Experiments and Numerical Simulation of N-decane/Ethanol Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Data Processing
3. Modeling and Simulation
3.1. Model for Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation
3.2. Simulation for Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation
4. Results and Discussion
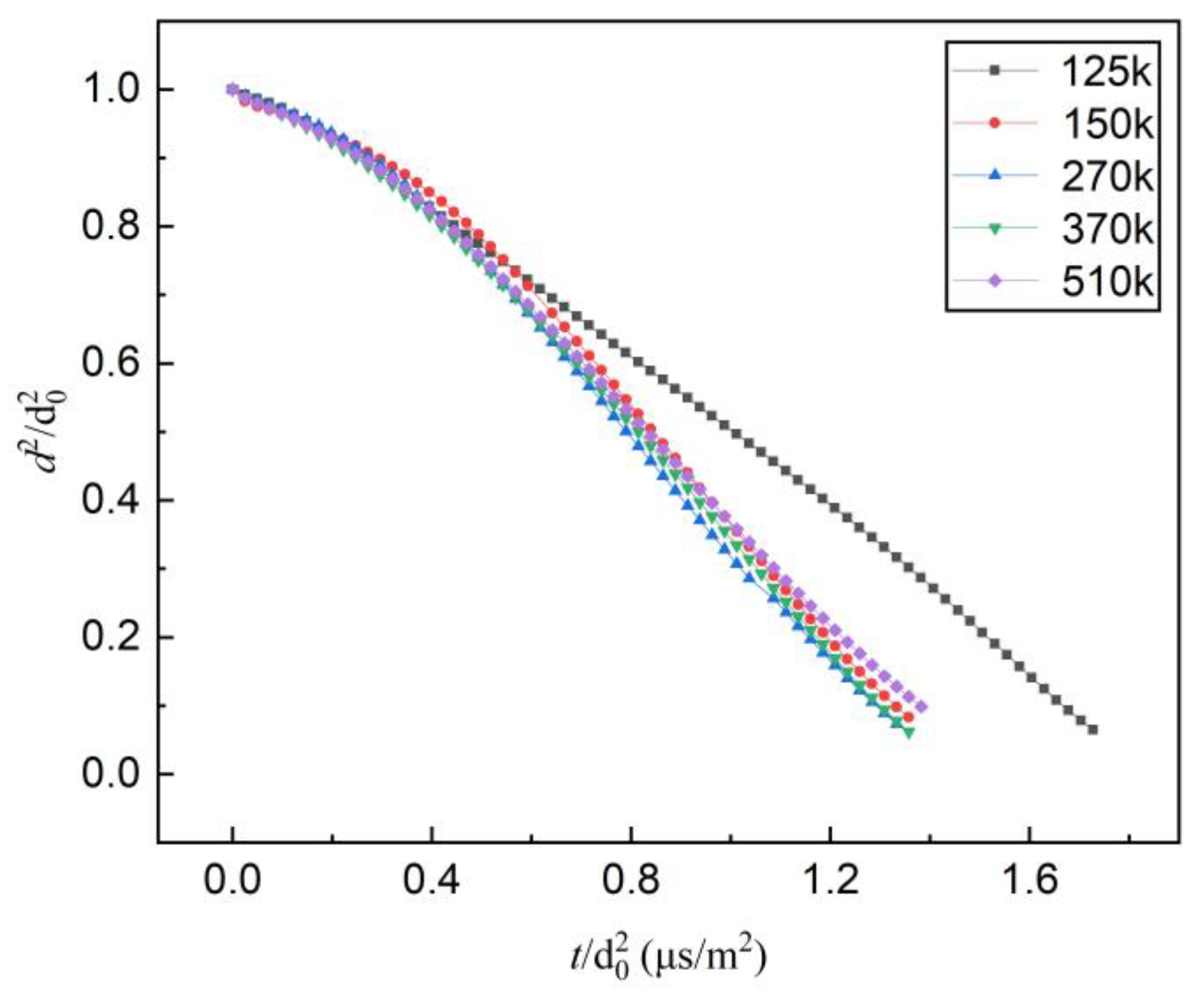
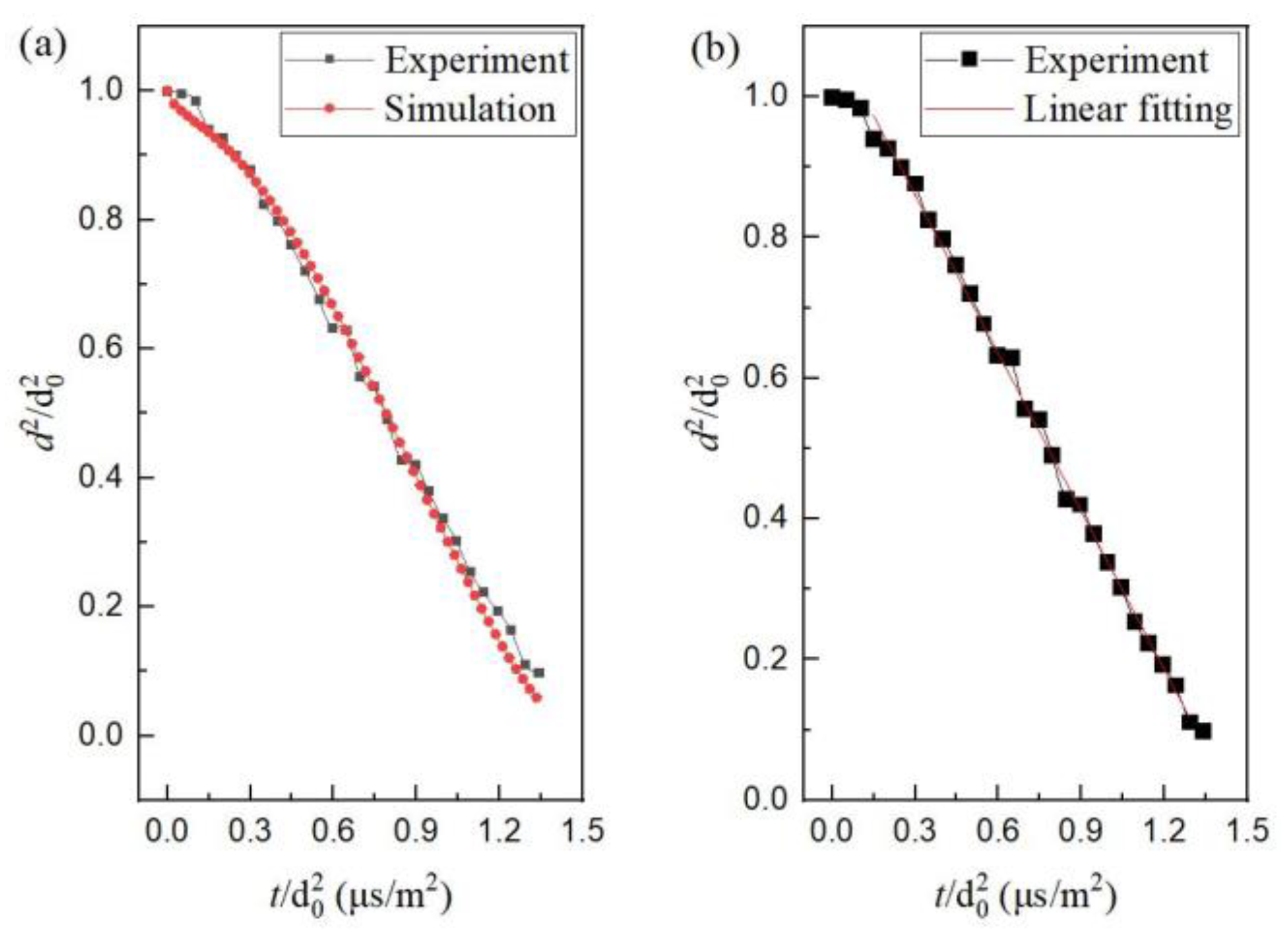
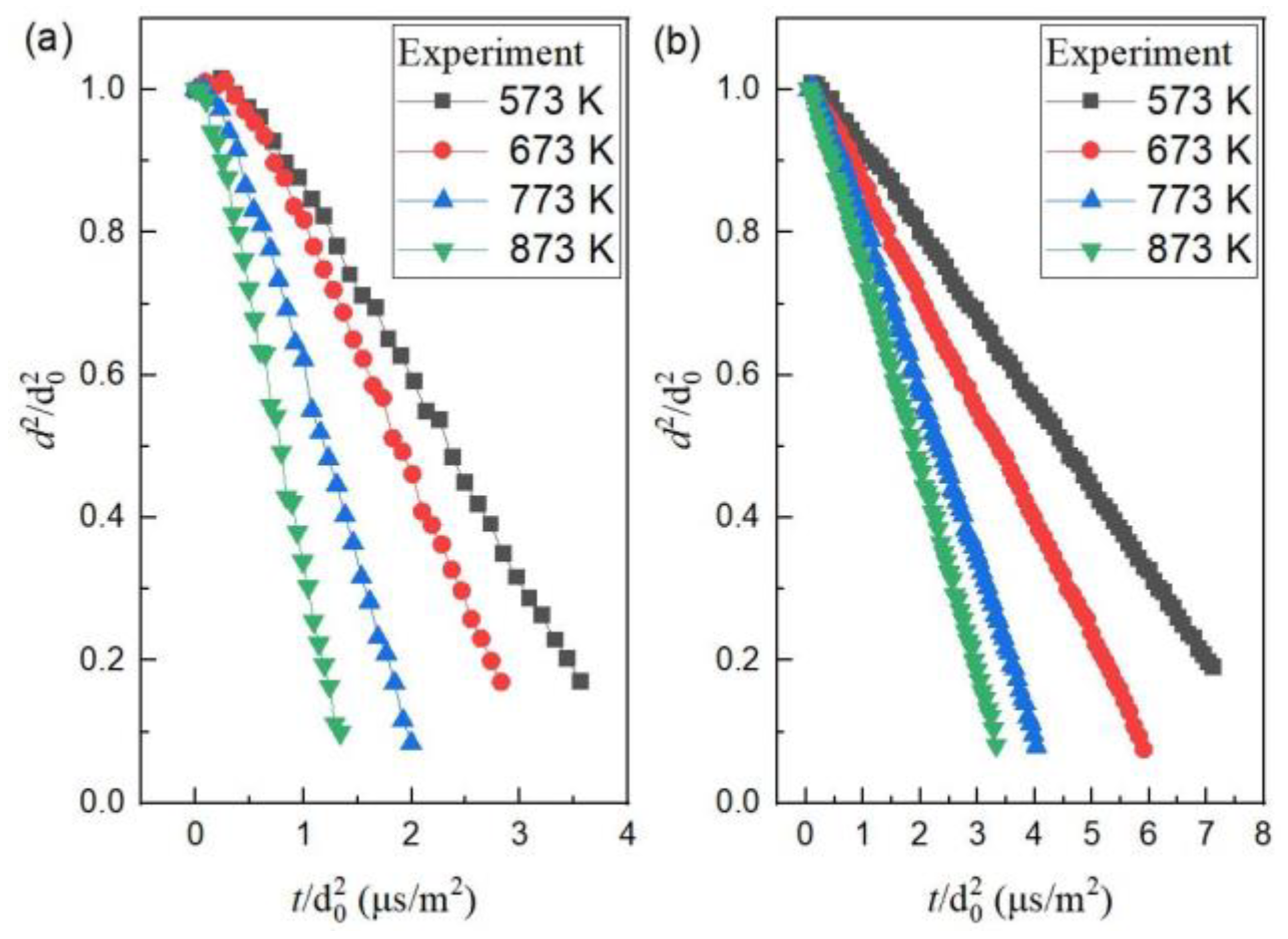
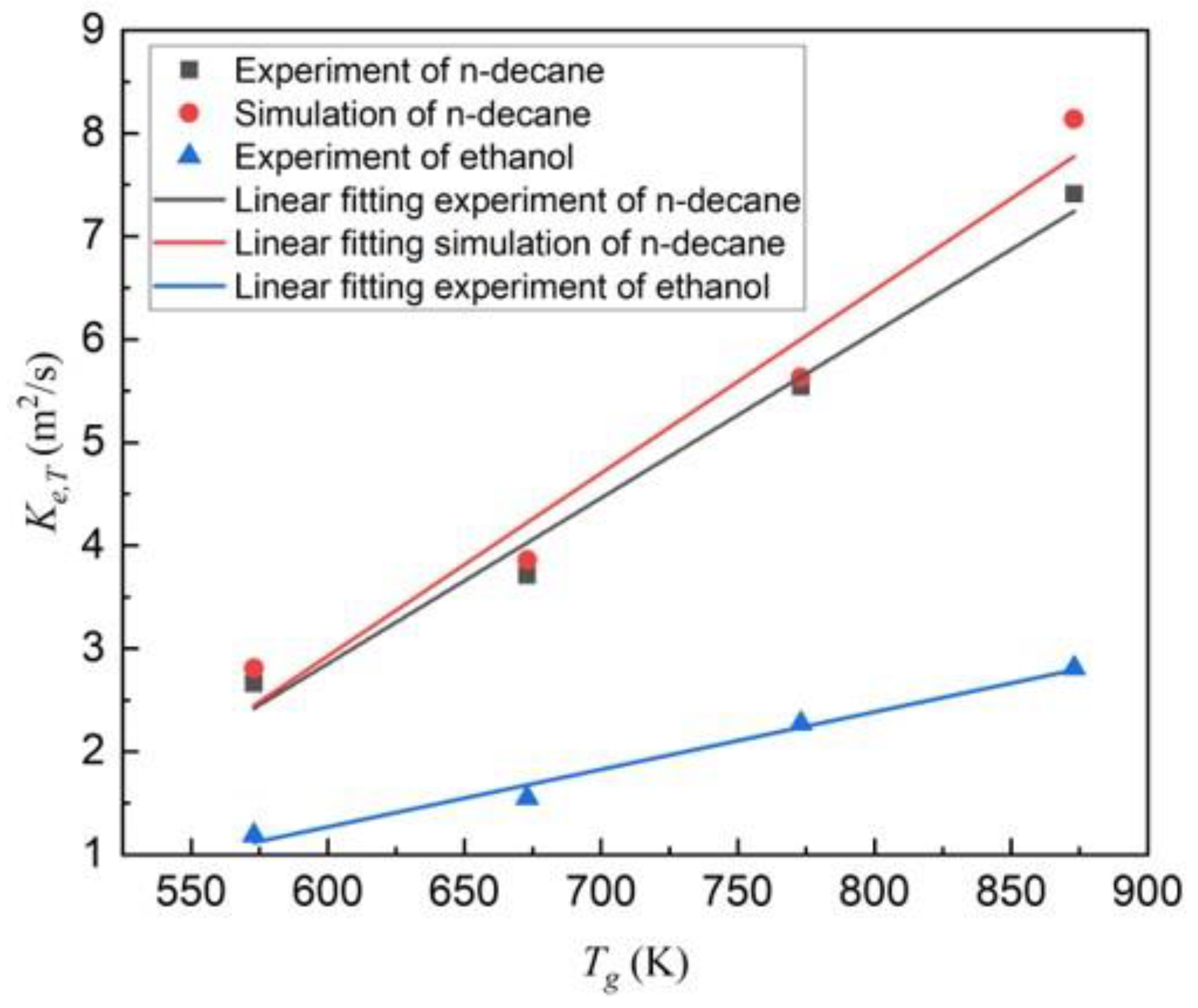
4.1. Evaporation of Mono-Component N-decane or Ethanol Droplets
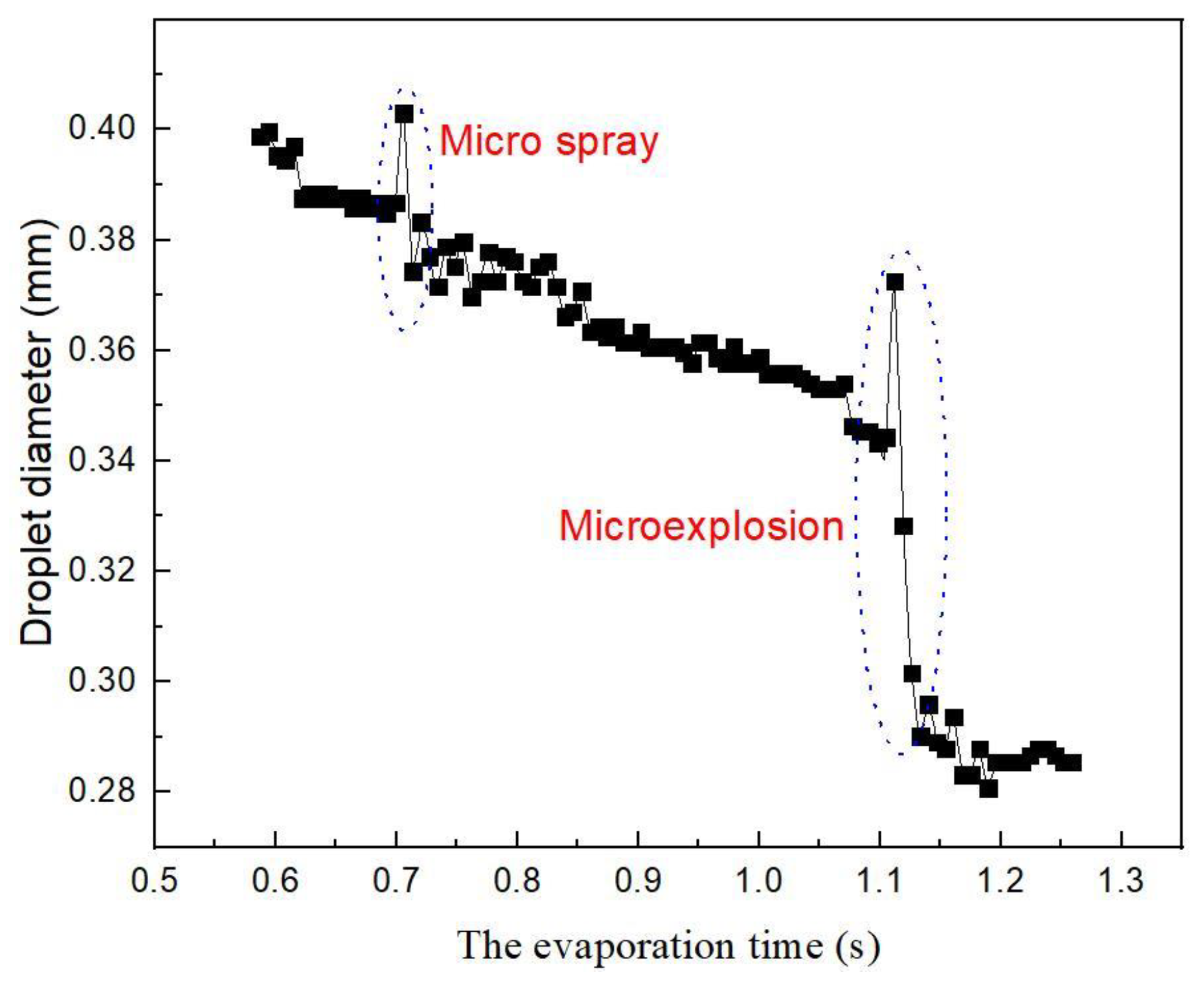
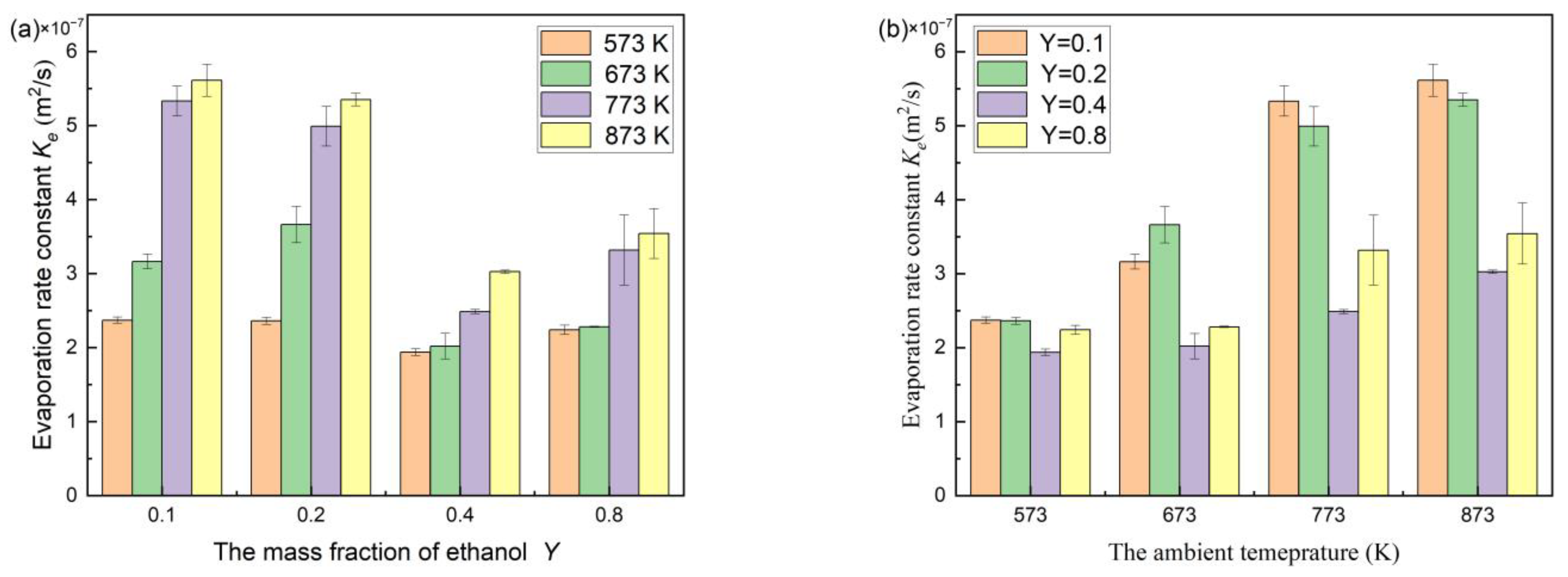
4.2. Evaporation of N-decane/Ethanol Bi-Component Droplets
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Item | Value |
| BM | Spalding mass transfer number |
| BT | The heat transfer number |
| cp | The specific heat capacity |
| coeff | The mass-transfer intensity factor |
| D | The mass diffusion coefficient |
| d | Droplet diameter |
| E | The total energy |
| e | Enthalpy |
| h | Convective heat transfer coefficient |
| L | The latent heat coefficient about evaporation |
| Ld | The perimeter of a droplet |
| Ke,T | The evaporation rate constant |
| k | The thermal conductivity |
