Phloretin Inhibits Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Serratia marcescens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Curve
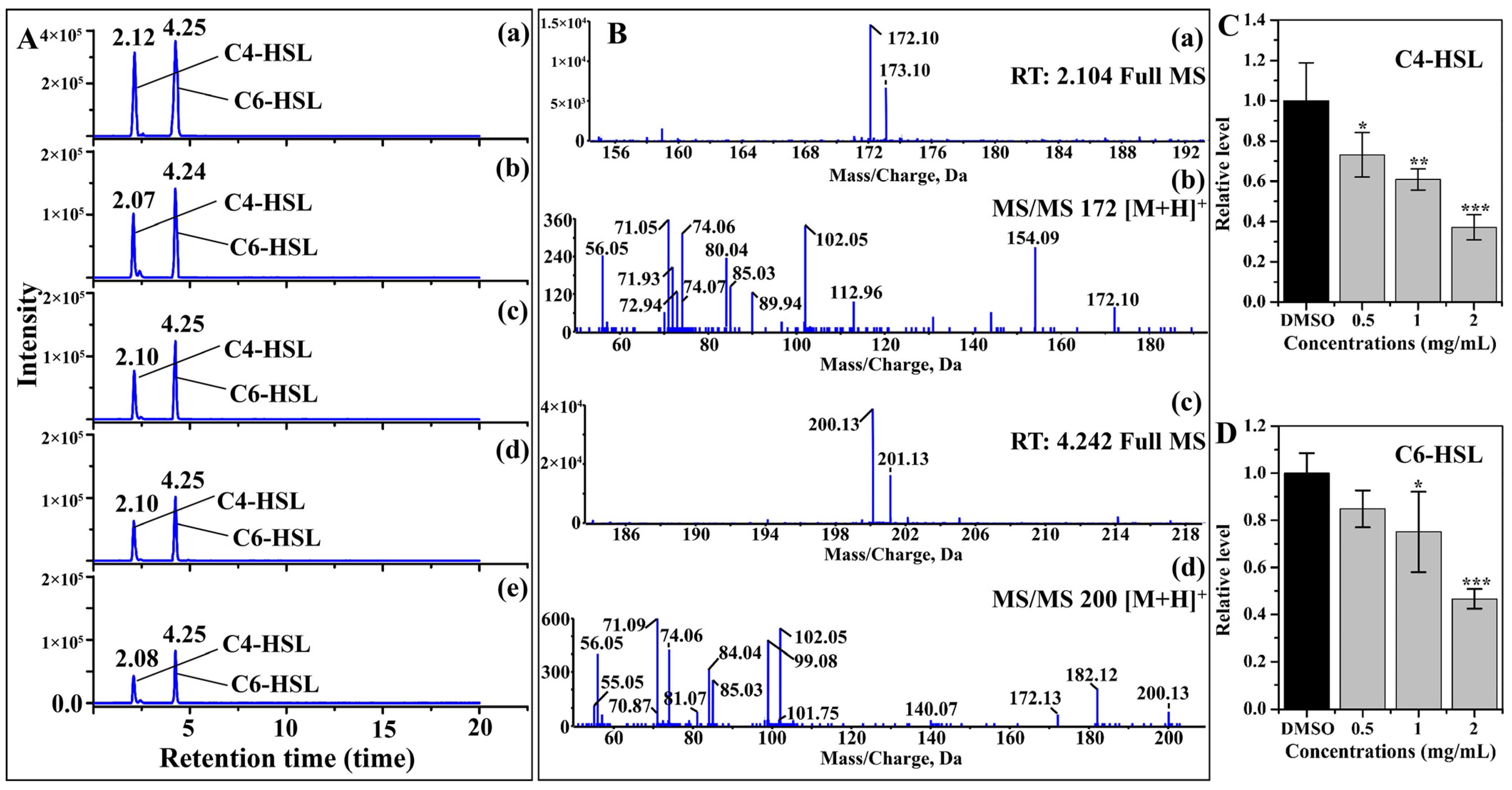
2.2. AHL Production
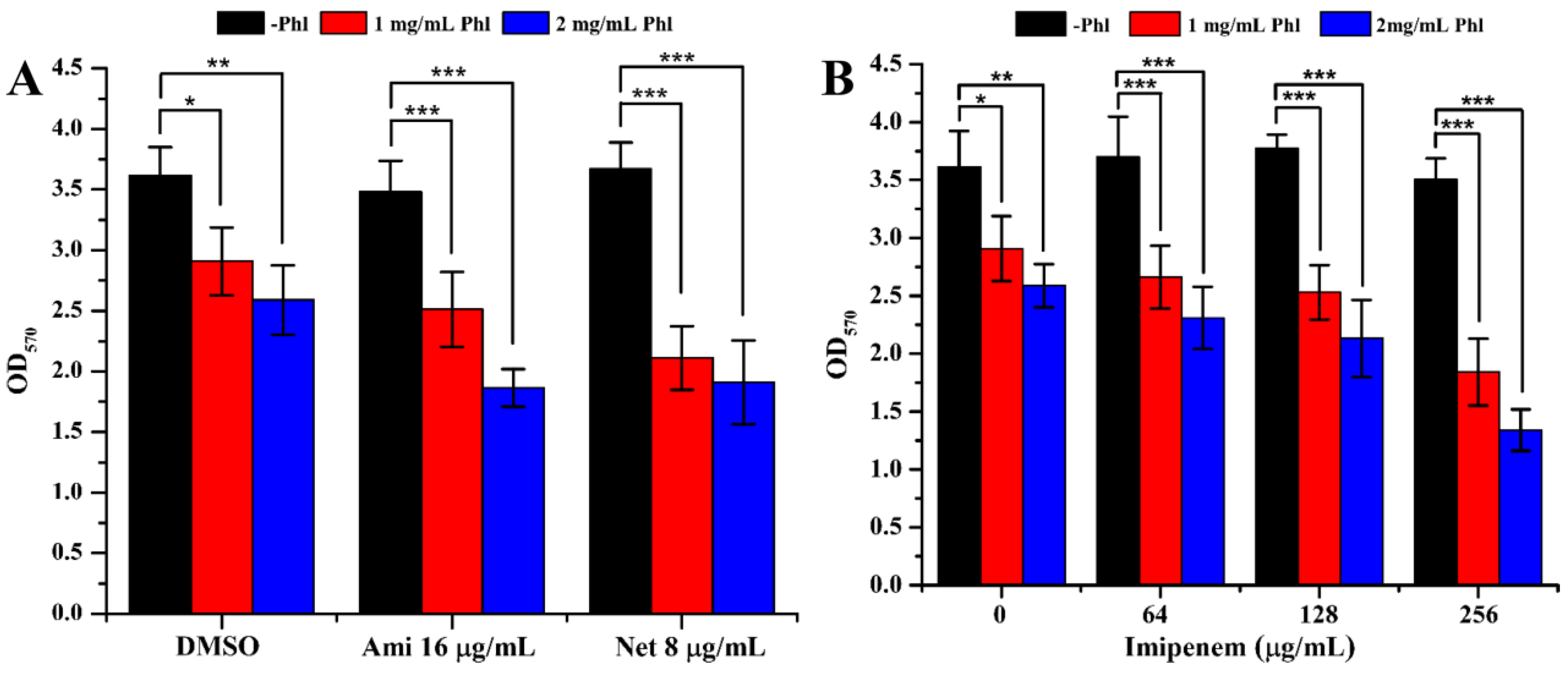
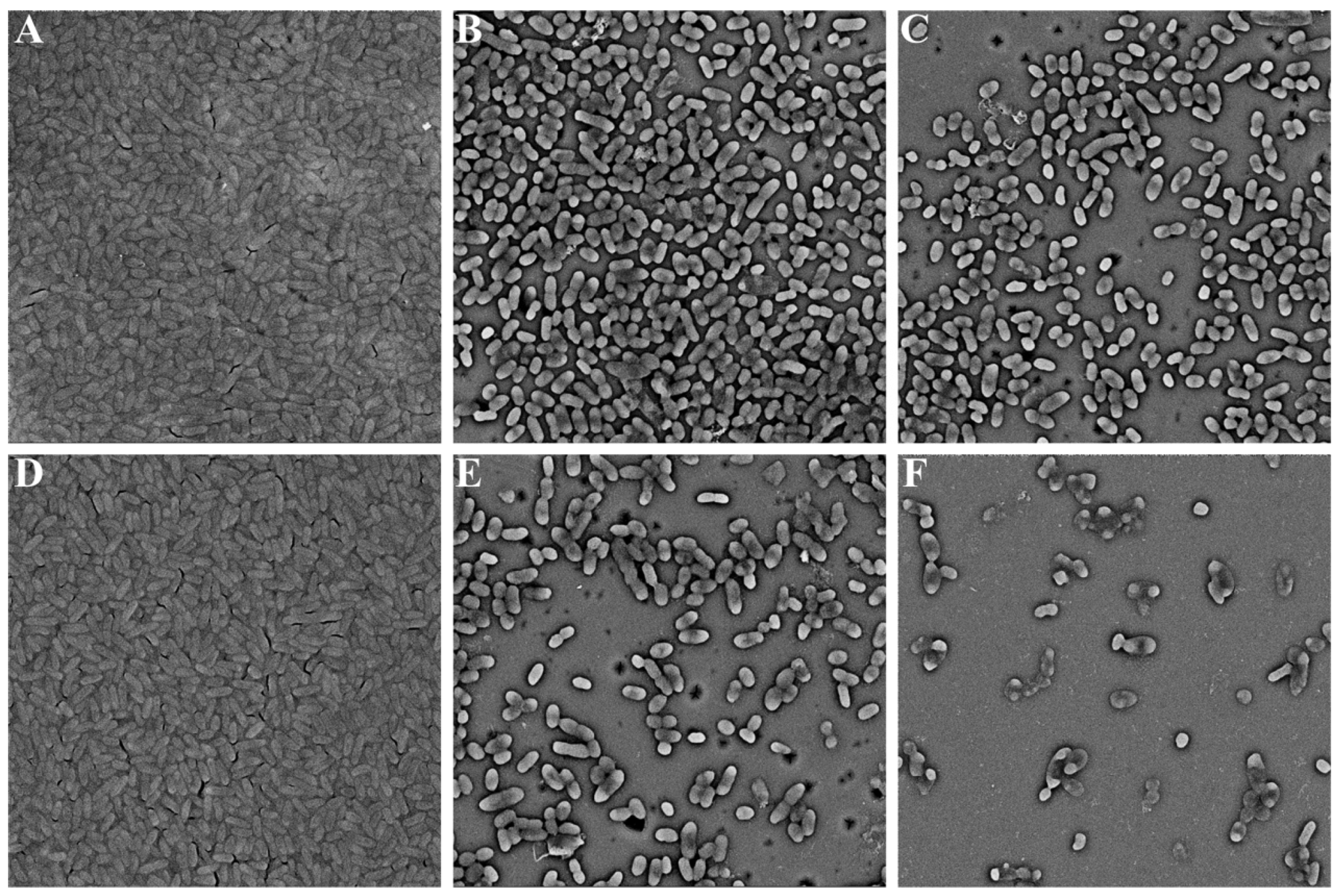
2.3. Biofilm Formation
2.4. Inhibition of Virulence Factors
2.5. Metabolic Analysis
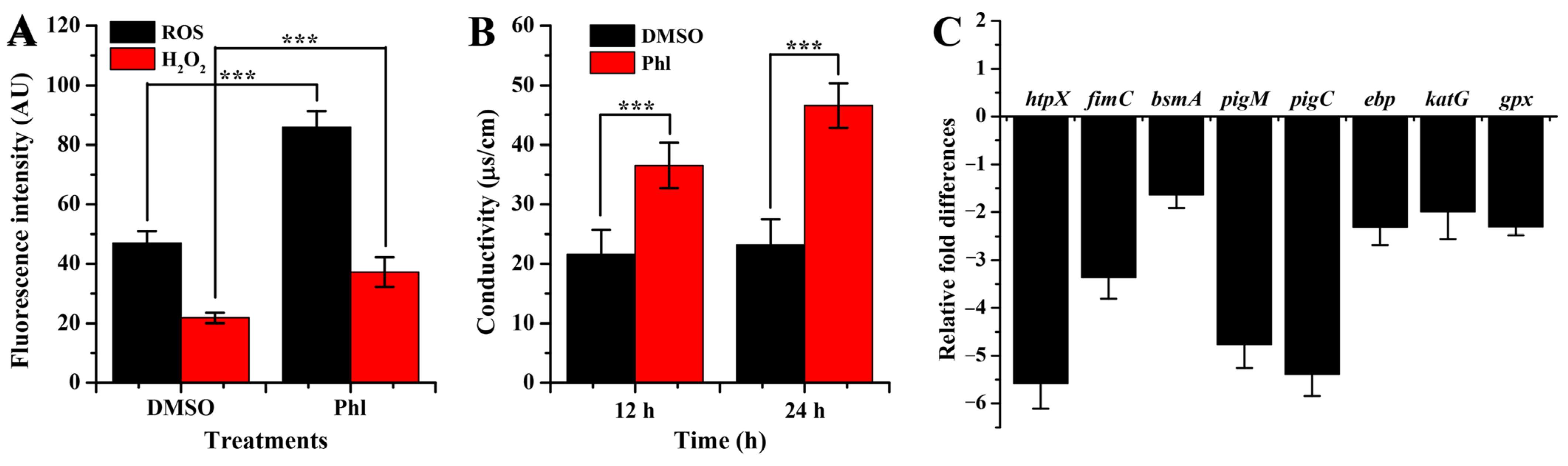
2.6. Oxidative Damage and Membrane Permeability
2.7. RT-qPCR Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Growth
3.2. Inhibition of AHL Production
3.3. Biofilm Development
3.4. Microscopic Analysis
3.5. Virulence Factors
3.6. Metabolomics Analysis
3.7. Analysis of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and H2O2
3.8. Membrane Permeability
3.9. Gene Expression
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Flecha, B.; Demple, B. Homeostatic Regulation of Intracellular Hydrogen Peroxide Concentration in Aerobically Growing Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 382–388. Available online: https://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC178707&blobtype=pdf (accessed on 24 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Hassett, D.J.; Ma, J.F.; Elkins, J.G.; McDermott, T.R.; Ochsner, U.A.; West, S.E.; Huang, C.T.; Fredericks, J.; Burnett, S.; Stewart, P.S.; et al. Quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa controls expression of catalase and superoxide dismutase genes and mediates biofilm susceptibility to hydrogen peroxide. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Ruan, L.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Luo, H.Z.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.S.; Jia, A.Q. Inhibition of Quorum Sensing and Virulence in Serratia marcescens by Hordenine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruton, B.D.; Mitchell, F.; Fletcher, J.; Pair, S.D.; Wayadande, A.; Melcher, U.; Brady, J.; Bextine, B.; Popham, T.W. Serratia marcescens, a Phloem-Colonizing, Squash Bug -Transmitted Bacterium: Causal Agent of Cucurbit Yellow Vine Disease. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Aminzadeh, S.; Zolgharnein, H.; Safahieh, A.; Daliri, M.; Noghabi, K.A.; Ghoroghi, A.; Motallebi, A. Characterization of a chitinase with antifungal activity from a native Serratia marcescens B4A. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, J.H.; Alamdar, A.; Mohammad, A.; Ahad, K.; Shabir, Z.; Ahmed, H.; Ali, S.M.; Sani, S.G.; Bokhari, H.; Gallagher, K.D.; et al. Pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from Pakistan: A review of the occurrence and associated human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13367–13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.L.; Geng, X.W.; Cui, H.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, Z.K.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, M.T.; Tan, C.L.; et al. Size engineering of 2D MOF nanosheets for enhanced photodynamic antimicrobial therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Yang, R.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Jia, A.Q. Anti-Biofilm and Antivirulence Activities of Metabolites from Plectosphaerella cucumerina against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.A.; Koh, K.S.; Queck, S.Y.; Labbate, M.; Lam, K.W.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilm Formation and Sloughing in Serratia marcescens are Controlled by Quorum Sensing and Nutrient Cues. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3477–3485. Available online: https://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC1111991&blobtype=pdf (accessed on 24 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shukla, R.; Singh, P.; Dubey, N.K. Chemical composition, antifungal and antiaflatoxigenic activities of Ocimum sanctum L. essential oil and its safety assessment as plant based antimicrobial. