Berberine Ameliorates Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Mediated Metabolism Disorder and Redox Homeostasis by Upregulating Clock Genes: Clock and Bmal1 Expressions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
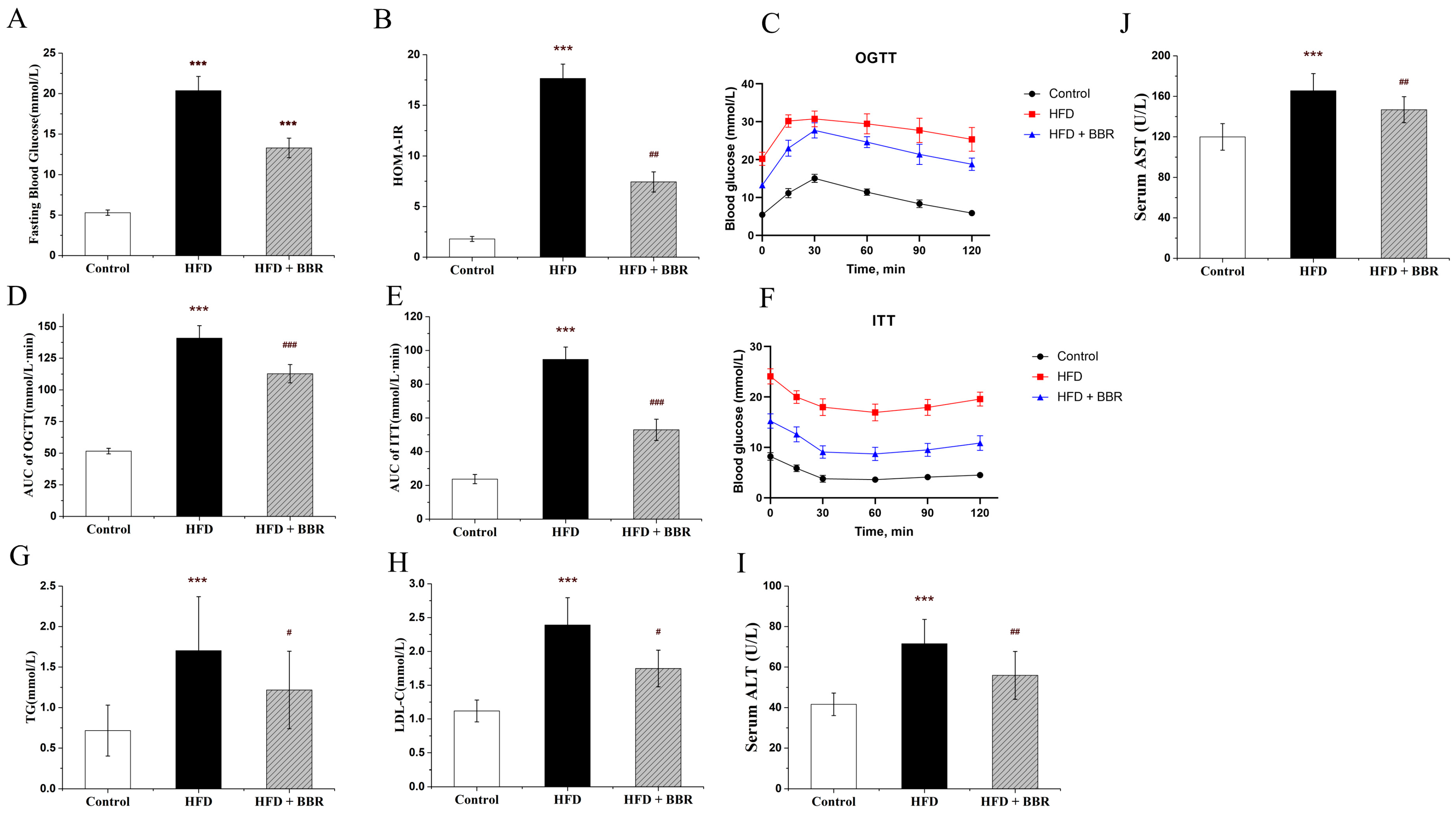
2.1. BBR Improves Insulin Resistance, Lipid Metabolism, and Hepatic Histology In Vivo
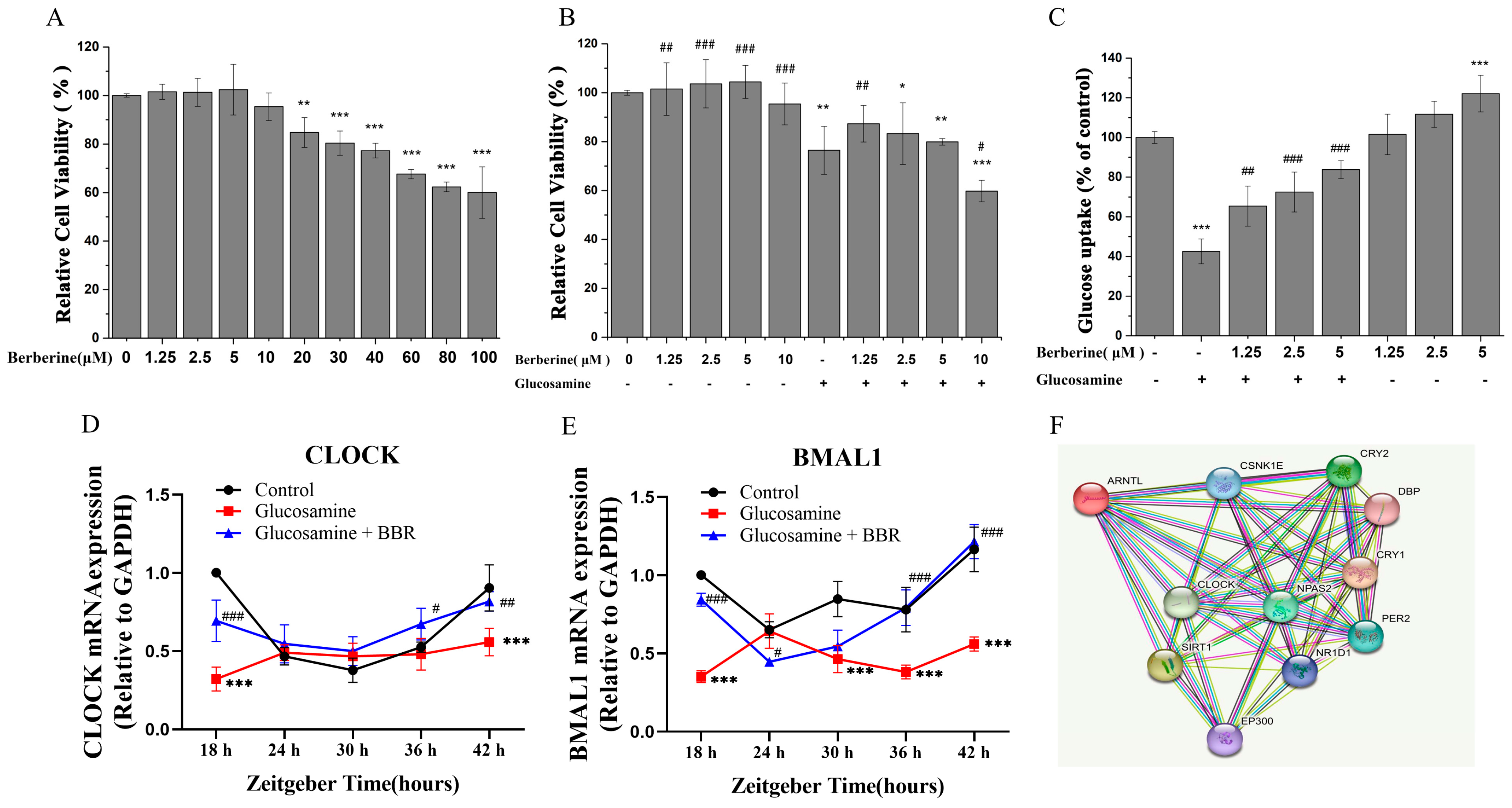
2.2. BBR Alleviated Glucosamine-Impaired Glucose Uptake in HepG2 Cells
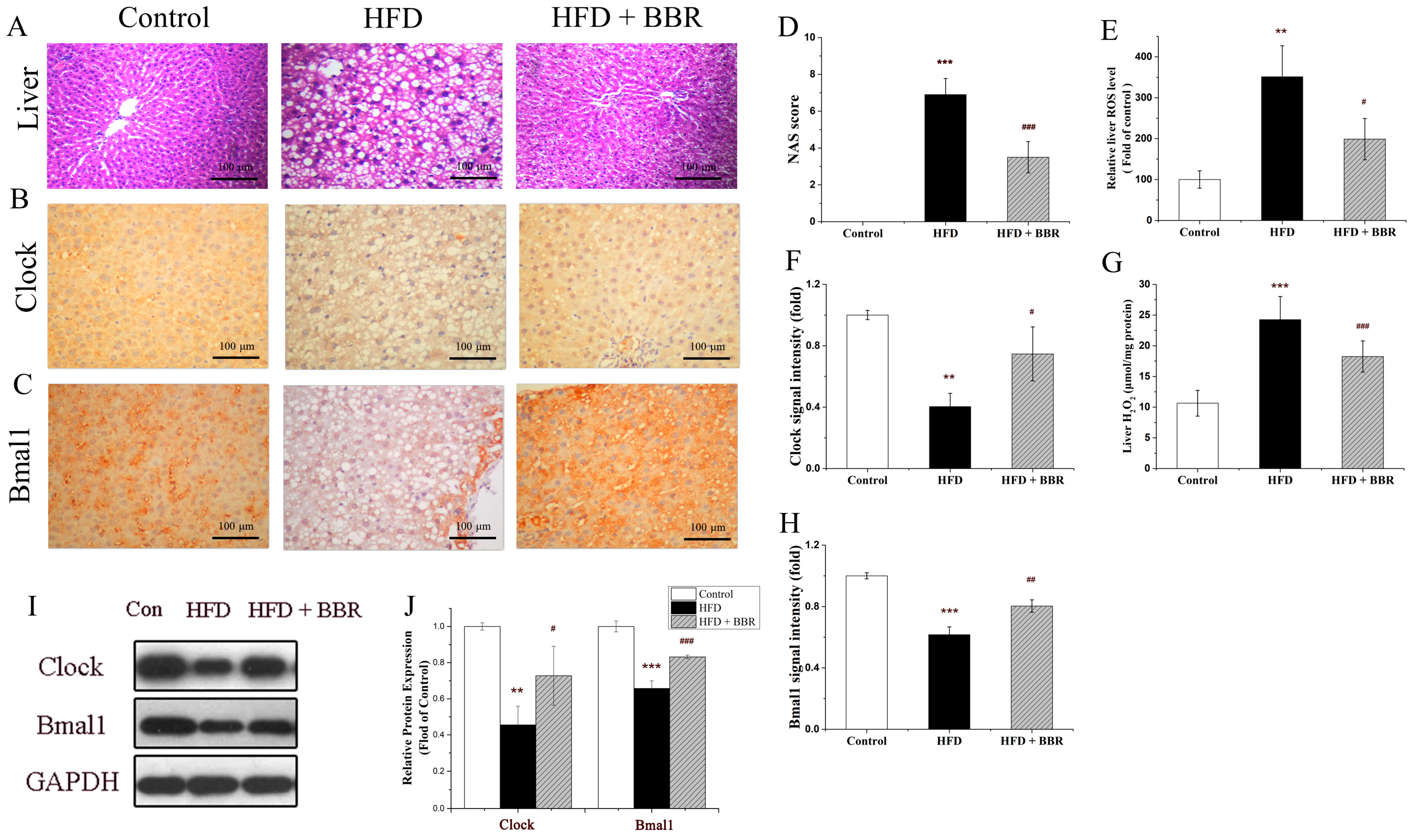
2.3. BBR Alleviated Redox Imbalance In Vivo and In Vitro
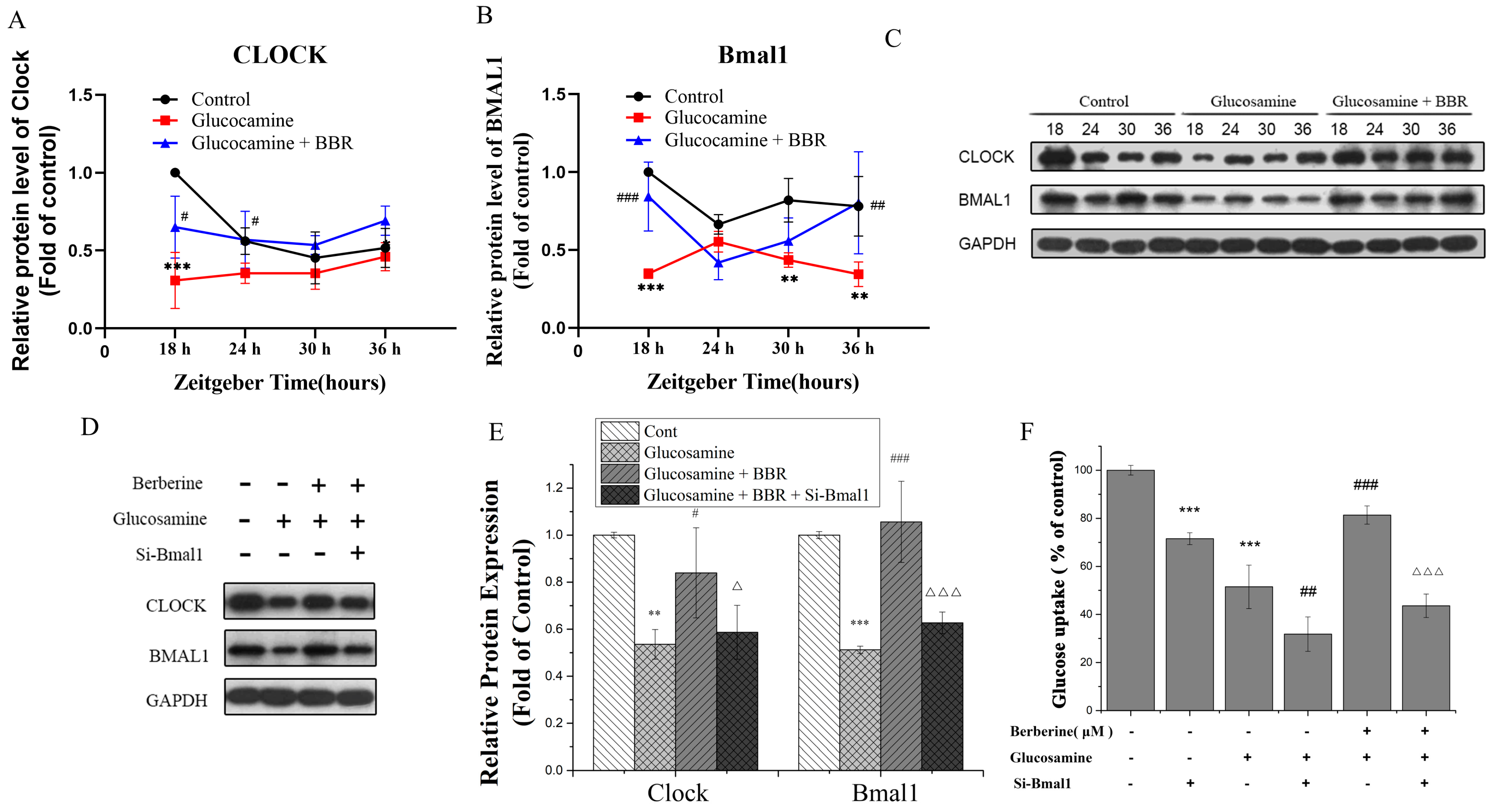
2.4. BBR Upregulated Clock/Bmal1 Expression In Vivo and In Vitro
2.5. BBR Alleviated Glucose Metabolism Disorder in a Bmal1-Dependent Manner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. MAFLD Model and Treatment
4.3. Serum Indexes
4.4. Hepatic ROS and H2O2 Levels by ELISA
4.5. H&E Staining
4.6. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.7. siRNAs Transfection of HepG2 Cells
4.8. CCK-8 Cell Viability Analysis
4.9. Glucose Uptake Assay
4.10. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Generation and H2O2 Level
4.11. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaya, E.; Yilmaz, Y. Metabolic-associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): A Multi-systemic Disease Beyond the Liver. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ayada, I.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wen, T.; Ma, Z.; Bruno, M.J.; de Knegt, R.J.; Cao, W.; et al. Estimating Global Prevalence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight or Obese Adults. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e573–e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Contreras, J.M.L.; Colado-Velázquez, J.; Gómez-Viquez, N.L.; Mailloux-Salinas, P.; Pérez-Torres, I.; Aranda-Fraustro, A.; Carvajal, K.; Bravo, G. Effects of topical capsaicin combined with moderate exercise on insulin resistance, body weight and oxidative stress in hypoestrogenic obese rats. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, R.; Yao, Y.; He, S.; Lei, M.; Wang, X.; Shi, C.; Gao, L.; Peng, X. Diosgenin Ameliorated Type II Diabetes-Associated Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Inhibiting De Novo Lipogenesis and Improving Fatty Acid Oxidation and Mitochondrial Function in Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhao, X.; Fu, X.; Xu, K.; Li, Z.; Miao, L.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Qiao, L.; Bao, J. Gender effect of hyperuricemia on the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A clinical analysis and mechanistic study. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 117, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvers, D.J.; Scheer, F.; Schrauwen, P.; la Fleur, S.E.; Kalsbeek, A. Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, N.W.; Ashbrook, L.H.; Fu, Y.H.; Ptacek, L.J. Human circadian variations. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e148282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, O.; Kaneita, Y.; Murata, A.; Yokoyama, E.; Ohida, T. Association of onset of obesity with sleep duration and shift work among Japanese adults. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, G.; Chen, X.; Fau Urbain, J.L.; Urbain, J.L. Evidence for a circadian rhythm of insulin sensitivity in patients with NIDDM caused by cyclic changes in hepatic glucose production. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, E246–E252. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Y.; Qi, G.; Fan, R.; Ji, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. EGCG ameliorates diet-induced metabolic syndrome associating with the circadian clock. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1575–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Ellies, L.G.; Kumar, D.; Sauceda, C.; Oberg, A.; Gross, E.; Mandt, T.; Newton, I.G.; Kaur, M.; Sears, D.D.; et al. Time-restricted feeding normalizes hyperinsulinemia to inhibit breast cancer in obese postmenopausal mouse models. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Trehanpati, N.; Nagarajan, P.; Ramakrishna, G.A.-O.X. The Clock-NAD+-Sirtuin connection in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 3164–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Y.; Qi, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, X. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in HepG2 Cells: Involvement of Bmal1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claustrat, B.; Leston, J. Melatonin: Physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie 2015, 61, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Miao, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Treating hyperuricemia related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats with resveratrol. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wei, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. Resveratrol Maintains Lipid Metabolism Homeostasis via One of the Mechanisms Associated with the Key Circadian Regulator Bmal1. Molecules 2019, 24, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Nohara, K.; Park, N.; Park, Y.S.; Guillory, B.; Zhao, Z.; Garcia, J.M.; Koike, N.; Lee, C.C.; Takahashi, J.S.; et al. The Small Molecule Nobiletin Targets the Molecular Oscillator to Enhance Circadian Rhythms and Protect against Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.F.; Zeng, C.M. The Degradation Products of Ascorbic Acid Inhibit Amyloid Fibrillation of Insulin and Destabilize Preformed Fibrils. Molecules 2018, 23, 3122. [Google Scholar]
- Tabeshpour, J.; Imenshahidi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. A review of the effects of Berberis vulgaris and its major component, berberine, in metabolic syndrome. Iran J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 557–568. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, B.; Liang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ye, L.; Yang, Q.; Shang, W. Adipose Tissue SIRT1 Regulates Insulin Sensitizing and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Berberine. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 591227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Pang, T.; Gu, M.; Gao, A.-H.; Xie, C.-M.; Li, J.-Y.; Nan, F.