Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water and Wastewaters by Electrochemical Processes: Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
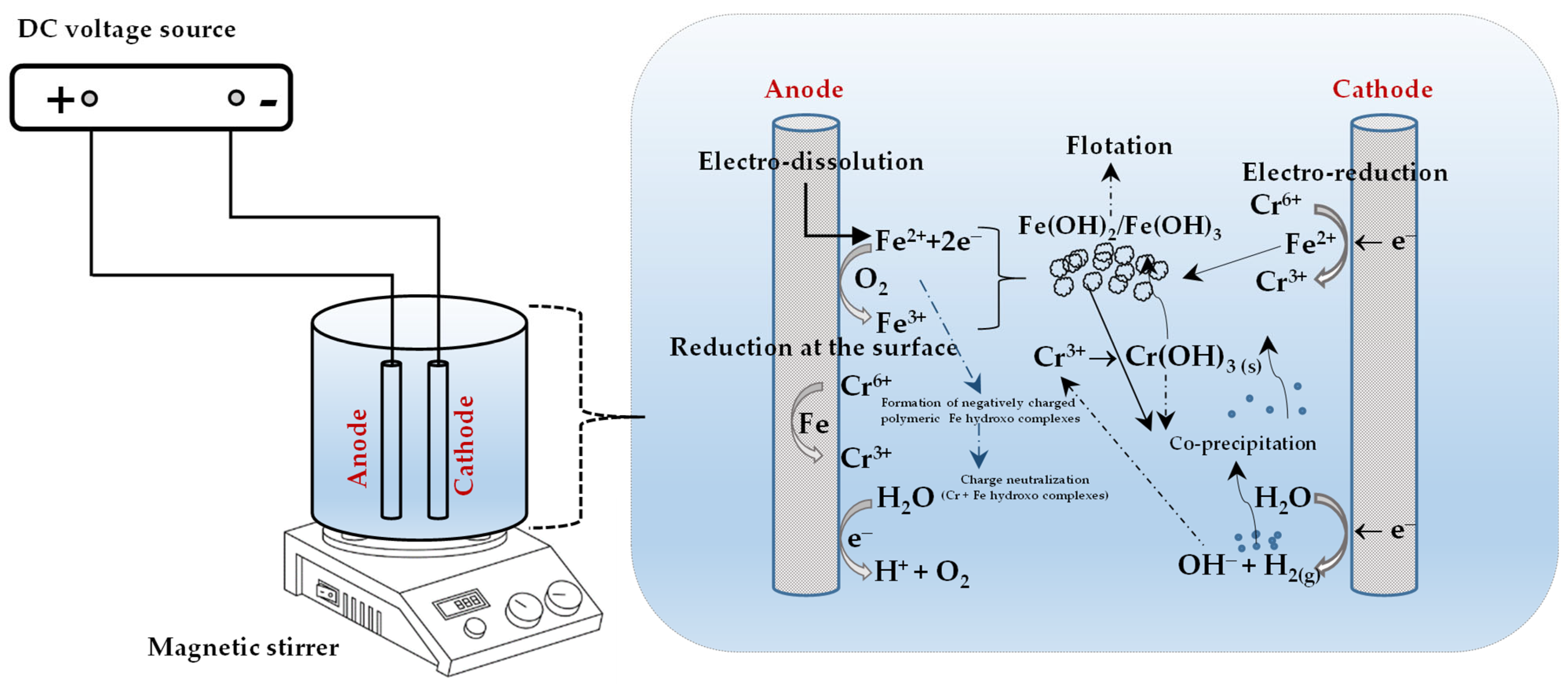
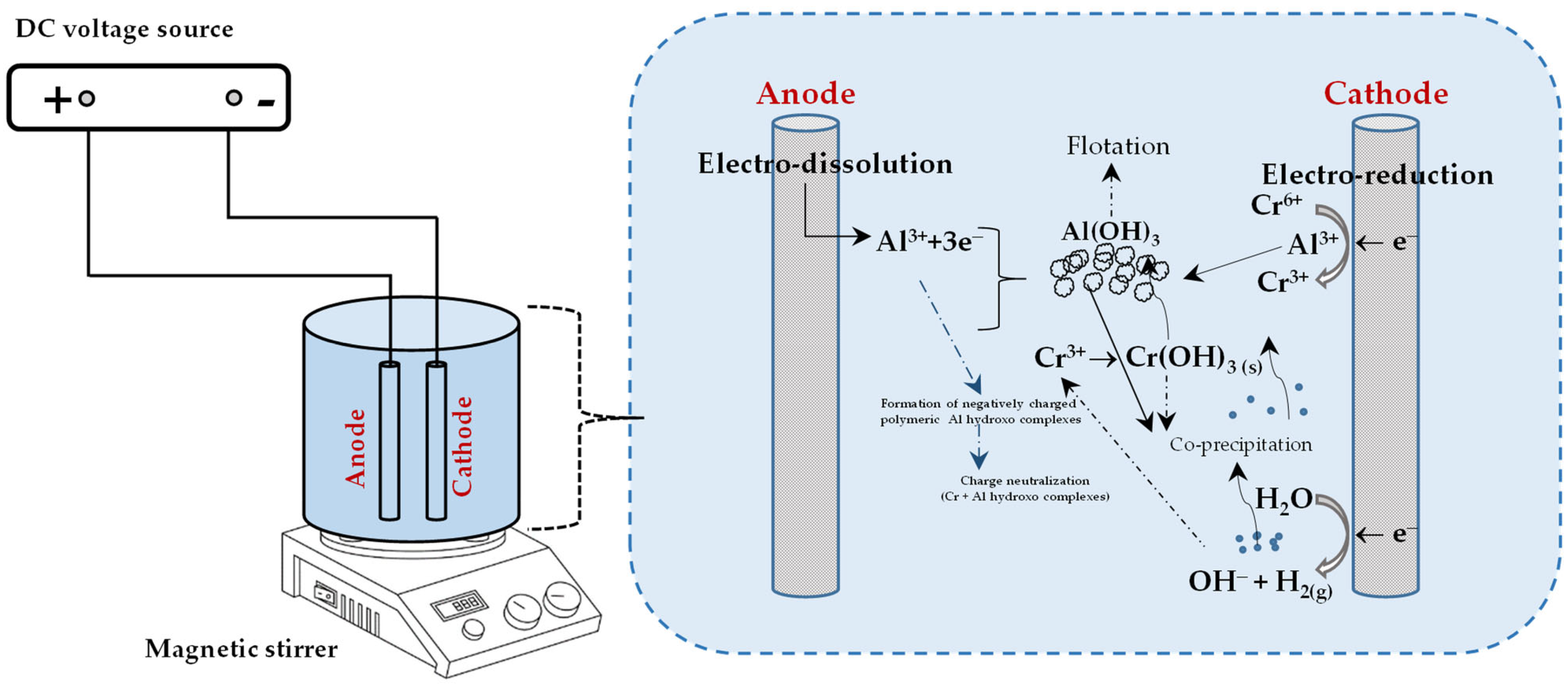
2. Responsible Chromium Removal Mechanisms in the Electrocoagulation Process
2.1. Iron-Based Electrodes
2.2. Aluminium Electrodes
3. Operating Parameters
3.1. Iron-Based Electrodes
3.1.1. Initial pH
3.1.2. Initial Cr(VI) Concentration
3.1.3. Current Density or Current
3.1.4. Supporting Electrolyte
3.2. Aluminium Electrodes
4. Optimum Operating Conditions and Interactions of Process Variables
5. Reactor Design and Other Issues Related to Electrode Type
| Electrocoagulator | Electrodes | A/C (ED) 1 | Connection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mL PMMA (100 × 100 × 50 mm) | Fe; 2 sections (50 cm2) | 1/1 (NA 2) | DC or PC | [3] |
| 2 L glass beaker (d:11 cm) | Fe; 4 rod+1 circular plate | 4/1(0.87 cm) | DC | [19] |
| 4 L P-G cylindrical (d:10 cm) | MS 3 rod anode + HC Fe MC 4 | NA | DC | [20] |
| 2 L P-E rectangular | SS 5; 6 rod | 3/3 (2 mm) | DC | [21] |
| 1 L cylindrical | Fe; 2 flat plate (80 cm2) | 1/1 (18 mm) | DC | [23] |
| 500 mL glass beaker | Fe; 2 flat plate | 1/1(NA) | DC/BP | [24] |
| 2.5 L | Fe; 2 rod (16 cm2) | 1/1 (25 mm) | DC | [25] |
| P-G rectangular | 2 SS | 1/1 (15 cm) | DC | [27] |
| P-G rectangular (L:109 w:74 h:208 mm) | Fe or Al; 6 flat plates | 3/3 (10 mm) | MP/DC | [28] |
| 2 L beaker | MS; 4 flat plates | NA (5 mm) | DC/BP | [30] |
| NA | Fe or Al sheet (7 × 7.7 cm) Pt Ti 6 anode/Fe or Al cathode | 1/1 (4 cm) | DC | [31] |
| 2 L beaker | Fe anode/steel cathode | 1/1 (1.4 cm) | DC | [39] |
| N.A. | Fe or Al anode/steel cathode | 1/1 (NA) | DC | [44] |
| P-G cylindrical (d:15 h:13 cm) | 2, 4, 6 | NA (1 cm) | [45] | |
| 5 L glass | Fe, Al or SS-2 Plate | 1/1; NA | MP/DC | [46] |
| P-G cylindrical (d:14 h:24 cm) | Fe- 2 concentric | 1/1 (0.5 cm) | MP/DC | [48] |
| 250 mL glass beaker | 2 plate electrode (1 cm2) | 1 × 1(0.5 cm) | DC | [50] |
| Glass beaker | 2 steel slice (2 × 2 cm) | 1/1 (2 cm) | DC | [57] |
| 2.5 L | Fe-2 iron (20 cm2) | 1/1 (2 cm) | DC | [59] |
| 3 L P-G cylindrical | Al/Al 7 (210.5 cm2) | 1/1(2 cm) | DC | [60] |
| P-G rectangular (24 × 17 × 18 cm)-St 8 | Al, 4 plates | 2/2 (1.5 cm) | DC | [61] |
| 1.5 L rectangular (L:15 w:10 h:12 cm) | Al (12.5 × 8 × 1 cm) | NA (2.5 cm) | DC | [62] |
| P-G cylindrical (d:15 h:25 cm) | Al, 6 (d: 2 cm) | NA (1 cm) | DC | [63] |
| 1 L reactor | Al, 4 (150 × 60 × 2 mm) | NA (1 cm) | DC/DP | [64] |
| 5 L P-G cylindrical reactor | Al, (d:15 cm; 126 cm2) | NA (3 cm) | DC | [65] |
| 1 L borosilicate glass reactor | Al, 2 plates (30.74 cm2 | 1/1 (22 mm) | DC | [66] |
| 400 mL glass beaker | Fe or Al sheets | 1/1 (1.5 cm) | DC | [72] |
| Acrylic rectangular (L: 7 w: 4 h: 30 cm) | 2 Al sheet(100 cm2) | 1/1 (15 mm) | DC | [70] |
| 2 L P-G cylindrical reactor | 2 Al (81.056 cm2) | 1/1 (2 cm) | DC | [74] |
| 7 L P-G rectangular (18 × 18 × 30 cm) | Al/Al or graphite (450 cm2) | 1/1 (2–4 cm) | DC | [73] |
| 0.7 L reactor | Fe/Al (36 cm2) | 1/1 (1.5 cm) | DC or AC | [75] |
| 2651 mL P-G (d:150 h:150 mm) | Fe/Fe or Al/Al (63 cm2) | 1/1 (NA) | DC | [76] |
| 1 L Pyrex reactor | Fe/SS | NA | DC | [77] |
| P-G rectangular (6.45 × 9.95 × 11.2 cm) | 6 Fe, Al, SS combinations 9 | 3/3 (6 mm) | MP/DC | [78] |
| 1L P-P beaker | 2 Fe/Fe rod | 1/1 (NA) | NA | [79,80] |
| P-G cylindrical (d: 9 cm; h:13 cm) | Fe/Fe (85 cm2) | 1/1 (NA) | DC | [81] |
6. Sludge Characteristics
7. Kinetics Analysis
+ kO2[Fe(II)]diss
8. Electrocoagulation Application to Industrial Effluents
9. Electroreduction by Redox Electrodes and Dimensionally Stable Electrodes
