Desert Endemic Plants in Algeria: A Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Collection of Information
2.2. Identification of Medicinal Plant
3. WHO’s View of Traditional Medicine
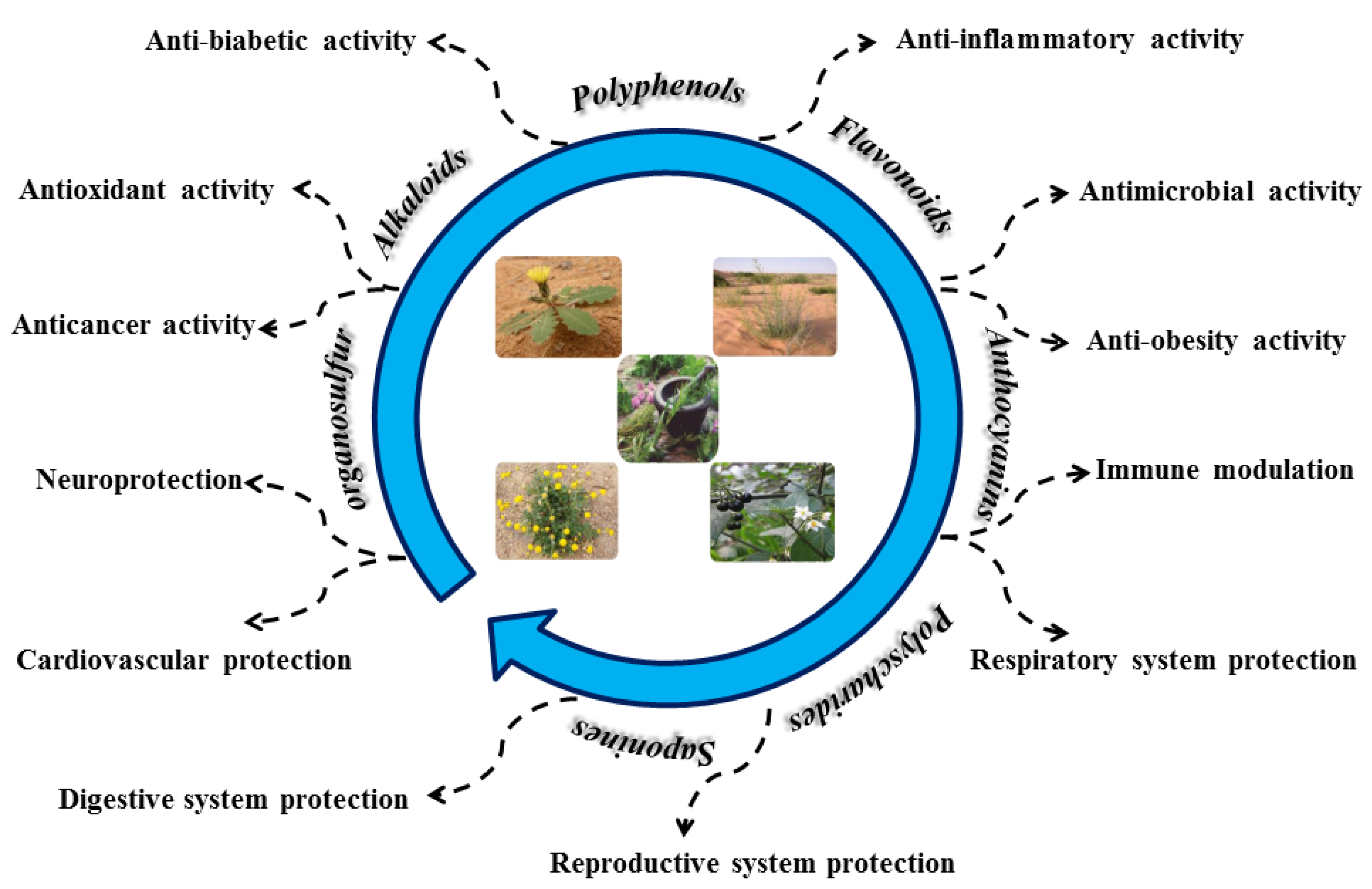
4. Polyphenolic Compounds and Bioactivity
4.1. Polyphenols
4.2. Flavonoids
4.3. Alkaloids
5. Discussion
5.1. Search Results
5.2. Ethnobotanical Studies
5.3. Pharmacological Studies
5.4. Ethnopharmacology and Toxicological Evidence
5.5. List of Multi-Purpose Plants and Their Uses in the Saharan Regions
5.5.1. Retama retam Webb. (Family: Fabaceae; Vernacular Name: Rtem)
5.5.2. Astragalus cruciatus Link (Family: Fabaceae; Vernacular Name: Akifa)
5.5.3. Genista saharae (Coss. & Dur.) (Family: Fabaceae; Vernacular Name: Marekh)
5.5.4. Astragalus gyzensis Bunge (Family: Fabaceae; Vernacular Name: Foul Alibil)
5.5.5. Euphorbia guyoniana Boiss. & Reut (Family: Euphorbiaceae; Vernacular Name: Lebina)
5.5.6. Ephedra alata DC. (Family: Ephedraceae; Vernacular Name: Alanda)
5.5.7. Heliathemum lipii (L.) Pers. (Family: Cistaceae; Vernacular Name: Samhari)
5.5.8. Cyperus conglomeratus (Family: Cyperaceae; Vernacular Name: Saad)
5.5.9. Calligonum comosum L’herit (Family: Polygonaceae; Vernacular Name: Larta)
5.5.10. Plantago albicans L. (Family: Plantaginaceae; Vernacular Name: Linem)
5.5.11. Limoniastrum guyonianum Coss & Dur. (Family: Plumbaginaceae; Vernacular Name: Zita)
5.5.12. Tamarix boveana (Family: Tamaricaceae; Vernacular Name: Tarfa)
5.5.13. Traganum nudatum Del. (Family: Chenopodiaceae; Vernacular Name: Damran)
5.5.14. Bassia muricata L. Asch. (Family: Chenopodiaceae; Vernacular Name: Ghabitha)
5.5.15. Atriplex halimus L. (Family: Chenopodiaceae; Vernacular Name: Gatef)
5.5.16. Zygophyllum album L. (Family: Zygophyllaceae; Vernacular Name: Agga)
5.5.17. Matricaria pubescens (Desf) (Family: Asteraceae; Vernacular Name: Guartoufa)
5.5.18. Launaea resedifolia O. K. (Family: Asteraceae; Vernacular Name: Athid)
5.5.19. Solanum nigrum L. (Family: Solanaceae; Vernacular Name: Anb Aldib)
5.5.20. Erodium glaucophyllum L. Her. (Family: Geraniaceae; Vernacular Name: Tommir)
5.5.21. Cleome arabica L. (Family: Capparidaceae; Vernacular Name: Nettin)
5.5.22. Neurada procumbens L. (Family: Rosaceae; Vernacular Name: Anfal/Saadan)
6. General Debate
7. Health Claims Based on Biological and/or Therapeutic Activities
7.1. Antioxidant and Detoxicating Activity
7.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
7.3. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
7.4. Antidiabetic Activity
7.5. Antiviral Effect
7.6. Antineoplastic Properties
8. Traditional Medicine
9. Status, Causes and Challenges of Medicinal Plants
10. The Cultivation of Medicinal Plants in Desert Areas a Solution?
| Name of the Plant | Part(s) Used | Toxicity Studies | Mode of Administration | Traditional Use | Administration and Application Area | Country | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RetamaRetam Web b. | Fruits, seeds | Not toxic | Decoction, Infusion | Diabetes, Cold, skin wounds, back pain | Oral | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Palestina | [41] |
| Genista saharae Cosson et Dur. | Aerial part | Not toxic | Decoction | Infections of the respiratory system | Oral External use | Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia and Egypt | [52] |
| Astragalus gombiformis Bomel. | Different parts | Including toxic species | Decoction | Antidote against bites of snakes and scorpions | External use | Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia | [155] |
| Eurphorbia guyoniana Bois et Reut. | Aerial parts roots | Toxic | Decoction | Against venomous bites of scorpions antitussive, analgesic | Oral External use | Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Morocco | [156] |
| Ephedra alata DC. | Aerial parts | Not toxic | Maceration | Cold, influenza, respiratory problems, hypertension | Oral External use | Asia, America, Europe, and North Africa | [157] |
| Heliathemum lipii (L.) Pers. | Aerial parts | Including toxic species | Maceration | Treat skin lesions common colds, as diuretic and for rheumatic | Oral External use | Asia and Africa | [158,159] |
| Cyperus conglomeratus | Aerial part | Not toxic | Maceration | Diuretic, analgesic and anthelmintic treatments | Oral External use | Africa, The Arabian Peninsula | [160] |
| Calligonum comosum L’her. | Aerial parts | Not toxic | Maceration Powder | Scorpion stings and snake bites | External use | Saudi Arabia, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Morocco | [161,162] |
| Plantago albicans L. | Seeds, leaves Powder | Not toxic | Infusion | Diabetes | Oral | Tunisia, Algeria and Libya | [41] |
| Limoniastrum guyonianum Dur. | Leaves | Not toxic | Decoction, infusion | Diabetes, scorpion stings and snake bites, anemia | Oral External use | Tunisia, Algeria and Libya | [41] |
| Tamarix boveana | Leaves | Not toxic | No reported | Diabetes, burn, illnesses of the kidney, diarrhea | Oral External use | Irano-Turanian, Mediterranean, Algeria | [163] |
| Traganum nudatum Del. | Aerial part | Not toxic | Decoction, powder | Diabetes, rheumatism, skin diseases, diarrhea | External use | Algeria | [41] |
| Bassia muricata (L.) | aerial parts | Not toxic | Powder | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | External use | Iran, Palestine, North Africa. | [83] |
| Atriplex halimus L. | Leaves | Not toxic | Decoction | Diabetes, ovarian cysts, rheumatism, goiter | Oral | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya | [164] |
| Zygophyllum album L. | Aerial part | Not toxic | Decoction | Diabetes | Oral | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia | [165] |
| Matricaria pubescens (desf) Schultz. | Aerial part Leaves | Not toxic | Decoction, infusion | Diabetes | Oral | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia | [41] |
| Erodium glaucophyllum L’Her. | Aerial part | Not toxic | Decoction | Oxytocic and astringent | Oral | Western Mediterranean coastal region | [166,167] |
| Cleome arabica L. | Aerial part | Toxic | Decoction, infusion | Diabestes, rheumatism | Oral | Distributed in the north of Africa | [168] |
| Neurada procumbens L. | Aerial par | Not toxic | Decoction, infusion | Antioxidant, diabetes, diarrhea | Oral | Sinai, Sudan, Ethiopia, Saudi Arabia | [91] |
11. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Fact sheetN°134. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/2003/fs134/en/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Gurib-Fakim, A. Medicinal plants: Traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świsłowski, P.; Dołhańczuk-Śródka, A.; Rajfur, M. Bibliometric analysis of European publications between 2001 and 2016 on concentrations of selected elements in mushrooms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22235–22250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaoue, O.G.; Moutouama, J.K.; Coe, M.A.; Bond, M.O.; Green, E.; Sero, N.B.; Bezeng, B.S.; Yessoufou, K. Methodological advances for hypothesis-driven ethnobiology. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 2281–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogol, C.K.P.O.; Ogola, P.; Odede, W.; Khayota, B. Indigenous knowledge of medicinal and utilitarian plants of Mfangano Island, Lake Victoria, Kenya. East Afr. J. Sci. 2002, 4, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Agisho, H.; Osie, M.; Lambore, T. Traditional medicinal plants utilization, management and threats in Hadiya Zone, Ethiopia. Tradit. Med. 2014, 2, 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, M.; Chenchouni, H.; Belarouci, M.E.H.; Bradai, L.; Bouallala, M.H. Diversity of psammophyte communities on sand dunes and sandy soils of the northern Sahara desert. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensizerara, D.; Menasria, T.; Melouka, M.; Cheriet, L.; Chenchouni, H. Antimicrobial Activity of Xerophytic Plant (Cotula cinerea Delile) Extracts Against Some Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 6, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradai, L.; Chenchouni, H. Effects of Sand Encroachment on Vegetation Diversity in the Sahara Desert. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Arabian Journal of Geosciences, Sousse, Tunisia, 2–5 November 2022; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal, M. Climatic resilient agriculture for root, tuber, and banana crops using plant growth-promoting microbes. Clim. Change Agric. Ecosyst. 2019, 2019, 307–329. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz, M.; Dhouib, A.; Loukil, S.; Boukhris, M.; Sayadi, S. Polyphenols content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts of some wild plants collected from the south of Tunisia. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 7017–7027. [Google Scholar]
- Pradesh, A.S.R.I.; Mani, N.S.; Sujatha, B.; Polumahanthi, S. Ethnobotanical investigation of underground Plant Parts of Kotia Hills of Vizianagaram District. J. Med. Plants Stud. 2015, 3, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Chehma, A. Catalogue des Plantes Spontanées du Sahara Septentrional Algérien; Algérie, D.H., Ed.; Éditions Universitaires Européennes: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- El Hafed, K.; Kaouthar, L.; Yamina Kh Tedjani, B.; Sam, B.; Mammar, I.; Abdelkamel, S. Atlas Floristique de la Vallée de Oued-Righ Par Écosystème; Centre de Recherche Scientifique et Technique sur la Région Aride, O.E.B., Station Milieu Biophysique: Touggourt, Algeria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mahomoodally, M.; Chintamunnee, V. Herbal medicine commonly used against infectious diseases in the tropical island of Mauritius. J. Herb. Med. 2012, 2, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kunle, O.F.; Egharevba, H.O.; Ahmadu, P.O. Standardization of herbal medicines-A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 4, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunkoo, D.H.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Ethnopharmacological survey of native remedies commonly used against infectious diseases in the tropical island of Mauritius. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suroowan, S.; Mahomoodally, F. Complementary and alternative medicine use among Mauritian women. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2013, 19, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jaber, N.A.; Awaad, A.S.; Moses, J.E. Review on some antioxidant plants growing in Arab world. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascu, M.; Pascu, D.-E.; Trăistaru, G.A.; Nechifor, A.C.; Bunaciu, A.A.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Different spectrophotometric methods for antioxidant activity assay of four Romanian herbs. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2014, 11, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.S.; Moharram, F.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Aboutabl, E.A. Anticancer and antioxidant tannins from Pimenta dioica leaves. Z. Für Nat. C 2007, 62, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Peng, X.; Ma, L.; Cui, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L. Enhanced secondary metabolites production and antioxidant activity in postharvest Lonicera japonica Thunb. in response to UV radiation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 13, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquiaga, I.; Leighton, F. Plant polyphenol antioxidants and oxidative stress. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Lin, Y.-M. Tannins from Canarium album with potent antioxidant activity. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S.; Luximon-Ramma, A.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bahorun, T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: Mechanism and actions. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2005, 579, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.M. A review of potential health benefits of flavonoids. Lethbridge Undergrad. Res. J. 2008, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Ilgün, S.; Koşar, M. Antioxidant properties and phenolic composition of Salvia virgata Jacq. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci 2016, 13, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, H.-M. Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotito, S.B.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Renart, M.L.; Caligiuri, M.; Rein, D.; Schmitz, H.H.; Steinberg, F.M.; Keen, C.L.; Fraga, C.G. Influence of oligomer chain length on the antioxidant activity of procyanidins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Revuelta, A.; Sánchez-Gallego, J.I.; Hernández-Hernández, A.; Sánchez-Yagüe, J.; Llanillo, M. Membrane cholesterol contents influence the protective effects of quercetin and rutin in erythrocytes damaged by oxidative stress. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 161, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C. Flavonoid antioxidants. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, T.; Songtao, J.; Faghihi, F.; Haider, M.S.; Fang, J. Naturally occurring anthocyanin, structure, functions and biosynthetic pathway in fruit plants. J. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Sáez-Plaza, P.; Ramos-Escudero, F.; Jiménez, A.M.; Fett, R.; Asuero, A.G. Analysis and antioxidant capacity of anthocyanin pigments. Part II: Chemical structure, color, and intake of anthocyanins. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 42, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, M.A.; Gonzales, R.; Linder, J.A.; Landefeld, C.S. Changing use of antibiotics in community-based outpatient practice, 19911999. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilonu, M.C.; Umesiobi, D.O. Bioactive phytochemicals: Bioactivity, sources, preparations, and/or modifications via silver tetrafluoroborate mediation. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 629085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.M.; Qiao, Y.; Ang, E.L.; Zhao, H. Using natural products for drug discovery: The impact of the genomics era. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A.; Desgagné-Penix, I. Metabolic engineering for the production of plant isoquinoline alkaloids. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, W.S.; Runguphan, W.; O’Connor, S.E. Recent progress in the metabolic engineering of alkaloids in plant systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, N.; Agrawal, R.; Khan, A. Chemopreventive potential of Centella asiatica on B6F10 melanoma cell lines in experimental mice. Pharmacologyonline 2011, 1, 748–758. [Google Scholar]
