Efficient Combination of Complex Chromatography, Molecular Docking and Enzyme Kinetics for Exploration of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Poria cocos
Abstract
1. Introduction
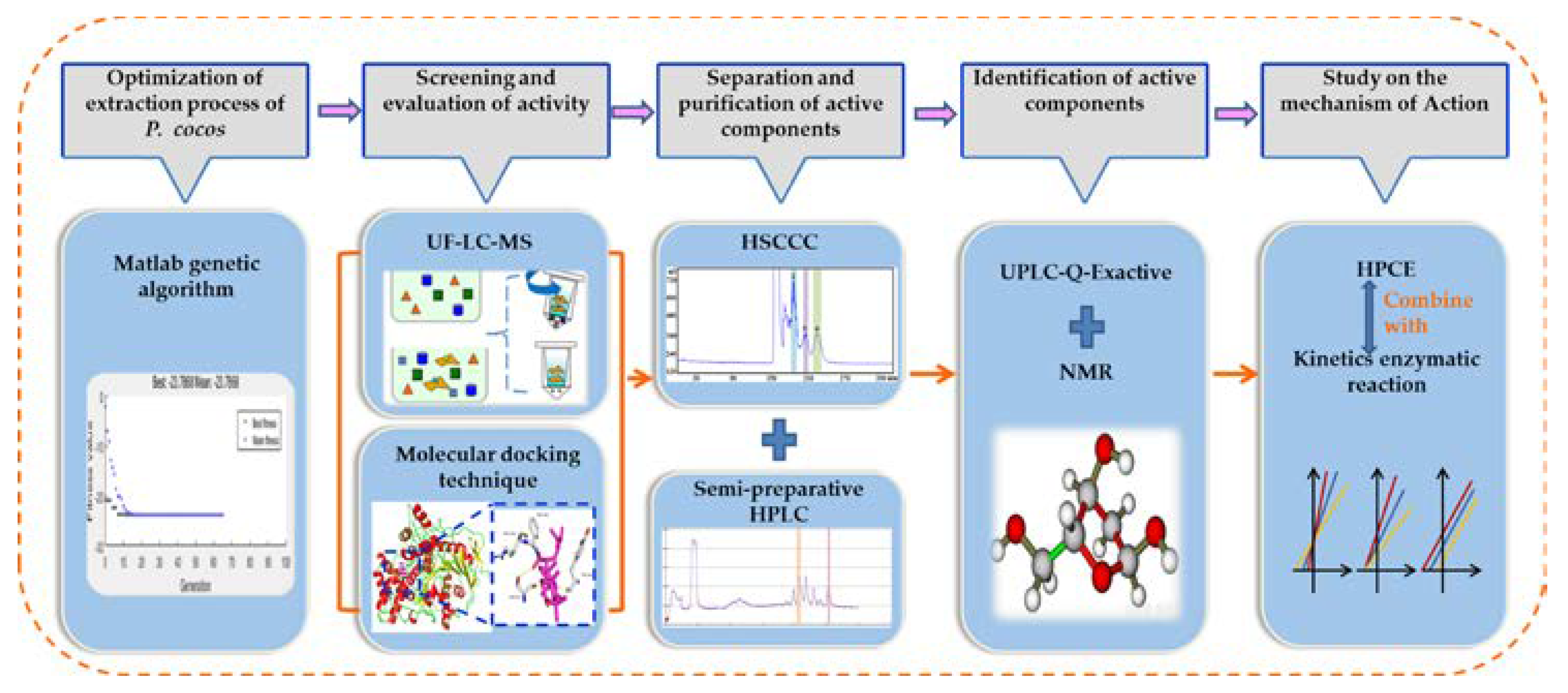
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of Extraction of P. cocos Reflux
2.2. Screening and Evaluation of Potential AChE Inhibitors in P. cocos
2.2.1. Screening of Potential AChEIs in P. cocos by UF-LC-MS
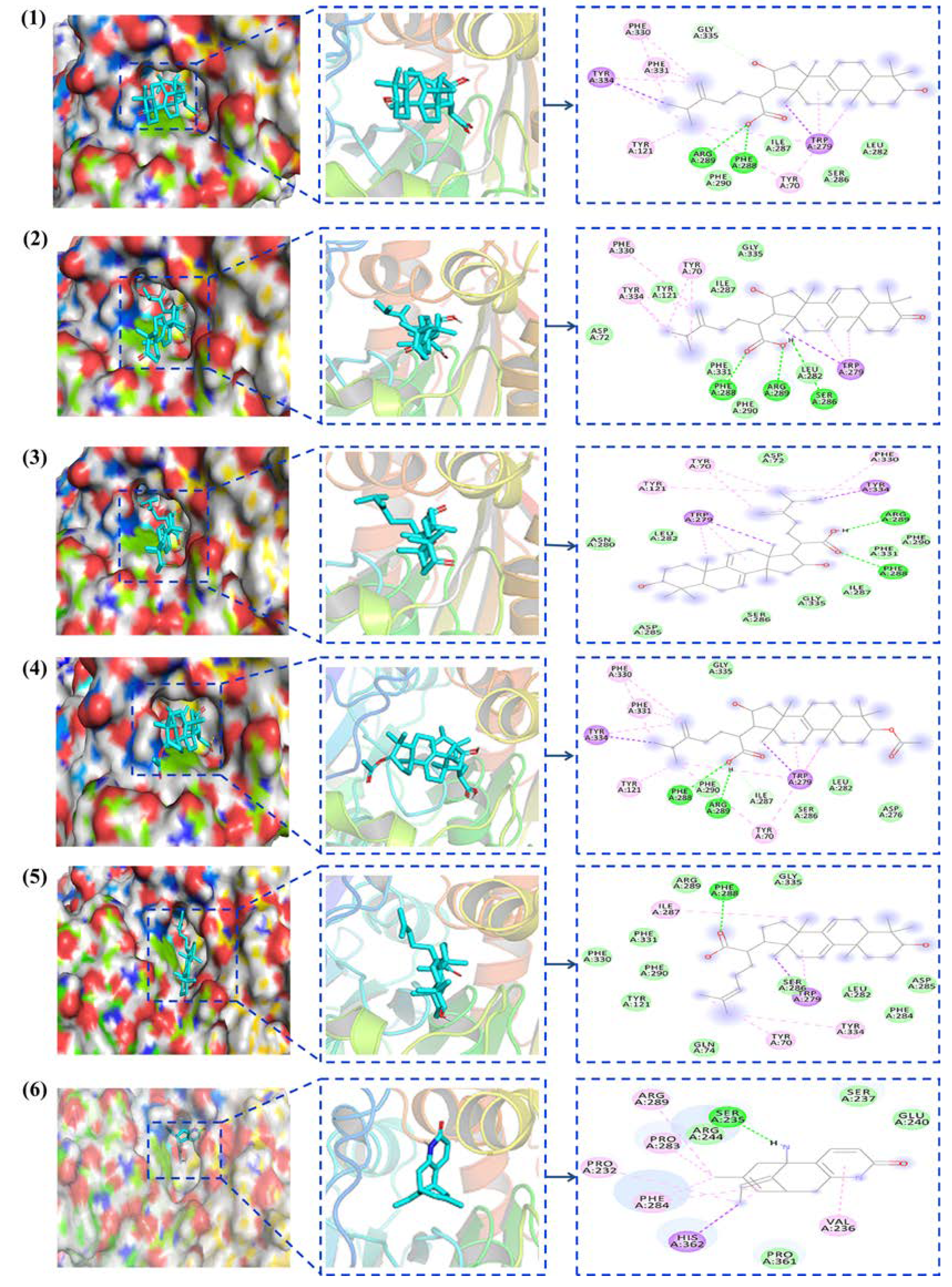
2.2.2. Molecular Docking Simulation of Active Compounds and AChE
2.3. Isolation of Active Compounds from P. cocos
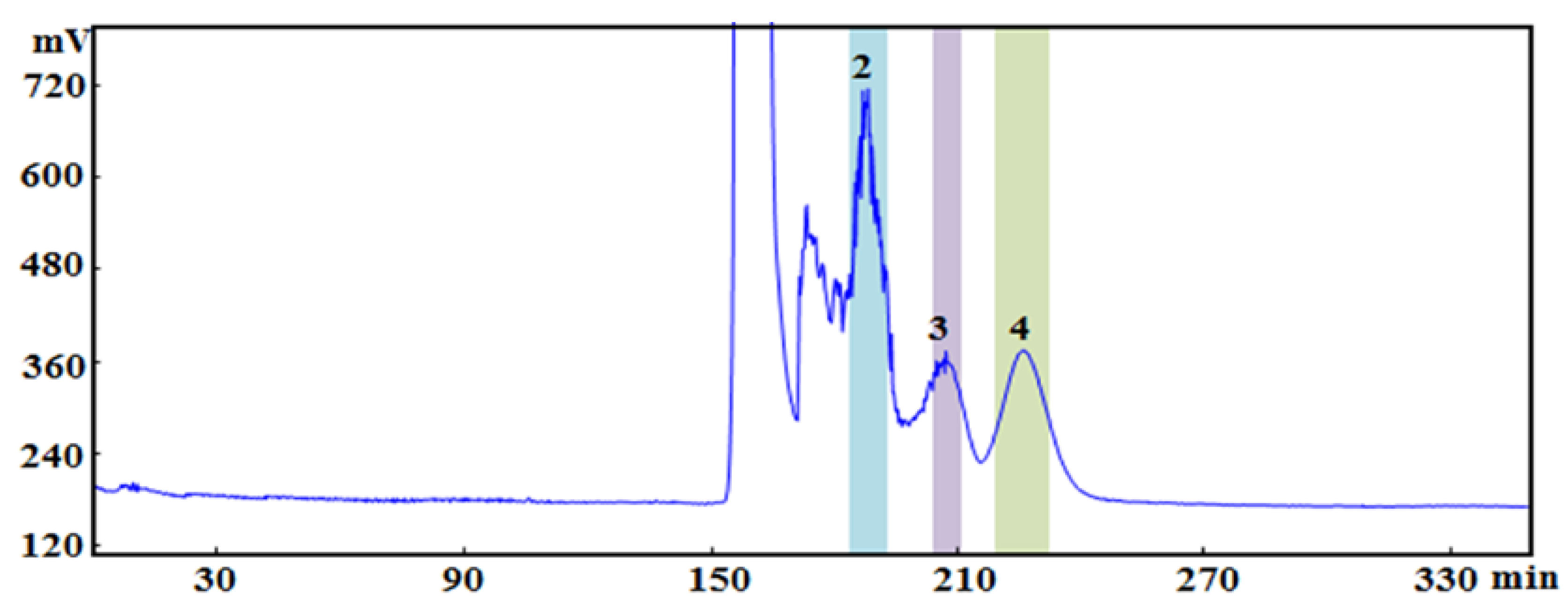
2.3.1. HSCCC Separation of Potential AChE Inhibitors from P. cocos
2.3.2. Semi−Preparative HPLC Separation of Potential AChEIs from P. cocos
2.4. Structural Identification of Active Compounds
2.4.1. Identification of Potential AChEIs Using UPLC−Q−Exactive−MS
2.4.2. Identification of Potential AChEIs Using 1H-NMR and 13C−NMR Spectroscopy
2.5. Study on Enzymatic Reaction Kinetics of the Inhibition of AChE by Active Compounds
2.5.1. Inhibitory Types of Active Compounds in P. cocos on AChE
2.5.2. Inhibition Kinetics Analysis of Active Compounds in P. cocos on AChE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Apparatus
4.2. Reagents and Materials
4.3. Screening for Potential AChEIs
4.4. HPLC Conditions
4.5. UPLC-Q-Exactive Conditions
4.6. Molecular Docking Simulation Verification of Active Compounds and AChE
4.7. Separation of Active Ingredients from P. cocos
4.7.1. HSCCC Separation Conditions
4.7.2. Semi−Preparative HPLC Separation Conditions
4.8. Study on Enzymatic Reaction Kinetics of AChE Inhibitors
4.8.1. Solution Preparation