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salini, R.; Pandian, S.K. Interference of quorum sensing in urinary pathogen Serratia marcescens by Anethum graveolens. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, ftv038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Ravindran, D.; Arunachalam, K.; Arumugam, V.R. Inhibition of quorum sensing-dependent biofilm and virulence genes expression in environmental pathogen Serratia marcescens by petroselinic acid. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Devi, K.R.; Kannappan, A.; Pandian, S.K.; Ravi, A.V. Piper betle and its bioactive metabolite phytol mitigates quorum sensing mediated virulence factors and biofilm of nosocomial pathogen Serratia marcescens in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pun, M.; Khazanov, N.; Galsurker, O.; Weitman, M.; Kerem, Z.; Senderowitz, H.; Yedidia, I. Phloretin, an Apple Phytoalexin, Affects the Virulence and Fitness of Pectobacterium brasiliense by Interfering With Quorum-Sensing. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 671807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.N.; Shi, C.Z.; Luo, C.X.; Hu, C.Y.; Meng, Y.H. Phloretin inhibits biofilm formation by affecting quorum sensing under different temperature. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Yin, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. A Practical Approach for Predicting Antimicrobial Phenotype Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Through Machine Learning Analysis of Genome Data. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 841289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchado, P.; Gimenez-Bastida, J.A.; Larrosa, M.; Castro-Ibanez, I.; Espin, J.C.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Allende, A. Inhibition of quorum sensing (QS) in Yersinia enterocolitica by an orange extract rich in glycosylated flavanones. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8885–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkiyaraj, D.; Sivasankar, C.; Pandian, S.K. Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated biofilm formation in Serratia marcescens causing nosocomial infections. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3089–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.H.; Chu, D.D.; Cui, H.H.; Li, Z.R.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, C.L.; Li, J.G. Activating MoO3 nanobelts via aqueous intercalation as a near-infrared type I photosensitizer for photodynamic periodontitis treatment. SmartMat 2023, e1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, T.; Hu, T.T.; Cheng, C.H.; Yu, S.L.; Li, H.; Liu, S.Y.; Ma, L.F.; Zhao, M.T.; Liang, R.Z.; et al. Facile synthesis of 2D Al-TCPP MOF nanosheets for efficient sonodynamic cancer therapy. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Z.; Zhou, J.W.; Sun, B.; Jiang, H.; Tang, S.; Jia, A.Q. Inhibitory effect of norharmane on Serratia marcescens NJ01 quorum sensing-mediated virulence factors and biofilm formation. Biofouling 2021, 37, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koorehdavoudi, H.; Bogdan, P.; Wei, G.; Marculescu, R.; Zhuang, J.; Carlsen, R.W.; Sitti, M. Multi-fractal characterization of bacterial swimming dynamics: A case study on real and simulated Serratia marcescens. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 20170154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Liao, Y.X.; Shen, J.L.; Hou, J.T. A stable NIR fluorescent probe for imaging lipid droplets in cells and tumors. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2024, 398, 134740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Sheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Jia, A.Q. 1H NMR-Based Global Metabolic Studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa upon Exposure of the Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Resveratrol. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, L.; He, S.; Chen, Q.; Peng, F.; Peng, H.; Xie, M. Comparative proteomic analysis of cellular response of human airway epithelial cells (A549) to benzo(a)pyrene. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusane, D.H.; Pawar, V.S.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S.S. Anti-biofilm potential of a glycolipid surfactant produced by a tropical marine strain of Serratia marcescens. Biofouling 2011, 27, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, W.R.; Zhang, L.L.; Feng, S.S.; Xu, J.G. Chemical composition, antibacterial activity, and mechanism of action of the essential oil from Amomum kravanh. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, C.; Rodriguez-Martinez, J.M.; Briales, A.; Diaz de Alba, P.; Calvo, J.; Pascual, A. Smaqnr, a new chromosome-encoded quinolone resistance determinant in Serratia marcescens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, H.S.; Rath, P.; Chauhan, A.; Ramniwas, S.; Vashishth, K.; Varol, M.; Jaswal, V.S.; Haque, S.; Sak, K. Phloretin, as a Potent Anticancer Compound: From Chemistry to Cellular Interactions. Molecules 2022, 27, 8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Regmi, S.C.; Kim, J.A.; Cho, M.H.; Yun, H.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J. Apple flavonoid phloretin inhibits Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation and ameliorates colon inflammation in rats. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4819–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, L.; Bornstein, M.M.; Shyp, V. Inhibition of biofilm formation and virulence factors of cariogenic oral pathogen Streptococcus mutans by natural flavonoid phloretin. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2230711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, W.; Tang, S.; Deng, S.M.; Jia, A.Q. 3-Phenylpropan-1-Amine Enhanced Susceptibility of Serratia marcescens to Ofloxacin by Occluding Quorum Sensing. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0182922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horng, Y.T.; Deng, S.C.; Daykin, M.; Soo, P.C.; Wei, J.R.; Luh, K.T.; Ho, S.W.; Swift, S.; Lai, H.C.; Williams, P. The LuxR family protein SpnR functions as a negative regulator of N-acylhomoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing in Serratia marcescens. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1655–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonkwo, C.C.; Ujor, V.; Cornish, K.; Ezeji, T.C. Inactivation of the Levansucrase Gene in Paenibacillus polymyxa DSM 365 Diminishes Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis during 2,3-Butanediol Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00196-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidley, J.W. Free radicals in central nervous system ischemia. Stroke 1990, 21, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.G.; Heyndrickx, M.; De Block, J.; Devreese, B.; Vandenberghe, I.; Vanetti, M.C.; Van Coillie, E. Identification and characterization of a heat-resistant protease from Serratia liquefaciens isolated from Brazilian cold raw milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 222, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, C.A.; Bagliniere, F.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Spoilage potential of a heat-stable lipase produced by Serratia liquefaciens isolated from cold raw milk. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 126, 109289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Jalah, R.; Sharma, Y.D. Expression and purification of HtpX-like small heat shock integral membrane protease of an unknown organism related to Methylobacillus flagellatus. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Nizet, V. Color me bad: Microbial pigments as virulence factors. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Zhou, W.; Xu, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, N.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, M.; Mo, X.