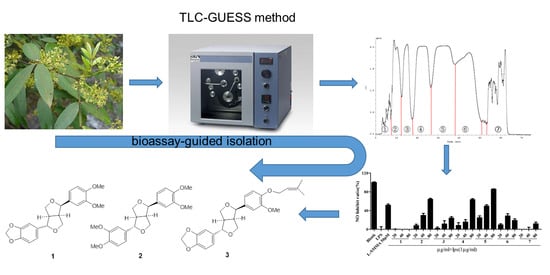
Bioactivity-Guided High Performance Counter-Current Chromatography and Following Semi-Preparative Liquid Chromatography Method for Rapid Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Lignins from Dai Medicinal Plant, Zanthoxylum acanthopodium var. timbor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nitric Oxide (NO) Production Inhibitor Screening Experiment
2.2. Optimization of HPCCC Solvent Systems
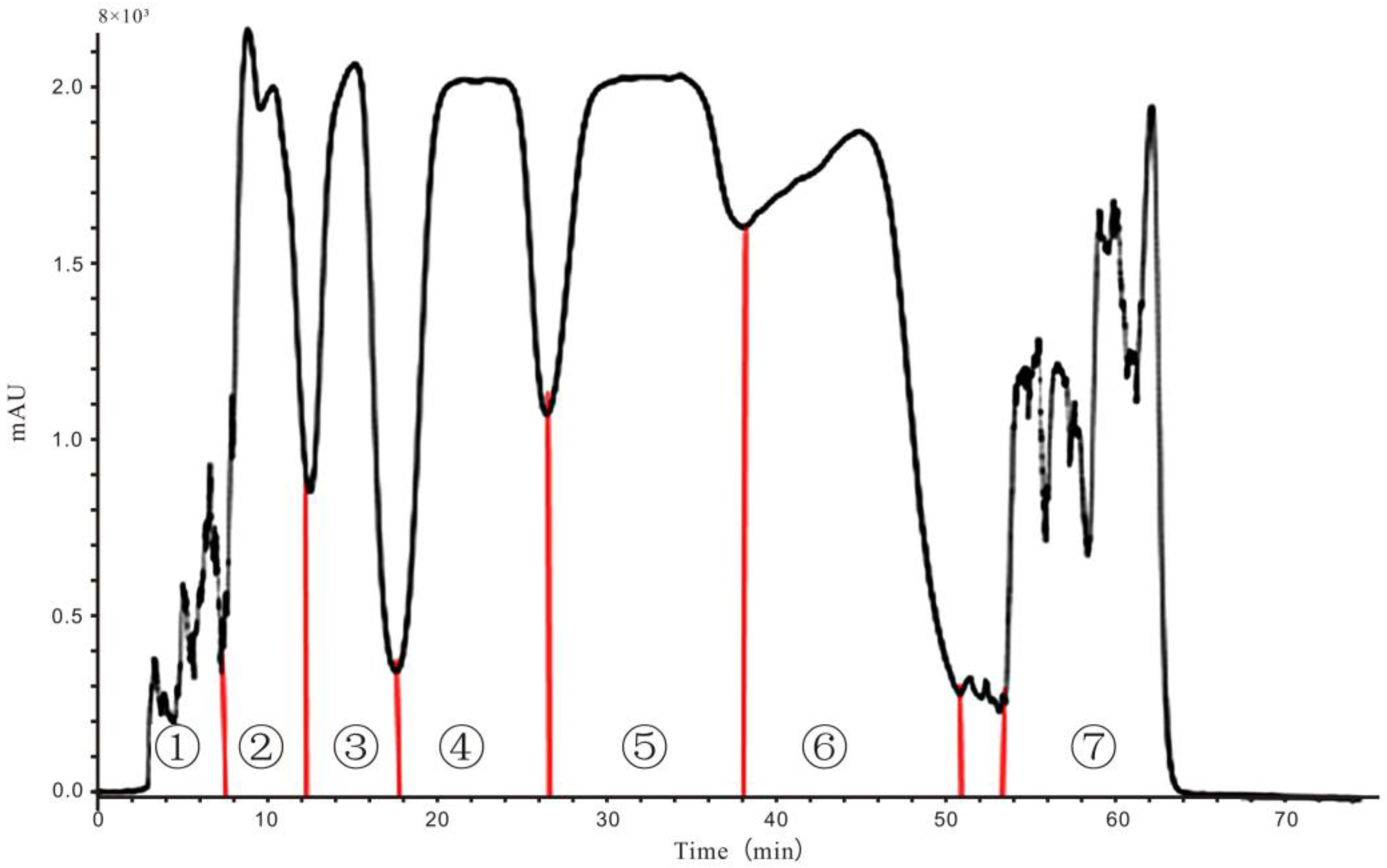
2.3. Screening of Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Different Fractions from HPCCC
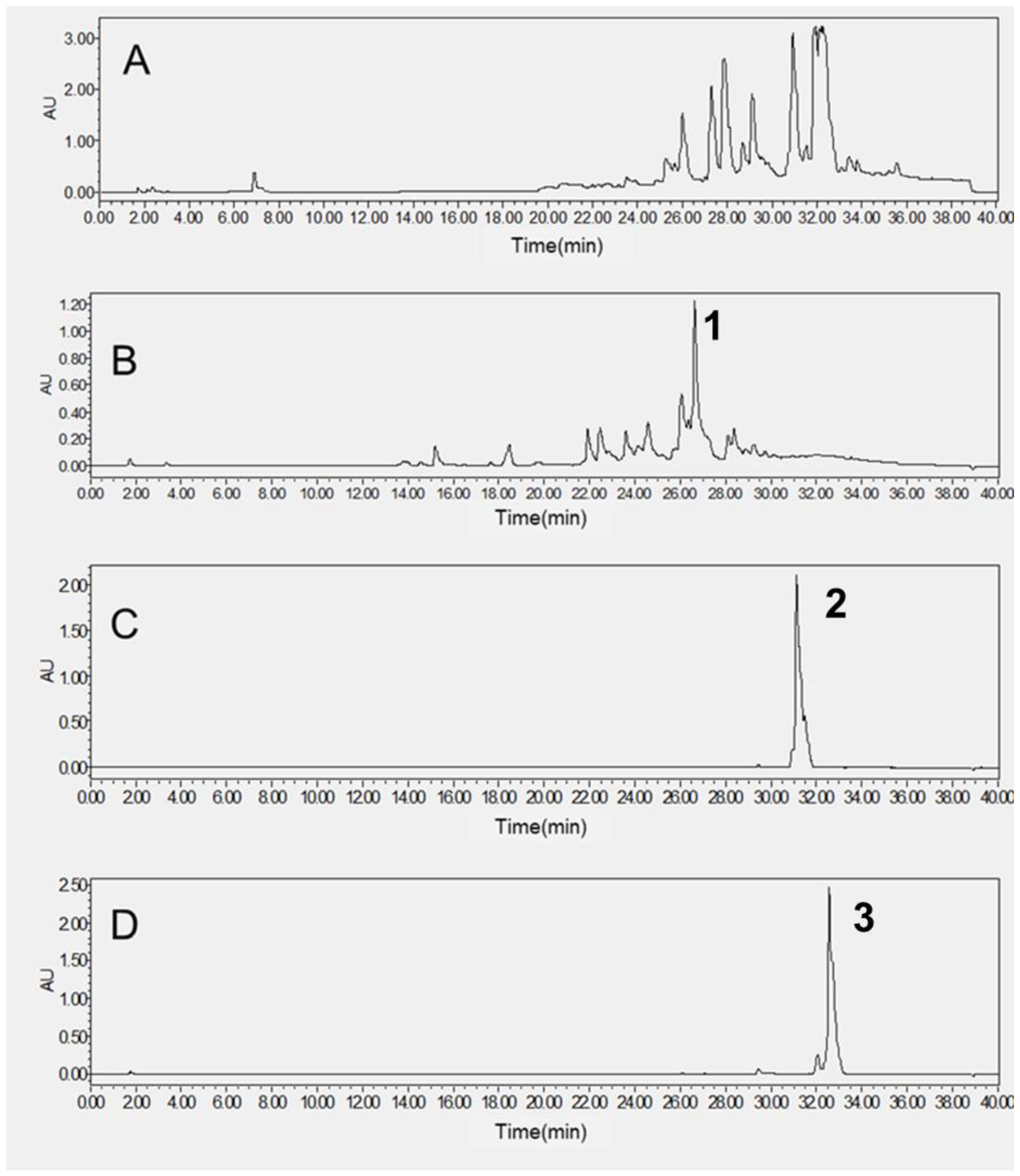
2.4. Purification of the Target HPCCC Peaks
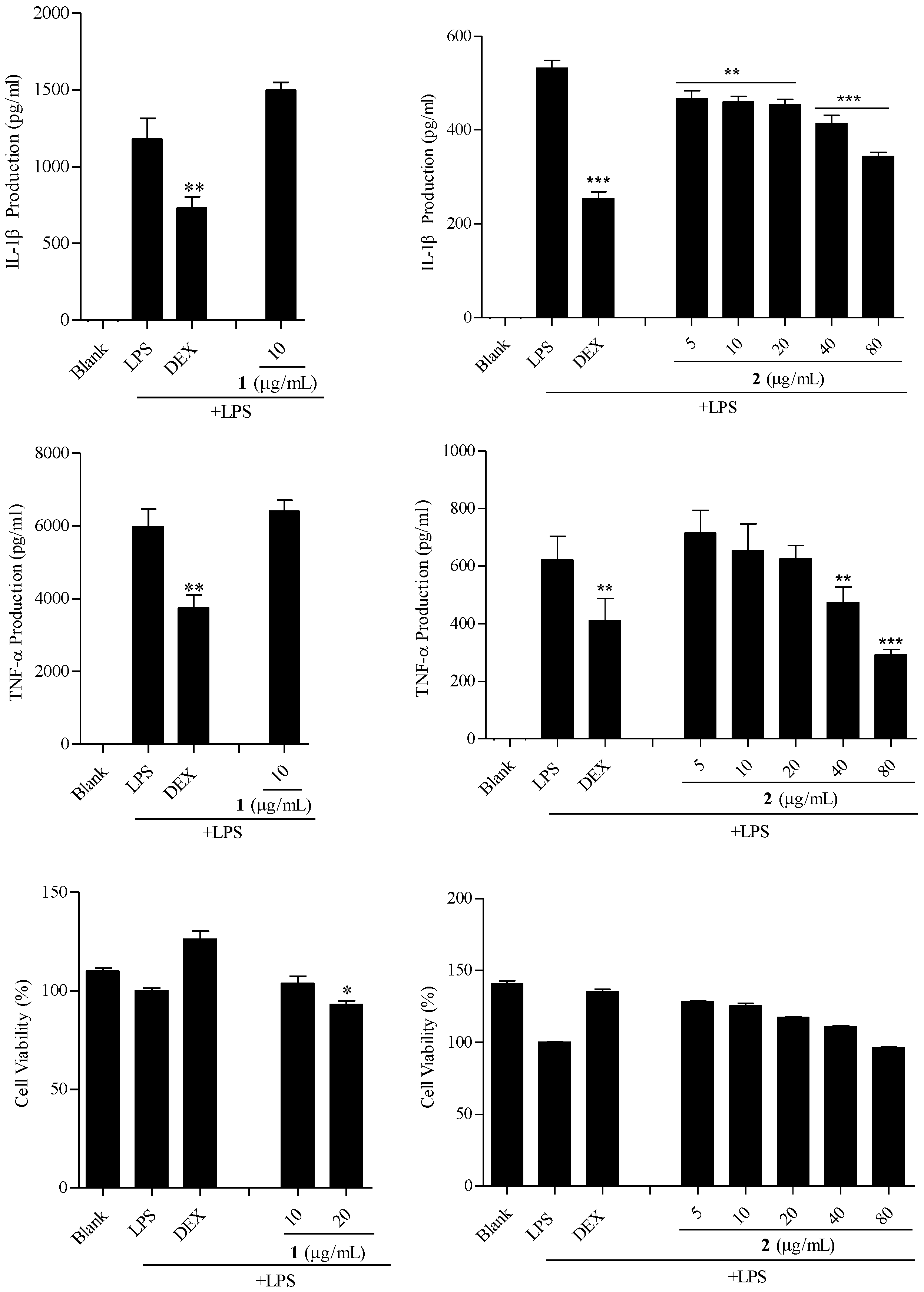
2.5. The Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Fargesin (1) and Epieudesmin (2) on TPH-1 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Selection of Two-Phase Solvent System
3.5. HPCCC Separation Process
3.6. HPLC Conditions
3.7. The Screening of NO Generation Inhibitors
3.8. Anti-Inflammatory Activity on THP-1 Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- State Adeministration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the People’ s Republic of China. Traditional Chinese Meteria Medica of Dai Nationality; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 2005; ISBN 9787532380091. [Google Scholar]
- Ethnic Medicine Research Office of Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture. Annals of Xishuangbanna Dai Medicine; Board of Health of Xishuangbanna: Xishuangbanna, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, S.J. Overview on research and development of ethno-medicine in China. In Herbal Globalisation: A New Paradigm for Malaysian Herbal Industry: Proceedings of the Seminar on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (MAPS 2008), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21–22 October 2009; Forest Research Institute Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.H.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.H.; Tong, Y.F.; Dong, H.; Nie, Q.; Office, S. A discussion of the path to accelerate the development of dai medical education in China. J. Res. EFEM 2018, 1, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, W.; Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Tan, B.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Yang, S.J. Preparative purification of peoniflorin and albiflorin from peony rhizome using macroporous resin and medium-pressure liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 35, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf-Khorassani, M.; Taylor, L.T.; Martin, M.J.C. Supercritical fluid extraction of Kava lactones from Kava root and their separation via supercritical fluid chromatography. Chromatographia 1999, 50, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Conway, W.D. High-speed countercurrent chromatography. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1986, 17, 65–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A. Countercurrent chromatography and the journal of liquid chromatography: A love story. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Knight, M.; Finn, T.M. Spiral Countercurrent Chromatography; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, I.A.; Fisher, D.J. Role of counter-current chromatography in the modernisation of Chinese herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.W.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Zhao, L.; He, Q.X.; Li, Y.B.; Chen, X.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, K.C. Tracking antiangiogenic components from Glycyrrhiza uralensis based on zebrafish assays using high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surup, F.; Tran, T.M.T.; Pfvtze, S.; Budde, J.; Moussa-Ayoub, T.E.; Rohn, S.; Jerz, G. Opuntisines, 14-membered cyclopeptide alkaloids from fruits of Opuntia stricta var. dillenii isolated by high-performance countercurrent chromatography. Food Chem. 2020, 334, 127552. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschick, T.; Wagner, T.; Vetter, W. Countercurrent chromatographic fractionation followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry identification of alkylresorcinols in rye. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 8417–8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Sun, X.; Ni, H.; Du, X.P.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Z.D.; Li, Q.B. Identification and characterization of the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of caffeine from Camellia Pollen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12741–12751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.N.; Tang, Y.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, Y.C. Development of a method to screen and isolate potential alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from Panax japonicus CA Meyer by ultrafiltration, liquid chromatography, and counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 2014–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, Y.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, S.S. Comprehensive evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of Perilla frutescens leaves extract and isolation of free radical scavengers using step-wise HSCCC guided by DPPH-HPLC. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieir, M.N.; Winterhalter, P.; Jerz, G. Flavonoids from the flowers of Impatiens glandulifera isolated by high performance countercurrent chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deamicis, C.; Yang, Q.; Bright, C.; Edwards, N.; Harris, G.; Kaur, S.; Wood, P.; Hewitson, P.; Ignatova, S. Development of a scalable and sustainable high performance countercurrent chromatography (HPCCC) purification for spinosyn A and spinosyn D from spinosad. Org. Process Res. 2017, 21, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee of Chinese Flora. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L. Studies on Chemical Constituents and Their Bioactivities of Zanthoxylum acanthopodium var. timbor, Fissistigma polyanthum and Mappianthus iodoides; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.S.; Tsai, I.W.; Teng, C.M.; Chen, J.J.; Chang, Y.L.; Ko, F.N.; Lu, M.C.; Pezzuto, J.M. Pyranoquinoline alkaloids from Zanthoxylum simulans. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, Y.N.; Yan, X.T.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, E.-J.; Kang, H.K.; Kim, Y.H. Coumarins and lignans from Zanthoxylum schinifolium and their anticancer activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10730–10740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yu, D.; Wu, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Wei, A.; Wang, D.J. Comparative transcriptome analysis and expression of genes reveal the biosynthesis and accumulation patterns of key flavonoids in different varieties of Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13258–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.W.; Liu, S.; He, F.T.; Li, X.Y.; Saira, B.; Zheng, T.L.; Chen, J.Y.; Dong, K.; Pei, X.F. Anticancer activities of Zanthoxylum bungeanum seed oil on malignant melanoma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 229, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.L.; Xia, X.; Luo, X.D. Comparison of chemical constituents in diverse Zanthoxylum herbs, and evaluation of their relative antibacterial and nematicidal activity. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barus, M.N.G.; Syafruddinilyas, M.S.; Bachtiar, A. Andaliman fruit extract (Zanthoxylum acantophodium) and it’s effect on preeclampsia as anti-inflammatory. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2020, 12, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooreen, Z.; Tandon, S.; Yadav, N.P.; Kumar, P.; Ahmad, A. Zanthoxylum: A systematic review of its traditional uses, naturally occurring constituents and pharmacological properties. Curr.Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 1307–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Conway, W.D. Development of countercurrent chromatography. Nature 1984, 326, 65–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, J.; Heping, L.I.; Yan, X.; Dianpeng, L.I.; Fenglai, L.U. Preparation of cucurbitacin compounds in Siraitia grosvenorii roots by high speed countercurrent chromatography. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2022, 40, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Hu, H.B.; Xu, Y.K.; Song, Q.S. Quick method for separating target compounds from the bark of Maqian (Zanthoxylum myriacanthum var. pubescens) by high-performance countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4049–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Friesen, J.B.; Grzelak, E.M.; Fan, Q.F.; Pauli, G.F. Sweet spot matching: A thin-layer chromatography-based countercurrent solvent system selection strategy. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1504, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.J. A new dimeric lignan from Zanthoxylum simulans. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, J.K.; Gottlieb, O.R.; Sarti, S.J.; Filho, D.S. Isolation of lignans and sesquiterpenoids from leaves of Zanthoxylum naranjillo. Nat. Prod. Let. 1996, 9, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yu, H.Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Huang, Y.; Zou, X.W.; Huang, B.S.; Tang, J.T. Separation of five naphtho-γ-pyrones from Pleurotus ostreatus by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 4551–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, D.W.; McCreedy, S.A. N-nitro-L-arginine and N-monomethyl-L-arginine exhibit a different pattern of inactivation toward the three nitricoxide synthases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 320, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.K.; Hyun, C.G. 4-Hydroxy-7-Methoxycoumarin inhibits inflammation in LPS-activated RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation. Molecules 2020, 25, 4424–4433. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Yang, J.J.; Shi, Y.X.; Zhao, M.; Ji, K.L.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.K.; Hu, H.B. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities of the essential oil from Maqian (Zanthoxylum myriacanthum var. pubescens) in Xishuangbanna, SW China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.D.; Huang, S.X.; Han, Q.B. Diterpenoids from Isodon species and their biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 673–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample Name | Concentration | Inhibition Rate of NO Production (%) |