4.8.2. Electrophoresis Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lee, K.Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Polysaccharide isolated from Poria cocos sclerotium induces NF-kappaB/Rel activation and iNOS expression in murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Nima, C.; Danpei, Q.Z.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y. Rapid characterization the chemical constituents of Bergenia purpurascens and explore potential mechanism in treating osteoarthritis by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with network pharmacology. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3165–3376. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, N.S.; Ghoneum, M.H.; Antia, A. Natural Antioxidant Product, Attenuates Cognitive Dysfunction in Streptozotocin-Induced Mouse Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease by Targeting the Amyloidogenic, Inflammatory, Autophagy, and Oxidative Stress Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 24, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhou, Y.H.; Li, X.N.; Sun, S.D.; Guo, J.D.; Wu, B.W.; Wu, M.S. Based on the traditional Chinese medicine inheritance computing platform to explore the ancient medication rules for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Chinese Mat. Med. 2022, 3, 748–751. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.T.; Li, L.Y.; Rui, W.J.; Diao, Z.W.; Zhuang, G.D.; Chen, X.M.; Qian, Z.M.; Wang, S.M.; Tang, D.; Ma, H.Y. Non-targeted metabolomic analysis of variation of volatile fractions of ginseng from different habitats by HS-SPME-GC-MS coupled with chemometrics. Anal. Methods 2022, 8, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, S.J.; El-Awar, M.; Schut, L.; Leach, L.; Freedman, M. Cognitive deficits in olivopontocerebellar atrophy: Ismplications for the cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s dementia. Annals of Neurology. 