Prediction of Protein Ion–Ligand Binding Sites with ELECTRA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparison with Other Tools
2.2. Ablation Tests
2.3. Running Some Test Examples
2.4. Tool
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
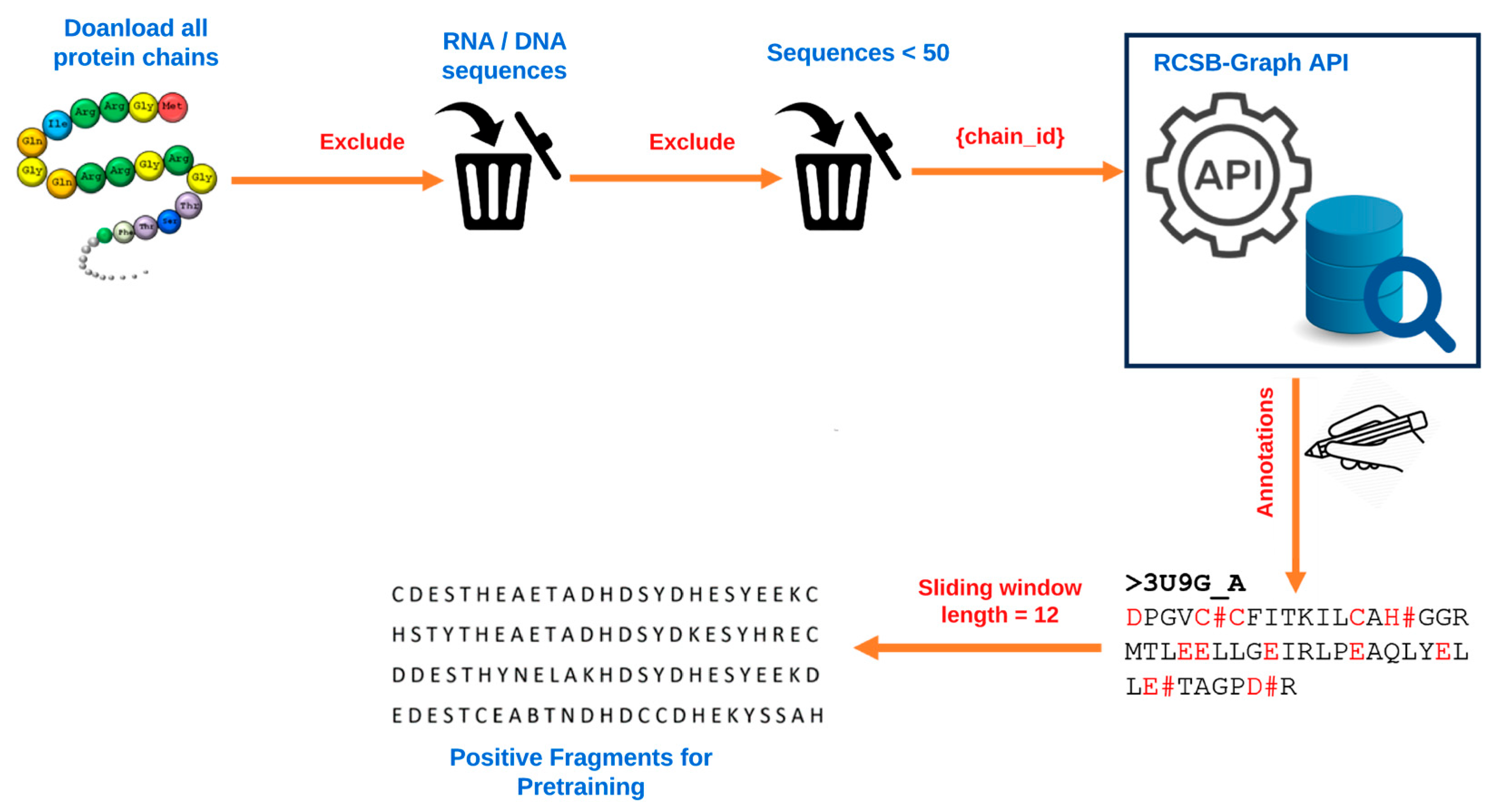
4.1. Data and Data Processing
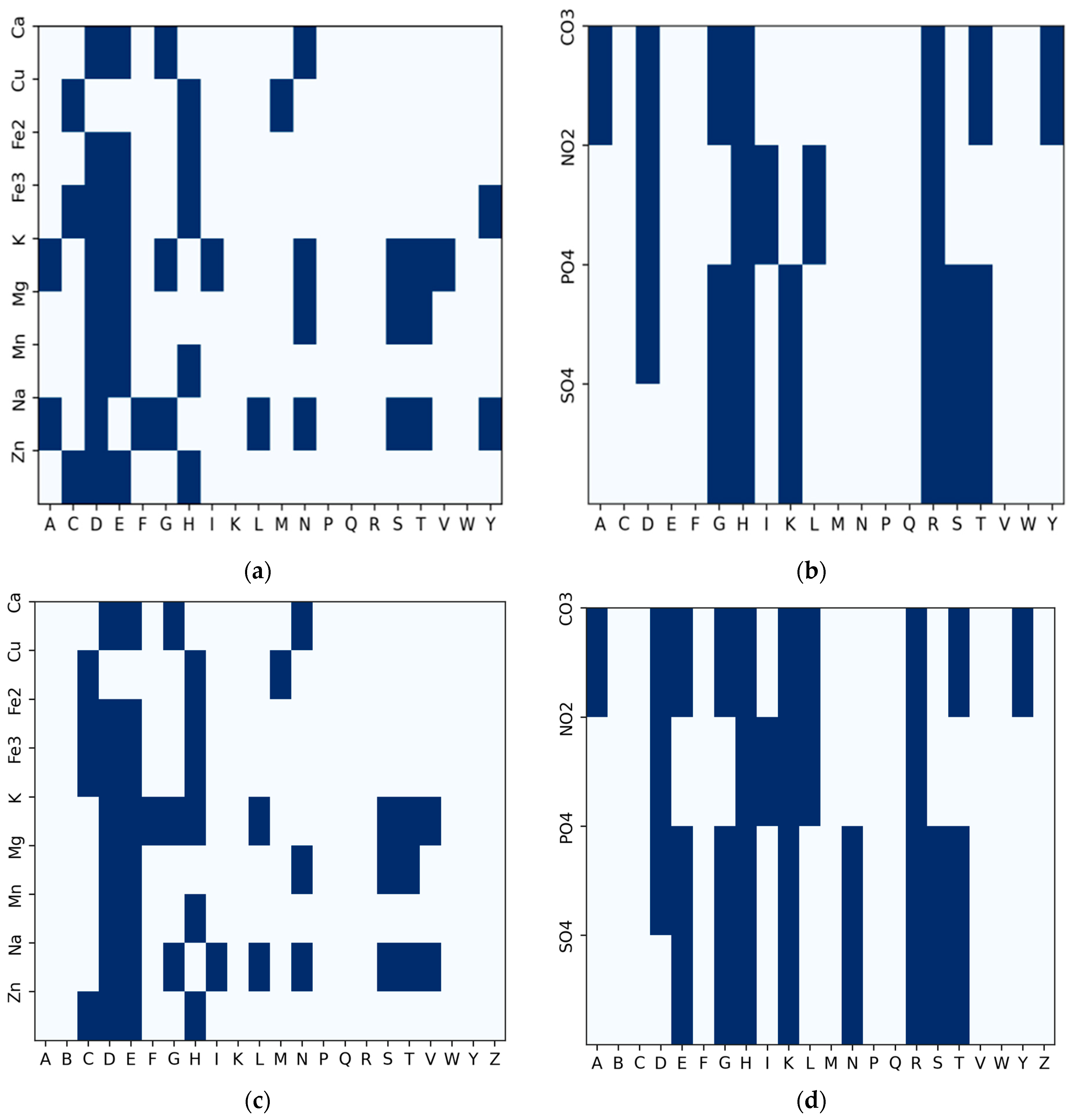
4.2. Candidate Residue Selection
4.3. Problem Definition
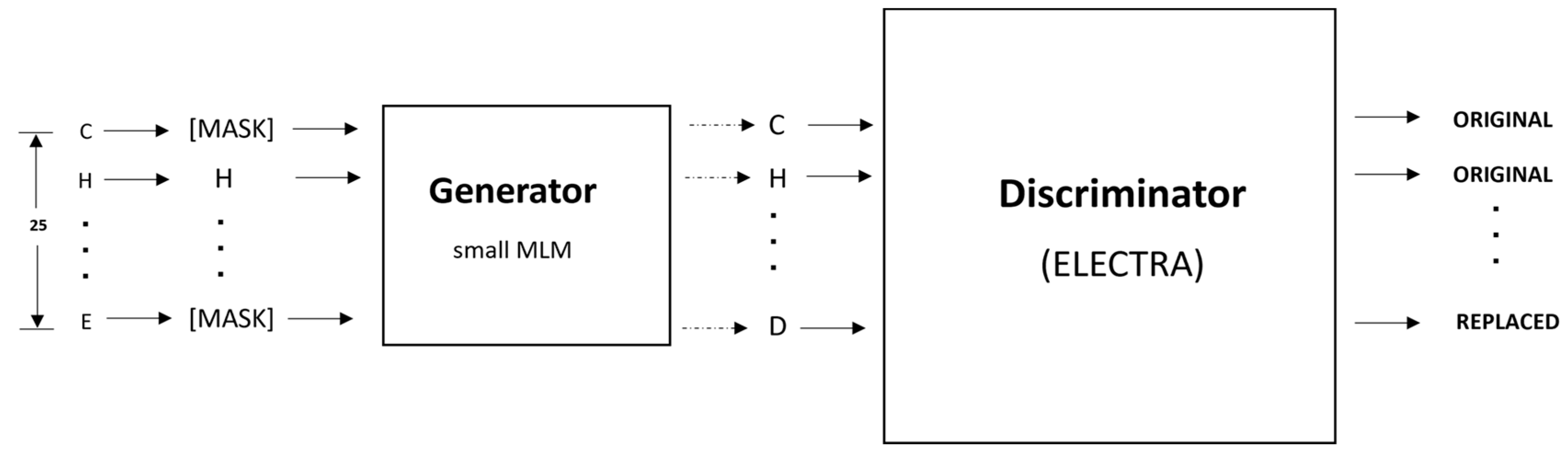
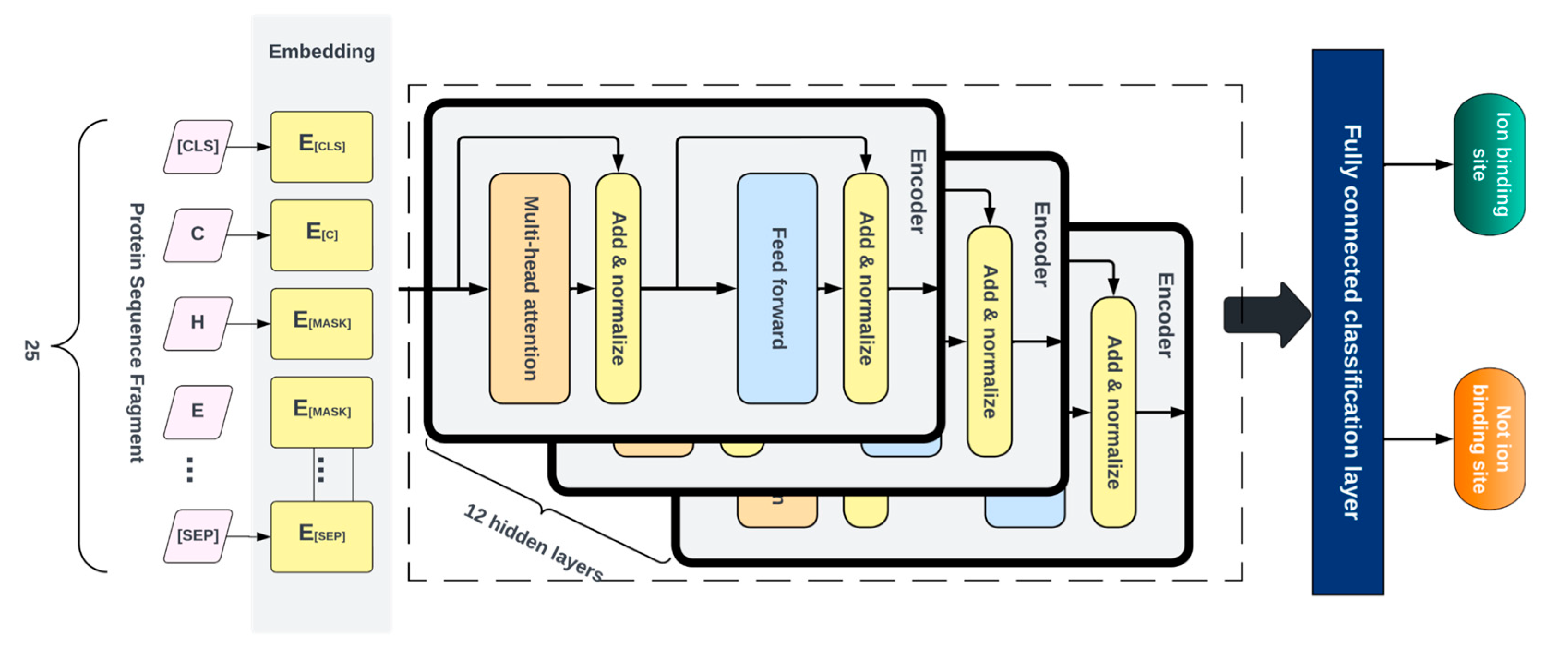
4.4. Deep Learning Model
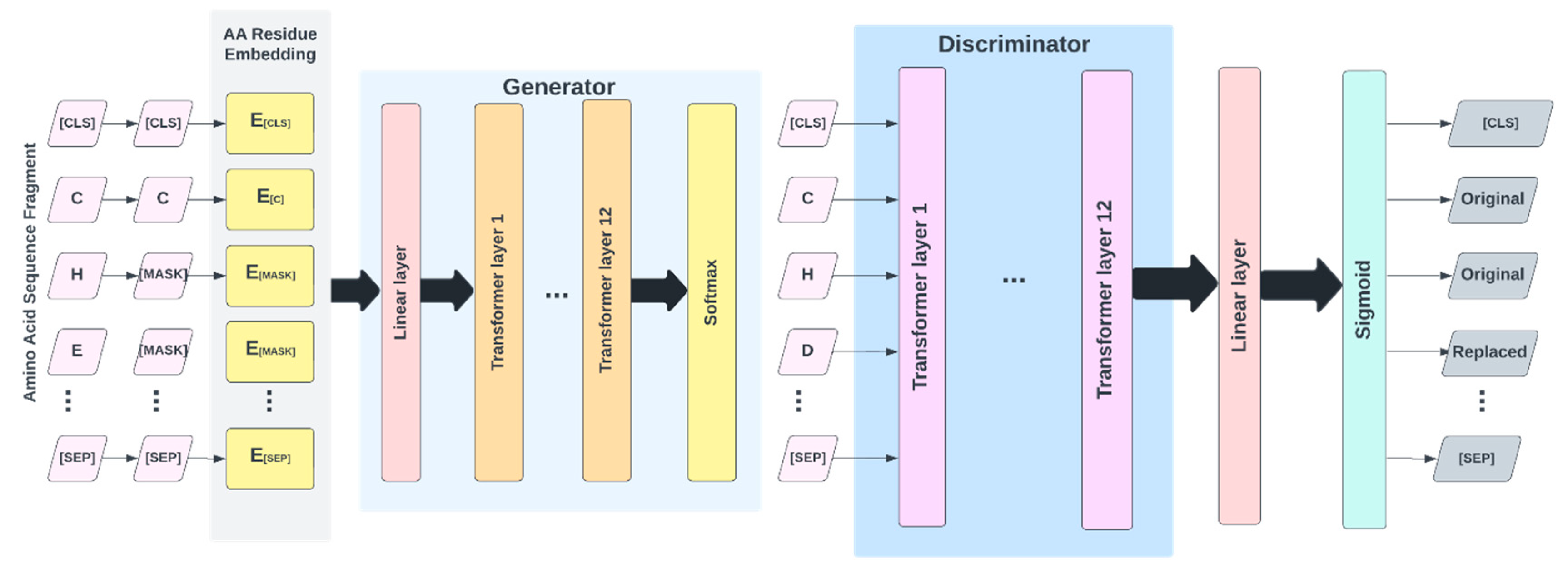
4.5. Pretraining
4.6. Fine-Tuning
4.7. Model Assessment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular biology of the cell. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 32, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Skolnick, J. The distribution of ligand-binding pockets around protein-protein interfaces suggests a general mechanism for pocket formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3784–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Skolnick, J. A comprehensive survey of small-molecule binding pockets in proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tainer, J.A.; Roberts, V.A.; Getzoff, E.D. Metal-binding sites in proteins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1991, 2, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.J.; Gray, H.B. Bio-inorganic chemistry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1998, 2, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, C.C.W. Respiratory function of hemoglobin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fracchia, K.M.; Pai, C.; Walsh, C.M. Modulation of t cell metabolism and function through calcium signaling. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Kurosaki, T. Role of calcium signaling in B cell activation and biology. In B Cell Receptor Signaling; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 143–174. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, K.A.; Huang, C.-c.; Fierke, C.A. Function and mechanism of zinc metalloenzymes. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1437S–1446S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower-Winter, S.D.; Levenson, C.W. Zinc in the central nervous system: From molecules to behavior. BioFactors 2012, 38, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Chuang, L.; Loziuk, P.L.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.C.; Shi, R.; Qu, G.Z.; Muddiman, D.C.; Sederoff, R.R.; Chiang, V.L. Phosphorylation is an on/off switch for 5-hydroxyconiferaldehyde o-methyl-transferase activity in poplar monolignol biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8481–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chi, L. Chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate-protein interactions and their biological functions in human diseases: Implications and analytical tools. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 693563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sletten, E. The binding of transition metal ions to DNA oligonucleotides studied by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In Cytotoxic, Mutagenic and Carcinogenic Potential of Heavy Metals Related to Human Environment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 493–509. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa, M.; Doi, N.; Higashinakagawa, T.; Yanagawa, H. DNA display of biologically active proteins for in vitro protein selection. J. Biochem. 2004, 135, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Huang, J.Z.; Gao, X. Ligandrfs: Random forest ensemble to identify ligand-binding residues from sequence information alone. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Hu, S.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, B. A sequence-based dynamic ensemble learning system for protein ligand-binding site prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Cofactor: An accurate comparative algorithm for structure-based protein function annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W471–W477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Protein–ligand binding site recognition using complementary binding-specific substructure comparison and sequence profile alignment. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Dong, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Recognizing metal and acid radical ion-binding sites by integrating ab initio modeling with templatebased transferals. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3260–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.; Edelman, M. Web tools for predicting metal binding sites in proteins. Isr. J. Chem. 2013, 53, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Lin, J.J.; Yu, C.S. Prediction of metal ion–binding sites in proteins using the fragment transformation method. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, K.; Dong, Q. Protein ligand-specific binding residue predictions by an ensemble classifier. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Biolip: A semi-manually curated database for biologically relevant ligand–protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D1096–D1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Ding, C.; Feng, Y.; Bao, W. Identification of metal ion binding sites based on amino acid sequences. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenside, P.; Hillenmeyer, M.; Kundaje, A. Prediction of protein-ligand interactions from paired protein sequence motifs and ligand sub-structures. In Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2018: Proceedings of the Pacific Symposium; World Scientific: Singapore, 2018; pp. 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, K.; Luong, M.T.; Le, Q.V.; Manning, C.D. ELECTRA: Pre-training Text Encoders as Discriminators Rather Than Generators. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10555. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.J.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Shen, H.B.; Tang, J.; Yang, J.Y. Designing template-free predictor for targeting protein-ligand binding sites with classifier ensemble and spatial clustering. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2013, 10, 994–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Essien, C.; Wang, D.; Xu, D. Capsule network for predicting zinc binding sites in metalloproteins. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 2337–2341. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, W. Prediction of ligand binding residues in protein sequences using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 2298–2304. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-F.; Cheng, C.-W.; Shih, C.-S.; Hwang, J.-K.; Yu, C.-S.; Lu, C.-H. Mib: Metal ion-binding site prediction and docking server. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.-Q.; Pan, X.; Shen, H.-B. Protein–ligand binding residue prediction enhancement through hybrid deep heterogeneous learning of sequence and structure data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3018–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Smetanin, N.; Costa, A.d.S.; Fazel-Zarandi, M.; Sercu, T.; et al. Language models of protein sequences at the scale of evolution enable accurate structure prediction. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with Alphafold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Antao, T.; Chang, J.T.; Chapman, B.A.; Cox, C.J.; Dalke, A.; Friedberg, I.; Hamelryck, T.; Kauff, F.; Wilczynski, B.; et al. Biopython: Freely available python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1422–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, J.; Rose, Y.; Westbrook, J.; Burley, S.K.; Duarte, J.M. Rcsb protein data bank 1d tools and services. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 5526–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Jaroszewski, L.; Godzik, A. Clustering of highly homologous sequences to reduce the size of large protein databases. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
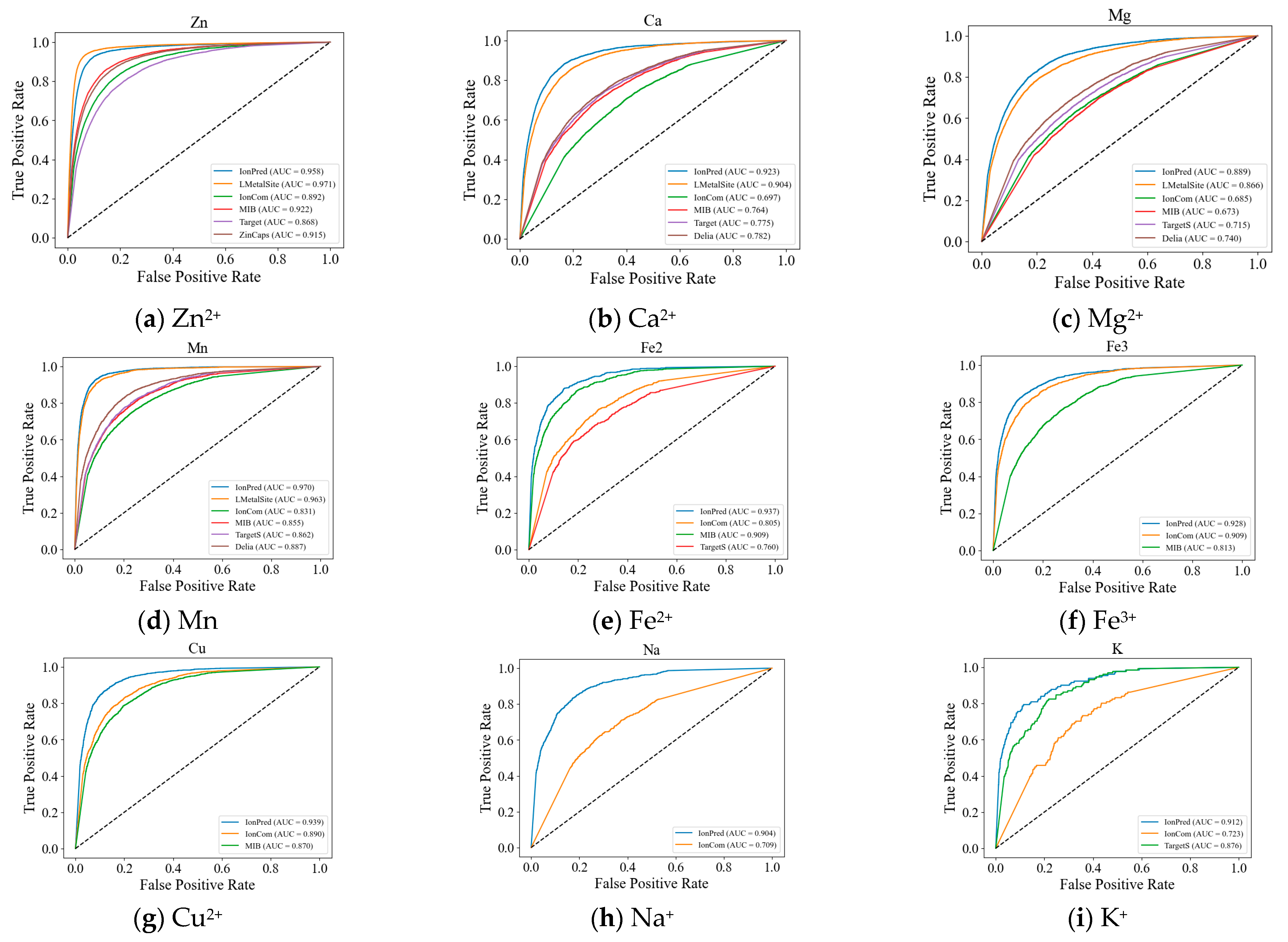
| Ion | Method | Rec | Pre | F1 | MCC | AUC | AUPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIB | 0.739 | 0.220 | 0.339 | 0.389 | 0.922 | 0.388 | |
| TargetS | 0.450 | 0.750 | 0.563 | 0.578 | 0.868 | 0.594 | |
| Zn2+ | ZinCaps | 0.753 | 0.780 | 0.766 | 0.601 | 0.915 | 0.768 |
| IonCom | 0.779 | 0.137 | 0.233 | 0.317 | 0.892 | 0.671 | |
| LMetalSite | 0.722 | 0.859 | 0.785 | 0.760 | 0.971 | 0.801 | |
| IonPred | 0.790 | 0.840 | 0.814 | 0.600 | 0.958 | 0.780 | |
