Purification, Identification and Evaluation of Antioxidant Peptides from Pea Protein Hydrolysates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
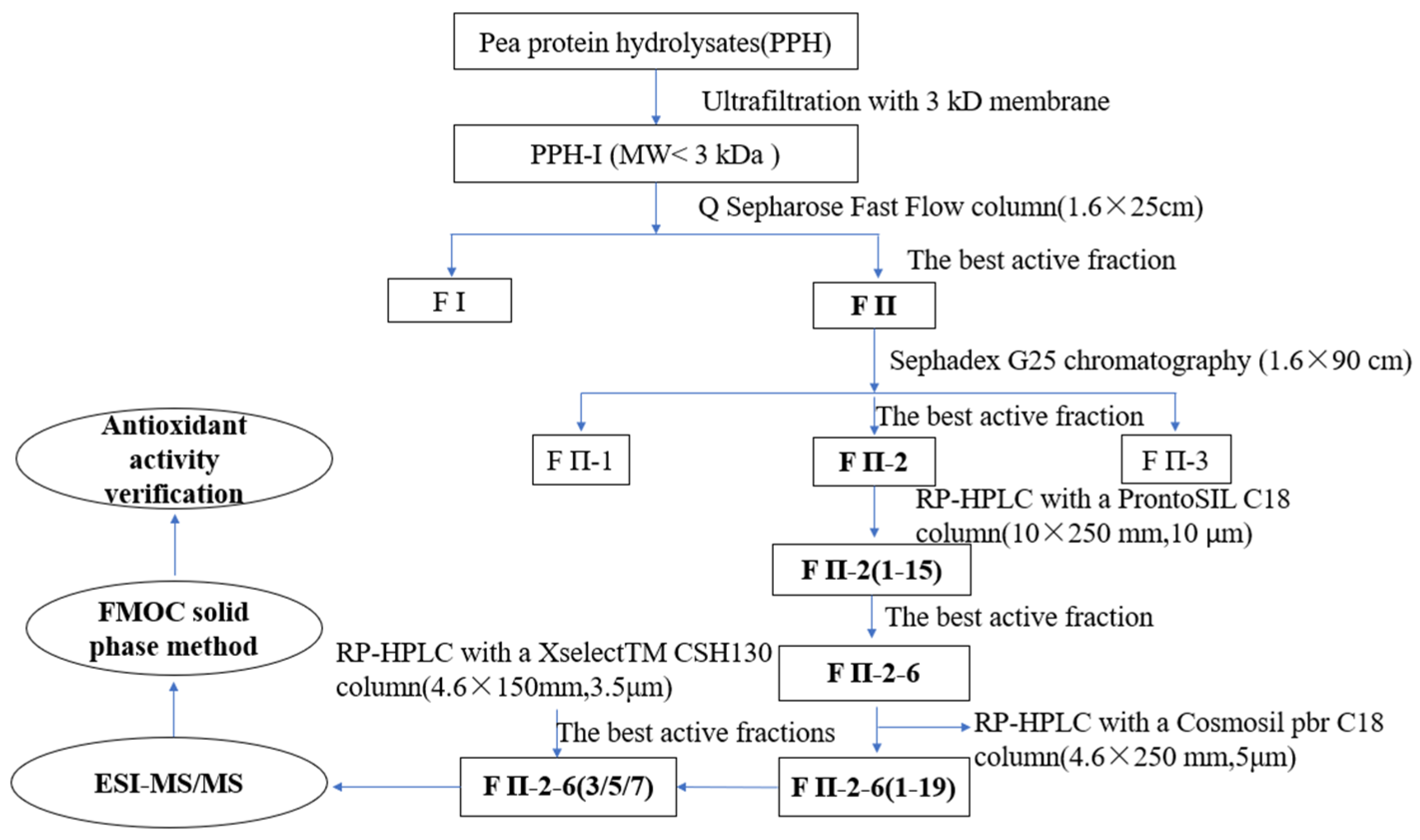
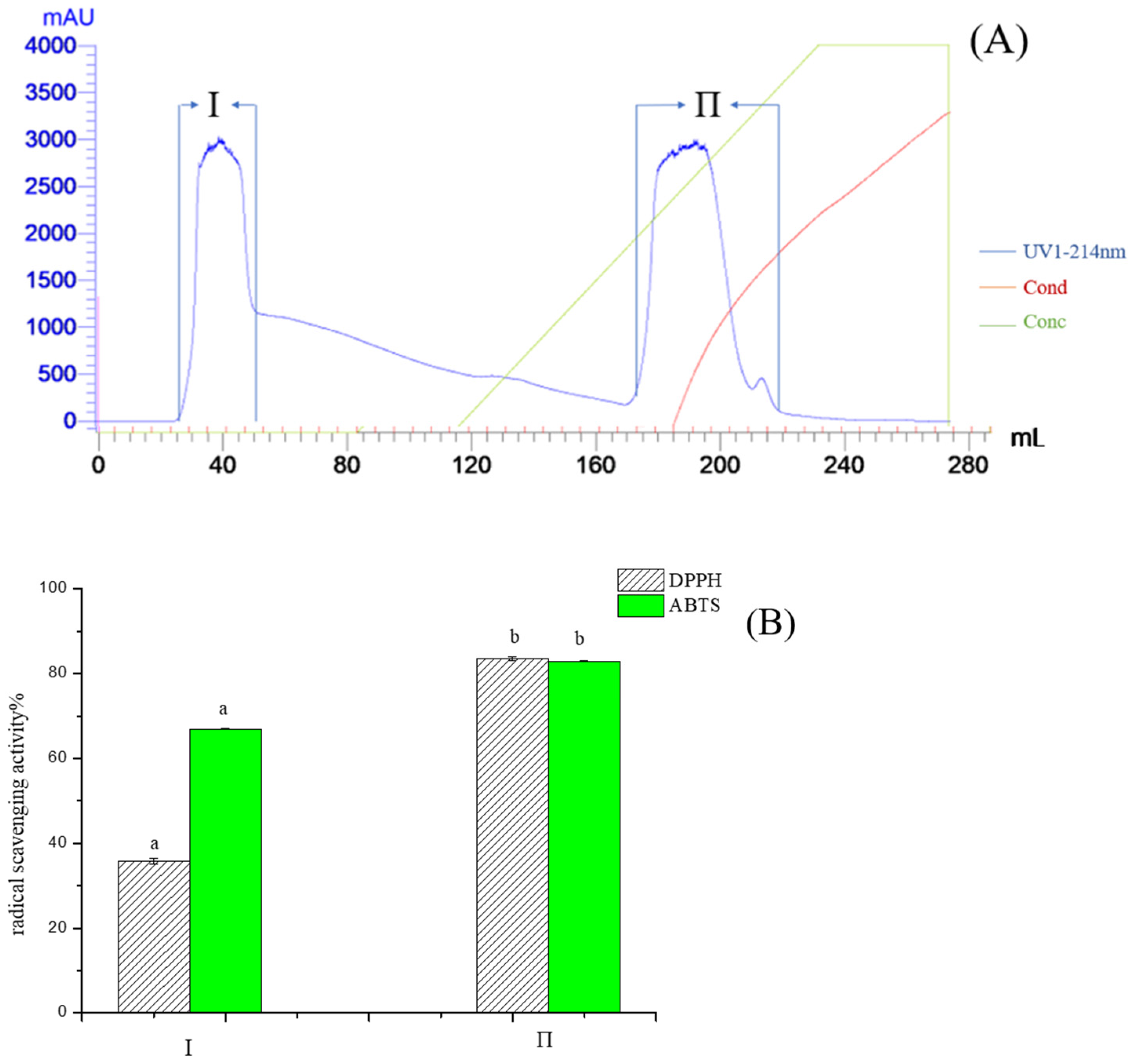
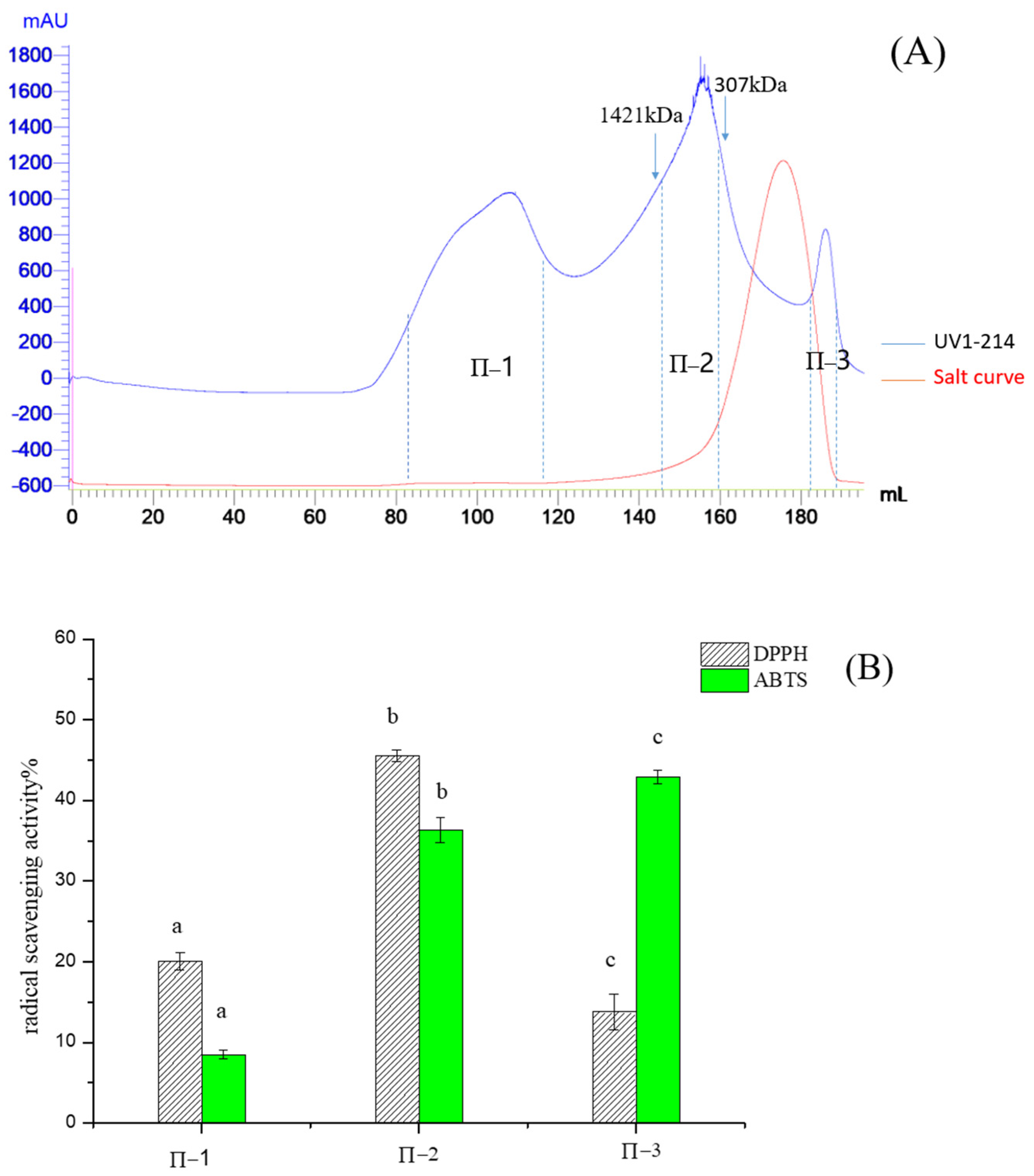
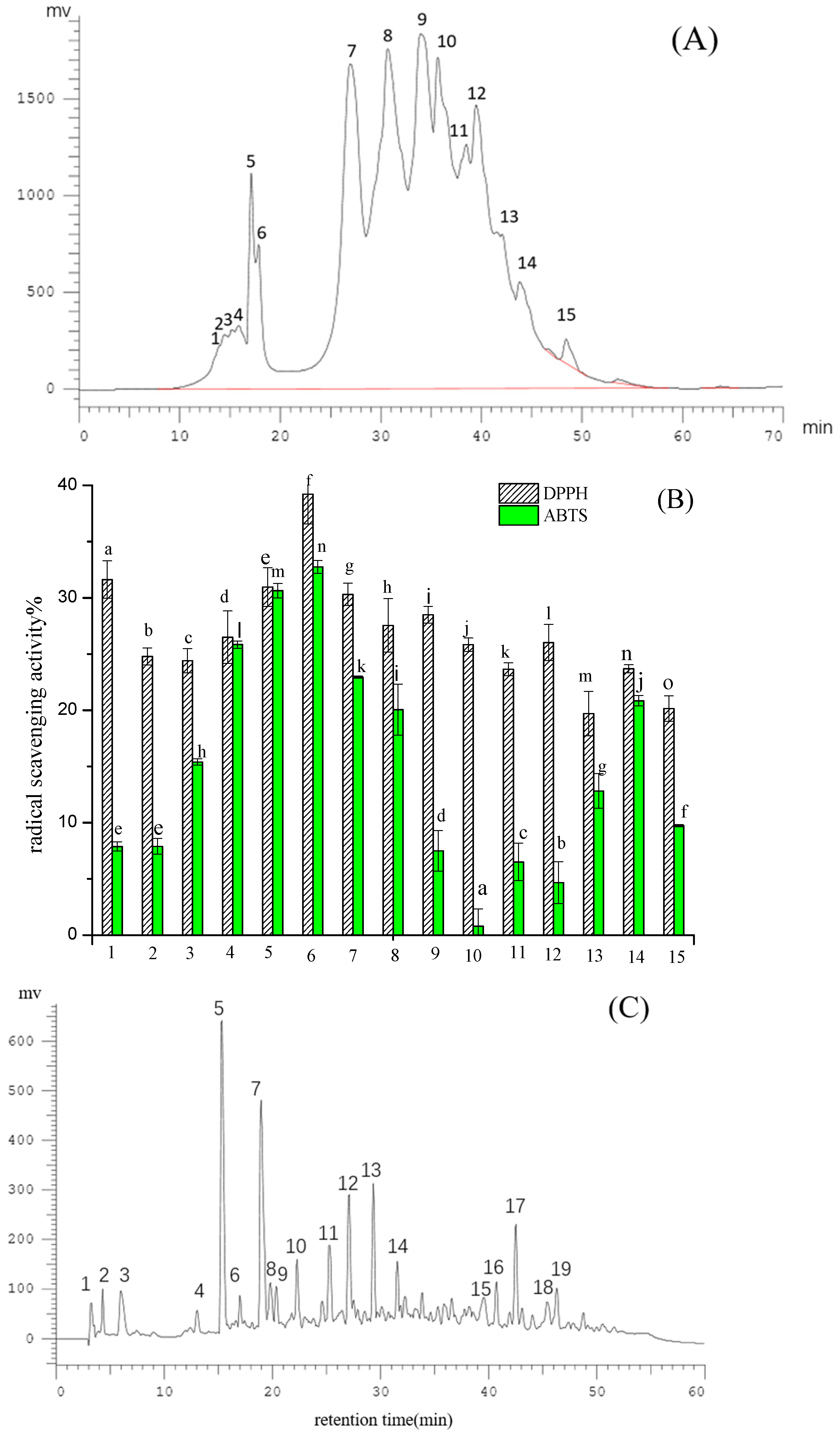
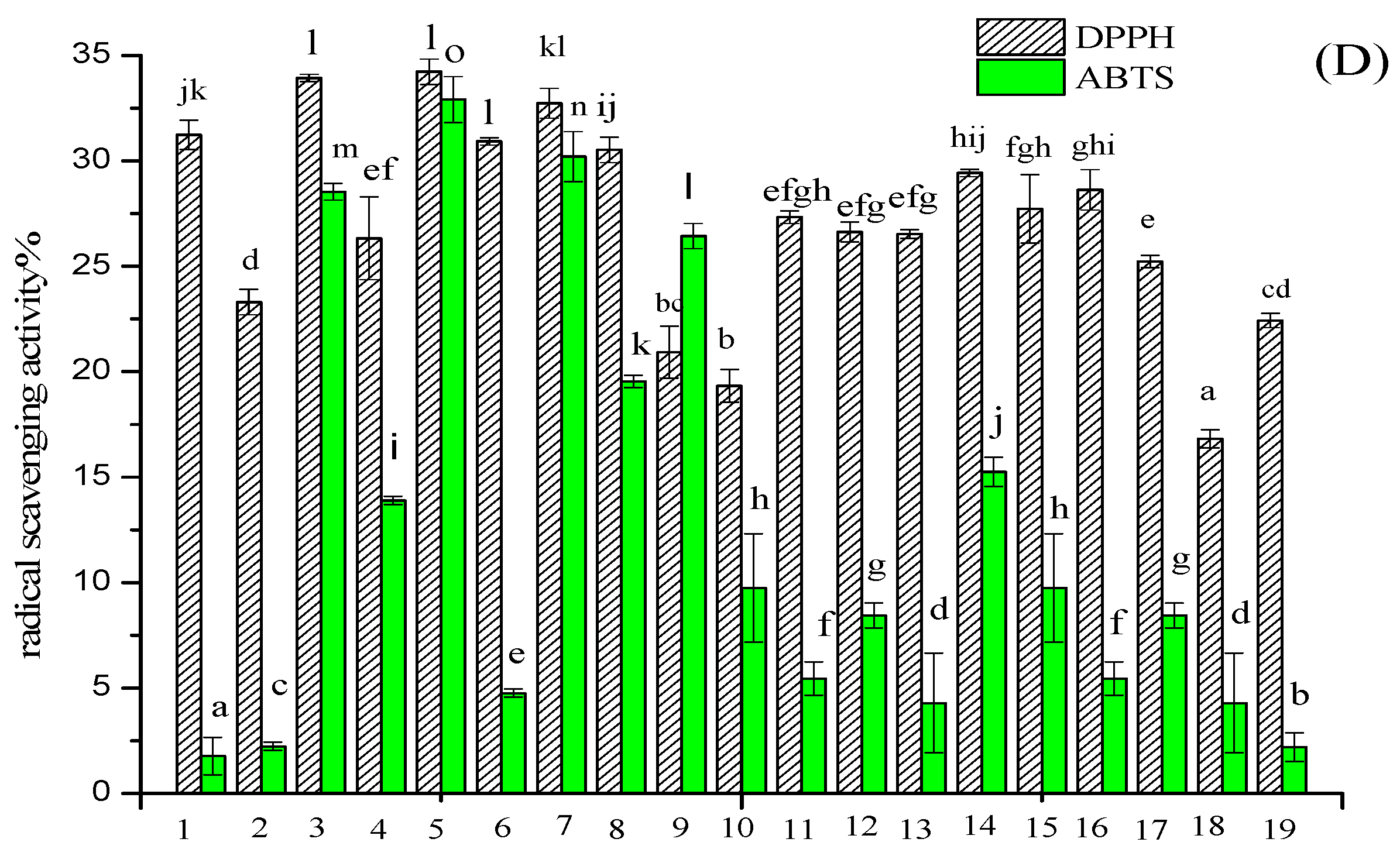
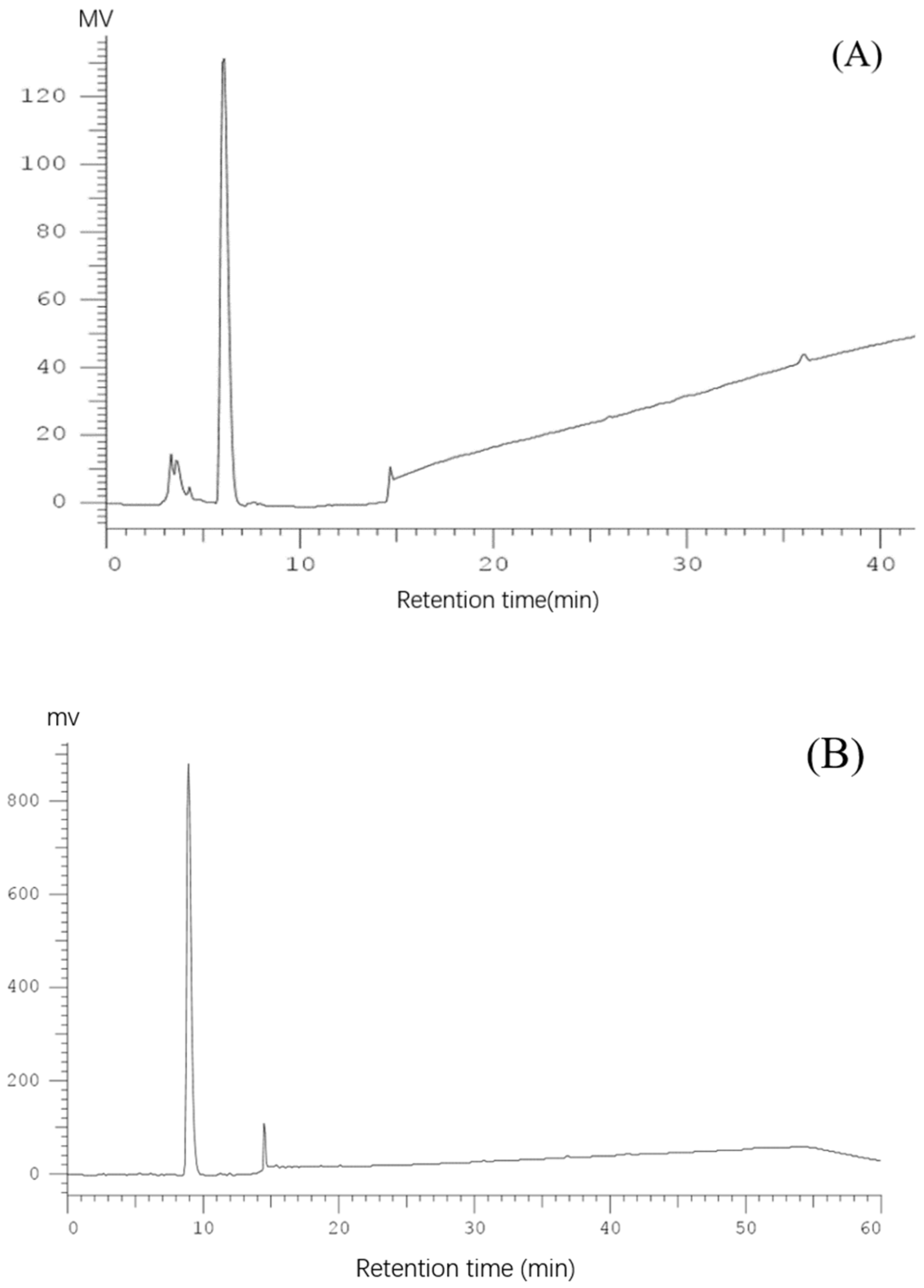
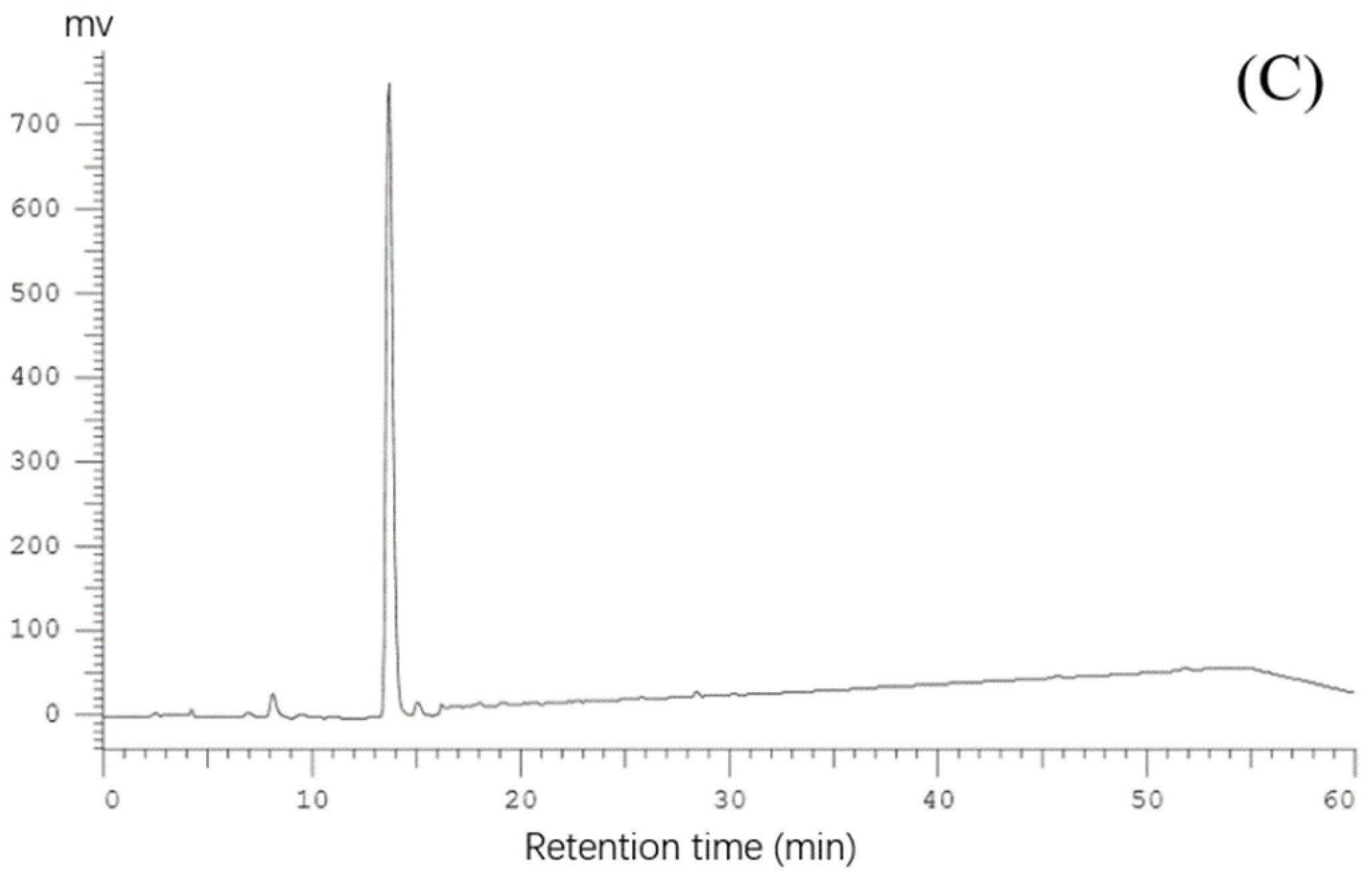
2.1. Purification of Pea Antioxidative Peptides
Subsubsection
2.2. Sequence Identification and Antioxidant Activities of Three Antioxidant Peptides
2.3. Relationship of Peptides Structure-Antioxidant Activity
2.4. Cytoprotective Effect of Three Novel Antioxidant Peptides on H2O2 Damaged LO2 Cells
2.5. Effects of Three Antioxidant Peptides on the Levels of ROS, SOD, GSH-Px and CAT Activities in H2O2 Injured LO2 Cells
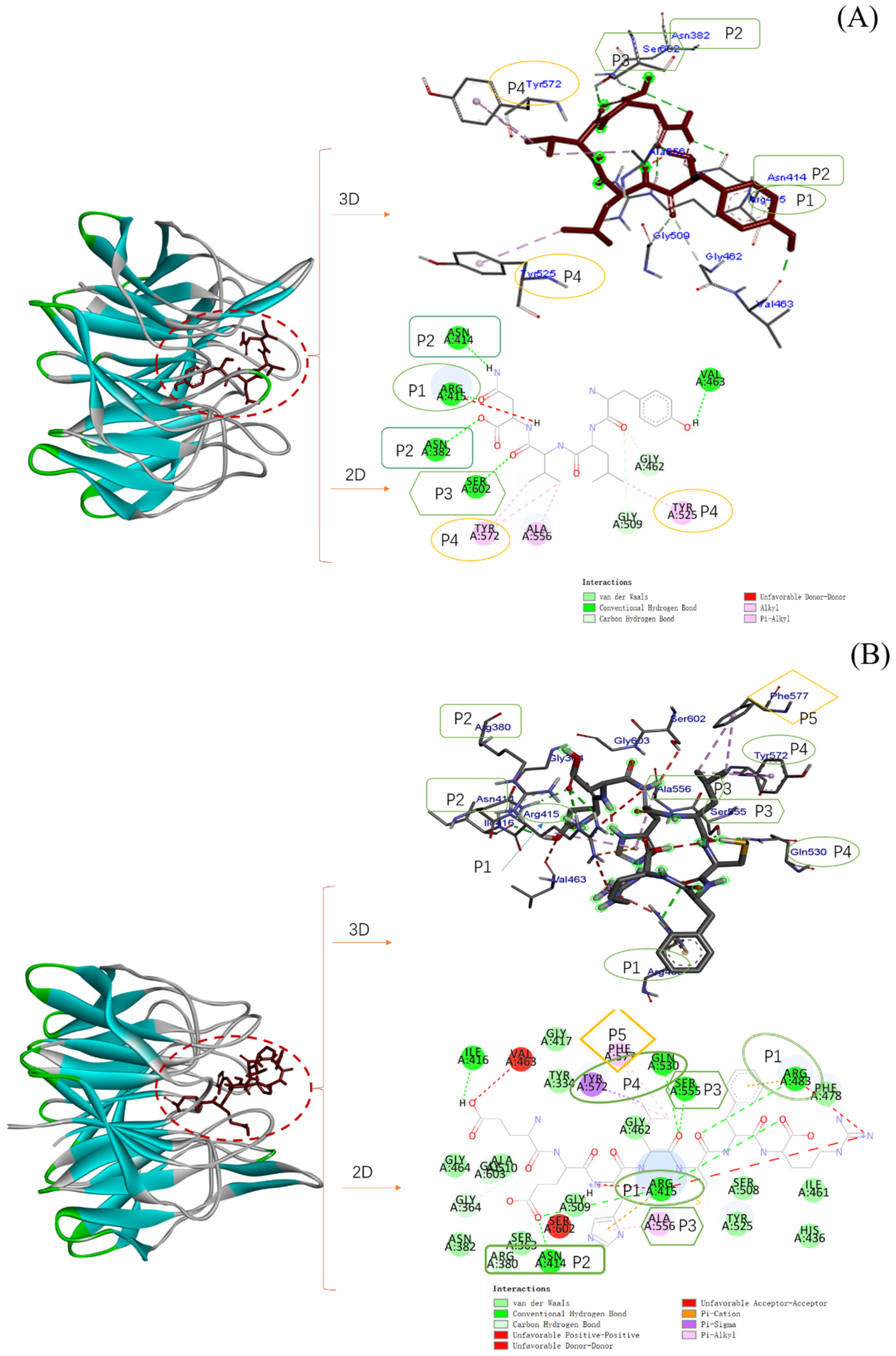
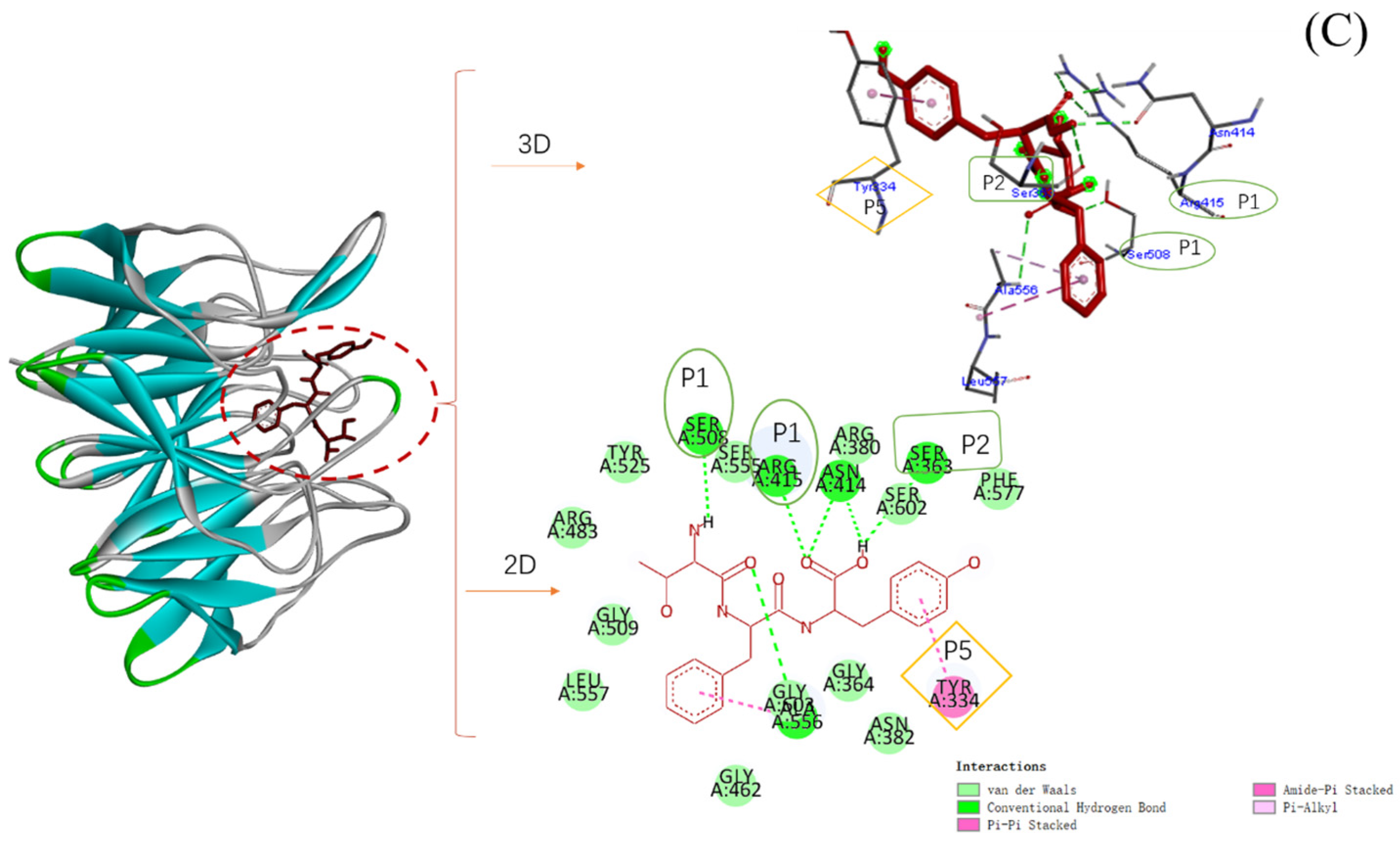
2.6. Molecular Docking of Three Antioxidant Peptides with Keap1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Pea Protein Hydrolysate
3.3. Isolation and Purification of Antioxidant Peptides
3.4. Identification of Pea Antioxidant Peptides
3.5. Synthesis of Peptides
3.6. Antioxidant Activity of Three Novel Antioxidant Peptides In Vitro
3.6.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.2. Hydroxyl Radical (OH·) Scavenging Activity
3.6.3. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.4. Superoxide (O2−) Scavenging Activity
3.6.5. Oxygen Radical Absorption Capacity (ORAC)
3.7. Effects of Peptides on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in LO2 Cells
3.7.1. Determination of Cell Viability
