The Size Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Reinforcing the Mechanical Properties of Regenerated Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
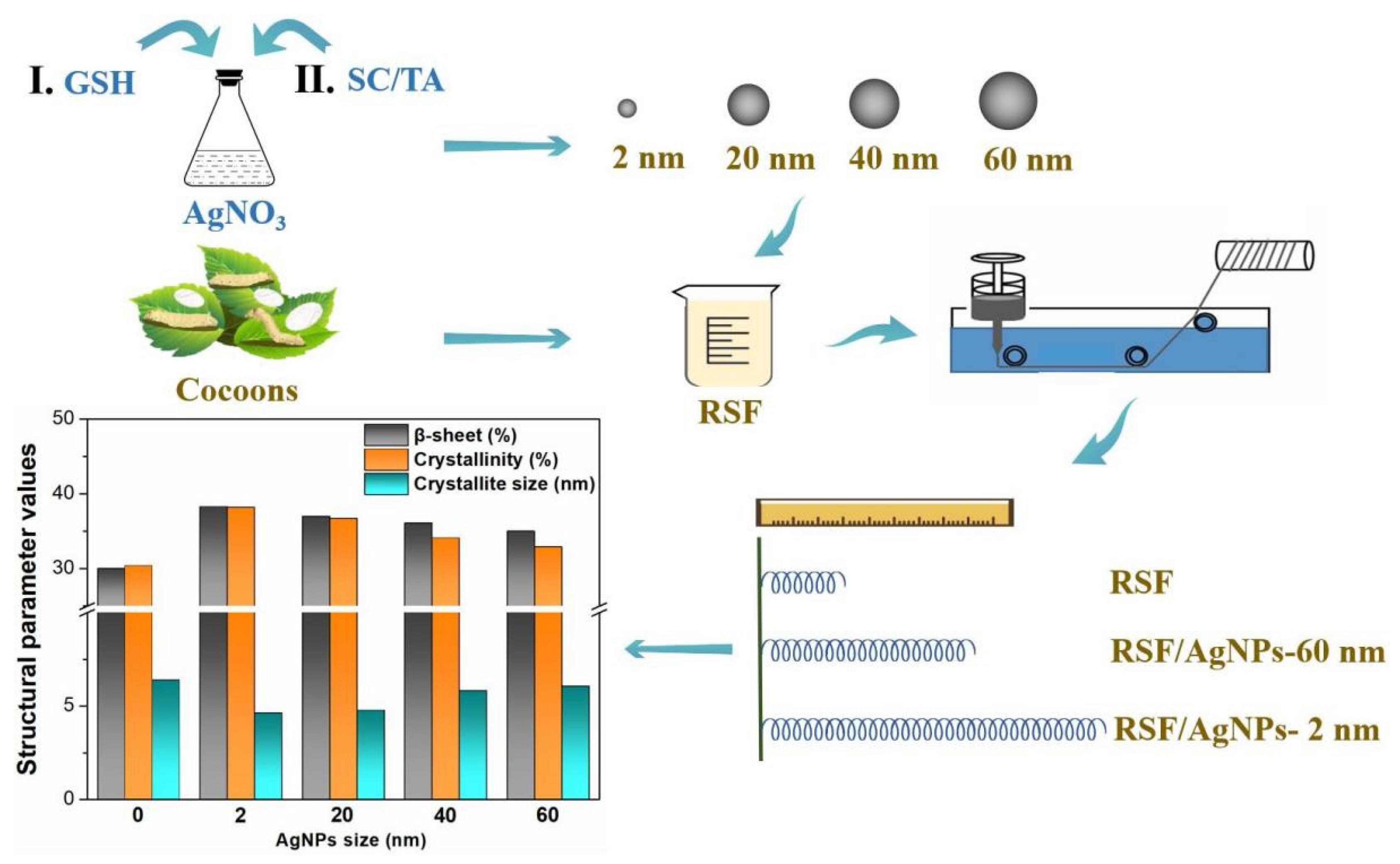
2.1. Morphology of AgNPs of Different Sizes
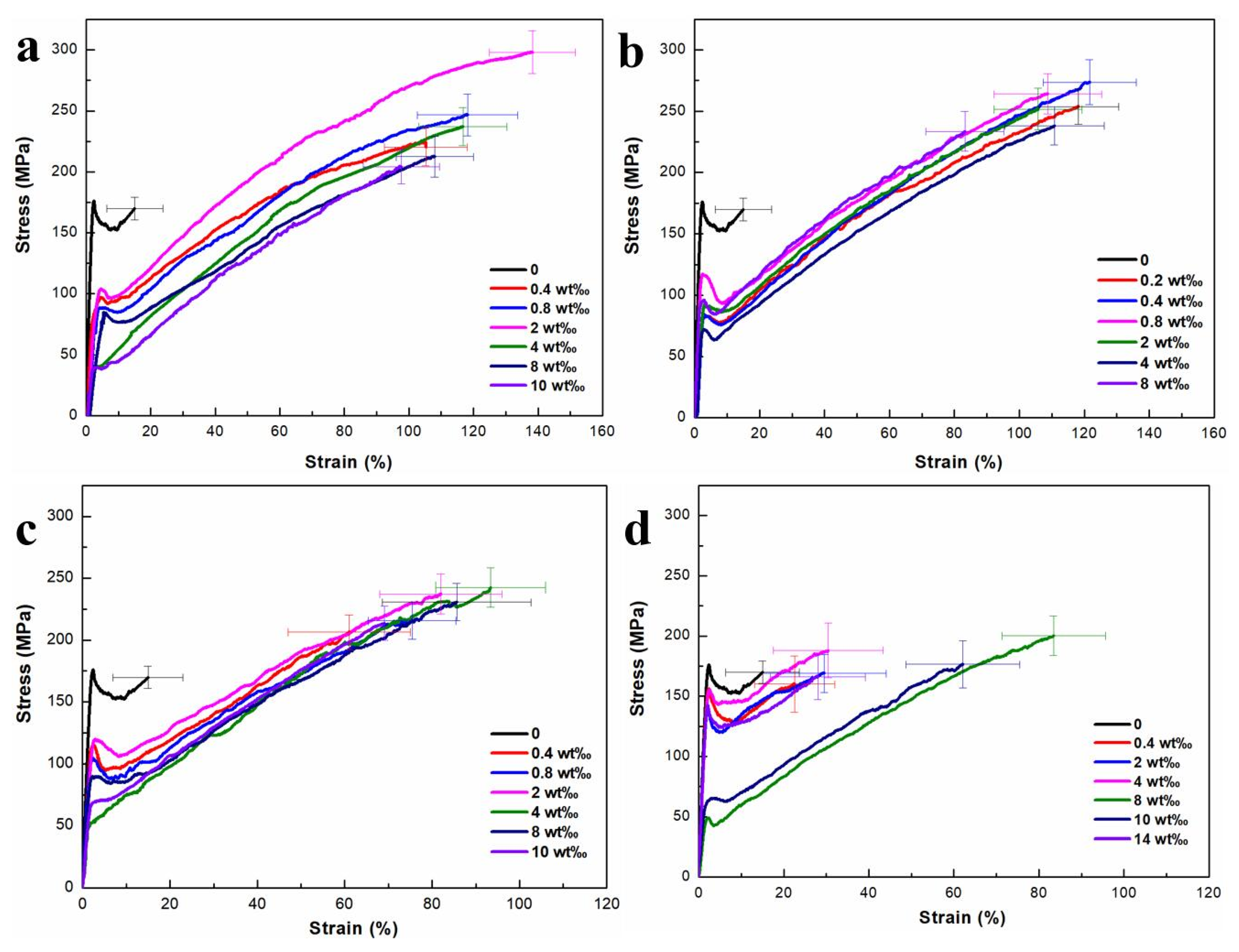
2.2. The Effect of AgNPs on the Mechanical Properties of the Hybrid Fibers
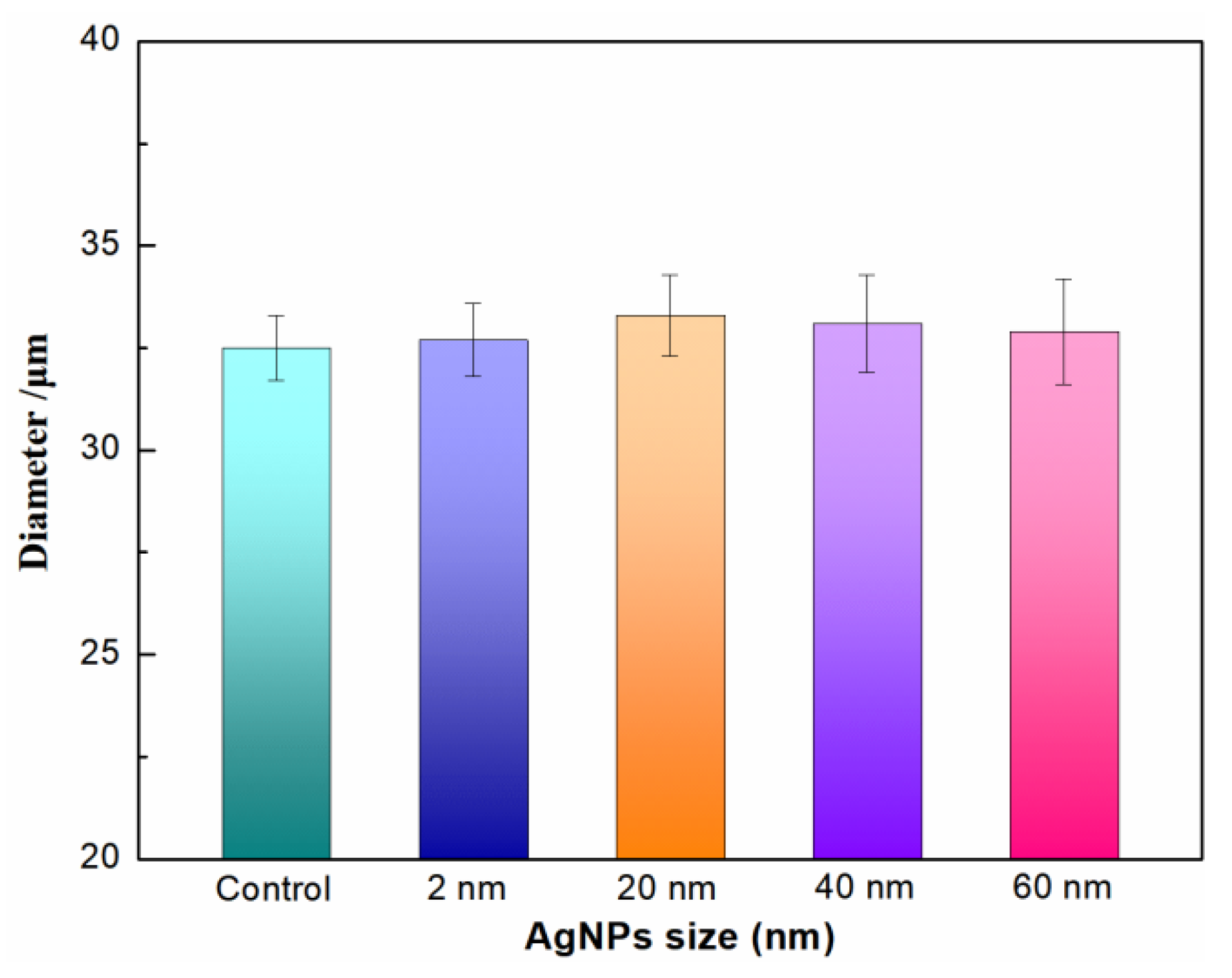
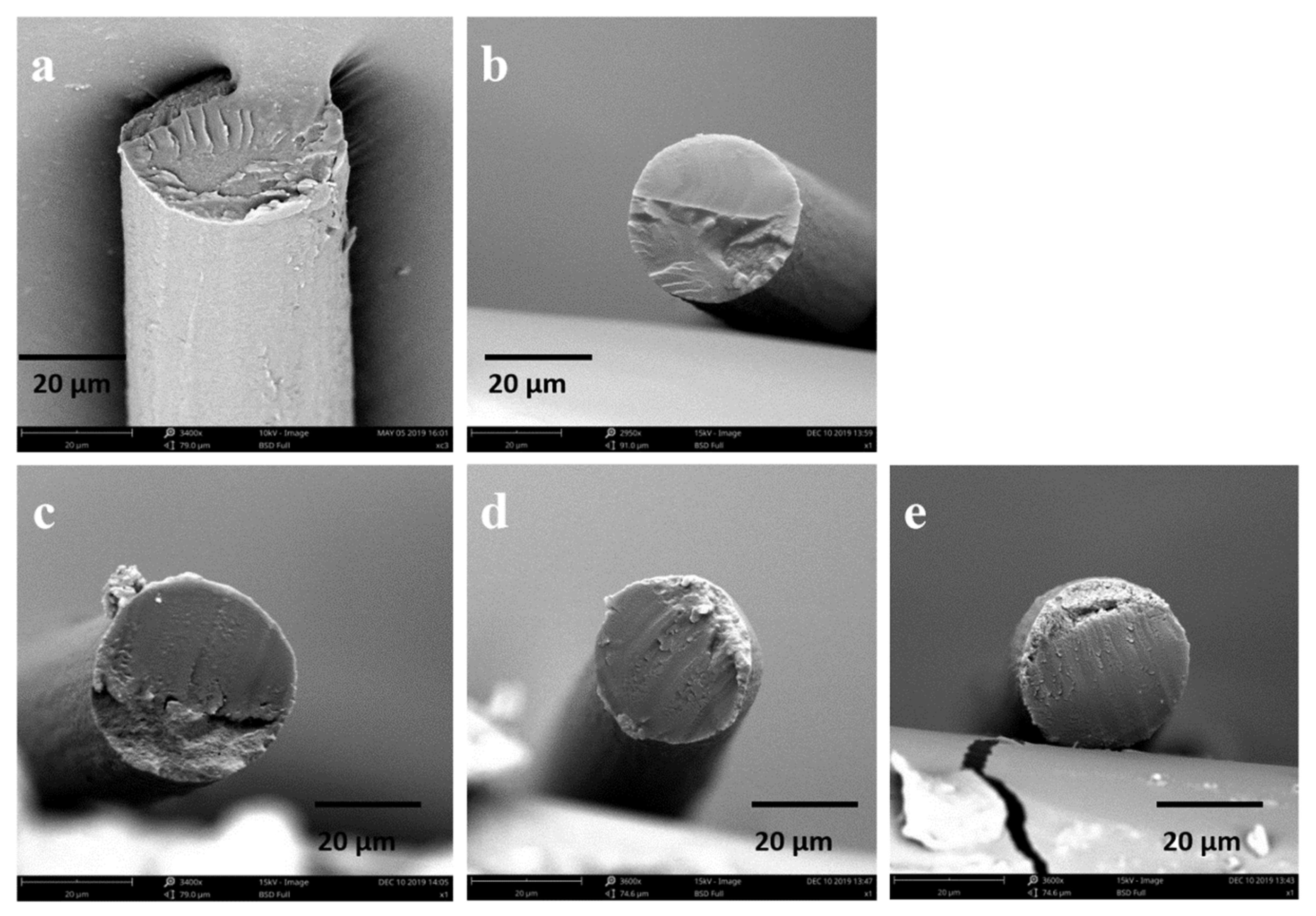
2.3. The Effect of AgNPs on the Morphology of the Hybrid Fibers
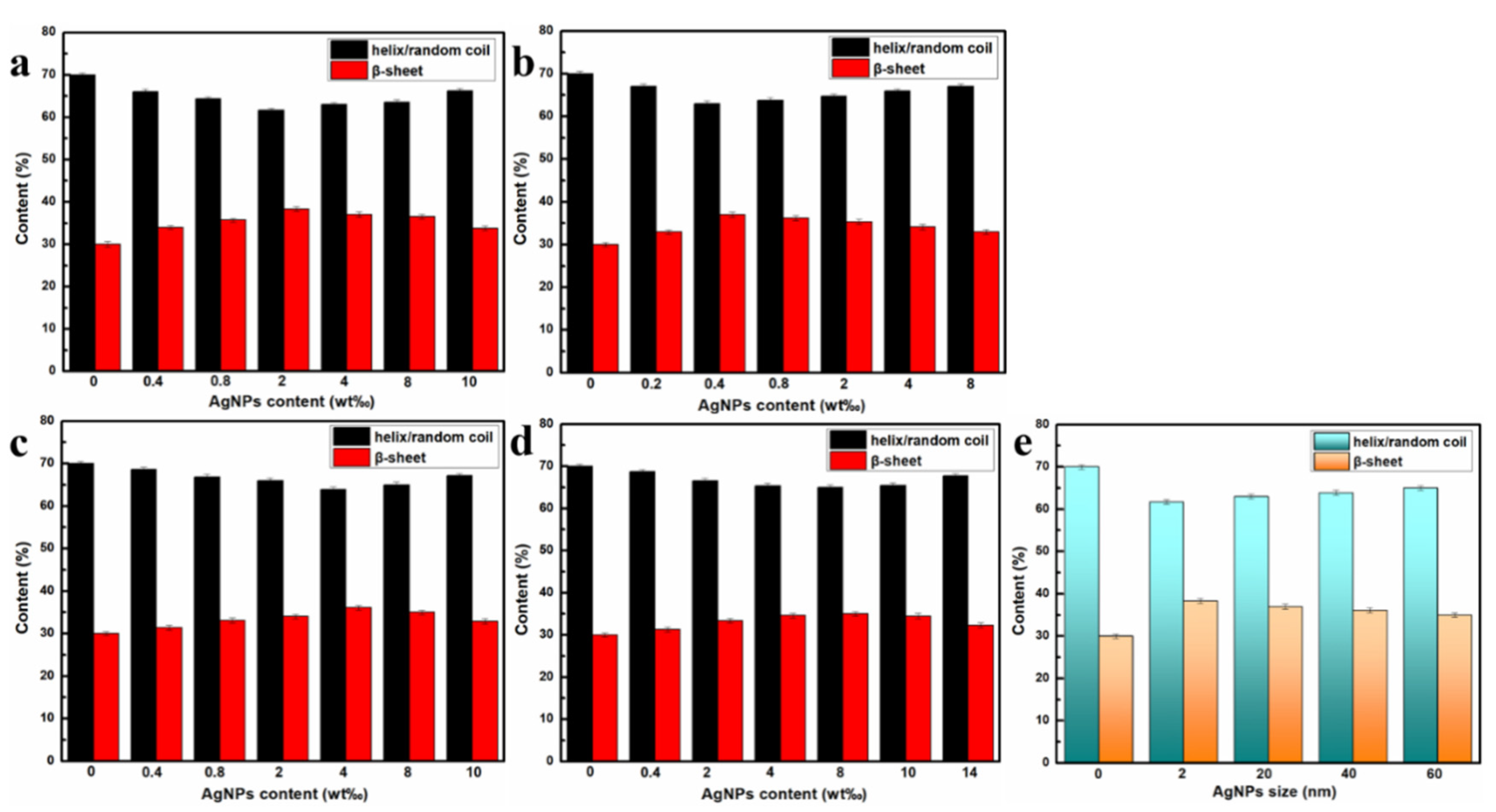
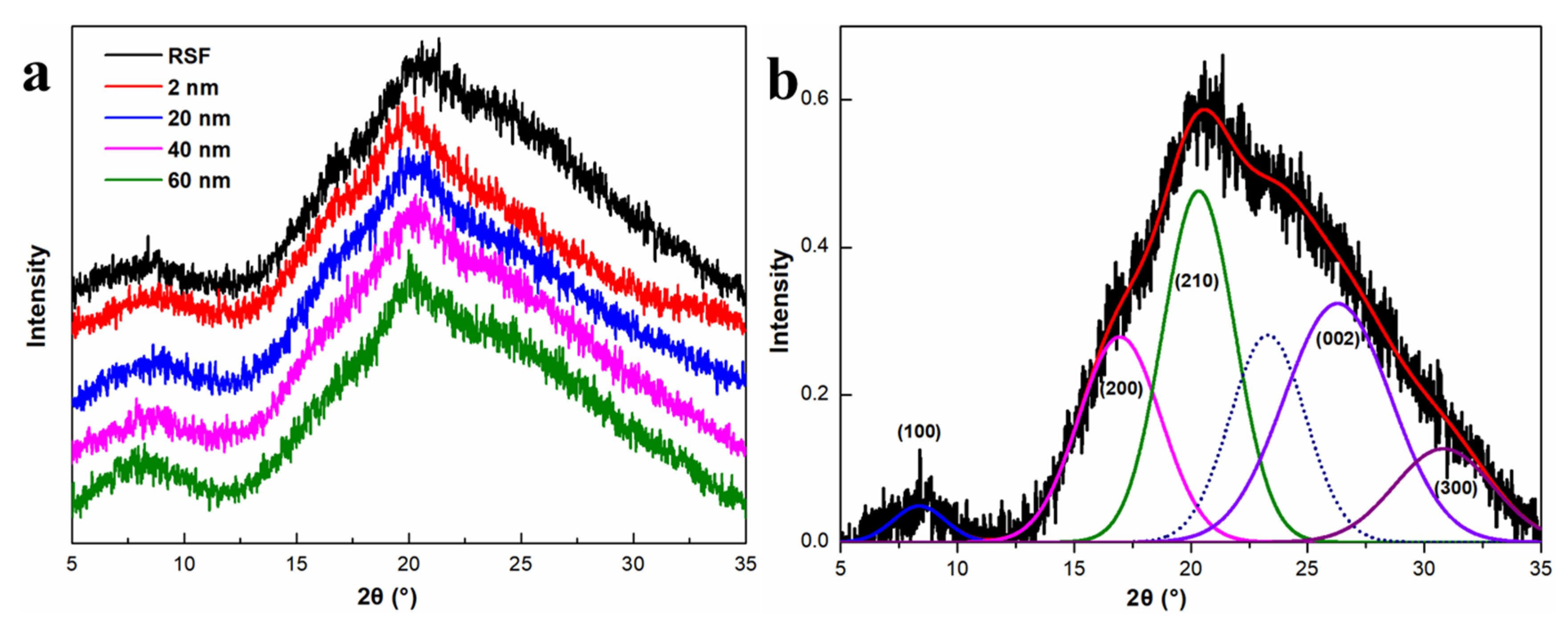
2.4. The Effect of AgNPs on Secondary Structure and Crystalline Structure of the Hybrid RSF Fibers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
3.2. Preparation of RSF Fibers
3.3. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles and Regenerated Silk
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Horan, R.; Bramono, D.; Stanley, J.; Simmons, Q.; Chen, J.; Boepple, H.; Altman, G. Biological and biomechanical assessment of a long-term bioresorbable silk-derived surgical mesh in an abdominal body wall defect model. Hernia 2009, 13, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyamud, C.; Phetdee, C.; Jaimalai, T.; Prangkio, P. Silk fibroin-coated liposomes as biomimetic nanocarrier for long-term release delivery system in cancer therapy. Molecules 2021, 26, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Gonzalez-Obeso, C.; Xia, Z.; Sahoo, J.; Li, G.; Cebe, P.; Zhang, Y.; Kaplan, D. 3D printing of monolithic proteinaceous cantilevers using regenerated silk fibroin. Molecules 2022, 27, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Bai, Y. Fabrication of high strength graphene/regenerated silk fibroin composite fibers by wet spinning. Mater. Lett. 2017, 194, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Chi, H.; Wei, G.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L. Preparation and antibacterial activity of polyvinyl alcohol/regenerated silk fibroin composite fibers containing Ag nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; Guo, J.; Zhao, S.; Wu, G. Preparation and properties of photochromic regenerated silk fibroin/tungsten trioxide nanoparticles hybrid fibers. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jia, L.; Fometu, S.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Wu, G. Fabrication of high toughness silk fibroin/tungsten disulfide nanoparticles hybrid fiber and self-heating textile by wet spinning. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 3373–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Wen, J.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z. Preparation and characterization of transparent silk fibroin/cellulose blend films. Polymer 2013, 54, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.; Yang, H.; Shor, L.; Ko, F. Post-spinning modification of electrospun nanofiber nanocomposite from Bombyx mori silk and carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2009, 50, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Y.; van Esch, J.; Liu, X. Programing performance of silk fibroin materials by controlled nucleation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8978–8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, J. Nanoconfined crystallites toughen artificial silk. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, X.; Xu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, L. Synthesis of nanoscale CeAl4 and its high catalytic efficiency for hydrogen storage of sodium alanate. Rare Met. 2017, 36, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fometu, S.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Ma, L.; Wu, G. Biological effect evaluation of different sized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Bombyx mori (silkworm) as a model animal. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 5260–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryczynski, I.; Malicka, J.; Holder, E.; Dicesare, N.; Lakowicz, J. Effects of metallic silver particles on the emission properties of [Ru (bpy) (3)]. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 372, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Q.; Yue, X.; Zuo, B.; Qin, M.; Li, F.; Kaplan, D.; Zhang, X. Regeneration of high-quality silk fibroin fiber by wet spinning from CaCl2–formic acid solvent. Acta Biomater. 