-J.; Li, J. Berberine-stimulated glucose uptake in L6 myotubes involves both AMPK and p38 MAPK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Duan, H.; Wu, F.; Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Xu, L.; Lu, F.; Wang, D. Berberine Alleviates Insulin Resistance and Inflammation via Inhibiting the LTB4-BLT1 Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 722360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, T.; Mitani, Y.; Kurumisawa, K.; Nomura, K.; Wang, W.; Nakashima, K.I.; Inoue, M. Berberine stimulates fibroblast growth factor 21 by modulating the molecular clock component brain and muscle Arnt-like 1 in brown adipose tissue. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 164, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Ferrell, L.d.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Lan, Y.; Xiao, J.; Song, M.; Chen, C.; Liang, C.; Huang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Ho, C.T. Capsaicin Ameliorates the Redox Imbalance and Glucose Metabolism Disorder in an Insulin-Resistance Model via Circadian Clock-Related Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10089–10096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilking, M.; Ndiaye, M.; Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. Circadian rhythm connections to oxidative stress: Implications for human health. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.D.; Lin, C.T.; McMillin, S.L.; Weyrauch, L.A.; Schmidt, C.A.; Smith, C.A.; Kurland, I.J.; Witczak, C.A.; Neufer, P.D. Genetically increasing flux through beta-oxidation in skeletal muscle increases mitochondrial reductive stress and glucose intolerance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E938–E950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Cocheme, H.M. Redox regulation of the insulin signalling pathway. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhunchha, B.; Kubo, E.; Singh, D.P. Clock Protein Bmal1 and Nrf2 Cooperatively Control Aging or Oxidative Response and Redox Homeostasis by Regulating Rhythmic Expression of Prdx6. Cells 2020, 9, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Wu, W.; Mi, Y.; Shi, R.; Sun, K.