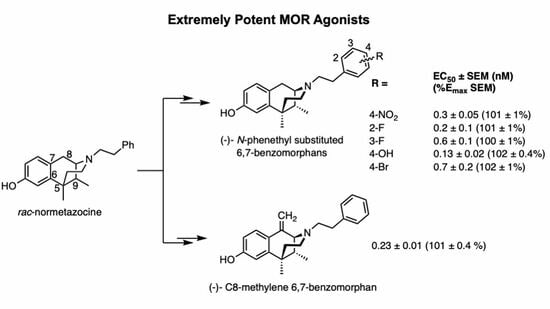
Potent MOR Agonists from 2′-Hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-N-phenethyl Substituted-6,7-benzomorphans and from C8-Hydroxy, Methylene and Methyl Derivatives of N-Phenethylnormetazocine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
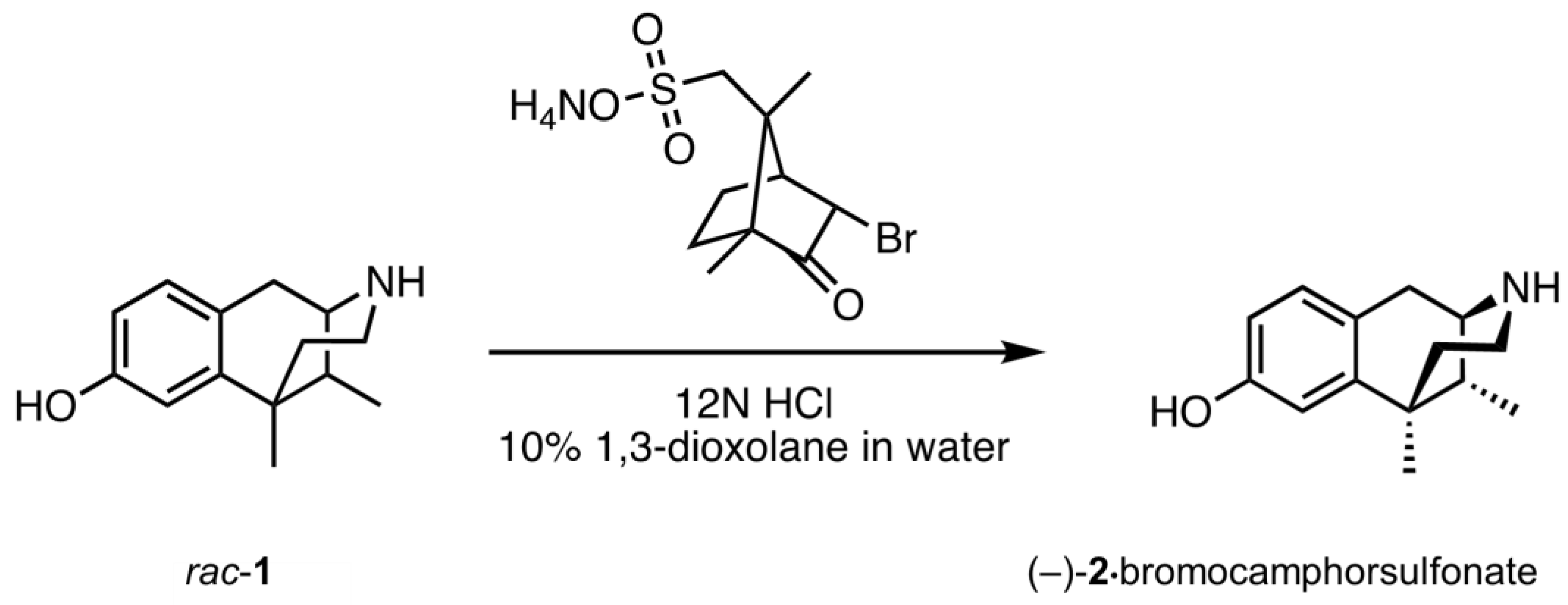
2.1. Optical Resolution of (±)-Normetazocine
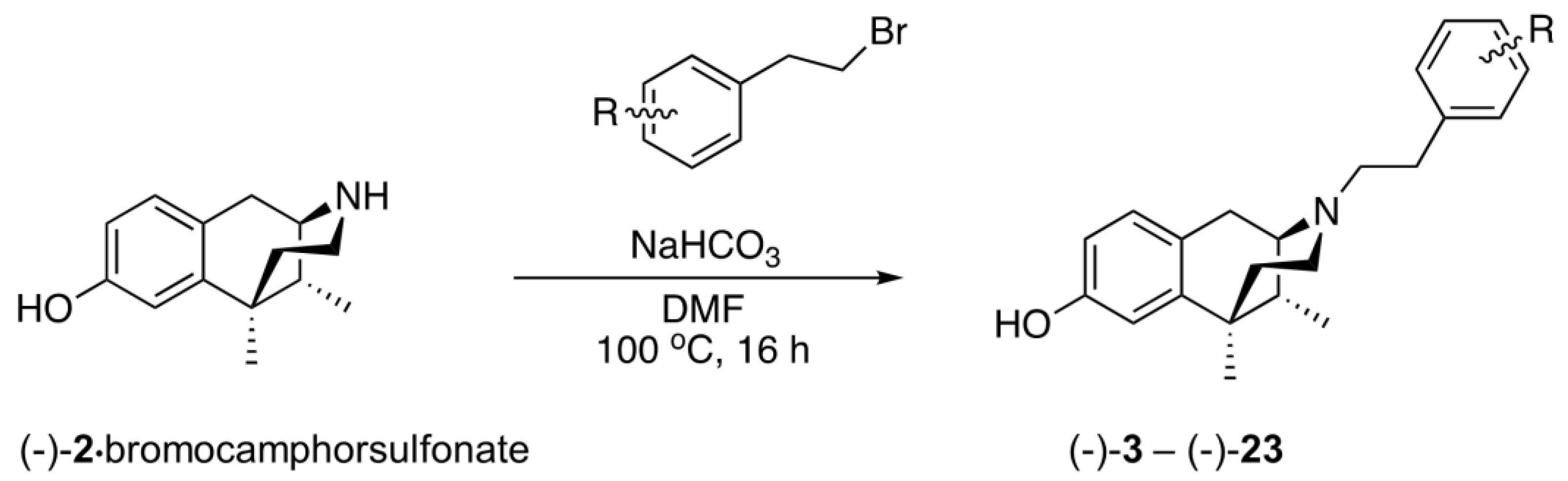
2.2. Substituents on the Aromatic Ring in the N-Phenethyl Side Chain
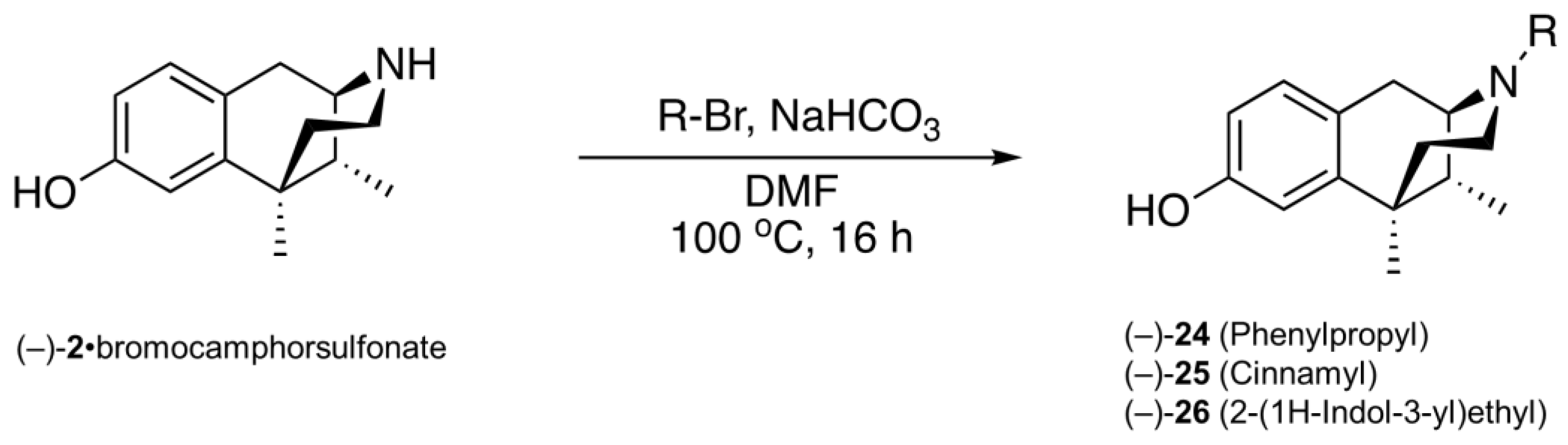
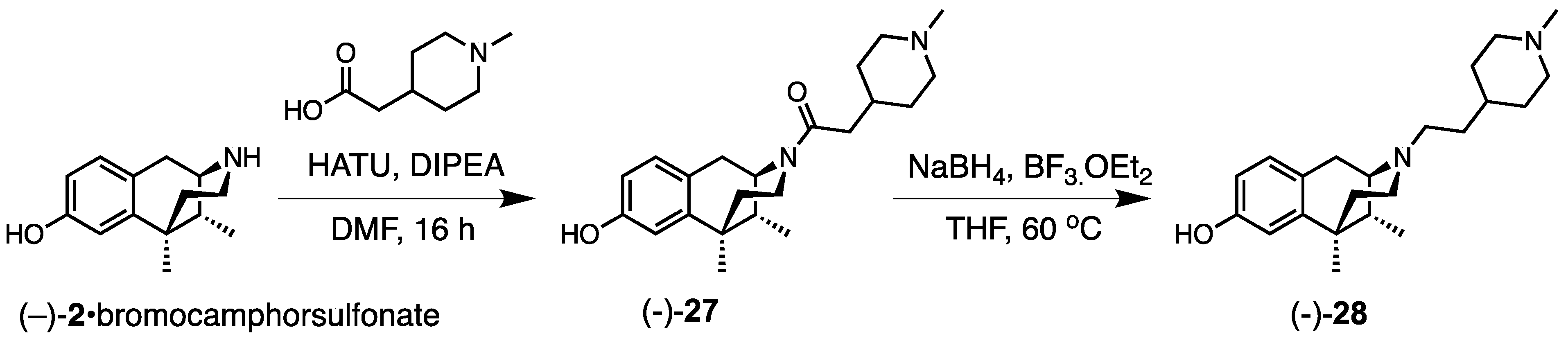
2.3. Modification of the N-Phenethyl Side Chain
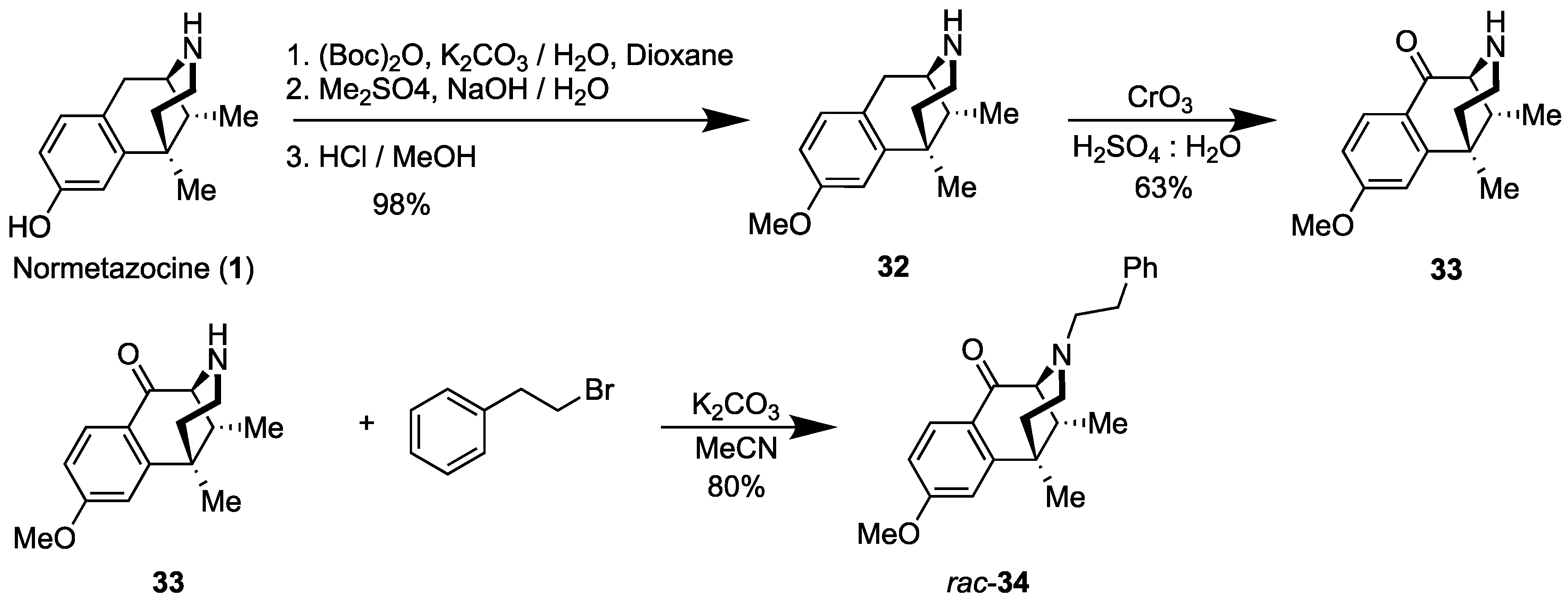
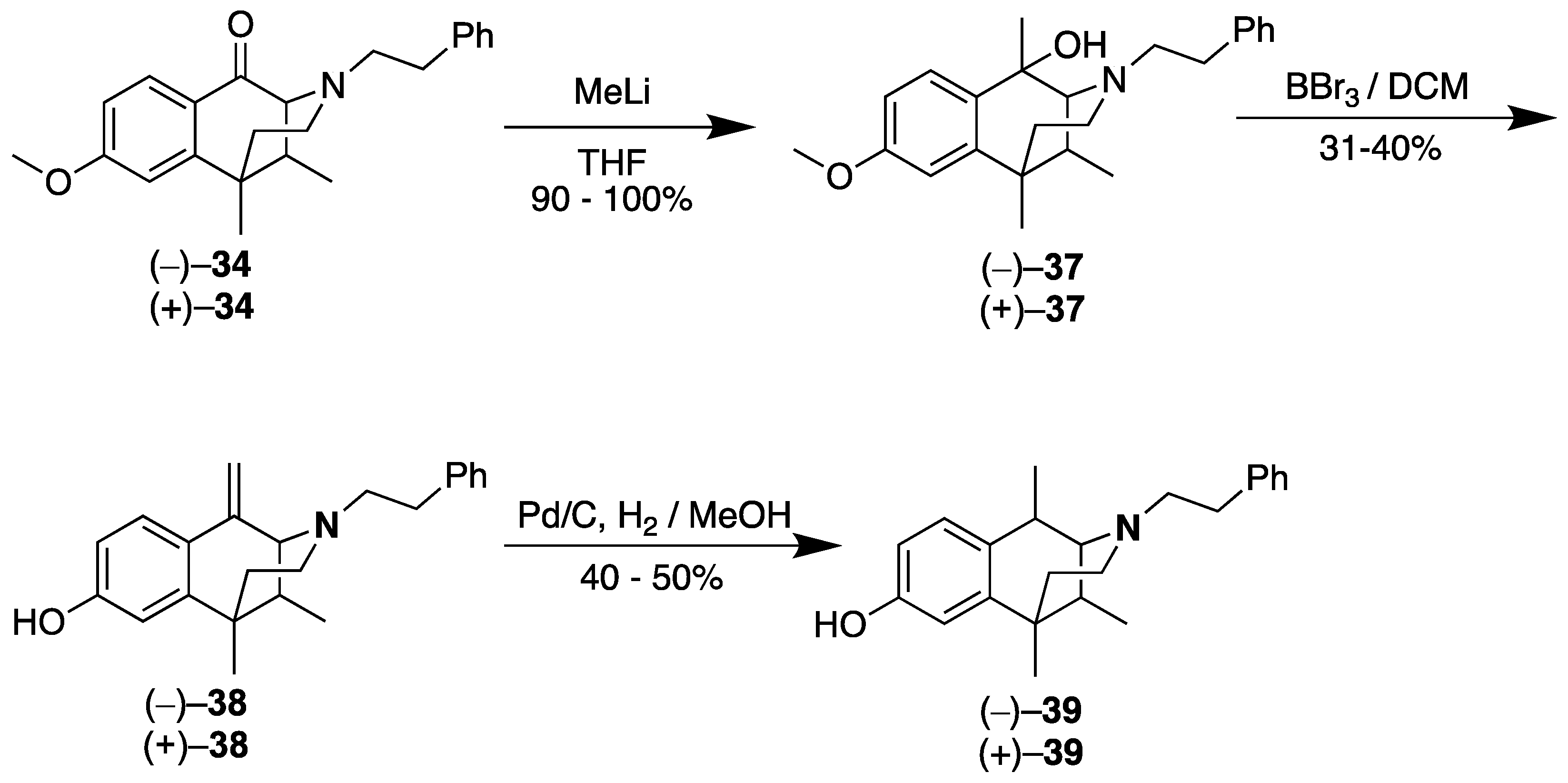
2.4. Synthesis of C8-Oxo-Normetazocine
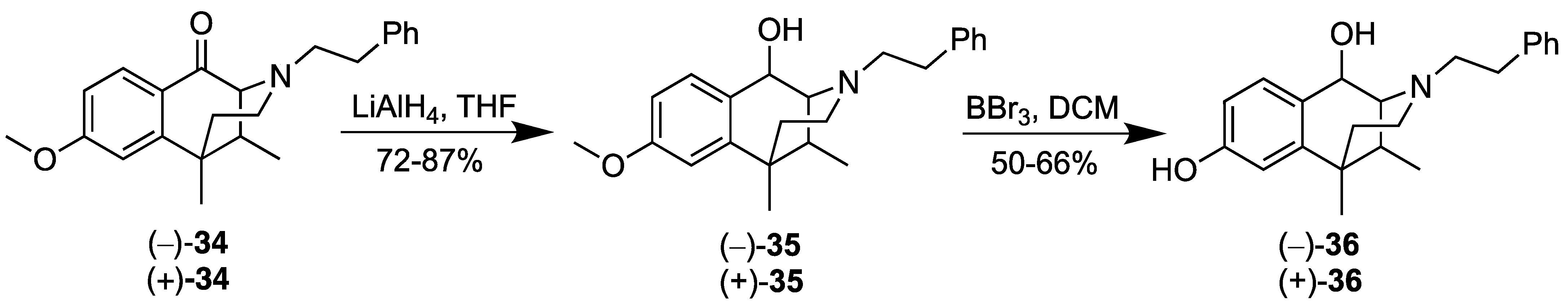
2.5. Synthesis of the Optical Isomers of C8-oxo m-Methoxy-N-phenethyl-6,7-benzomorphan
2.6. Forskolin-Induced cAMP Accumulation Assay for In Vitro Determination of the Potency and Efficacy of the Benzomorphans
| MOR | MOR | DOR | DOR | KOR | KOR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonist | Antagonist b | Agonist | Antagonist c | Agonist | Antagonist d | |||
| Compound Number (3–31 (−)-Enantiomers) | Structure | EC50 ± SEM (nM) (%Emax ± SEM) | IC50 ± SEM (nM) (%Imax ± SEM) | EC50 ± SEM (nM) (%Emax ± SEM) | IC50 ± SEM (nM) (%Imax ± SEM) | EC50 ± SEM (nM) (%Emax ± SEM) | IC50 ± SEM (nM) (%Imax ± SEM) | |
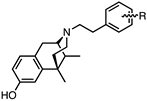 R = | ||||||||
| 3 | 02-0011 | 4-NO2 | 0.3 ± 0.05 (101 ± 1%) | N/D | 2.7 ± 1.0 (88 ± 5%) | N/D | 13 ± 0.5 (46 ± 7%) | N/D |
| 4 | 02-0015 | 3-NO2 | 26 ± 4.0 (71 ± 12%) | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| 5 | 02-0018 | 2-NO2 | 2.7 ± 0.4 (101 ± 0.2%) | N/D | 37 ± 6 (73 ± 14%) | N/D | 16 ± 4 (23 ± 8%) | 717 ± 132 (89 ± 5%) |
| 6 | 02-0006 | 4-F | 1.8 ± 0.3 (103 ± 0.2%) | N/D | 12 ± 3 (73 ± 11%) | N/D | 7 ± 3 (34± 6%) | 368 ± 92 (71 ± 2%) |
| 7 | 02-0023 | 3-F | 0.6 ± 0.1 (100 ± 1%) | N/D | 11± 4 (86 ± 5%) | N/D | >10,000 | 274 ± 83 (87 ± 2%) |
| 8 | 02-0020 | 2-F | 0.2 ± 0.1 (101 ± 1%) | N/D | 6 ± 2 (87± 5%) | N/D | 6 ± 1 (45 ± 7%) | N/D |
| 9 | 02-0017 | 4-CF3 | 2 ± 1 (102 ± 1%) | N/D | 3 ± 1 (72 ± 14%) | N/D | 23 ± 5 (100 ± 2%) | N/D |
| 10 | 02-0024 | 3-CF3 | 167 ± 72 (63 ± 13%) | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| 11 | 02-0008 | 2-CF3 | 6 ± 0.2 (102 ± 1%) | N/D | 24 ± 5 (77 ± 9%) | N/D | 36 ± 3 (72 ± 6%) | N/D |
| 12 | 02-0010 | 4-Br | 0.7 ± 0.2 (102 ± 1%) | N/D | 1.1 ± 0.3 (89± 4%) | N/D | 5 ± 2 (100 ±1%) | N/D |
| 13 | 02-0014 | 3-Br | 18 ± 7 (78 ± 9%) | N/D | 110 ± 24 (51 ± 4%) | N/D | >10,000 | 90 ± 37 (99 ± 2%) |
| 14 | 02-0021 | 2-Br | 2 ± 0.4 (101 ± 2%) | N/D | 13 ± 2 (89 ± 6%) | N/D | 16 ± 2 (80 ± 6%) | N/D |
| 15 | 02-0009 | 4-Cl | 1.3 ± 0.4 (103 ± 1%) | N/D | 1.2 ± 0.5 (89 ± 6%) | N/D | 5 ± 1 (97 ± 1%) | N/D |
| 16 | 02-0012 | 3-Cl | 13 ± 2 (95 ± 2%) | N/D | 93 ± 25 (64 ± 6%) | N/D | >10,000 | 111 ± 43 (108 ± 10%) |
| 17 | 02-0022 | 2-Cl | 1.4 ± 0.3 (101 ± 1%) | N/D | 15 ± 4.0 (87 ± 5%) | N/D | 8 ± 1 (57 ±11%) | N/D |
| 18 | 02-0007 | 4-OMe | 1.2 ± 0.4 (103 ± 0.3%) | N/D | 4 ± 1 (87 ± 6%) | N/D | 9 ± 2 (89 ± 3%) | N/D |
| 19 | 02-0005 | 4-Me | 1.4 ± 0.4 (103 ± 1%) | N/D | 5 ± 2 (87± 5%) | N/D | 13 ± 3 (93 ± 3%) | N/D |
| 20 | 02-0019 | 4-OH | 0.13 ± 0.02 (102 ± 0.4%) | N/D | 5 ± 1 (84 ± 5%) | N/D | 8 ± 3 (97 ± 1%) | N/D |
| 21 | 02-0025 | 2,4-dichloro | 5 ± 3 (103 ± 1%) | N/D | 37 ± 9 (86 ± 12%) | N/D | 42 ± 10 (93± 5%) | N/D |
| 22 | 02-0026 | 2,6-dichloro | 4 ± 1 (99 ± 2%) | N/D | 59 ± 25 (78 ± 11%) | N/D | >10,000 | 65 ± 24 (87 ± 7%) |
| 23 | 02-013 | H | 0.27 ± 0.1 (101 ± 0.3%) | N/D | 4 ± 1 (85 ± 6%) | N/D | 3.4 ± 0.4 (25 ± 5%) | 281± 94 (81 ± 5%) |
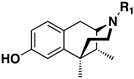 | ||||||||
| N-R1 = | ||||||||
| 24 | 02-0027 |  | 69 ± 13 (100 ± 1%) | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| 25 | 02-0029 | 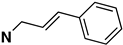 | 244 ± 58 (101 ± 1%) | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| 26 | 02-0034 | 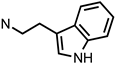 | 12 ± 1 (102 ± 1%) | N/D | 343 ± 35 (91 ± 5%) | N/D | >10,000 | >10,000 |
| 28 | 02-0057 | 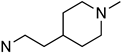 | >10,000 | >10,000 | >10,000 | >10,000 | 0.05 ± 0.02 (15 ± 3%) | >10,000 |
| 31 | 02-0033 | 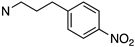 | >10,000 | >10,000 | N/D | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| C8-Substituted | ||||||||
| (+)-36 | GW-S-01-73 |  | 25.2 ± 5.9 (103 ± 0.3%), | N/D | 1906 ± 232 (97 ± 4.2%) | N/D | >10,000 | N/D |
| (+)-38 | GW-S-01-75 | 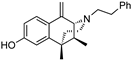 | 70 ± 15 (102 ± 1%) | N/D | 978 ± 374 (92 ± 3.6%) | N/D | 1181 ± 46 (53 ± 6.3%) | N/D |
| (−)-38 | GW-S-01-76 |  | 0.23 ± 0.01 (101 ± 0.4%) | N/D | 4.9 ± 3.0 (89 ± 2.6%) | N/D | 9.5 ± 2.0 (57 ± 7.6%) | N/D |
| (+)-39 | GW-01-106 | 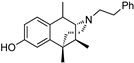 | 21.7 ± 10.4 (103% ± 1.5%) | N/D | 1338 ± 389 (94 ± 1.7%) | N/D | 953 ± 120 (37 ± 5.4%) | >10,000 |
| (−)-39 | GW-01-107 | 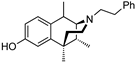 | 1.2 ± 0.5 (102% ± 1%) | N/D | 12.6 ± 3.9 (91± 2.2%) | N/D | 20.7 ± 6.1 (38 ± 8.0%) | 731 ± 362 (57 ± 5%) |
| Standards | ||||||||
| Morphine | 5.8 ± 0.3 (102 ± 0.1%) | |||||||
| DAMGO | 0.3 ± 0.1 (103 ± 1%) | |||||||
| U50488H | 0.3 ± 0.03 (100 ± 0.3%) | |||||||
| SNC80 | 1.7 ± 0.2 (79 ± 2%) | |||||||
| Naltrexone | 2.1 ± 1.2 (30 ± 6%) | 11 ± 1 (104 ± 1%) | >10,000 | 295 ± 48 (99 ± 1%) | 0.6 ± 0.3 (57 ± 7%) | 6 ± 1 (41 ± 7%) | ||
| nor-BNI | 2.3 ± 0.3 (102 ± 1%) | |||||||