| MIB | 0.341 | 0.082 | 0.132 | 0.139 | 0.764 | 0.105 | |
| TargetS | 0.119 | 0.487 | 0.191 | 0.244 | 0.775 | 0.165 | |
| Ca2+ | DELIA | 0.172 | 0.630 | 0.270 | 0.330 | 0.782 | 0.251 |
| IonCom | 0.297 | 0.247 | 0.270 | 0.258 | 0.697 | 0.166 | |
| LMetalSite | 0.413 | 0.720 | 0.525 | 0.540 | 0.904 | 0.490 | |
| IonPred | 0.467 | 0.759 | 0.578 | 0.615 | 0.923 | 0.520 | |
| MIB | 0.246 | 0.043 | 0.073 | 0.082 | 0.673 | 0.053 | |
| TargetS | 0.118 | 0.491 | 0.190 | 0.237 | 0.715 | 0.148 | |
| Mg2+ | IonCom | 0.240 | 0.250 | 0.245 | 0.237 | 0.685 | 0.184 |
| DELIA | 0.129 | 0.065 | 0.086 | 0.287 | 0.740 | 0.198 | |
| LMetalSite | 0.245 | 0.728 | 0.367 | 0.419 | 0.866 | 0.316 | |
| IonPred | 0.400 | 0.780 | 0.529 | 0.470 | 0.889 | 0.450 | |
| MIB | 0.462 | 0.096 | 0.159 | 0.193 | 0.855 | 0.168 | |
| TargetS | 0.271 | 0.496 | 0.350 | 0.362 | 0.862 | 0.322 | |
| Mn2+ | DELIA | 0.502 | 0.665 | 0.572 | 0.574 | 0.887 | 0.489 |
| IonCom | 0.511 | 0.245 | 0.331 | 0.344 | 0.831 | 0.304 | |
| LMetalSite | 0.613 | 0.719 | 0.662 | 0.661 | 0.963 | 0.625 | |
| IonPred | 0.620 | 0.700 | 0.658 | 0.670 | 0.970 | 0.670 | |
| MIB | 0.586 | 0.620 | 0.603 | 0.573 | 0.909 | 0.354 | |
| Fe2+ | TargetS | 0.345 | 0.254 | 0.293 | 0.245 | 0.760 | 0.299 |
| IonPred | 0.749 | 0.728 | 0.738 | 0.723 | 0.937 | 0.771 | |
| IonCom | 0.610 | 0.498 | 0.548 | 0.579 | 0.909 | 0.567 | |
| Fe3+ | MIB | 0.474 | 0.399 | 0.433 | 0.383 | 0.813 | 0.438 |
| IonPred | 0.743 | 0.612 | 0.671 | 0.652 | 0.928 | 0.724 | |
| IonCom | 0.596 | 0.398 | 0.477 | 0.592 | 0.890 | 0.399 | |
| Cu2+ | MIB | 0.466 | 0.280 | 0.350 | 0.358 | 0.870 | 0.419 |
| IonPred | 0.789 | 0.634 | 0.703 | 0.620 | 0.939 | 0.677 | |
| IonCom | 0.210 | 0.178 | 0.193 | 0.160 | 0.723 | 0.156 | |