| Nu | The Nusselt number |
| Pr | The Prandtl number |
| p | Pressure |
| Re | The Reynolds number |
| S | The energy source term |
| Sd | Area of a droplet |
| Sl | The mass source term |
| t | Time |
| T | The temperature |
| u | The average velocity |
| Ve | The volume of the ethanol |
| Vn | The volume of the n-decane |
| Y | The ethanol mass fraction |
| Greek symbols | |
| ρ | The density |
| α | The volume fraction |
| β | The pixel scale factor |
| μ | The average dynamic viscosity coefficient |
| Subscripts | |
| b | Boiling |
| e | Ethanol |
| g | Gas-phase |
| l | Liquid-phase |
| n | n-decane |
| Sat | Saturation |
| s | Surface |
| ∞ | At infinity space |
| 0 | Initial |
References
- Honnet, S.; Seshadri, K.; Niemann, U.; Peters, N. A surrogate fuel for kerosene. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagaut, P.; Reuillon, M.; Cathonnet, M. SHORT COMMUNICATION High Pressure Oxidation of Liquid Fuels from Low to High Temperature. 3.n-Decane. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1994, 103, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagaut, P.; Reuillon, M.; Cathonnet, M.; Voisin, D. High pressure oxidation of normal decane and kerosene in dilute conditions from low to high