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-nitrophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-3). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-nitrophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (300 mg, 67%), mp (HCl salt) 273–274 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.43–7.40 (m, 2H), 7.17–7.14 (m, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.56 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.02 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.92 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.80–2.74 (m, 3H), 2.72–2.61 (m, 3H), 2.13 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.34 (s, 3H), 1.32 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 148.4, 146.5, 142.2, 129.4, 127.7, 126.7, 123.0, 112.7, 111.6, 57.6, 55.7, 45.5, 41.5, 41.2, 35.9, 33.3, 24.4, 22.8, 13.0. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27N2O3, 367.2022 (M+H)+; found, 367.2016. [α]20D –94.8° (c 1.17, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27ClN2O3 • 0.15 C3H8O: C, 65.46; H, 6.90; N, 6.80. Found: C, 65.60; H, 6.94; N, 6.66.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(3-nitrophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-4). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 3-nitrophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (276 mg, 81%), mp (HCl salt) 259–262 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 8.16 (t, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.10–8.07 (m, 1H), 7.67 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.57 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.04 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.95 (dt, J = 10.4, 4.2 Hz, 3H), 2.89–2.81 (m, 1H), 2.78–2.64 (m, 3H), 2.18 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.89 (dd, J = 7.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.36 (s, 3H), 1.32 (d, J = 20.7 Hz, 1H), 0.88 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 148.3, 142.5, 142.2, 134.9, 129.1, 127.7, 126.6, 123.1, 120.7, 112.8, 111.6, 57.6, 55.8, 45.5, 41.5, 41.2, 35.9, 32.9, 24.5, 22.8, 13.0. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27N2O3, 367.2022 (M+H)+; found, 367.2022[α]20D –94.5° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27ClN2O3 • 0.25 C3H8O: C, 65.38; H, 6.99; N, 6.70. Found: C, 65.19; H, 6.80; N, 6.82.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2-nitrophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((-)-5). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2-nitrophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (265 mg, 76%), mp (HCl salt) 237–239 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.89 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.59 (td, J = 7.5, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (dd, J = 7.7, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.44–7.40 (m, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.13 (ddd, J = 12.5, 10.5, 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.03–2.94 (m, 2H), 2.91 (d, J = 18.4 Hz, 1H), 2.86–2.79 (m, 1H), 2.71–2.64 (m, 2H), 2.59 (dd, J = 11.9, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.14 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.87 (dd, J = 7.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 12.8, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.29 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.84 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.3, 149.7, 142.3, 134.7, 132.7, 132.3, 127.7, 127.2, 126.8, 124.1, 112.7, 111.6, 57.7, 55.6, 45.6, 41.4, 41.0, 35.9, 30.5, 24.5, 23.1, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27N2O3, 367.2022 (M+H)+; found, 367.2020. [α]20D –87.8° (c 1.4, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27ClN2O3 • 0.3 H2O • 0.5 C3H8O: C, 64.39; H, 7.27; N, 6.39. Found: C, 64.34; H, 7.32; N, 6.42.
- (2R,6R,11R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-fluorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-6). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-fluorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (500 mg, 83%), mp (HCl salt) 303–304 °C(dec). 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.23–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.00–6.95 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.02 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (d, J = 18.4 Hz, 1H), 2.80–2.59 (m, 6H), 2.12 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.87 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.80 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.30 (t, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 160.2 (2), 155.4, 142.2, 135.90 (2), 129.84 (2), 127.7, 126.6, 114.5 (2), 112.8, 111.6, 57.3, 56.6, 47.87, 47.83, 47.5, 45.6, 41.4, 41.1, 35.9, 32.5, 24.5, 22.5, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27FNO, 340.2077 (M+H)+; found, 340.2075[α]20D –109.7° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27ClFNO: C, 70.29; H, 7.24; N, 3.73. Found: C, 70.55; H, 7.23; N, 3.71.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(3-fluorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-7). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 3-fluorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (200 mg, 64%), mp (HCl salt) 268–270 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.26 (td, J = 7.9, 6.1 Hz, 1H), 7.03 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.97 (dt, J = 10.1, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.92–6.88 (m, 2H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.07 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.92 (d, J = 18.4 Hz, 1H), 2.85–2.78 (m, 3H), 2.75–2.63 (m, 3H), 2.17 (td, J = 12.