13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Skin Cancer A431 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Cytotoxic Effect of 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide and Berberine on A431 Cells
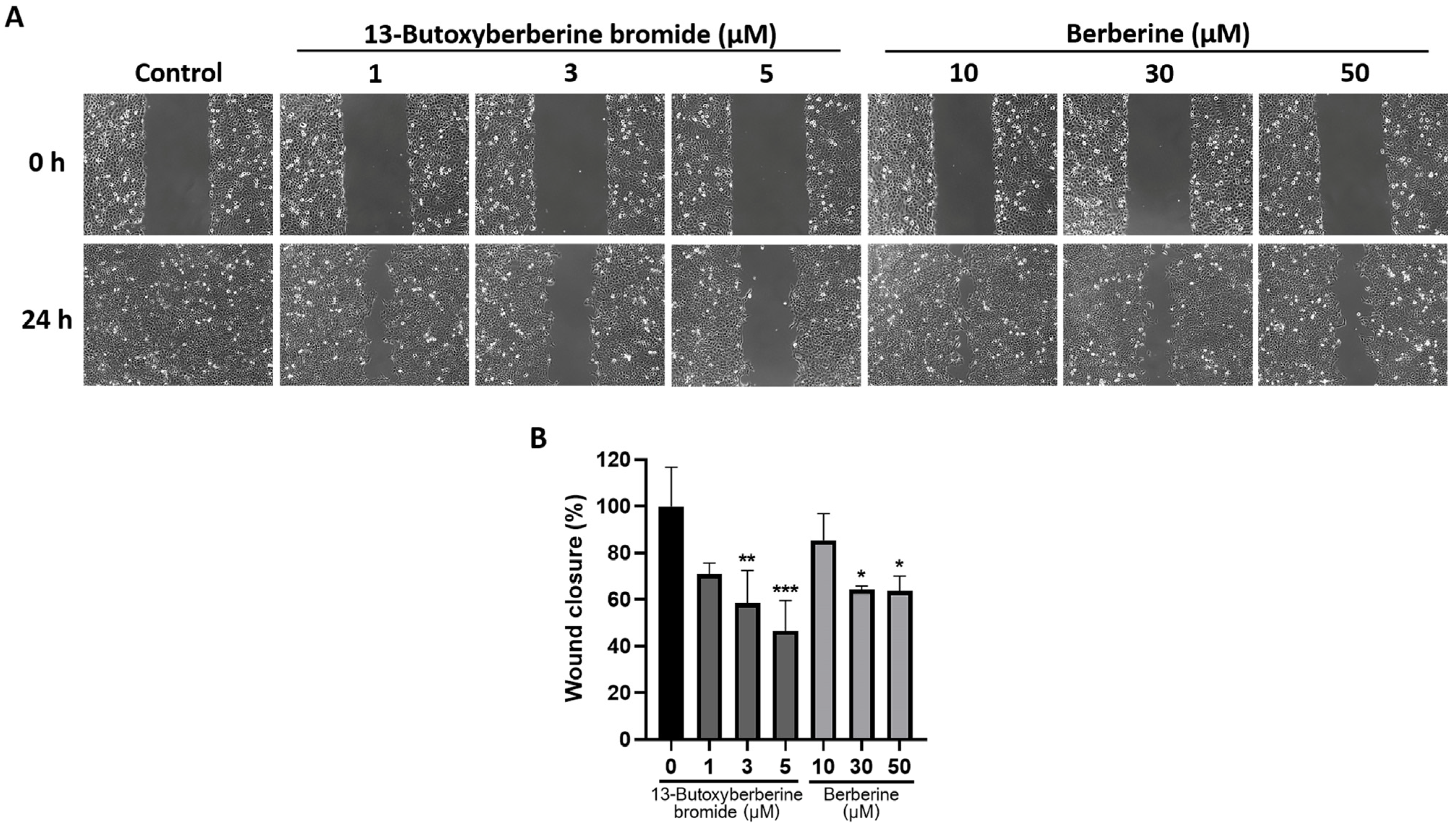
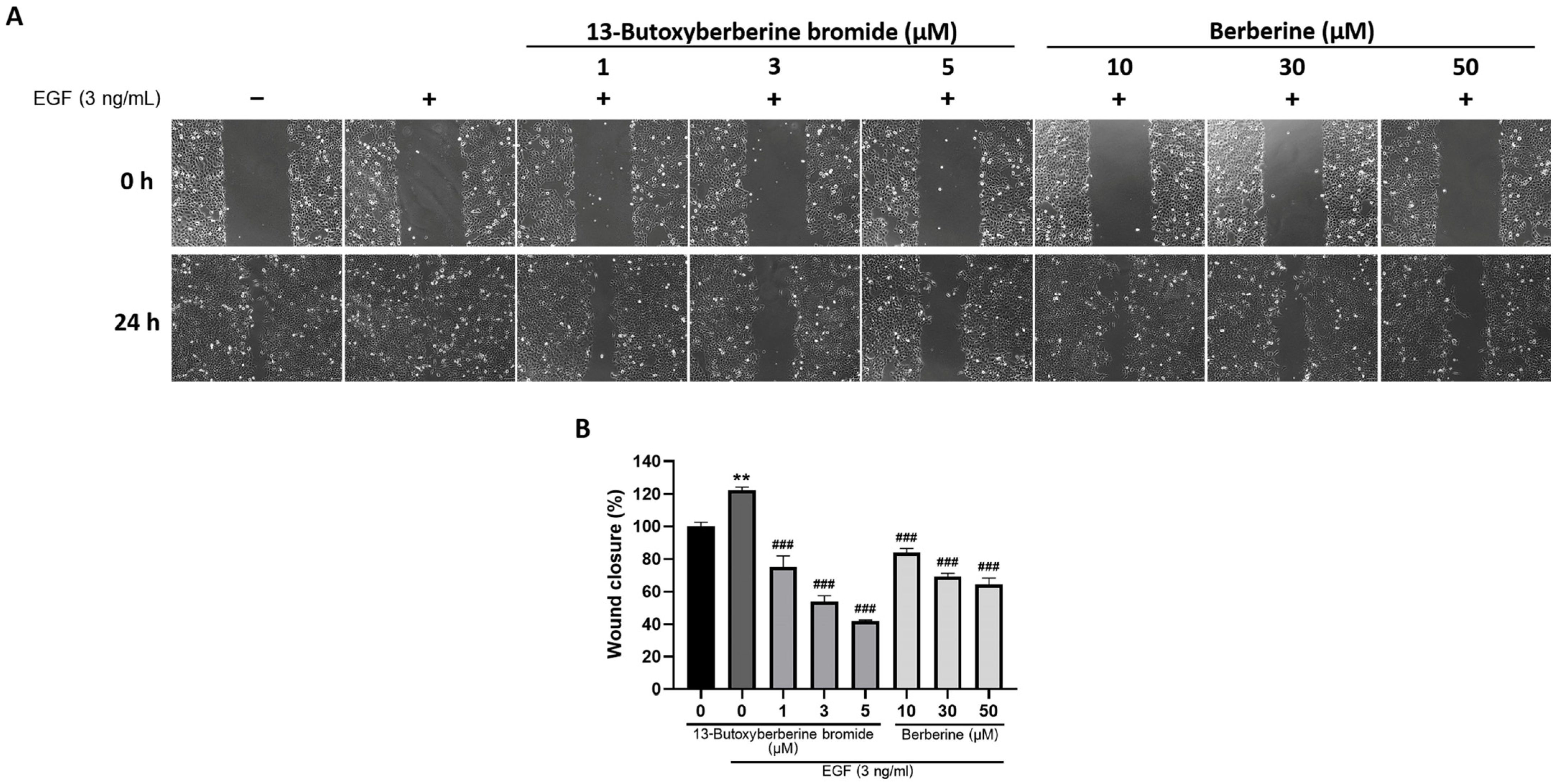
2.2. 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibited A431 Cell Migration More Effectively Than Berberine
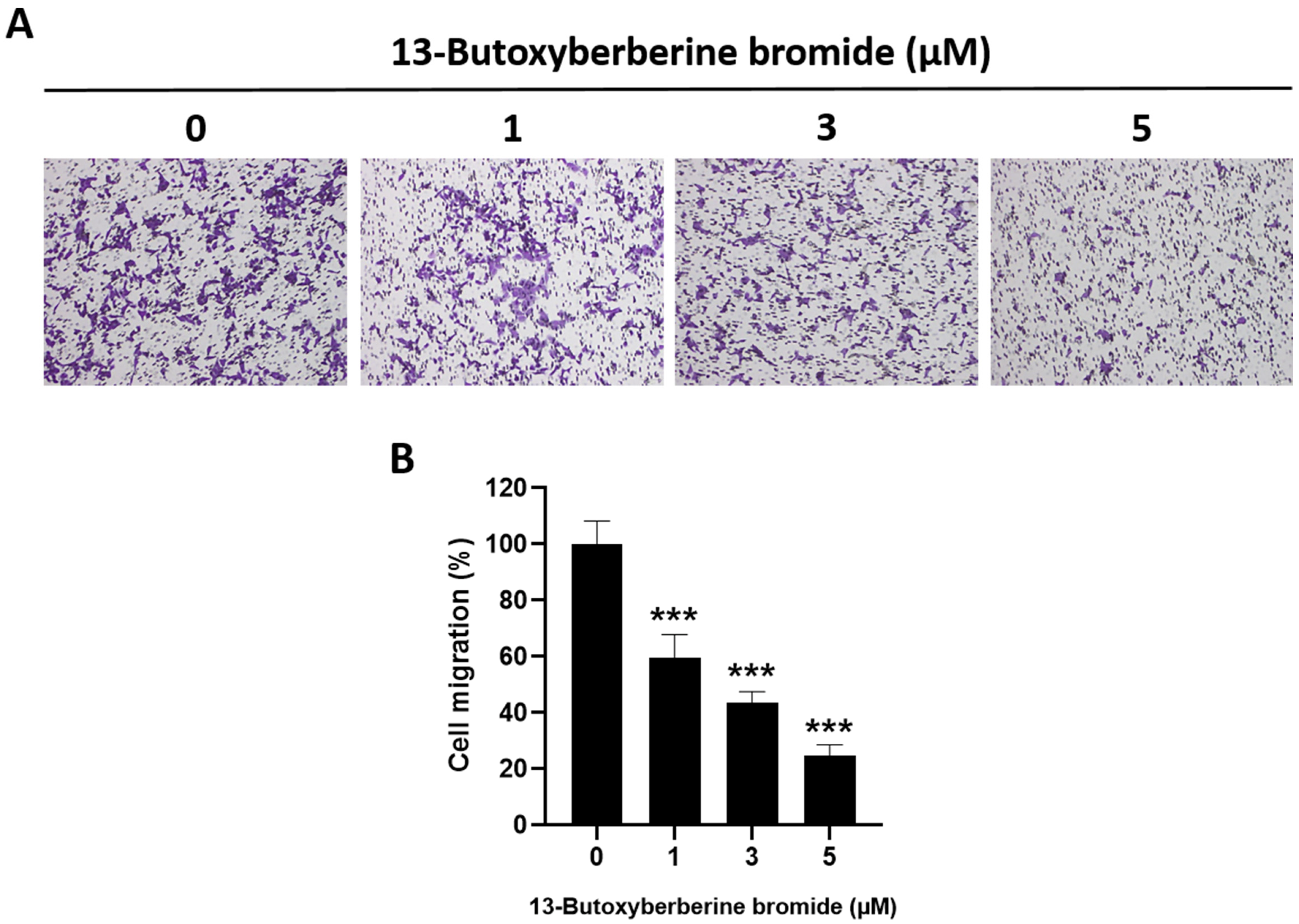
2.3. Effect of 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide on A431 Cell Migration using Transwell Migration Assay
2.4. Effect of 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide on A431 Cell Invasion by Transwell Invasion Assay
2.5. Effect of 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide on Cell Adhesion in A431 Cells
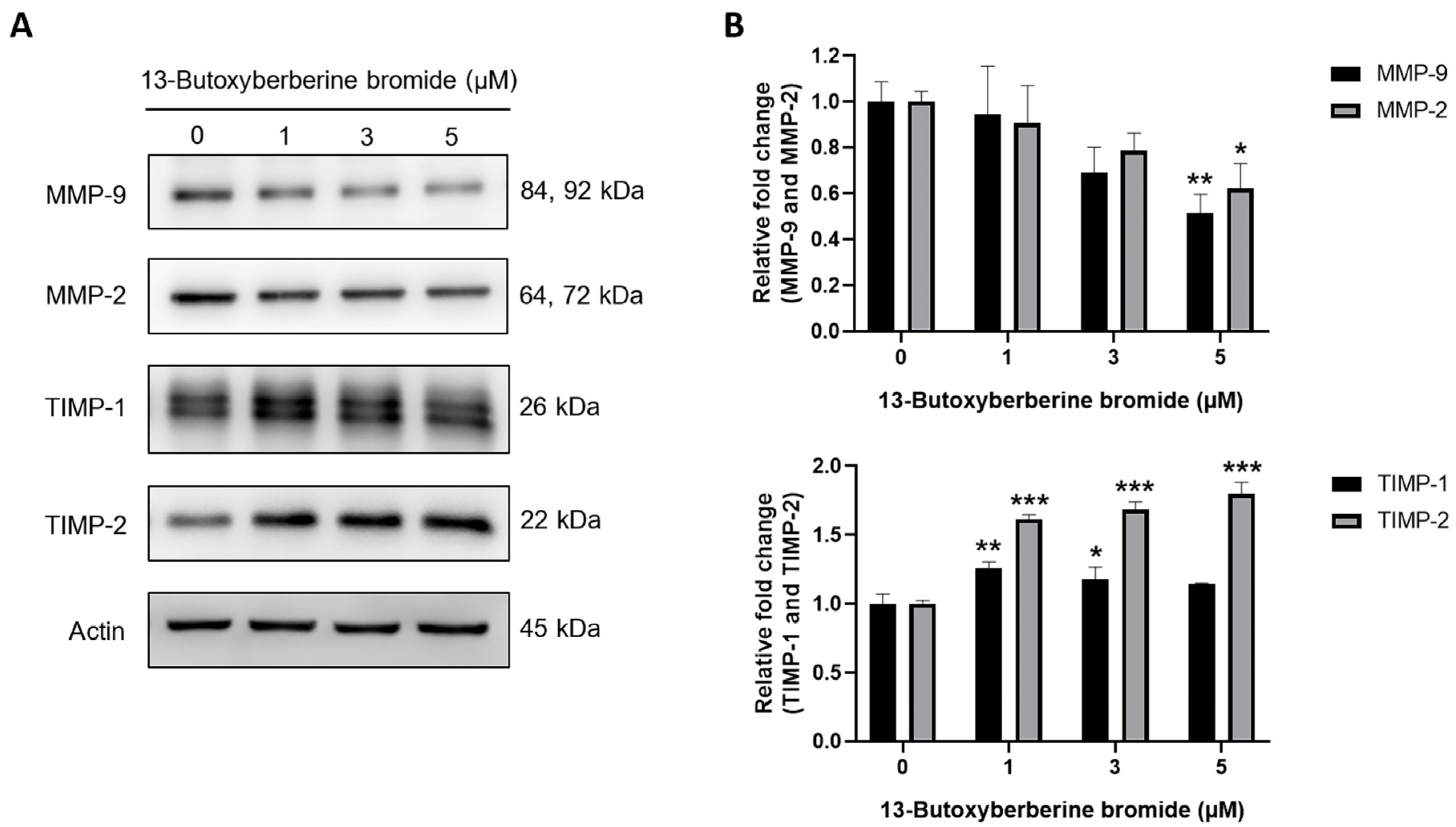
2.6. Effect of 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide on MMPs and TIMPs Expressions in A431 Cells
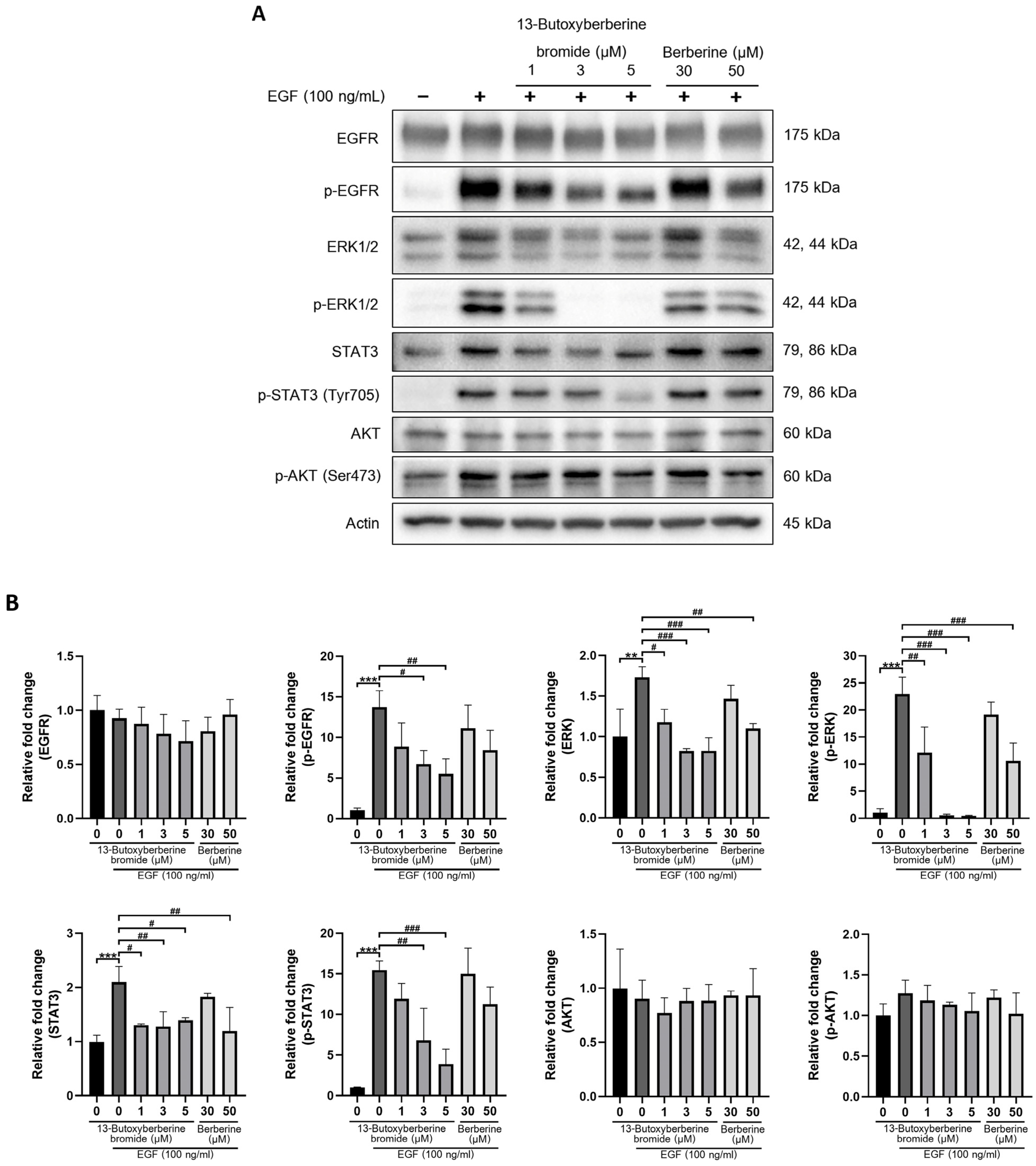
2.7. Effect of 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide on EGFR Signaling Pathway
2.8. 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibited EGF-Induced A431 Cell Migration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Chemical Reagents
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Wound-Healing Assay
4.5. Transwell Invasion and Migration Assay
4.6. Adhesion Assay
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Guan, X. Cancer metastases: Challenges and opportunities. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Huysentruyt, L.C. On the origin of cancer metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2013, 18, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zijl, F.; Krupitza, G.; Mikulits, W. Initial steps of metastasis: Cell invasion and endothelial transmigration. Mutat. Res. 2011, 728, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.C.