A Novel Drug Delivery System: Hyodeoxycholic Acid-Modified Metformin Liposomes for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Liposomes
2.2. Assay for Anti-Type 2 Diabetes Activity
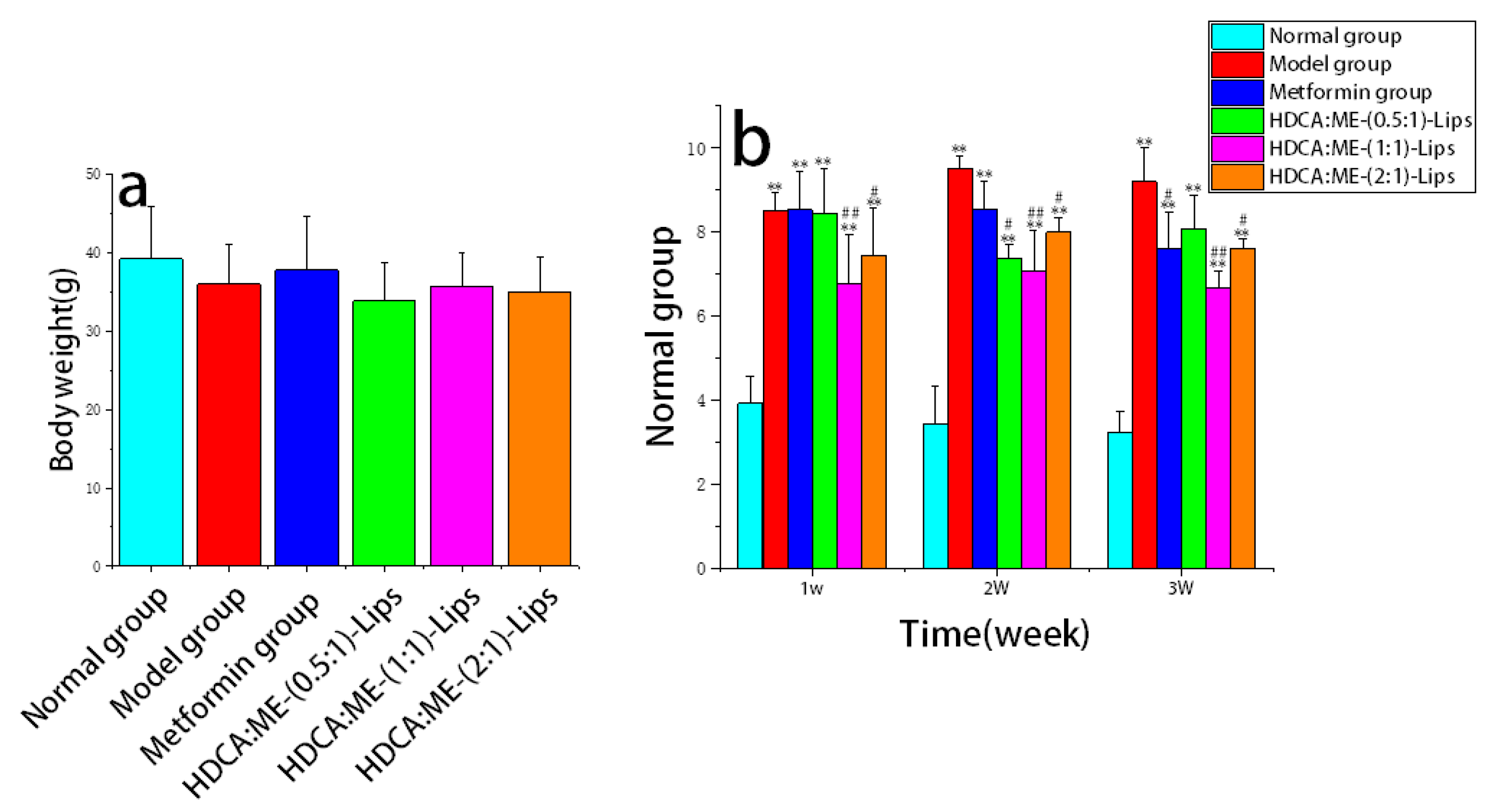
2.2.1. Reduction in the Fasting Blood Glucose Level
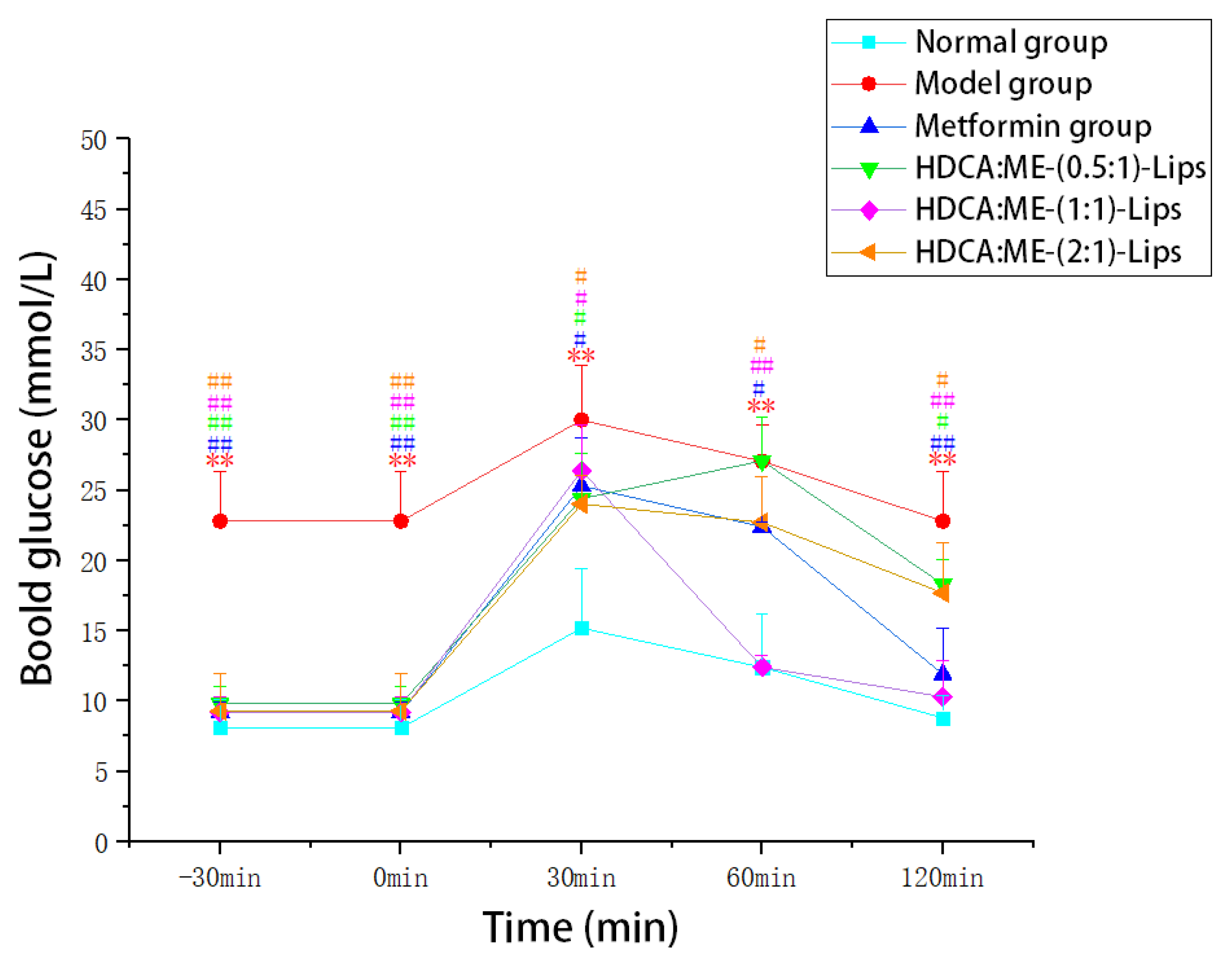
2.2.2. Improvement in the Oral Glucose Tolerance
2.2.3. Regulation of the Biochemical Indices
2.2.4. Protection of the Liver Tissue
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of HDCA Dosage on Liposomes
3.2. Anti-Type 2 Diabetes Activity of Liposomes
3.3. Potential of HDCA as an Excipient for Liposomes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Liposomes
4.3. Characterization of Liposomes
4.3.1. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
4.3.2. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) and Drug Loading (DL)
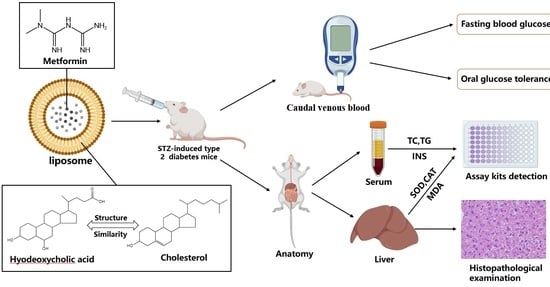
4.4. Animal Experiments
4.4.1. Establishment of the Type 2 Diabetic Mice Model
4.4.2. Grouping and Administration
4.4.3. Measurement of Fasting Blood Glucose Levels
4.4.4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
4.4.5. Assessment of Biochemistry Indices
4.4.6. Histopathological Examination
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polsky, S.; Ellis, S.L. Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2015, 22, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Ko, E.; Jin, H.Y. Factors influencing psychological insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes patients. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2019, 25, e12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodorou, K.; Banach, M.; Bekiari, E.; Rizzo, M.; Edmonds, M. Complications of Diabetes 2017. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 3086167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, J.; Lipska, K. Metformin in 2019. JAMA 2019, 321, 1926–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.J.; Peters, D.H. Metformin. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Drugs 1995, 49, 721–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1996, 30, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.X.; Huang, L.; Gauthier, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q. Recent advances in liposome surface modification for oral drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Fu, C.; Lin, J.; Ke, X.; Zou, W.; Xu, R.; Han, L.; Yang, M. Application value of “Combination of medicine and Supplement” in Traditional Chinese Medicine preparation. Chin. Tradit. Med. 2017, 48, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Liu, W.; Qing, Y.; Yao, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; He, L. Study on sustained release of Chinese herbal Compound based on “unification of medicines and excipients”—A case study of Shaoyao and Licorice Wei Floating Tablets. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 9, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Du, P.; Qing, Y.; Yao, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; He, L.; Shi, Y. Effect and mechanism of Shaoyao and Licorice Wei Floating Tablets on rabbits with acute gastric ulcer. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 50, 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Application of the concept of unification of medicines and excipients” in the design of delivery system of Traditional Chinese Medicine preparation. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (TCM) 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Peng, C.; Shi, S. Ginsenosides emerging as both bifunctional drugs and nanocarriers for enhanced antitumor therapies. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Shen, L. Formulation, Preparation and Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Containing Naringin and Coix Seed Oil for Anti-Tumor Application Based on “Unification of Medicines and Excipients”. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Compendium of Materia Medica, 6th ed.; Northern Literature and Art Publishing House: Harbin, China, 2016; pp. 1016–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, T.; Zhao, A.; Ning, Z.; Kuang, J.; Wang, S.; You, Y.; Bao, Y.; Ma, X.; Yu, H.; et al. Hyocholic acid species as novel biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, T.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Q.; Kuang, J.; Sun, D.; Ren, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, M.; et al. Hyocholic acid species improve glucose homeostasis through a distinct TGR5 and FXR signaling mechanism. Cell Metab. 2020, 33, 791–803.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Cai, B. Uptake of diphenylate liposomes modified with cholic acid into hepatocellular parenchymal cells. J. China Pharm. Univ. 2010, 41, 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.J. Preparation of Cholic Acid-Baicalin Nasal Liposome and Its Protective Effect on Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats; Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Thin-Film Hydration Followed by Extrusion Method for Liposome Preparation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1522, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, J.; Wu, W. Preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluations of 10-hydroxycamptothecin liposomes modified with stearyl glycyrrhetinate. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnick, G.R. Measurement of Cholesterol and other Lipoprotein Constituents in the Clinical Laboratory. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994, 344, 1383–1389.