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.89 (tt, J = 7.0, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 13.0, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.35 (dd, J = 3.1, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 0.86 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 162.9 (2), 155.5, 142.6 (2), 142.0, 129.7 (2), 127.7, 126.3, 124.1 (2), 115.0 (2), 112.9, 112.4 (2), 111.6, 57.6, 56.0, 45.6, 41.2, 40.9, 35.8, 32.9, 24.4, 22.6, 13.0. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27FNO, (M+H)+ 340.2077; found, 340.2071[α]20D –99.1° (c 0.97, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27ClFNO: C, 70.13; H, 7.25; N, 3.72. Found: C, 69.90; H, 6.96; N, 3.75.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2-fluorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-8). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2-fluorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (200 mg, 62%), mp (HCl salt) 263–265 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.25 (td, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (ddd, J = 7.6, 5.5, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.09–7.05 (m, 1H), 7.04–6.99 (m, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.05 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.93–2.84 (m, 2H), 2.78 (ddt, J = 19.8, 12.3, 6.4 Hz, 2H), 2.70–2.67 (m, 1H), 2.65–2.61 (m, 2H), 2.13 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 161.1 (2), 155.4, 142.1, 130.7 (2), 127.8 (2), 127.7, 126.5 (2), 126.4, 123.9 (2), 114.8, 114.6, 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 54.9, 45.6, 41.3, 40.9, 35.8, 26.59, 26.57, 24.4, 22.6, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27FNO, 340.2077 (M+H)+; found, 340.2082[α]20D –107.1° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27ClFNO: C, 70.29; H, 7.24; N, 3.73. Found: C, 70.13; H, 6.94; N, 3.75.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-9). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-trifluoromethylphenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (260 mg, 59%), mp (HCl salt) 283–285 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.58 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.70 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.57 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.04 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.96–2.87 (m, 3H), 2.86–2.77 (m, 1H), 2.74–2.62 (m, 3H), 2.15 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.90 (td, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 12.8, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.35 (s, 3H), 1.33 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.88 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CD3OD): d 155.4, 144.8, 142.2, 129.0, 128.0 (4), 127.5, 126.6, 124.8 (4), 124.4 (4), 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 56.0, 45.5, 41.4, 41.1, 35.9, 33.2, 24.5, 22.6, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H27NOF3, 390.2045 (M+H)+; found, 390.2043[α]20D –87.5° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H27ClF3NO • 0.05 C3H8O: C, 64.83; H, 6.44; N, 3.27. Found: C, 64.84; H, 6.30; N, 3.10.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(3-trifluoromethylphenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-10). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 3-trifluoromethylphenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (280 mg, 77%), mp (HCl salt) 282.2–284.0 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.53 (s, 1H), 7.49–7.42 (m, 3H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.00 (dd, J = 5.3, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.92–2.84 (m, 3H), 2.80–2.75 (m, 1H), 2.73–2.58 (m, 3H), 2.13 (td, J = 12.4, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 1.86 (dd, J = 7.0, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 1.79 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (s, 1H), 0.84 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 141.5, 132.2, 130.2 (4), 128.8, 127.7, 126.7, 125.0 (4), 124.3 (4), 122.5 (4), 112.8, 111.6, 57.5, 56.1, 45.5, 41.5, 41.1, 35.9, 33.1, 24.5, 22.7, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H27F3NO, (M+H)+ 390.2045; found, 390.2040[α]20D –91.0° (c 1.2, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H27ClF3NO: C, 64.86; H, 6.39; N, 3.29. Found: C, 64.64; H, 6.12; N, 3.23.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2-trifluoromethylphenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-11). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2-trifluoromethylphenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (100 mg, 14%), mp (HCl salt) 215–217 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.63 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.02–2.94 (m, 3H), 2.89 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.77 (td, J = 11.6, 5.9 Hz, 1H), 2.70–2.61 (m, 3H), 2.14 (td, J = 12.4, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 1.89 (dd, J = 7.0, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 1.82 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.29 (d, J = 18.1 Hz, 1H), 0.86 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 138.5, 131.9, 131.6, 128.2, 127.7, 126.6, 126.5 (4), 126.21, 125.4 (4), 112.8, 111.6, 57.7, 56.5, 48.2, 47.8, 46.9, 45.6, 41.4, 41.0, 35.9, 30.3, 24.5, 22.8, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H27F3NO2, 390.2045 (M+H)+; found, 390.2050[α]20D –109.8° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H27ClF3NO2 • 0.6 C3H8O: C, 64.48; H, 6.94; N, 3.03. Found: C, 64.51; H, 6.95; N, 3.03.