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor-host cell communication. Differentiation 2002, 70, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.H.; Landström, M.; Moustakas, A. Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Boyd, D.D. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, A.; Futter, C.E.; Eden, E.R. EGF receptor trafficking: Consequences for signaling and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Jadhav, H.R. Targeting non-small cell lung cancer with small-molecule EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siena, S.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Balfour, J.; Bardelli, A. Biomarkers predicting clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1308–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieduwilt, M.J.; Moasser, M.M. The epidermal growth factor receptor family: Biology driving targeted therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1566–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Guo, Q. EGFR signaling pathway occupies an important position in cancer-related downstream signaling pathways of Pyk2. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 44, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Werb, Z. How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 463–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Van Meter, T.E.; Fillmore, H.L. Epidermal growth factor induces matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) expression and invasion in glioma cell lines via the MAPK pathway. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 104, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Halicka, H.D.; Li, J.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Berberine suppresses gero-conversion from cell cycle arrest to senescence. Aging 2013, 5, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.M.; Luo, M.H. Study progress of berberine for treating cardiovascular disease. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2015, 1, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao-ong, T.; Chatuphonprasert, W.; Nemoto, N.; Jarukamjorn, K. Alteration of hepatic glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by berberine. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ekavali; Chopra, K.; Mukherjee, M.; Pottabathini, R.; Dhull, D.K. Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 761, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Tao, S.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Lan, T.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Huang, W.; Chen, F.; et al. Berberine inhibits aldose reductase and oxidative stress in rat mesangial cells cultured under high glucose. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 475, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Pathak, N.; Fatima, E.; Negi, A.S. Plant isoquinoline alkaloids: Advances in the chemistry and biology of berberine. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, C.R.; Gaikwad, S.; Agrawal-Rajput, R. Berberine induces neuronal differentiation through inhibition of cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in neuroblastoma cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, K.; Du, B. Berberine suppressed epithelial mesenchymal transition through cross-talk regulation of PI3K/AKT and RARα/RARβ in melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, E.J.; Yang, Y.; Lee, M.S.; Lim, J.S. Berberine-induced AMPK activation inhibits the metastatic potential of melanoma cells via reduction of ERK activity and COX-2 protein expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Lu, N.