3.7.2. Establishment of H2O2 Oxidative Damage Model and Protective Effect on LO2 Cells
3.7.3. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
3.7.4. Analysis of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
3.8. Molecular Docking Simulation
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Gómez, B.; Barba, F.J.; Mora, L.; Pérez- Santaescolástica, C.; Toldrá, F. Bioactive peptides as natural antioxidants in food products—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois- Deruy, E.; Peugnet, V.; Turkieh, A.; Pinet, F. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, E.; Granato, D.; Azevedo, L.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Barba, F.J.; Carrillo, C.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; et al. Current perspectives in cell-based approaches towards the definition of the antioxidant activity in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, I. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: An updated overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Li, T.; Chen, D.; Gu, H.; Mao, X. Identification and molecular docking of antioxidant peptides from hemp seed protein hydrolysates. LWT 2021, 147, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.P.; Lai, S.J.; Chang, C.R.; Chen, W.C.; Wu, S.H.; Lu, C.P. Peptidomic analysis of low molecular weight antioxidative peptides prepared by lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seed protein hydrolysates. LWT 2021, 144, 11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tong, X.; Sui, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Antioxidant activity and protective effects of Alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean hydrolysate in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, M.; Zhao, H.; Lv, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhang, B. A Novel Insight into Screening for Antioxidant Peptides from Hazelnut Protein: Based on the Properties of Amino Acid Residues. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.X.; Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Wang, X.J.; He, J.F. Preparation of antioxidative corn protein hydrolysates, purification and evaluation of three novel corn antioxidant peptides. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gobba, C.; Tompa, G.; Otte, J. Bioactive peptides from caseins released by cold active proteolytic enzymes from Arsukibacterium ikkense. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L. Identification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from Chinese dry-cured mutton ham. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, W.H.; Wang, P.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) hydrolysate: Preparation, identification and cytoprotection on H2O2-induced oxidative stress. J. Funct. 2021, 86, 104701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Luo, Q.B.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, and activity evaluation of ten antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy). J. Funct. 2018, 47, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, A.U.; Abuine, R.; Palanisamy, S.; Lee, J.K.; Byun, H.G. Characterization and purification of 𝛽−secretase inhibitory peptides fraction from sea cucumber (Holothuria spinifera) enzymatic hydrolysates. Process. Biochem. 