- Selaimia, A. Contribution à L’étude Phytochimique de Plantes Médicinales Appartenant à la Famille des Fabaceae. Ph.D. Thesis, Mohamed-Cherif Messaadia University-Souk Ahras, Souk Ahras, Algeria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Telli, A.; Esnault, M.-A.; Khelil, A.O.E.H. An ethnopharmacological survey of plants used in traditional diabetes treatment in south-eastern Algeria (Ouargla province). J. Arid. Environ. 2016, 127, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, N.; Slimani, N.; Hechifa, D.; Merad, K.; Khelil, A. Study of the effect of drying methods on biochemical determination of some spontaneous plants character medicinales in the Northen Algerian Sahara. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Quezel, P.; Santa, S.; Schotter, O. Nouvelle flore de l’Algerie et des regions desertiques meridionales. Ed. Cent. Natl. Rech. Sci. 1962, 2, 1170. [Google Scholar]
- Tattou, M. Flore vasculaire du Maroc. Inventaire et chorologie. Trav. Inst. Sci. Rabat 2005, 50, 115–201. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Snafi, A.E. Traditional uses of Iraqi medicinal plants. IOSR J. Pharm. 2018, 8, 32–96. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sebakhy, L. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry: Bioactive Natural Products; Elsevier: Amesterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Yalçın, F.N.; Piacente, S.; Perrone, A.; Capasso, A.; Duman, H.; Çalış, İ. Cycloartane glycosides from Astragalus stereocalyx Bornm. Phytochemistry 2012, 73, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistelli, L.; Giachi, I.; Lepori, E.; Bertoli, A. Further saponins and flavonoids from Astragalus verrucosus Moris. Pharm. Biol. 2003, 41, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halis, Y. Atlas Floristique de La region de Souf: Les Plantes Sahariennes Connues Dans le Grand Erg-Oriental; Oued Souf: El-Walid, Algeria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guettaf, S.; Abidli, N.; Kariche, S.; Bellebcir, L.; Bouriche, H. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of aqueous extract of Genista Saharae. Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Meriane, D.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Kaabeche, M.; Michel, S.; Boutefnouchet, S. Rapid identification of antioxidant compounds of Genista saharae Coss. & Dur. by combination of DPPH scavenging assay and HPTLC-MS. Molecules 2014, 19, 4369–4379. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchouka, E.; Djilani, A.; Bekkouche, A. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of three endemic plants from Algerian Sahara. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2012, 11, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lograda, T.; Chaker, A.N.; Chalard, P.; Ramdani, M.; Chalchat, J.C.; Silini, H.; Figueredo, G. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oil of Genista numidica Spach. and G. saharae Coss et Dur. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2009, 8, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherraze, M.H.L.K.; Kherfi, Y.; Benzaoui, T.; Berroussi, S.; Bouhanna, M. Atlas Floristique de la Vallée de l’Oued Righ Par Écosystème; Centre de Recherche Scientifique et Technique sur les Régions Arides: Touggourt, Algeria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.-S.; Huang, C.-G.; Chen, Y.-J.; Yu, J.-J.; Chen, W.-J.; Chang, S.-T. Chemical compositions and larvicidal activities of leaf essential oils from two eucalyptus species. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostić, M.; Popović, Z.; Brkić, D.; Milanović, S.; Sivčev, I.; Stanković, S. Larvicidal and antifeedant activity of some plant-derived compounds to Lymantria dispar L. (Lepidoptera: Limantriidae). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7897–7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaradj, A.; Boucherit, H.; Mederbal, K.; Benabdeli, K.; Baghdadi, D. Effect the exclosure on plant diversity of the Hammada scoparia steppe in the Naama steppe courses (Algeria). J. Mater Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 564–571. [Google Scholar]
- Dehliz, A.A.F.; Mlik, R.; Hammi, H.; Doumandji-Mitiche, B.; Gheriani, S.; Berrekbia, M.; Guermit, K.; Chergui, S. Ethnobotanical study of some plants used in traditional medicine in the region of Oued Righ (Algerian Sahara). J. Med. Plants Stud. 2016, 4, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Smara, O. Etude Éthnobotanique et Chimique d’Euphorbia Guyoniana Boiss; etReut. Univ.: Annaba, Algeria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- El Hadj, M.D.O.; Hadj-Mahammed, M.; Zabeirou, H. Place of the spontaneous plants samples in the traditional pharmacopoeia of the area of Ouargla (Septentrional east Sahara). Courr. Du Savoir 2003, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjadj, K.; Daoudi, B.B.; Guerine, L. Importance thérapeutique de la plante ephedra alata subsp. Alenda dans la médecine traditionnelle pour la population de la région de Guettara (Djelfa, Algérie). Lejeunia Rev. De Botanique. 2020. Available online: https://popups.uliege.be/0457-4184/index.php?id=2026 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Kubitzki, K.; Bayer, C. Flowering Plants. Dicotyledons: Malvales, Capparales, and Non–betalain Caryophyllales. In The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Sambamurty, A. Taxonomy of Angiosperms; IK International Pvt Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mandaville, J.P. Flora of Eastern Saudi Arabia; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitoun, S.T.; Vorwohl, G. Major pollen plant species in relation to honeybees’ activity in the Jordanian desert area. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2003, 4, 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, A.; Gtari, M.; Mohamed, N. Micropropagation of Helianthemum lippii L. var Sessiliforuim (Cistaceae) an important pastoral plant of North African arid areas. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 6468–6473. [Google Scholar]