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Hu, T.; Israel, D.A.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Polk, D.B.; Yan, F. Berberine inhibits proliferation and down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor through activation of Cbl in colon tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samosorn, S.; Tanwirat, B.; Suksamrarn, A. Anticancer activity of 13-alkoxy berberine derivatives. Thai Patent 1101002293, 27 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.C.; Yu, C.C.; Hsu, L.S.; Chen, K.S.; Su, M.Y.; Chen, P.N. Berberine reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inhibits metastasis and tumor-induced angiogenesis in human cervical cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sheng, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Yao, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, R. Effects of berberine and its derivatives on cancer: A systems pharmacology review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; Wu, X.; Guan, J.L. Wound-healing assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 294, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 88, e51046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, K.; Yong, P.V.; Lim, Y.M.; Navaratnam, V.; Ho, A.S. 2-Methoxy-1,4-Naphthoquinone (MNQ) suppresses the invasion and migration of a human metastatic breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231). Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, M.J. Cell adhesion assays. Mol. Biotechnol. 2001, 18, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Lai, K.C.; Peng, S.F.; Maraming, P.; Huang, Y.P.; Huang, A.C.; Chueh, F.S.; Huang, W.W.; Chung, J.G. Berberine inhibits human melanoma A375.S2 cell migration and invasion via affecting the FAK, uPA, and NF-κB signaling pathways and inhibits PLX4032 resistant A375.S2 cell migration in vitro. Molecules 2018, 23, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, M.; Nilwarangoon, S.; Mahabusarakum, W.; Watanapokasin, R. Anti-metastatic effect of rhodomyrtone from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa on human skin cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naglich, J.G.; Jure-Kunkel, M.; Gupta, E.; Fargnoli, J.; Henderson, A.J.; Lewin, A.C.; Talbott, R.; Baxter, A.; Bird, J.; Savopoulos, R.; et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis and metastasis in two murine models by the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, BMS-275291. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8480–8485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.L.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Wang, C.J.; Hsu, J.L.; Chou, F.P. Inhibitory effect of berberine on the invasion of human lung cancer cells via decreased productions of urokinase-plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 214, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, K.H.; Chung, J.H. Berberine inhibits TPA-induced MMP-9 and IL-6 expression in normal human keratinocytes. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Han, J.; Lee, S.K.; Choi, M.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, S.P.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choe, J.H.; et al. Berberine suppresses the TPA-induced MMP-1 and MMP-9 expressions through the inhibition of PKC-α in breast cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 176, e21–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.W.; Yang, L.M. Inhibitory effect of berberine on human skin squamous cell carcinoma A431 cells. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 10553–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Cai, X.; Dong, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Cao, H.; Lu, D.; Jin, T.; et al. Berberine inhibits EGFR signaling and enhances the antitumor effects of EGFR inhibitors in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76076–76086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Zheng, H.F.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.F.; Wu, J.L.; Li, Q.X. Berberine targets epidermal growth factor receptor signaling to suppress prostate cancer proliferation in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, S.; Saeki, Y.; Kasamatsu, M.; Tashiro, E.; Imoto, M. Chemical genomic-based pathway analyses for epidermal growth factor-mediated signaling in migrating cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laomethakorn, P.; Tayeh, M.; Samosorn, S.; Tananyuthawongse, C.; Watanapokasin, R. 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Skin Cancer A431 Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030991
Laomethakorn P, Tayeh M, Samosorn S, Tananyuthawongse C, Watanapokasin R. 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Skin Cancer A431 Cells. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030991
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaomethakorn, Phuriwat, Malatee Tayeh, Siritron Samosorn, Chantra Tananyuthawongse, and Ramida Watanapokasin. 2023. "13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Skin Cancer A431 Cells" Molecules 28, no. 3: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030991
APA StyleLaomethakorn, P., Tayeh, M., Samosorn, S., Tananyuthawongse, C., & Watanapokasin, R. (2023). 13-Butoxyberberine Bromide Inhibits Migration and Invasion in Skin Cancer A431 Cells. Molecules, 28(3), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030991