2021, 111, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea protein isolates: Structure, extraction, and functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, G.X.; Suo, S.K.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Purification, Identification, Activity Evaluation, and Stability of Antioxidant Peptides from Alcalase Hydrolysate of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Proteins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Song, G.; Huang, J. Extraction, identification and structure-activity relationship of antioxidant peptides from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.T.; Xiao, J.B.; Mohana Dass, S.; Teoh, J.Y.; Ee, K.Y.; Ng, W.J.; Wong, F.C. Identification of antioxidant peptides derived from tropical jackfruit seed and investigation of the stability profiles. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.X.; Ruan, G.R.; Jin, F.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.J. Purification, identification, and synthesis of five novel antioxidant peptides from Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume) protein hydrolysates. LWT 2018, 92, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulueta, A.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A. ORAC and TEAC assays comparison to measure the antioxidant capacity of food products. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khammuang, S.; Sarnthima, R.; Sanachai, K. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori) protein hydrolysate and molecular docking study. Biocatal 2022, 42, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Joshi, R.; Gupta, M. Purification, identification and characterization of two novel antioxidant peptides from finger millet (Eleusine coracana) protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, A.; Yue, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, J. Purification and identification of five novel antioxidant peptides from goat milk casein hydrolysates. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4242–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, H.; Su, G.; Zhao, M. Structure-activity relationship of antioxidant dipeptides: Dominant role of Tyr, Trp, Cys and Met residues. J. Funct. 2016, 21, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Cai, X.; Yan, A.; Tian, Y.; Du, M.; Wang, S. A specific antioxidant peptide: Its properties in controlling oxidation and possible action mechanism. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 126984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamdad, F.; Ahmed, S.; Chen, L. Specifically designed peptide structures effectively suppressed oxidative reactions in chemical and cellular systems. J. Funct. 2015, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.B.; He, T.P.; Li, H.B.; Tang, H.W.; Xia, E.Q. The Structure-Activity Relationship of the Antioxidant Peptides from Natural Proteins. Molecules 2016, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from watermelon seed protein hydrolysates and their cytoprotective effects on H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Chen, T.T.; Hu, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.Y. Purification and characterization of an antioxidant peptide (GSQ) from Chinese leek (Allium tuberosum Rottler) seeds. J. Funct. 2014, 10, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xiong, H.; Huang, X.; Guyonnet, V.; Ma, M.