- Lindkvist, B.; Appelros, S.; Regnér, S.; Manjer, J. A prospective cohort study on risk of acute pancreatitis related to serum triglycerides, cholesterol and fasting glucose. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak-Pajor, I.; Drzewoski, J.; Śliwińska, A. The Molecular Mechanisms by Which Vitamin D Prevents Insulin Resistance and Associated Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Huang, W.; Young, R.; Jones, K.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.; Wu, T. Role of Bile Acids in the Regulation of Food Intake, and Their Dysregulation in Metabolic Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansome, D.J.; Xie, C.; Veedfald, S.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K.; Wu, T. Mechanism of glucose-lowering by metformin in type 2 diabetes: Role of bile acids. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 22, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, G.; da Cruz, I.B.M.; González-Gallego, J. Manganese Superoxide Dismutase and Oxidative Stress Modulation. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 68, 87–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebicka, L.; Krych-Madej, J. The role of catalases in the prevention/promotion of oxidative stress. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 197, 110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasson, S. Nutrient overload, lipid peroxidation and pancreatic beta cell function. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 111, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M. Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloy, J.O.; de Souza, M.C.; Petrilli, R.; Barcellos, J.P.A.; Lee, R.J.; Marchetti, J.M. Liposomes as carriers of hydrophilic small molecule drugs: Strategies to enhance encapsulation and delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daeihamed, M.; Dadashzadeh, S.; Haeri, A.; Akhlaghi, M.F. Potential of Liposomes for Enhancement of Oral Drug Absorption. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagayasu, A.; Uchiyama, K.; Kiwada, H. The size of liposomes: A factor which affects their targeting efficiency to tumors and therapeutic activity of liposomal antitumor drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 40, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Jung, K.H. Total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein and triglyceride for cardiovascular disease in elderly patients treated with metformin. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.S. Lipids for Psychiatrists—An overview. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Maranduca, M.A.; Ouatu, A.; Floria, M. The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3920196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samini, F. Anti-oxidative effects of curcumin on immobilization-induced oxidative stress in rat brain, liver and kidney. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, E.L. Oxidative stress and diabetes: Glucose response in the cROSsfire. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, M.J.; Marin, J.J.; Antelo, A.; Vazquez-Tato, J. Bile acids: Chemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustino, C.; Serafim, C.; Rijo, P.; Reis, C.P. Bile acids and bile acid derivatives: Use in drug delivery systems and as therapeutic agents. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Rajani, C.; Zheng, X.; Jia, W. Hyocholic acid and glycemic regulation: Comments on ‘Hyocholic acid species improve glucose homeostasis through a distinct TGR5 and FXR signaling mechanism’. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 13, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Liposomes | Particle Size | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) | Drug Loading (DL%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDCA:ME-(0.5:1)-Lips | 196.36 | 0.259 | 67.15 | 5.52 |
| HDCA:ME-(1:1)-Lips | 232.30 | 0.256 | 61.28 | 5.35 |
| HDCA:ME-(2:1)-Lips | 332.40 | 0.258 | 59.53 | 5.16 |
| Group | Concentrations of Fasting Blood Glucose(mmol/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | D7 | D14 | D21 | |
| Normal group | 6.67 | 5.16 | 7.55 | 6.65 |
| Model group | 18.26 ** | 19.08 ** | 21.3 * | 20.48 * |
| Metformin group | 18.44 ** | 15.24 ## | 15.73 # | 12.42 ## |
| HDCA:ME-(0.5:1)-Lips | 18.42 ** | 13.08 # | 13.22 ## | 12.34 ## |
| HDCA:ME-(1:1)-Lips | 18.68 * | 14.94 # | 14.64 # | 11.62 # |
| HDCA:ME-(2:1)-Lips | 18.8 * | 15.88 ## | 14.6 # | 15.8 ## |
| Biochemical Indices | HDCA:ME-(0.5:1)-Lips | HDCA:ME-(1:1)-Lips | HDCA:ME-(2:1)-Lips |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 3.63 ** | 3.28 ** | 3.91 ** |
| TG | 2.62 * | 1.87 ** | 2.44 * |
| INS | 1.169 * | 1.082 ** | 1.277 |
| GLP-1 | 0.761 * | 0.807 ** | 0.764 * |
| SOD | 162.18 | 360.72 ** | 188.65 |
| CAT | 134.66 ** | 156.52 ** | 99.56 ** |
| MDA | 69.02 ** | 58.70 ** | 6039 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Gou, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, R.; Zhou, T.; Liu, J.; Peng, C.; Ye, Q. A Novel Drug Delivery System: Hyodeoxycholic Acid-Modified Metformin Liposomes for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062471
Hu M, Gou T, Chen Y, Xu M, Chen R, Zhou T, Liu J, Peng C, Ye Q. A Novel Drug Delivery System: Hyodeoxycholic Acid-Modified Metformin Liposomes for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062471
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Minghao, Tingting Gou, Yuchen Chen, Min Xu, Rong Chen, Tao Zhou, Junjing Liu, Cheng Peng, and Qiang Ye. 2023. "A Novel Drug Delivery System: Hyodeoxycholic Acid-Modified Metformin Liposomes for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062471
APA StyleHu, M., Gou, T., Chen, Y., Xu, M., Chen, R., Zhou, T., Liu, J., Peng, C., & Ye, Q. (2023). A Novel Drug Delivery System: Hyodeoxycholic Acid-Modified Metformin Liposomes for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment. Molecules, 28(6), 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062471