| K+ | TargetS | 0.389 | 0.411 | 0.400 | 0.341 | 0.876 | 0.336 |
| IonPred | 0.498 | 0.672 | 0.572 | 0.524 | 0.912 | 0.478 | |
| Na+ | IonCom | 0.451 | 0.292 | 0.355 | 0.218 | 0.709 | 0.233 |
| IonPred | 0.523 | 0.731 | 0.610 | 0.595 | 0.904 | 0.487 |
| Radicals | Method | Rec | Pre | F1 | MCC | AUC | AUPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO32− | IonCom | 0.610 | 0.498 | 0.548 | 0.579 | 0.909 | 0.567 |
| IonPred | 0.743 | 0.612 | 0.671 | 0.652 | 0.928 | 0.724 | |
| NO2− | IonCom | 0.596 | 0.398 | 0.477 | 0.592 | 0.890 | 0.399 |
| IonPred | 0.789 | 0.634 | 0.703 | 0.620 | 0.939 | 0.677 | |
| SO43− | IonCom | 0.210 | 0.178 | 0.193 | 0.160 | 0.723 | 0.156 |
| IonPred | 0.389 | 0.411 | 0.400 | 0.341 | 0.876 | 0.336 | |
| PO43− | IonCom | 0.451 | 0.292 | 0.355 | 0.218 | 0.709 | 0.233 |
| IonPred | 0.523 | 0.731 | 0.610 | 0.595 | 0.904 | 0.487 |
| Configuration | AUC | AUPR |
|---|---|---|
| ELECTRA-0.25G-100K | 0.916 | 0.698 |
| ELECTRA-0.25G-200K | 0.951 | 0.756 |
| IonPred-0.25G-1M | 0.958 | 0.780 |
| ELECTRA-0.5G-200K | 0.926 | 0.739 |
| ELECTRA-1.0G-200K | 0.904 | 0.676 |
| ELECTRA-no-pretraining | 0.857 | 0.519 |
| Protein | Residue | Residue Position | Predicted Probability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3GKR_A (Fe3+) | D | 65 | 0.558 |
| D | 67 | 0.551 | |
| D | 151 | 0.516 | |
| E | 309 | 0.410 | |
| E | 311 | 0.499 | |
| 3DHG_D (Mg2+) | E | 104 | 0.891 |
| E | 134 | 0.912 | |
| H | 137 | 0.896 | |
| E | 197 | 0.903 | |
| E | 231 | 0.920 | |
| H | 234 | 0.899 |
| Category | Ion | Nprot | Rpos | Rneg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal ions | Ca2+ | 179 | 1360 | 119,192 |
| Cu2+ | 110 | 535 | 38,488 | |
| Fe2+ | 227 | 1115 | 73,813 | |