2015, 12, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Wet-spinning of regenerated silk fiber from aqueous silk fibroin solutions: Influence of calcium ion addition in spinning dope on the performance of regenerated silk fiber. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 32, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhou, G.; Knight, D.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Wet-spinning of regenerated silk fiber from aqueous silk fibroin solution: Discussion of spinning parameters. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, I.; Aswal, V.; Kohlbrecher, J. Size-dependent interaction of silica nanoparticles with lysozyme and bovine serum albumin proteins. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 052601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, A. Biosafety and bioapplication of nanomaterials by designing protein–nanoparticle interactions. Small 2013, 9, 1635–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaz, B.; Charron, G.; Pfeiffer, C.; Zhao, Y.; Fuente, J.; Liang, X.; Parak, W.; del Pino, P. Interfacing engineered nanoparticles with biological systems: Anticipating adverse nano–bio interactions. Small 2013, 9, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Qi, Z.; Knight, D.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Synchrotron FTIR microspectroscopy of single natural silk fibers. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3344–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Dong, M. Size Effect of Graphene Oxide on Modulating Amyloid Peptide Assembly. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 9632–9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Yao, J.; Chen, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhong, J.; Qi, Z.; Li, Z.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Tough protein-carbon nanotube hybrid fibers comparable to natural spider silks. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3940–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Shao, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Role of humidity on the structures and properties of regenerated silk fibers. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2015, 25, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gong, D.; Gong, Y. Insight into the orientation behavior of thermal-aged and historic silk fabrics by polarized FTIR microspectroscopy. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 38, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bhunia, K.; Munoz, N.; Li, L.; Dolgovskij, M.; Rasco, B.; Tang, J.; Sablani, S. Linking morphology changes to barrier properties of polymeric packaging for microwave-assisted thermal sterilized food. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, F.