Classification and Authentication of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos by Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Chemical Pattern Recognition Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
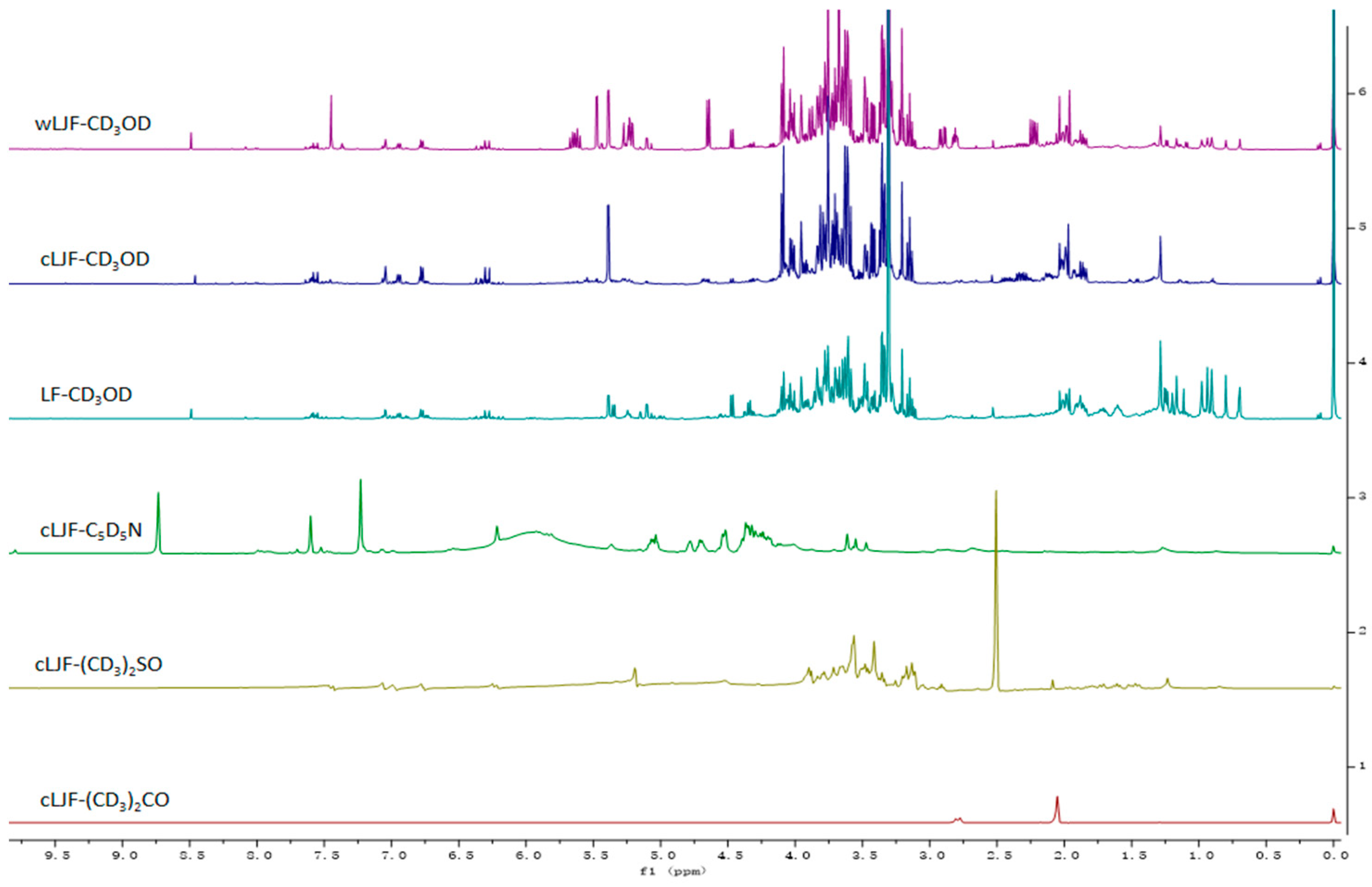
2.1. Optimization of Sample Preparation
2.2. Identification and Analysis of Different Species and Growth Modes
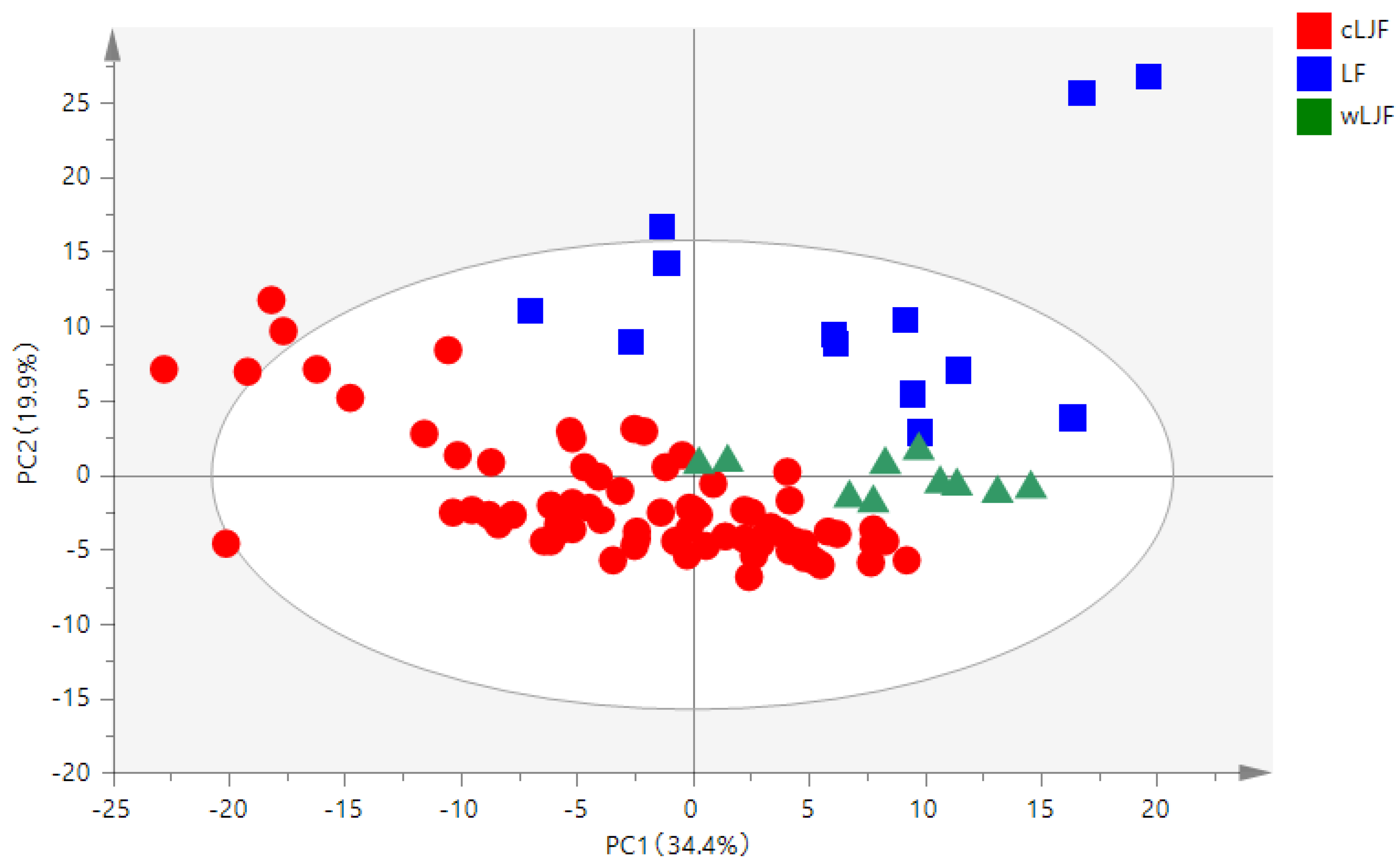
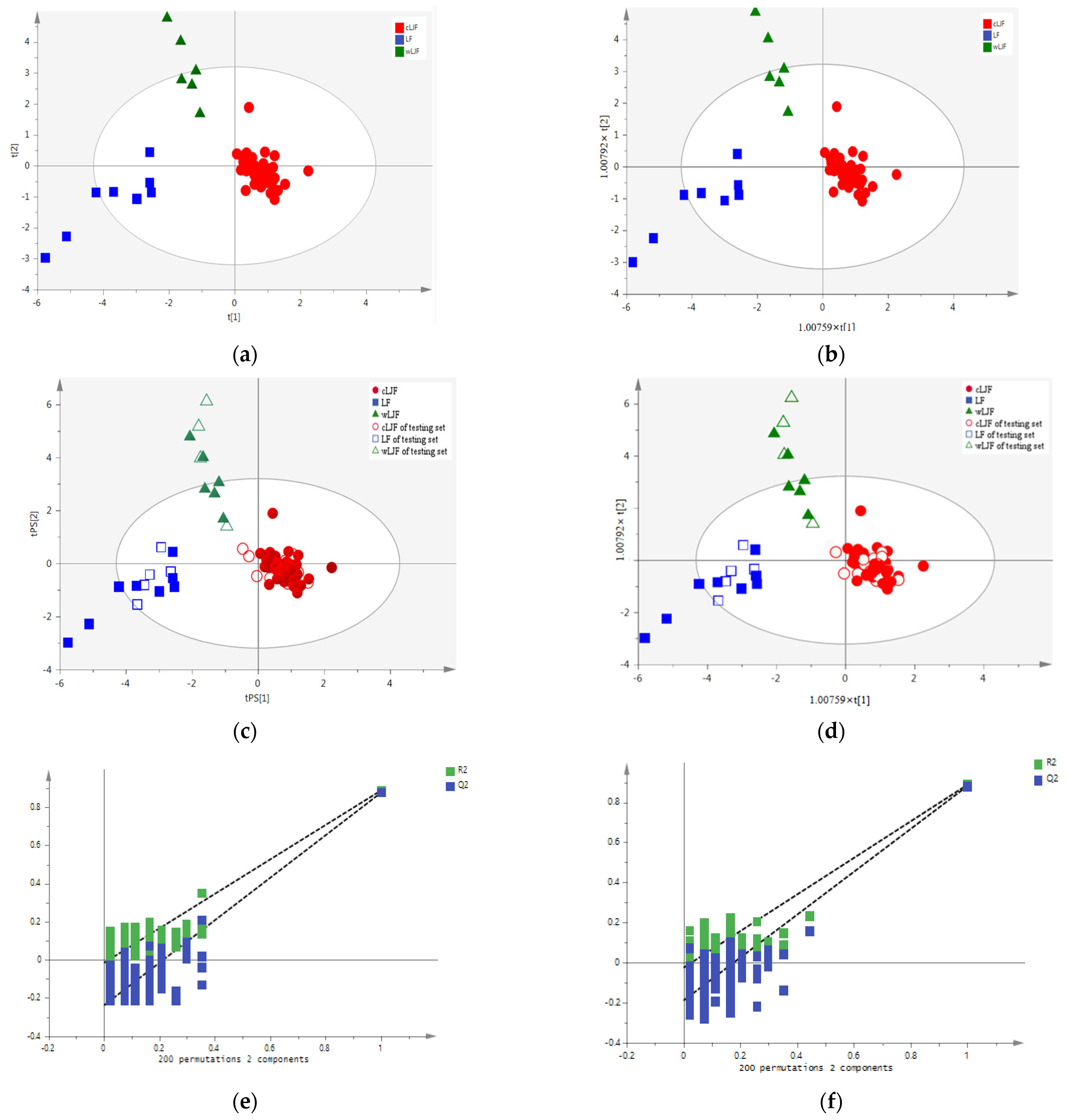
2.2.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
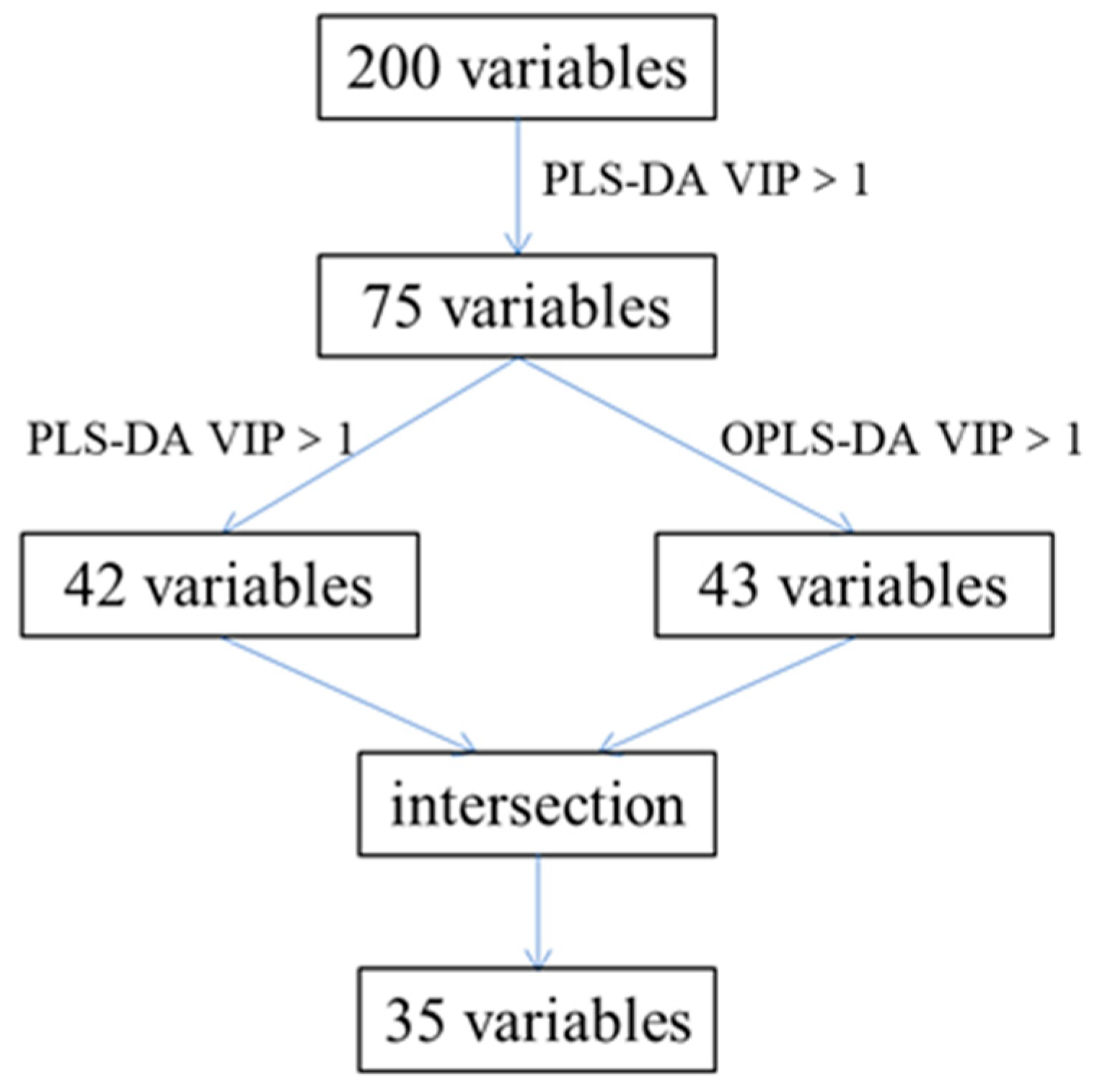
2.2.2. Extraction of the Specific Variation
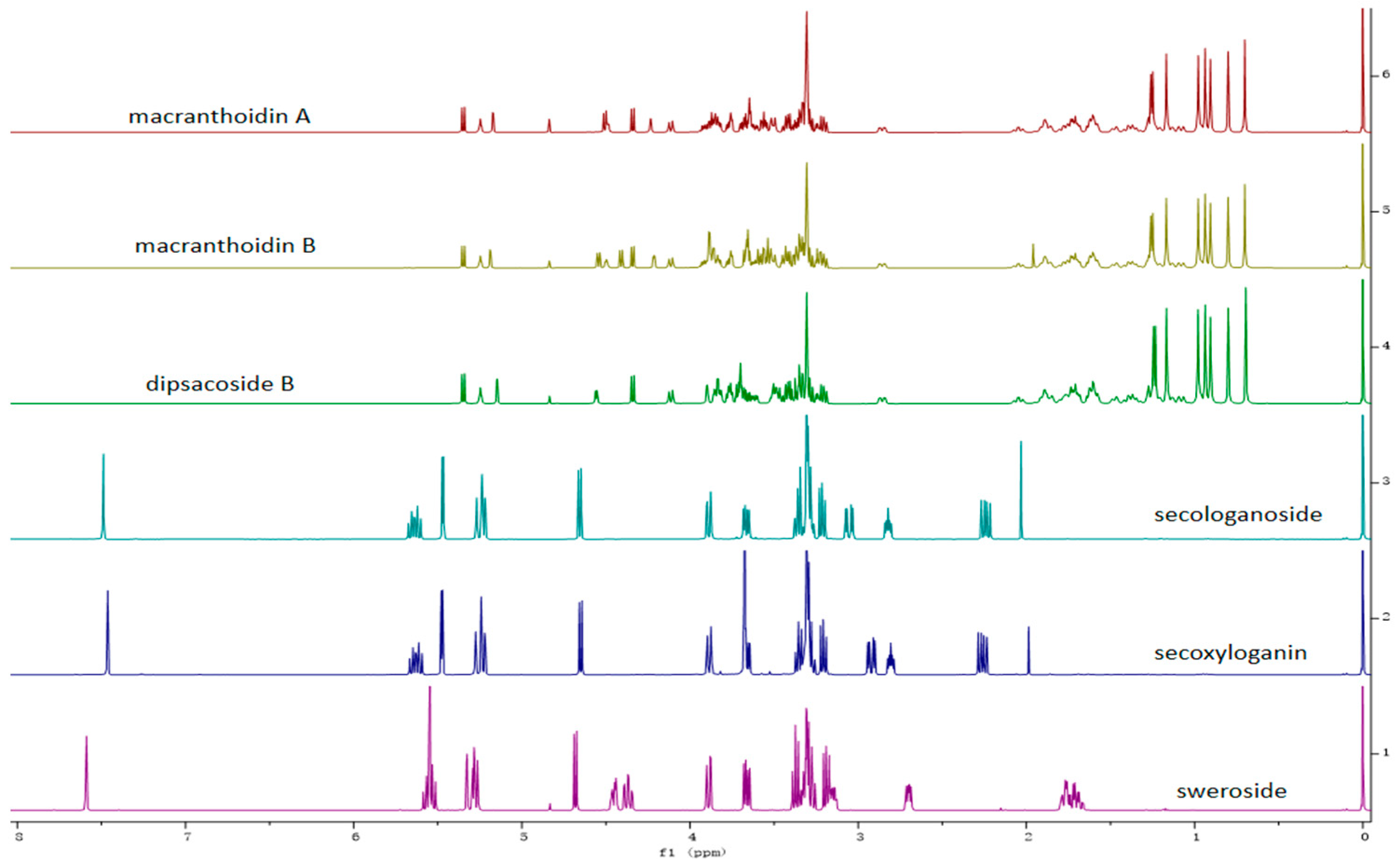
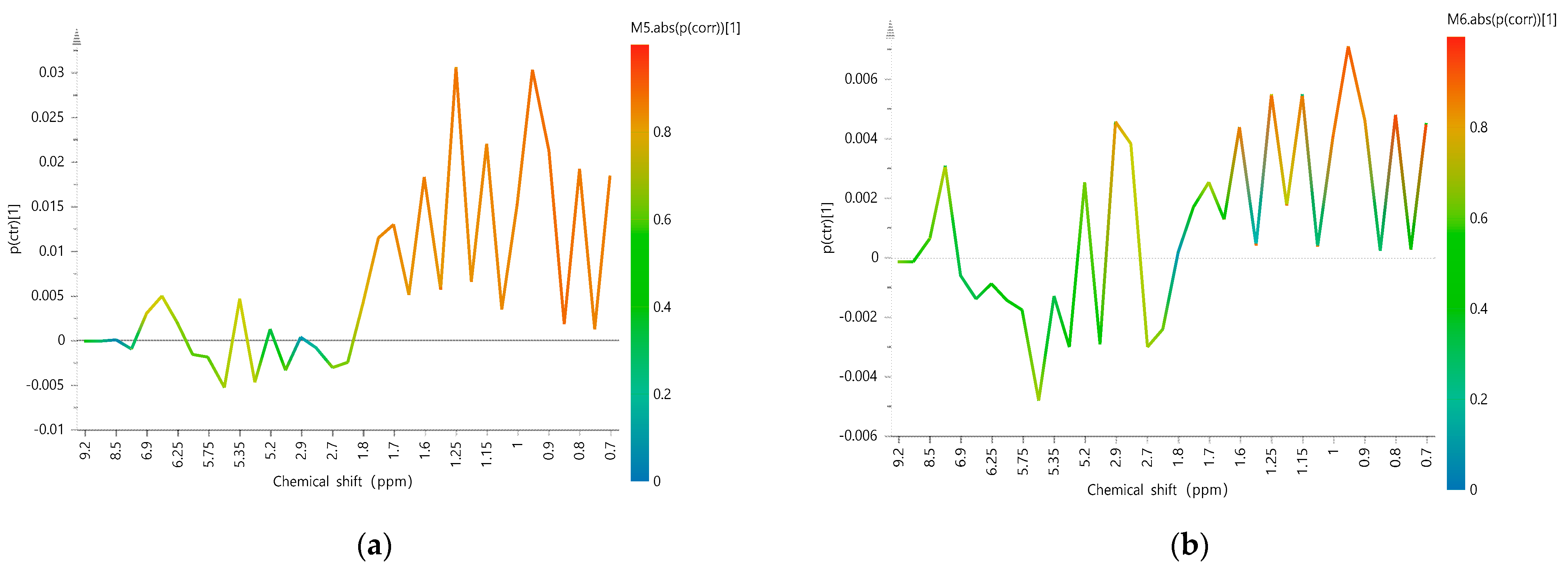
2.2.3. Identification of the Characteristic Variables
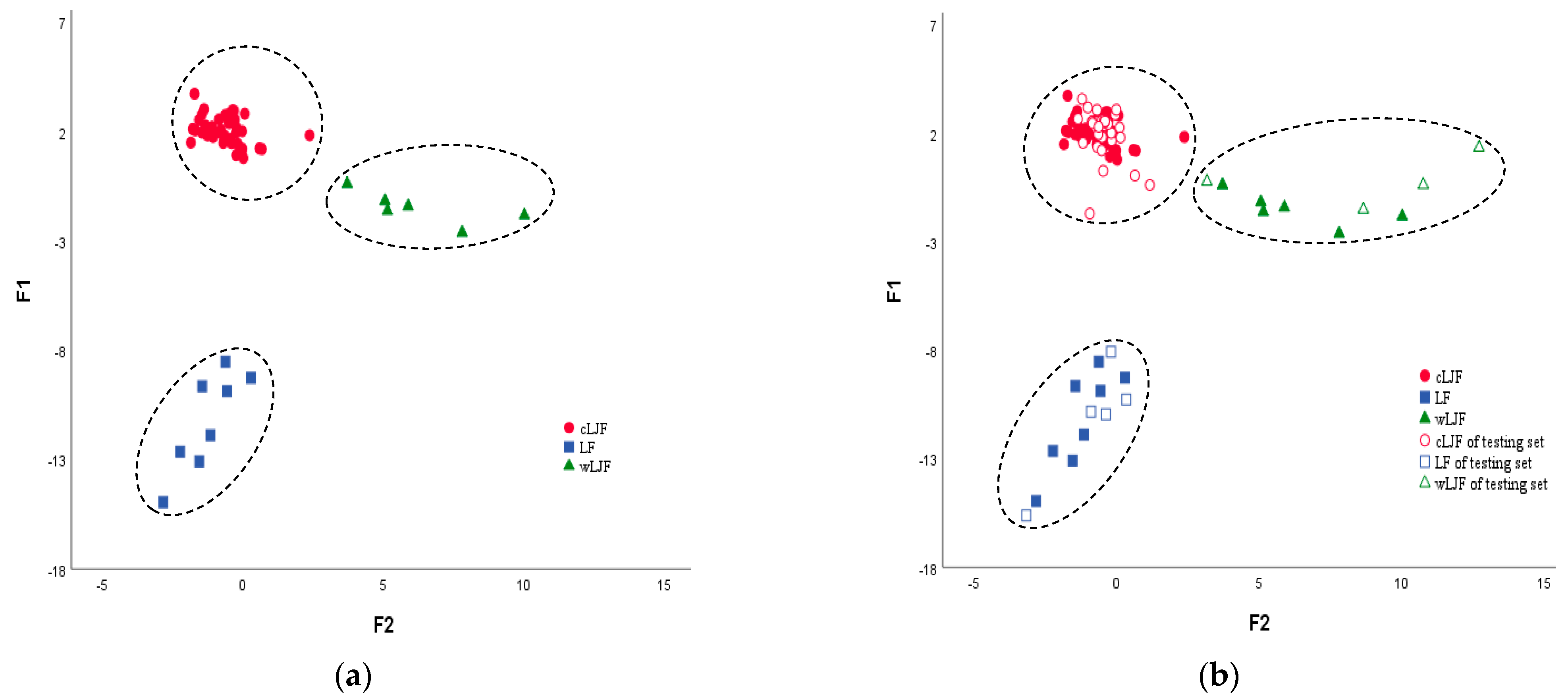
2.2.4. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
2.2.5. Verification of the Distinguishing Ability of the Characteristic Variables
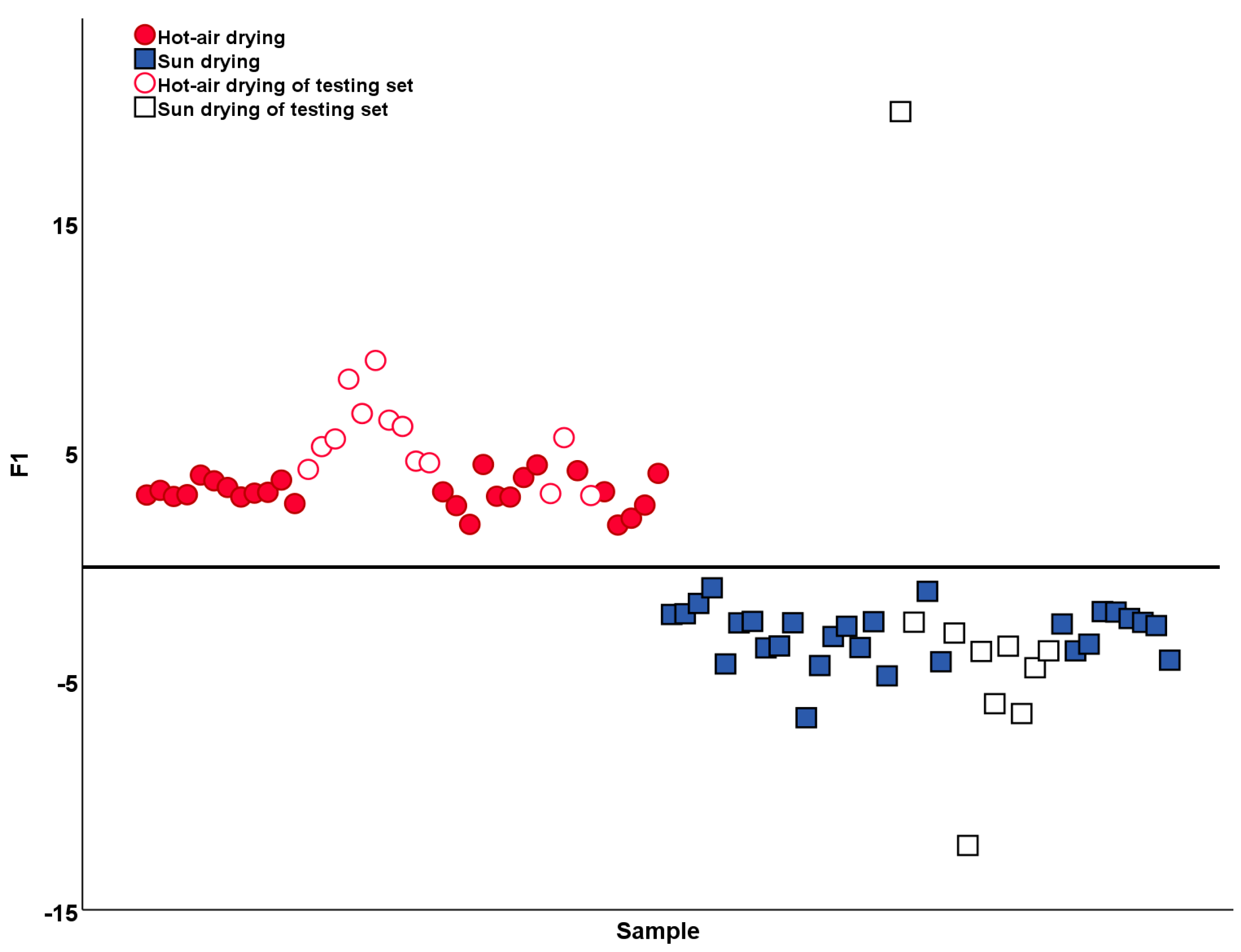
2.3. Identification and Analysis of Two Processing Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. 1H-NMR Spectra Measurement
3.4. Data Processing of the NMR Spectra
3.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ming, C.; Wu, Q.; Su, H.; Ma, X.; Zang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, X. Spectrum-Effect Relationships Between Chemical Fingerprints and Antibacterial Effects of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos Base on UPLC and Microcalorimetry. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Pu, G. A Simple, Rapid, and Practical Method for Distinguishing Lonicerae Japonicae Flos from Lonicerae Flos. Molecules 2019, 24, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, S.; Hou, A.; Wang, S.; Na, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, H.; Yang, L. Systematic review of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos: A significant food and traditional Chinese medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1013992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.C.-Y.; Ma, X.-Q.; Kwan, H.-Y.; Tse, K.-W.; Cao, H.-H. A herbal formula consisting of Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos inhibits inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Ji, L. Lonicera japonica Attenuates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Pan, H.; Li, M.; Miao, X.; Ding, H. Lonicera japonica Thunb.: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Long, W.W.; Qing, Z.J.; Rui, B.Q.; Yuan, L.J.; Ikhlas, K.; Rudolf, B.; An, G.D. Traditional Chinese Medicines Against COVID19: A Global Overview. World Chin. Med. 2022, 8, 279–313. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Z.; Sha, Z.; Li, C.; Qiang, S.; Maolun, L.; Han, Y.; Shan, R.; Tianqi, M.; Xianli, M.; Haibo, X. Updated pharmacological effects of Lonicerae japonicae flos, with a focus on its potential efficacy on coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 60, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, L.; Ming, Y.; Ling, T.Q.; Yang, H.X.; Willcox, M.L.; Ping, L.J. Characteristics of registered clinical trials on traditional. Chinese medicine for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A scoping review. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 41, 101251. [Google Scholar]