temperature. J. Chim. Phys. Physico-Chimie Biol. 1995, 92, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Du, H.; Zhuo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Huang, X. Dispersion Stability, Physical Properties, and Electrostatic Breakup of Surfactant-Loaded Aluminum/n-Decane Nanofluid Fuel: Nanoparticle Size Effect. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, S.; Isabel, J.B.; Kavitha, S.; Karthik, V.; Mohamed, B.A.; Gizaw, D.G.; Sivashanmugam, P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances in consolidated bioprocessing for conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into bioethanol—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, X.; Yáñez, R.; Gullón, B. Evaluation of strategies for enhanced bioethanol production from melon peel waste. Fuel 2023, 334, 126710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, K.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Dai, M. Evaporation of single moving liquid nitrogen droplet: Experimental study and numerical simulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 201, 123584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R. Numerical investigation of evaporation of a single ethanol/iso-octane droplet. Fuel 2013, 107, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Ye, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, J. Effect of Nanoparticle Concentration on Physical and Heat-Transfer Properties and Evaporation Characteristics of Graphite/n-Decane Nanofluid Fuels. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3284–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwey, C.; Birouk, M. Fuel vaporization: Effect of droplet size and turbulence at elevated temperature and pressure. Combust. Flame 2018, 189, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Yang, B.; Zhao, C.; Fu, G.; Ma, X.; Song, G. Experimental study on evaporation characteristics of ethanol–diesel blend fuel droplet. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 70, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengele, J.; Prommersberger, K.; Willmann, M.; Wittig, S. Experimental and theoretical study of one- and two-component droplet vaporization in a high pressure environment. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, A.; Makino, A.; Law, C. Liquid-phase diffusional resistance in multicomponent droplet gasification. Symp. Int. Combust. 