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Hong, C. Crystallite size variations of nanosized Fe2O3 powders during γ-to α-phase transformation. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keten, S.; Xu, Z.; Ihle, B.; Buehler, M. Nanoconfinement controls stiffness, strength and mechanical toughness of β-sheet crystals in silk. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Li, C.; Adamcik, J.; Wang, S.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X.; Mezzenga, R. Directed growth of silk nanofibrils on graphene and their hybrid nanohybrids. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, C.; Cai, X. Glutathione-triggered luminescent silver nanoparticle: A urinary clearable nanoparticle for potential clinical practice. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 135, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastús, N.; Merkoi, F.; Piella, J.; Puntes, V. Synthesis of highly monodisperse citrate-stabilized silver nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Kinetic control and catalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Breaking Strength/MPa | Breaking Strain/% |
|---|---|---|
| RSF | 158.13 ± 9.27 | 15.02 ± 8.67 |
| RSF/AgNPs-2 nm-2 wt‰ | 297.97 ± 17.51 | 138.27 ± 13.29 |
| RSF/AgNPs-20 nm-0.4 wt‰ | 273.74 ± 18.36 | 121.61 ± 14.32 |
| RSF/AgNPs-40 nm-4 wt‰ | 242.61 ± 15.91 | 93.41 ± 12.58 |
| RSF/AgNPs-60 nm-8 wt‰ | 200.29 ± 16.28 | 83.46 ± 12.17 |
