0.938 | 18.485 | 0.809 | 25.615 |
| Elements | Models | Number of Latent Variables | Calibration | Prediction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc2 | RMSEC (mg/kg) | Rp2 | RMSEP (mg/kg) | RPD | |||
| Cd | CARS-BP | 104 | 0.975 | 5.307 | 0.914 | 9.743 | 3.17 |
| SPA-BP | 4 | 0.968 | 5.944 | 0.968 | 5.951 | 5.74 | |
| PCA-BP | 6 | 0.978 | 4.902 | 0.743 | 16.899 | 2.30 | |
| Cu | CARS-BP | 134 | 0.983 | 10.598 | 0.650 | 47.917 | 2.05 |
| SPA-BP | 5 | 0.960 | 16.136 | 0.943 | 19.367 | 4.27 | |
| PCA-BP | 6 | 0.981 | 11.064 | 0.931 | 21.311 | 3.84 | |
| Pb | CARS-BP | 91 | 0.982 | 8.269 | 0.950 | 13.835 | 4.55 |
| SPA-BP | 3 | 0.881 | 21.303 | 0.849 | 24.007 | 2.35 | |
| PCA-BP | 9 | 0.951 | 13.665 | 0.889 | 20.589 | 3.21 | |
| Elements | Models | Modeling Duration (s) | Calibration | Prediction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc2 | RMSEC (mg/kg) | Rp2 | RMSEP (mg/kg) | RPD | |||
| Cd | PCA-PSO-BP | 62.33 | 0.988 | 3.643 | 0.982 | 4.461 | 7.72 |
| PCA-SSA-BP | 15.09 | 0.989 | 3.551 | 0.972 | 5.553 | 6.04 | |
| SPA-PSO-BP | 57.83 | 0.976 | 5.138 | 0.971 | 5.658 | 5.88 | |
| SPA-SSA-BP | 13.52 | 0.975 | 5.264 | 0.970 | 5.753 | 5.82 | |
| Cu | PCA-PSO-BP | 69.30 | 0.996 | 5.013 | 0.988 | 9.038 | 9.16 |
| PCA-SSA-BP | 20.73 | 0.994 | 6.081 | 0.991 | 7.810 | 10.34 | |
| SPA-PSO-BP | 57.15 | 0.971 | 13.816 | 0.970 | 13.963 | 5.83 | |
| SPA-SSA-BP | 17.43 | 0.971 | 13.808 | 0.966 | 14.960 | 5.44 | |
| Pb | PCA-PSO-BP | 61.49 | 0.974 | 10.042 | 0.964 | 11.791 | 5.47 |
| PCA-SSA-BP | 18.06 | 0.975 | 9.790 | 0.956 | 12.906 | 4.94 | |
| SPA-PSO-BP | 84.03 | 0.927 | 16.724 | 0.884 | 21.057 | 2.89 | |
| SPA-SSA-BP | 26.68 | 0.899 | 19.671 | 0.882 | 21.208 | 2.83 | |
| Elements | Calibration | Prediction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rc2 | RMSEC (mg/kg) | Rp2 | RMSEP (mg/kg) | RPD | |
| Cd | 0.960 | 6.641 | 0.877 | 11.671 | 2.86 |
| Cu | 0.954 | 17.453 | 0.951 | 17.996 | 4.50 |
| Pb | 0.879 | 21.514 | 0.847 | 24.181 | 2.56 |
| Number | Brand | Origin | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bing Ran | Zhejiang, China | Changchun Fangyitang Economic and Trade Co., Ltd. |
| 2 | Xian Weng Song Bao | Zhejiang, China | GuangDong TianCheng Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd. |
| 3 | Chuan Cheng | Zhejiang, China | JiangSu ChuanCheng Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd. |
| 4 | Hui Jing Hua Zun | Zhejiang, China | Bozhou Huijingtang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
| 5 | Yong Gang | Zhejiang, China | Yonggang Pieces Factory Co., Ltd. |
| 6 | Shen Yue | Zhejiang, China | Tonghua Sanbao Ginseng Antler Trading Co., Ltd. |
| 7 | Kang Mei | Zhejiang, China | Kangmei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Guangdong) |
| 8 | Yi Ling | Zhejiang, China | Shijiazhuang Yiling Herbal Pieces Co., Ltd. |
| NO. | Cd | Cu | Pb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (mg/kg) | Mean ± SD (mg/kg) | Range (mg/kg) | Mean ± SD (mg/kg) | Range (mg/kg) | Mean ± SD (mg/kg) | |
| 1 | 0.25–1.2 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 1.9–4.7 | 3 ± 1 | 0.16–0.55 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | 5.0–7.1 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 18–28 | 21 ± 3 | 4.1–7.5 | 5.5 ± 1.0 |
| 3 | 9.9–12 | 11.0 ± 0.5 | 33–38 | 36 ± 2 | 22–24 | 22.4 ± 0.5 |
| 4 | 19–27 | 22 ± 3 | 48–70 | 57 ± 8 | 41–110 | 50 ± 20 |
| 5 | 21–27 | 25 ± 2 | 51–69 | 65 ± 5 | 45–70 | 63 ± 7 |
| 6 | 47–51 | 49 ± 2 | 81–84 | 82 ± 1 | 63–90 | 83 ± 8 |
| 7 | 63–120 | 80 ± 15 | 160–370 | 190 ± 70 | 100–110 | 110 ± 4 |
| 8 | 84–100 | 93 ± 6 | 220–250 | 230 ± 10 | 140–230 | 200 ± 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Chen, R.; Kabir, M.H.; Liu, F.; Tao, Z.; Liu, L.; Kong, W. Fast Detection of Heavy Metal Content in Fritillaria thunbergii by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy with PSO-BP and SSA-BP Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083360
Luo X, Chen R, Kabir MH, Liu F, Tao Z, Liu L, Kong W. Fast Detection of Heavy Metal Content in Fritillaria thunbergii by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy with PSO-BP and SSA-BP Analysis. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xinmeng, Rongqin Chen, Muhammad Hilal Kabir, Fei Liu, Zhengyu Tao, Lijuan Liu, and Wenwen Kong. 2023. "Fast Detection of Heavy Metal Content in Fritillaria thunbergii by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy with PSO-BP and SSA-BP Analysis" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083360
APA StyleLuo, X., Chen, R., Kabir, M. H., Liu, F., Tao, Z., Liu, L., & Kong, W. (2023). Fast Detection of Heavy Metal Content in Fritillaria thunbergii by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy with PSO-BP and SSA-BP Analysis. Molecules, 28(8), 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083360