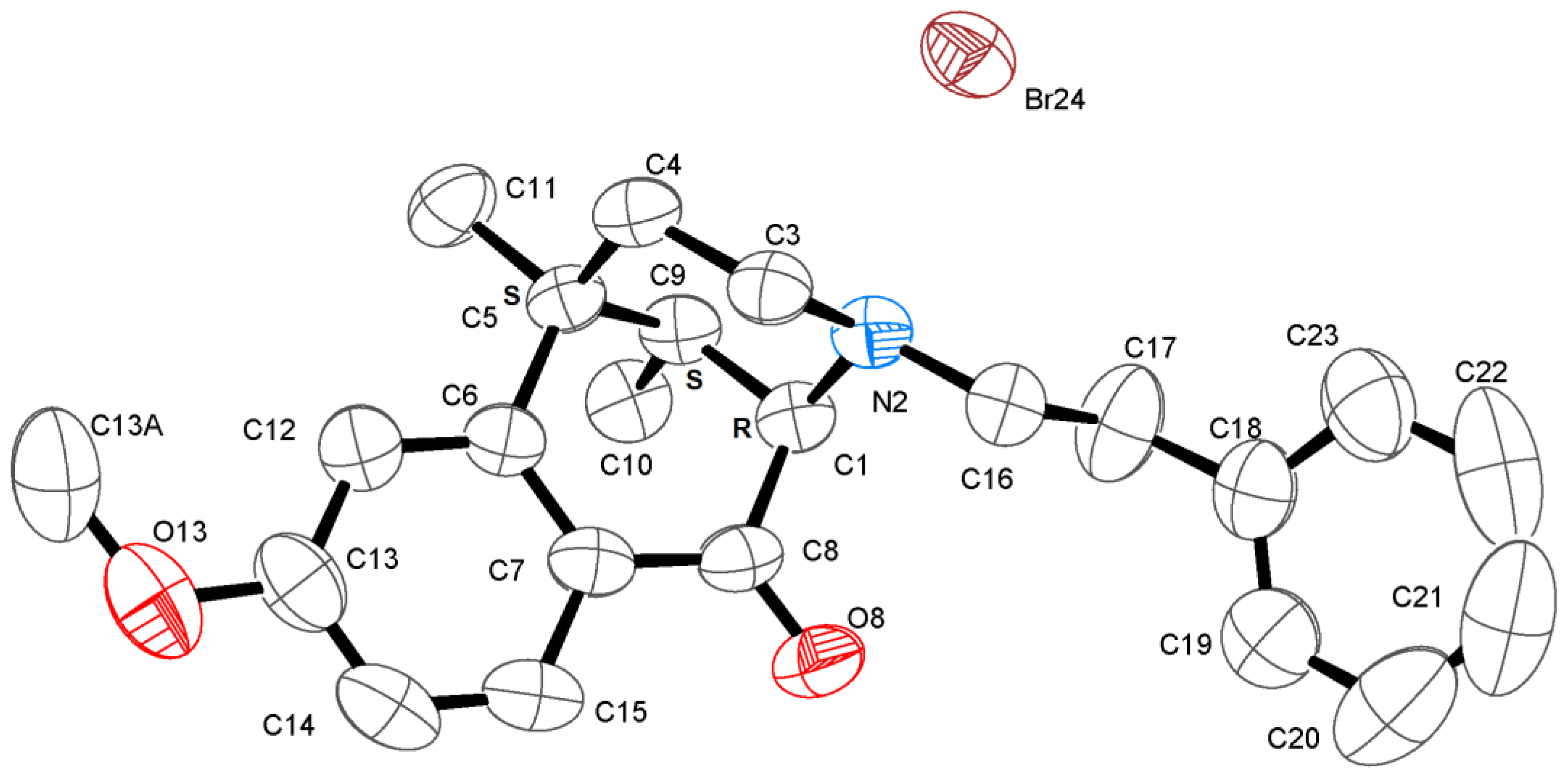
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-bromophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-12). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-bromophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (311 mg, 63%), mp (HCl salt) 292–293 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.43–7.40 (m, 2H), 7.17–7.14 (m, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.56 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.02 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.92 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.80–2.74 (m, 3H), 2.72–2.61 (m, 3H), 2.13 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.34 (s, 3H), 1.32 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 139.3, 131.1, 130.3, 127.7, 126.6, 119.4, 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 56.2, 45.6, 41.4, 41.1, 35.9, 32.7, 24.4, 22.6, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27BrNO, 400.1276 (M+H)+; found, 400.1271[α]20D –105.5° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH, (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27BrClNO • 0.45 C3H8O: C, 60.46; H, 6.65; N, 3.02. Found: C, 60.40; H, 6.58; N, 2.96.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(3-bromophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-13). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 3-bromophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (276 mg, 81%), mp (HCl salt) 255–257 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.42 (s, 1H), 7.34 (dt, J = 6.5, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.21–7.19 (m, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.56 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.02 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.92 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.81–2.75 (m, 3H), 2.72–2.60 (m, 3H), 2.14 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.82 (dt, J = 12.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H), 1.34 (s, 3H), 1.32 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.8, 142.2, 131.3, 129.8, 128.8, 127.7, 127.2, 126.7, 121.9, 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 56.2, 45.6, 41.4, 41.1, 35.9, 33.0, 24.5, 22.6, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27NOBr, 400.1276 (M+H)+; found, 400.1277. [α]20D –92.5° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27BrClNO: C, 60.49; H, 6.23; N, 3.21. Found: C, 60.67; H, 6.33; N, 3.16.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2-bromophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-14). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2-bromophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (200 mg, 59%), mp (HCl salt) 233–235 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.51 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.31–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.10–7.06 (m, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.05 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 3.00–2.87 (m, 3H), 2.76 (dt, J = 11.8, 5.9 Hz, 1H), 2.71 (t, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.66–2.57 (m, 2H), 2.15 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.89 (qd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.1, 139.1, 132.4, 130.7, 127.85, 127.71, 127.5, 126.6, 123.8, 112.8, 111.6, 57.5, 54.7, 45.7, 41.3, 40.9, 35.9, 33.6, 24.5, 22.9, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27BrNO, 400.1276 (M+H)+; found, 400.1278. [α]20D –88.2° (c 0.85, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27BrClNO • 0.1 H2O • 0.2 C3H8O: C, 60.24; H, 6.44; N, 3.11. Found: C, 60.32; H, 6.37; N, 3.02.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-chlorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-15). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-chlorophenethyl bromide. The product ((−)-15) was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (310 mg, 71%), mp (HCl salt) 300–302 °C (dec). 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.26–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.21–7.18 (m, 2H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.01 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.80–2.72 (m, 3H), 2.68 (dd, J = 9.9, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 2.64–2.62 (m, 1H), 2.61–2.58 (m, 1H), 2.12 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.86 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.80 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 138.8, 131.5, 129.9, 128.0, 127.7, 126.6, 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 56.3, 45.6, 41.4, 41.1, 35.9, 32.7, 24.5, 22.6, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27ClNO, 356.1781 (M+H)+; found, 356.1779. [α]20D –105.0° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27Cl2NO: C, 67.35; H, 6.94; N, 3.57. Found: C, 67.38; H, 6.69; N, 3.57.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(3-chlorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-16). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 3-chlorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (300 mg, 69%), mp (HCl salt) 258–260 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.26–7.22 (m, 2H), 7.18–7.13 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.00 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.90 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.80–2.72 (m, 3H), 2.67 (dd, J = 5.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 2.65–2.57 (m, 2H), 2.12 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.85 (dt, J = 7.5, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.79 (dt, J = 12.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (dd, J = 2.8, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.5, 142.2, 133.7, 129.5, 128.3, 127.7, 126.74, 126.69, 125.8, 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 56.2, 45.6, 41.5, 41.1, 35.9, 33.1, 24.5, 22.6, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27NOCl, 356.1781 (M+H)+; found, 356.1785. [α]20D –104° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27Cl2NO: C, 67.35; H, 6.94; N, 3.57. Found: C, 67.37; H, 6.72; N, 3.50.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2-chlorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-17). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2-chlorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (250 mg, 74%), Mp (HCl salt) 249–251 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.31 (ddd, J = 15.6, 7.6, 1.5 Hz, 2H), 7.23–7.14 (m, 2H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.04 (dd, J = 5.4, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 3.00–2.86 (m, 3H), 2.75 (td, J = 11.6, 5.6 Hz, 1H), 2.72–2.58 (m, 3H), 2.14 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 13.0, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (s, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 137.4, 133.5, 130.7, 129.1, 127.70, 127.61, 126.9, 126.6, 112.8, 111.6, 57.5, 54.6, 45.7, 41.3, 40.9, 35.9, 31.1, 24.5, 22.8, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H27ClNO, 356.1781 (M+H)+; found, 356.1781. [α]20D –90.6° (c 1.2, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H27Cl2NO • 0.15 H2O • 0.1 C3H8O: C, 66.78; H, 7.06; N, 3.49. Found: C, 66.87; H, 6.97; N, 3.39.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-methoxyphenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-18). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-methoxyphenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (465 mg, 82%), mp (HCl salt) 164–166 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.12–7.09 (m, 2H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.83–6.79 (m, 2H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.73 (s, 3H), 3.03 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.73–2.59 (m, 6H), 2.12 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.87 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.80 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.30 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 158.2, 155.4, 142.1, 131.8, 129.1, 127.7, 126.6, 113.5, 112.8, 111.6, 57.3, 56.8, 54.2, 45.7, 41.3, 41.0, 35.9, 32.4, 24.4, 22.5, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H30NO2, 352.2277 (M+H)+; found, 352.2278. [α]20D –109.0° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H30ClNO2 • 0.5 H2O: C, 69.59; H, 7.87; N, 3.53. Found: C, 69.88; H, 8.22; N, 3.23.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-methylphenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-19). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-methylphenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (460 mg, 72%), mp (HCl salt) 305–306 °C (dec). 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.09 (s, 4H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.56 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.05 (dd, J = 5.7, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.93 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.79–2.60 (m, 6H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 2.13 (td, J = 12.4, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 1.90 (td, J = 6.9, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 1.82 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.35 (s, 3H), 1.32 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 156.9, 143.7, 138.3, 136.8, 130.1, 129.6, 129.2, 128.1, 114.3, 113.1, 58.7, 58.2, 47.2, 42.9, 42.5, 37.4, 34.4, 26.0, 24.0, 21.1, 14.6. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H30NO, 336.2327 (M+H)+; found, 336.2324. [α]20D –110.8° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H30ClNO • 0.05 H2O: C, 74.09; H, 8.14; N, 3.76. Found: C, 74.10; H, 8.18; N, 3.74.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(4-hydroxyphenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-20). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 4-hydroxyphenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (170 mg, 52%), mp (HCl salt) 300–302 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.03–6.99 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.70–6.66 (m, 3H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.03 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 2.96–2.83 (m, 2H), 2.73–2.59 (m, 6H), 2.11 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.87 (dt, J = 7.0, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 1.80 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 0.85 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.40, 155.35, 142.1, 130.5, 129.1, 127.7, 126.6, 114.8, 112.8, 111.6, 57.2, 56.9, 45.7, 41.3, 40.9, 35.9, 32.4, 24.4, 22.4, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H28NO2, 338.2120 (M+H)+; found, 338.2122. [α]20D –120° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1Anal. Calcd. For C22H28ClNO2 • 0.05 H2O • 0.2 C3H8O: C, 70.17; H, 7.74; N, 3.62. Found: C, 70.24; H, 7.83; N, 3.70.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2,4-dichlorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-21). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2,4-dichlorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (220 mg, 61%), Mp (HCl salt) 240–241 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.39 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.23 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.01 (dt, J = 5.6, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 2.96–2.89 (m, 2H), 2.87–2.83 (m, 1H), 2.77–2.71 (m, 1H), 2.68 (t, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 2.63–2.56 (m, 2H), 2.13 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.87 (tt, J = 7.0, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 1.79 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.29–1.25 (m, 1H), 0.84 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 136.4, 134.3, 132.4, 131.8, 128.6, 127.7, 127.0, 126.6, 112.8, 111.6, 57.6, 54.3, 45.6, 41.4, 41.0, 35.9, 30.6, 24.5, 22.9, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H26Cl2NO, (M+H)+ 390.1391; found, 390.1387. [α]20D –95.6° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H26Cl3NO • 0.55 H2O: C, 61.56; H, 6.09; N, 3.12. Found: C, 61.59; H, 6.17; N, 3.03.