- Uncu, O.; Ozen, B.; Tokatli, F. Authentication of Turkish olive oils by using detailed pigment profile and spectroscopic techniques. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarighat, M.A.; Abdi, G.; Tarighat, F.A.; Bayatiyani, K.S. Authentication and identification of Lamiaceae family with cyclic voltammetry fingerprint-PCA-LDA and determination of the used phenolic contents for classification using chromatographic analyses. Talanta 2023, 265, 124894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Rui, H.; Yixin, H.; Qiaoling, F.; Runlan, C.; Yun, Q. Shuang-Huang-Lian injection induces an immediate hypersensitivity reaction via C5a but not IgE. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3572. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z. Study on Quality Control of Lonicera Japonica Flos and Lonicera Flos; Zhejiang University of Technology: Hangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xingyue, Y.; Yali, L.; Aijuan, H.; Yang, Y.; Xin, T.; Liyun, H. Systematic review for geo-authentic Lonicerae Japonicae Flos. Med. Front. 2017, 11, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.; Pengdi, C.; Huan, L.; Chunhua, W.; Tongchuan, S. Rapid screening and quantitative analysis of adulterant Lonicerae Flos in Lonicerae Japonicae Flos by Fourier-transform near infrared spectroscopy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 104, 103139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhichen, C.; Chengcheng, W.; Cuihua, C.; Lisi, Z.; Chuan, C.; Jiali, C.; Mengxia, T.; Xunhong, L. Quality evaluation of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos based on simultaneous determination of multiple bioactive constituents combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Phytochem. Anal. 2021, 32, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lifei, G.; Xueqing, X.; Bing, W.; Yibao, J.; Lijun, W.; Jue, W.; Guo, Y.; Kaishun, B.; Tiejie, W. Discrimination of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos according to species, growth mode, processing method, and geographical origin with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography analysis and chemical pattern recognition. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 219, 114924. [Google Scholar]
- Xueqing, X.; Lifei, G.; Wanyi, X.; Guo, Y.; Jue, W.; Yibao, J.; Lijun, W.; Bing, W.; Tiejie, W. Integrating Anti-Influenza Virus Activity and Chemical Pattern Recognition to Explore the Quality Evaluation Method of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos. Molecules 2022, 27, 5789. [Google Scholar]
- Riswanto, F.D.O.; Windarsih, A.; Lukitaningsih, E.; Rafi, M.; Fadzilah, N.A.; Rohman, A. Metabolite Fingerprinting Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Liquid Chromatography for the Authentication of Herbal Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, D.; Aguiar, L.M.d.; Bona, E.; Marini, F.; Killner, M.H.M. Successful combination of benchtop nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and chemometric tools: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1273, 341495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Xuan, H.; Qiaoqi, L. Metabolomic Differentiation of Rhodiola Crenulata from Different Geographical Origins of Sichuan Province and Tibet, China. Pak. J. Bot. 2017, 49, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar]