- Alsabri, S.G.; Zetrini, A.; Fitouri, S.; Hermann, A. Screening of analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities for two Libyan medicinal plants: Helianthemum lippii and Launaea residifolia. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 4201–4205. [Google Scholar]
- Alsabri, S.G.; Rmeli, N.B.; Zetrini, A.A.; Mohamed, S.B.; Meshri, M.I.; Aburas, K.M.; Bensaber, S.M.; Mrema, I.A.; Mosbah, A.A.; Allahresh, K.A. Phytochemical, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer properties of Helianthemum lippii. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chouikh, A.A.E.; Adaika, A.; Chefrour, A. Screening chimique d’une plante pastorale Saharienne Heliathemum lippii (famille Cistaceae) dans différents phases de la croissance (végétative; floraison; fructification) à Sahara d’Oued Souf (Est-sud Algérie). ScienceLib 2014, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.S.; Kasoju, N.; Luthra, A.; Singh, A.; Sharanabasava, H.; Sahu, A.; Bora, U. Indian medicinal herbs as source of antioxidants. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zakaria, M.; Islam, M.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Ismail, A.; Chen, H.; Chan, K.; Al-Attas, A. Anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer activity of Calligonum comosum in rats. Fitoterapia 2001, 72, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, D. In-vitro antibacterial activity of ethanol extract of Calligonum comosum plant against four human pathogens in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Badria, F.A.; Ameen, M.; Akl, M.R. Evaluation of cytotoxic compounds from Calligonum comosum L. growing in Egypt. Z. Für Nat. C 2007, 62, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamil, M.; Jayaraj, A.; Ahmad, F.; Gunasekhar, C.; Samuel, S.; Chan, K.; Habibullah, M.; Attas, A. Pharmacognostic and phytochemical standardization of Calligonum comosum. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Türel, I.; Özbek, H.; Erten, R.; Öner, A.C.; Cengiz, N.; Yilmaz, O. Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory activities of Plantago major L. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2009, 41, 120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samout, N.; Ettaya, A.; Bouzenna, H.; Ncib, S.; Elfeki, A.; Hfaiedh, N. Beneficial effects of Plantago albicans on high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janković, T.; Zdunić, G.; Beara, I.; Balog, K.; Pljevljakušić, D.; Stešević, D.; Šavikin, K. Comparative study of some polyphenols in Plantago species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 42, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, S.; Bayoussef, Z.; El Hadj-Khelil, A.O.; Beggat, H.; Bouhafs, Z.; Boukaka, Y.; Khaldi, I.A.; Mimouni, S.; Sayah, F.; Tey, M. Ethnobotanical study and phytochemical screening of six medicinal plants used in traditional medicine in the Northeastern Sahara of Algeria (area of Ouargla). J. Med. Plants Res. 2015, 9, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, L. Medicinal plants of North Africa. Med. Plants N. Afr. 1983, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Chemsa, A.E.; Derdouri, S.; Labbi, Z.; Acila, S.; Amara, D.G.; Chouikh, A.; Kherraz, K.; Allali, A.; Zellagui, A. Total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of different solvent extracts of Bassia muricata (L.) Asch. and evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Syed Najmuddin, S.U.F.; Romli, M.F.; Hamid, M.; Alitheen, N.B.; Nik Abd Rahman, N.M.A. Anti-cancer effect of Annona Muricata Linn Leaves Crude Extract (AMCE) on breast cancer cell line. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hossary, G.; Selim, M.; Sayed, A.E.; Khaleel, A. Study of the flavonoid content of Bassia muricata and Bauhinia racemosa. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2000, 38, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, M.S.; Mohamed, K.M.; Hassanean, H.A.; Ohtani, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Acylated flavonoid glycosides from Bassia muricata. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, K.H.; Al Jubiri, S.M.; El-Hady, F.; Al-Sehemi, A.G. New compounds from Bassia muricata and Fagonia indica. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res 2013, 23, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Adouane, S. Etude Ethnobotanique des Plantes Médicinales dans la Région Méridionale des Aurès; Université Mohamed Khider-Biskra: Biskra, Algeria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chikhi, I.; Allali, H.; Dib, M.E.A.; Medjdoub, H.; Tabti, B. Antidiabetic activity of aqueous leaf extract of Atriplex halimus L.(Chenopodiaceae) in streptozotocin–induced diabetic rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnafgui, K.; Hamden, K.; Ben Salah, H.; Kchaou, M.; Nasri, M.; Slama, S.; Derbali, F.; Allouche, N.; Elfeki, A. Inhibitory activities of Zygophyllum album: A natural weight-lowering plant on key enzymes in high-fat diet-fed rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 620384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V.; Ventura, H.O. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Khan, D.; Zaki, M.J. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from some Coastal Plants of Karachi (Pakistan). Int. J. Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 13, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin, M.; Rakib, H.H.; Biplob, A.; Islam, M.S.; Foyasal, M.K.; Tanvir, R.Z.; Jahan, N. Medicinal plants used by a Traditional Ayurvedic Practitioner at Asadnagar Village in Narsingdi District, Bangladesh. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2015, 4, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Khurshid, U.; Ahmad, S.; Saleem, H.; Nawaz, H.A.; Zengin, G.; Locatelli, M.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Abidin, S.A.Z.; Tousif, M.I.; Ahemad, N. Phytochemical composition and in vitro pharmacological investigations of Neurada procumbens L. (Neuradaceae): A multidirectional approach for industrial products. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 142, 111861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, F.S.; Ashour, M.L.; El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Singab, A.N.B.; Wink, M. Metabolic profiling of Buddleia indica leaves using LC/MS and evidence of their antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity using different in vitro and in vivo Experimental models. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Benarfa, A.; Ouakouak, H.; Begaa, S. Determination of some chemical elements of common spices used by algerians and possible health risk assessment. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2498–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlat, N.; Benarfa, A.; Beladel, B.; Begaa, S.; Messaoudi, M.; Hassani, A. Assessment of the contents of essential and potentially toxic elements in Pistacia terebinthus L. and Pistacia lentiscus L. by INAA technique. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2019, 322, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begaa, S.; Messaoudi, M. Toxicological aspect of some selected medicinal plant samples collected from Djelfa, Algeria Region. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 187, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Begaa, S. Application of INAA technique for analysis of essential trace and toxic elements in medicinal seeds of Carum carvi L. & Foeniculum vul-gare Mill. used in Algeria. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 9, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gurib-Fakim, A.; Mahomoodally, M.F. African flora as potential sources of medicinal plants: Towards the chemotherapy of major parasitic and other infectious diseases: A review. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 147, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchikha, N.; Chelalba, I.; Debbeche, H.; Messaoudi, M.; Begaa, S.; Larkem, I.; Amara, D.G.; Rebiai, A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Sawicka, B.; et al. Lobularia libyca: Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity Using In Vitro and In Silico Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelalba, I.; Rebiai, A.; Debbeche, H.; Begaa, S.; Messaoudi, M.; Benchikha, N. Total phenol and flavonoid content, antioxidant and cytotoxicity assessment of Algerian Launaea glomerata (Cass.) Hook. f. extracts. Eur. J. Biol. Res. 2021, 11, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Efferth, T.; Kaina, B. Toxicities by herbal medicines with emphasis to traditional Chinese medicine. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Zhou, S.-F.; Gao, S.-H.; Yu, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.-F.; Tang, M.-K.; Sun, J.-N.; Ma, D.-L.; Han, Y.-F.; Fong, W.-F. New perspectives on how to discover drugs from herbal medicines: CAM’s outstanding contribution to modern therapeutics. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 627375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangchuk, P. Quality assurance of the university medical education, hospital services and traditional pharmaceutical products of the Bhutanese So-wa-rig-pa health care system. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.D.; Daswani, P.G.; Birdi, T.J. Approaches in fostering quality parameters for medicinal botanicals in the Indian context. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, R.; Saklani, A.; Jachak, S.M. Indian medicinal plants as a source of antimycobacterial agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 110, 200–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndhlala, A.; Stafford, G.; Finnie, J.; Van Staden, J. Commercial herbal preparations in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: The urban face of traditional medicine. South Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, P.; Clares, B.; Hmadcha, A.; Ruiz, A.; Soria, B. Development of a cell-based medicinal product: Regulatory structures in the European Union. Br. Med. Bull. 2013, 105, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasilo, O.M.; Trapsida, J.-M. Regulation of traditional medicine in the WHO African region. Afr. Health Monit. 2010, 3, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbouchi, M.; Elamrani, K.; El Idrissi, M. A comparative study on phytochemical screening, quantification of phenolic contents and antioxidant properties of different solvent extracts from various parts of Pistacia lentiscus L. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlifi, D.; Sghaier, R.M.; Amouri, S.; Laouini, D.; Hamdi, M.; Bouajila, J. Composition and anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities of Artemisia herba-alba, Ruta chalpensis L. and Peganum harmala L. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahla, N.; Nima, S.; Batool, S.N.; Maryam, A.B.; Ehsan, S. Phytochemical screening and antibacterial activity of Citrullus colocynthis (Linn.) Schrad against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Benariba, N.; Djaziri, R.; Bellakhdar, W.; Belkacem, N.; Kadiata, M.; Malaisse, W.J.; Sener, A. Phytochemical screening and free radical scavenging activity of Citrullus colocynthis seeds extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Luo, Q.; Sun, M.; Corke, H. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2157–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górniak, I.; Bartoszewski, R.; Króliczewski, J. Comprehensive review of antimicrobial activities of plant flavonoids. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.; Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Irshad, K.; Imran, I. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Association of risk factors and treatment strategies using plant-based bioactive compounds. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Shen, T.; Lou, H. Dietary polyphenols and their biological significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 950–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiecik, D.; Korczak, J.; Rudzińska, M.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Hęś, M.; Kobus-Cisowska, J. Stabilisation of phytosterols by natural and synthetic antioxidants in high temperature conditions. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopylov, A.T.; Malsagova, K.A.; Stepanov, A.A.; Kaysheva, A.L. Diversity of Plant Sterols Metabolism: The Impact on Human Health, Sport, and Accumulation of Contaminating Sterols. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahnit, W.; Smara, O.; Bechki, L.; Bensouici, C.; Messaoudi, M.; Benchikha, N.; Larkem, I.; Awuchi, C.G.; Sawicka, B.; Simal-Gandara, J. Phytochemical Profiling, Mineral Elements, and Biological Activities of Artemisia campestris L. Grown in Algeria. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautwein, E.A.; Demonty, I. Phytosterols: Natural compounds with established and emerging health benefits. Oléagineux Corps Gras Lipides 2007, 14, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, H.; Bodla, R.B.; Kant, R. Green tea (Camellia sinensis) and its antioxidant property: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Aversa, R.; Petrescu, R.V.; Apicella, A.; Petrescu, F.I. One can slow down the aging through antioxidants. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.; Aiyelaagbe, O.; Usman, L.; Ameen, O.; Lawal, A. Antioxidants: Its medicinal and pharmacological applications. Afr. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 4, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Pham-Huy, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. IJBS 2008, 4, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, M.G.; Webby, R.F.; Markham, K.R.; Mitchell, K.A.; Da Cunha, A.P. Age-induced diminution of free radical scavenging capacity in bee pollens and the contribution of constituent flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leja, M.; Mareczek, A.; Wyżgolik, G.; Klepacz-Baniak, J.; Czekońska, K. Antioxidative properties of bee pollen in selected plant species. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, H.; Farzaei, M.H.; Khodarahmi, R. Polyphenols and their benefits: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1700–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, A. Tamarix nilotica (Ehrenb) bunge: A review of phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2017, 9, 544–553. [Google Scholar]