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2,6-dichlorophenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-22). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 2,6-dichlorophenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (245 mg, 66%), mp (HCl salt) 241–243 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.34 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.17 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.21–3.13 (m, 2H), 3.10 (t, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.93 (d, J = 18.4 Hz, 1H), 2.73 (dtd, J = 17.4, 11.5, 5.4 Hz, 3H), 2.59 (td, J = 11.9, 5.1 Hz, 1H), 2.19 (td, J = 12.4, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 1.93–1.87 (m, 1H), 1.83 (dt, J = 12.9, 6.5 Hz, 1H), 1.34–1.31 (m, 4H), 0.86 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.1, 135.18, 135.07, 128.26, 128.08, 127.7, 126.4, 112.8, 111.6, 57.7, 52.2, 45.8, 41.2, 40.7, 35.8, 28.8, 24.4, 23.0, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H26Cl2NO, (M+H)+ 390.1391; found, 390.1389. [α]20D –89.1° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H26Cl3NO • 0.4 H2O • 0.2 C3H8O: C, 60.86; H, 6.42; N, 3.14. Found: C, 60.92; H, 6.35; N, 3.07.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(phenethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-23). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with phenethyl bromide. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (244 mg, 64%), mp (HCl salt) 277–280 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.27–7.19 (m, 4H), 7.18–7.14 (m, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.07 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.97–2.90 (m, 1H), 2.83–2.76 (m, 3H), 2.73–2.63 (m, 3H), 2.15 (td, J = 12.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (ddd, J = 6.4, 5.8, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (dt, J = 13.0, 6.5 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.31 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 0.86 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.1, 139.8, 128.24, 128.05, 127.7, 126.5, 125.8, 112.8, 111.6, 57.4, 56.5, 45.7, 41.2, 40.9, 35.8, 33.3, 24.4, 22.5, 13.0. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H28NO, 322.2171 (M+H)+; found, 322.2170. [α]20D –101.5° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H28ClNO • 0.05 H2O: C, 73.64; H, 7.89; N, 3.90. Found: C, 73.67; H, 7.79; N, 3.83.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(phenylpropyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-24). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with phenylpropyl bromide. The product (−)-24 was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (255 mg, 80%), mp (HCl salt) 209–211 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.26–7.22 (m, 2H), 7.19–7.12 (m, 3H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (dd, J = 8.3, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.06 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.87 (d, J = 18.5 Hz, 1H), 2.72–2.56 (m, 6H), 2.15 (td, J = 12.6, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 1.90–1.75 (m, 4H), 1.34–1.31 (m, 4H), 0.84 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.6, 141.8, 141.5, 128.0, 127.8, 125.9, 125.6, 113.0, 111.6, 57.4, 53.7, 45.8, 40.8, 40.5, 35.7, 33.2, 28.1, 24.3, 22.5, 12.9. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H30NO, (M+H)+ 336.2327; found, 336.2329. [α]20D –73.1° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H30ClNO • 0.2 H2O: C, 73.56; H, 8.16; N, 3.73. Found: C, 73.57; H, 8.02; N, 3.64.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(cinnamyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-25). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with cinnamyl bromide. The product (−)-25 was obtained as an off-white foam (200 mg, 66%), mp (HCl salt) 162–164 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.39–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.29–7.25 (m, 2H), 7.21–7.17 (m, 1H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.60–6.55 (m, 2H), 6.26 (dt, J = 15.8, 7.0 Hz, 1H), 3.37 (ddd, J = 13.4, 7.1, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 3.01–2.95 (m, 2H), 2.65 (dd, J = 18.4, 6.0 Hz, 1H), 2.59–2.55 (m, 1H), 2.12 (td, J = 12.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 1.79 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.30 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.83 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.2, 136.8, 133.4, 128.2, 127.7, 127.2, 126.6, 125.9, 125.4, 112.8, 111.6, 57.2, 56.8, 45.4, 41.3, 41.0, 35.9, 24.5, 22.5, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H28NO, (M+H)+ 334.2171; found, 334.2171. [α]20D –118.3° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H28ClNO • 0.5 H2O: C, 72.9; H, 7.71; N, 3.70. Found: C, 73.00; H, 7.52; N, 3.48.
- (1R,5R,9R)-3-(2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)ethyl)-6,11-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-26). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 3-(2-bromoethyl)-1H-indole. The product was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (250 mg, 80%), mp 115–118 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.52 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.08–7.04 (m, 2H), 6.98 (td, J = 7.5, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.13 (dd, J = 5.5, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 2.98–2.92 (m, 3H), 2.90–2.85 (m, 1H), 2.81 (dd, J = 10.7, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.71–2.65 (m, 2H), 2.19–2.13 (m, 1H), 1.92 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 1.85 (dt, J = 13.0, 6.5 Hz, 1H), 1.35–1.32 (m, 4H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.1, 136.7, 127.7, 127.2, 126.5, 121.6, 120.9, 118.1, 117.7, 112.8, 112.3, 111.6, 110.8, 57.2, 55.4, 45.8, 41.2, 40.9, 35.9, 24.4, 22.63, 22.50, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C24H29N2O, (M+H)+ 361.2280; found, 361.2285. [α]20D –78.5° (c 1.0, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C24H28N2O • 0.7 H2O • 0.25 CHCl3: C, 72.28; H, 7.42; N, 6.95. Found: C, 72.37; H, 7.51; N, 6.80.
- 1-((1R,5R,9R)-8-Hydroxy-6,11-dimethyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-3(2H)-yl)-2-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)ethan-1-one (−)-27). To a stirred solution of 2-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)acetic acid (219 mg, 1.05 equiv, 1.39 mmol), N,N-diisopropylethylamine (685 mg, 923 µL, 4 equiv, 5.30 mmol) and (−)-2•bromocamphorsulfonate (700 mg, 1 equiv, 1.32 mmol) in DMF at 0 °C, HATU (529 mg, 1.05 equiv, 1.39 mmol) was added. The reaction was stirred for 16 h. The reaction was diluted with water, and saturated NaHCO3 was added to it to adjust the pH to ~8.5. The aqueous solution was extracted with CHCl3/MeOH (9/1). The organic extractions were combined and washed with H2O (3 × 20 mL) to remove DMF. The organic extractions were then washed with brine (2 × 20 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The crude residue was purified by flash chromatography (2–25% CMA in CHCl3) to give (−)-27 as an off-white foam (400 mg, 97%). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 2.96 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 2.91–2.83 (m, 3H), 2.67–2.47 (m, 4H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.08 (td, J = 12.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 2.00 (t, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (qd, J = 7.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (ddd, J = 15.4, 11.3, 3.9 Hz, 3H), 1.45 (dd, J = 10.2, 5.7 Hz, 2H), 1.31–1.26 (m, 7H), 0.84 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.1, 127.7, 126.5, 112.8, 111.6, 57.0, 55.2, 52.0, 45.7, 44.9, 41.3, 40.9, 35.9, 33.5, 33.1, 31.64, 31.56, 24.4, 22.3, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H33N2O2, (M+H)+ 357.2542; found, 357.2539.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(2-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-28). Amide (−)-27 (0.307 g, 1 equiv, 861 µmol) was dissolved in THF (7 mL). To this, a freshly prepared borane solution (2.58 mL, 4 molar, 12 equiv, 10.03 mmol) was added. The solution was heated at 60 °C for 24 h. The reaction was quenched with anhydrous MeOH at 0 °C and stirred for 30 min. The solvent was removed in vacuo and then redissolved in MeOH and acidified with 2N HCl. The mixture was refluxed for 4 h. The reaction was cooled to room temperature and then basified with NH4OH solution to pH 9. The aqueous solution was extracted with CHCl3: MeOH (9:1). The organic layers were washed with brine and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and solvent removed in vacuo to give (−)-28 as a white solid (170 mg, 58%), mp (HCl salt) 309–310 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 6.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 2.96 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 2.91–2.83 (m, 3H), 2.67–2.47 (m, 4H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.08 (td, J = 12.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 2.00 (t, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 1.84 (qd, J = 7.5, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (ddd, J = 15.4, 11.3, 3.9 Hz, 3H), 1.45 (dd, J = 10.2, 5.7 Hz, 2H), 1.31–1.26 (m, 7H), 0.84 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 142.1, 127.7, 126.5, 112.8, 111.6, 57.0, 55.2, 52.0, 45.7, 44.9, 41.3, 40.9, 35.9, 33.5, 33.1, 31.64, 31.56, 24.4, 22.3, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C22H35N2O, (M+H)+ 343.2749; found, 343.2746. [α]20D –87.5° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C22H36Cl2N2O • 0.2 C3H8O • 1.15 H2O: C, 60.57; H, 8.97; N, 6.25. Found: C, 60.57; H, 8.99; N, 6.26.
- (1R,5R,9R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-(3-(4-nitrophenyl)propyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol ((−)-31). General procedure was used, and the alkylation was achieved with 30 as the alkylating agent (obtained from 3-(4-nitrophenyl)propan-1-ol, 29). The product (−)-31 was obtained as a pale-yellow solid (252 mg, 70%), mp (HCl salt) 265–266 °C (dec). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 8.15–8.11 (m, 2H), 7.46–7.42 (m, 2H), 6.85 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 2.92 (dd, J = 5.6, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 2.85 (d, J = 18.3 Hz, 1H), 2.76 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 2.65–2.45 (m, 4H), 2.06 (td, J = 12.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 1.90–1.80 (m, 3H), 1.76 (td, J = 12.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.30 (s, 3H), 1.27 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 0.82 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 155.4, 150.2, 146.3, 142.2, 129.11, 129.06, 127.6, 126.6, 123.1, 112.7, 111.6, 57.2, 53.7, 45.6, 41.4, 41.0, 35.9, 33.1, 28.0, 24.5, 22.5, 13.1. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C23H29N2O3, (M+H)+ 381.2178; found, 381.2174. [α]20D –77.5° (c 1.1, CHCl3/MeOH (9/1)). Anal. Calcd. For C23H29ClN2O3 • 0.05 H2O: C, 66.11; H, 7.02; N, 6.70. Found: C, 65.97; H, 6.75; N, 6.62.