- Marchev, A.S.; Koycheva, I.K.; Aneva, I.Y.; Georgiev, M.I. Authenticity and quality evaluation of different Rhodiola species and commercial products based on NMR-spectroscopy and HPLC. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuanhao, L.; Xiaobo, W.; Daoxin, H.; Shangyu, Z.; Jinsong, S.; Gang, F.; Yi, Z. Metabolic Discrimination of Different Rhodiola Species Using 1H-NMR and GEP Combinational Chemometrics. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveri, P.; Malegori, C.; Mustorgi, E.; Casale, M. Qualitative pattern recognition in chemistry: Theoretical background and practical guidelines. Microchem. J. 2020, 162, 105725–105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohua, Z.; Renjun, L.; Jingjing, Z.; Xiangdong, Q.; Kailong, Y.; Yaqian, Z.; Leyuan, P.; Jinfang, N. Authentication of the production season of Xinyang Maojian green tea using two-dimensional fingerprints coupled with chemometric multivariate calibration and pattern recognition analysis. LWT 2023, 176, 114556. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, D.; Wenli, C.; Yutian, L.; Fengchao, L.; Huimin, L.; Wei, D.; Guihua, J. Discrimination of authenticity of Fritillariae Cirrhosae Bulbus based on terahertz spectroscopy and chemometric analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106440. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, C.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q. Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: A systematic review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.S.J.; Jin, Y.; Bi, Y.A.; Wu, H.X.; Hao, Q.X.; Guo, L.P.; Xiao, W. Standard operating procedure for raw materials of reduning injection—Lonicerae Japonicae Flos. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2014, 45, 2707–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.L.