| Fe3+ | 103 | 439 | 34,113 | |
| K+ | 53 | 536 | 18,776 | |
| Mg2+ | 103 | 391 | 76,382 | |
| Mn2+ | 379 | 1778 | 148,618 | |
| Na+ | 78 | 489 | 27,408 | |
| Zn2+ | 142 | 697 | 93,952 | |
| Acid radicals | CO32− | 62 | 316 | 22,766 |
| NO2− | 22 | 98 | 8144 | |
| PO43− | 303 | 2125 | 99,729 | |
| SO42− | 339 | 2168 | 112,279 |
| Category | Ion | Training | Test | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal ions | Ca2+ | 849,087 | 108,857 | 95,919 |
| Cu2+ | 23,977 | 4074 | 3070 | |
| Fe2+ | 51,398 | 6589 | 6345 | |
| Fe3+ | 106,114 | 13,604 | 13,100 | |
| K+ | 26,864 | 5848 | 6010 | |
| Mg2+ | 594,193 | 76,179 | 73,357 | |
| Mn2+ | 195,499 | 24,065 | 24,672 | |
| Na+ | 46,070 | 7450 | 5493 | |
| Zn2+ | 712,169 | 104,856 | 91,922 | |
| Acid radicals | CO32− | 11,465 | 1919 | 1417 |
| NO2− | 9057 | 1305 | 1180 | |
| PO43− | 114,234 | 23,836 | 13,240 | |
| SO42− | 76,134 | 12,937 | 11,534 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Essien, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Xu, D. Prediction of Protein Ion–Ligand Binding Sites with ELECTRA. Molecules 2023, 28, 6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196793
Essien C, Jiang L, Wang D, Xu D. Prediction of Protein Ion–Ligand Binding Sites with ELECTRA. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196793
Chicago/Turabian StyleEssien, Clement, Lei Jiang, Duolin Wang, and Dong Xu. 2023. "Prediction of Protein Ion–Ligand Binding Sites with ELECTRA" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196793
APA StyleEssien, C., Jiang, L., Wang, D., & Xu, D. (2023). Prediction of Protein Ion–Ligand Binding Sites with ELECTRA. Molecules, 28(19), 6793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196793