- 3-(4-Nitrophenyl)propyl methanesulfonate (30). 3-(4-Nitrophenyl)propan-1-ol (510 mg, 1 equiv, 2.81 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane (15 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. Triethylamine (427 mg, 588 µL, 1.5 equiv, 4.22 mmol) and methanesulfonyl chloride (355 mg, 241 µL, 1.1 equiv, 3.10 mmol) were added to it, and the reaction was stirred at 0 °C for 1 h. The reaction was diluted with water and extracted with dichloromethane (15 mL). The organic layer was washed with saturated NaHCO3 (15 mL) and brine (15 mL) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The organic layer was filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo to give a pale-yellow oil. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography (0–80% EtOAc/hexanes) to give 30 as a pale-yellow oil that solidified on standing (700 mg, 96%). 1HNMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 8.16–8.13 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.44 (m, 2H), 4.24 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 2H), 3.05 (s, 3H), 2.86 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.11–2.04 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CD3OD): δ 148.9, 146.5, 129.2, 123.2, 69.1, 35.6, 31.0, 30.0. HRMS (ES+) Calcd. For C10H13NO5S, (M+Na)+ 282.0412; found, 282.0413.
- rac-8-Methoxy-6,11-dimethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocine (32) [29]. 6,11-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol (rac-normetazocine, (rac-1), 10 g, 1 equiv, 46 mmol) and potassium carbonate (13 g, 2 equiv, 92 mmol) were added to H2O (0.15 L), and the mixture was cooled to 0 °C for 20 min. In a separate Erlenmeyer flask, di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (10 g, 11 mL, 1 equiv, 46 mmol) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (75 mL). This solution was added to the aqueous mixture, and the reaction was warmed at 23 °C over the course of 18 h. The organic products were extracted with CHCl3 3x, and the organic solution was washed with 1M HCl and brine. The combined organic phase was dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo to provide tert-butyl 8-hydroxy-6,11-dimethyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocine-3(2H)-carboxylate (15 g, 47 mmol, 100%) as a yellow/orange oil. The tert-butyl compound, as a crude oil (15 g, 1 equiv, 46 mmol), was dissolved in 2N NaOH (94 mL) and cooled to 0 °C for 20 min. Dimethyl sulfate (5.8 g, 4.4 mL, 1 equiv, 46 mmol) was added, and the mixture kept at 23 °C for 4 h. Diethyl ether was added to dilute the reaction, and the aqueous phase extracted 3x with diethyl ether. The combined organic phase was washed with brine and concentrated in vacuo to a white foam. The foam was dissolved in 1M HCl (0.11 L) and methanol (0.11 L) and kept at 50 °C until TLC showed full conversion. Volatiles and H2O were removed in vacuo to provide rac-normetazocine methyl ether 32 (7.65 g, 33.1 mmol, 72%) as a foam. 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.06 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.80 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 3.23–3.05 (m, 3H), 2.74 (td, J = 13.3, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.15 (dd, J = 7.0, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 1.99 (dd, J = 13.7, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.51 (dd, J = 14.0, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 1.42 (s, 3H), 0.88 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; cdcl3): δ 158.8, 140.4, 128.7, 125.0, 111.9, 111.5, 55.2, 52.2, 38.6, 37.71, 37.54, 35.5, 27.1, 24.8, 13.1. The NMR spectra corresponded to those in the literature [29].
- rac-8-Methoxy-6,11-dimethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-1(2H)-one (33). In an argon-charged flame-dried flask, CrO3 (7.5 g, 1.5 equiv, 74.6 mmol) was dissolved in 10:1 H2O: H2SO4, 330 mL. To this, the methyl ether 32 (13 g, 1 equiv, 57.4 mmol) in 330 mL of 10:1 H2O: H2SO4, was added rapidly, and the mixture was refluxed for 5 h. The mixture was cooled and basified with NH4OH to pH 9. The chromium precipitate (grey solid) was filtered off. The filtrate was extracted 2x with EtOAc. The organic phase was washed with brine, dried, and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified via flash chromatography with CMA (50:45:5) to provide 8.9 g (63% yield) of the ketone 33 as a yellow syrup. 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 8.05 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.89 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H), 3.28 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 2.75 (ddd, J = 12.0, 5.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 2.60 (td, J = 12.4, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 2.18–2.08 (m, 2H), 1.92 (td, J = 12.9, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 1.49 (ddd, J = 13.0, 3.2, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 1.44 (s, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CDCl3): δ 198.8, 164.8, 149.4, 128.1, 127.6, 112.0, 111.6, 63.2, 55.3, 43.6, 40.8, 39.2, 37.8, 25.9, 14.2, 13.7. HRMS: [C15H19NO2]H+ Calcd: 246.1494; Found: 246.1490. NMR spectra corresponded to those in the literature [29].
- rac-8-Methoxy-6,11-dimethyl-3-phenethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-1(2H)-one (rac-34). In a flame-dried flask, the C8-ketone 33 (8.9 g, 1 equiv, 36 mmol), (2-bromoethyl) benzene (20 g, 15 mL, 3 equiv, 0.11 mol), and potassium carbonate (20 g, 4 equiv, 0.15 mol) were added to acetonitrile (120 mL). The mixture was heated at 80 °C for 18 h. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite to remove the remaining potassium carbonate. The filtrate was concentrated in vacuo, and the residual material was purified by flash chromatography using 30% ethyl acetate in hexanes. The N-phenethyl compound rac-34 (10.2 g, 29.2 mmol, 80%) was isolated as a light brown oil. The oil was concentrated overnight in vacuo to give a light-yellow solid. 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.99 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.25–7.20 (m, 4H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 6.82 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.77 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 3H), 3.23 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 3.01–2.94 (m, 1H), 2.80–2.73 (m, 3H), 2.56–2.49 (m, 1H), 2.10 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 3H), 1.40 (s, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz; CDCl3): δ 194.9, 164.7, 149.1, 140.4, 128.8, 128.2, 127.95, 127.83, 125.9, 111.9, 67.4, 57.1, 55.4, 46.3, 44.1, 41.6, 37.5, 34.0, 25.6, 13.7. NMR spectra agreed with those in the literature [29].
- (2R,6S,11S)-8-Methoxy-6,11-dimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-1-ol ((2R,6S,11S)-(+)-35). In a flame-dried flask, (+)-34 (0.580 g, 1 equiv, 1.66 mmol) was dissolved in THF (10 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. Lithium aluminum hydride (75.6 mg, 1.2 equiv, 1.99 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm slowly to room temperature. The reaction was quenched successively with iPrOH, MeOH and water, followed by dilution with CHCl3. The heterogeneous mixture was diluted further with brine and extracted 3x with CHCl3. The combined organic phases were washed with ammonium chloride, dried, and the concentrated residue was purified by flash chromatography. The alcohol (+)-35 (0.508 g, 1.45 mmol, 87.1%) was isolated as a colorless oil, and only a single diastereomer was observed in the NMR. The optical rotation was essentially the same as that determined for (−)-35, except for the sign of rotation, as expected for an enantiomeric pair. [α]25D = +52.3° (c, 2.8, MeOH). 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.47 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.22–7.18 (m, 3H), 6.80 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 3.14–3.08 (m, 1H), 2.93–2.86 (m, 2H), 2.78 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.49 (dd, J = 9.9, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 2.08–2.02 (m, 1H), 1.83–1.76 (m, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.01 (dt, J = 13.0, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.82 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 158.86, 141.26, 140.04, 132.89, 128.70, 128.38, 126.09, 111.22, 110.89, 63.80, 62.96, 55.98, 55.11, 43.61, 37.61, 37.54, 37.19, 35.95, 25.98, 13.03. HRMS [C23H29NO2]H+ Calcd: 352.2277; Found: 352.2277.
- (2S,6R,11R)-8-Methoxy-6,11-dimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-1-ol (2S,6R,11R-(−)-35). In a flame-dried flask, (−)-34 (0.550 g, 1 equiv, 1.57 mmol) was dissolved in THF (10 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. Lithium aluminum hydride (71.7 mg, 1.2 equiv, 1.89 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm slowly to room temperature. The reaction was quenched successively with iPrOH, MeOH and H2O, followed by addition of CHCl3. Brine was added to the heterogeneous mixture, and it was extracted 3x with CHCl3. The combined organic phases were washed with NH4OH, dried, and purified by flash chromatography. The alcohol (−)-35 (0.398 g, 1.13 mmol, 71.9%) was isolated as a colorless oil, [α]25D –51.7° (c, 2.08, MeOH). 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.47 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.22–7.18 (m, 3H), 6.80 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 3.11 (dt, J = 13.0, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 2.93–2.86 (m, 2H), 2.78 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.49 (dd, J = 9.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 2.08–2.02 (m, 1H), 1.83–1.76 (m, 1H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.01 (dt, J = 13.0, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 0.82 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 158.87, 141.25, 140.04, 132.89, 128.69, 128.38, 126.08, 111.23, 110.89, 63.81, 62.96, 55.98, 55.11, 43.62, 37.61, 37.54, 37.20, 35.96, 25.98, 13.03. HRMS: [C23H29NO2]H+ Calcd: 352.2277; Found: 352.2279.
- (2R,6S,11S)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocine-1,8-diol (2R,6S,11S-(+)-36). In a flame-dried flask, the aromatic ether (+)-35 (0.493 g, 1 equiv, 1.40 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (10 mL) and cooled to –78 °C. To this solution, boron tribromide (703 mg, 265 µL, 2 equiv, 2.81 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction was cooled to 0 °C and quenched with MeOH followed by 2M HCl. The reaction was allowed to stir for 1 h and then basified with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. The aqueous phase was separated and extracted 3x with CHCl3, followed by washing the combined organic phases with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. After drying, the organic phase was concentrated in vacuo, and the residue purified via flash chromatography, eluting with 7% CMA in CHCl3, to give the phenol (+)-36 (0.312 g, 925 µmol, 65.9%) as a white foam, [α]25D +58.1° (c 1.14, MeOH). 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.40 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.31–7.18 (m, 8H), 6.72–6.69 (m, 2H), 6.63 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 3.54 (s, 1H), 3.11 (td, J = 10.8, 5.3 Hz, 2H), 2.93–2.86 (m, 3H), 2.78 (q, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 2.51 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 2.04 (dq, J = 10.6, 3.5 Hz, 2H), 1.83–1.75 (m, 2H), 1.34 (s, 1H), 1.31 (d, J = 12.9 Hz, 4H), 1.01 (dt, J = 13.0, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 0.82 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 154.99, 141.50, 139.99, 132.58, 130.07, 128.75, 128.68, 128.62, 128.40, 128.36, 126.11, 113.64, 111.53, 63.81, 62.91, 55.97, 43.60, 37.52, 37.49, 37.14, 35.93, 25.95, 13.00. HRMS: [C22H28NO2]+ Calcd: 338.2120; Found: 338.2116. The HCl salt of the phenol (+)-36 was formed by dissolving the free base in a minimal amount of acetone, followed by the addition of 6 drops of concentrated HCl. The solution was concentrated to a thick wax that was triturated in diethyl ether at room temperature overnight to provide the HCl salt as a free-flowing off-white solid. Anal. Calcd. For C22H28ClNO2 • 0.7 H2O: C, 68.36; H, 7.67; N, 3.62. Found C, 68.53; H, 7.81; N, 3.45.