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, G. Identification and molecular mechanisms of novel antioxidant peptides from two sources of eggshell membrane hydrolysates showing cytoprotection against oxidative stress: A combined in silico and in vitro study. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.L.; Yen, G.C. Modulation of Akt, JNK, and p38 Activation Is Involved in Citrus Flavonoid-Mediated Cytoprotection of PC12 Cells Challenged by Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Long, Y.; Peng, S.; Huang, Y. Study of the selenizing Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides protects RAW264.7 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyenle, I.D.; Divine, U.C.; Adeyemi, R.; Ayinde, K.S.; Olaoba, O.T.; Apu, C.; Du, L.; Lu, Q.; Yin, X.; Adelusi, T.I. Direct Keap1-kelch inhibitors as potential drug candidates for oxidative stress-orchestrated diseases: A review on in silico perspective. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, M.; Morales-Gonzalez, J.A. Molecular recognition between potential natural inhibitors of the Keap1-Nrf2 complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Hu, L. Nrf2 activation through the inhibition of Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 846–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pownall, T.L.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of pea seed (Pisum sativum L.) enzymatic protein hydrolysate fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4712–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Lan, Y.Q.; Miao, J.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Chen, B.B.; Liu, G.; Wu, X.; Zhu, X.A.; Gao, Y. Phytochemicals, antioxidant capacity and cytoprotective effects of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) axis extracts on HepG2 cells. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimalaratne, C.; Bandara, N.; Wu, J. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed chicken egg white. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Miao, J.Y.; Chen, B.B.; Gao, J.B.; Ou, Y.Y.; Liang, X.T.; Yin, Y.Z.; Tong, X.; Gao, Y. Purification, identification, and antioxidative mechanism of three novel selenium-enriched oyster antioxidant peptides. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermeño, M.; Bascón, C.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Felix, M.; FitzGerald, R.J. Identification of peptides from edible silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori) protein hydrolysates with antioxidant activity. J. Funct. 2022, 92, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
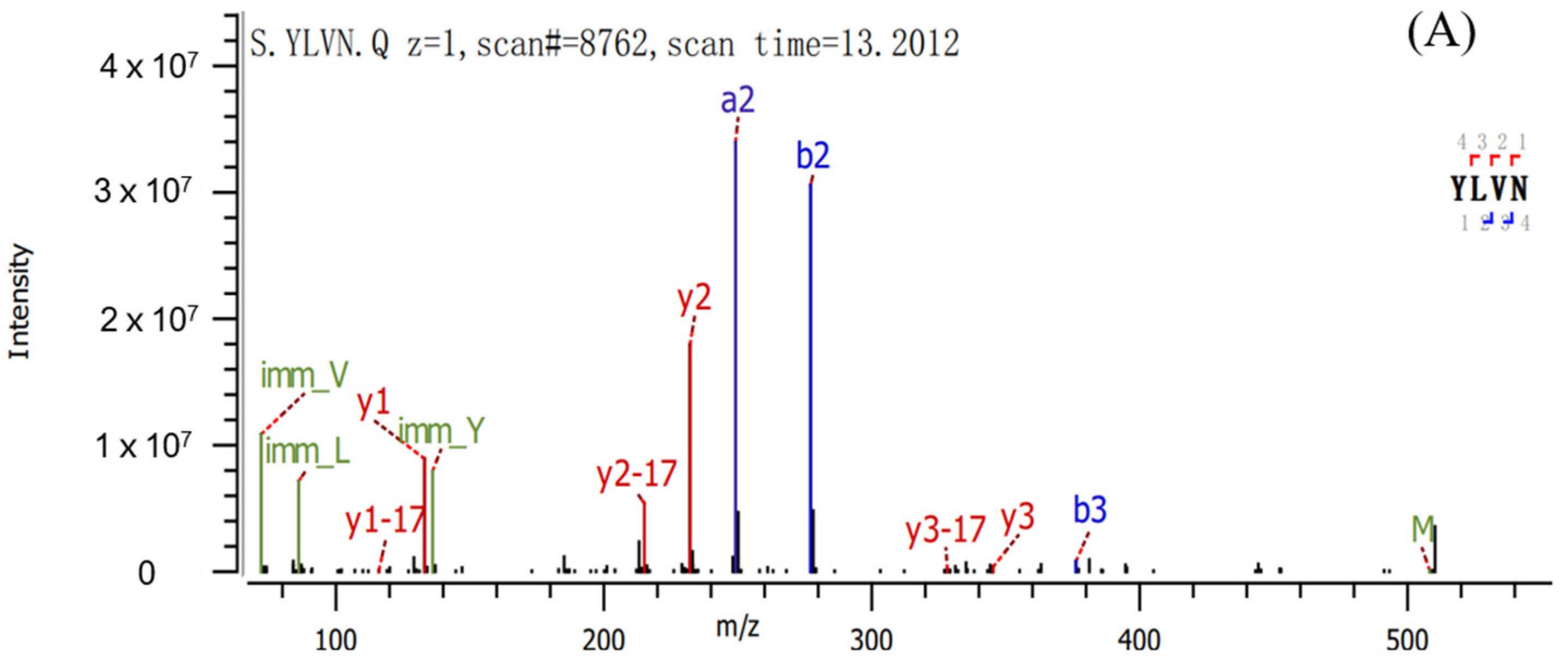
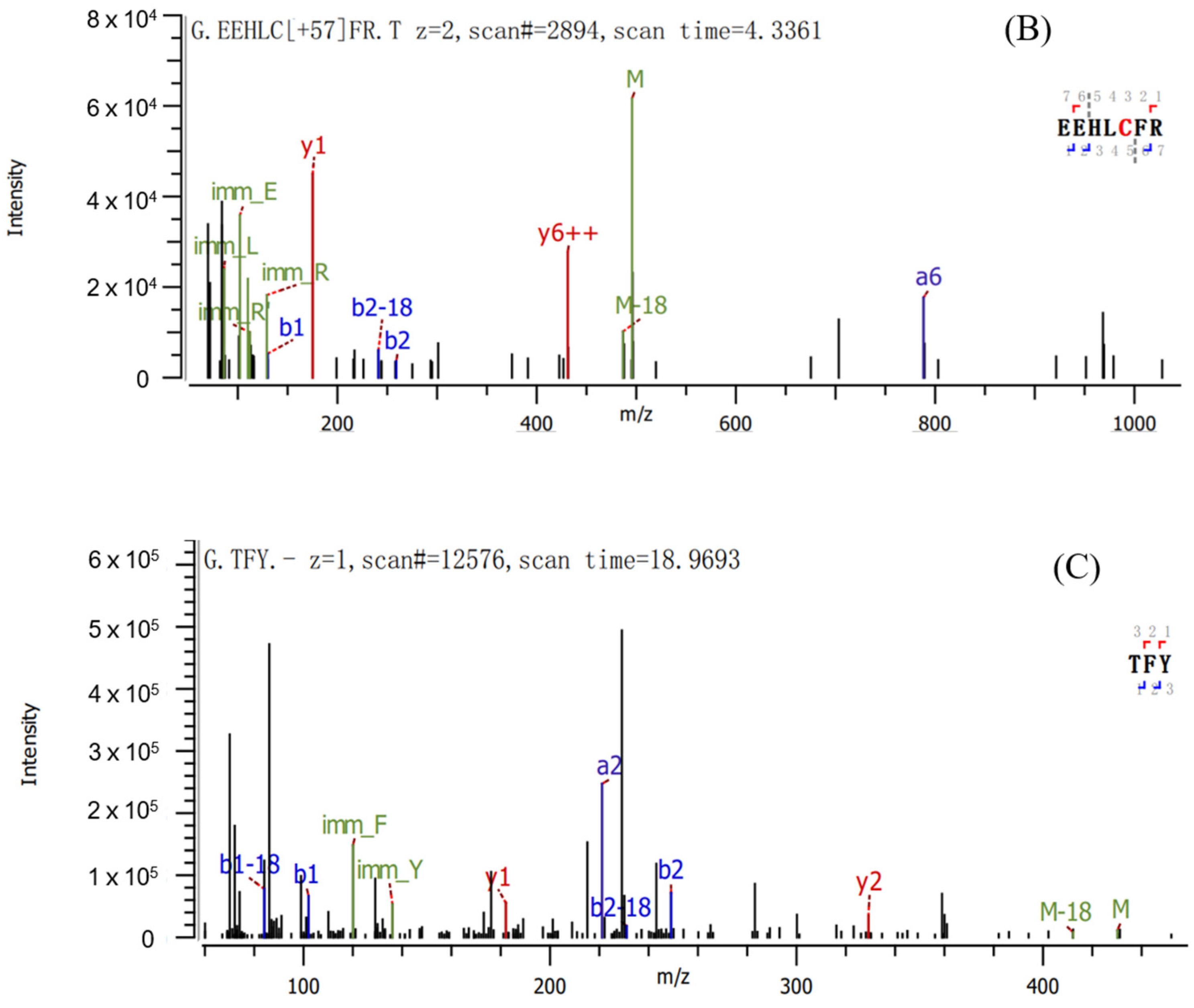
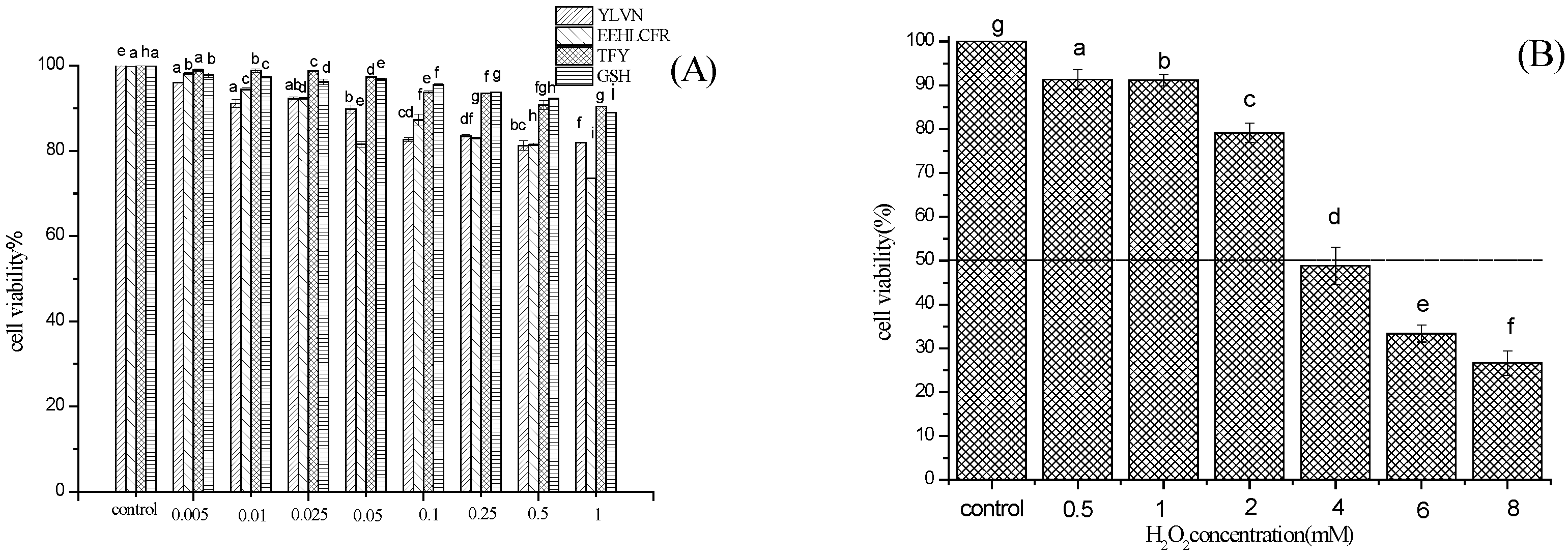
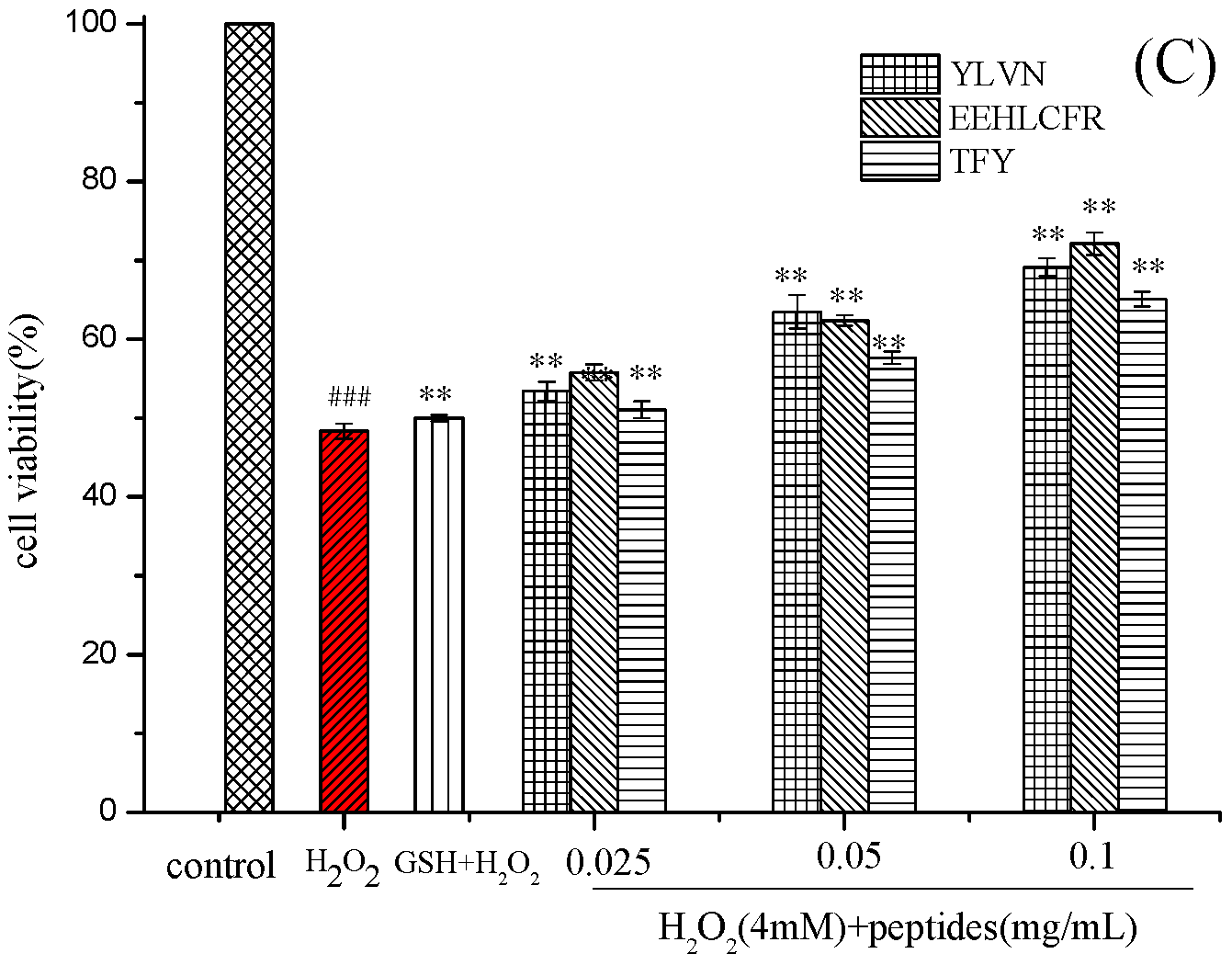
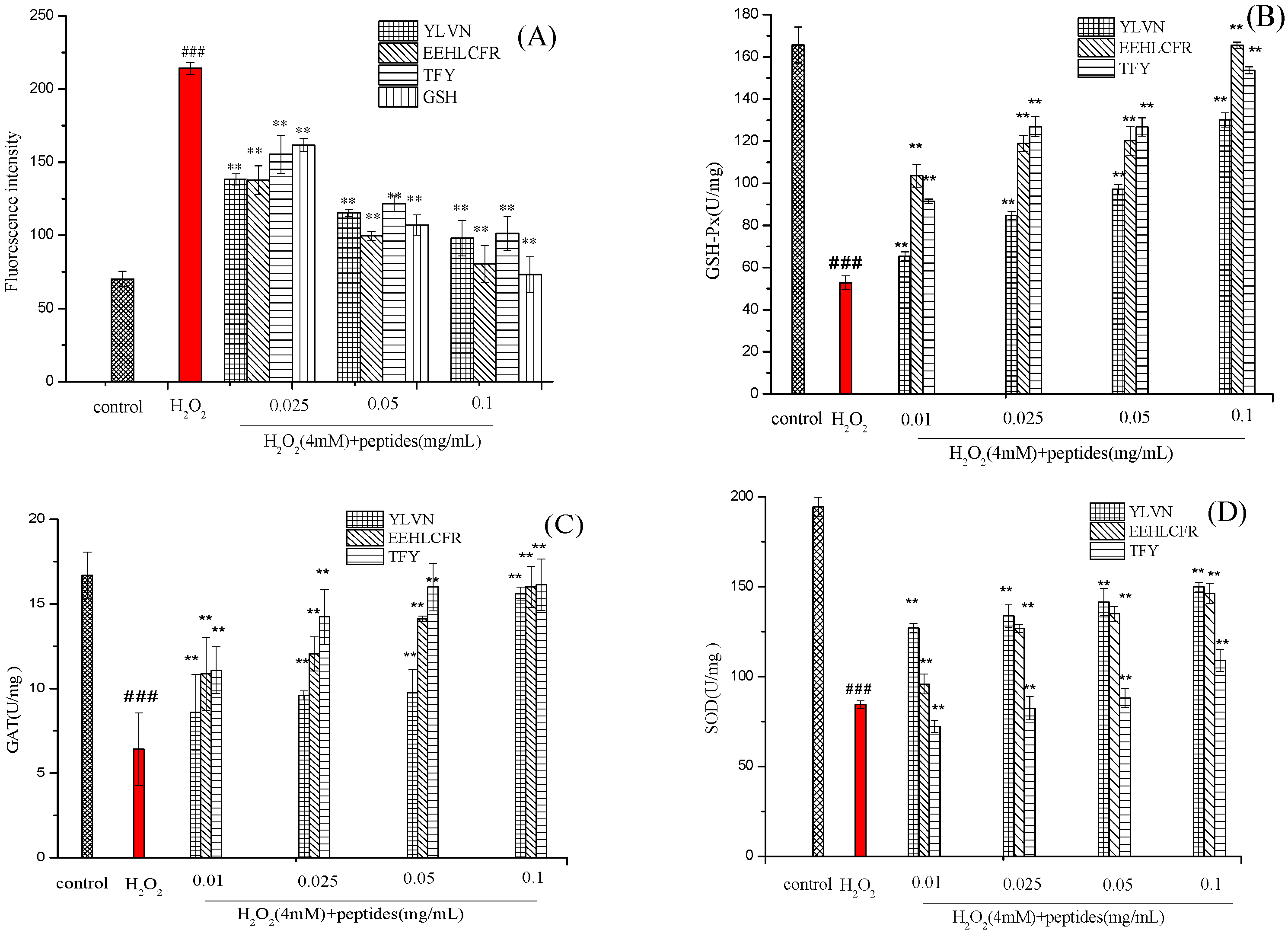
| Peptide | Sequence | Length | Mass | Hydrophobic Ratio a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide 1 | YLVN | 4 | 507.59 | 50.00 |
| Peptide 2 | EEHLCFR | 7 | 933.06 | 28.57 |
| Peptide 3 | TFY | 3 | 429.47 | 33.33 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | DPPH· IC50 (mg/mL) | OH· IC50 (mg/mL) | ABTS+ IC50 (mg/mL) | O2−· IC50 (mg/mL) | ORAC (μmol TE/μmol Peptide) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YLVN | - | - | 0.002 ± 0.000 a | 1.357 ± 0.458 c | 1.120 ± 0.231 a |
