Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of the Selective Inhibition of Coagulation Factor IXa over Factor Xa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Basic Analysis
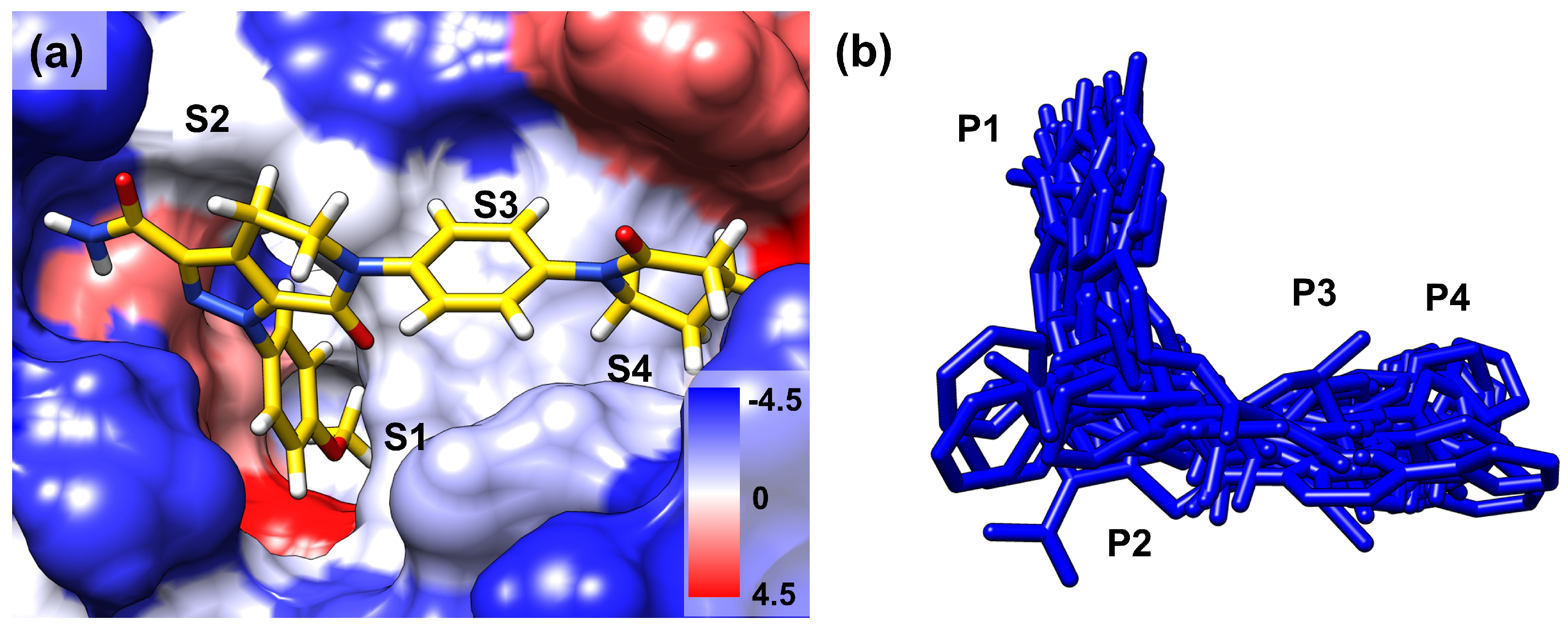
2.2. Ligand Dynamics
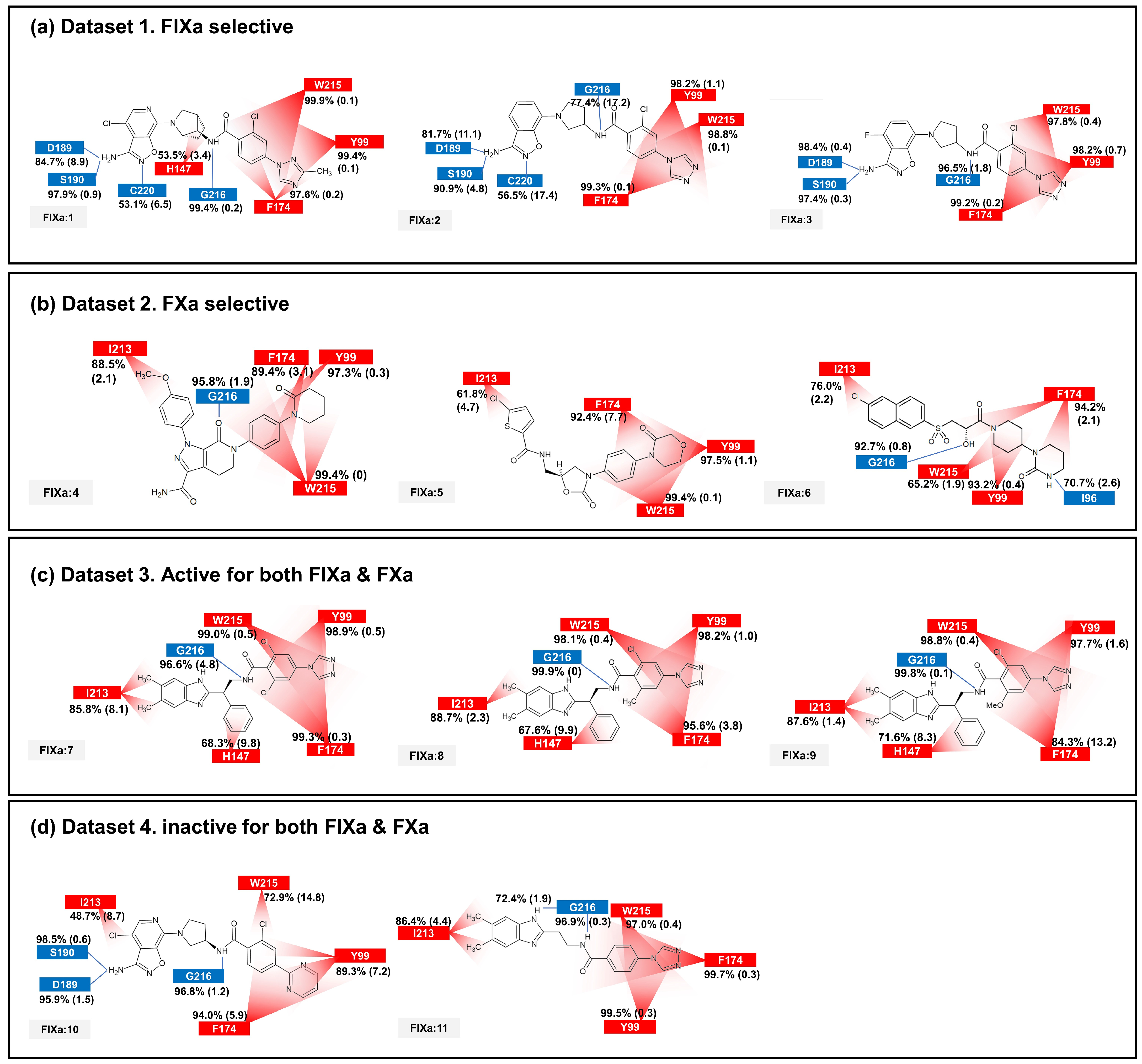
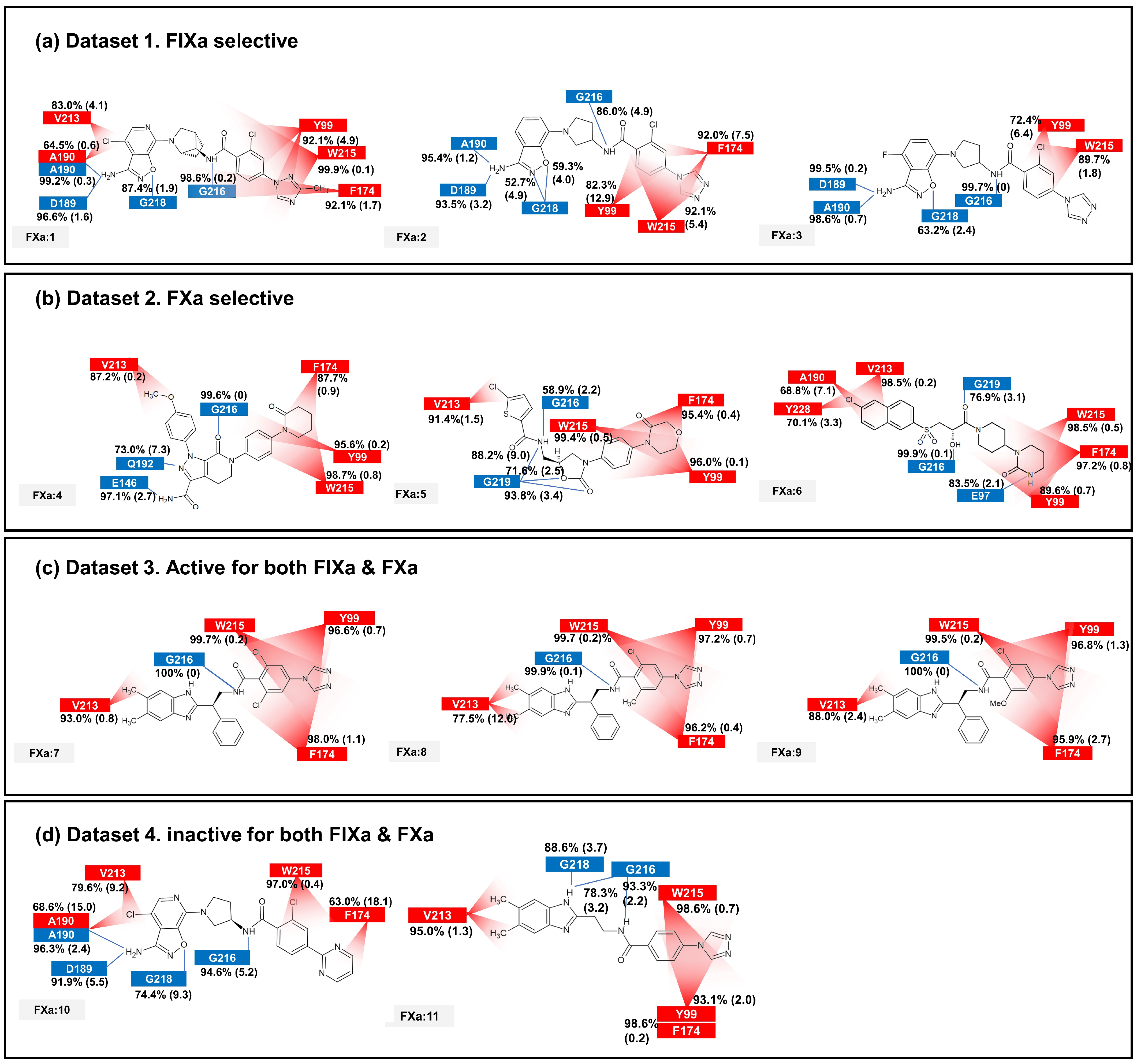
2.3. Contact Analysis of Protein–Ligand Complex
2.4. Binding Free-Energy Calculation by MM-PBSA
2.5. Binding Site Volume
2.6. Comparison of Static and Dynamic IFP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Protein–Ligand Complexes
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.3. Computational Analysis
3.3.1. The Movement Level of Ligands
3.3.2. Contact Frequency Calculation
3.3.3. Binding Free-Energy Calculation
3.3.4. Binding Site Volume Calculation
3.3.5. Protein–Ligand Interaction Fingerprint (IFP)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| DOAC | Direct Oral Anticoagulants |
| FIXa | Activated Coagulation Factor IX |
| FXa | Activated Coagulation Factor X |
References
- Fischer, P.M. Design of Small-Molecule Active-Site Inhibitors of the S1A Family Proteases as Procoagulant and Anticoagulant Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3799–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabankin, A.S.; Sinauridze, E.I.; Lipets, E.N.; Ataullakhanov, F.I. Computer Design of Low-Molecular-Weight Inhibitors of Coagulation Factors. Biochemistry 2019, 84, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Wu, S. A Structure Based Study of Selective Inhibition of Factor IXa over Factor Xa. Molecules 2021, 26, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.R.; Conley, P.B.; Sinha, U.; Andre, P. Therapeutic approaches in arterial thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolberg, A.S.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Weitz, J.I.; Jaffer, I.H.; Agnelli, G.; Baglin, T.; Mackman, N. Venous thrombosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.K. Ischemic Stroke. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, S.Z.; Bounameaux, H. Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, S.M.; Hachinski, V.C. The Cardiac Consequences of Stroke. Neurol. Clin. 1992, 10, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenburgh, J.C.; Weitz, J.I. New anticoagulants: Moving beyond the direct oral anticoagulants. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heestermans, M.; Poenou, G.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Cognasse, F.; Bertoletti, L. Anticoagulants: A Short History, Their Mechanism of Action, Pharmacology, and Indications. Cells 2022, 11, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduah, E.I.; Linhardt, R.J.; Sharfstein, S.T. Heparin: Past, Present, and Future. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Chen, X.; Jin, D.Y.; Stafford, D.W.; Pedersen, L.G.; Tie, J.K. Warfarin and vitamin K epoxide reductase: A molecular accounting for observed inhibition. Blood 2018, 132, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.J.P.; Orwat, M.J.; Koch, S.; Rossi, K.A.; Alexander, R.S.; Smallwood, A.; Wong, P.C.; Rendina, A.R.; Luettgen, J.M.; Knabb, R.M.; et al. Discovery of 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (Apixaban, BMS-562247), a Highly Potent, Selective, Efficacious, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Factor Xa. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5339–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Eikelboom, J.; Joyner, C.; Diener, H.C.; Hart, R.; Golitsyn, S.; Flaker, G.; Avezum, A.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Diaz, R.; et al. Apixaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrig, S.; Straub, A.; Pohlmann, J.; Lampe, T.; Pernerstorfer, J.; Schlemmer, K.H.; Reinemer, P.; Perzborn, E. Discovery of the Novel Antithrombotic Agent 5-Chloro-N-({(5S)-2-oxo-3-[4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl}methyl)thiophene- 2-carboxamide (BAY 59-7939): An Oral, Direct Factor Xa Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5900–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T.; Imaeda, Y.; Konishi, N.; Hiroe, K.; Kawamura, M.; Textor, G.P.; Aertgeerts, K.; Kubo, K. Discovery of a Tetrahydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one Derivative (TAK-442) as a Potent, Selective, and Orally Active Factor Xa Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3517–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohrt, J.T.; Bigge, C.F.; Bryant, J.W.; Casimiro-Garcia, A.; Chi, L.; Cody, W.L.; Dahring, T.; Dudley, D.A.; Filipski, K.J.; Haarer, S.; et al. The Discovery of (2R,4R)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-(2-fluoro-4-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-yl)phenyl)-4-methoxypyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxamide (PD 0348292), an Orally Efficacious Factor Xa Inhibitor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2007, 70, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, I.; Endo, T.; Hikita, K.; Hirabayashi, T.; Hosaka, Y.; Kato, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Mizuno, T.; Nagasue, H.; et al. Discovery of novel aminobenzisoxazole derivatives as orally available factor IXa inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2622–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.L.; Walsh, S.; Li, B.; Kim, E.; Sharipour, A.; Smith, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Berger, R.; Harper, B.; Zhang, T.; et al. Rapid development of two factor IXa inhibitors from hit to lead. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Andre, P.; Bateman, T.J.; Berger, R.; Chen, Y.H.; Desai, K.; Dewnani, S.; Ellsworth, K.; Feng, D.; Geissler, W.M.; et al. Development of a novel tricyclic class of potent and selective FIXa inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5437–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Andre, P.; Bateman, T.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Desai, K.; Ellsworth, K.; Geissler, W.M.; Guo, L.; Hruza, A.; Jian, T.; et al. Development of a novel class of potent and selective FIXa inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4945–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, D.J.; Sherman, W.; Tidor, B. Rational approaches to improving selectivity in drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1424–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, R.A.; Pompliano, D.L.; Meek, T.D. Drug–target residence time and its implications for lead optimization. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congreve, M.; Chessari, G.; Tisi, D.; Woodhead, A.J. Recent developments in fragment-based drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3661–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Stevens, R.C.; Roth, B.L. How ligands illuminate GPCR molecular pharmacology. Cell 2017, 170, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, S.K.; Chodera, J.D.; Volkamer, A.; Keng, S.; Abel, R.; Wang, L. Is structure-based drug design ready for selectivity optimization? J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 6211–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congreve, M.; Andrews, S.P.; Doré, A.S.; Hollenstein, K.; Hurrell, E.; Langmead, C.J.; Mason, J.S.; Ng, I.W.; Tehan, B.; Zhukov, A.; et al. Discovery of 1, 2, 4-triazine derivatives as adenosine A2A antagonists using structure based drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshleman, A.J.; Nagarajan, S.; Wolfrum, K.M.; Reed, J.F.; Nilsen, A.; Torralva, R.; Janowsky, A. Affinity, potency, efficacy, selectivity, and molecular modeling of substituted fentanyls at opioid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Wang, C.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Huang, X.P.; Vardy, E.; McCorvy, J.D.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, M.; Siu, F.Y.; et al. Structural features for functional selectivity at serotonin receptors. Science 2013, 340, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Deng, J.N. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal the selectivity mechanism of structurally similar agonists to TLR7 and TLR8. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0260565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bhattarai, A.; Do, H.N.; Akhter, S.; Miao, Y. Molecular simulations and drug discovery of adenosine receptors. Molecules 2022, 27, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, J.D.; McCammon, J.A. Molecular dynamics simulations and drug discovery. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbinden, K.G.; Anselm, L.; Banner, D.W.; Benz, J.; Blasco, F.; Décoret, G.; Himber, J.; Kuhn, B.; Panday, N.; Ricklin, F.; et al. Design of novel aminopyrrolidine factor Xa inhibitors from a screening hit. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallheer, J.M.; Alexander, R.S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Nakajima, S.; Rossi, K.A.; Smallwood, A.; Barbera, F.; Burdick, D.; Luettgen, J.M.; et al. SAR and factor IXa crystal structure of a dual inhibitor of factors IXa and Xa. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5263–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, S.; Guilloteau, J.P.; Choi-Sledeski, Y.M.; Becker, M.R.; Ewing, W.R.; Pauls, H.W.; Spada, A.P.; Mikol, V. Molecular Structures of Human Factor Xa Complexed with Ketopiperazine Inhibitors: Preference for a Neutral Group in the S1 Pocket. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfner, K.P.; Brandstetter, H.; Karcher, A.; Kopetzki, E.; Huber, R.; Engh, R.A.; Bode, W. Converting blood coagulation factor IXa into factor Xa: Dramatic increase in amidolytic activity identifies important active site determinants. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6626–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccinardi, T. What is the current value of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods in drug discovery? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Greene, D.; Xiao, L.; Qi, R.; Luo, R. Recent Developments and Applications of the MMPBSA Method. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Hou, T. End-Point Binding Free Energy Calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: Strategies and Applications in Drug Design. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9478–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.J.; Yin, Y.W.; Ma, Y.Q.; Ding, H.M. Improving the Performance of MM/PBSA in Protein–Protein Interactions via the Screening Electrostatic Energy. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkarhat, Z.; Charoute, H.; Elkhattabi, L.; Barakat, A.; Rouba, H. Potential inhibitors of SARS-cov-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase protein: Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and MM-PBSA analyses. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, V.K.; Purohit, R. Computational targeting of allosteric site of MEK1 by quinoline-based molecules. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2022, 40, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA. Discovery Studio Visualizer, v21. 1.0. 