|---|---|---|
| L-NMMA | 50 μM | 51.88 ± 1.17 |
| Residual water fraction | 40 μg/mL | - |
| N-butanol extract | 40 μg/mL | 8.83 ± 1.67 |
| Ethyl acetate extract | 40 μg/mL | 74.59 ± 1.40 |
| Petroleum ether extract | 40 μg/mL | 93.88 ± 0.67 |
| Total extract | 40 μg/mL | 39.35 ± 0.42 |
| NO | Solvent Systems (v/v/v/v) Petroleum Ether/Ethyl Acetate/Methanol/Water | Solvent Systems (v/v) Petroleum Ether / Ethyl Acetateof TLC | Average Rf Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4:1:4:1 | 4:1 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 5:2:5:2 | 5:2 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 1:1:1:1 | 1:1 | 0.6 |
| 4 | 3:2:3:2 | 3:2 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.-F.; Zhou, L.; Gongpan, P.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Chang, H.; Xiang, X. Bioactivity-Guided High Performance Counter-Current Chromatography and Following Semi-Preparative Liquid Chromatography Method for Rapid Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Lignins from Dai Medicinal Plant, Zanthoxylum acanthopodium var. timbor. Molecules 2023, 28, 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062592
Fan Q-F, Zhou L, Gongpan P-C, Lu C-L, Chang H, Xiang X. Bioactivity-Guided High Performance Counter-Current Chromatography and Following Semi-Preparative Liquid Chromatography Method for Rapid Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Lignins from Dai Medicinal Plant, Zanthoxylum acanthopodium var. timbor. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062592
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qing-Fei, Lan Zhou, Pian-Chou Gongpan, Chuan-Li Lu, Hua Chang, and Xun Xiang. 2023. "Bioactivity-Guided High Performance Counter-Current Chromatography and Following Semi-Preparative Liquid Chromatography Method for Rapid Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Lignins from Dai Medicinal Plant, Zanthoxylum acanthopodium var. timbor" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062592
APA StyleFan, Q.-F., Zhou, L., Gongpan, P.-C., Lu, C.-L., Chang, H., & Xiang, X. (2023). Bioactivity-Guided High Performance Counter-Current Chromatography and Following Semi-Preparative Liquid Chromatography Method for Rapid Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Lignins from Dai Medicinal Plant, Zanthoxylum acanthopodium var. timbor. Molecules, 28(6), 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062592