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Competitive Growth Advantage of Non-pigmented Serratia marcescens Mutants. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 793202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Jia, A.Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, P.L.; Chen, H.; Tan, X.J.; Liu, E.Q. 1-(4-Amino-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone from Phomopsis liquidambari showed quorum sensing inhibitory activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, L.; Ravn, L.; Rasch, M.; Bruhn, J.B.; Christensen, A.B.; Givskov, M. Food spoilage-interactions between food spoilage bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomini, A.M.; Paccola-Meirelles, L.D.; Marsaioli, A.J. Acyl-homoserine lactones produced by Pantoea sp. isolated from the “maize white spot” foliar disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongvaux, A.; Galli, M.; Denanglaire, S.; Van Gool, F.; Dreze, P.L.; Szpirer, C.; Bureau, F.; Andris, F.; Leo, O. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor/visfatin is required for lymphocyte development and cellular resistance to genotoxic stress. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4685–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


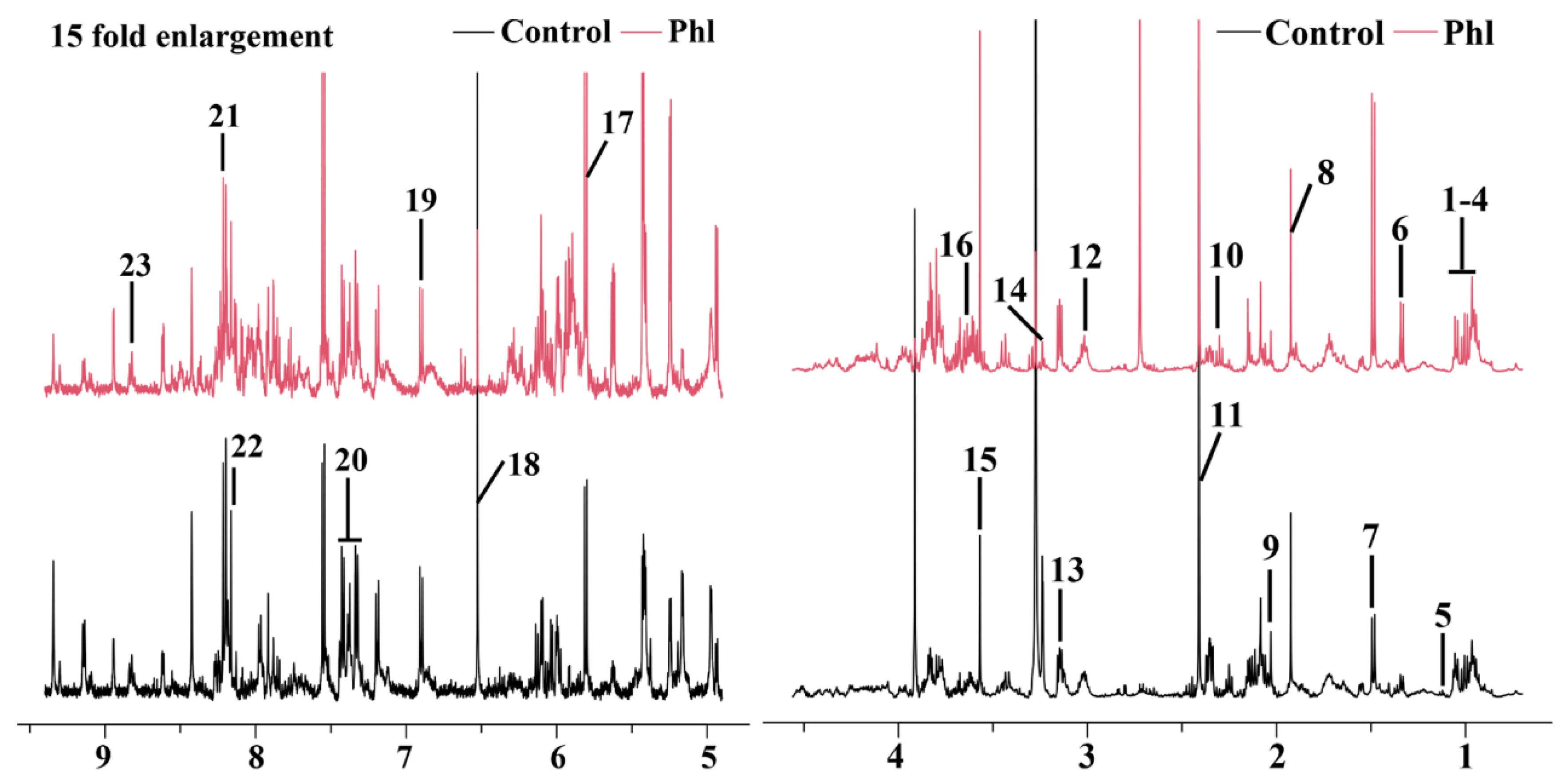
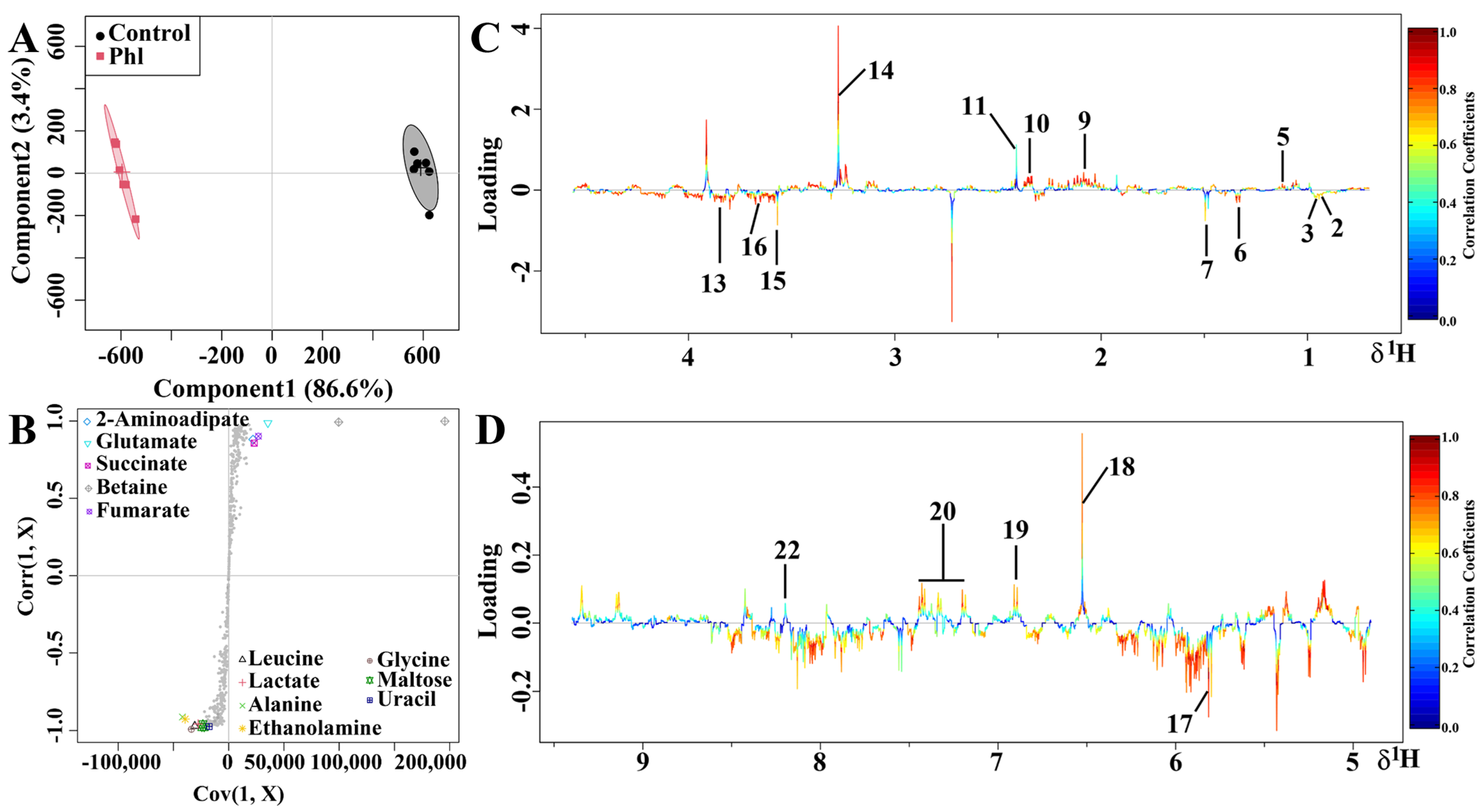
| No. | Compound | Assignments | Chemical Shift (ppm) a | Fold b | p c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glycocholate | CH3 | 0.93 (t) | 0.1 | |
| 2 | Isoleucine | d-CH3, g-CH3, a-CH | 0.94 (t), 1.01 (d), 3.67 (d) | 0.73 | * |
| 3 | Leucine | d-CH3, d-CH3, a-CH | 0.96 (t), 0.97 (d), 3.72 (d) | 0.56 | *** |
| 4 | Valine | g-CH3, g-CH3, a-CH | 0.99 (d), 1.05 (d), 3.59 (d) | 0.07 | |
| 5 | 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate | CH3 | 1.1 (d) | −0.67 | |
| 6 | Lactate | CH3 | 1.33 (d) | 1.13 | *** |
| 7 | Alanine | CH3, CH | 1.49 (d), 3.78 (q) | 0.92 | *** |
| 8 | Acetate | CH3 | 1.92 (s) | −0.07 | |