1988, 21, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazhin, S.; Elwardany, A.; Krutitskii, P.; Castanet, G.; Lemoine, F.; Sazhina, E.; Heikal, M. A simplified model for bi-component droplet heating and evaporation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 4495–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Law, C.K. Effects of temporally varying liquid-phase mass diffusivity in multicomponent droplet gasification. Combust. Flame 2008, 153, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Won, J.; Baek, S.W. Evaporation of a single emulsion fuel droplet in elevated temperature and pressure conditions. Fuel 2018, 226, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, S.; Ye, L.; Huang, X. Understanding of Contradiction on Concentration Effect on Stability, Physical Properties, Evaporation and Microexplosion Characteristics of Al/JP-10/Oleic Acid Nanofluid Fuel. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqua, C.; Castanet, G.; Lemoine, F. Bicomponent droplets evaporation: Temperature measurements and modelling. Fuel 2008, 87, 2932–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhuo, Z.; He, L.; Huang, X. Atomization characteristics of nano-Al/ethanol nanofluid fuel in electrostatic field. Fuel 2018, 236, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazhin, S.S. Modelling of fuel droplet heating and evaporation: Recent results and unsolved problems. Fuel 2017, 196, 69–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybdylova, O.; Al Qubeissi, M.; Braun, M.; Crua, C.; Manin, J.; Pickett, L.; de Sercey, G.; Sazhina, E.; Sazhin, S.; Heikal, M. A model for droplet heating and its implementation into ANSYS Fluent. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 76, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybdylova, O.; Poulton, L.; Al Qubeissi, M.; Elwardany, A.; Crua, C.; Khan, T.; Sazhin, S. A model for multi-component droplet heating and evaporation and its implementation into ANSYS Fluent. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 90, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-L.; Xu, J.-L.; Wang, L. Development of a vapor–liquid phase change model for volume-of-fluid method in FLUENT. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H. A pressure iteration scheme for two-phase flow modeling. In Multiphase Transport Fundamentals, Reactor Safety, Applications; Veziroglu, T.N., Ed.; Hemisphere Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Abramzon, B.; Sazhin, S. Convective vaporization of a fuel droplet with thermal radiation absorption. Fuel 2006, 85, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, S.; Dederer, E.; Charmeteau, S.; Wagenfeld, S.; Kiefer, J.; Schröer, W.; Rathke, B. Revisiting the Liquid-Liquid Phase Behavior of n-Alkanes and Ethanol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| N-decane | |
|---|---|
| 2090 | |
| 0.843 | |
| ethanol | |
| 2.06 | |
| 2407 | |
| Ambient Temperature | 573 K | 673 K | 773 K | 873 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.66 | 3.71 | 5.54 | 7.41 |
| Numerical evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.81 | 3.86 | 5.63 | 8.14 |
| Relative error | 5.6% | 4.0% | 1.6% | 9.9% |
| Ambient Temperature | 573 K | 673 K | 773 K | 873 K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | Experimental evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.37 | 3.16 | 5.33 | 5.61 |
| Numerical evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.33 | 3.16 | 5.56 | 5.82 | |
| Relative error | 1.7 | 0 | 4.3 | 3.7 | |
| 0.2 | Experimental evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.36 | 3.66 | 4.99 | 5.35 |
| Numerical evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.34 | 3.35 | 5.05 | 5.33 | |
| Relative error | 0.8 | 8.5 | 1.2 | 0.4 | |
| 0.4 | Experimental evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 1.94 | 2.02 | 2.49 | 3.03 |
| Numerical evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.41 | 2.86 | 3.07 | 3.50 | |
| Relative error | 24.2 | 41.6 | 23.3 | 15.5 | |
| 0.8 | Experimental evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.24 | 2.28 | 3.32 | 3.54 |
| Numerical evaporation rate (×10−7 m2/s) | 2.20 | 2.60 | 3.48 | 3.89 | |
| Relative error | 1.8 | 14.0 | 4.8 | 9.9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, J. Experiments and Numerical Simulation of N-decane/Ethanol Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation. Molecules 2023, 28, 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052391
Zhang Z, Huang X, Xu J. Experiments and Numerical Simulation of N-decane/Ethanol Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052391
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenzhong, Xuefeng Huang, and Jiangrong Xu. 2023. "Experiments and Numerical Simulation of N-decane/Ethanol Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052391
APA StyleZhang, Z., Huang, X., & Xu, J. (2023). Experiments and Numerical Simulation of N-decane/Ethanol Bi-Component Droplet Evaporation. Molecules, 28(5), 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052391