2010, 24, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, D.E. Improving Anti-Neurodegenerative Benefits of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in Alzheimer’s Disease: Are Irreversible Inhibitors the Future? IJMS 2020, 21, 3438–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, L.; Pu, F.; Xie, Z.; Tong, S.; Yan, J. An efficient high-speed countercurrent chromatography method for preparative isolation of highly potent anti-cancer compound antroquinonol from Antrodia camphorata after experimental design optimized extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, Q.; Qin, M. Separation of acteoside and linarin from Buddlejae Flos by high-speed countercurrent chromatography and their anti-inflammatory activities. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmi, M.; Prasad, S.; Panduranga, N.S.; Jayaraman, K.; Bhutani, H. Identification of extractables by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry: A case study to understand the extraction profile of different disposable syringes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 191, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Guo, L.P.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, S.N. Total Triterpenoid Extraction from Inonotus Obliquus Using Ionic Liquids and Separation of Potential Lactate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors via Ultrafiltration High-Speed Countercurrent Chromatography. Molecules 2021, 26, 2467–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulabagal, V.; Caldern, I.A. Development of an Ultrafiltration-Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (UF-LC/MS) Based Ligand-Binding Assay and an LC/MS Based Functional Assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shikimate Kinase. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3616–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Song, F.R.; Liu, Z.Q. The screening of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from the Polygonum multiflorum extract using ultrafiltration combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods. 2014, 6, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.J.; Cheng, P.; Wang, W.; Yan, S.; Tang, Q.; Liu, D.B.; Xie, H.Q. Rapid Investigation and Screening of Bioactive Components in Simo Decoction via LC-Q-TOF-MS and UF-HPLC-MD Methods. Molecules. 2018, 23, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, H. Determination of Quinic Acids in Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench by Ultrafiltration Affinity and Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight mass spectrometry (UF-UPLC-Q-TOF-MS). Analytical Letters 2021, 12, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geromichalos, G.D.; Lamari, F.N.; Papandreou, M.A.; Trafalis, D.T.; Margarity, M.; Papageorgiou, A.; Sinakos, Z. Saffron as a Source of Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Molecular Docking and in Vitro Enzymatic Studies. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 6131–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, M.B.; Dinparast, L.; Valizadeh, H.; Farimani, M.M.; Ebrahimi, S.N. Bioactive constituents from roots of Salvia syriaca L.: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and molecular docking studies. South African Journal of Botany. 2016, 106, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, R.; Sharma, J.; Rao, S. Identification of Potential Inhibitors against Acetylcholinesterase Associated With Alzheimer’s Diseases: A Molecular Docking Approach. J. Comput. Method Mol. Design. 2011, 1, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.L.; Li, S.N.; Tang, Y.; Liu, C.M.; Chen, L.N.; Zhang, Y.C. Ultrafiltration-LC-MS combined with semi-preparative HPLC for the simultaneous screening and isolation of lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors from Belamcanda chinensis. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4533–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.Q.; Xu, J.J.; Xia, X.H.; Chen, H.Y. Real-Time Monitoring of Mass-Transport-Related Enzymatic Reaction Kinetics in a Nanochannel-Array Reacto. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 16, 10186–10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoursa, X.; Vironab, C.; Morina, P.; Renimelb, I.; Andréb, P.; Lafossea, M. Short-end injection procedure in capillary electrophoresis for determination of enzymatic reaction kinetics. Anal. Chimica. Acta. 2001, 441, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.G.; Wan, Y.T.; Liang, X.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhao, G.W. Compatible effects of Corydalis Rhizoma and Angelicae Dahuricae Radix components on enzymatic reaction kinetics of dl-tetrahydropalmatine in rat liver microsomes. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Wu, Q.H.; Xiao, H.; Chen, H. Online Monitoring of Enzymatic Reactions Using Time-Resolved Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, M.F.; Rodríguez, R.; Cañal, M.J. Rapid quantification of DNA methylation by high performance capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2015, 21, 2990–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.M.; Francis, P.L.; Rhodes, P.; Moncada, S. A Rapid and Simple Method for the Measurement of Nitrite and Nitrate in Plasma by High Performance Capillary Electrophoresis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 200, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, P.; Yang, B.; Zhou, C.; Yu, Z.G. LC-ESI-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of eleven bioactive compounds in rat plasma after oral administration of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction and its application to a pharmacokinetics study. Talanta 2018, 190, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Cheng, Y.J.; Zhu, Q.N.; Kong, D.X.; Chen, X.J.; Tamai, I.; Lu, Y. Identification of Triterpene Acids in Poria cocos Extract as Bile Acid Uptake Transporter Inhibitors. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2021, 49, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Wang, K.F.; Xin, M.; Liang, W.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Li, S.; Qi, Q.; Cui, Y.P.; Zhang, L.Z. Screening and Analysis of the Potential Bioactive Components of Poria cocos(Schw.) Wolf by HPLC and HPLC-MSn with the Aid of Chemometrics. Molecules 2016, 21, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapter, L.; Wang, Z.; Glinski, J.; Ng, K.Y. Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by pachymic acid from Poria cocos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.S.; Zhao, X.J.; Han, Y.Y. Determination of Dehydrotrametenolic acid in peels of Poria cocos by HPLC. Drugs & Clinic. 2014, 29, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
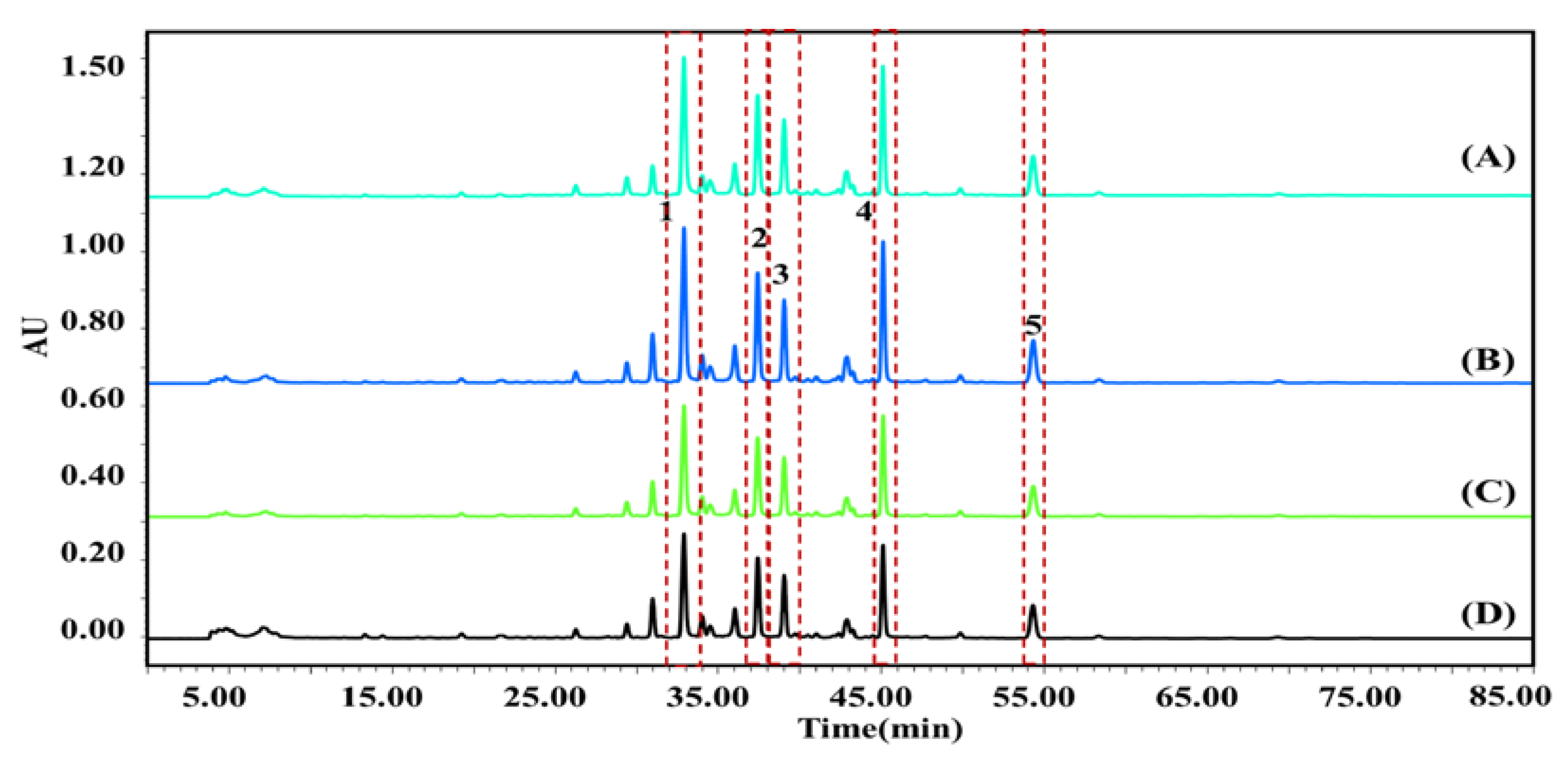

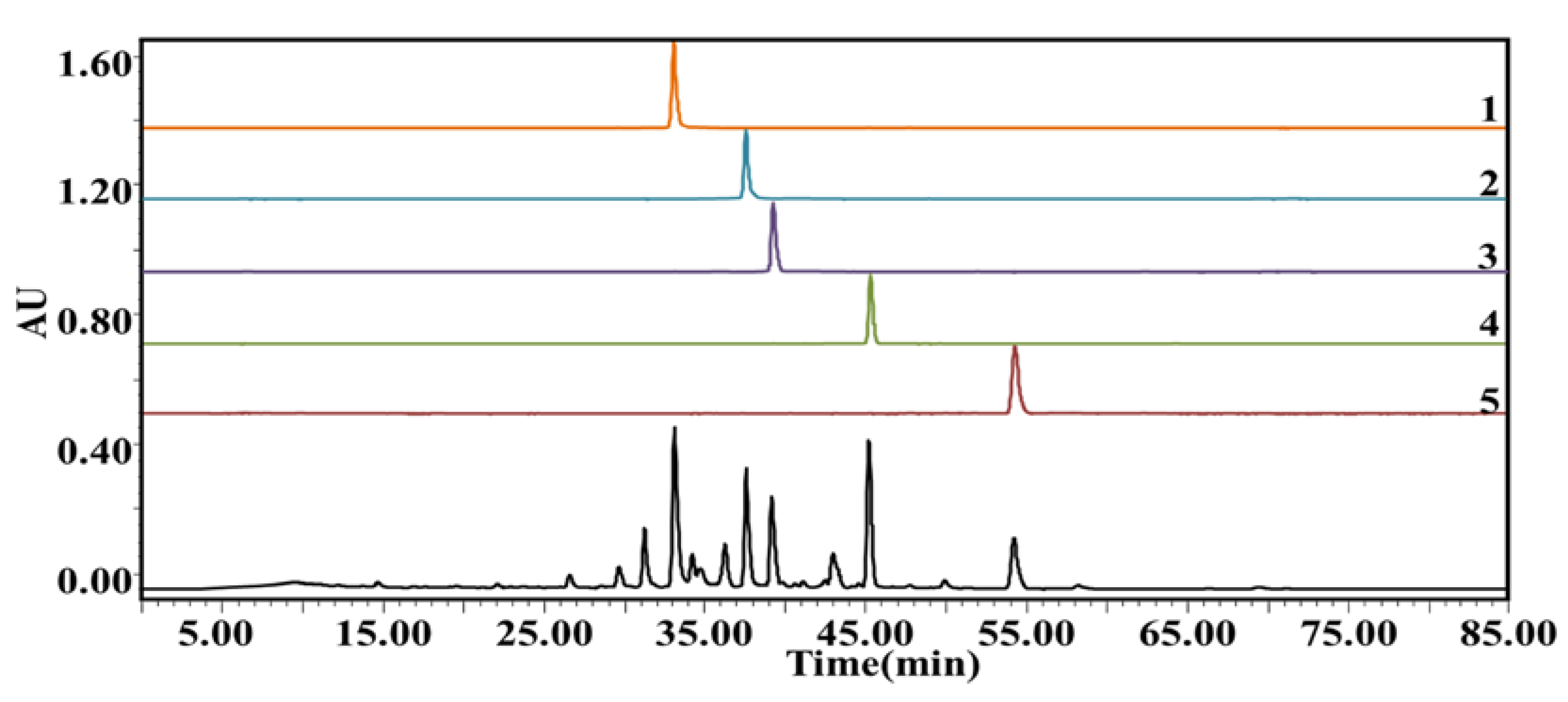
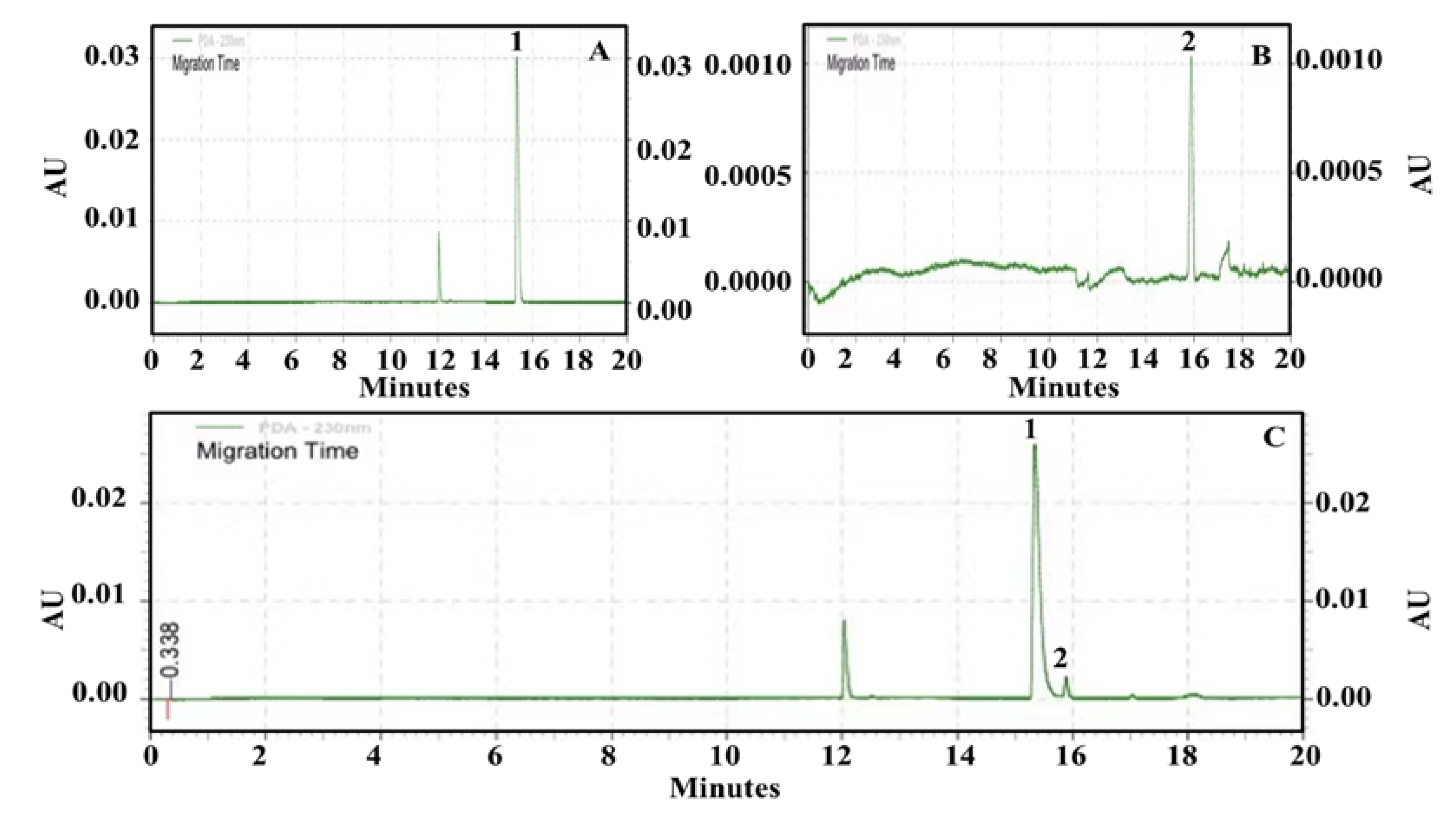

| Peak No. | tR (min) | MS (Primary Mass Spectrometry) (neg.) m/z | MS2 (Secondary Mass Spectrometry) (neg.) m/z | Compound | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12.137 | 485.2734 | 469.3123,467.2641, 439.1472, 423.2659, 337.0428 | Tumulosic acid | C31H50O4 |
| 2 | 15.683 | 481.3371 | 463.4434, 437.2927, 421.3485, 403.3042 | Polyporenic acid C | C31H45O4 |
| 3 | 17.562 | 483.7835 | 467.0731, 465.2334, 439.1454, 437.2517, 421.2265, 405.1832, 337.1517 | 3-Epidehydrotumulosic acid | C31H48O4 |
| 4 | 22.461 | 527.3791 | 509.1385, 481.2173, 482.8624, 467.2475, 465.1022, 449.1631 | Pachymic acid | C33H52O5 |