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorny, J.; Billon, G.; Noiriel, C.; Dumoulin, D.; Lesven, L.; Madé, B. Chromium behavior in aquatic environments: A review. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium Pollution in European Water, Sources, Health Risk, and Remediation Strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Liu, F.; Wei, N.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C. Comparison of Cr (VI) removal by direct and pulse current electrocoagulation: Implications for energy consumption optimization, sludge reduction and floc magnetism. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Jaikumar, V.; Kumar, P.S.; SundarRajan, P. A review on cleaner strategies for chromium industrial wastewater: Present research and future perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, D.L.; Chan, P.G. Reduction of hexavalent chromium by ferrous iron. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, H. Horizontal and Vertical Distributions of Chromium in a Chromate Production District of South Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerur, S.; Bandekar, S.; Hanagadakar, M.S.; Nandi, S.S.; Ratnamala, G.; Hegde, P.G. Removal of hexavalent Chromium-Industry treated water and Wastewater: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Parikh, S.P. Statistical optimizing of electrocoagulation process for the removal of Cr(VI) using response surface methodology and kinetic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7032–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.D.; Puls, R.W. Natural Attenuation of Hexavalent Chromium in Groundwater and Soils: Ground water issue. Environ. Prot. Agency 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shanker, A.; Venkateswarlu, B. Chromium: Environmental Pollution, Health Effects and Mode of Action. Encycl. Environ. Health 2011, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evliyaogullari, N.E.; Oden, M.K.; Kucukcongar, S. The removal of chromium from aqueous solutions using an industrial waste material. Int. J. Ecosyst. Ecol. Sci.-Ijees 2017, 7, 671–676. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Itankar, N.; Patil, Y. Biomanagement of hexavalent chromium: Current trends and promising perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 279, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Díaz, C.E.; Lugo-Lugo, V.; Bilyeu, B. A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr(VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 223–224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tünay, O.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Hung, Y.-T. Treatment of metal finishing wastes. In Handbook of Industrial Hazardous Waste Treatment; Wang, L.K., Hung, Y.-T., Lo, H.H., Yapijakis, C., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 289–359. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Du, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Electrochemical processes for the environmental remediation of toxic Cr(VI): A review. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Kang, D.J.; Chen, Z.; Zhan, J.J.; Wu, X.Q. Removal of Chromium Using Electrochemical Approaches: A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghaki, N.S.; Jonoush, Z.A.; Rezaee, A. Improving the performance of Cr (VI) removal by electrochemical process using microbial cellulose/magnetic nanoparticles electrode. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, O.A.; Matta, M.E.; Safwat, S.M. Nickel and chromium removal by electrocoagulation using copper electrodes. DESALINATION Water Treat. 2021, 213, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taweel, Y.A.; Nassef, E.M.; Elkheriany, I.; Sayed, D. Removal of Cr(VI) ions from waste water by electrocoagulation using iron electrode. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Islam, D.T.; Farooqi, I.H.; Ayub, S.; Basheer, F. Hexavalent chromium removal in an electrocoagulation column reactor: Process optimization using CCD, adsorption kinetics and pH modulated sludge formation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 122, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ölmez, T. The optimization of Cr(VI) reduction and removal by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, M.; Naghdali, Z.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Sandoval, M.A.; Titchou, F.E.; Malekdar, F.; Nasr, M.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Lichtfouse, E.; Emamjomeh, M.M. Reclamation of forward osmosis reject water containing hexavalent chromium via coupled electrochemical-physical processes. Environ. Technol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, M.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Montañés, M.; Garcia-Anton, J.; Guiñón, J. Effect of pH and chloride concentration on the removal of hexavalent chromium in a batch electrocoagulation reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Tan, D.; Jing, X.; Xu, Q. Modeling and optimization of the electric flocculation of wastewater containing Cr6+ using response surface methodology. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-Y.; Yang, Z.-H.; Zeng, G.-M.; Luo, Y.-L.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.-K.; Song, P.-P.; Mo, X. Investigation of pH evolution with Cr(VI) removal in electrocoagulation process: Proposing a real-time control strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 239, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystynik, P.; Masin, P.; Krusinova, Z.; Kluson, P. Application of electrocoagulation for removal of toxic metals from industrial effluents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 4167–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhotra, V.; Yadav, R.; Sugha, A.; Das, L.; Vashisht, A.; Bhatti, R.; Bhatti, M.S. Electrochemical treatment of high strength chrome bathwater: A comparative study for best-operating conditions. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 2, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Z.-R.; Liu, Y.-L.; Tang, Q. Removal of Cr ions from aqueous solution using batch electrocoagulation: Cr removal mechanism and utilization rate of in situ generated metal ions. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocke, D.L.; Gomes, J.A.G.; Morkovsky, P.; Parga, J.R.; Peterson, E.; Garcia, C. Electrochemical Reactions for Electrocoagulation Using Iron Electrodes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidmann, I.; Calmano, W. Removal of Cr(VI) from model wastewaters by electrocoagulation with Fe electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouedhen, G.; Feki, M.; De Petris-Wery, M.; Ayedi, H. Electrochemical removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous media using iron and aluminum as electrode materials: Towards a better understanding of the involved phenomena. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmipathiraj, P.; Raju, G.B.; Basariya, M.R.; Parvathy, S.; Prabhakar, S. Removal of Cr (VI) by electrochemical reduction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 60, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Hug, S.J. Kinetics and pH Dependence of Chromium(VI) Reduction by Iron(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golder, A.K.; Chanda, A.K.; Samanta, A.N.; Ray, S. Removal of hexavalent chromium by electrochemical reduction–precipitation: Investigation of process performance and reaction stoichiometry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 76, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Díaz, C.; Lugo-Lugo, V.; Roa-Morales, G.; Natividad, R.; Martínez-Delgadillo, S. Enhancing the electrochemical Cr(VI) reduction in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.N.; Amirtharajah, A. Ferric-chloride and alum as single and dual coagulants. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1983, 75, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, B.M.; Rai, D. Solubility of amorphous chromium(III)-iron(III) hydroxide solid solutions. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 2228–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouedhen, G.; Feki, M.; Wery, M.D.P.; Ayedi, H. Behavior of aluminum electrodes in electrocoagulation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thella, K.; Verma, B.; Srivastava, V.C.; Srivastava, K.K. Electrocoagulation study for the removal of arsenic and chromium from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, F.; Chen, G. Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater by combined electrocoagulation–electroflotation without a filter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 43, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, D.; Sass, B.M.; Moore, D.A. Chromium(III) hydrolysis constants and solubility of chromium(III) hydroxide. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermentzis, K.; Christoforidis, A.; Valsamidou, E.; Lazaridou, A.; Kokkinos, N. Removal of hexavalent chromium from electroplating wastewater by electrocoagulation with iron electrodes. Glob. Nest J. 2011, 13, 412–418. [Google Scholar]
- Aber, S.; Amani-Ghadim, A.; Mirzajani, V. Removal of Cr(VI) from polluted solutions by electrocoagulation: Modeling of experimental results using artificial neural network. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheballah, K.; Sahmoune, A.; Messaoudi, K.; Drouiche, N.; Lounici, H. Simultaneous removal of hexavalent chromium and COD from industrial wastewater by bipolar electrocoagulation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2015, 96, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Nandi, B.K. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater by Electrocoagulation (EC): Parametric Evaluation, Kinetic Study and Operating Cost. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Khandegar, V.; Saroha, A.K. Removal of Chromium from Electroplating Industry Effluent Using Electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2013, 17, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewail, T.; Yousef, N. Chromium ions (Cr6+ & Cr3+) removal from synthetic wastewater by electrocoagulation using vertical expanded Fe anode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 735, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.M.; Mubarak, A.A.; Nosier, S.A. Removal of Cr(VI) by Electrocoagulation Using Vertical and Horizontal Rough Cylinder Anodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Leng, Y.; Guo, J. Electrochemical Removal of Chromium (VI) from Wastewater. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Arslan, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Ölmez-Hancı, T.; Tünay, O. Organic matter and heavy metal removals from complexed metal plating effluent by the combined electrocoagulation/Fenton process. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Ölmez-Hancı, T.; Tünay, O. Electrocoagulation applications for industrial wastewaters: A critical review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2012, 1, 2–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Arslan, T.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Tünay, O. Complexing agent and heavy metal removals from metal plating effluent by electrocoagulation with stainless steel electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Huang, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Sha, S. Primary concentration—The critical step in implementing the wastewater based epidemiology for the COVID-19 pandemic: A mini-review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 747, 141245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G. Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Vardar, B.; Tünay, O. Electrocoagulation of simulated reactive dyebath effluent with aluminum and stainless steel electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Leng, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Shang, Q.; Shu, J.; Guo, J. Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction. Processes 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, V.; Alyoussef, G.; Gatcha-Bandjun, N.; Gwenzi, W.; Noubactep, C. Characterizing the impact of MnO2 addition on the efficiency of Fe0/H2O systems. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-Y.; Yang, Z.-H.; Luo, Y.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.-K.; Song, P.-P.; Yang, X. A novel approach to sustain Fe 0 -electrocoagulation for Cr(VI) removal by optimizing chloride ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Basu, D. Optimization of Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater by Electrocoagulation Process Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Hazardous, Toxic, Radioact. Waste 2023, 27, 04022038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhosh, M.; Atafar, Z.; Ahmadi, E.; Nazari, S.; Fakhri, Y.; Rezaei, S.; Mohseni, S.M.; Saghi, M.H.; Torkashvand, M. Treatment of Electroplating Cr(VI) for Reduction Cr(VI) by Electrocoagulation in Continuous Operation. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukaina, N.M.; Chaimaa, M.; Kabriti, M.; Abdelmotalib, N.; Naamane, A.; Mohamed, C.; Nadia, I. Treatment of Surface Treatment Effluents by Electrocoagulation Process Using Aluminium Electrodes. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashtoukhy, E.-S.Z.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Sedahmed, G.H. Simultaneous Removal of Greases and Hexavalent Chromium from Electroplating and Chromate Conversion Coating Waste Solution by Electrocoagulation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, A.; Hossini, H.; Masoumbeigi, H.; Soltani, R.D.C. Simultaneous Removal of Hexavalent Chromium and Nitrate from Wastewater using Electrocoagulation Method. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2011, 2, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, W.; Xie, J.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z. A novel electrocoagulation process with centrifugal electrodes for wastewater treatment: Electrochemical behavior of anode and kinetics of heavy metal removal. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golder, A.; Chanda, A.K.; Samanta, A.N.; Ray, S. Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution: Electrocoagulation vs Chemical Coagulation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 2177–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezeth, P.; Palmer, D.A.; Wesolowski, D.J. The aqueous chemistry of aluminum. A new approach to high-temperature solubility measurements. Geothermics 1997, 26, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, J.C. The Fundamentals of Corrosion, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun, M.; Lurie, M. Control of Organic Matter by Coagulation and Floc Separation. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.S.; Reddy, A.S.; Kalia, R.K.; Thukral, A.K. Modeling and optimization of voltage and treatment time for electrocoagulation removal of hexavalent chromium. Desalination 2011, 269, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Tünay, O.; Gülhan, D.; Ecer, C. Application of response surface methodology for dimethyl phthalate treatment via H2O2/UV-C process. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 26165–26173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Khandegar, V. Dataset on statistical reduction of highly water-soluble Cr (VI) into Cr (III) using RSM. Data Brief 2018, 22, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Sonal, S.; Mishra, B.K. Hexavalent chromium removal by monopolar electrodes based electrocoagulation system: Optimization through Box–Behnken design. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2017, 67, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Basu, D. Economic and performance evaluation of electrocoagulation unit for the treatment of hexavalent chromium using Taguchi method. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshmirizadeh, E.; Yousefi, S.; Rofouei, M.K. An investigation on the new operational parameter effective in Cr(VI) removal efficiency: A study on electrocoagulation by alternating pulse current. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, S.S.; El-Naas, M.H. Characterization of the removal of Chromium(VI) from groundwater by electrocoagulation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharfan, N.; Shobri, A.; Anindria, F.A.; Mauricio, R.; Tafsili, M.A.B.; Slamet, S. Treatment of Batik Industry Waste with a Combination of Electrocoagulation and Photocatalysis. Int. J. Technol. 2018, 9, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Yin, W.; Hou, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, K.; Wang, X. Adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium on magnetic greigite (Fe3S4)-CTAB: Leading role of Fe(ii) and S(−ii). RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31568–31574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Troyer, L.D.; Catalano, J.G.; Giammar, D.E. Dynamics of Chromium(VI) Removal from Drinking Water by Iron Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13502–13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Troyer, L.D.; Liao, P.; Catalano, J.G.; Li, W.; Giammar, D.E. Effect of Humic Acid on the Removal of Chromium(VI) and the Production of Solids in Iron Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6308–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oden, M.K.; Sari-Erkan, H. Treatment of metal plating wastewater using iron electrode by electrocoagulation process: Optimization and process performance. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 119, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.W. Role of Carbonate Speciation on the Oxidation Rate of Fe(II) in Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2997–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazit, N. Copper(II), Chromium(VI) and Nickel(II) Removal from Metal Plating Effluent by Electrocoagulation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 4315–4330. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Bai, H.; Li, H.; Lv, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Disposable plastic electrode for electrochemical determination of total chromium and hexavalent chromium. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 794, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, S.; Watanabe, T.; Akai, K.; Einaga, Y. Highly sensitive detection of Cr6+ on boron doped diamond electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 82, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.M.; Nekrassova, O.; Compton, R.G. Reduction of hexavalent chromium at solid electrodes in acidic media: Reaction mechanism and analytical applications. Talanta 2004, 65, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Yan, K. Recent advances in electrochemical detection of toxic Cr(vi). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37440–37450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, G.; Gutiérrez-Granados, S.; de León, C.P.; Alatorre, A.; Walsh, F.; Rodríguez-Torres, I. The electrochemical reduction of Cr(VI) ions in acid solution at titanium and graphite electrodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3610–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; German, S.; Basak, S.; Rajeshwar, K. Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions by Polypyrrole. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, L60–L62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, C. Electroreduction of hexavalent chromium using a polypyrrole-modified electrode under potentiostatic and potentiodynamic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, K.G.; Breslin, C.B. Reduction of hexavalent chromium at a polypyrrole-coated aluminium electrode: Synergistic interactions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, L.; Gubulin, J. Reduction of hexavalent chromium using polyaniline films. Effect of film thickness, potential and flow velocity on the reaction rate and polymer stability. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2003, 33, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cr(VI)o (mg/L) | A/C | Operation Condition | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| =2.32 × 10−4 × CD | 100 | Cu/Cu | pHo: 5.65; C: 0.1–0.3 A | [8] | |
| =−5.14 × 10−4 × Co + 0.109 | 50–150 | Cu/Cu | pHo: 5.65; C: 0.3 A | [8] | |
| =−0.0128 × ED + 0.083 | 100 | Cu/Cu | pHo: 5.65; C: 0.3 A | [8] | |
| 0.0305 | 60 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 3; J: 0.2 mA/cm2 | [20] | |
| 0.0226 | 80 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 3; J: 0.2 mA/cm2 | [20] | |
| 0.0139 | 100 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 3; J: 0.2 mA/cm2 | [20] | |
| k1 | 0.1271 | 10 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 4; J: 43.03 A/m2 | [46] |
| k1 | 0.1171 | 40 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 4; J: 43.03 A/m2 | [46] |
| 0.0729 | 50 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 4; J: 43.03 A/m2 | [46] | |
| 0.0148 | 100 | Fe/Fe | pHo: 4; J: 43.03 A/m2 | [46] | |
| qmax | 14.06 | 50 | Al/Al | pHo: 5; J: 25 mA/cm2; ERS: 120 rpm | [65] |
| qmax | 12.78 | 50 | Al/Al | pHo: 5; J: 25 mA/cm2; ERS: 180 rpm | [65] |
| qmax | 10.11 | 50 | Al/Al | pHo: 5; J: 25 mA/cm2; ERS: 240 rpm | [65] |
| Samples | A/C | Optimum Operating Conditions | Efficiency [%] | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hard chromium coating | SS/SS | pHo 1.85; 7.4 A; 70 min; NaCl: 33.6 mM; 1470 mg/L1 | 100 | [21] |
| Chrome bathwater | SS/SS | pHo 5; 68 A/m2; 17 min; 1500 mg/L1 | 97.5 | [27] |
| Electroplating effluent | Fe/S | pHo 6.9; 50 mA/cm2; 30 min; 17.1 mg/L1 | 97 | [44] |
| Electroplating effluent | Fe/Fe | pHo 4; 50 mA/cm2; 15 min; 889.29 mg/L1 | 100 | [47] |
| Surface treatment effluent | Al/Al | pHo 7; 8.6 A; 60 min; 10020 mg/L1 | 99.99 | [62] |
| Batik industry | TD 2-Al/SS | pHo 7;15 V; 4 h; 3 mg/L1 | 100 | [77] |
| Metal plating effluent | Fe/Fe | pHo 7.4; 35 mA/cm2; 30 min; 358 ± 2.1 mg/L1 | 98.9 | [81] |
| Metal plating effluent | Fe/SS | pHo 2.42; 50 mA/cm2; 30 min; 13.9 mg/L1 | 98 | [83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water and Wastewaters by Electrochemical Processes: Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052411
Kabdaşlı I, Tünay O. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water and Wastewaters by Electrochemical Processes: Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052411
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabdaşlı, Işık, and Olcay Tünay. 2023. "Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water and Wastewaters by Electrochemical Processes: Review" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052411
APA StyleKabdaşlı, I., & Tünay, O. (2023). Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Water and Wastewaters by Electrochemical Processes: Review. Molecules, 28(5), 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052411