20298; Dassault Systèm: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://3ds.com/products-services/biovia/products (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakalian, A.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J. Comput. Chem. 2002, 23, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S.; Klein, M. Constant pressure molecular dynamics for molecular systems. Mol. Phys. 1983, 50, 1055–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S. A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H. Free Energy Calculations by the Molecular Mechanics Poisson–Boltzmann Surface Area Method. Mol. Inform. 2012, 31, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Lynn, A. g_mmpbsa—A GROMACS Tool for High-Throughput MM-PBSA Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Sørensen, J.; Hensley, N.; Wong, C.; Zhu, C.; Perison, T.; Amaro, R.E. POVME 3.0: Software for Mapping Binding Pocket Flexibility. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 4584–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouysset, C.; Fiorucci, S. ProLIF: A library to encode molecular interactions as fingerprints. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Compound | hFIXa IC50 (nM) | hFXa IC50 (nM) | PDB ID (FIXa) | PDB ID (FXa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset 1 a FIXa selective | 1 | 4.9 | 31,000 | 5TNT | - |
| 2 | 98 | >100,000 | 5TNO | - | |
| 3 | 172 | >100,000 | - | - | |
| Dataset 2 FXa selective | 4 b | Inactive | 0.08 | - | 2P16 |
| 5 c | Inactive | 0.7 | - | 2W26 | |
| 6 d | Inactive | 3.5 | - | 3KL6 | |
| Dataset 3 e Active for both FIXa and FXa | 7 | 3.6 | 105 | 4ZAE | - |
| 8 | 8 | 195 | - | - | |
| 9 | 14.8 | 245 | - | - | |
| Dataset 4 Inactive for both FIXa and FXa | 10 a | >3000 | >100,000 | - | - |
| 11 f | 9000 | 62,500 | 4YZU | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, H.J.; Kundu, S.; Wu, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of the Selective Inhibition of Coagulation Factor IXa over Factor Xa. Molecules 2023, 28, 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196909
Yoon HJ, Kundu S, Wu S. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of the Selective Inhibition of Coagulation Factor IXa over Factor Xa. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196909
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Hyun Jung, Sibsankar Kundu, and Sangwook Wu. 2023. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of the Selective Inhibition of Coagulation Factor IXa over Factor Xa" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196909
APA StyleYoon, H. J., Kundu, S., & Wu, S. (2023). Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of the Selective Inhibition of Coagulation Factor IXa over Factor Xa. Molecules, 28(19), 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196909