| 5 | 26.330 | 453.3451 | 435.2734, 393.1805, 371.0163 | Dehydrotrametenolic acid | C30H46O3 |
| No. | Solvent System | v/v/v/v | K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 | K5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HEX:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 3.0:6.0:4.0:2.0 | 0.53 | 0.92 | 0.68 | 1.43 | 0.81 |
| 2 | HEX:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 5.0:1.0:5.0:1.0 | —— | 0.01 | —— | 0.04 | —— |
| 3 | HEX:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 6.0:2.0:5.0:1.0 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1.35 | 0.02 |
| 4 | HEX:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 7.0:3.0:2.0:8.0 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.20 |
| 5 | PET:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 1.5:0.5:1.3:0.8 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.35 | 0.94 | 1.76 |
| 6 | PET:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 1.0:0.5:1.3:0.8 | 0.16 | 0.56 | 0.24 | 1.30 | 0.95 |
| 7 | PET:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 4.0:1.0:3.0:2.0 | 0.63 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.92 | 1.31 |
| 8 | PET:EtOAc:MeOH:H2O | 5.0:1.0:5.0:2.0 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| 9 | HEX:MeOH:H2O | 2.0:1.0:1.0 | 0.04 | —— | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| 10 | HEX:MeOH:H2O | 3.0:2.0:4.0 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| 11 | HEX:Ethanol:H2O | 2.0:1.0:5.0 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.94 |
| 12 | HEX:Ethanol:H2O | 3.0:3.0:5.0 | —— | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| 13 | EtOAc:MeOH:n-BuOH:H2O | 5.0:2.0:5.0:15.0 | 11.56 | 12.25 | 12.56 | 10.79 | —— |
| 14 | EtOAc:MeOH:n-BuOH:H2O | 5.0:2.0:2.5:12.0 | —— | —— | —— | —— | —— |
| 15 | EtOAc:MeOH:n-BuOH:H2O | 6.0:2.0:1.0:10.0 | 15.38 | 22.49 | 18.06 | 18.65 | —— |