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. Tea polyphenols direct Bmal1-driven ameliorating of the redox imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ho, C.T.; Lu, M. Piperine Improves Lipid Dysregulation by Modulating Circadian Genes Bmal1 and Clock in HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, I.; Leinweber, B.; Brandenburger, M.; Oster, H. Circadian clock network desynchrony promotes weight gain and alters glucose homeostasis in mice. Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patke, A.; Murphy, P.J.; Onat, O.E.; Krieger, A.C.; Ozcelik, T.; Campbell, S.S.; Young, M.W. Mutation of the Human Circadian Clock Gene CRY1 in Familial Delayed Sleep Phase Disorder. Cell 2017, 169, 203–215.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalic, T.; Steponenaite, A.; Wei, L.; Vasudevan, S.R.; Mathie, A.; Peirson, S.N.; Lall, G.S.; Cader, M.Z. TRESK is a key regulator of nocturnal suprachiasmatic nucleus dynamics and light adaptive responses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalm, G.; Bruns, K.; Drachenberg, N.; Geyer, N.; Foulkes, N.S.; Bertolucci, C.; Gerlach, G. Finding Nemo’s clock reveals switch from nocturnal to diurnal activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.E.A.; Kalume, F.; De La Iglesia, H.O. Sleep timing and the circadian clock in mammals: Past, present and the road ahead. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 126, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, M.; Dankova, P.; Solc, R.; Bettazova, N.; Cerna, M. Epigenetic Regulation of Circadian Rhythm and Its Possible Role in Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, E.; Navez, B.; Brichard, S.M. Circadian clock dysfunction in human omental fat links obesity to metabolic inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcheva, B.; Ramsey, K.M.; Buhr, E.D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Su, H.; Ko, C.H.; Ivanova, G.; Omura, C.; Mo, S.; Vitaterna, M.H.; et al. Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes. Nature 2010, 466, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.; Bailey, S.M.; Staels, B.; Baumert, T.F. The circadian clock and liver function in health and disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Dai, C.; et al. CLOCK/BMAL1 regulates circadian change of mouse hepatic insulin sensitivity by SIRT1. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.F.N.; Cavadas, C.; Silva, M.M.C. Small-molecule modulators of the circadian clock: Pharmacological potentials in circadian-related diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1620–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Berberine protects against diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting cell apoptosis via deactivation of the NFkappaB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4227–4235. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.J.; Dong, H.; Li, J.B.; Xu, L.J.; Zou, X.; Wang, K.F.; Lu, F.E.; Yi, P. Berberine inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis via the LKB1-AMPK-TORC2 signaling pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7777–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Liang, S.; Guo, C.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Shang, W. Inhibition of M1 macrophage activation in adipose tissue by berberine improves insulin resistance. Life Sci. 2016, 166, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treadway, J.L.; Mendys, P.; Fau Hoover, D.J.; Hoover, D.J. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2001, 10, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Greco, C.M. Expanding the link between circadian rhythms and redox metabolism of epigenetic control. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 170, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangvarasittichai, S. Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, J.; He, W.; Lv, J.; Zhuang, K.; Huang, H.; Quan, S. Effect of berberine on the HPA-axis pathway and skeletal muscle GLUT4 in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, A.L.F.D.A.; Carvalho, L.D.; Oliveira, A.C.; Santos, V.N.D.; Vieira, J.G.; Parise, E.R. Insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) in the differentiation of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and healthy individuals. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Cichoric Acid Reverses Insulin Resistance and Suppresses Inflammatory Responses in the Glucosamine-Induced HepG2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10903–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Zhan, T.