- (2S,6R,11R)-6,11-Dimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocine-1,8-diol (2S,6R,11R)-(−)-36. In a flame-dried flask, the aromatic ether ((−)-35 (0.396 g, 1 equiv, 1.13 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (10 mL) and cooled to –78 °C. To this solution, boron tribromide (0.564 mg, 213 µL, 2 equiv, 2.25 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction was cooled to 0 °C and quenched with MeOH followed by 2M HCl. The reaction was allowed to stir for 1 h and then basified with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. The aqueous phase was extracted 3x with CHCl3, and the combined organic phases were washed with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. After drying, the organic phase was purified by flash chromatography, eluting with 7% CMA in CHCl3, to give (−)-36 as a white foam (0.190 g, 563 µmol, 50.0%). [α]25D –57.4° (c 1.45, MeOH) 1H-NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.40 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.31–7.16 (m, 8H), 6.70 (td, J = 6.0, 2.8 Hz, 2H), 6.63 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 4.17 (s, 1H), 3.54 (s, 1H), 3.11 (dt, J = 13.0, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 2.89 (dq, J = 11.4, 7.2 Hz, 3H), 2.82–2.74 (m, 3H), 2.50 (t, J = 4.5 Hz, 2H), 2.04 (dtd, J = 14.2, 7.2, 3.5 Hz, 2H), 1.86–1.75 (m, 2H), 1.36–1.33 (m, 2H), 1.30 (s, 3H), 1.01 (dt, J = 12.9, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 0.88 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 0.82 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.12, 141.48, 139.97, 132.39, 130.07, 128.75, 128.68, 128.61, 128.40, 128.37, 126.12, 126.09, 113.69, 111.73, 111.56, 73.50, 63.83, 62.90, 59.67, 57.78, 55.96, 43.60, 37.49, 37.13, 35.92, 25.96, 14.38, 13.00.
- (2S,6R,11R)-8-Methoxy-1,6,11-trimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-1-ol (2S,6R,11R-(−)-37). In an argon-charged, flame-dried flask, ((−)-34 (0.5 g, 1 equiv, 1 mmol) was dissolved in THF (15 mL) and cooled to –78 °C. Methyllithium (0.09 g, 3 mL, 1.3 molar, 3 equiv, 4 mmol) was added, and the reaction was warmed to room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was quenched with a concentrated NH4Cl solution, and it was extracted with CHCl3. The aqueous phase was separated and extracted with CHCl3 2x, and the combined organic phases were washed with brine. The organic phase was then dried with sodium sulfate, filtered, and purified via flash chromatography.to give (−)-37 as a dark amber oil (0.454 g, 1.24 mmol, 90%). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.52 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.32–7.25 (m, 3H), 7.24–7.19 (m, 3H), 6.83 (dt, J = 8.6, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 3.80 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H), 3.14–3.07 (m, 1H), 2.98–2.89 (m, 2H), 2.82–2.73 (m, 3H), 2.66–2.42 (m, 4H), 2.15 (qd, J = 7.2, 3.4 Hz, 1H), 1.82 (td, J = 13.2, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 1.54 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 3H), 1.34 (d, J = 10.3 Hz, 3H), 0.95 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 3H). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 128.85, 128.70, 128.42, 128.15, 127.79, 126.15, 111.64, 110.83, 69.26, 67.29, 60.31, 55.76, 55.10, 55.08, 43.38, 43.34, 37.97, 37.95, 36.99, 35.99, 33.62, 26.32, 23.69, 16.35. HRMS: [C24H32NO2]+ Calcd: 366.2433; found: 366.2437.
- (2R,6S,11S)-8-Methoxy-1,6,11-trimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-1-ol (2R,6S,11S-(+)-37). In an argon-charged flame-dried flask, (+)-34 (0.5 g, 1 equiv, 1 mmol) was dissolved in THF (15 mL) and cooled to –78 °C. Methyllithium (0.09 g, 3 mL, 1.3 molar, 3 equiv, 4 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction mixture was quenched with a concentrated aqueous NH4Cl solution and extracted with CHCl3. The aqueous phase was separated and extracted 2x with CHCl3, and the combined organic phases were washed with brine. The organic phase was then dried with sodium sulfate, filtered, and purified by flash chromatography to give (+)-37 as a dark amber oil (0.51 g, 1.4 mmol, 100%). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.52 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.31–7.23 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.19 (m, 3H), 6.84 (dt, J = 8.6, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H), 3.13–3.06 (m, 1H), 2.98–2.88 (m, 2H), 2.84–2.77 (m, 2H), 2.65 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 2.59–2.45 (m, 2H), 2.15 (qd, J = 7.0, 3.4 Hz, 1H), 1.81 (td, J = 13.2, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 1.53 (s, 3H), 1.33 (s, 3H), 1.07–1.04 (m, 1H), 0.95 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 158.67, 140.41, 128.82, 128.69, 128.40, 128.21, 127.77, 126.13, 111.88, 111.64, 110.82, 69.25, 67.27, 55.80, 55.10, 43.42, 38.09, 38.07, 37.99, 37.02, 36.03, 33.62, 26.33, 16.36. HRMS: [C24H32NO2]+ Calcd: 366.2433; found: 366.2433.
- (2R,6S,11S)-6,11-Dimethyl-1-methylene-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol (2R,6S,11S-(+)-38). In a flame-dried flask, (+)-37 (0.5 g, 1 equiv, 1 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (7 mL) and cooled to –78 °C. To this solution, boron tribromide (498 mg, 0.188 mL, 1 equiv, 1.99 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction was quenched with MeOH followed by an equal volume of 2M HCl. The solution was heated to 75 °C for 2 h, followed by addition of a sodium bicarbonate to a pH of 7.5–8. The aqueous phase was extracted with CHCl3 3x. The combined organic phases were washed with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and brine, then dried with sodium sulfate. The organic phase was purified by flash chromatography, eluting with 15% CMA in CHCl3 to give (+)-38. 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.53 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.23–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.13 (td, J = 6.8, 2.9 Hz, 3H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.60 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (s, 1H), 4.80 (s, 1H), 3.33 (s, 1H), 3.30 (t, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.83 (dq, J = 6.6, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.76–2.68 (m, 2H), 2.61–2.57 (m, 1H), 2.46–2.41 (m, 1H), 1.97–1.90 (m, 2H), 1.84 (dt, J = 12.7, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 1.34–1.31 (m, 3H), 0.78 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CD3OD): δ 157.92, 142.09, 140.03, 136.67, 128.27, 128.02, 126.59, 125.70, 123.34, 113.34, 111.82, 110.61, 65.90, 56.79, 45.86, 41.80, 41.78, 36.94, 33.12, 24.66, 13.24. HRMS: [C23H28NO]+ Calculated: 334.2171; Found: 334.2165. The HCl salt of (+)-38 was obtained by dissolving the free base in a minimal amount of acetone. The solution was concentrated to a pale syrup in vacuo, followed by addition of diethyl ether. The mixture was stirred overnight to give (+)-38•HCl as a pale beige solid. Anal. Calcd. For C23H28ClNO • 0.7 H2O C, 72.21; H, 7.75; N, 3.66. Found C, 72.13; H, 7.55; N, 3.55.
- (2S,6R,11R)-6,11-Dimethyl-1-methylene-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol (2S,6R,11R-(−)-38). In a flame-dried flask, (−)-37 (0.454 g, 1 equiv, 1.24 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (7 mL) and cooled to –78 °C. To this solution, boron tribromide (615 mg, 0.232 mL, 1.98 equiv, 2.45 mmol) was added, and the reaction was allowed to warm to room temperature. The reaction was quenched with MeOH followed by an equal volume of 2M HCl. The solution was heated to 75 °C for 2 h, followed by addition of a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution to a pH of 7.5–8. Chloroform was added, and the aqueous phase was extracted with CHCl3 3x. The combined organic phase was washed with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and brine, then dried with sodium sulfate. The organic phase was purified by flash chromatography, eluting with 15% CMA in CHCl3 to give (−)-38 (0.125 g, 375 µmol, 30.2%). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CD3OD): δ 7.55 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.25–7.22 (m, 2H), 7.17–7.12 (m, 3H), 6.67 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.60 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.71 (s, 1H), 4.84 (s, 1H), 3.34 (d, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (dt, J = 11.6, 5.7 Hz, 1H), 2.79–2.68 (m, 2H), 2.65–2.61 (m, 1H), 2.47 (td, J = 13.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H), 2.00–1.91 (m, 2H), 1.85 (td, J = 12.8, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.34 (s, 3H), 0.80 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CD3OD): δ 159.35, 143.52, 141.46, 138.12, 129.69, 129.44, 128.04, 127.12, 124.76, 114.74, 113.21, 112.05, 67.35, 58.22, 47.30, 43.23, 43.21, 38.37, 34.53, 26.05, 14.61. HRMS: [C23H28NO]+ Calcd: 334.2171; found: 334.2165. The -(−)-38•HCl salt was formed by dissolving the free base in a minimal amount of acetone. The solution was concentrated to a pale syrup, and diethyl ether was added. The mixture was stirred overnight to give (−)-38•HCl as a pale beige solid. Anal. Calcd. For C23H28ClNO • 0.4 H2O C, 73.25; H, 7.70; N, 3.71. Found: C, 73.24; H, 7.82; N, 3.57.
- (2R,6S,11S)-1,6,11-Trimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol (2R,6S,11S-(+)-39). In a Parr Shaker flask, (+)-38 (0.107 g, 1 equiv, 321 µmol), palladium on carbon (205 mg, 5% wt, 0.3 equiv, 96.3 µmol), and acetic acid (18.4 µL, 1 equiv, 321 µmol) were dissolved in methanol (10 mL) under an argon atmosphere. The vessel was charged with 30 psi of hydrogen gas and shaken overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite and rinsed multiple times with methanol. The filtrate was purified via flash chromatography to give (+)-39 as a light brown foam (56 mg, 0.17 mmol, 52%). 1H NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.29–7.25 (m, 2H), 7.22–7.19 (m, 3H), 7.05 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 6.76–6.73 (m, 2H), 3.22 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 3.05–2.93 (m, 5H), 2.89 (dd, J = 12.2, 3.9 Hz, 1H), 2.26 (td, J = 12.6, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 2.19–2.13 (m, 1H), 2.11 (s, 2H), 1.95 (td, J = 13.3, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.37 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 3H), 1.29 (s, 3H), 0.87 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.80, 141.25, 138.45, 130.41, 128.76, 128.61, 128.20, 126.57, 114.10, 112.31, 64.12, 55.48, 45.33, 40.38, 39.36, 36.13, 32.46, 25.47, 24.12, 15.36. HRMS: [C23H30NO]+ Calcd: 336.2327; Found: 336.2327. The free base was dissolved in a minimal amount of acetone, and 6 drops of concentrated HCl was added. Upon stirring, a syrup formed. Diethyl ether was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight to give (+)-39. HCl as an off-white solid (32 mg), mp 178–181 °C, [α]25D = +70.7° (c 0.39, MeOH). Anal. Calcd. For C23H30ClNO • 0.75 H2O C, 71.67; H, 8.24; N, 3.63. Found: C, 71.83; H, 8.40; N:3.54.
- (2S,6R,11R)-1,6,11-Trimethyl-3-phenethyl-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzo[d]azocin-8-ol (2S,6R,11R-(−)-39). In a Parr Shaker flask, (−)-38 (0.120 g, 1 equiv, 360 µmol), palladium on carbon (230 mg, 5% wt, 0.3 equiv, 108 µmol), and acetic acid (20.6 µL, 1 equiv, 360 µmol) were added to methanol (10 mL) under an argon atmosphere. The vessel was charged with 30 psi of hydrogen gas and shaken overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite and rinsed multiple times with methanol. The filtrate was purified via flash chromatography to give (−)-39 as a light brown foam (71 mg, 0.21 mmol, 59%), 1H NMR (400 MHz; CDCl3): δ 7.31–7.27 (m, 2H), 7.27–7.20 (m, 3H), 7.07 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 6.83–6.81 (m, 2H), 3.32 (s, 1H), 3.13–3.00 (m, 4H), 3.00–2.94 (m, 1H), 2.41–2.35 (m, 2H), 2.16–2.08 (m, 2H), 1.40 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 3H), 1.33 (s, 2H), 0.89 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.84, 140.71, 137.58, 128.78, 128.74, 128.31, 126.86, 114.42, 112.38, 64.56, 55.44, 45.69, 39.72, 38.76, 35.96, 31.86, 25.19, 24.08, 15.24. HRMS: [C23H30NO]+ Calcd: 336.2327; Found: 336.2326. The free base was dissolved in a minimal amount of acetone, and 6 drops of concentrated HCl was added. Diethyl ether was added to the syrup that was obtained, and the mixture was stirred overnight to give (−)-39•HCl as an off-white solid (57 mg), mp 181–184 °C, [α]25D –69.1° (c 0.59, MeOH). Anal. Calcd. For C23H30ClNO • 0.75 H2O C, 71.67; H, 8.24; N, 3.63. Found: C, 71.73; H, 8.34; N, 3.48.