- Adu-Gyamfi, S. From Vital Force To The Scientific or an Admixture: A Historical Discourse On Individuals Value for Indigenous Medical Practices In Ghana. J. Basic Appl. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kapinova, A.; Stefanicka, P.; Kubatka, P.; Zubor, P.; Uramova, S.; Kello, M.; Mojzis, J.; Blahutova, D.; Qaradakhi, T.; Zulli, A. Are plant-based functional foods better choice against cancer than single phytochemicals? A critical review of current breast cancer research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrovánková, S.; Mišurcová, L.; Machů, L. Antioxidant activity and protecting health effects of common medicinal plants. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 67, 75–139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ahmeda, A.; Malek, Z.; Mansooridara, S.; Zangeneh, A.; Zangeneh, M.M. Chemical characterization and therapeutic properties of Achillea biebersteinii leaf aqueous extract synthesized copper nanoparticles against methamphetamine-induced cell death in PC12: A study in the nanotechnology and neurology fields. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Debnath, B.; Qasim, M.; Bamisile, B.S.; Islam, W.; Hameed, M.S.; Wang, L.; Qiu, D. Role of saponins in plant defense against specialist herbivores. Molecules 2019, 24, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintamunnee, V.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Herbal medicine commonly used against non-communicable diseases in the tropical island of Mauritius. J. Herb. Med. 2012, 2, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofowora, A.; Ogunbodede, E.; Onayade, A. The role and place of medicinal plants in the strategies for disease prevention. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affolter, J.M.; Pengelly, A. Conserving medicinal plant biodiversity. In Veterinary Herbal Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrends, A.; Rahbek, C.; Bulling, M.T.; Burgess, N.D.; Platts, P.J.; Lovett, J.C.; Kindemba, V.W.; Owen, N.; Sallu, A.N.; Marshall, A.R. Conservation and the botanist effect. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwu, M.M. Pharmacognostical profile of selected medicinal plants. In Handbook of African Medicinal Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 125–380. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, A.C. Medicinal plants, conservation and livelihoods. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 1477–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzoyem, J.P.; Tshikalange, E.; Kuete, V. Medicinal plants market and industry in Africa. In Medicinal Plant Research in Africa; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 859–890. [Google Scholar]
- Van Andel, T.; Myren, B.; van Onselen, S. Ghana’s herbal market. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.L.; Witkowski, E.T.; Balkwill, K. Volume and financial value of species traded in the medicinal plant markets of Gauteng, South Africa. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2007, 14, 584–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towns, A.M.; Quiroz, D.; Guinee, L.; de Boer, H.; van Andel, T. Volume, value and floristic diversity of Gabon’s medicinal plant markets. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillen, H.L. Conserving the Roots of Trade: Local Ecological Knowledge of Ethnomedicines from Tanga, Tanzania Markets; University of Hawaii at Manoa: Hawaii, HI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jusu, A.; Sanchez, A.C. Economic Importance of the Medicinal Plant Trade in Sierra Leone 1. Econ. Bot. 2013, 67, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, M.; Aremu, A.O.; Van Staden, J. Medicinal plants: An invaluable, dwindling resource in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbe, A.; Verpoorte, R. Cultivation of medicinal and aromatic plants for specialty industrial materials. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 34, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirungi, J.; Fabricius, C. Selecting medicinal plants for cultivation at Nqabara on the Eastern Cape Wild Coast, South Africa: Research in action. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2005, 101, 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, V.; Balkwill, K.; Witkowski, E.F. Unraveling the commercial market for medicinal plants and plant parts on the Witwatersrand. S. Afr. 2000, 54, 310–327. [Google Scholar]
- Ticktin, T. The ecological implications of harvesting non-timber forest products. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 41, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.G.; Mahajan, V.; Bedi, Y.S. Changing trends in biotechnology of secondary metabolism in medicinal and aromatic plants. Planta 2015, 241, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Andel, T.; Croft, S.; Van Loon, E.; Quiroz, D.; Towns, A.; Raes, N. Prioritizing West African medicinal plants for conservation and sustainable extraction studies based on market surveys and species distribution models. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 181, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshi, M.J.; Mhame, P.P. Legislation on medicinal plants in Africa. Med. Plant Res. Afr. 2013, 2013, 843–858. [Google Scholar]
- Salud, O.M.D.L.; World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Good Agricultural and Collection Practices [GACP] for Medicinal Plants; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Montoro, P.; Teyeb, H.; Masullo, M.; Mari, A.; Douki, W.; Piacente, S. LC–ESI-MS quali-quantitative determination of phenolic constituents in different parts of wild and cultivated Astragalus gombiformis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 72, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kúsz, N.; Orvos, P.; Csorba, A.; Tálosi, L.; Chaieb, M.; Hohmann, J.; Rédei, D. Jatrophane diterpenes from Euphorbia guyoniana are new potent inhibitors of atrial GIRK channels. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5724–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadef, K.; Smaoui, S.; Hlima, H.B.; Ennouri, K.; Fourati, M.; Mtibaa, A.C.; Sellem, I.; Mellouli, L. Chemometric multivariate analyses of phenolics and biological activities for characterization and discrimination of Tunisian Ephedra alata. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1495–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atef, C.; Anouar, F.; El-Hadda, A.; Azzedine, C. Phytochemicals study, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Helianthemum lippii (L.) pers. in different stages of growth (somatic, flowering and fruiting). World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 4, 338–349. [Google Scholar]