| 9 | 2-Aminoadipate | CH2 | 2.07 (m) | −1.05 | * |
| 10 | Glutamate | b-CH2, g-CH2, a-CH | 2.06 (m), 2.35 (dt), 3.76 (q) | −1.21 | *** |
| 11 | Succinate | CH2 | 2.41 (s) | −0.43 | * |
| 12 | 2-Oxoglutarate | CH | 3.0 (t) | −0.96 | |
| 13 | Ethanolamine | CH2 | 3.13 (t), 3.81 (t) | 0.74 | * |
| 14 | Betaine | CH2 | 3.23 (s) | −3.82 | ** |
| 15 | Glycine | CH2 | 3.56 (s) | 0.7 | *** |
| 16 | Maltose | CH | 3.63 (dd) | 0.97 | *** |
| 17 | Uracil | CH | 5.81 (d), 7.54 (d) | 0.71 | *** |
| 18 | Fumarate | CH | 6.52 (s) | −2.19 | *** |
| 19 | Tyrosine | 2-CH, 6-CH | 6.91 (d) | −0.52 | ** |
| 20 | Phenylalanine | ph-H | 7.3–7.46 (m) | −0.3 | ** |
| 21 | Hypoxanthine | 2-H, 8-H | 8.2 (s), 8.22 (s) | 0.03 | |
| 22 | NAD+ | 7-CH, 39-CH | 8.13 (s), 8.83 (s), 8.84 (d) | −0.86 | * |
| 23 | Nicotinate | CH | 8.89 (dd) | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Ji, P.; Yin, K.; Zheng, Y.; Niu, J.; Jia, A.; Zhou, J.; Li, J. Phloretin Inhibits Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Serratia marcescens. Molecules 2023, 28, 8067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248067
Qi Y, Ji P, Yin K, Zheng Y, Niu J, Jia A, Zhou J, Li J. Phloretin Inhibits Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Serratia marcescens. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):8067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248067
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yueheng, Pengcheng Ji, Kunyuan Yin, Yi Zheng, Jiangxiu Niu, Aiqun Jia, Jinwei Zhou, and Jingguo Li. 2023. "Phloretin Inhibits Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Serratia marcescens" Molecules 28, no. 24: 8067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248067
APA StyleQi, Y., Ji, P., Yin, K., Zheng, Y., Niu, J., Jia, A., Zhou, J., & Li, J. (2023). Phloretin Inhibits Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Serratia marcescens. Molecules, 28(24), 8067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248067