3.3. X-ray Crystal Structure Experimental Data
3.4. In Vitro Assay
3.4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
3.4.2. Forskolin-Induced cAMP Accumulation Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MOR | mu-opioid receptor |
| DOR | delta-opioid receptor |
| KOR | kappa-opioid receptor |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| cAMP assay | Inhibition of forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation assay |
References
- May, E.L.; Murphy, J.G. Structures Related to Morphine. III. Synthesis of an Analog of N-Methylmorphinan. J. Org. Chem. 1955, 20, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ager, J.H.; May, E.L. Structures Related to Morphine. XIII. 2-Alkyl-2′-hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-6,7-benzomorphans and a More Direct Synthesis of the 2-Phenethyl Compound (NIH 7519). J. Org. Chem. 1960, 25, 984–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, M.; Motoike, S.; Yokota, C.; Usuki, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Urabe, T.; Katarao, K.; Hide, I.; Tanaka, S.; Kawamoto, M.; et al. SKF-10047, a prototype Sigma-1 receptor agonist, augmented the membrane trafficking and uptake activity of the serotonin transporter and its C-terminus-deleted mutant via a Sigma-1 receptor-independent mechanism. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 139, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, M.D.; May, E.L. Antinociceptive Studies of Optical Isomers of N-Allylnormetazocine SKF 10,047. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1983, 91, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarin, M.K.; Dehaen, W.; Salehi, P.; Asl, A.A. Synthesis and Modification of Morphine and Codeine, Leading to Diverse Libraries with Improved Pain Relief Properties. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, D.C.; Strauss, M.J. Benzomorphans: Synthesis, stereochemistry reactions, and spectroscopic characterizations. Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquinucci, L.; Prezzavento, O.; Marrazzo, A.; Amata, E.; Ronsisvalle, S.; Georgoussi, Z.; Fourla, D.-D.; Scoto, G.M.; Parenti, C.; Arico, G.; et al. Evaluation of N-substitution in 6,7-benzomorphan compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4975–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanematsu, K.; Takeda, M.; Jacobson, A.E.; May, E.L. Synthesis of 6,7-benzomorphan and related nonquaternary carbon structures with marked analgetic activity. J. Med. Chem. 1969, 12, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A.E.; May, E.L. Structures Related to Morphine. XXVII. α- and β-5,9-Diethyl-2-methyl-6,7-benzomorphans. J. Med. Chem. 1964, 7, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, E.L.; Aceto, M.D.; Bowman, E.R.; Bentley, C.; Martin, B.R.; Harris, L.S.; Medzihradsky, F.; Mattson, M.V.; Jacobson, A.E. Antipodal α-N-(Methyl through Decyl)-N-Normetazocines (5,9α-Dimethyl-2′-hydroxy-6,7-benzomorphans): In Vitro and In Vivo Properties. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 3408–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A.E.; May, E.L. Structures related to morphine. XXXI. 2′-Substituted benzomorphans. J. Med. Chem. 1965, 8, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, G.; Turnaturi, R.; Parenti, C.; Spoto, S.; Piana, S.; Dichiara, M.; Zagni, C.; Galambos, A.R.; Essmat, N.; Marrazzo, A.; et al. New Insights into the Opioid Analgesic Profile of cis-(-)-N-Normetazocine-derived Ligands. Molecules 2023, 28, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, E.L.; Jacobson, A.E.; Mattson, M.V.; Traynor, J.R.; Woods, J.H.; Harris, L.S.; Bowman, E.R.; Aceto, M.D. Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo activity of (-)-(1R,5R,9R)- and (+)-(1S,5S,9S)-N-alkenyl-, -N-alkynyl-, and N--cyanoalkyl-5,9-dimethyl-2′-hydroxy-6,7-benzomorphan homologues. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 5030–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanAlstine, M.; Wentland, M.; Alvarez, J.; Cao, Q.; Cohen, D. Redefining the structure-activity relationships of 2,6-methano-3-benzazocines. Part 9: Synthesis, characterization and molecular modeling of pyridinyl isosteres of N-BPE-8-CAC (1), a high affinity ligand for opioid receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2128–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wentland, M.P.; VanAlstine, M.; Kucejko, R.; Lou, R.; Cohen, D.J.; Parkhill, A.L.; Bidlack, J.M. Redefining the Structure–Activity Relationships of 2,6-Methano-3-benzazocines. 4. Opioid Receptor Binding Properties of 8-[N-(4′-phenyl)-phenethyl)carboxamido] Analogues of Cyclazocine and Ethylketocycalzocine. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5635–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnaturi, R.; Chiechio, S.; Pasquinucci, L.; Spoto, S.; Costanzo, G.; Dichiara, M.; Piana, S.; Grasso, M.; Amata, E.; Marrazzo, A.; et al. Novel N-normetazocine Derivatives with Opioid Agonist/Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist Profile as Potential Analgesics in Inflammatory Pain. Molecules 2022, 27, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Irvin, T.C.; Herdman, C.A.; Hanna, R.D.; Hassan, S.A.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kaska, S.; Crowley, R.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Withey, S.L.; et al. The Intriguing Effects of Substituents in the N-Phenethyl Moiety of Norhydromorphone: A Bifunctional Opioid from a Set of “Tail Wags Dog” Experiments. Molecules 2020, 25, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, E.L.; Aceto, M.D.; Bowman, E.R.; Traynor, J.R.; Woods, J.H.; Jacobson, A.E.; Harris, L.S. Enantiomeric (-)-(1R,5R,9R and (+)-(1S,5S,9S) Heterocyclic N-Substituted-Normetazocines: Synthesis of Potent and Selective Antinociceptives and Opioid Antagonists by Modification of the N-Substituent. Med. Chem. Res. 2000, 10, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquinucci, L.; Turnaturi, R.; Aricò, G.; Parenti, C.; Pallaki, P.; Georgoussi, Z.; Ronsisvalle, S. Evaluation of N-substituent structural variations in opioid receptor profile of LP1. Bioorg. Med.Chem. 2016, 24, 2832–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, E.S.; Bow, E.; Li, F.; Sulima, A.; Kaska, S.; Crowley, R.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Lee, Y.-S.; Hassan, S.A.; Imler, G.H.; et al. G-Protein biased opioid agonists: 3-hydroxy-N-phenethyl-5-phenylmorphans with three-carbon chain substituents at C9. RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.R.; Sulima, A.; Luo, D.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Goldberg, A.; Xie, B.; Shi, L.; Paronis, C.A.; Bergman, J.; Selley, D.; et al. A Journey Through Diastereomeric Space: The Design, Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo Pharmacological Activity, and Molecular Modeling of Novel Potent Diastereomeric MOR Agonists and Antagonists. Molecules 2022, 27, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, J.A.; Sulima, A.; Gutman, E.S.; Bow, E.W.; Luo, D.; Kaska, S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Paronis, C.A.; Bergman, J.; Imler, G.H.; et al. Discovery of a Potent Highly Biased MOR Partial Agonist among Diastereomeric C9-Hydroxyalkyl-5-phenylmorphans. Molecules 2023, 28, 4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, W.A. Improved resolution of (+/−)-cis-2’-hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-6,7- benzomorphan and preparation of racemic, (+)-, and (−)-cis-2- methylcyclopropyl-2 ‘-hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-6,7-benzomorphan (cyclazocine). Synth. Commun. 1999, 29, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Rothman, R.B.; Dersch, C.M.; Deschamps, J.R.; Jacobson, A.E.; Rice, K.C. Probes for Narcotic Receptor Mediated Phenomena. 39. Enantiomeric N-Substituted Benzofuro[2,3-c]pyridin-6-ols: Synthesis and Topological Relationship to Oxide-Bridged Phenylmorphans. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7570–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, E.L.; Eddy, N.B. Structures Related to Morphine. XII.1 (±)-2′-Hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-2-phenethyl-6,7-benzomorphan (NIH 7519) and Its Optical Forms. J. Org. Chem. 1959, 24, 1435–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, E.L. Structures Related to Morphine. VI. N-Phenylethyl Derivatives of Some Phenyl- and Benz-morphans. J. Org. Chem. 1956, 21, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brine, G.A.; Berrang, B.; Hayes, J.P.; Carroll, F.I. An improved resolution of (±)-cis-N-normetazocine. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1990, 27, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, S.L.; Luo, D.; Kaska, S.; Niloy, K.K.; Jackson, K.; Sarma, R.; Horn, J.; Baynard, C.; Leggas, M.; Eduardo, R.; et al. Design, synthesis, and preliminary evaluation of a potential synthetic opioid rescue agent. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeyer, J.L.; Bidlack, J.M.; Zong, R.; Bakthavachalam, V.; Gao, P.; Cohen, D.J.; Negus, S.S.; Mello, N.K. Synthesis and Opioid Receptor Affinity of Morphinan and Benzomorphan Derivatives: Mixed κ Agonists and μ Agonists/Antagonists as Potential Pharmacotherapeutics for Cocaine Dependence. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.P.; Groer, C.E.; Young, D.; Ewald, A.W.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthesis and κ-Opioid Receptor Activity of Furan-Substituted Salvinorin A Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10464–10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, M.; Ward, G.W.; Sulima, A.; Luo, D.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Imler, G.H.; Kerr, A.T.; Jacobson, A.E.; Rice, K.C. Potent MOR Agonists from 2′-Hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-N-phenethyl Substituted-6,7-benzomorphans and from C8-Hydroxy, Methylene and Methyl Derivatives of N-Phenethylnormetazocine. Molecules 2023, 28, 7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237709
Das M, Ward GW, Sulima A, Luo D, Prisinzano TE, Imler GH, Kerr AT, Jacobson AE, Rice KC. Potent MOR Agonists from 2′-Hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-N-phenethyl Substituted-6,7-benzomorphans and from C8-Hydroxy, Methylene and Methyl Derivatives of N-Phenethylnormetazocine. Molecules. 2023; 28(23):7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237709
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Madhurima, George W. Ward, Agnieszka Sulima, Dan Luo, Thomas Edward Prisinzano, Gregory H. Imler, Andrew T. Kerr, Arthur E. Jacobson, and Kenner C. Rice. 2023. "Potent MOR Agonists from 2′-Hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-N-phenethyl Substituted-6,7-benzomorphans and from C8-Hydroxy, Methylene and Methyl Derivatives of N-Phenethylnormetazocine" Molecules 28, no. 23: 7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237709
APA StyleDas, M., Ward, G. W., Sulima, A., Luo, D., Prisinzano, T. E., Imler, G. H., Kerr, A. T., Jacobson, A. E., & Rice, K. C. (2023). Potent MOR Agonists from 2′-Hydroxy-5,9-dimethyl-N-phenethyl Substituted-6,7-benzomorphans and from C8-Hydroxy, Methylene and Methyl Derivatives of N-Phenethylnormetazocine. Molecules, 28(23), 7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237709