- Djemam, N.; Lassed, S.; Gül, F.; Altun, M.; Monteiro, M.; Menezes-Pinto, D.; Benayache, S.; Benayache, F.; Zama, D.; Demirtas, I. Characterization of ethyl acetate and n-butanol extracts of Cymbopogon schoenanthus and Helianthemum lippii and their effect on the smooth muscle of the rat distal colon. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 252, 112613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razik, A.F.; Nassar, M.I.; El-Khrisy, E.-D.A.; Dawidar, A.-A.M.; Mabry, T.J. New prenylflavans from Cyperus conglomeratus. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Abrahim, J.S.; Mohammed, A.E.; Elobeid, M.M. Received: 23 Research article Assessment of In-Vitro Anti-Fungal Potential of Ethanolic Extract of Calligonum Comosum against Two Fungal Postharvest Pathogens of Fruits and Vegetables in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. 2013, 2013, 167637. [Google Scholar]
- Bannour, M.; Fellah, B.; Rocchetti, G.; Ashi-Smiti, S.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Lucini, L.; Khadhri, A. Phenolic profiling and antioxidant capacity of Calligonum azel Maire, a Tunisian desert plant. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miara, M.; Hammou, M.A.; Aoul, S.H. Phytothérapie et taxonomie des plantes médicinales spontanées dans la région de Tiaret (Algérie). Phytothérapie 2013, 11, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A. Contribution a l’etude de plantes medicinales utilisees dans le traitement traditionnel du diabete sucre dans l’Ouest Algerien: Enquete ethnopharmacologique. In Analyse Pharmaco-Toxicologique de Figuier (Ficus Carcia) et de Coloquinte (Citrillus Colocynthis) Chez Le Rat Wistar; Universite Abou Bekr Belkaid: Telemcen, Algeria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chehma, A.; Djebar, M.R. Les espèces médicinales spontanées du Sahara septentrional algérien: Distribution spatio-temporelle et étude ethnobotanique. Synthèse Rev. Sci. Technol. 2008, 17, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bakari, S.; Hajlaoui, H.; Daoud, A.; Mighri, H.; Ross-Garcia, J.M.; Gharsallah, N.; Kadri, A. Phytochemicals, antioxidant and antimicrobial potentials and LC-MS analysis of hydroalcoholic extracts of leaves and flowers of Erodium glaucophyllum collected from Tunisian Sahara. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, A.A.; Lahloub, M.F.; Niwa, M. Antibacterial polyphenol from Erodium glaucophyllum. Z. Für Nat. C 2003, 58, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhari, A.; Tufano, I.; DellaGreca, M. Influence of new effective allelochemicals on the distribution of Cleome arabica L. community in nature. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeddi, S.; Karioti, A.; Yannakopoulou, E.; Papadopoulos, K.; Chatter, R.; Skaltsa, H. Analgesic and antioxidant activities of Algerian Retama raetam (Forssk.) Webb & Berthel extracts. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2013, 7, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmadjide, A.M.S.; Atef, C.; Nadia, Z.; Néji, B. Phytochemical study, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of flavonoids and diethyl ether extracts from leaves and seeds of medicinal plant of algeria flora: Retama monosperma (L.) boiss. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 76, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bouredja, N.; Bouredja, M.; Mehdadi, Z. Study of the impact of the anthropological actions and the climate on the degradation of Retama monosperma (L.). Boiss growing in natural conditions in the Algerian western coast. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. JBES 2015, 6, 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Chouikh, A.; Alia, F.; Neffar, S.; Rebiai, A.; Adjal, E.H.; Chefrour., A. Evaluation of phenolic contents (quantitative and qualitative) and antioxidant activities in different physiological phases of genista saharae coss. & dur. Growing in the Sahara of Algeria. An. Univ. Oradea Fasc. Biol. 2018, 25, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lekmine, S.; Boussekine, S.; Kadi, K.; Martín-García, A.I.; Kheddouma, A.; Nagaz, K.; Bensouici, C. A comparative study on chemical profile and biological activities of aerial parts (stems, flowers, leaves, pods and seeds) of Astragalus gombiformis. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyeb, H.; Mabrouk, H.; Neffati, M.; Douki, W.; Najjar, M.F. Anticholinesterase activity of Astragalus gombiformis extracts. J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2011, 1, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Abdellah, K.; Zakaria, B.; Zakaria, M.; Mounira, K.; Fouzi, B.; Aek, H.; Toufik, G. Ould El Hadj-Khelil Aminata et Ould elhadj Mohamed Didi Étude de la toxicité des extraits foliaires d’Euphorbia guyoniana Boiss. et Reut. (Euphorbiaceae) chez Schistocerca gregaria (Forskål, 1775) (Orthoptera-Acrididea). PhytoChem. BioSub. J. 2013, 7, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dehliz, A.; Lakhdari, W.; Acheuk, F.; Aoudjit, R.; Benlamoudi, W.; Mlik, R.; Hammi, H.; Chergui, S.; Guermit, K.; Matallah, S. Euphorbia guyoniana aqueous extract efficiency against tomato leaf miner in southern East Algeria. Org. Agric. 2018, 8, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouikh, A. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant, Analgesic and Hypolipidaemic Effects of Ephedra Alata Decne. Female Cones Extract. Farmacia 2020, 68, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerbi, A.; Zehri, S.; Abdnnabi, R.; Gharsallah, N.; Kammoun, M. Essential oil composition, free-radical-scavenging and antibacterial effect from stems of Ephedra alata alenda in Tunisia. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2016, 19, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyagoubi-Benhammou, N.; Belyagoubi, L.; Bekkara, F.A. Phenolic contents and antioxidant activities in vitro of some selected Algerian plants. J. Med. Plants Res. 2014, 8, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hazmi, G.H.; Awaad, A.S.; Alothman, M.R.; Alqasoumi, S.I. Anticandidal activity of the extract and compounds isolated from Cyperus conglomertus Rottb. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nuairi, A.G.; Mosa, K.A.; Mohammad, M.G.; El-Keblawy, A.; Soliman, S.; Alawadhi, H. Biosynthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles from cyperus conglomeratus root extracts on breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.A.; Ross, S.A.; El-Amier, Y.A.; Khan, I.A. New flavans and stilbenes from Cyperus conglomeratus. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 26, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouikh, A.; Chemsa, A.E.; Aounallah, C.; Aounallah, I.; Fatma, A. Phytochemical study, nutritive value, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of phenolic extracts from desert plant Calligonum comosum L’Hér. Alger. J. Biosci. 2020, 1, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Al–Saadi, M.; Fa, B.; Ah, A.S. Cytogenetic effects of Myrtus communis AND Plantago albicans Infusions on Bean root-Tip and Mice Bone-Marrow Cells. Arab. Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2005, 13, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhaled, A.; Senator, A. Effects of aqueous leaf extract of Limoniastrum guyonianum pretreatment on nickel induced acute heamatotoxicity in male mice. Glob. Vet. 2015, 15, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjadj, S.; Khadir, A.; Bensaci, S.; El Hadj, M.O.; El Hadj-Khelil, A.O. Comparison of phenolic content and antioxidant activity of methanolic and ethanolic extracts of Limoniastrum guyonianum. Int. J. Biosci. 2016, 9, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Belfar, A.; Hadjadj, M.; Dakmouche, M.; Ghiaba, Z. Evaluation of antioxidants in ethanol extracts of Limoniastrum guyonianum (Zeïta) in Sahara of Algeria. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Saidana, D.; Mahjoub, M.; Boussaada, O.; Chriaa, J.; Chéraif, I.; Daami, M.; Mighri, Z.; Helal, A. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of volatile compounds of Tamarix boveana (Tamaricaceae). Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaoui, M.; Cheriti, A.; Chebouat, E.; Dadamoussa, B.; Gherraf, N. Comparative study of the antioxidant activity and phenols and flavonoids contents of the ethyl acetate extracts from two saharan chenopodacea: Haloxylon scoparium AND Traganum nudatum. Alger. J. Arid. Environ. AJAE 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Labed, B.; Gherraf, N.; Hameurlaine, S.; Ladjel, S.; Zellagui, A. The antibacterial activity of water extracts of Traganum nudatum Del (Chenopodiaceae) growing in Algeria. Pharm. Lett. 2010, 2, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-ElGawad, A.; El Gendy, A.E.-N.; El-Amier, Y.; Gaara, A.; Omer, E.; Al-Rowaily, S.; Assaeed, A.; Al-Rashed, S.; Elshamy, A. Essential oil of Bassia muricata: Chemical characterization, antioxidant activity, and allelopathic effect on the weed Chenopodium murale. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1900–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammedi, H.; Idjeri-Mecherara, S.; Menaceur, F.; Hassani, A. The effect of solvents and extraction procedure on the recovery of phenolic compounds and the antioxidant capacity of Algerian Bassia muricata L. extracts. Chem. J. Mold. 2019, 14, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Benreguieg, M.; Merah, M. Phytochemical screening of Algerian medicinal plants and their antimicrobial effects. Mycopath 2020, 16, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Can, Z.; Yildiz, O.; Sahin, H.; Turumtay, E.A.; Silici, S.; Kolayli, S. An investigation of Turkish honeys: Their physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacities and phenolic profiles. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amssayef, A.; Eddouks, M. Aqueous extract of matricaria pubescens exhibits antihypertensive activity in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats through its vasorelaxant effect. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents 2019, 17, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.S.; Ferrah, R.; Bennacer, A.; Tail, G.; Saidi, F. Traditional Use of Matricaria Pubescens (Desf.) Schultz in Two Regions of Southern Algeria and Contribution to Study the Antioxidant Activity; NISCAIR-CSIR: New Delhi, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bouguerra, A.; Hadjadj, M.; Dekmouche, M.; Rahmani, Z.; Dendougui, H. Determination of phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of Launaea resedifolia from Algerian Sahara. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Moussaoui, F.; Zellagui, A.; Segueni, N.; Touil, A.; Rhouati, S. emFlavonoid Constituents from Algerian Launaea resedifolia (OK), and their Antimicrobial Activity. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2010, 4, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mouhajir, F.; Hudson, J.; Rejdali, M.; Towers, G. Multiple antiviral activities of endemic medicinal plants used by Berber peoples of Morocco. Pharm. Biol. 2001, 39, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.H.; Hamza, L.F.; Kamal, S.A. Analysis of bioactive chemical compounds of Aspergillus niger by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Pharmacogn. Phytother. 2015, 7, 132–163. [Google Scholar]
- Atef, C.; Abdelkrim, R.; Mahdia, A.; Mounira, H.; El Hadda, A.; Fatma, A. Effects of extraction methods on total polyphenols, free radical scavenging and antibacterial activity of crude extracts of Cleome arabica L. growing in Oued Souf region. Alger. J. Biosci. 2020, 1, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Chelalba, I.; Benchikha, N.; Begaa, S.; Messaoudi, M.; Debbeche, H.; Rebiai, A.; Youssef, F.S. Phytochemical composition and biological activity of Neurada procumbens L. growing in southern Algeria. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hemmami, H.; Seghir, B.B.; Zeghoud, S.; Ben Amor, I.; Kouadri, I.; Rebiai, A.; Zaater, A.; Messaoudi, M.; Benchikha, N.; Sawicka, B.; et al. Desert Endemic Plants in Algeria: A Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities. Molecules 2023, 28, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041834
Hemmami H, Seghir BB, Zeghoud S, Ben Amor I, Kouadri I, Rebiai A, Zaater A, Messaoudi M, Benchikha N, Sawicka B, et al. Desert Endemic Plants in Algeria: A Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041834
Chicago/Turabian StyleHemmami, Hadia, Bachir Ben Seghir, Soumeia Zeghoud, Ilham Ben Amor, Imane Kouadri, Abdelkrim Rebiai, Abdelmalek Zaater, Mohammed Messaoudi, Naima Benchikha, Barbara Sawicka, and et al. 2023. "Desert Endemic Plants in Algeria: A Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041834
APA StyleHemmami, H., Seghir, B. B., Zeghoud, S., Ben Amor, I., Kouadri, I., Rebiai, A., Zaater, A., Messaoudi, M., Benchikha, N., Sawicka, B., & Atanassova, M. (2023). Desert Endemic Plants in Algeria: A Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities. Molecules, 28(4), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041834