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, D.P. 1H-NMR fingerprint identification for Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 39, 222–224. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Qi, L.W.; Liu, E.H.; Ren, M.T.; Yan, Y.T.; Chen, J.; Li, P. Unbiased metabolite profiling by liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis for herbal authentication: Classification of seven Lonicera species flower buds. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1245, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Putr, A.R. The Chemometrics Techniques in Combination with Instrumental Analytical Methods Applied in Halal Authentication Analysis. Indones. J. Chem. 2019, 19, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.D.; Chen, H.G.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, E.M.; Jiang, Z.M.; Zhao, C.; Gong, X.-J.; Deng, Q.-F. Studies on Chromatographic Fingerprint and Fingerprinting Profile-Efficacy Relationship of Saxifraga stolonifera Meerb. Molecules 2015, 20, 22781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Sun, L.; Li, D.; You, G.; Wang, M.; Ren, X. Quality Evaluation of Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex by Fingerprint–Chemical Pattern Recognition. Molecules 2018, 23, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model | Categories | Number of Samples | Number of Correct Classification (%) | R2X (cum) | R2Y (cum) | Q2 (cum) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Testing Set | Training Set | Testing Set | |||||
| PLS-DA | cLJF | 47 | 30 | 61 (100%) | 39 (100%) | 0.647 | 0.839 | 0.821 |
| wLJF | 6 | 4 | ||||||
| LF | 8 | 5 | ||||||
| OPLS-DA | cLJF | 47 | 30 | 61 (100%) | 39 (100%) | 0.647 | 0.839 | 0.817 |
| wLJF | 6 | 4 | ||||||
| LF | 8 | 5 | ||||||