| EEHLCFR | 0.027 ± 0.003 c | 2.796 ± 0.597 a | 0.019 ± 0.001 b | 1.247 ± 0.041 b | 0.921 ± 0.131 b |
| TFY | 1.492 ± 0.001 b | - | 0.006 ± 0.004 ab | - | 0.367 ± 0.092 c |
| GSH | 0.081 ± 0.015 a | 0.102 ± 0.091 b | 0.007 ± 0.003 ab | 0.667 ± 0.009 a | 0.484 ± 0.190 d |
| Peptide | Affinity (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic | Electrostatic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YLVN | −8.2 | Asn414, Arg415, Asn382, Ser602, Val463, Gly462, Gly509 | Tyr572, Tyr525, Ala556 | |
| EEHLCFR | −7.2 | Arg415, Arg483, Ser555, Gln530, Ile416, Asn414, Arg380, Gly364, Gly603 | Phe577, Ala556 | Tyr572 |
| TFY | −8.9 | Ser508, Arg415, Asn414, Ser363, Ala556 | Tyr334, Ala556 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Liu, X. Purification, Identification and Evaluation of Antioxidant Peptides from Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Molecules 2023, 28, 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072952
Zhao D, Liu X. Purification, Identification and Evaluation of Antioxidant Peptides from Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072952
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Dan, and Xiaolan Liu. 2023. "Purification, Identification and Evaluation of Antioxidant Peptides from Pea Protein Hydrolysates" Molecules 28, no. 7: 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072952
APA StyleZhao, D., & Liu, X. (2023). Purification, Identification and Evaluation of Antioxidant Peptides from Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Molecules, 28(7), 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072952