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Selenium deficiency-induced redox imbalance leads to metabolic reprogramming and inflammation in the liver. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 5′-ACCCAGAAGACTGTGGATGG-3′ | 5′-ACCCAGAAGACTGTGGATGG-3′ |
| CLOCK | 5′-ACAGGGCACCACCCATAATA-3′ | 5′-TCCACTGTTGCCCCTTAGTC-3′ |
| BMAL1 | 5′-GTAACCTCAGCTGCCTCGTC-3′ | 5′-AGCTGTTGCCCTCTGGTCT-3′ |
| PER1 | 5′-CAATGGTTCAAGTGGCAATG-3′ | 5′-TGTAGGCAATGGAACTGCTG-3′ |
| PER2 | 5′-CCGGAGTTAGAGATGGTGGA-3′ | 5′-AGTAATGGCAGTGGGACTGG-3′ |
| CRY1 | 5′-GTGTTTCCCAGGCTTTTCAA-3′ | 5′-TGGTTCCATTTTGCTGATGA-3′ |
| CRY2 | 5′-TACCTGCCCAAATTGAAAGC-3′ | 5′-GCGAAAGCTGCTGGTAAATC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, H.; Fang, G.; Quan, S. Berberine Ameliorates Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Mediated Metabolism Disorder and Redox Homeostasis by Upregulating Clock Genes: Clock and Bmal1 Expressions. Molecules 2023, 28, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041874
Ye C, Zhang Y, Lin S, Chen Y, Wang Z, Feng H, Fang G, Quan S. Berberine Ameliorates Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Mediated Metabolism Disorder and Redox Homeostasis by Upregulating Clock Genes: Clock and Bmal1 Expressions. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041874
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Cunsi, Yajing Zhang, Shaomin Lin, Yi Chen, Zimiao Wang, Haoyinghua Feng, Guangqing Fang, and Shijian Quan. 2023. "Berberine Ameliorates Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Mediated Metabolism Disorder and Redox Homeostasis by Upregulating Clock Genes: Clock and Bmal1 Expressions" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041874
APA StyleYe, C., Zhang, Y., Lin, S., Chen, Y., Wang, Z., Feng, H., Fang, G., & Quan, S. (2023). Berberine Ameliorates Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Mediated Metabolism Disorder and Redox Homeostasis by Upregulating Clock Genes: Clock and Bmal1 Expressions. Molecules, 28(4), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041874