| Model | Categories | Number of Samples | Number of Correct Classification (%) | R2X (cum) | R2Y (cum) | Q2 (cum) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Testing Set | Training Set | Testing Set | |||||
| OPLS-DA | Hot air drying | 26 | 13 | 54 (90.74%) | 23 (95.65%) | 0.793 | 0.671 | 0.456 |
| Sun drying | 28 | 10 | ||||||
| Sample No. | Species | Growth Modes | Processing Methods | Origins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1–J3/J5/J9/J23–J29 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Henan |
| J4/J6–J8/J10–J15/J17–J18/J43–J53/J55–J58 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Sun drying | Shandong |
| J16/J34–J41 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Shandong |
| J19–J22/J30–J33 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Hebei |
| J42/J54/J59–J63 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Sun drying | Henan |
| J64–J68 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Sun drying | Hebei |
| J69–J71 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Anhui |
| J72–J73 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Hubei |
| J74 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Sichuan |
| J75 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Guizhou |
| J76 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Hunan |
| J77 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Gansu |
| J78 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Cultivated | Hot-air drying | Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region |
| Y1–Y10 | Lonicerae japonicae flos | Wild | Sun drying | Hubei |
| S1–S2 | Lonicerae Flos | Wild | Sun drying | Jiangxi |
| S3 | Lonicerae Flos | Wild | Sun drying | Guizhou |
| S4–S7 | Lonicerae Flos | Wild | Sun drying | Hunan |
| S8–S12 | Lonicerae Flos | Wild | Sun drying | / |
| S13 | Lonicerae Flos | Wild | Sun drying | Sichuan |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Jin, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Yin, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, B. Classification and Authentication of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos by Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Chemical Pattern Recognition Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196860
Liu K, Jin Y, Gu L, Li M, Wang P, Yin G, Wang S, Wang T, Wang L, Wang B. Classification and Authentication of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos by Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Chemical Pattern Recognition Analysis. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196860
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Kaishuang, Yibao Jin, Lifei Gu, Meifang Li, Ping Wang, Guo Yin, Shuhong Wang, Tiejie Wang, Lijun Wang, and Bing Wang. 2023. "Classification and Authentication of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos by Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Chemical Pattern Recognition Analysis" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196860
APA StyleLiu, K., Jin, Y., Gu, L., Li, M., Wang, P., Yin, G., Wang, S., Wang, T., Wang, L., & Wang, B. (2023). Classification and Authentication of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos by Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Chemical Pattern Recognition Analysis. Molecules, 28(19), 6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196860