| Samples | Crystallite Size (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | V/nm3 | Crystallinity | |
| RSF | 1.92 | 2.47 | 1.35 | 6.40 | 30.41% |
| RSF/AgNPs-2 nm-2 wt‰ | 1.65 | 2.35 | 1.20 | 4.65 | 38.21% |
| RSF/AgNPs-20 nm-0.4 wt‰ | 1.67 | 2.33 | 1.23 | 4.79 | 36.74% |
| RSF/AgNPs-40 nm-4 wt‰ | 1.83 | 2.57 | 1.24 | 5.83 | 34.12% |
| RSF/AgNPs-60 nm-8 wt‰ | 1.87 | 2.56 | 1.27 | 6.08 | 32.92% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; Wu, G. The Size Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Reinforcing the Mechanical Properties of Regenerated Fibers. Molecules 2023, 28, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041750
Guo J, Xu C, Yang B, Li H, Wu G. The Size Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Reinforcing the Mechanical Properties of Regenerated Fibers. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041750
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jianjun, Chen Xu, Bo Yang, Hang Li, and Guohua Wu. 2023. "The Size Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Reinforcing the Mechanical Properties of Regenerated Fibers" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041750
APA StyleGuo, J., Xu, C., Yang, B., Li, H., & Wu, G. (2023). The Size Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Reinforcing the Mechanical Properties of Regenerated Fibers. Molecules, 28(4), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041750