| 16 | EtOAc:n-BuOH:H2O | 5.0:1.0:8.0 | 7.56 | 10.47 | 8.25 | 12.69 | 6.99 |
| Time (min) | Event | Value | Duration | Inlet Vial | Outlet Vial | Summary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rinse-Pressure | 20.0 psi | 3.00 min | BI1:A13 | BO2:A24 | forward | |
| 2 | Inject-Pressure | 0.5 psi | 5.0 s | BI:E15 | BO:A2 | Override, forward | |
| 3 | Inject-Pressure | 0.5 psi | 5.0 s | BI:F26 | BO:A2 | No override, forward | |
| 4 | 0.00 | Separate-Voltage | 10.0 kV | 20.00 min | BI:A1 | BO:A1 | 10.00 Min ramp, normal polarity |
| 5 | 20.00 | End |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.; Hou, W.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Efficient Combination of Complex Chromatography, Molecular Docking and Enzyme Kinetics for Exploration of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Poria cocos. Molecules 2023, 28, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031228
Wu T, Hou W, Liu C, Li S, Zhang Y. Efficient Combination of Complex Chromatography, Molecular Docking and Enzyme Kinetics for Exploration of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Poria cocos. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031228
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Tong, Wanchao Hou, Chunming Liu, Sainan Li, and Yuchi Zhang. 2023. "Efficient Combination of Complex Chromatography, Molecular Docking and Enzyme Kinetics for Exploration of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Poria cocos" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031228
APA StyleWu, T., Hou, W., Liu, C., Li, S., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Efficient Combination of Complex Chromatography, Molecular Docking and Enzyme Kinetics for Exploration of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Poria cocos. Molecules, 28(3), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031228





